|
The palace was built between 1639-1642 by Lorenzo de Sent for the Grand Crown Chancellor Jerzy Ossoliński in Mannerist style. It was constructed on the plan of an elongated rectangle with two hexagonal towers at garden side of the building. The palace was crowned with a terrace with a balustrade, above which stood the upper part of the great representative hall, covered with a spherical roof. A possible inspiration for the palace's upper pavilion and its characteristic roof was Bonifaz Wohlmut's reconstruction of Queen Anne's Summer Palace in Prague, 1557-1563.
Adam Jarzębski, styling himself as Musician of His Highness Ladislaus IV and manager of the construction of the royal palace at Ujazdów, in his "Short Description of Warsaw" (The Main Road, or a Short Description of Warsaw) from 1643, described the residence of Jerzy Ossoliński: Facade with statues of four kings, below inscriptions and a brass statue of Poland holding a sickle, with a plow and a sheaf and marble portal (2427-2435), in the middle of a building a hall covered with roof tiles with gilded brass statues in the corners (2445-2450), Elongated outbuilding with servant lodgings and a kitchen (2711-2713), stables building opposit with a gate (2720-2725), Vestibule with marble portals and iron doors of master craftsmanship (2505-2508), and a staircase with a grille and a large, solid lock (2520-2525), Large dining room (2465) with niches with statues of white marble and a brass statue of a Cupid holding a bow above the door, chandelier and tapestries (2475-2485), with a door to a wine cellar (2491) and a room with silver and gold tableware (2495-2496), Hall with upper windows and a fireplace of black highly polished marble with equestrian portrait of king Ladislaus IV Vasa on white horse against a battle scene (2527-2538), a row of family portraits by painter Hans (?) Amman, and paintings reproducing the epic tales of the ancestors, including a story of a knight wounded during a jousting tournament who was healed by Saint Anne, other stories and battle scenes, above busts of Roman Emperors of white marble (2553-2570), stucco trees in corners, most probably by Giovanni Battista Falconi, ceiling decorated with figures, animals and floral motifs and a painting depicting coronation of Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria in presence of chancellor Ossoliński, door portals of black marble with portiere tapestries with Topór (the Axe) coat of arms (2575-2600), polished marble floor (2605-2607), Lord's chambers with tapestries, French-style parade bed, tables with gold trinkets and silverware and decorative clocks beside the bed, coffers, fireplace adorned with a mosaic (2611-2632), Cabinet of curiosities in a right side tower with bronze statues of different horses, birds and people (2635-2644), silver plated cupboard-cabinet with gold inscriptions describing the contents of each drawer (2649-2652), marble table with rarities on it (2659-2662), Chapel in the left side tower with an altar with an exquisite painting, relics in glass vessels, offered by the Pope, silver coffer reliquary with bones bound by gold chains, wax miniatures, a table with a casket and a door to a staircase (2667-2692). In 1633 Ossoliński was sent with a diplomatic mission to the Pope in Rome by newly elected monarch of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Ladislaus IV Vasa. The King offered him the starostwo of Bydgoszcz, 60,000 zlotys, six horses, a saber (scimitar) worth 10,000 zlotys, five Brussels' tapestries making up the series of the Story of Moses commissioned by King Sigismund Augustus in the 1550s, three of which were given to the Pope, and a construction site in Warsaw. An event from 1633 is also worth mentioning when Ossoliński, traveling to Rome via Veneto, fascinated by the beauty of one of the villas near Padua, ordered to immediately take its dimensions. He made his entry to Eternal City wearing a żupan, richly embroidered with gold, buttoned up with 20 large buttons with diamonds, gold sabre set with jewels valued at 20,000 Polish zlotys and mounting a Turkish stallion having golden horseshoes and a horse tack set with precious stones. In 1638 a life-size statue was cast in brass by Gerdt Benning in Gdańsk according to the design by Georg Münch for then the vice-chancellor Jerzy Ossoliński, most probably to his Castle in Ossolin. It is possible that the same workshop created statues to his Warsaw's palace. Contrary to the Crown Court Marshall Adam Kazanowski, who had a transgender man at his court, the Chancellor Ossoliński kept a transgender woman in his palace: "a boy who thinks he is a girl, and who also wears a dress: He imitates a girl quite well; especially in that, he is very eager of being cuddled", as recounted Jean Le Laboureur in his "Account of the voyage of the Queen of Poland", published in Paris in 1647 (p. 212). An engraved effigy of the Chancellor by Willem Hondius from 1648 was created after a portrait by Bartholomäus Strobel. It is possible then that Strobel created more painting for Ossoliński, including for his Warsaw's residence. In 1645 the chancellor commissioned the silver-ebony altar for the Chapel of Black Madonna of Częstochowa adorned with his coat of arms. The design was most probably by a Royal court artist Giovanni Battista Gisleni, while silver elements were created by the Royal goldsmith Johann Christian Bierpfaff in Warsaw in 1650. The "Inventory of belongings spared from Swedes and escapes made on December 1, 1661 in Wiśnicz" in the Central Archives of Historical Records in Warsaw, lists some of the preserved paintings from Chancellor's rich collection inherited by his daughter Helena Tekla Ossolińska, wife of Aleksander Michał Lubomirski, owner of the Wiśnicz Castle. 30 paintings from Chancellor's collection in the inventory include the paintings by Raphael, Titian, Guido Reni, Guercino, Domenichino, Veronese, Ribera, Albrecht Dürer and Daniel Seghers. There were also there a painting of the Leda and a swan, a gift from the Emperor, a Cupid sharpening his bow, possibly a copy of the famous work by Parmigianino, acquired in Rome, a "large Blessed Virgin Mary, a wreath around her made of fruits, which the angels holds", most probably by duo of Rubens and Jan Brueghel, and a large canvas showing Chancellor's Entry into Rome in 1633. Ossoliński died in his palace in Warsaw on August 9, 1650, at the age of 55. He was buried in the church of St. Joseph in Klimontów, which he built. His opulent palace in Warsaw was destroyed during the invasion of the Commonwealth by neighbouring countries, known as the Deluge (1655-1660).
Adam Jarzębski, styling himself as Musician of His Highness Ladislaus IV and manager of the construction of the royal palace at Ujazdów, in his "Short Description of Warsaw" (The Main Road, or a Short Description of Warsaw) from 1643, dedicated to his benefactor Crown Court Marshall Adam Kazanowski, thoroughly described the residence of this baroque celebrity.
Kazanowski gained prominence as a close friend and companion of crown prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa, who was elected monarch of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth from 1632 as Ladislaus IV. Together with his brother, Stanisław Kazanowski, Adam was raised with crown prince and accompanied him during his attempt to become a Russian Tsar, in the Khotyn war of 1621 and the 1624 to 1625 European voyage. A breakthrough event for Adam was when his elder brother Stanisław, favourite of crown prince, attacked with syphilis was expelled from the court for promiscuity in 1620. Zygmunt Kazanowski, father of both, had great hopes for the relationship of his older son and young Vasa. Faced with the threat of his imminent death, he persuaded the sick to recommend his younger brother to the prince. Both brothers were accused by Jerzy Ossoliński in his Memoirs of organizing "suspicious" amusements for young prince. When the crown prince became king, Adam was showered with gifts and new official titles. In 1628, at the age of about 29, Kazanowski decided to get married. He chose Elżbieta Słuszczanka, a daughter of wealthy Castellan of Minsk, Aleksander Słuszko, for the future bride. The marriage meant for him not only a substantial dowry, but also valuable connections in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. Aleksander Słuszko dismissed the suitor, justifying the refusal with his daughter's young age, as Elżbieta was then only 9 years old. However, thanks to the intervention of the crown prince, Aleksander Słuszko changed his mind. The wedding took place in the spring of 1633, when Elżbieta has reached the legal age of 14. Adam, who also became the Grand Pantler of the Crown that year, gained 50,000 zlotys of dowry. In addition, the young couple received 20,000 zlotys from the king and the value of the gifts was estimated at 40,000 zlotys. When crown prince Ladislaus Sigismund became an adolescent, his father Sigismund III Vasa bought him a wooden mansion of Andrzej Bobola at the Cracow Suburb Street in Warsaw. In 1628, shortly after his return from a journey to Western Europe, the prince ordered Constantino Tencalla a court architect to build him a new palace in the Italian style. Four yers later, in 1632, Ladislaus gave the palace to Kazanowski, which caused serious misunderstanding with his father, and a special Parliament committee was appointed to determine the circumstances behind this gesture. In 1637, Kazanowski enlarged the building, holding to Tencalla's original designs. The new structure was a large four-storied palace with a garden, enormous terrace, central courtyard, copper roofs and tower tops decorated with gilded crowns. 629 verses (1025-1654) of Jarzębski's work portray the lavish mannerist and early baroque palace constructed between 1628 and 1643 in the center of informal capital of the Commonwealth: Large arsenal filled with cannons, muskets, excellent armors, tents and turkish garments, lances and spears arranged on the walls, field guns, matchlocks and a skin of a lioness (1057-1066), Long gallery filled with paintings on both sides with nudes above the table, portraits of the King Ladislaus IV Vasa and his wife Cecilia Renata of Austria, painted Ad vivium and noble ladies, stone statue of Atlas supporting the armillary sphere on the table in the middle (1095-1108), Small arbor room adjacent to gallery with a French window, columns, stone floor and a view of the river Vistula (1121-1127), Dining room with windows on two storeys, a large chandelier with a clock showing hours, a balcony for musicians and Flemish tapestries woven with golden thread (1131-1153), chairs covered with gilded cordovan, plaques with coat of arms of the Lords and Marshals between windows in upper part and landscape paintings and cordovan in lower part, tile stove (1177-1187), window with a wine lift from basement, a large silver wine vessel of 150 litres on wheels in the shape of Bacchus wearing a wreath, sitting on a barrel and holding a goblet, several other barrels half the size of the main and a silver wine fountain in the middle of the room, silver ewers, pitchers and trays (1188-1214), the King and the Queen, envoys from Muscovy, the emperor, the king of Spain, Turkey, France and Persia were received there (1162-1171), Vaulted steam baths near the coach house with two chambers, hot stone, heating house, cold and hot water, copper bathtubs and white benches (1255-1272), Room on upper floor covered with cordovan, with a fireplace, marble portals with gold inscriptions, statues in overdoor (1305-1318) and muskets on the walls (1323), Rooms with paintings and tapestries: animalistic paintings and still-lifes with vegetables by master painters in the first, next room with staircase, seascapes and paintings of ships, casket regals, a harpsichord, a lute, a violin, cymbals, a viol and a harp and doors hung with portieres (1325-1343), next room with live animals, monkey on a chain, white parrot, singing birds in cages, still life paintings with fruits and wines, tapestries, a fireplace and a marble table (1349-1364), Lord's bedroom with a table, a painting of Adam and Eve, a bed against tapestries, good paintings, a fireplace and marble floor, a folding bench with wheels (1381-1392), trellis giving to the chapel, altar with gilded grille and a window to the ladies' room (1365-1376), Lord's study with a mirror, angels' statues holding candles, paintings, tapestries and polished marble floor (1407-1418), Library with foreign books in different languages, khanjar daggers on the table, daggers set with turquoises, gold bowls and rock crystal vessels (1425-1431), Lady's rooms, in one of them tortoiseshell caskets, pendant paintings, one with an old man with a sore eye, tapestries and looms (1437-1449), bedroom covered with goldcloth, a draped bed made of a rich fabric, mirror in silver frame above the table, the other in gold plated frame, automaton clock with a man, paintings in ebony frames, marble floor and marble table (1457-1469), a bedroom with a bed of green goldcloth with fringe and a portrait of mother of Her Majesty, Zofia Konstancja Zenowicz, in the next room in the corner of the palace a portrait of father of Her Majesty, Aleksander Słuszka, in his old age above the door, in both rooms marble fireplaces, tables covered with kilims and marble floors (1473-1495), Treasury on the groundfloor, the first room filled with guns: bird shotguns, Turkish trench guns, carabins, muskets and Italian pistols, laid with gold and silver, tables covered with Persian kilims (1508-1520), treasury room with gilded stuff set with turquoises, eastern backswords, gold sabres, gold and gilded saddles and horse tacks, sable coats, large trays and ewers in boxes and antique treasures, snake skin and a turtle from India (1530-1561), Belvedere room with grille with a view of a garden (1579-1582), wine basement with barrels of wine, mild, sweet and spicy (1590-1596), and a beer basement (1601), in the room above a workshop of Dutch painters (1603-1608), next a room with silverware (1612), and a room with hunting falcons (1613), marble pantry with venison, partridges (1641-1645) and a room of captive Muslim Tatar servants (1649-1651). Three years later, in 1646, Jean Le Laboureur, a companion of the French Ambassador Extraordinaire to Poland, Renée du Bec-Crespin, comtesse de Guébriant, visited the palace and described it in his "Account of the voyage of the Queen of Poland", published in Paris in 1647. He devoted five pages of his book to the building: Five or six large chambers and several smaller rooms, filled with silk and gold oriental fabrics, beds of gold fabric, cabinets of uncommon workmanship, tables with different items of gold, silver, amber and stones (p. 211). Large room with marble floor, as the rest of the lodgings, with a large wine fountain, made of silver in the middle, large platform above the door for the musicians, table with 80 silver-gilt Italian style tazzas (four rows of twenty each) with dried fruit, large pears in sugar, oranges, lemons, melons (p. 213), buffet with extraordinary gold and silver vessels, including Bacchus "of a natural height" sitting on a silver barrel with gold wheels, rock crystal glasses with silver-gilt mountings, Elżbieta Słuszczanka was dancing here with her brother Bogusław Jerzy Słuszka, Court Treasurer of Lithuania and marquis Gonzaga Myszkowski with his wife (p. 214). Kazanowski, struck by the sudden invasion of gout, welcomed the guests at the staircase of his palace carried in a litter (p. 210), accompanied by 300 armed guards, more than 50 pages dressed in yellow satin and short jackets of blue satin, his wife and her ladies (p. 211). In one of the chambers Le Laboureur noted "two extraordinarily small female dwarfs who were standing up like a sentry, to guard two small dogs, who were not less dwarf in their species, for they are the size of a mice, and both were resting in a white basket little larger than the hand, on a pillow of perfumed satin", while the ladies of Elżbieta Słuszczanka had a transgender man, a woman who behaved like a man, "for their entertainment" (p. 212). In 1643 Kazanowski also arranged a marriage of dwarfs, "an unheard wedding, full of laughter", according to Albrycht Stanisław Radziwiłł. Following her visit, Kazanowski and his wife, sent to Madame de Guébriant some small amber cabinets and clocks set with diamonds (p. 212). Little is known about artistic patronage of the Crown Court Marshall. Among confirmed artists at his court was certain Ezechiel Sykora, born in Litomysl in Czechia in 1622, who latinized his family name to Paritius. After Kazanowski's death in 1649 he left Warsaw and went to Silesia. As a żupnik (manager) of the Royal Salt Mines, he commissioned from Gdańsk engraver Willem Hondius in 1645 a series of views of the Wieliczka salt mine. Kazanowski had also a book of friendship (album amicorum/Stammbuch), wich was in collection of Edward Rastawiecki in Warsaw in 1853. Small oblong book bind in crimson velvet had 125 parchment leaves and majority of contributions from the years of between 1624 and 1625 of his European journey and a few from 1627 to 1644, mainly of ambassadors of the Spanish Empire. During his stay in Brussels in 1624 with the crown prince he received from infanta Isabella Clara Eugenia a gold medallion set with precious stones on a gold chain. It is possible that he intentionally tried to emulate great validos of his time, Duke of Lerma or Count-Duke of Olivares. Kazanowski died childless in 1649, leaving all his property to his wife Elżbieta. His opulent palace in Warsaw was destroyed during the invasion of the Commonwealth by neighbouring countries, known as the Deluge (1655-1660).
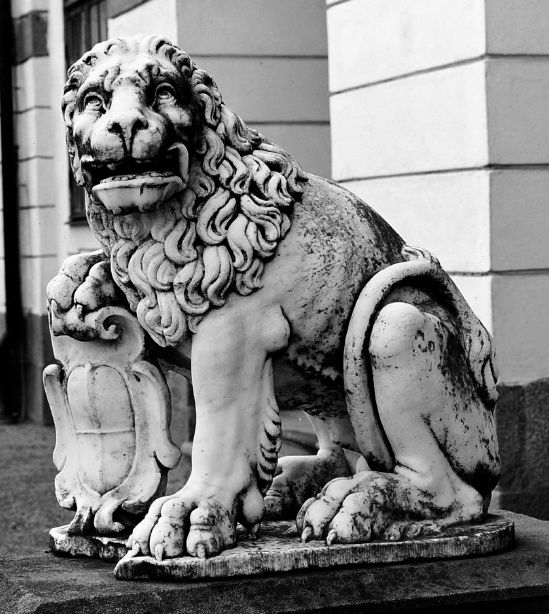
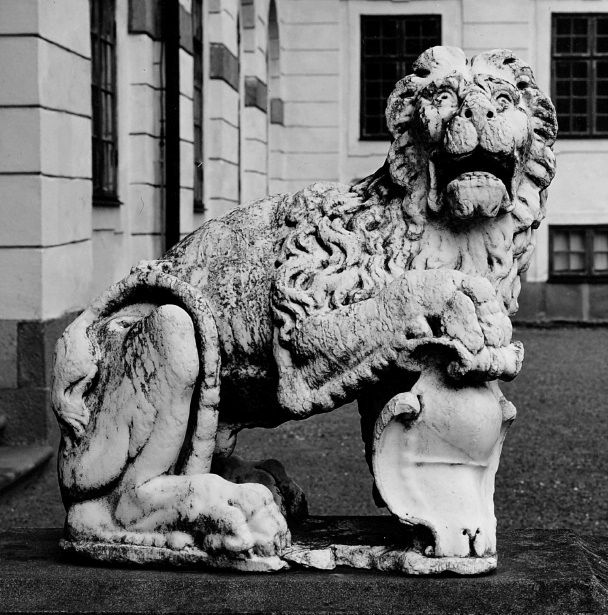
Two marble lions at the main gate of the Drottningholm Palace in Sweden, credited by some sources as possibly taken by the Swedish forces from the Frederiksborg Castle in Denmark, could be rather, beyond any doubt, identifed with four marble lions described by Adam Jarzębski in his "Short Description of Warsaw" from 1643, as adorning the entrance to the Ujazdów Castle in Warsaw - I lwy cztery generalne, Między nimi, naturalne, Właśnie żywe wyrobione, A z marmuru są zrobione; Nie odlewane to rzeczy, Mistrzowską robotą grzeczy (2273-2278).
In the 1630s, before his wedding with Cecilia Renata of Austria, Ladislaus IV Vasa made several commissions for sculptures in Florence, including possibly lions for his palace in Ujazdów. Both material, Italian marble, and a form similar to Medici lions, makes this assumption more probable. Also quarterly divided fields of lions' escutcheons with wiped away crests, suggest an eagle and a knight of Poland-Lithuania, rather than more complex emblems of Christian IV of Denmark.
Marble lion from the Ujazdów Castle by Anonymous from Italy, 1630s, Drottningholm Palace. Photo: Nationalmuseum (CC BY-SA).
Marble lion from the Ujazdów Castle by Anonymous from Italy, 1630s, Drottningholm Palace. Photo: Nationalmuseum (CC BY-SA).
The first wooden manor on the site was constructed for Dukes of Masovia in the 15th century. It then belonged, from 1516, to Anna Radziwill, Regent Duchess of Mazovia and to Queen Bona Sforza after 1546 for whom an Italian-style Renaissance garden was created. The new lavish wooden manor in mannerist style was built in 1570s for Anna Jagiellon. It was here that the premiere of blank-verse tragedy "The Dismissal of the Greek Envoys" by Jan Kochanowski took place on January 12, 1578.
"The palace is all wood, according to local custom, but beautiful [...] we went up to the highest part of the palace with a beautiful view, where we had a sumptuous breakfast in a large room" (palazzo, che è tutto di legno alla foggia di qua ma bello [...] ascendemmo alla parte più alta del palazzo a una bella vista, dove travammo in una gran sala una sontuosa collazione), wrote in a letter dated May 2, 1586 Giovanni Andrea Caligari (1527-1613), papal nuncio to Poland. In 1596 Giovanni Paolo Mucante, secretary to the papal legate Cardinal Enrico Gaetani, described the exquisite Italian Renaissance-style interiors and furnishings of the residence. The villa, although designed in modo Italiano by Italian architects, perhaps Bernardo Morando or Santi Gucci, was built by the royal carpenter Matys Wąsik. Sigismund III Vasa resided in the manor during the summer. Between 1602 and 1603, according to the Royal accounting books, the old manor was renovated and a new wooden house was built nearby. In 1606 the plan of the manor and garden was prepared for the king by Alessandro Albertini. When in 1619 the king purchased the allotments belonging to Augustinian friars the construction of a new brick palace become possible. The spot for a Royal summer palace was chosen approximately 120 meters north from the original manor. According to the cornerstone found in 1972 in the foundations of the eastern wing the construction started on September 16, 1624. The structure was designed by Matteo Castelli and Constantino Tencalla and accomplished after king's death by his son Ladislaus IV Vasa. In 1655 during the so-called Deluge of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth (invasion of allied forces of Sweden from north, Brandenburg from west, Transilvania from south and Muscovy from East), the castle was devastated and remained practically uninhabited till 1668 when it was given to Teodor Denhoff. It is a rectangular building with four octagonal towers at the corners, arcaded courtyard and a loggia with a view on Vistula River. Largely destroyed several times, it was reconstructed in 1975. Near the palace there was also a wooden church. In 1593, at the request of elected Queen Anna Jagiellon, the then bishop of Poznań, Łukasz Kościelecki, transferred the former church in Solec with all its funds to the newly built church in Jazdów. In 1603, Wawrzyniec Goślicki, bishop of Poznań, visited the church and described it as follows: "The church in Jazdów is newly built of wood and well covered with boards. It is dedicated to Saint Anne and Saint Margaret, and contains three altars" (Kościół w Jazdowie jest z nowa z drzewa postawiony i dobrze deskami pokryty. Jest pod wezwaniem świętej Anny i świętej Małgorzaty, zawiera w sobie trzy ołtarze). It is possible that the painting of Saint Anne and the Infant Virgin Mary by Leandro Bassano kept in the Nationalmuseum in Stockholm (inventory number NM 132) comes from this church. During the Deluge (1655-1660), the queen's wooden palace as well as the new royal castle in Ujazdów (built after 1624) were ransacked and burned. The marble lions attributed to the Italian sculptor in front of Drottningholm Palace near Stockholm most likely come from Ujazdów. Later, the only partially rebuilt estate was purchased by the Lubomirski family, who probably renovated or built the new church in Ujazdów. It possibly stood near where the Chopin monument stands today. It survived until 1818, when it was demolished, due to its age, and the parish and surviving furnishings were transferred to the new church of Saint Alexander. The Raising of Lazarus, magnificently painted around 1643, signed by Carel Fabritius (Car. Fabr), student of Rembrandt (National Museum in Warsaw, M.Ob.563), as well as the marble statue of the Dead Christ by Giusto Le Court (Josse de Corte), Flemish sculptor, mainly active in Venice after 1655 (St. Alexander's Church in Warsaw), most probably comes from the church in Ujazdów after renovation carried out by the Lubomirski family.
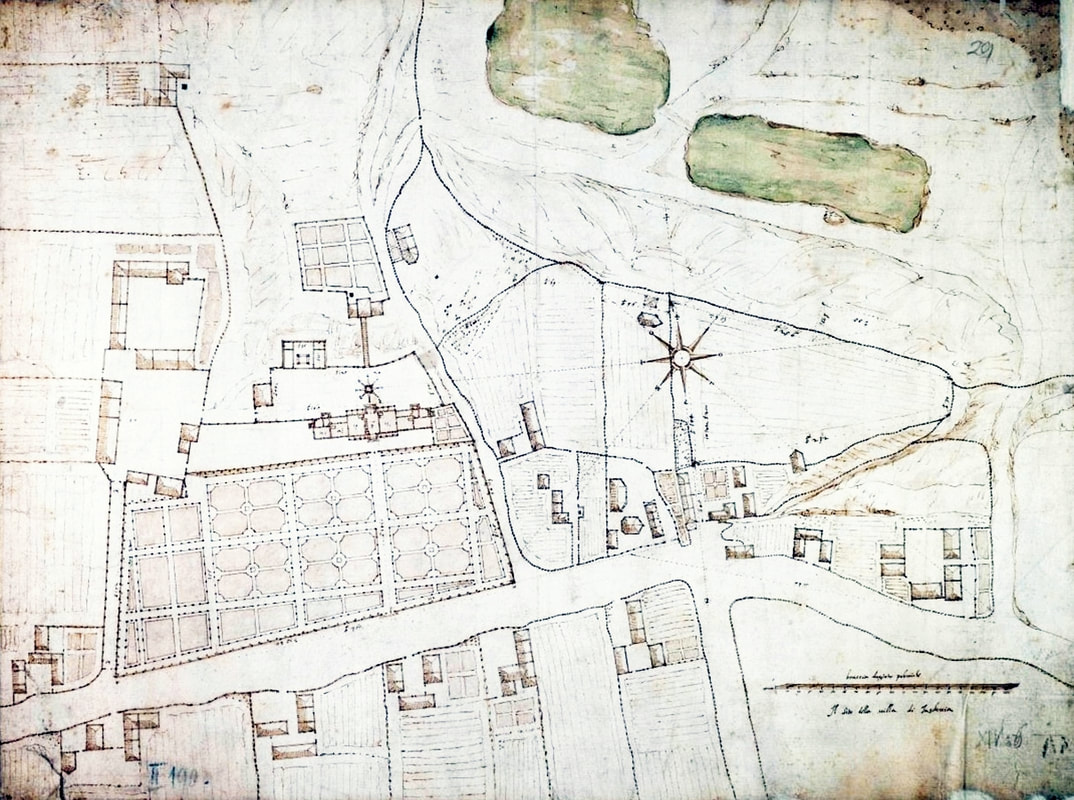
Plan of the manor and garden in Ujazdów near Warsaw in 1606 by Alessandro Albertini, scale from. 1: 800, hand drawn multicolored document, 42 × 56 cm (16.5 × 22 in), signed: Il sito della villa di Jasdovia; Alessandro Albertini, 1606, Central Archives of Historical Records in Warsaw, Zb. Kart. 570-1.
Cornerstone of the Ujazdów Castle, sandstone, 57 × 57 × 10 cm (22.4 × 22.4 × 3.9 in), inscription in Latin: REGIAE AMOENITATI / SACRA / COELO SOLO LVCO LACV COLLE VALLE / LAETA / PALATIA AESTIVA / FELICIB[us]. FVNDAMENTIS AVSPICATVRV[m.] SAXVM / ANNO D[omi]NI MDCXXIV SEPTEMBR[e] / SIGISMVNDO III POLONIAE XXXVII / CO[n]STANCIA ANNO REGE / POSITVM / ANNO D[omi]NI 1624 DIE 7[septem]BRIS (Devoted Royal delight (...) summer palace), Museum of the Castle and Military Hospital at Ujazdów.
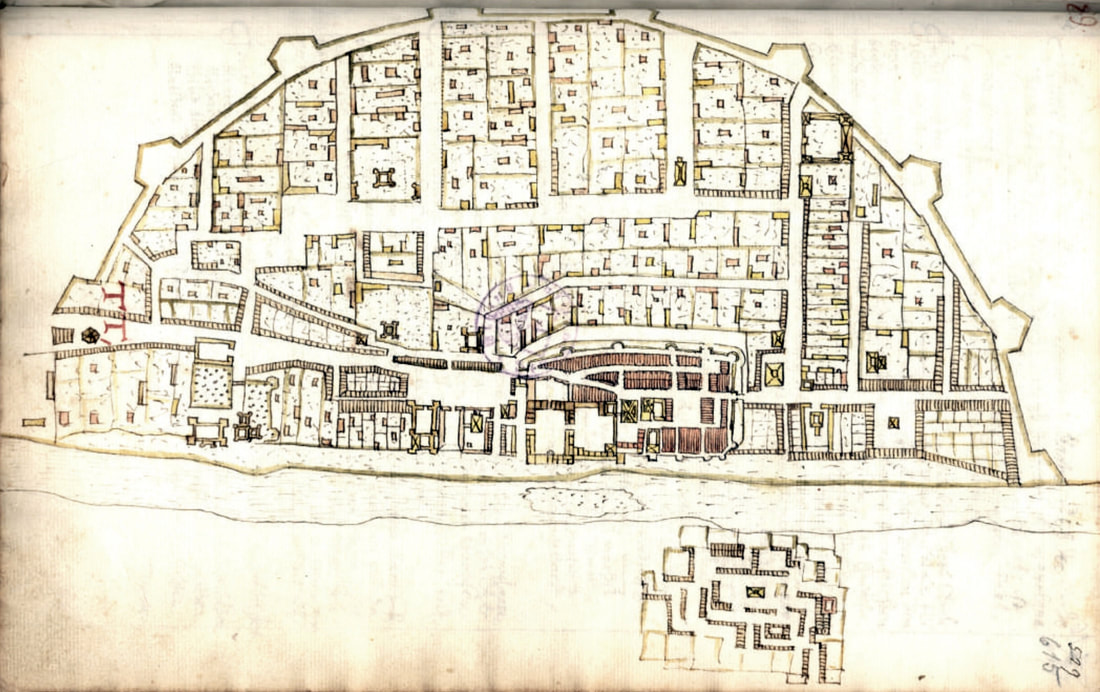
Plan of Warsaw (Varsavia Masoviae caput et Regia) by Israel Hoppe, ca. 1641, State Archives in Gdańsk, 492/654.
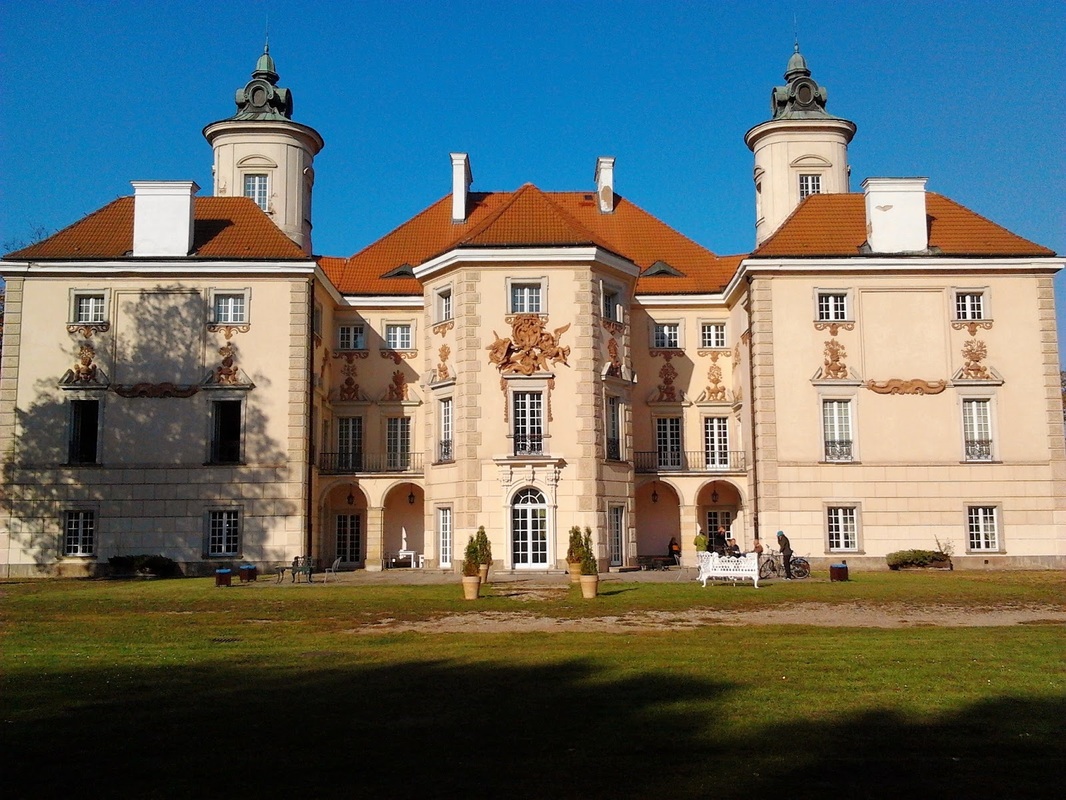
The Palace in Otwock Wielki was constructed as a summer residence for Bieliński family. The construction started after 1682 at the initiative of Kazimierz Ludwik Bieliński and it was accomplished in about 1689, possibly under supervision of Tylman Gamerski, Carlo Ceroni or Józef Fontana. The main tympanum was adorned with a scene of bacchanal with nymphs, satyrs and God Pan in the center.
The subsequent owner, Franciszek Bieliński, Grand Marshal of the Crown renovated the palace in 1757. The modernization in Rococo style was conducted by Jakub Fontana. At that time the interior was remodelled and adjusted for the purpose of a yearlong living - tile stoves were installed instead of fireplaces in some rooms, the outdoor staircase was demolished and a new one was constructed inside. Also new outbuildings were constructed to house guest rooms, kitchens and rooms for servants. Marianna Bielińska
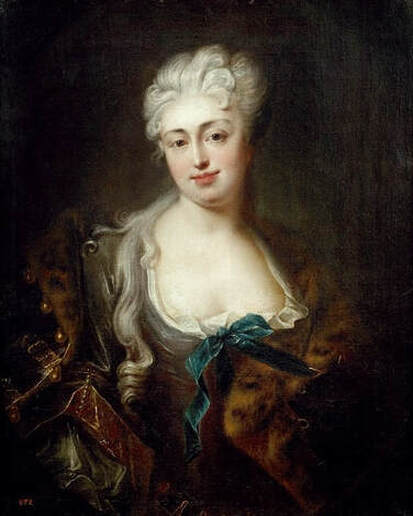
One of the most renowned of the palace's inhabitants was Marianna Bielińska (c. 1685-1730) - mistress of King Augustus II of Poland. Marianna was a daughter of Grand Marshal of the Crown Kazimierz Ludwik Bieliński, a leader of French party in Poland. His lavish estate in Otwock Wielki was frequented by many state figures including the King himself, who become a lover of his daughter. Soon afterwards Bieliński married his daughter to Bogusław Ernest Denhoff. Despite that Marianna remained King's mistress and eventually divorced Denhoff with Pope's approval. She had a large influence on the King and persuaded him to enter into an alliance with France in 1714. When the new alliance become less beneficial then expected she was dismissed by the King.
Her portrait painted by Ádám Mányoki, along with some other portraits of Royal Mistresses preserved in the Palace on the Water in Warsaw. The Hungarian painter educated in Germany developed his own style and largely influenced the portraiture in Poland. Room of Roman ruins
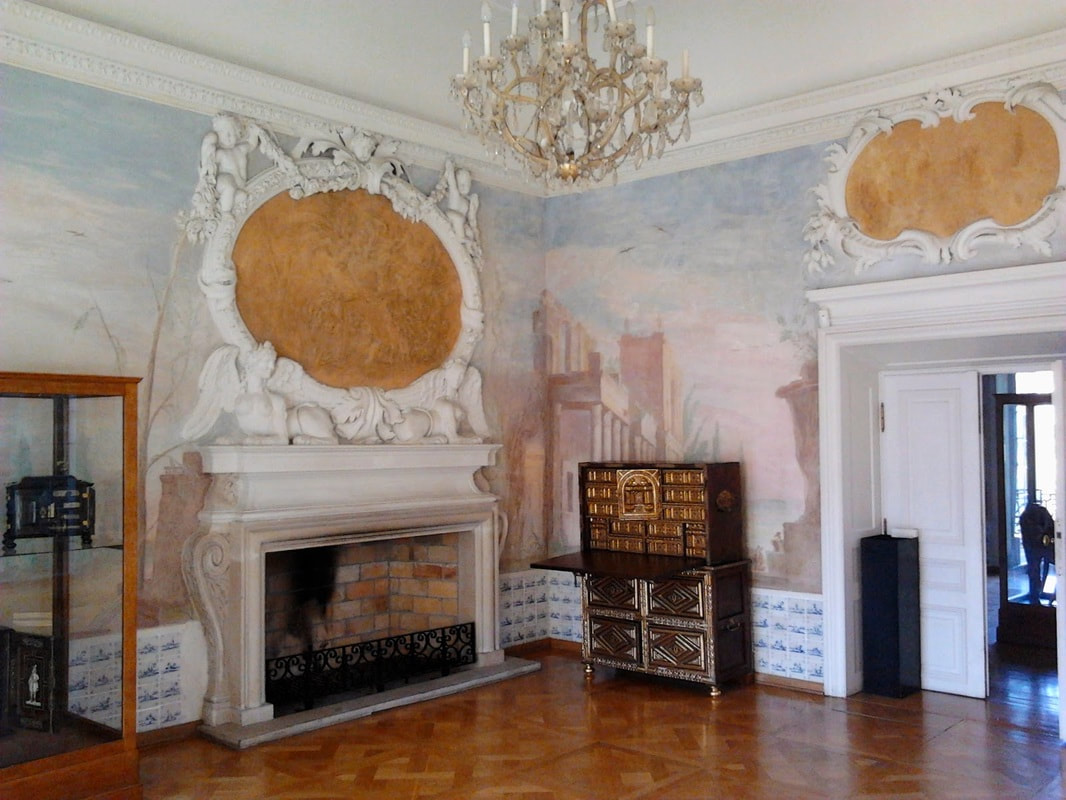
During the renovation in the second half of the 17th century the palace was adorned in late baroque style. With a certain level of probability the frescoes can be attributed to Tylman Gamerski or his circle, due to similarity to some other works. Although predominantly known as an architect, Gamerski was also a good painter, educated in his native Low Countries and in Venice. Approximately 30% of original decoration was restored after the war.
Initially the room served as a bedchamber for master of the house. The walls were covered with frescoes depicting ancient ruins (colonnades, fountains, gates, arcades, vases) and a wooden panneling to the one sixth of its hight, which was replaced with copies of Dutch tiles after the war. The style of decoration referring to the work of Claude Lorrain was completed with floral and mythological stuccoes in overdoor and above fireplace. Room of marine landscapes
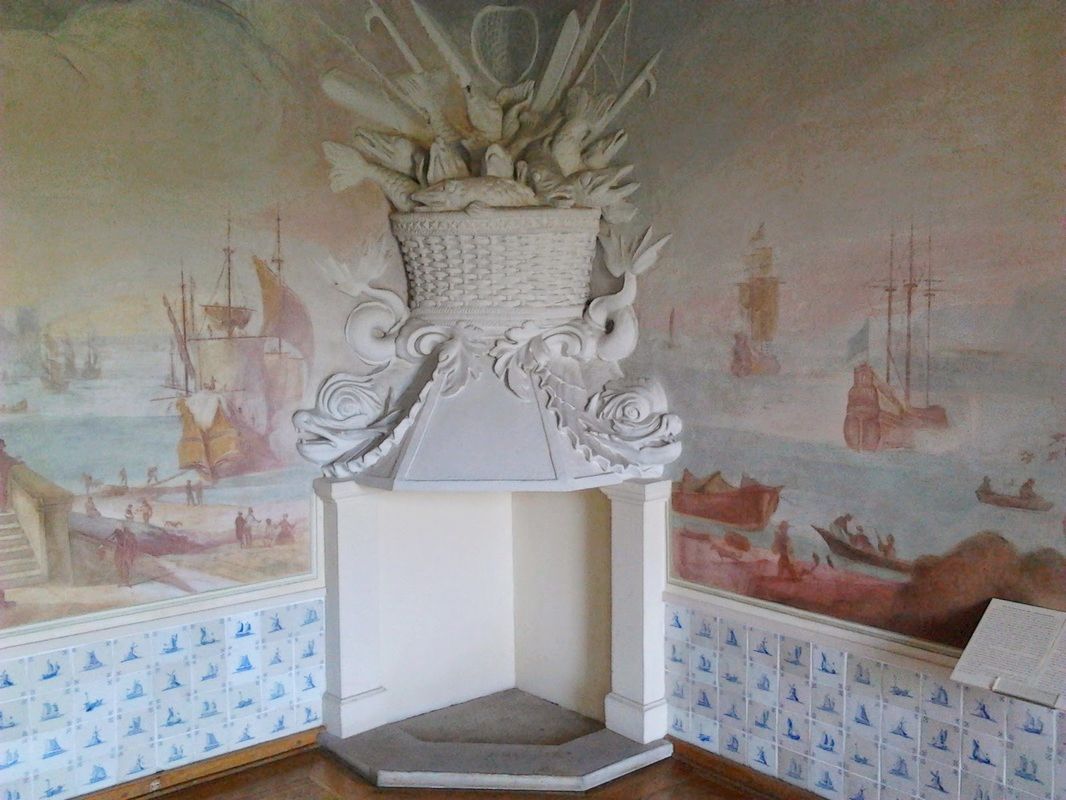
The room was originally an antechamber of Kazimierz Ludwik Bieliński. The preserved frescoes were created during second reconstruction of the palace in the second half of the 17th century and are attributed to Tylman Gamerski. Approximately 75% of the original decoration preserved.
Among elements depicted are two and three masthead boats moored in the port or entering the port, small boats filled with people, lighthouses and the rocky coast. The lower parts of the walls were covered with Dutch tiles. As in the other rooms the decoration included rich stuccos in the form of oval cartouches in overdoor, adorned with shells, acanthus twigs and grass blades. The cartouches were filled with images in sepia (only one of them preserved). Chimney with phoenix
The chimney with phoenix born from ashes, that once adorned the rooms of Ludwika Maria Bielińska, was moved to the staircase. The original decoration of wife's rooms did not preserved.
Vestibule
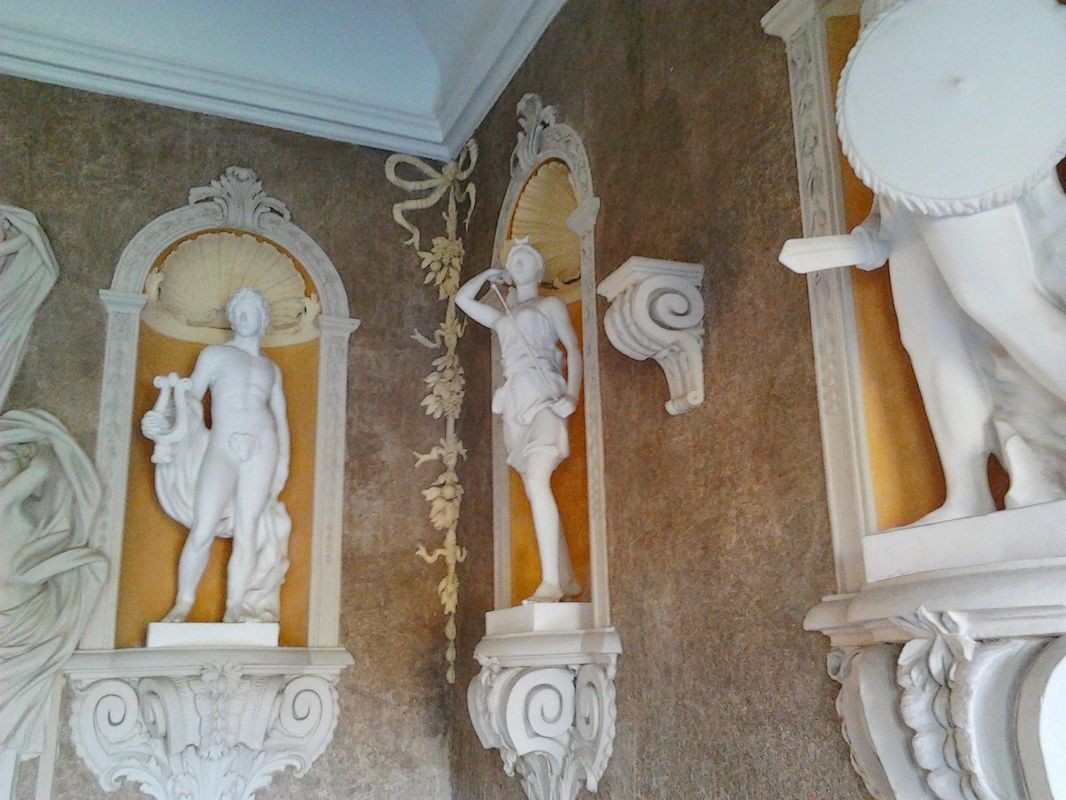
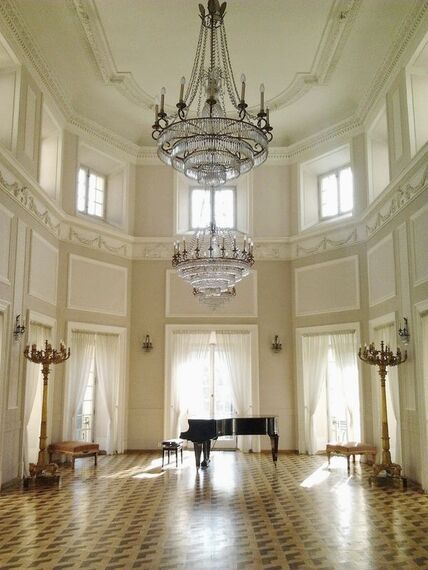
The vestibule of the Otwock Wielki Palace was initially a representative hall into which the double external staircase led directly from the courtyard. It is one of the 4 rooms of the palace with original decoration.
The semi circular niches supported by richly decorated corbels are the main features. The original Baroque sculptures that filled the niches were destroyed between 1809 and 1828. Present statues depicting mythological deities were executed in 1975 by Stanisław Kulon. The decoration of the vestibule was to resemble an antique grotto and a Palladian Corinthian hall. The walls were covered with a mixture of sand, lime, green glass and granite. The southern wall is filled with a wide semi circular entry into the ballroom framed with stucco decoration in the form a fabric supported by 4 putti and two herms in the form of a semi nude female and male. The herms indicated the initial division of the palace's structure into the wife and husband's space and bears strong resemblance to the owners Ludwika Maria Bielińska and her husband Kazimierz Ludwik. Between 1787 and 1790, Franciszek Bieliński, the palace's owner, has visited Italy several times. During his sojourn in Naples he acquired a collection of 85 teraccotta busts and copies of antique sculptures from the collection of Farnese family and originating from the Pompei and Herculanum excavations. As the collection was intended to be housed in Otwock Wielki, the palace underwent some structural changes inside. Ballroom
The ballroom with a balcony raise at the height of the two stories. The original baroque furnishings and decoration not preserved to our days. The room was adorned after the war with neoclassical stuccos and furnished with 19th century furniture including a pair of Russian candlesticks. External arcade terrases connect the room with husband's and wife's part of the palace.
|
Artinpl is individual, educational project to share knowledge about works of art nowadays and in the past in Poland.
If you like this project, please support it with any amount so it could develop. © Marcin Latka Categories
All
Archives
April 2023
|