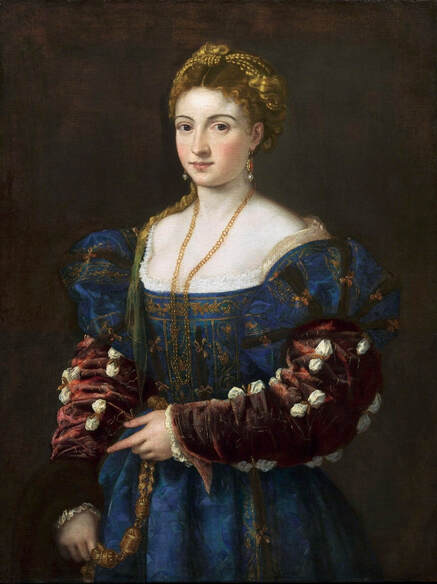
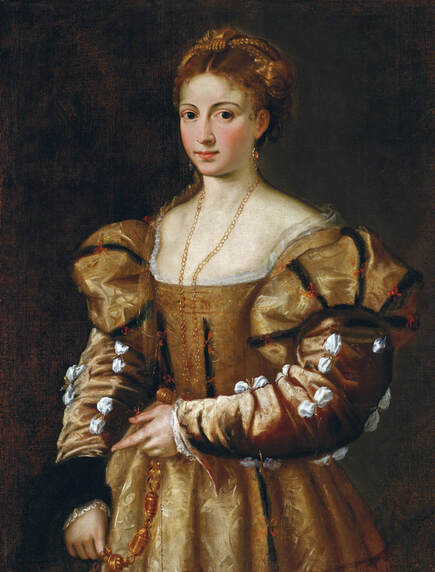
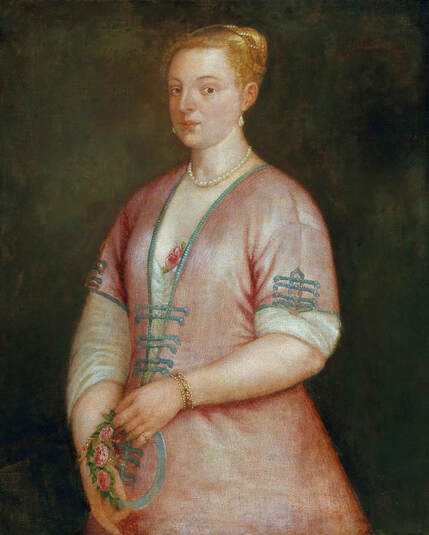|
Renaissance Poland-Lithuania - The Realm of Venus, goddess of love, destroyed by Mars, god of war. Discover its "Forgotten portraits", its sovereigns and its unique culture ...
Forgotten portraits - Introduction - part A Forgotten portraits of the Jagiellons - part I (1470-1505) Forgotten portraits of the Jagiellons - part II (1506-1529) Forgotten portraits of the Jagiellons - part III (1530-1540) Forgotten portraits of the Jagiellons - part IV (1541-1551) Forgotten portraits of the Jagiellons - part V (1552-1572) Forgotten portraits of the Jagiellons - part VI (1573-1596) Forgotten portraits - Introduction - part B Forgotten portraits of the Polish Vasas - part I (1587-1623) Forgotten portraits of the Polish Vasas - part II (1624-1636) Forgotten portraits of the Polish Vasas - part III (1637-1648) Forgotten portraits of the Polish Vasas - part IV (1649-1668) Forgotten portraits of the "compatriot kings" (1669-1696)
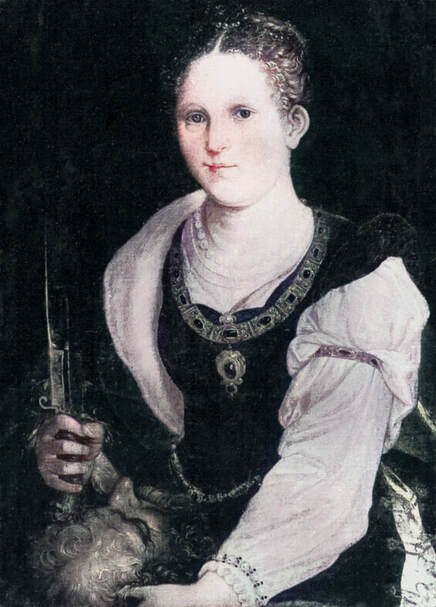
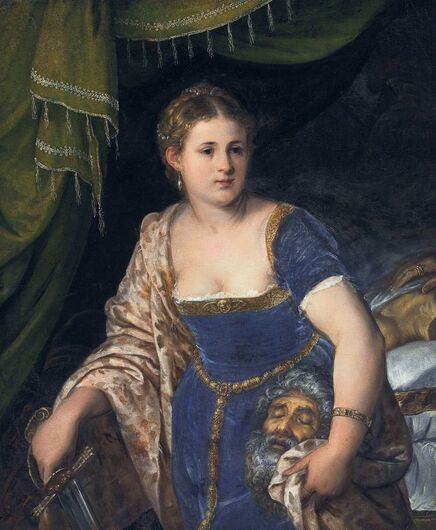
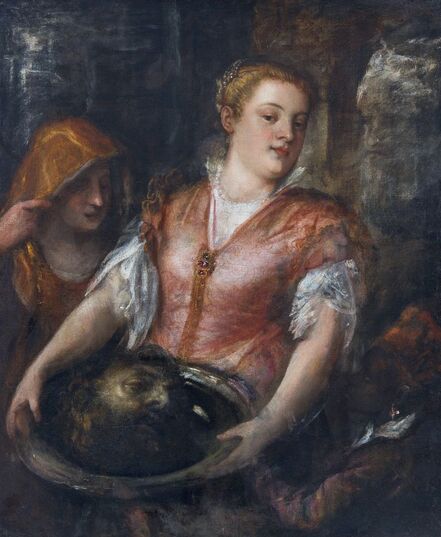
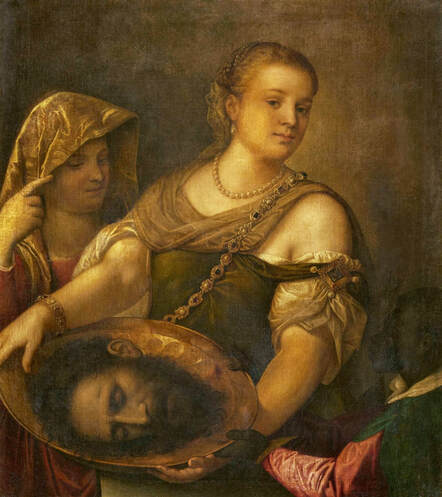
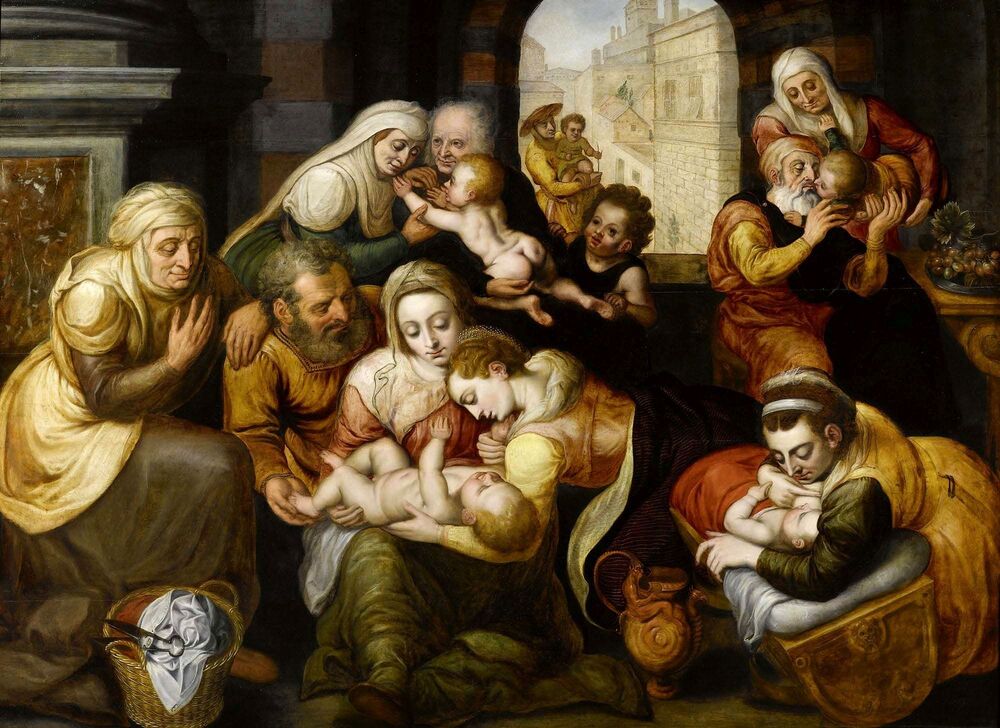
"Before the Deluge", it is a former title of a painting now identified to depict the Feast of the prodigal son. It was painted by Cornelis van Haarlem, a painter from the Protestant Netherlands, best known for his highly stylized works with Italianate nudes, in 1615, when the elected monarch of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth was a descendant of the Jagiellons - Sigismund III Vasa. Despite huge losses in the collections of paintings, the oeuvre of Cornelis van Haarlem is represented significantly in one of the largest museums in Poland - the National Museum in Warsaw, the majority of which comes from old Polish collections (three from the collection of Wojciech Kolasiński: Adam and Eve, Mars and Venus as lovers, Vanitas and the Feast of the prodigal son from the collection of Tomasz Zieliński in Kielce).
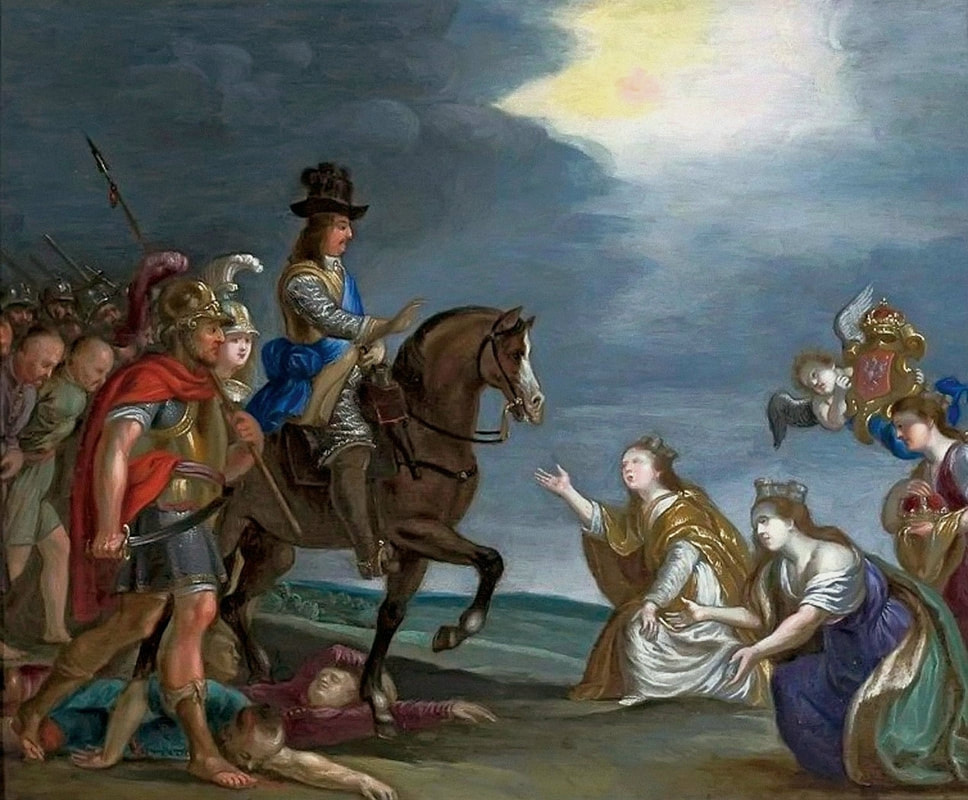
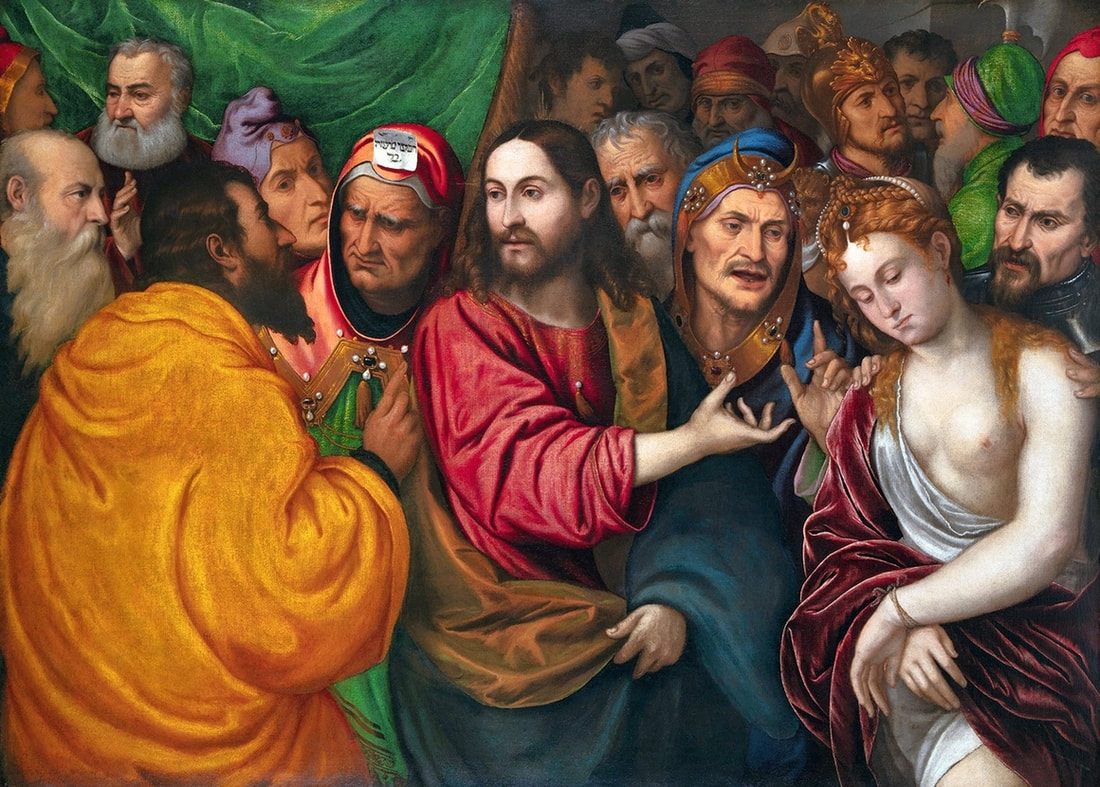
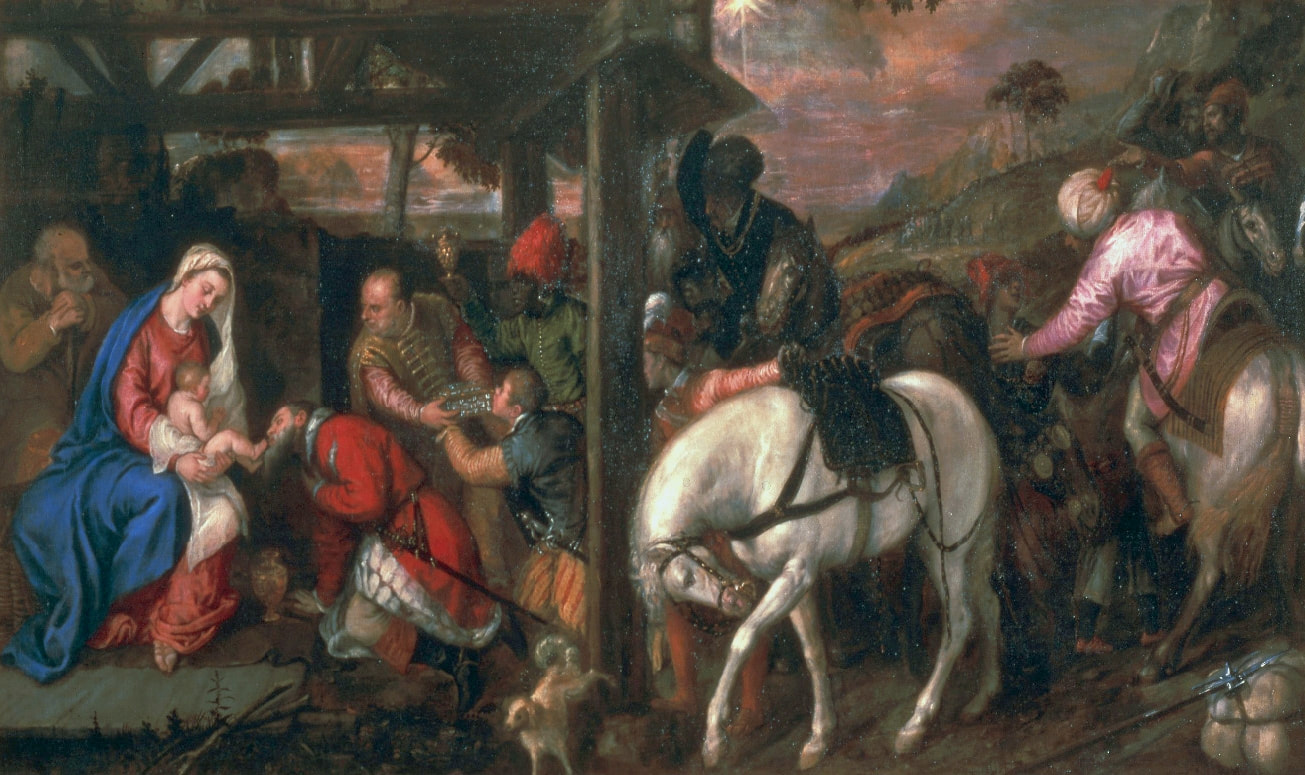
Sadly, its earlier history is unknown, so it cannot be unmistakably associated with the Golden Age of Poland-Lithuania, which, almost as in the Bible, ended with the Deluge (1655-1660), a punishment for sins as some might believe or like the opening of Pandora's box unleashing evil upon the world. "The Swedes and the notorious Germans, for whom murder is a play, the violation of faith is a joke, robbery a pleasure, arson, rape of women and all crimes a joy, our city, destroyed by numerous contributions, they destroyed with fire, leaving only the Koźmin suburb unburned", describes the atrocities in the city of Krotoszyn, burned down on July 5, 1656, an eyewitness - an altarist, brother Bartłomiej Gorczyński (after "Lebenserinnerungen" by Bar Loebel Monasch, Rafał Witkowski, p. 16). Descriptions of the destroyed Vilnius after the withdrawal of the Russian and Cossack armies, and other cities of the Most Serene Republic, are equally terrifying. Polish troops responded with similar ruthlessness, sometimes also towards their own citizens, who collaborated with the invaders or were accused of collaboration. The invasion was accompanied by epidemics related to the marches of various armies, destruction of the economy, exacerbation of conflicts and social and ethnic divisions. An unimaginable Apocalypse, sent not by God but by human greed. War should be a forgotten relic of the past, but unfortunately it is still not. Another painting in the National Museum in Warsaw recalls these events. This small painting (oil on copper, 29.6 x 37.4 cm, inventory number 34174) was very probably made by Christian Melich, court painter of the Polish-Lithuanian Vasas, active in Vilnius between 1604 and 1655 (similar in style to the Surrender of Mikhail Shein in the National Museum in Krakow, MNK I-12) or other Flemish painter. It was initially thought to represent King John II Casimir Vasa after the Battle of Berestechko in 1651, but the distinctive features of a man on horseback allowed to identify him with great certainty as Charles X Gustav the "Brigand of Europe", as he was called in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, "who was capable of beginning horrors of war in any part of the old continent" (after "Acta Universitatis Lodziensis: Folia historica", 2007, p. 56), and the subject as his triumph over the country. Female personifications of the Commonwealth, most likely Poland, Lithuania and Ruthenia (or Prussia) like three goddesses from the Judgement of Paris, pay homage to the "Brigand of Europe" supported by Mars and Minerva and trampling Polish enemies in national costumes. One of the women (Venus-Poland) offers the crown and a putto or Cupid offers the symbol of Poland, the White Eagle. Mars, with his sword drawn, looks at the humble woman. Dramatic events change not only individuals but also entire nations.
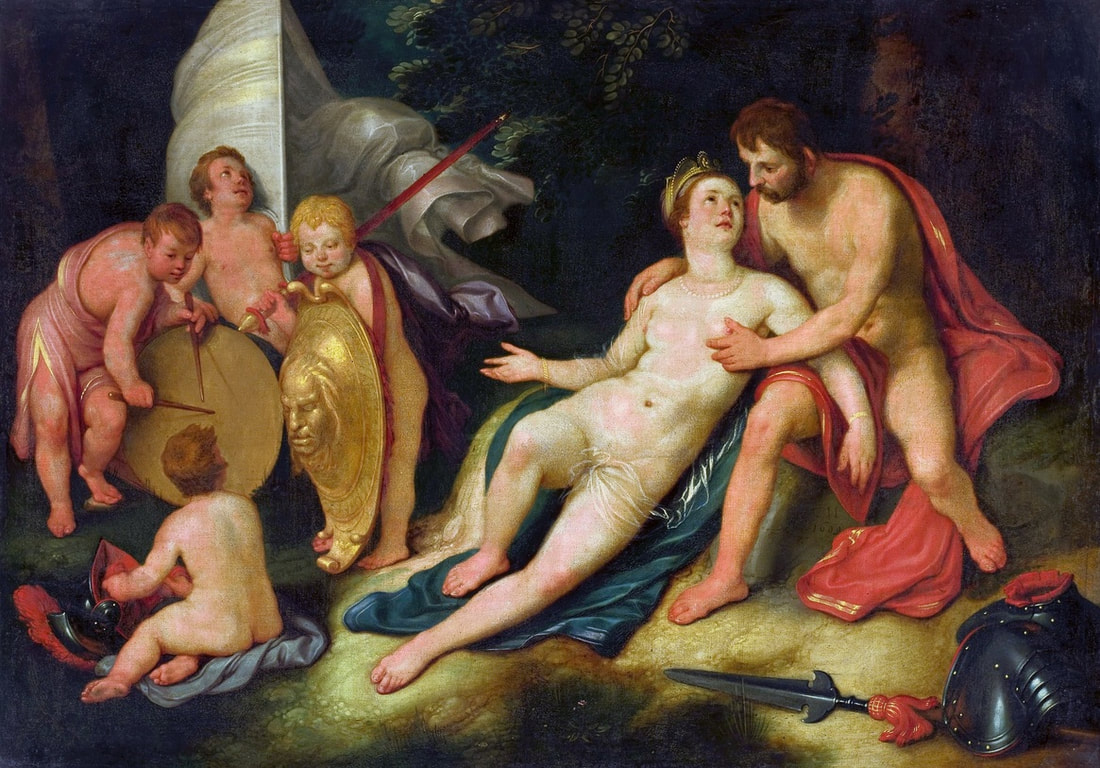
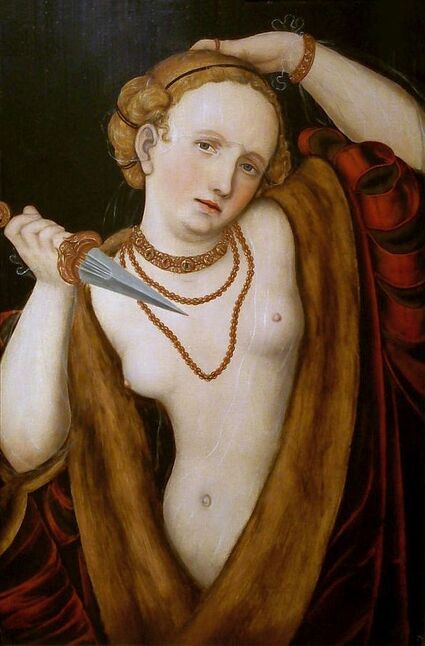
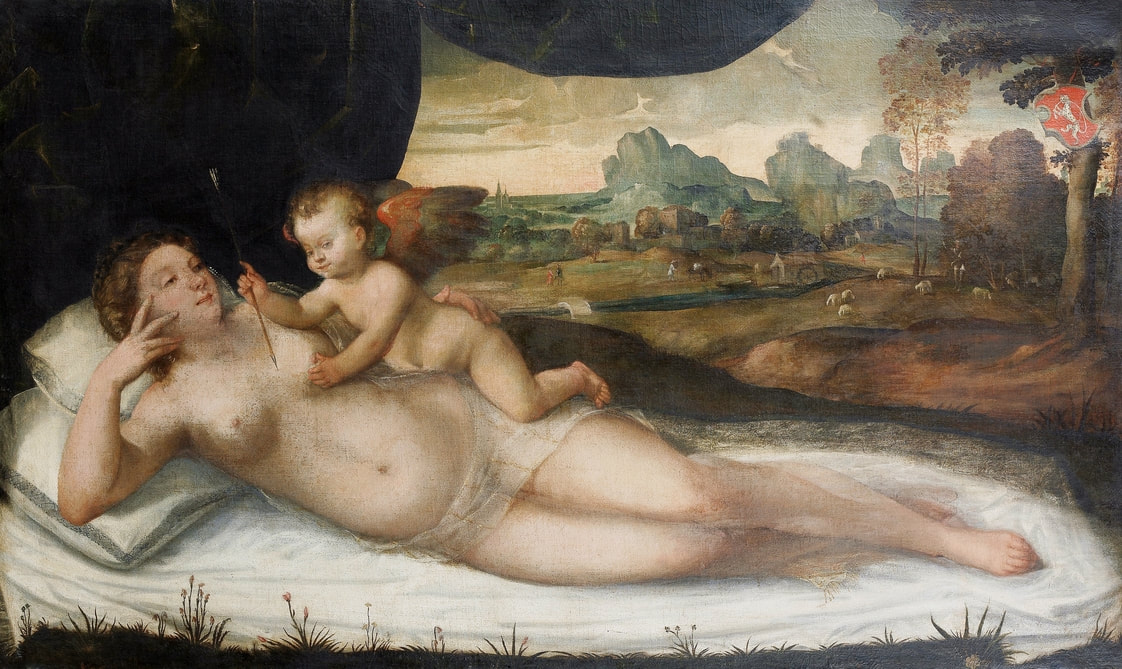
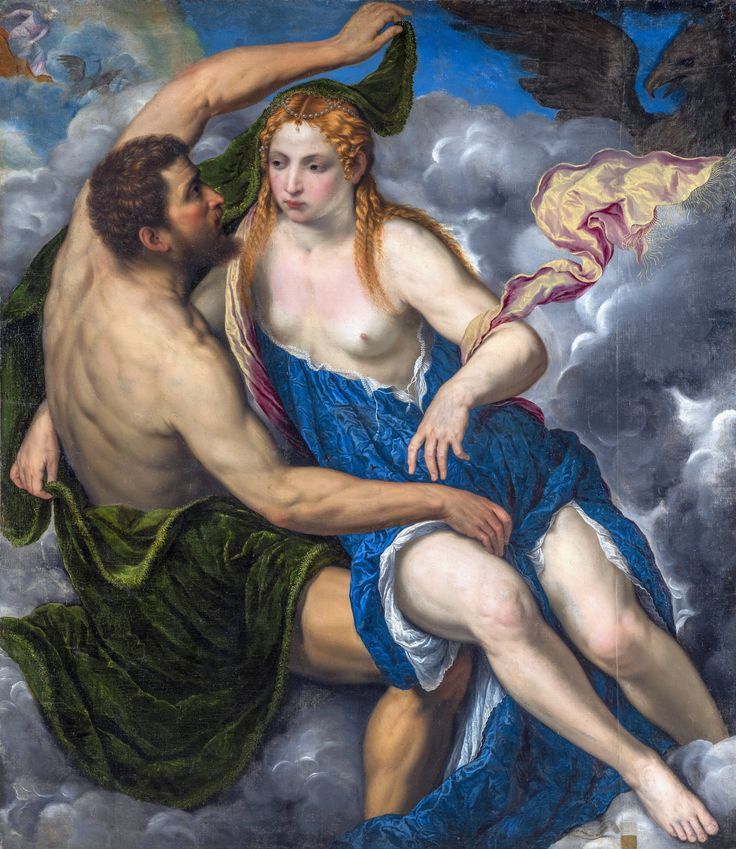
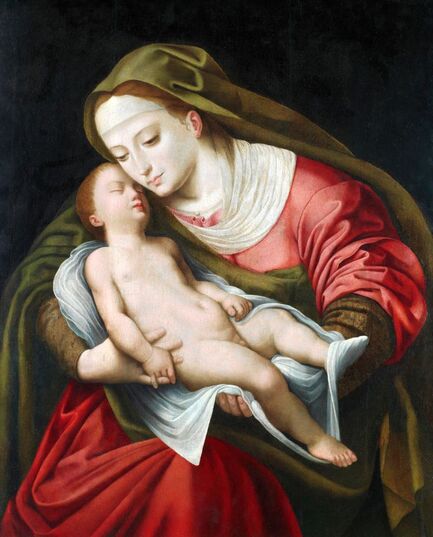
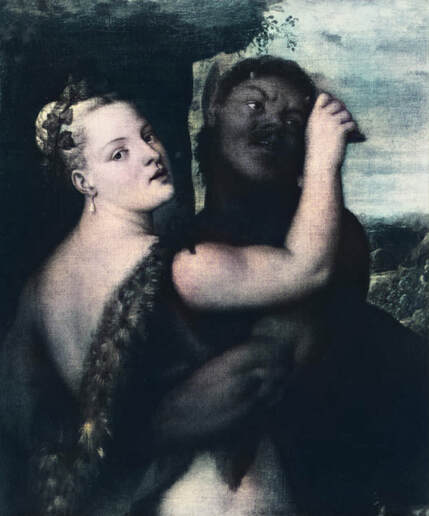
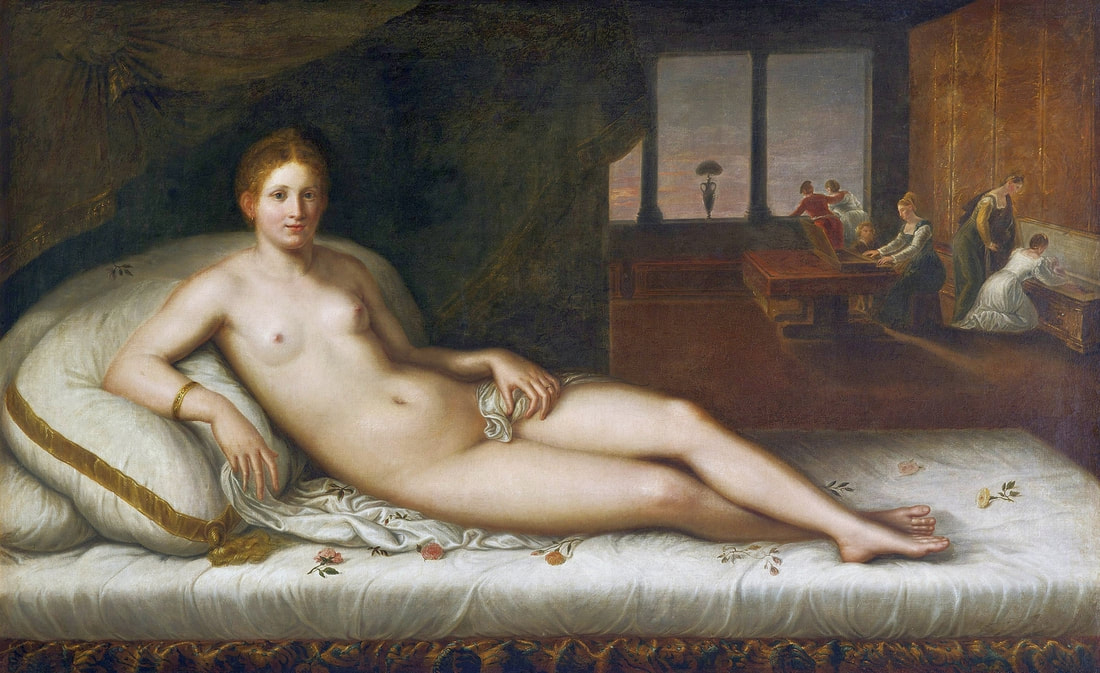
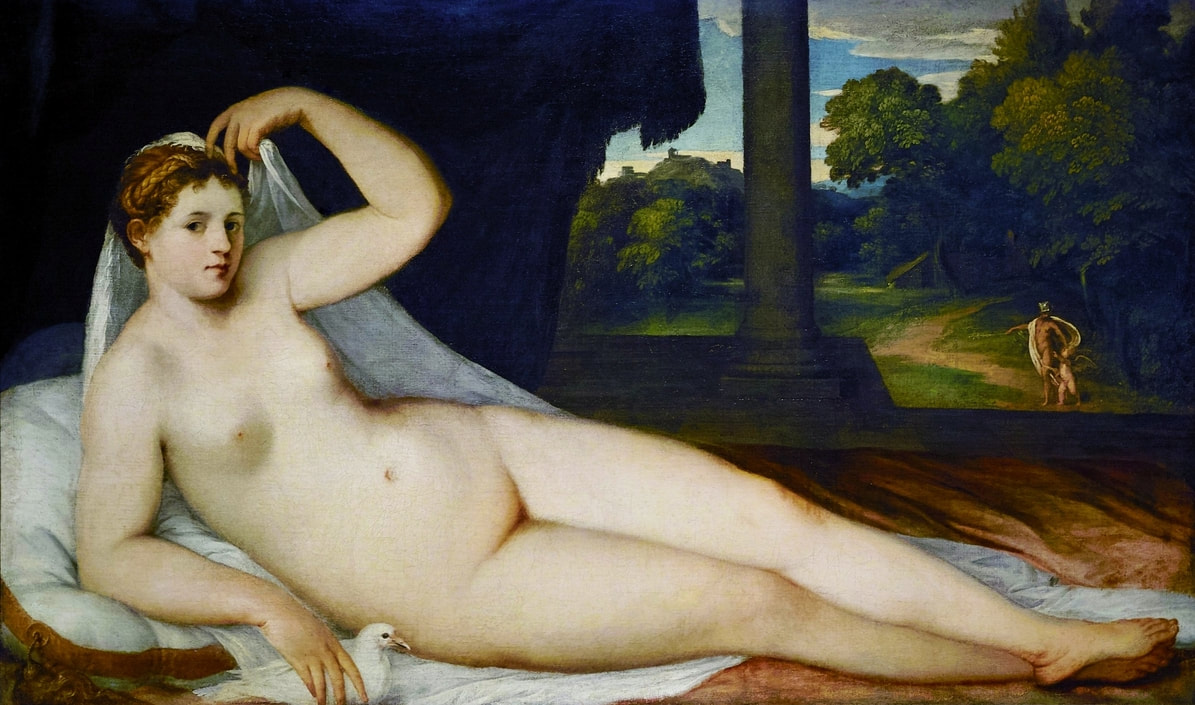
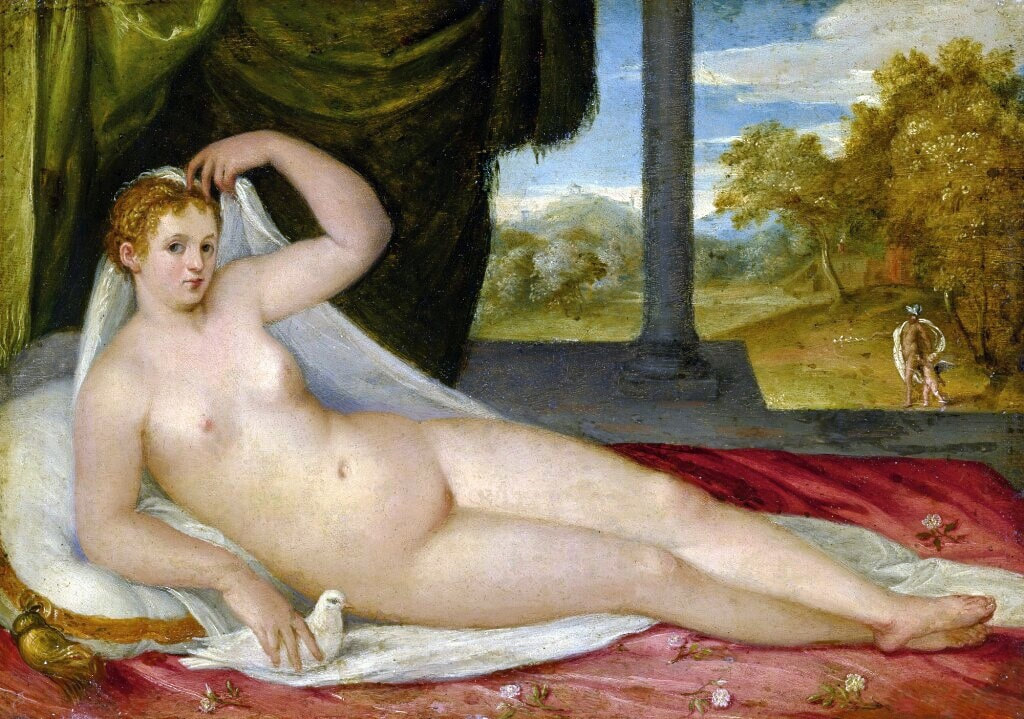
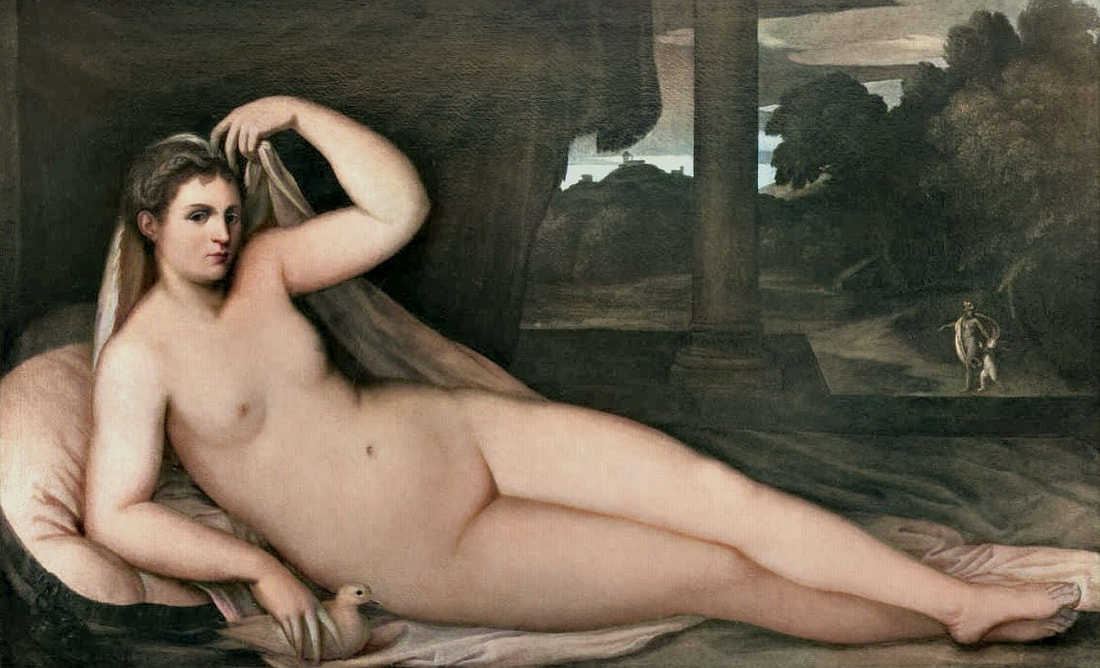
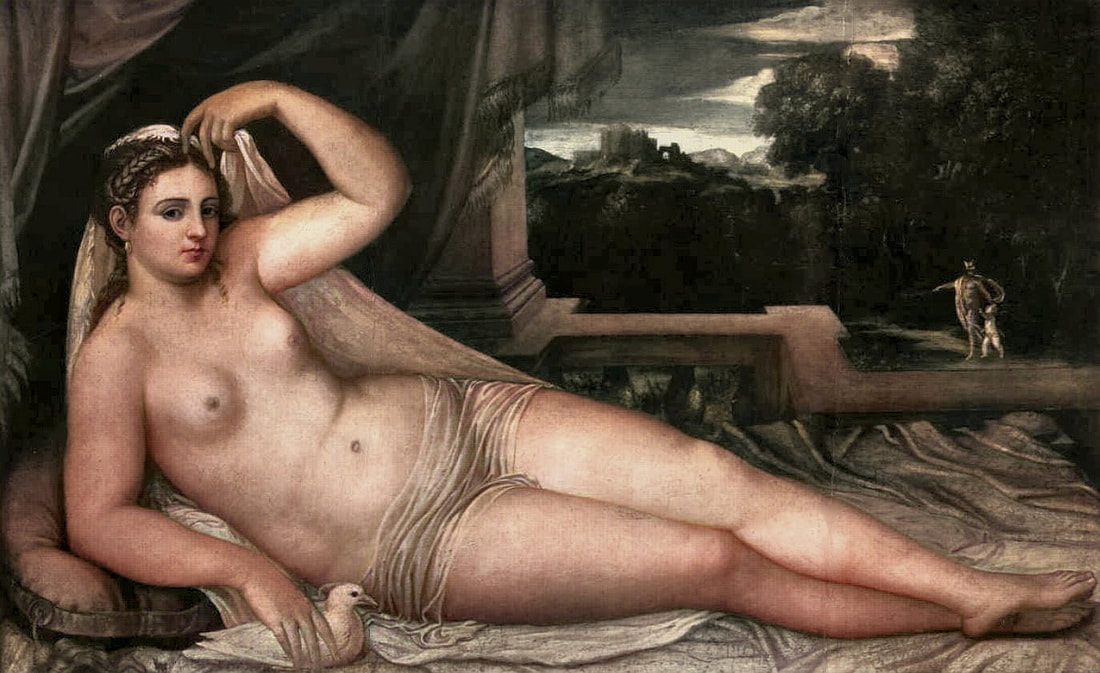
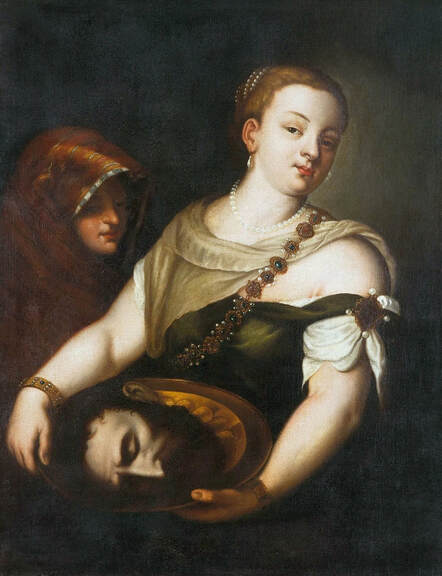
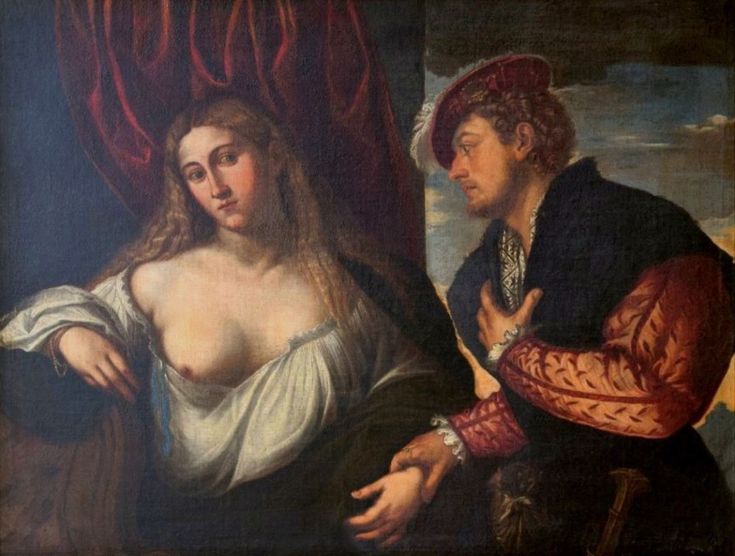
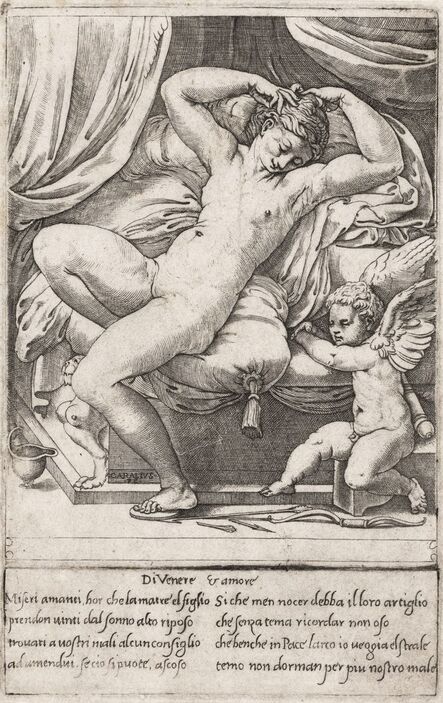
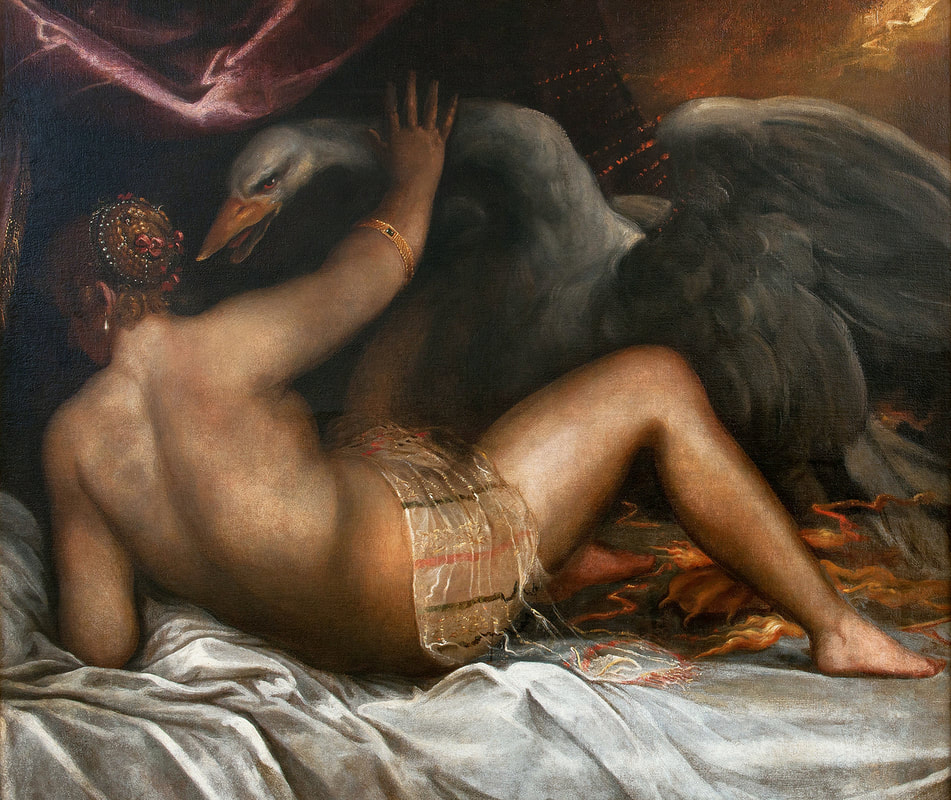
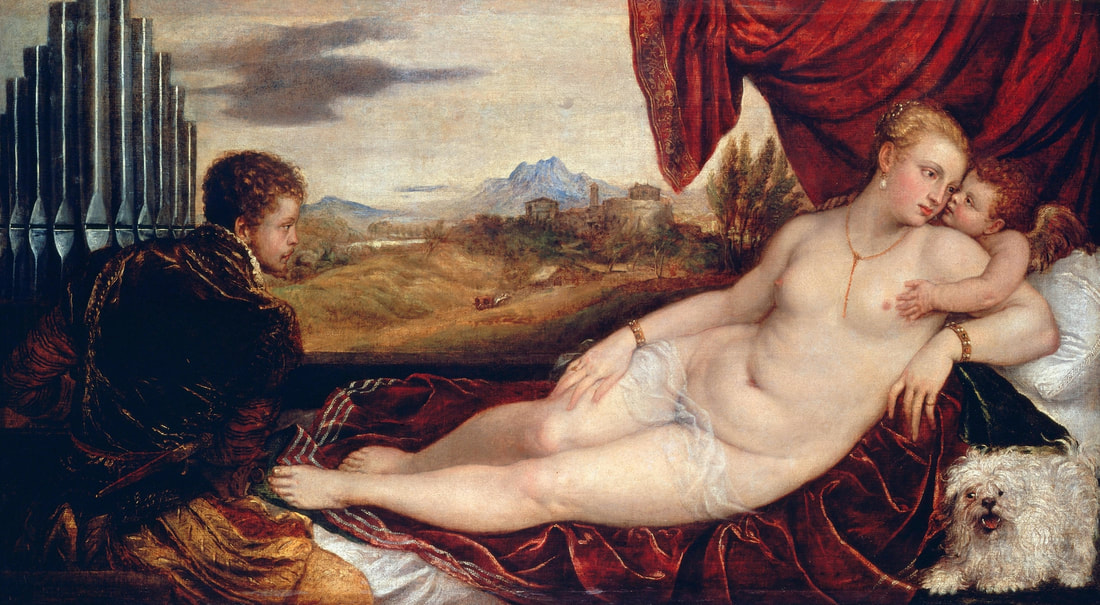
Mars and Venus as lovers (Mars being disarmed by Venus) by Cornelis van Haarlem, 1609, National Museum in Warsaw.
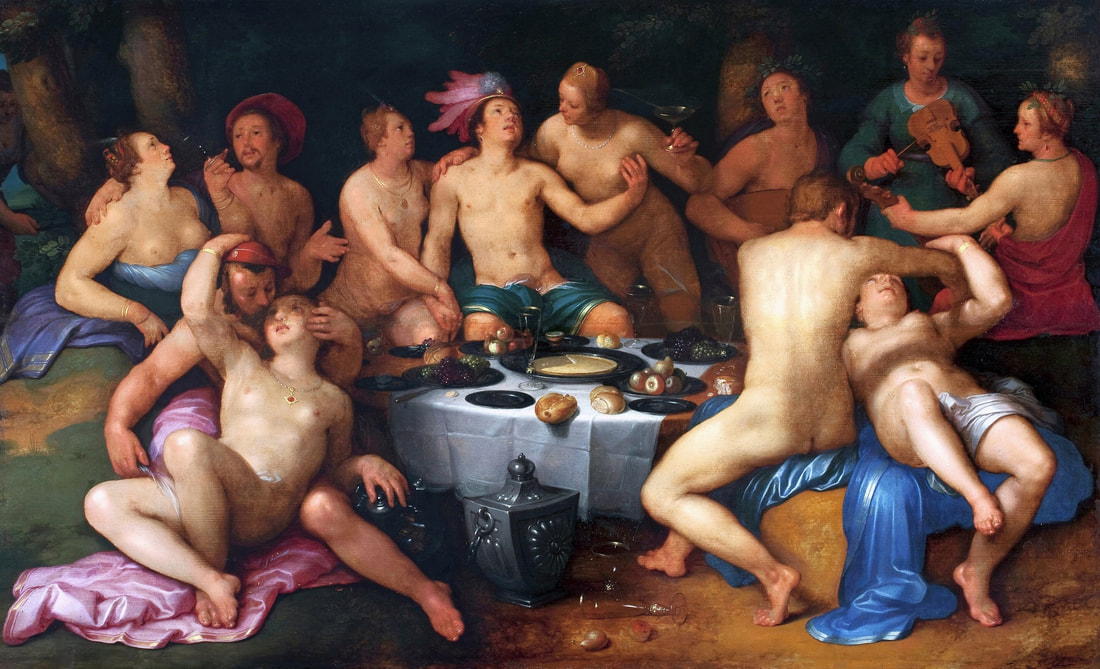
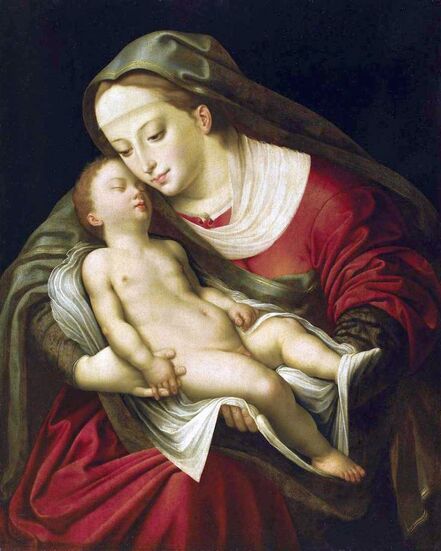
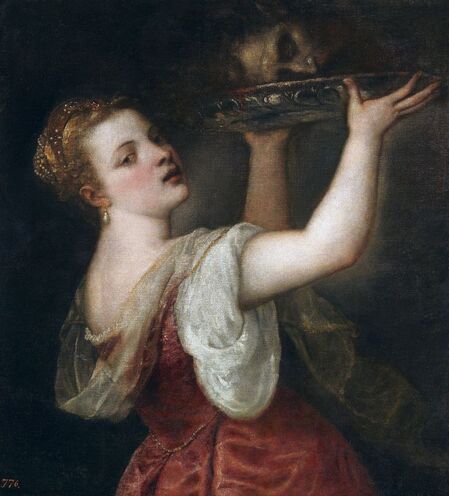
Feast of the prodigal son (Before the Deluge) by Cornelis van Haarlem, 1615, National Museum in Warsaw.
Triumph of Charles X Gustav the "Brigand of Europe" over the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth by Flemish painter, most probably Christian Melich, ca. 1655, National Museum in Warsaw.
Bibliography and legal notice. The majority of historical facts in the "Forgotten portraits" and information on works of art are easily verifiable on reliable sources available on the Internet, otherwise I invite you to visit the National Libraries of Poland - personally or virtually (Polona). The majority of translations, if not specifically attributed to someone else in the text or cited sources, are my authorship. Original paintings reproduced in "Forgotten portraits" are considered to be in the public domain (faithful photographic reproduction of a two-dimensional, public domain work of art, copyright term is the author's life plus 100 years or fewer) in accordance with international copyright law (photos from publicly available photo libraries, websites of relevant institutions, my own photos and scans from various publications with credit to the owner), however, all have been retouched and enhanced without significant interference with the quality of the original artwork, where possible (Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported, CC BY-SA 3.0). All interpretations, identifications and attributions, not specifically attributed to other authors in the text or cited sources, must be considered as my authorship - Marcin Latka (Artinpl).
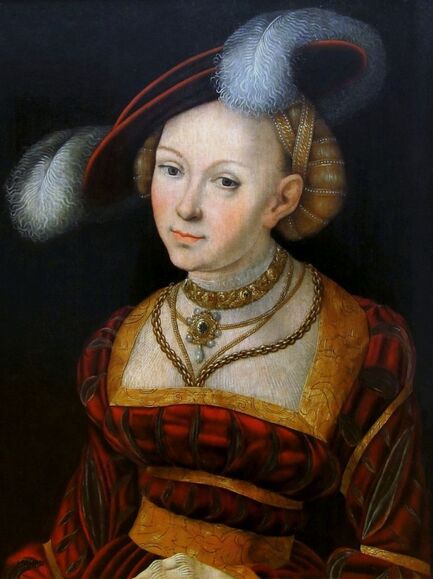
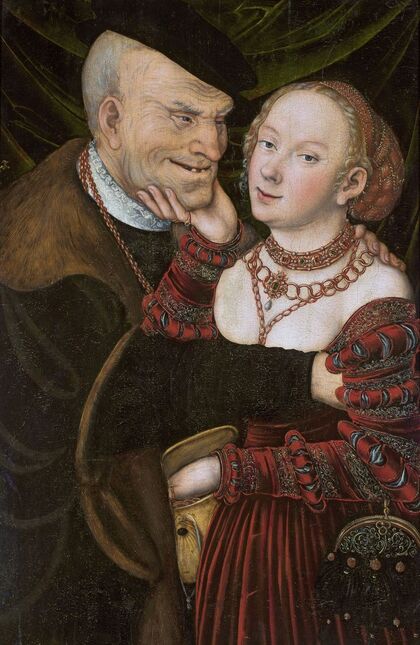
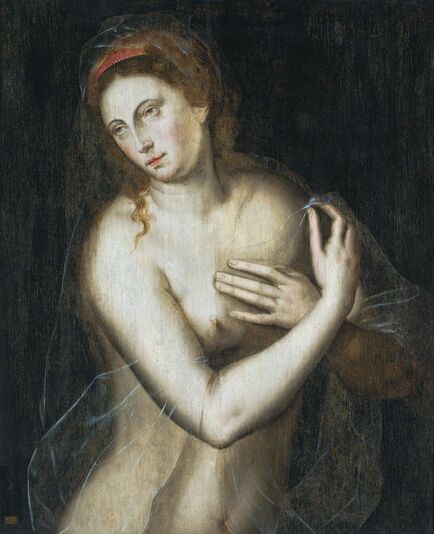
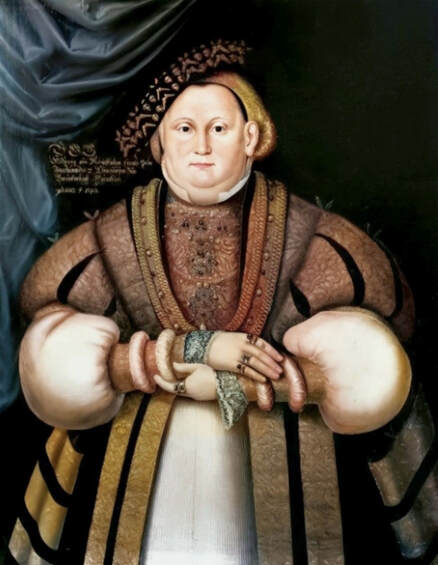
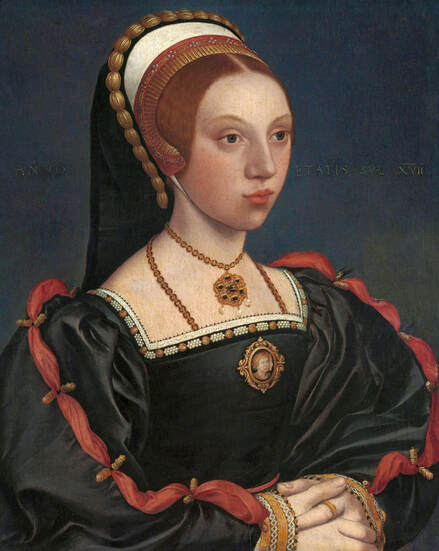
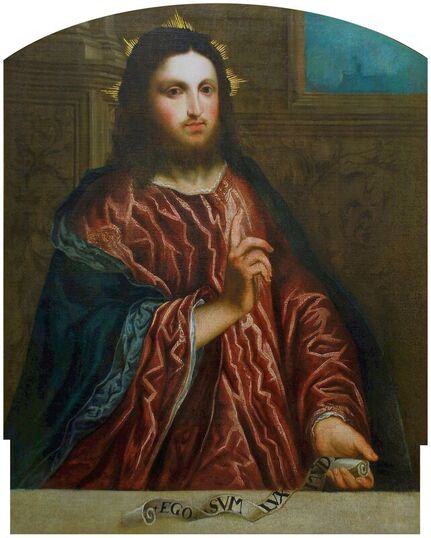
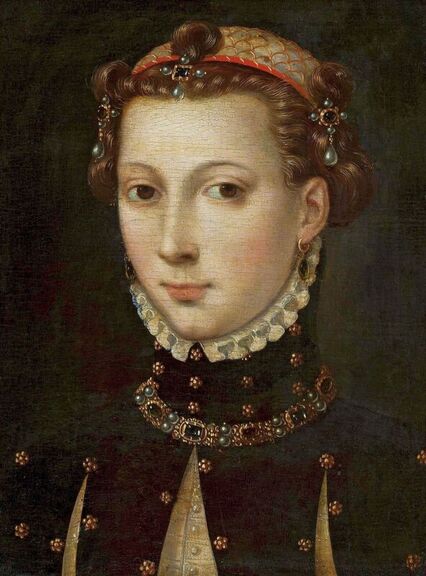
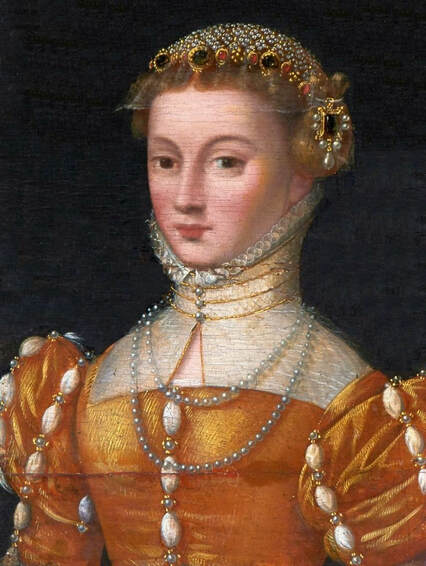
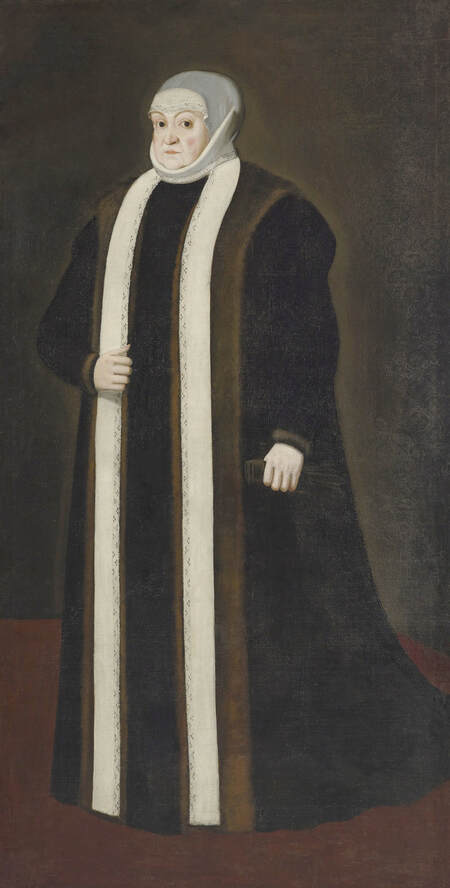
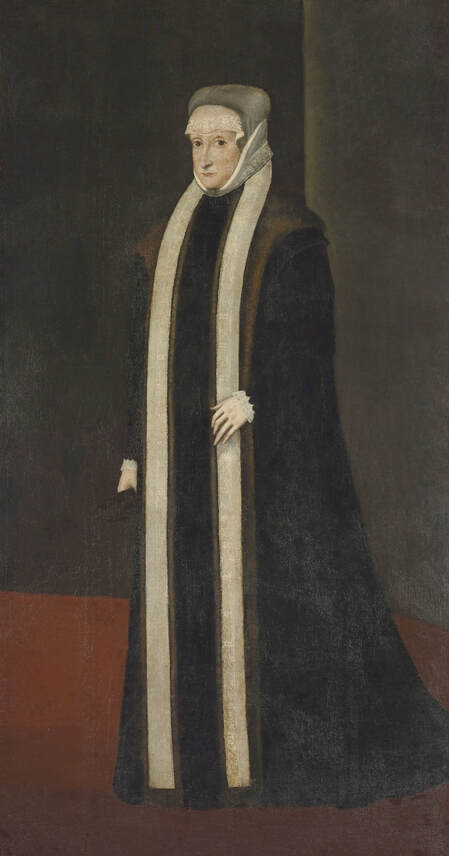
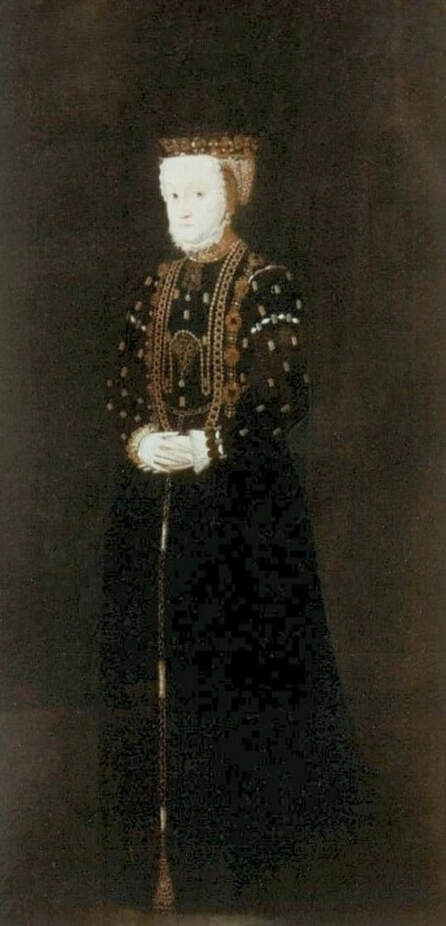
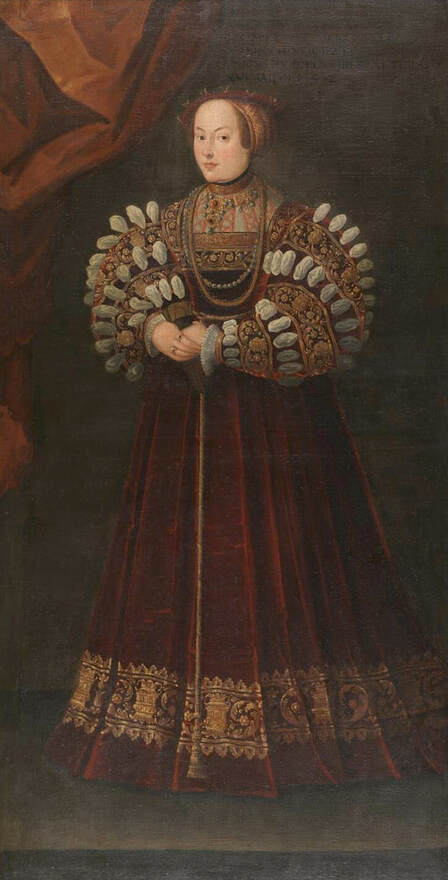
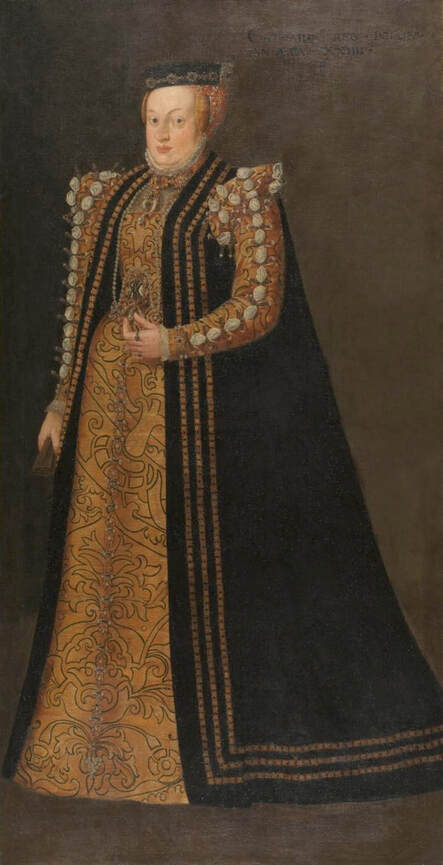
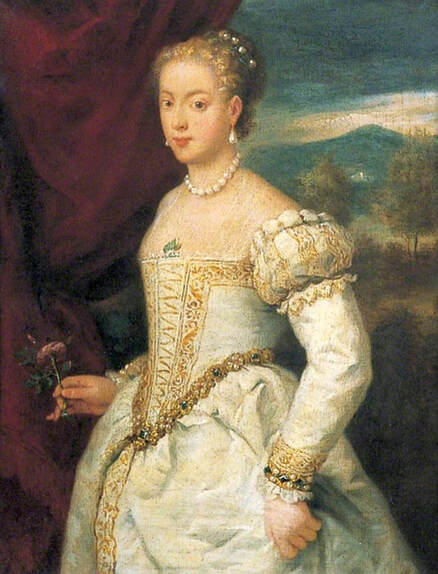
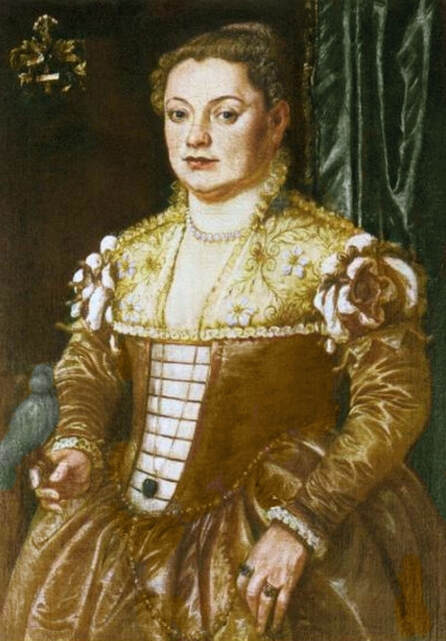
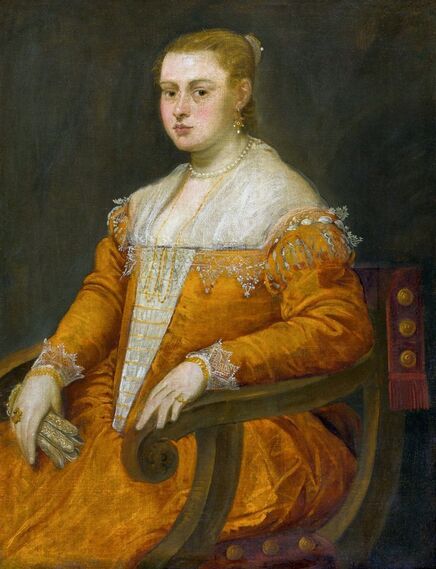
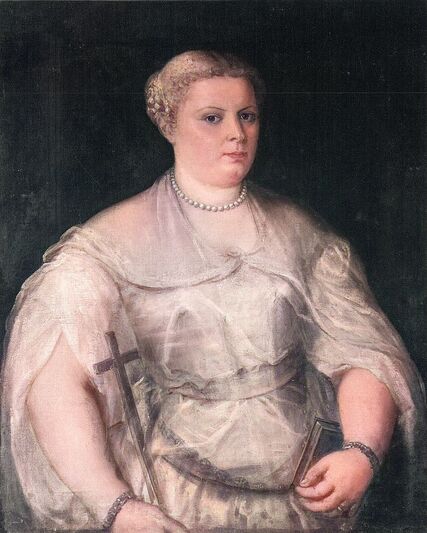
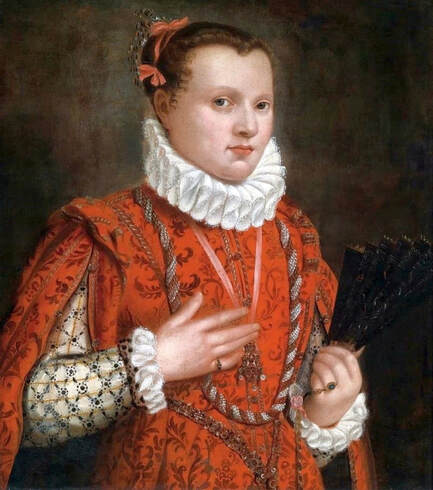
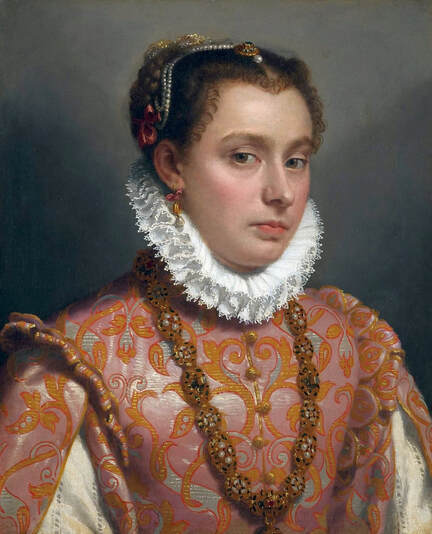
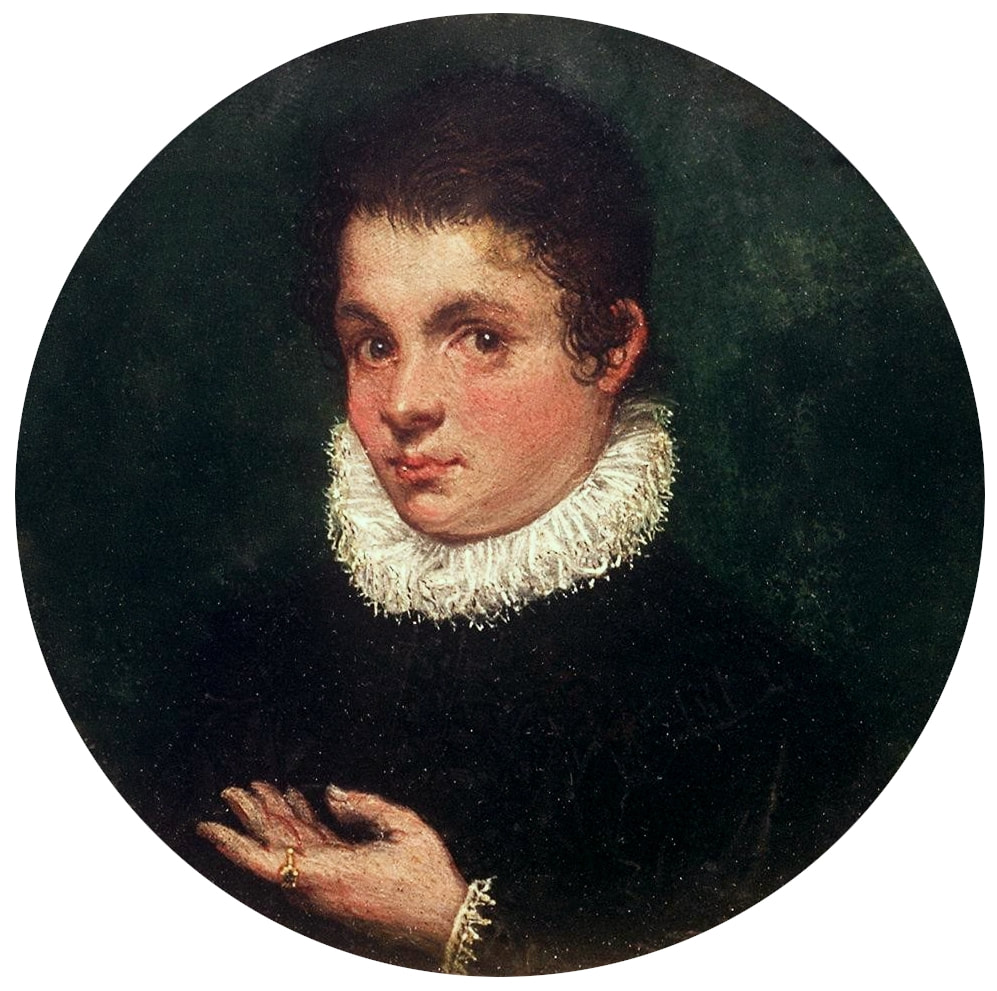
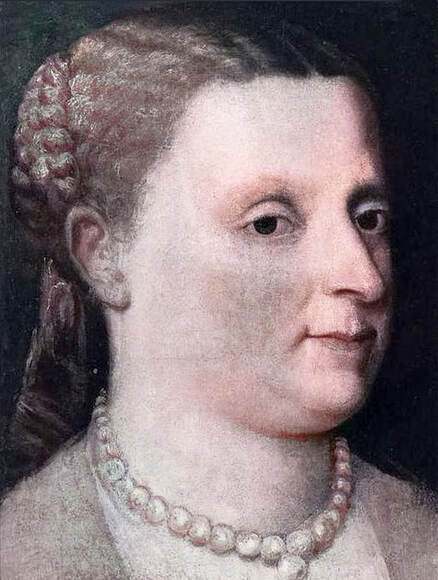
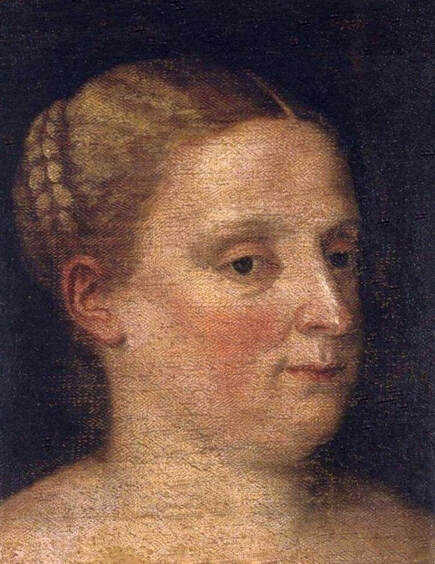
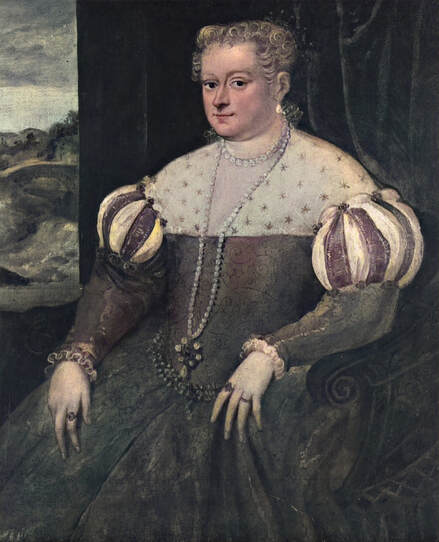
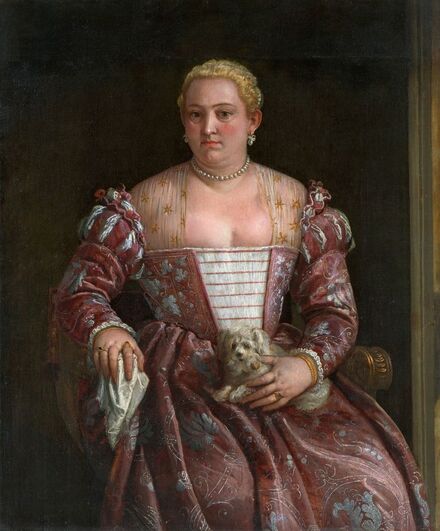
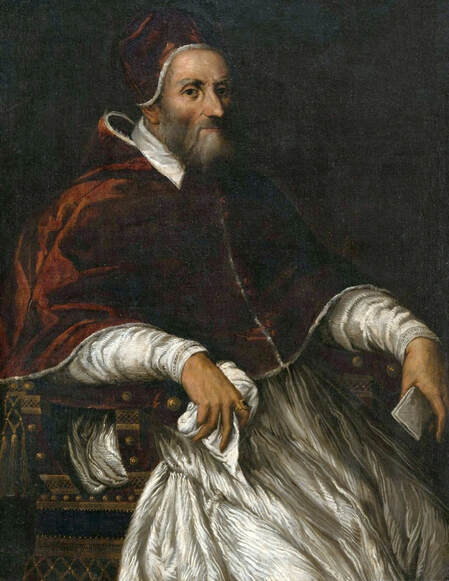
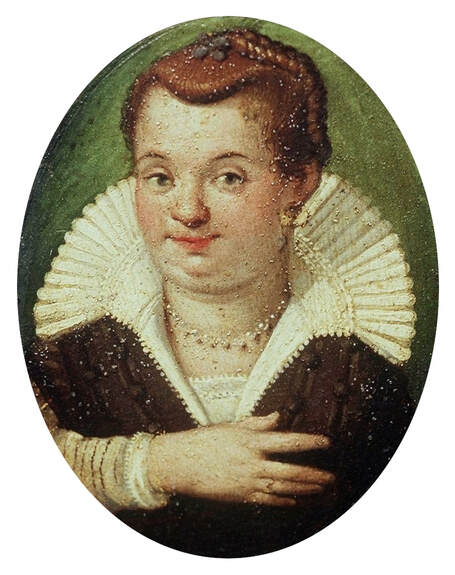
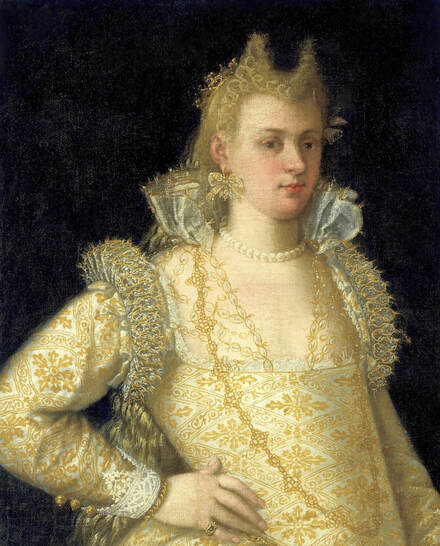
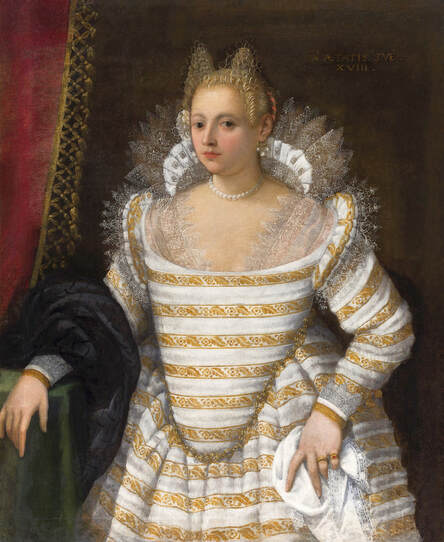
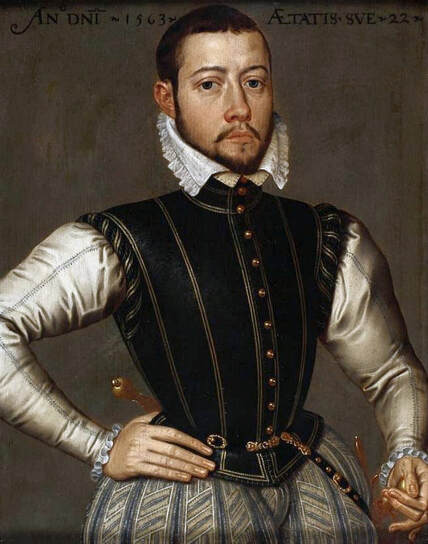
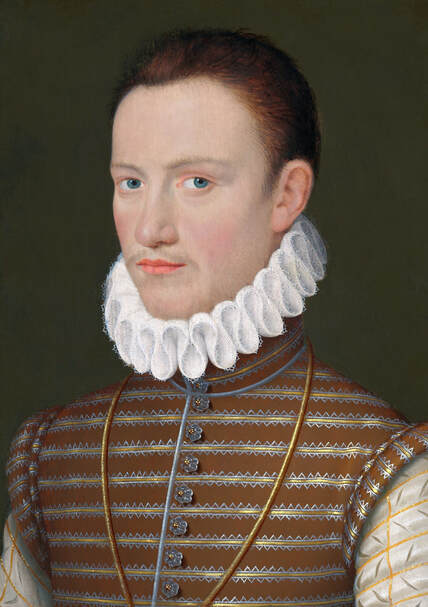
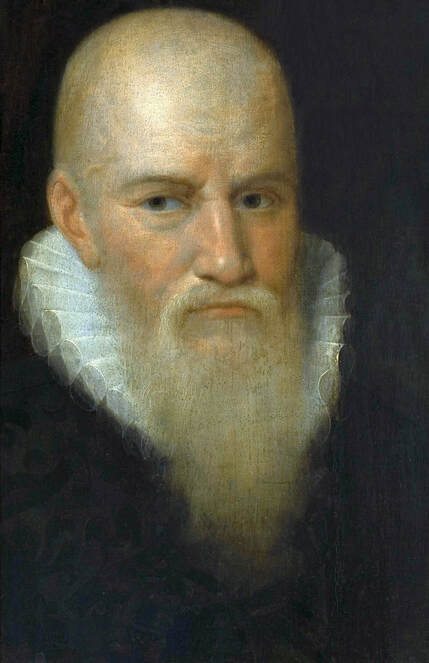
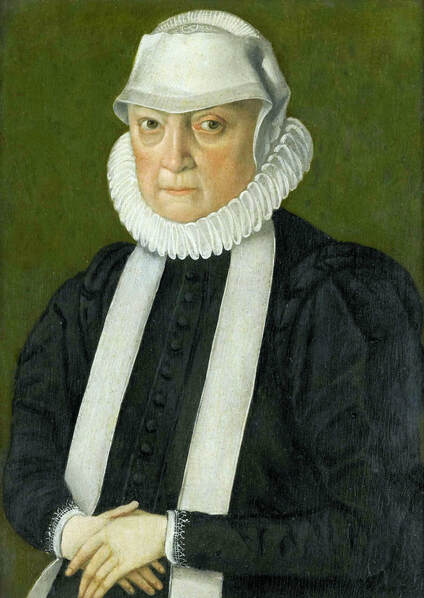
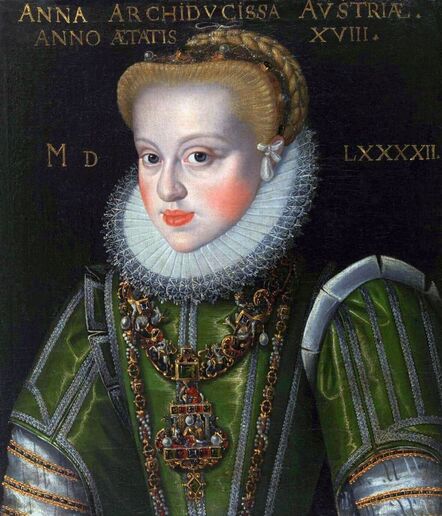
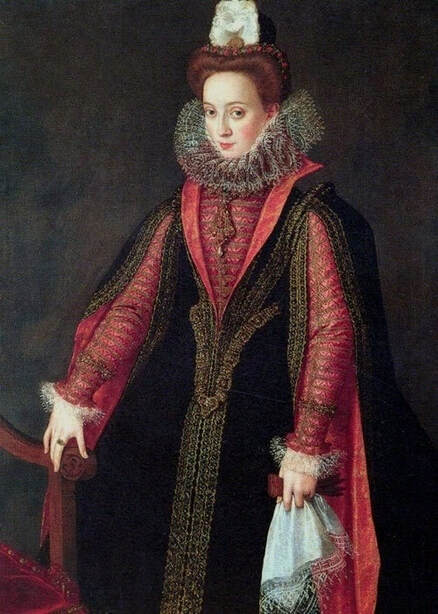
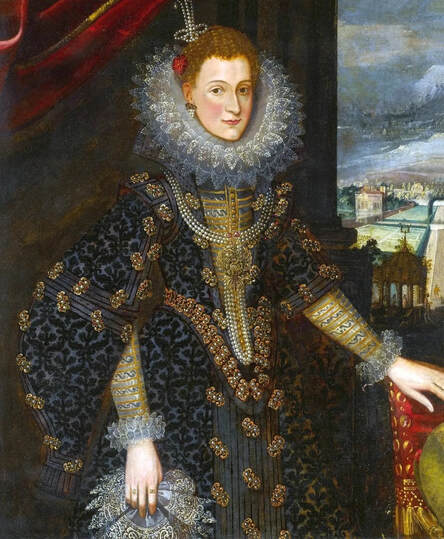
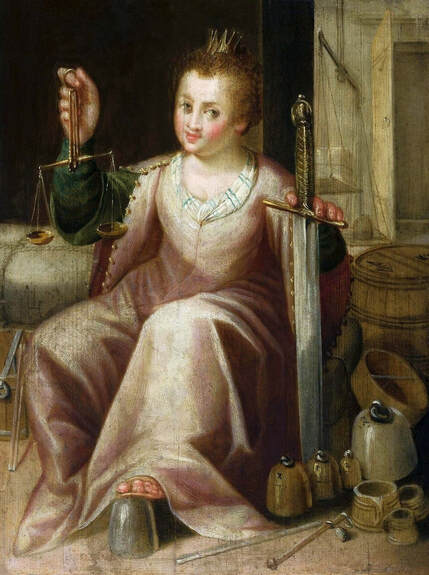
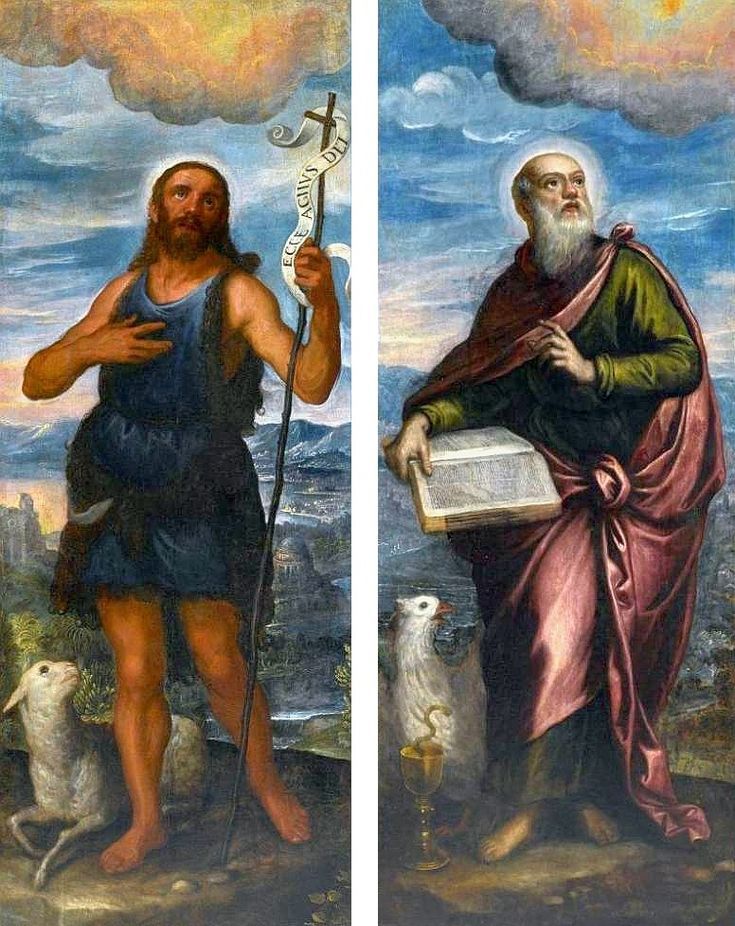
Majority of confirmed effigies of the Last Polish-Lithuanian Jagiellons are official, popular portraits pertaining to northern school of painting. As in some countries today, in the 16th century, people wanted a portrait of their monarch at home. Such effigies were frequently idealized, simplified and inscribed in Latin, which was the official language, apart from Ruthenian and Polish, of the multicultural country. They provided the official titulature (Rex, Regina), coat of arms and even age (ætatis suæ). Private and paintings dedicated to upper class were less so direct. Painters were operating with a complex set of symbols, which were clear then, however, are no longer so obvious today.
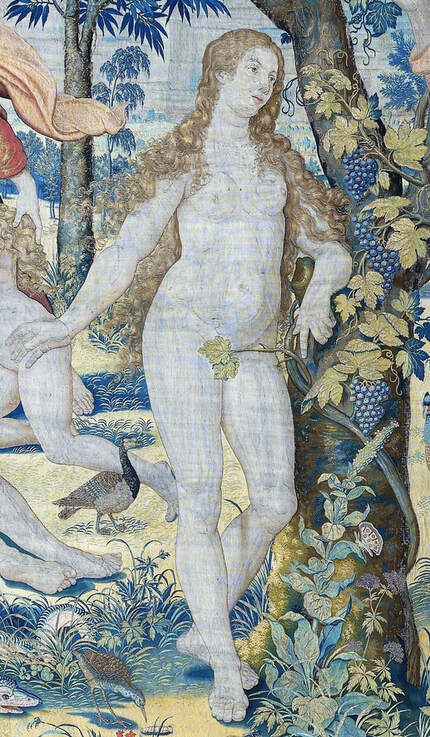
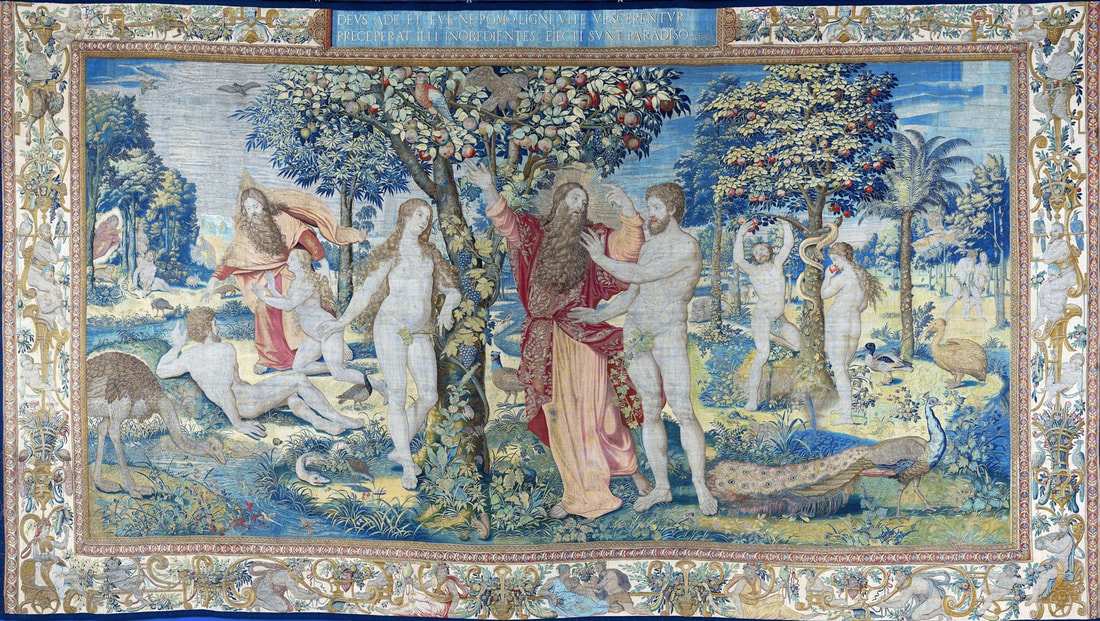
Since the very beginning of the Jagiellonian monarchy in Poland-Lithuania, art was characterized by syncretism and great diversity, which is best illustrated by the churches and chapels founded by the Jagiellons. They were built in a Gothic style with typical pointed arches and ribbed vaults and decorated with Russo-Byzantine frescoes, thus joining Western and Eastern traditions. Perhaps the oldest portraits of the first Jagiellonian monarch - Jogaila of Lithuania (Ladislaus II Jagiellon) are his effigies in the Gothic Holy Trinity Chapel at the Lublin Castle. They were commissioned by Jogaila and created by Ruthenian Master Andrey in 1418. On one, the king was represented as a knight on horseback and on the other as a donor kneeling before the Blessed Virgin Mary. The vault was adorned with the image of Christ Pantocrator above the coat of arms of the Jagiellons (Jagiellonian Cross). Similar church murals were created for Jogaila by the Orthodox priest Hayl around 1420 in the Gothic choir of Sandomierz Cathedral and for his son Casimir IV Jagiellon in the Holy Cross Chapel of the Wawel Cathedral by Pskov painters in 1470. Jogaila's portrait as one of the Magi in the mentioned Holy Cross Chapel (Adoration of the Magi, section of the Our Lady of Sorrows Triptych) is attributed to Stanisław Durink, whose father came from Silesia, and his marble tomb monument in the Wawel Cathedral to artists from Northern Italy. Perfectly conversant with Latin and the other languages of medieval and renaissance Europe, Poles, Lithuanians, Ruthenians, Germans and other ethnic groups of the multi-ethnic country, traveled to different countries of Western Europe, thus various fashions, even the strangest ones, like the effigies of Christ with Three Faces or effigies of crucified, bearded female Saint Wilgefortis, easily penetrated Poland-Lithuania. Disguised portraits, especially likenesses in guise of the Virgin Mary were popular in different parts of Europe from at least the mid-15th century (e.g. portraits of Agnès Sorel, Bianca Maria Visconti and Lucrezia Buti). Often unpopular rulers and their wives or mistresses were depicted as members of the Holy Family or saints. This naturally led to frustration and sometimes the only possible response was satire. The diptych by anonymous Flemish painter, most likely Marinus van Reymerswaele, from the 1520s (Wittert Museum in Liège, inventory number 12013), referring to diptychs by Hans Memling, Michel Sittow, Jehan Bellegambe, Jan Provoost, Jan Gossaert and other painters is obviously a satirical criticism of these representations. Instead of the rosy cheeks of a "virgin" holding a red carnation flower, a symbol of love and passion, the curious viewer will see brown cheeks and a thistle, a symbol of earthly pain and sin. In a 1487 diptych of Hieronymus Tscheckenburlin by the German painter, the rosy virgin is replaced by a rotting skeleton - memento mori (Kunstmuseum Basel). Sometimes also, historical scenes were represented in a mythological or biblical disguise or in a fantastic entourage. This is the case of a painting depicting the Siege of Malbork Castle in 1454 seen from the west - one of four paintings by Martin Schoninck, commissioned around 1536 by the Malbork Brotherhood to hang above the Brotherhood bench in the Artus Court in Gdańsk. To emphasize the victory of Gdańsk and the Jagiellonian monarchy over the Teutonic Order, the painting is accompanied by the Story of Judith, a mere woman, who overcomes a superior enemy, and effigies of Christ Salvator Mundi and Madonna and Child (lost during World War II). The widespread popularity of the "Metamorphoses" and other works of the Roman poet Ovid (43 BC – 17/18 AD) also contributed to the popularity of disguised portraits. The poet lived among the Sarmatians, legendary ancestors of the nobles of Poland-Lithuania, and was therefore considered the first national poet (compare "Ovidius inter Sarmatas" by Barbara Hryszko, p. 453, 455). In the "Metamorphoses" he deals with transformation into different beings, disguise, illusion and deception, as well as the deification of Julius Caesar and Augustus since both leaders trace their lineage through Aeneas to Venus, who "struck her breast with both hands, and tried to hide Caesar in a cloud" in an attempt to rescue him from the conspirators' swords. Poland-Lithuania was the most tolerant country of Renaissance Europe, where in the early years of the Reformation many churches simultaneously served as Protestant and Catholic temples. There are no known sources regarding organized iconoclasm, known from western Europe, in most cases works of art were sold, when churches were completely taken over by the Reformed denominations. Disputes over the nature of the images remained mainly on paper - the Calvinist preacher Stanisław Lutomirski called the Jasna Góra icon of the Black Madonna "an idolatry table", "a board from Częstochowa" that made up the doors of hell, and he described worshiping it as adultery and Jakub Wujek refuted the charges of iconoclasts, saying that "having thrown away the images of the Lord Christ, they replace them with images of Luther, Calvin and their harlots" (after "Ikonoklazm staropolski" by Konrad Morawski). Unlike other countries where effigies of "The Fallen Madonna with the Big Boobies", nude or half-naked images of saints or disguised portraits in churches and public places were destroyed in mob actions by Protestant crowds, in Poland-Lithuania such incidents were rare. Before the Great Iconoclasm, many temples were filled with nudity and so-called falsum dogma appearing at the time of the the Council of Trent (twenty-fifth session of the Tridentium, on December 3 and 4, 1563), which "means not so much a heretical view, but a lack of orthodoxy from the Catholic point of view. Iconography was to be cleansed of such errors as lewdness (lascivia), superstition (superstitio), shameless charm (procax venustas), and finally disorder and thoughtlessness" (after "O świętych obrazach" by Michał Rożek). The "divine nakedness" of ancient Rome and Greece, rediscovered by the Renaissance, was banished from churches, however many beautiful works of art preserved - like naked Crucifixes by Filippo Brunelleschi (1410-1415, Santa Maria Novella in Florence), by Michelangelo (1492, Church of Santo Spirito in Florence and another from about 1495, Bargello Museum in Florence) and by Benvenuto Cellini (1559-1562, Basilica of Escorial near Madrid). Nudity in Michelangelo's Last Judgment (1536-1541, Sistine Chapel) was censored the year after the artist's death, in 1565 (after "Michelangelo's Last Judgment - uncensored" by Giovanni Garcia-Fenech). In this fresco nearly everyone is naked or seminaked. Daniele da Volterra painted over the more controversial nudity of mainly muscular naked male bodies (Michelangelo's women look more like men with breasts, as the artist had spent too much time with men to understand the female form), earning Daniele the nickname Il Braghettone, "the breeches-maker". He spared some female effigies and obviously homosexual scenes among the Righteous Men (two young men kissing and a young man kissing an old man's beard and two naked young men in a passionate kiss). The provisions of Trent reached Poland through administrative ordinances and they were accepted at the provincial synod in Piotrków in 1577. Diocesan synod of Kraków, convened by Bishop Marcin Szyszkowski in 1621, dealt with issues of sacred art. The resolutions of the synod were an unprecedented event in the artistic culture of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. Published in Chapter LI (51) entitled "On sacred images" (De sacris imaginibus) of Reformationes generales ad clerum et populum ..., they created guidelines for the iconographic canon of sacred art. Holy images could not have portrait features, pictures of the naked Adam and Eve, Saint Mary Magdalene half-naked or embracing a cross in an obscene and multi-colored outfit, Saint Anne with three husbands, Virgin Mary painted or carved in too profane, foreign and indecent clothing should be removed from temples, because they contain false dogma, give the simple people an opportunity to fall into dangerous errors or are contrary to Scripture. However, the bans were not overly respected, because representations of the Holy Family, numbering more than twenty people, including Christ's siblings, have been preserved in the vast diocese of Kraków (after "O świętych obrazach" by Michał Rożek). The victorious Counter-Reformation and the victorious Reformation opposed shameless lust and shameless charm and a kind of paganism (after "Barok: epoka przeciwieństw" by Janusz Pelc, p. 186), but church officials could not ban "divine nakedness" from lay homes, and nude effigies of saints were still popular after the Council of Trent. Many of such paintings were acquired by clients from the Commonwealth abroad, in the Netherlands, in Venice and Rome, like, most likely, the Busty Madonna by Carlo Saraceni from the Krosnowski collection (National Museum in Warsaw, M.Ob.1605 MNW). It was the time of high infant and maternal mortality, less developed medicine, lack of public health care, when wars and epidemics ravaged large parts of Europe. Therefore, virility and fertility were considered by many to be a sign of God's blessing (after "Male Reproductive Dysfunction", ed. Fouad R. Kandeel, p. 6). In 1565 Flavio Ruggieri from Bologna, who accompanied Giovanni Francesco Commendone, a legate of Pope Pius IV in Poland, described the country in the manuscript preserved in the Vatican Library (Ex codice Vatic. inter Ottobon. 3175, Nr. 36): "Poland is quite well inhabited, especially Masovia, in other parts there are also dense towns and villages, but all wooden, counting up to 90,000 of them in total, one half of which belongs to the king, the other half to the nobility and clergy, the inhabitants apart from the nobility are a half and a quarter million, that is, two and a half million peasants and a million townspeople. [...] Even the craftsmen speak Latin, and it is not difficult to learn this language, because in every city, in almost every village there is a public school. They take over the customs and language of foreign nations with unspeakable ease, and of all transalpine countries, they learn the customs and the Italian language the most, which is very much used and liked by them as well as the Italian costume, namely at court. The national costume is almost the same as the Hungarian, but they like to dress up differently, they change robes often, they even change up several times a day. Since Queen Bona of the House of Sforza, the mother of the present king, introduced the language, clothes and many other Italian customs, some lords began to build in the cities of Lesser Poland and Masovia. The nobility is very rich. [...] Only townspeople, Jews, Armenians, and foreigners, Germans and Italians trade. The nobility only sells their own grain, which is the country's greatest wealth. Floated into the Vistula by the rivers flowing into it, it goes along the Vistula to Gdańsk, where it is deposited in intentionally built granaries in a separate part of the city, where the guard does not allow anyone to enter at night. Polish grain feeds almost all of King Philip's Netherlands, even Portuguese and other countries' ships come to Gdańsk for Polish grain, where you will sometimes see 400 and 500 of them, not without surprise. The Lithuanian grain goes along the Neman to the Baltic Sea. The Podolian grain, which, as has been said, perishes miserably, could be floated down the Dniester to the Black Sea, and from there to Constantinople and Venice, which is now being thought of according to the plan given by the Cardinal Kommendoni [Venetian Giovanni Francesco Commendone]. Apart from grain, Poland supplies other countries with flax, hemp, beef hides, honey, wax, tar, potash, amber, wood for shipbuilding, wool, cattle, horses, sheep, beer and some dyer's herb. From other countries they imports costly blue silks, cloth, linen, rugs, carpets, from the east precious stones and jewels, from Moscow, sables, lynxes, bears, ermines and other furs that are absent in Poland, or not as much as their inhabitants need to protect them from cold or for glamor. [...] The king deliberate on all important matters with the senate, although he has a firm voice, the nobility, as it has been said, has so tightened his power that he has little left over it" (after "Relacye nuncyuszow apostolskich ..." by Erazm Rykaczewski, pp. 125, 128, 131, 132, 136). Marcin Kromer (1512-1589), Prince-Bishop of Warmia, in his "Poland or About the Geography, Population, Customs, Offices, and Public Matters of the Polish Kingdom in Two Volumes" (Polonia sive de situ, populis, moribus, magistratibus et Republica regni Polonici libri duo), first published in Cologne in 1577, emphasized that "In almost our time, Italian merchants and craftsmen also reached the more important cities; moreover, the Italian language is heard from time to time from the mouths of more educated Poles, because they like to travel to Italy". He also stated that that "even in the very center of Italy it would be difficult to find such a multitude of people of all kinds with whom one could communicate in Latin" and as for the political system, he added that "the Republic of Poland is not much different […] from the contemporary Republic of Venice" (after "W podróży po Europie" by Wojciech Tygielski, Anna Kalinowska, p. 470). Mikołaj Chwałowic (d. 1400), called the Devil of Venice, a nobleman of Nałęcz coat of arms, mentioned as Nicolaus heres de Wenacia in 1390, is said to have named his estate near Żnin and Biskupin where he built a magnificent castle - Wenecja (Wenacia, Veneciae, Wanaczia, Weneczya, Venecia), after returning from his studies in the "Queen of the Adriatic". The country was formed by two major states - the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, but it was a multiethnic and multicultural country with a large Italian community in many cities. The locals most often called it in Latin simply Res Publicae (Republic, Commonwealth) or Sarmatia (as the Greeks, Romans and Byzantines of Late Antiquity called the great territories of Central Europe), more literary and by nobility. Nationality was not considered in today's terms and was rather fluid, as in the case of Stanisław Orzechowski, who calls himself either Ruthenian (Ruthenus / Rutheni), Roxolanian (Roxolanus / Roxolani) or of Ruthenian origin, Polish nation (gente Ruthenus, natione Polonus / gente Roxolani, natione vero Poloni), published in his In Warszaviensi Synodo provinciae Poloniae Pro dignitate sacerdotali oratio (Kraków, 1561) and Fidei catholicae confessio (Cologne, 1563), most likely to emphasize his origin and his attachment to the Republic. The role of women in Polish-Lithuanian society during the Renaissance is reflected in distinct women's literature, which has its beginning in anonymous "Senatulus, or the council of women" (Senatulus to jest sjem niewieści) from 1543 and especially Marcin Bielski's "Women's Parliament" (Syem Niewiesci), written in 1566-1567. The idea derives from the satirical Senatus sive Gynajkosynedrion by Erasmus of Rotterdam, published in 1528, which caused a wave of imitations in Europe. Bielski's work, however, brings a whole bunch of articles proposed by married women, widows and unmarried women to be passed at the Sejm, which have no equivalent in Erasmus's work. There is almost no satirical content, which is the core of Erasmus's work willing to point out the faults of women. The main element in Bielski's work is criticism of men (after "Aemulatores Erasmi? ..." by Justyna A. Kowalik, p. 259). The women point to the inefficiency of men's power over the country and their lack of concern for the common good of the Republic. Their arguments about the role of women in the world are based on the ancient tradition, when women not only advised men, but also ruled and fought for their own. This work provoked a whole series of brochures devoted to female matters, in which, however, the emphasis has been shifted more to discussion of women's clothing - "Reprimand of Women's Extravagant Attire" (Przygana wymyślnym strojom białogłowskim) from 1600 or "Maiden's Parliament" (Sejm panieński) by Jan Oleski (pseudonym), published before 1617. Authors like Klemens Janicki (1516-1543), Mikołaj Rej (1505-1569), Krzysztof Opaliński (1609-1655) and Wacław Potocki (1621-1696), condemned the variability of costumes as a national vice (after "Aemulatores Erasmi? ...", p. 253) and index of forbidden books of Bishop Marcin Szyszkowski of 1617 banned a large group of humorous, entertaining, often obscene texts, imbued with ambiguous eroticism, and for these reasons condemned by the counter-reformation and the new model of culture. Later, in 1625, in his "Votum on the improvement of the Commonwealth" (Votvm o naprawie Rzeczypospolitey) Szymon Starowolski railed against the Italian or Italianized women spoiling the youth, effeminacy of men and their reluctance to defend the eastern lands against invasions: "He, whom the caressed Italian courtesans have raised in pillows, being entangled with their gentle words and delicacies, he can't stand the hardships with us". The great diversity of costume dates at least to the time of Sigismund I. Janicki in his poem "On the Variety and Inconstancy of Polish Dress" (In poloni vestibus varietatem et inconstanciam) describes King Ladislaus Jagiello rising from the grave and unable to recognize Poles and Mikołaj Rej in his "Life of the Honest Man" (Żywot człowieka poczciwego), published in 1568, writes about "elaborate Italian and Spanish inventions, those strange coats [...] he will order the tailor to make him what they wear today. And I also hear in other countries, when you happen to paint [describe] every nation, then they paint a Pole naked and put the cloth in front of him with scissors, cut yourself as you deign". Venetian-born Polish writer Alessandro Guagnini dei Rizzoni (Aleksander Gwagnin), attributes this to the habit of Poles of visiting the most distant and diverse countries, from which foreign costumes and customs were brought to their homeland - "One can see in Poland, costumes of various nations, especially Italian, Spanish, and Hungarian, which is more common than others" (after "Obraz wieku panowania Zygmunta III ..." by Franciszek Siarczyński, p. 71). Works of art were commissioned from the best masters in Europe - silverware and jewelry in Nuremberg and Augsburg, paintings and fabrics in Venice and Flanders, armours in Nuremberg and Milan and other centers. For the tapestries representing the Deluge (about 5 pieces) commissioned in Flanders by Sigismund II Augustus in the early 1550s, considered one of the finest in Europe, the king paid the staggering sum of 60,000 (or 72,000) ducats. More than a century later, in 1665, their value was estimated at 1 million florins, while the Żywiec land at 600,000 thalers and the richly equipped Casimir Palace in Warsaw at 400,000 florins (after "Kolekcja tapiserii ..." by Ryszard Szmydki, p. 105). It was only a small part of the rich collection of fabrics of the Jagiellons, some of which were also acquired in Persia (like the carpets purchased in 1533 and 1553). Made of precious silk and woven with gold, they were much more valued than paintings. "The average price of a smaller rug on the 16th-century Venetian market was around 60 to 80 ducats, which was equal to the price for an altarpiece commissioned from a famous painter or even for an entire polyptych by a less-known master" (after "Jews and Muslims Made Visible ...", p. 213). In 1586, second-hand rug in Venice cost 85 ducats and 5 soldi and wall hangings bought from Flemish merchants 116 ducats, 5 lire and 8 soldi (after "Marriage in Italy, 1300-1650", p. 37). Around that time, in 1584, Tintoretto was only paid 20 ducats for a large painting of Adoration of the Cross (275 x 175 cm) with 6 figures for the church of San Marcuola and 49 ducats in 1588 for an altarpiece showing Saint Leonard with more then 5 figures for the Saint Mark's Basilica in Venice. In 1564 Titian informed King Philip II of Spain that he would have to pay 200 ducats for an autograph replica of the Martyrdom of Saint Lawrence, but that he could have one by the workshop for just 50 ducats (after "Tintoretto ..." by Tom Nichols, p. 89, 243). The lesser value of the paintings meant that they were not so prominently displayed in inventories and correspondence. The royal collections in Spain were largely unaffected by major military conflicts, so many paintings as well as related letters were retained. Perhaps we will never know how many letters Titian sent to the monarchs of Poland-Lithuania, if any. When Poland regained independence in 1918 and quickly began to rebuild the devastated interiors of Wawel Royal Castle, there was no effigy of any monarch inside (possibly except for a portrait of a ruling Emperor of Austria, as the building served the military). In 1919, the systematic collection of museum collections for Wawel began (after "Rekonstrukcja i kreacja w odnowie Zamku na Wawelu" by Piotr M. Stępień, p. 39). The practice of creating portraits for clients from the territories of present-day Poland from study drawings can be attested from at least the early 16th century. The oldest known is the so-called "Book of effigies" (Visierungsbuch), which was lost during World War II. This was a collection of preparatory drawings depicting the Pomeranian dukes, who were related to the Jagiellons, mainly by Cranach's workshop. Among the oldest were portraits of Bogislaw X (1454-1523), Duke of Pomerania and his daughter-in-law Amalia of the Palatinate (1490-1524) by circle of Albrecht Dürer, created after 1513. All were probably made by members of the workshop sent to Pomerania or less likely by local artists and returned to patrons with ready effigies. On the occasion of the division of Pomerania in 1541 with his uncle Duke Barnim XI (IX), Duke Philip I commissioned a portrait from Lucas Cranach the Younger. This portrait, dated in upper left corner, is now in the National Museum in Szczecin, while the preparatory drawing, previously attributed to Hans Holbein the Younger or Albrecht Dürer, is in the Musée des Beaux-Arts de Reims. A monogramist I.S. from Cranach's workshop used the same set of study drawings to create another similar portrait of the duke, now in the Kunstsammlungen der Veste Coburg. Studies for the portraits of Princess Margaret of Pomerania (1518-1569) and Anne of Brunswick-Lüneburg (1502-1568), wife of Barnim XI (IX), both dating from around 1545, were meticulously described by a member of the workshop sent to Pomerania to create them indicating colors, fabrics, shapes to facilitate work in the artist's studio. Undoubtedly, based on similar drawings, Cranach's workshop created miniatures of the Jagiellons in the Czartoryski Museum. In the 1620s a court painter of Sigismund III Vasa created drawings or miniatures after which Peter Paul Rubens painted the portrait of the king (Heinz Kisters collection in Kreuzlingen), most likely as one of a series. The same court painter painted the full-length portrait of Sigismund at Wilanów Palace. Between 1644-1650 Jonas Suyderhoef, a Dutch engraver, active in Haarlem, created a print with effigy of Ladislaus IV Vasa after a painting by Pieter Claesz. Soutman (P. Soutman Pinxit Effigiavit et excud / I. Suÿderhoef Sculpsit) and around that time Soutman, also active in Haarlem, created a similar drawing with king's effigy (Albertina in Vienna). After the destructive Deluge (1655-1660), the country slowly recovered and the most important foreign orders were mainly silverware, including a large silver Polish eagle, the heraldic base for the royal crown, created by Abraham I Drentwett and Heinrich Mannlich in Augsburg, most likely for the coronation of Michael Korybut Wiśniowiecki in 1669, now in the Moscow Kremlin. Foreign commissions for portraits revived more significantly during the reign of John III Sobieski. French painters such as Pierre Mignard, Henri Gascar and Alexandre-François Desportes (a brief stay in Poland, between 1695 and 1696), active mainly in Paris, are frequently credited as authors of portraits of members of the Sobieski family. Dutch painter Adriaen van der Werff, must have painted the 1696 portrait of Hedwig Elisabeth of Neuburg, wife of James Louis Sobieski, in Rotterdam or Düsseldorf, where he was active. The same Jan Frans van Douven, active in Düsseldorf from 1682, who made several effigies of James Louis and his wife. In the Library of the University of Warsaw preserved a preparatory drawing by Prosper Henricus Lankrink or a member of his workshop from about 1676 for a series of portraits of John III (Coninck in Polen conterfeyt wie hy in woonon ...), described in Dutch with the colors and names of the fabrics (violet, wit satin). Lankrink and his studio probably created them all in Antwerp as his stay in Poland is unconfirmed. A few years later, around 1693, Henri Gascar, who after 1680 moved from Paris to Rome, painted a realistic apotheosis of John III Sobieski surrounded by his family, depicting the king, his wife, their daughter and their three sons. A French engraver Benoît Farjat, active in Rome, made a print from this original painting which has probably not survived, dated '1693' (Romae Superiorum licentia anno 1693) lower left and signed in Latin upper right: "H. Gascar painted, Benoît Farjat engraved" (H. GASCAR PINX. / BENEDICTVS FARIAT SCVLP.). Two workshop copies of this painting are known - one in Wawel Castle in Kraków, and the other, most likely from a dowry of Teresa Kunegunda Sobieska, is in the Munich Residence. Such a realistic depiction of the family must have been based on study drawings created in Poland, as Gascar's stay in Poland is not confirmed in the sources. The French painter Nicolas de Largillière, probably worked in Paris on the portrait of Franciszek Zygmunt Gałecki (1645-1711), today in the State Museum in Schwerin. Also one of the most famous portraits in Polish collections - Equestrian portrait of Count Stanisław Kostka Potocki by Jacques Louis David from 1781 was created "remotely". A collection catalogue of the Wilanów Palace, published in 1834 mentioned that the portrait was completed in Paris "after a sketch made from life in the Naples Riding School". One of such modello or ricordo drawings is in the National Library of Poland (R.532/III). It was the same for the statues and reliefs with portraits. Some of the most beautiful examples preserved in Poland were ordered from the best foreign workshops. Among the oldest and best are the bronze epitaphs made in Nuremberg by the workshop of Hermann Vischer the Younger, Peter Vischer the Elder and Hans Vischer in the late 15th and early 16th centuries, such as the epitaph of Filippo Buonaccorsi, called Callimachus in Kraków, epitaph of Andrzej Szamotulski (d. 1511), voivode of Poznań, in Szamotuły, tomb of Piotr Kmita of Wiśnicz and of Cardinal Frederick Jagiellon (d. 1503), both at the Wawel Cathedral and tomb of King Sigismund I's banker, Seweryn Boner and his wife Zofia Bonerowa née Bethman at St. Mary's Basilica in Kraków. Around 1687, "Victorious King" John III Sobieski ordered large quantities of sculptures in Antwerp from the workshop of Artus Quellinus II, his son Thomas II and Lodewijk Willemsens and in Amsterdam from the workshop of Bartholomeus Eggers for the decoration of the Wilanów Palace in Warsaw, including busts of the royal couple, today in Saint Petersburg. All of these statues and reliefs were based on drawings or portraits, possibly similar to the triple portrait of Cardinal Richelieu, made as a study for a bust to be made by the Italian sculptor Gian Lorenzo Bernini in Rome. For the equestrian statue of Prince Józef Poniatowski (1763-1813), made between 1826 and 1832 and inspired by the statue of Marcus Aurelius in Rome, the Danish-Icelandic sculptor Bertel Thorvaldsen (1770-1844), although he arrived from Rome to Warsaw in 1820, had to use other effigies of the prince. The initiator of the construction of the monument was Anna Potocka née Tyszkiewicz (1779-1867). The monument was confiscated by the Russian authorities after the November Uprising (1830-1831) and was returned to Warsaw in March 1922. After the suppression of the Warsaw Uprising, the Nazi German invaders ordered the statue to be blown up on December 16, 1944. A new cast of the sculpture, made in the years 1948-1951, was donated to Warsaw by the Kingdom of Denmark. Some sources also confirm this practice. During his second stay in Rome, Stanisław Reszka (1544-1600), who admired the paintings by Federico Barocci in Senigallia or the work of Giulio Romano in Mantua, again buys paintings, silver and gold plates. He sends many works of this kind as gifts to Poland. To Bernard Gołyński (1546-1599) he sends paintings, including a portrait of the king and his own effigy and for King Stephen Bathory a portrait of his nephew. These portraits of the monarch and his nephew were therefore made in Rome or Venice from study drawings or miniatures that Reszka brought. On another occasion, he sends eight porcelain "vessels" in a decorative casket to the king, purchased in Rome and to Wojciech Baranowski (1548-1615), Bishop of Przemyśl, a relief of St. Albert, carved in ebony. Through Cardinal Ippolito Aldobrandini (later Pope Clement VIII), papal nuncio in Poland between 1588-1589, he sends paintings purchased for the king, one of the Savior, embroidered "of the most excellent work" and St. Augustine, made of bird feathers, "the most beautiful" (pulcherrimum), as he says. To the royal secretary Rogulski, who came to Rome, he gives a silver inkwell, and the chamberlain of the chancellor Jan Zamoyski entrusts him with a precious stone to be repaired in Italy, but before that, Reszka consulted the Kraków goldsmiths. All of these objects, including the paintings, must have been the work of the best Italian artists, but names rarely appear in the sources. In 1584, King Stephen's nephew, Andrew Bathory, with his companions, purchased and commissioned many exquisite items from Venice, including gold cloth with coats of arms, gold-embossed Cordovan (cuir de Cordoue) leather wallpapers, made by the goldsmith Bartolomeo del Calice. Another time he bought "12 bowls, 16 silver orbs" (12 scudellas, orbes 16 argenteos) from Mazziola and supervised the artist working on the execution of "glass vessels" (vasorum vitreorum). In Rome, they visit a certain Giacomo the Spaniard to see the "marvels of art" (mirabilia artis), where Bathory probably bought the trinkets and fine paintings, later shown to the delegates of the Jędrzejów Abbey. Visitors from Poland-Lithuania gave and received many valuable gifts. In 1587, the Venetian Senate, through two important citizens, offered Cardinal Andrew Bathory, who came as an envoy of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth with the announcement of the election of Sigismund III, two silver basins and jugs, four trays and six candelabra "of beautiful work" (pulchri operis). The Pope gives two medals with his image to Rogulski, and a gold chain to Cardinal Aldobrandini. After returning to Poland, Cardinal Bathory gives Queen Anna Jagiellon a coral cross, received from Cardinal Borromeo, and a box of nacre (ex madre perla), receiving a beautiful, expensive ring in return. Many artists were also engaged in Italy for the Commonwealth. King Stephen entrusts his nephew with the mission of bringing to the royal court architects who master the art of building fortresses and castles. Urged by the king, Reszka makes efforts through Count Taso, however, only a few months after his arrival he manages to get into the royal service Leopard Rapini, a Roman architect for an annual salary of 600 florins. On his way back to Poland, Simone Genga, architect and military engineer from Urbino, was admitted as a courtier in the presence of the Archbishop of Senigallia. We learn from Giorgio Vasari that Wawrzyniec Spytek Jordan (1518-1568), an art lover who frequented the thermal baths near Verona, was offered a small painting depicting the Deposition from the Cross, painted by Giovanni Francesco Caroto. Stanisław Tomkowicz (1850-1933) speculated that the Lamentation of Christ, inspired by Michelangelo's "Florentine Pieta" in the Biecz Collegiate Church, could be this painting. However, it is very likely that it was brought to Poland by a member of the Sułkowski family and its attribution to Caroto is rejected. Wawrzyniec, "a man of great authority with the King of Poland", according to Vasari, also brought to Poland-Lithuania the Italian sculptor Bartolomeo Ridolfi and his son Ottaviano, where they created numerous works in stucco, large figures and medallions and prepared designs for palaces and other buildings. Ridolfi was employed by King Sigismund Augustus "with honorable salaries" (Spitech Giordan grandissimo Signore in Polonia appresso al Re, condotto con onorati stipendi al detto Re di Polonia), but all his works were most likely destroyed during the Deluge. Bartolomeo Orfalla, a townsman from Verona, carried out exploratory drilling in the Spytek's estates to find salt similar to that mined in Bochnia and Wieliczka and Wawrzyniec's magnificent tombstone in the Church of St. Catherine and St. Margaret in Kraków was sculpted by Santi Gucci in 1603. The Italians also had many effigies of Polish-Lithuanian monarchs, many of which were forgotten when the Commonwealth ceased to be a leading European power after the Deluge (1655-1660). According to Maciej Rywocki's peregrination books from 1584-1587, written by the mentor and steward of the Kryski brothers from Masovia, during their three-year journey to Italy for study and education, in the Villa Medici in Rome, owned by Cardinal Ferdinando, later Grand Duke of Tuscany, in the gallery of portrait paintings, he saw "with all Polish kings and King Stephen and the queen [Anna Jagiellon] very resembling". This effigy of the elected queen of the Commonwealth, possibly by a Venetian painter, undoubtedly resembled the portraits of her dear friend Bianca Cappello, a noble Venetian lady and Grand Duchess of Tuscany. According to Stanisław Reszka, who was Ferdinando's guest in Florence in 1588, the Grand Duke owned a ritrat (portrait, from the Italian ritratto) of King Sigismund III Vasa and his father John III of Sweden. Reszka sent him a map of the Commonwealth made on satin on which there was also a portrait of Sigismund III (Posłałem też księciu Jegomości aquilam na hatłasie pięknie drukowaną Regnorum Polonorum, który był barzo wdzięczen. Tam też jest wyrażona twarz Króla Jmci, acz też ma ritrat i Króla Jmci szwedzkiego, a także i Pana naszego) (after "Włoskie przygody Polaków ..." by Alojzy Sajkowski, p. 104). A few decades earlier, Jan Ocieski (1501-1563), secretary of King Sigismund I, wrote in his travel diary to Rome (1540-1541) the information about a portrait of King Sigismund, which was in the possession of the cardinal S. Quatuor with an extremely flattering note: "this is a king like never before" (hic est rex, cui similis non est inventus), and "who is the wisest king, and the most experienced in dealing with things" (qui est prudentissimus rex et usu tractandarum rerum probatissimus), according to this cardinal (after "Polskie dzienniki podróży ..." by Kazimierz Hartleb, pp. 52, 55-57, 67-68). The situation was similar in other European countries. After the death of Ladislaus IV Vasa in 1648, Francesco Magni (1598-1652), lord of Strážnice in Moravia, ordered the portrait of the Polish-Lithuanian monarch to be moved from the representative piano nobile, a gallery with portraits of the Habsburgs, his ancestors, relatives, and benefactors, to his private room on the second floor of the castle (after "Portrait of Władysław IV from the Oval Gallery ..." by Monika Kuhnke, Jacek Żukowski, p. 75). The original portraits of King Ladislaus IV and Queen Marie Casimire, after which copies were made in the 18th century for the Ancestral Gallery (Ahnengalerie) of the Munich Residence, were considered to represent Charles X Gustavus of Sweden (CAROLUS X GUSTAVUS) and his granddaughter Ulrika Eleonora (1688-1741), Queen of Sweden (UDALRICA ELEONORA). The massive destruction of the Commonwealth's heritage and post-war chaos also contributed to such mistakes in Poland. Thus, in the gallery of 22 portraits of the kings of Poland, painted between 1768 and 1771 by Marcello Bacciarelli to embellish the so-called Marble Room of the Royal Castle in Warsaw, King Sigismund II Augustus is Jogaila (VLADISLAUS JAGIELLO, inventory number ZKW/2713/ab) and son of Anna Jagellonica (1503-1547), Archduke Charles II of Austria (1540-1590) was presented as Sigismund II Augustus (SIGISMUNDUS AUGUSTUS, ZKW/2719/ab), according to the descriptions under the images. These portraits are copies of paintings by Peter Danckerts de Rij dating from around 1643 (Nieborów Palace, NB 472 MNW, NB 473 MNW, deposited at the Royal Castle in Warsaw), based on lost originals. During the Deluge (1655-1660), when the situation was desperate and many people expected the barbarian invaders to totally destroy the Realm of Venus - they plundered and burned the majority of the Commonwealth's cities and fortresses and planned the first partition of the country (Treaty of Radnot), King John Casimir Vasa, a descendant of the Jagiellons, turned to a woman - the Virgin Mary for protection. At the initiative of his wife Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga in the fortified city of Lviv in Ruthenia on April 1, 1656, he proclaimed the Virgin his Patroness and Queen of his countries (Ciebie za Patronkę moją i za Królowę państw moich dzisiaj obieram). Soon, when the invaders were repelled, the medieval Byzantine icon of the Black Madonna (Hodegetria) of Częstochowa with scars on her face, revered by both Catholics and Eastern Orthodox Christians, and already surrounded by a cult, became the holiest of all Poland. The fortified sanctuary of the Black Madonna at Bright Mountain (Jasna Góra) was defended from pillage and destruction by the armies of the "Brigand of Europe" in late 1655, a Ruthenian-style riza (robe) was made for the Virgin and adorned with the most beautiful examples of Baroque and Renaissance jewelry offered by pilgrims, a perfect illustration of the country's culture and its diversity. The main statue of the beautiful residence of the "Victorious King" John III Sobieski, who saved Vienna from plunder and destruction in 1683 - Wilanów Palace, except for the planned equestrian monument of the king, was not the statue of Mars, god of war, nor of Apollo, god of the arts, nor even of Jupiter, king of the gods, but of Minerva - Pallas, goddess of wisdom. It was most likely created by the workshop of Artus Quellinus II in Antwerp or by Bartholomeus Eggers in Amsterdam and placed in the upper pavilion crowning the entire structure. Unfortunately, this large marble statue, as well as many others, including busts of the king and queen, were looted by the Russian army in 1707. In "The Register of Carrara marble statues and other objects taken from Willanów in August 1707" (Connotacya Statui Marmuru Karrarskiego y innych rzeczy w Willanowie pobranych An. August 1707), it was described as a "Satue of Pallas [...] in the window of the room above the entrance to the palace, resting her right hand on a gilded marble shield with the inscription Vigilando Quiesco [In watching I rest]" (Statua Pallas [...] w oknie salnym nad weysciem do Pałacu podpierayacey ręką prawą o tarczę z Marmuru wyrobioną pozłocistą, na ktorey Napis Vigilando Quiesco). Later, it most likely decorated the Kamenny Theater in Saint Petersburg (demolished after 1886), which Johann Gottlieb Georgi described in his "Description of the Russian Imperial Capital ...", published in 1794: "Above the main entrance is the image of a seated Minerva made of Carrara marble, with her symbols, and on the shield: Vigilando quiesco". The fact that nothing (or almost) preserved does not mean that nothing existed, so perhaps even the stay of some or several great European artists in Poland-Lithuania is still to be discovered.
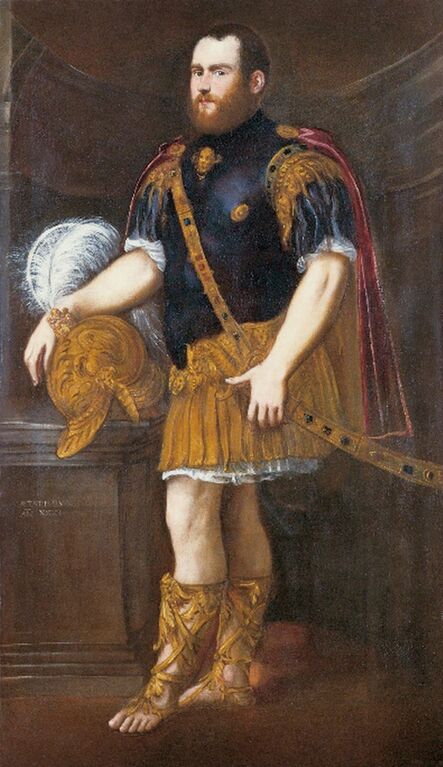
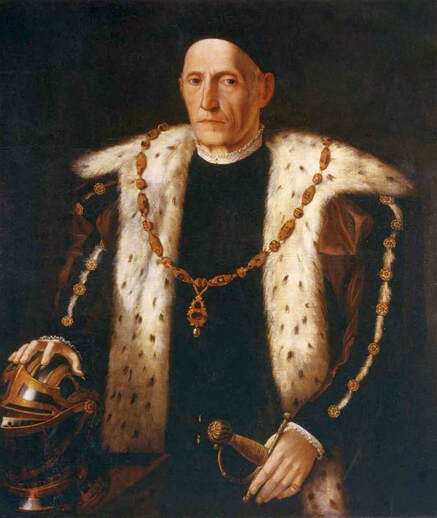
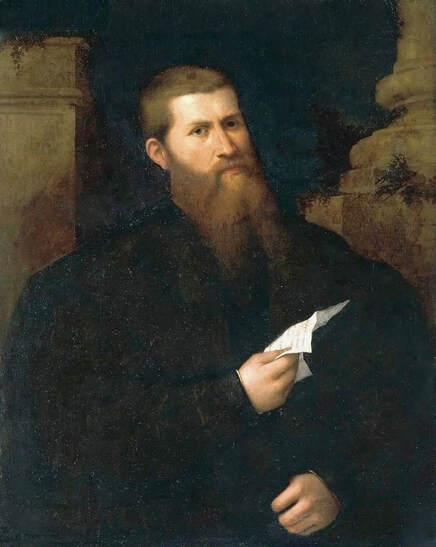
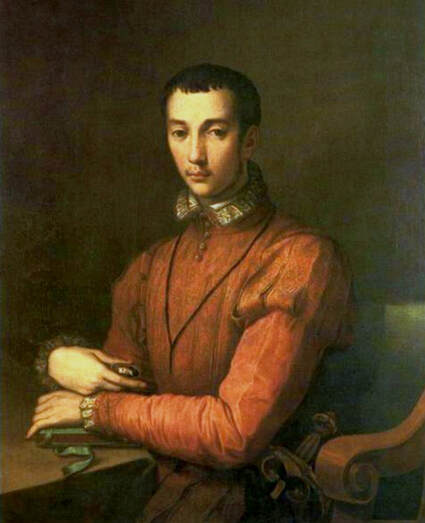
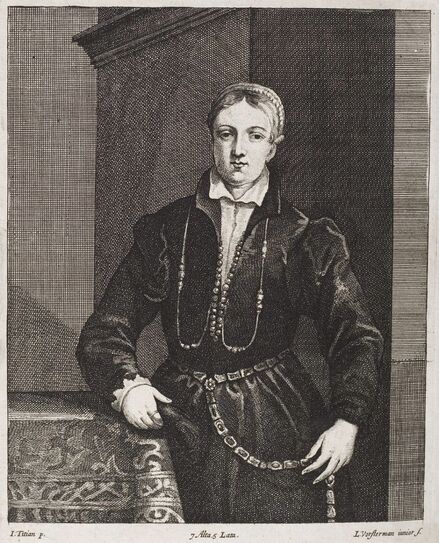
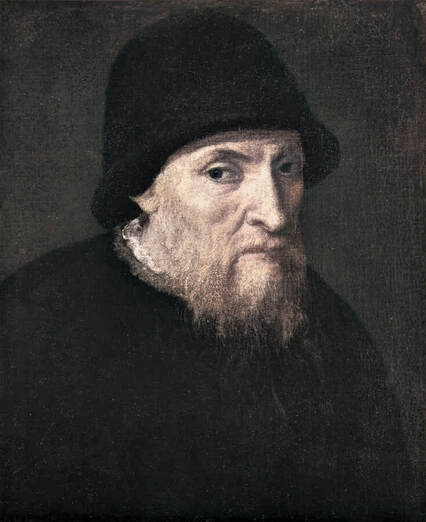
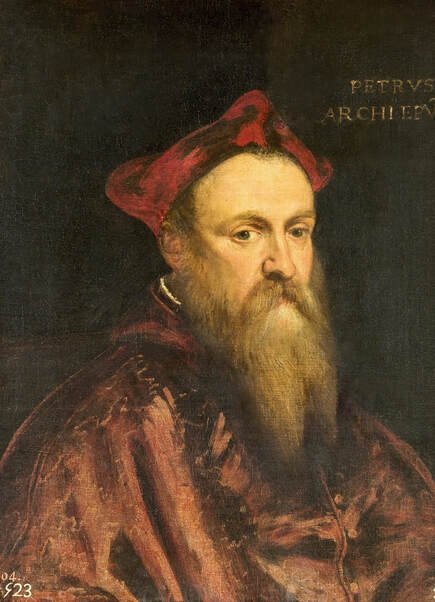
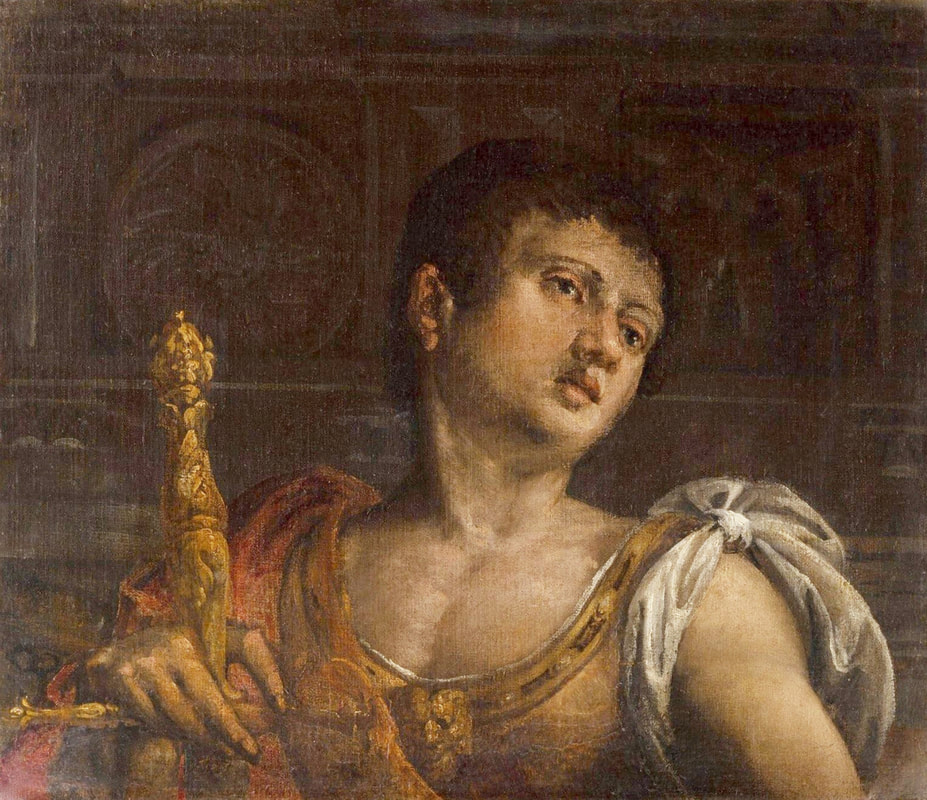
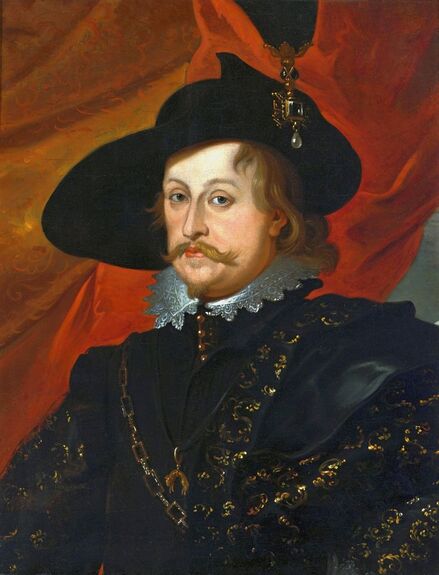
Portrait of Royal jeweller Giovanni Jacopo Caraglio aged 47 receiving a medallion from the Polish Royal Eagle with monogram of King Sigismund Augustus (SA) on his chest by Paris Bordone, 1547-1553, Wawel Royal Castle.
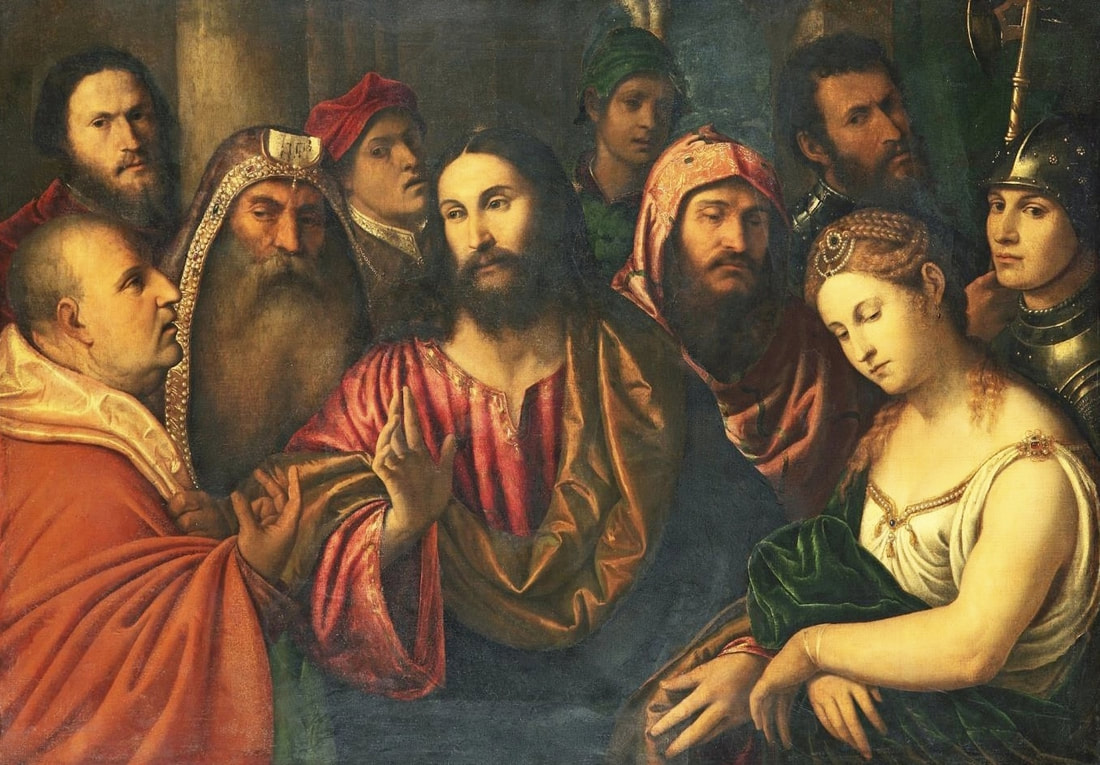
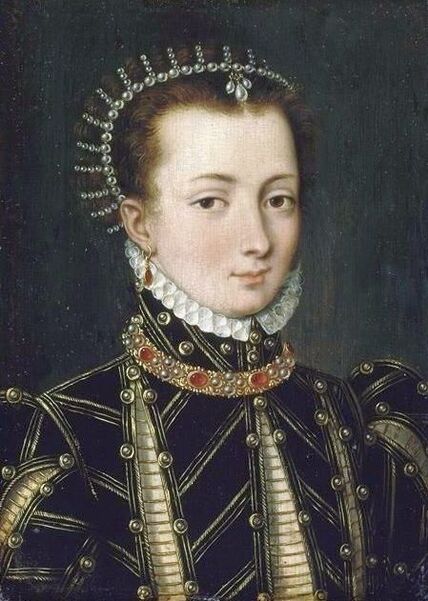
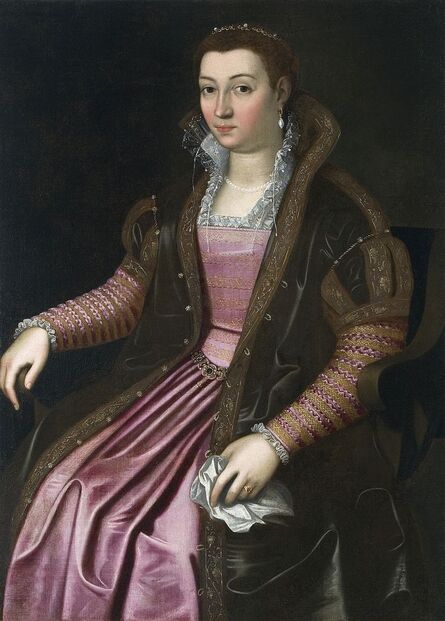
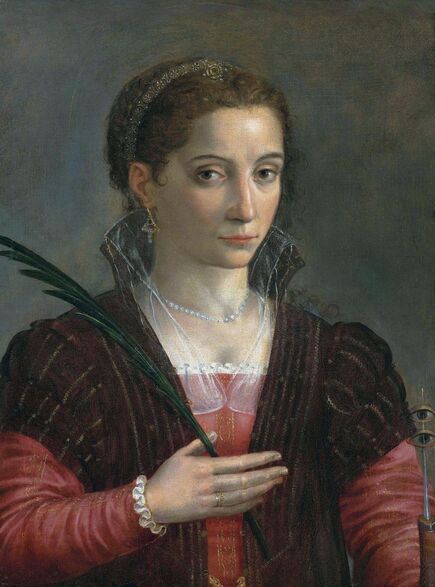
Portraits of Isabella Jagiellon and John Sigismund Zapolya by Jacopino del Conte and Tintoretto
Just few months after her arrival to Hungary, on July 7, 1540 in Buda Isabella Jagiellon gave birth to her only son John Sigismund Zapolya. 15 days after his birth, his father died suddenly on July 22, 1540 and the infant John Sigismund was elected king by a Hungarian noble assembly in Buda and Isabella as his regent. The bishop of Oradea, George Martinuzzi (Frater Georgius), took over the guardianship. John Sigismund claim to the throne was challenged by Ferdinand I of Austria. Under the pretext of wanting to protect John's interests, Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent had his troops invade central Hungary in 1541 and occupy Buda.
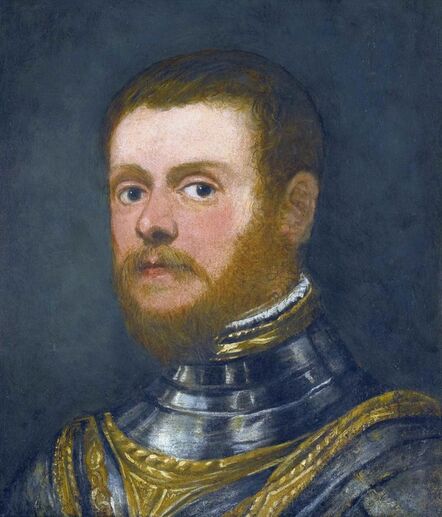
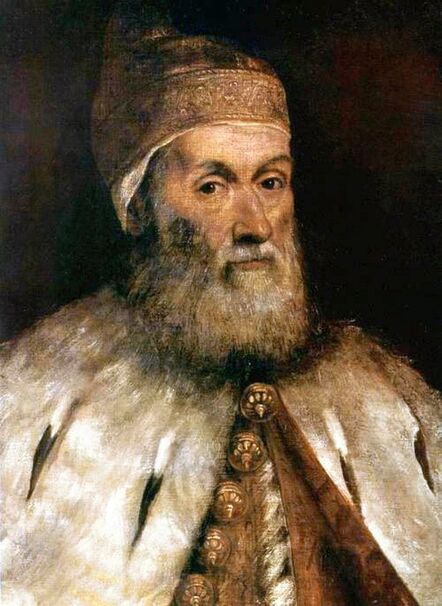
After the Hungarian royal court had to leave Buda, Queen Isabella settled in Lipova and then from the spring of 1542 to the summer of 1551 in the former episcopal palace in Alba Iulia in Transylvania. Isabella was young, noted for her beauty, and scolded for her expensive tastes. She began reconstruction of the former bishop's palace in Alba Iulia in the Renaissance style. This decade was a period of unceasing hostilities and fierce disputes with Martinuzzi. Isabella kept a regular correspondence with her Italian relatives including her third cousin, Ercole II d'Este, Duke of Ferrara and her close advisor was Giovanni Battista Castaldo, an Italian mercenary leader (condottiere), First Marquis of Cassano, Imperial general and commander in the service of Emperor Charles V and his younger brother, Archduke Ferdinand I. Castaldo was a patron of arts and his preserved effigies were created by the best artists connected with the Spanish court - Titian (portrait in private collection), Antonis Mor (portrait in the Thyssen-Bornemisza Museum) and Leone Leoni (bust in the Church of San Bartolomeo in Nocera Inferiore and a medal in the Wallace Collection). In July 1551, facing superior forces, Isabella surrendered and she agreed to give up Transylvania in exchange for Silesian duchies (Opole, Racibórz, Ziębice, Ząbkowice Śląskie) and other territories offered by Ferdinand. The Silesian duchies turned out to be ruined after the earlier rule of the Hohenzollerns, to whom Ferdinand handed them over for 20 years in exchange for a loan. There was not even a residence that could accommodate Isabella's court. She departed towards Poland where she lived with her family for the next five years. To provide her with income, her brother granted her Krzepice and Sanok, while her mother gave her Wieluń. She returned to Transylvania in 1556 with her son. Isabella surrounded herself with foreigners - primarily Italians and Poles. Her secretary was Paolo Savorgnano of Cividale del Friuli and personal physician Giorgio Biandrata, who specialized in gynecology. In 1539 Biandrata published a medical treatise on gynecology entitled Gynaeceorum ex Aristotele et Bonaciolo a Georgio Blandrata medico Subalpino noviter excerpta de fecundatione, gravitate, partu et puerperio, a compilation taken from the writings of Aristotle and from Enneas muliebris by Ludovico Bonaccioli, dedicated to Queen Bona Sforza and her daughter, Isabella Jagiellon. In 1563 John Sigismund Zapolya made him his personal physician and councilor. Biandrata was a Unitarian and one of the co-founders of the Unitarian Churches in Poland and Transylvania. According to "The Art of Love: an Imitation of Ovid, De Arte Amandi" by William King, published in London in 1709 (page XXI), "Isabella Queen of Hungary, about the year 1540, shewed to Petrus Angelus Barcæus [Pier Angelio Bargeo], when he was at Belgrade, a silver pen with this inscription, Ovidii Nasonis Calamus; denoting that it had belonged to Ovid. This had not long before been found amongst some old ruins, and the esteemed it as a venerable piece of antiquity" (also in: "The Original Works of William King", published in 1776, p. 114). This fragment give some impression of the quality of patronage and collection of Isabella. Portrait of Matthias Corvinus, King of Hungary, Croatia and Bohemia in the Museum of Fine Arts in Budapest was painted in the style of Andrea Mantegna, an Italian painter and a student of Roman archeology born in Isola di Carturo in the Venetian Republic, who probably never visited Hungary. A portrait of Matthias' son, John Corvinus, in the Alte Pinakothek in Munich is attributed to Baldassare Estense, a painter who worked at the court of the Dukes of Este in Ferrara from 1471 to 1504 and who probably also never visited Hungary. Similar is the case of medal with bust of Queen Beatrice d'Aragona of Naples, Matthias's third wife in the National Gallery of Art in Washington, created in the style of Giovanni Cristoforo Romano, a sculptor born in Rome who later worked as medallist for the courts of Ferrara and Mantua. After Isabella's death on September 15, 1559 John Sigismund took control of the country. He spoke and wrote in eight languages: Hungarian, Polish, Italian, Latin, Greek, Romanian, German and Turkish. He was a passionate lover of books, as well as music and dance and could play a number of musical instruments. Despite his slim build he adored hunting and made use of the spear on such occasions. He converted from Catholicism to Lutheranism in 1562 and from Lutheranism to Calvinism in 1564. Around five years later, he became the only Unitarian monarch in history and in 1568 he proclaimed freedom of religion in Turda. In the Treaty of Speyer of 1570 between John Sigismund and the Emperor, Transylvania was recognized as an independent Principality under vassalage to the Ottomans and John Sigismund renounced his royal title. After John Sigismund's death on March 14, 1571, his uncle Sigismund II Augustus, King of Poland, and his aunts inherited a portion of his treasures. Papal nuncio Vincenzo dal Portico reported from Warsaw to Rome on August 15, 1571 about the enormous value of the inheritance valued by some at 500,000 thalers, which the king denied, claiming that it was worth only 80,000 thalers. Polish legation returning from Alba Iulia at the beginning of August 1571 brought only some of the valuables to Warsaw, including a great number of gold and silver objects and jewellery, including "1 crown with which the queen was crowned; 1 golden scepter; 1 golden apple" (1 corona, qua regina coronata est; 1 sceptrum aureum; 1 pomum aureum), "4 large, ancient and old-fashioned vases" (4 magnae, antiquae et vetustae amphorae), but also some paintings like "the golden altar, in which is the image of the Blessed Mary, valued at one hundred and forty-eight Hungarian florins" (altare aureum, in quo effigies Beatae Mariae, aestimatum centum quadraginta octo item Ungaricorum) or "portrait of Gastaldi - 4 fl. in the currency" (item Gastaldi effigies - 4 fl. in moneta), perhaps the effigy of Giacomo Gastaldi (ca. 1500-1566), an Italian astronomer and cartographer, who created maps of Poland and Hungary or Giovanni Battista Castaldo. "The image of Castaldi in gilt silver frame" (Imago Castaldi ex argento inaurato fuso), possibly even the same effigy by Titian sold by the Dickinson Gallery, was included in the list of items inherited by the king and his sisters. Among the inheritance, there was also an effigy of Queen Bona, mentioned in the letter of Queen of Sweden Catherine Jagiellon to her sister Sophia, dated August 22, 1572 in Stegeborg. "The remains of the legacy of the infanta, which will soon be here, is worth 70 to 80 thousand thalers" (vi resta il legato, della infanta, che sara presto qua che e di valore di 70 in 80 millia tallari) added dal Portico in his message about the inheritance of Intanta Anna Jagiellon (after Katarzyna Gołąbek, "Spadek po Janie Zygmuncie Zápolyi w skarbcu Zygmunta Augusta"). The painting of Madonna and Child with Saint John and angels in the National Museum in Warsaw, attributed to Jacopino del Conte, was purchased in 1939 from F. Godebski. The effigy of the Virgin is identical with portrait of Isabella Jagiellon in the Samek Art Museum. The painting was therefore commissioned shortly after the birth of Isabella's son in 1540. Both paintings were painted on wood panel and are stylistically very close to Florentine Mannerist painters Pontormo, Bronzino or Francesco Salviati. In 1909 in the Przeworsk collection of Prince Andrzej Lubomirski, who also owned Marco Basaiti's Portrait of Nicolaus Copernicus, there was a painting (oil on wood, 53.5 x 39 cm) attributed to 16th century Florentine school, "maybe Jacopo Carrucci called Jacopo da Pontormo (1494-1557)", depicting Madonna and Child (after "Katalog wystawy obrazów malarzy dawnych i współczesnych urządzonej staraniem Andrzejowej Księżny Lubomirskiej" by Mieczysław Treter, item 34, p. 11). In the National Gallery in London there is a portrait of approximately ten years old boy, also attributed to Jacopino del Conte, in a rich princely costume similar to that visible in a portrait of 19 years old Archduke Ferdinand (1529-1595), governor of Bohemia, son of Anna Jagellonica and Ferdinand I, in the Kunsthistorisches Museum, painted by Jakob Seisenegger in 1548. It was also painted on wooden panel. According to Gallery's description, "although full-length portraits were common in Venice and its states, where pictures were normally painted on canvas, they were rare in Florence where painting on wooden panels persisted longer", it is therefore possible that it was created by a Florentine painter active or trained in Venice, like Salviati who created a portrait of Isabella's brother king Sigismund II Augustus (Mint Museum of Art in Charlotte). The portrait of a boy in London was initially attributed to Pontormo, Bronzino or Salviati and was purchased in Paris in 1860 from Edmond Beaucousin. It was formerly in the collection of the Duke of Brunswick, while in 1556 when Isabella returned with her son to Transylvania, her mother Bona departed through Venice to Bari in southern Italy, Isabella's younger sister Sophia Jagiellon, married Duke Henry V and departed to Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, taking a large dowry and undoubtedly portraits of the members of the royal family. The same boy, albeit a little older, was also depicted in a painting which was before 1917 in Wojciech Kolasiński's collection in Warsaw, included in the catalogue of his collection sold in Berlin (item 102). It was painted against a green background and attributed to Jacopo Pontormo. The boy has an order on his chest, similar to the cross of the Knights Hospitaller (Knights of Malta), enemies of the Ottomans, like the cross visible on the coat of the 12-year-old Ranuccio Farnese (1530-1565), who was created prior titular of the Venice Priory of the Order in 1540, in his portrait by Titian, or to the cross of the Order of the Golden Spur, which was frequently awarded by Hungarian monarchs, like in 1522, when István Bárdi was made a knight of the golden spur by king Louis II in presence of several high ranked noble gentlemen. He was finally depicted as a grown-up man in a painting by Jacopo Tintoretto, which was later in the collection of the Spanish Ambassador in Rome and later Viceroy of Naples, Don Gaspar Méndez de Haro, 7th Marquis of Carpio, as his initials D.G.H. are inscribed on the reverse of the canvas with a ducal crown. The painting was later in the collection of Prince Brancaccio in Rome and was sold at an auction in London in 2011. According to Catalogue Note (Sotheby's, 06 July 2011, Lot 58): "The unusual hat with its ornate brooch was not commonly seen on Venetian sitters of this period and has led some to suggest that the sitter was a visitor to Venice rather than a native of the city". If John Sigismund's uncle Sigismund Augustus, commissioned his effigies in Tintoretto's workshop in Venice, the same could John Sigismund. Another contender for the Hungarian crown, Ferdinand of Austria, also commissioned his effigies abroad, like a portrait by Lucas Cranach the Elder in Güstrow Palace, dated '1548' or a portrait by Titian from Spanish royal collection, created in mid-16th century, both most probably basing on some preparatory, study drawings and not seeing the model. In all three portraits the boy/man bears great resemblance to effigies of John Sigismund's paternal aunt, Barbara Zapolya, Queen of Poland, and his mother by Cranach and his workshop.
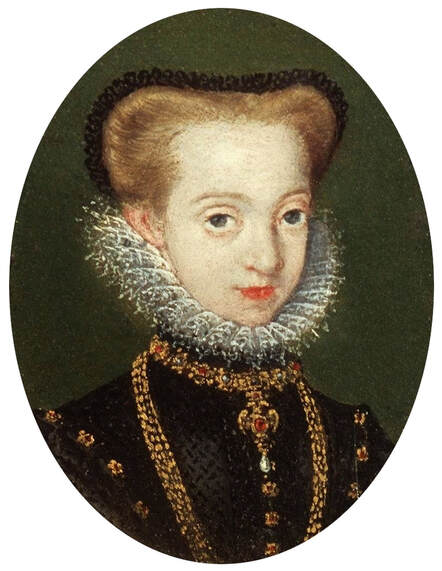
Portrait of Isabella Jagiellon (1519-1559), Queen of Hungary as Madonna and Child with Saint John and angels by Jacopino del Conte, ca. 1540, National Museum in Warsaw.
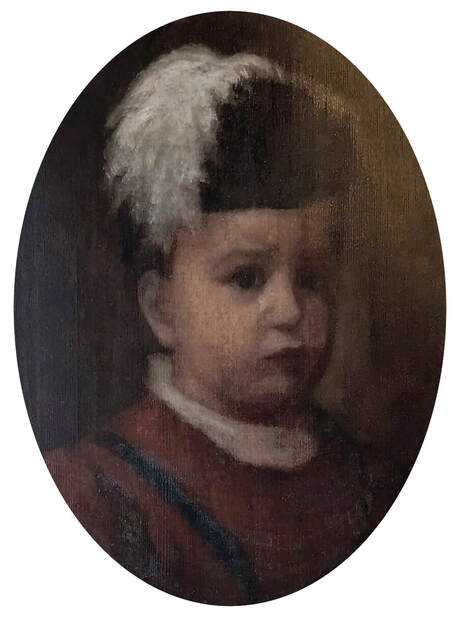
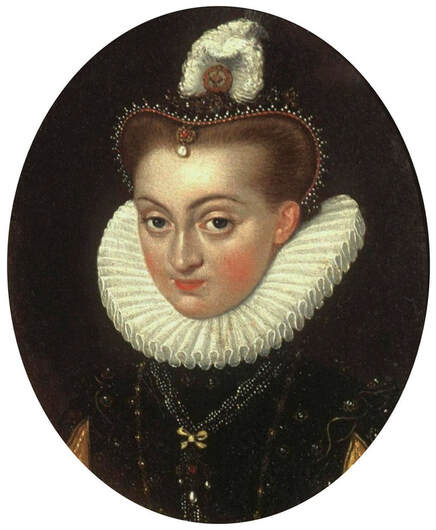
Portrait of John Sigismund Zapolya (1540-1571), King of Hungary as a child by Jacopino del Conte, ca. 1550, National Gallery in London.
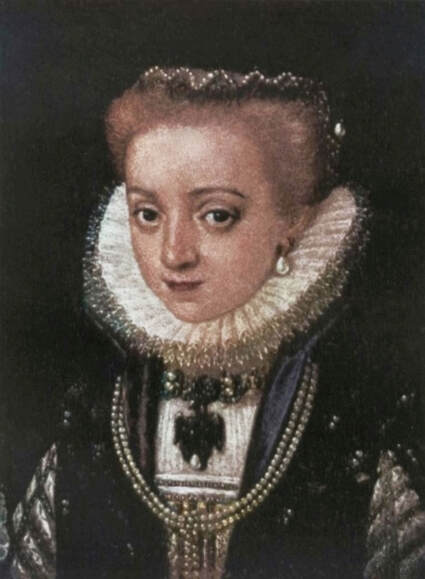
Portrait of John Sigismund Zapolya (1540-1571), King of Hungary as a boy from Kolasiński collection by Jacopino del Conte, ca. 1556, Private collection.
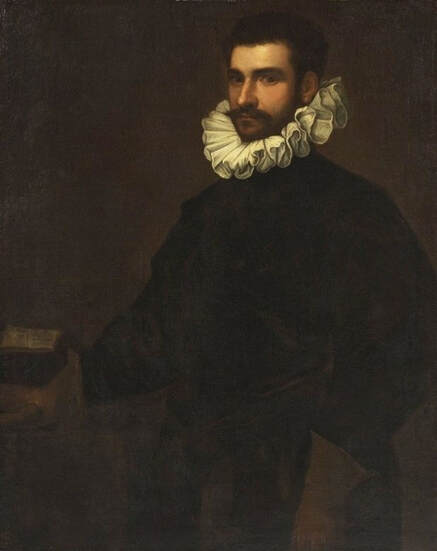
Portrait of John Sigismund Zapolya (1540-1571), King of Hungary by Tintoretto, 1560s, Private collection.
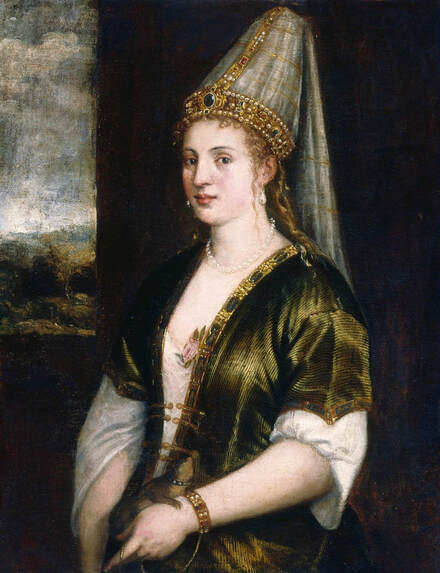
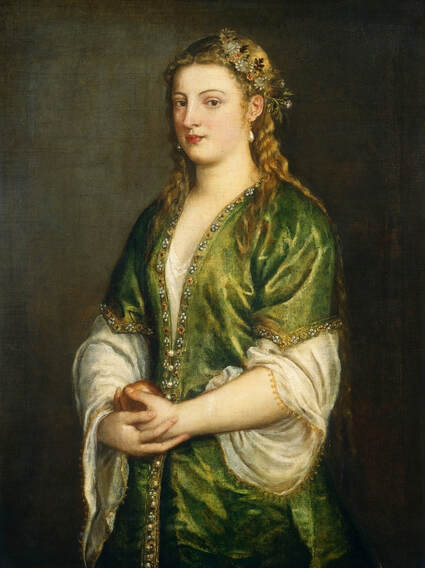
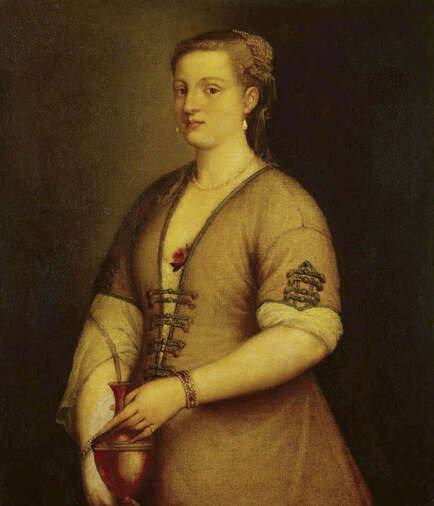
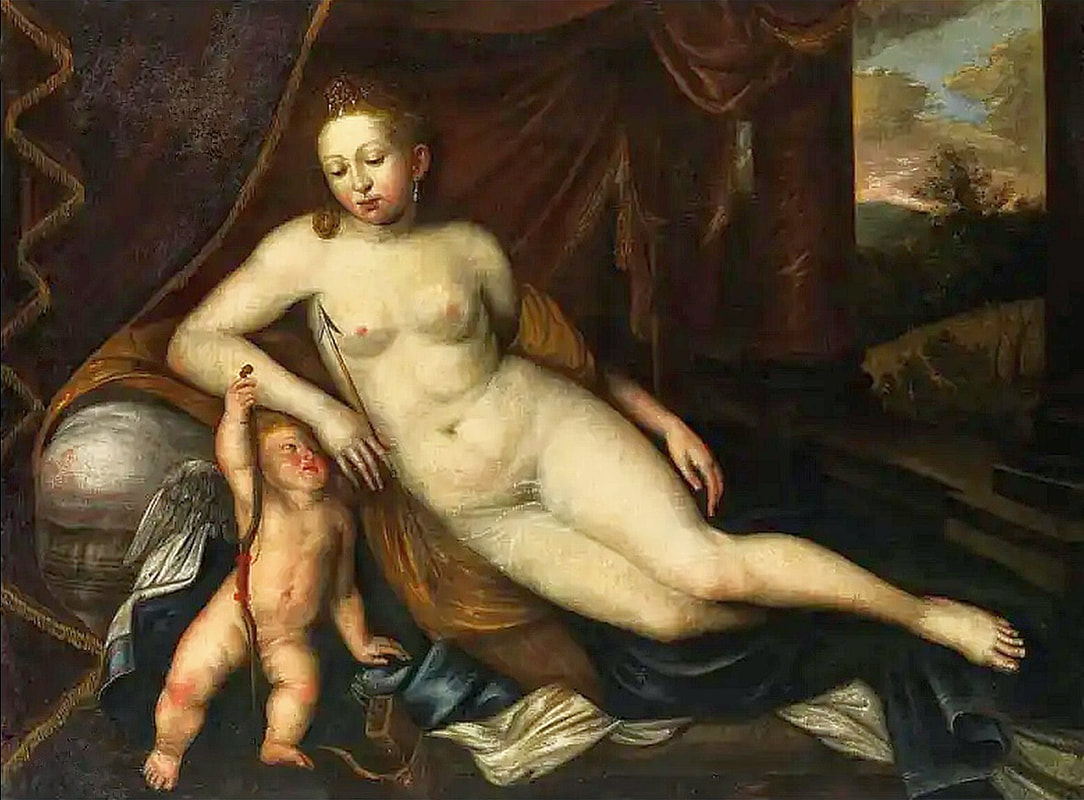
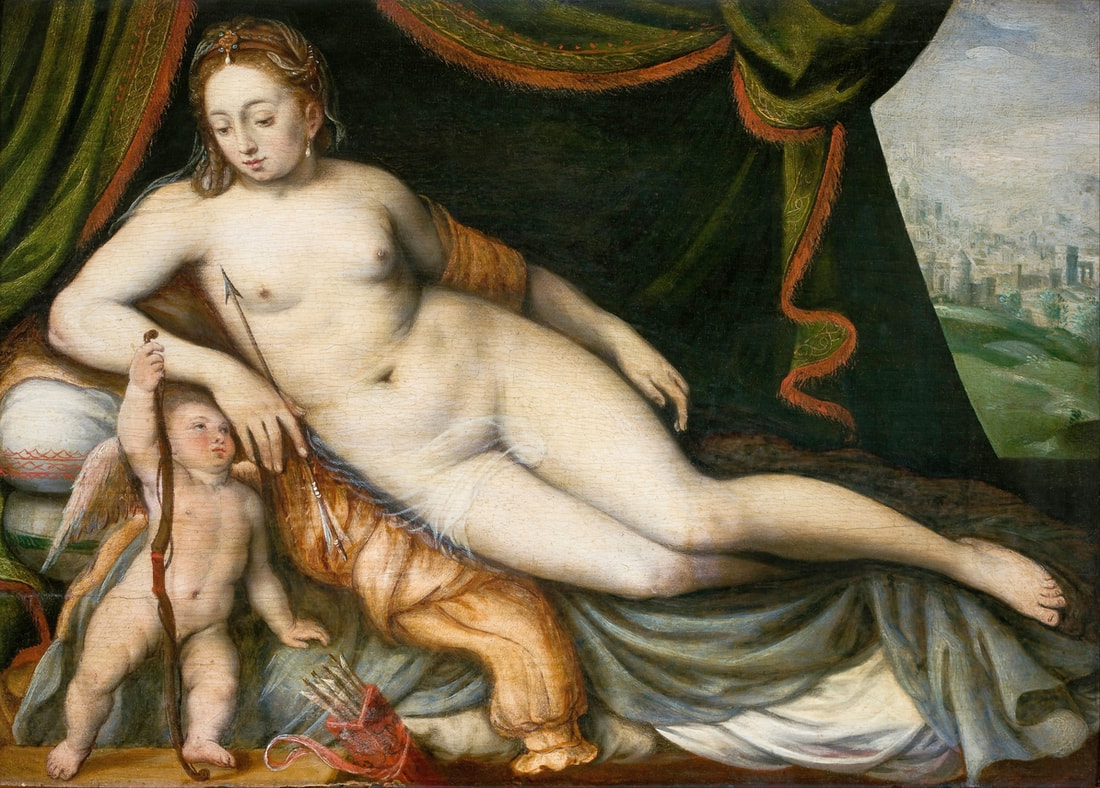
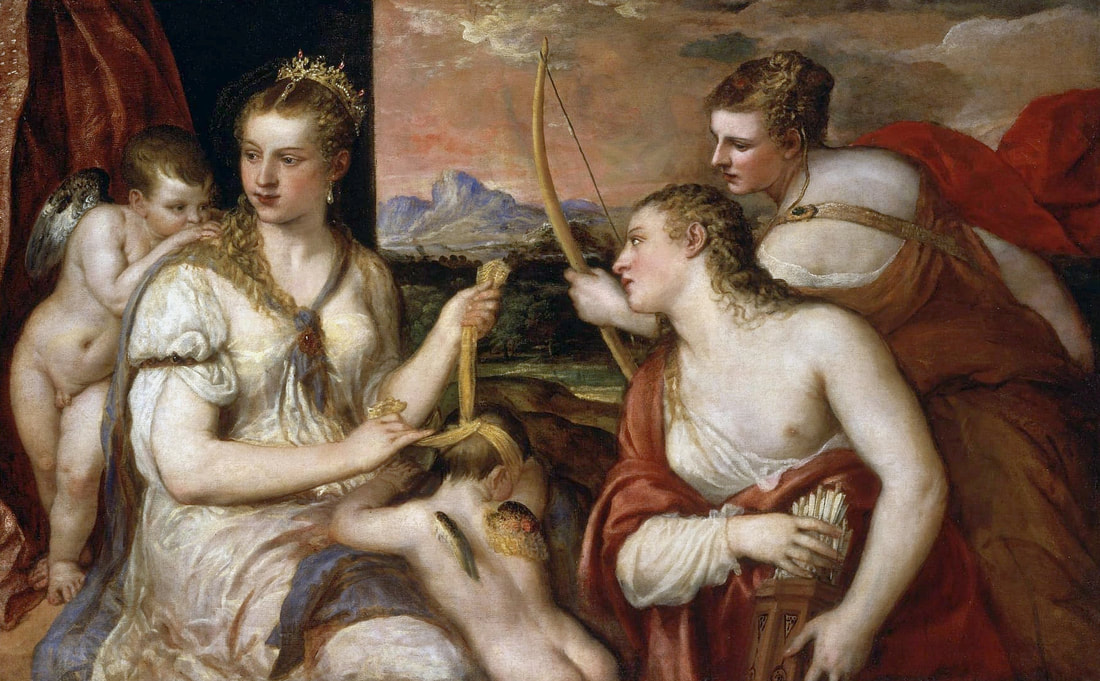
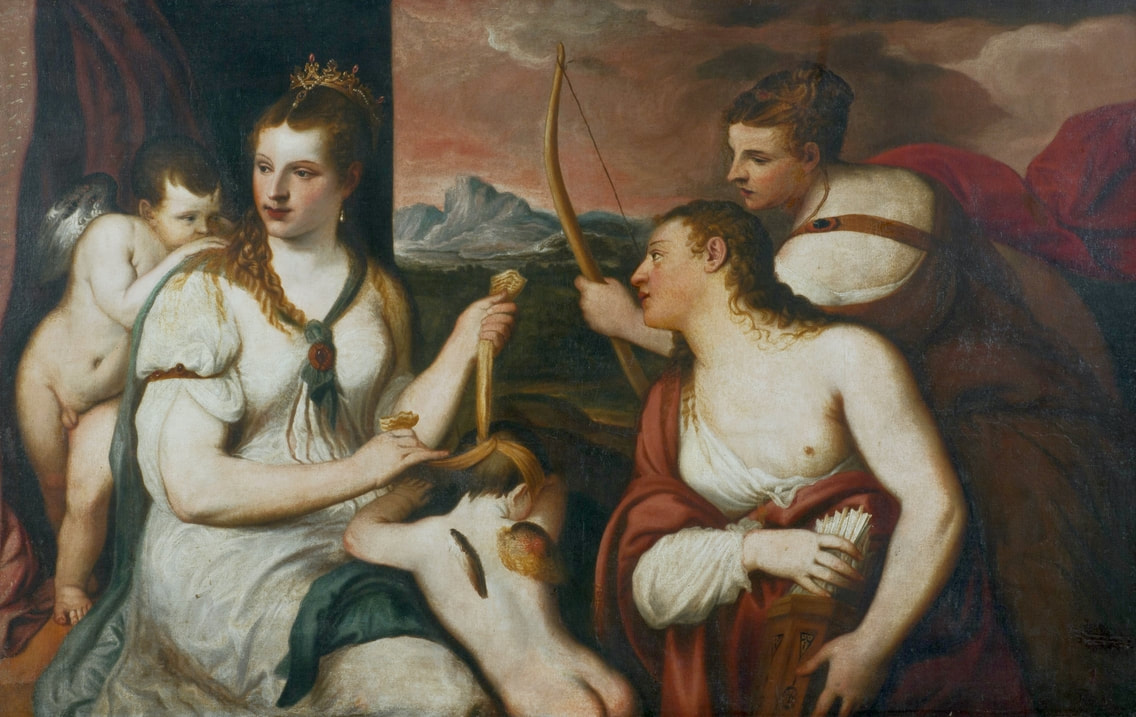
Portraits of Hurrem Sultan and her daughter Mihrimah by Titian and workshop
"May Allah grant Your Royal Majesty long life and make one day a thousand days. The humbled one conveys: When I received your letter filled with love, I was so happy and glad that it is difficult to express it in words. [...] Along with this letter of sympathy, so as not to be empty words, we send two pairs of shirts and trousers with belts, six handkerchiefs and hand and face towels. We ask you to accept and enjoy them, even though the clothes sent are not worthy of you. God willing, next time I'll make them more ornate. In conclusion: may your God grant you long life, and may your state endure forever. Haseki Sultan", is a letter of 1549 (956) from Hurrem Sultan (ca. 1504-1558), the chief consort and legal wife of the Ottoman sultan Suleiman the Magnificent, to elected monarch of Poland-Lithuania Sigismund II Augustus (Central Archives of Historical Records in Warsaw, regest KDT, nr 103). A gift in the form of underwear is an expression of special intimacy between the sultana and the king, who wore shirts made by his sisters (according to documents from 1545 and September 1547).
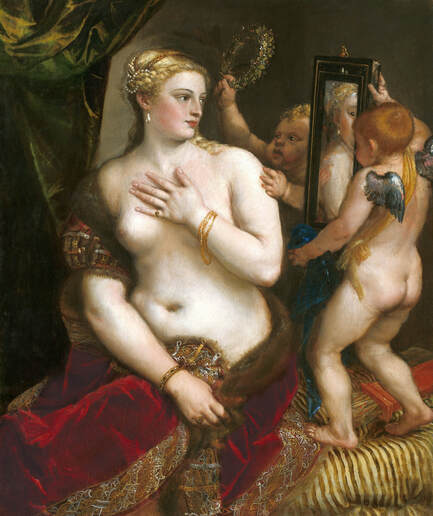
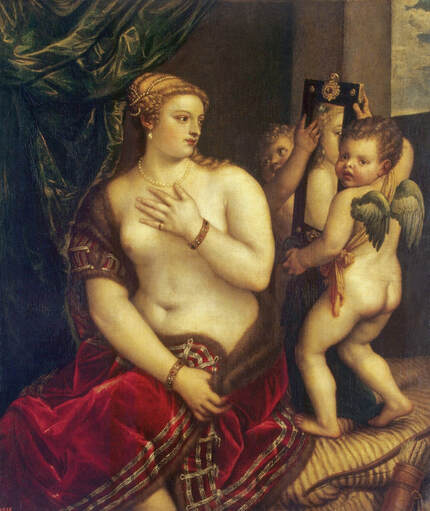
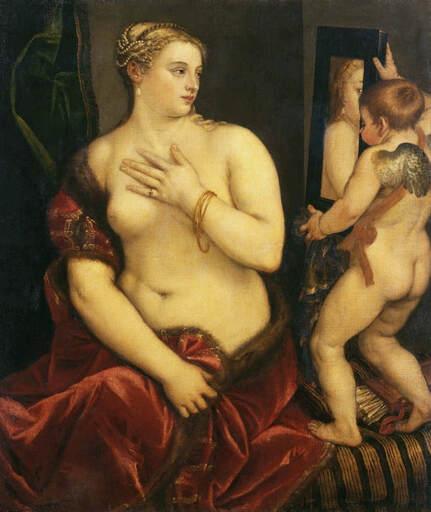
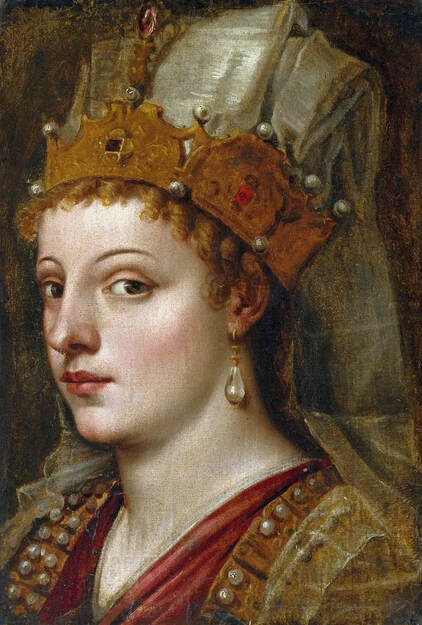
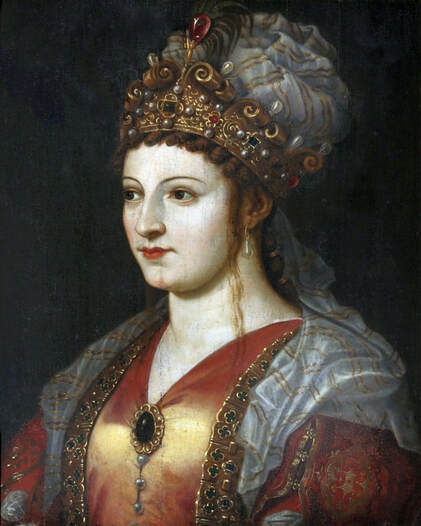
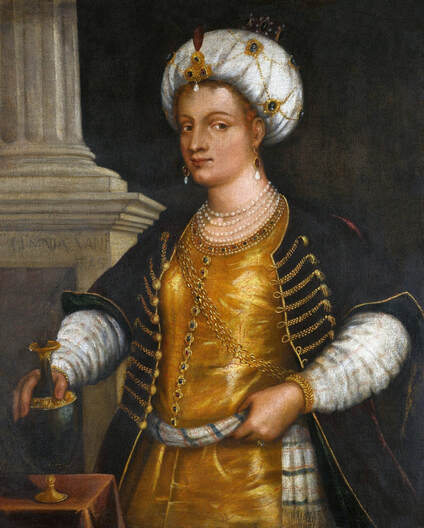
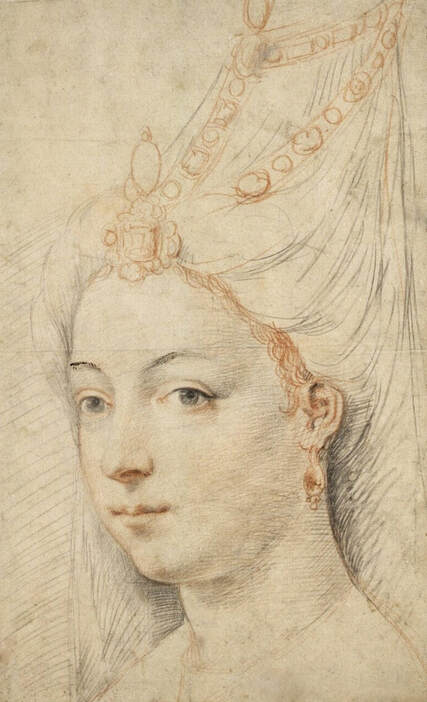
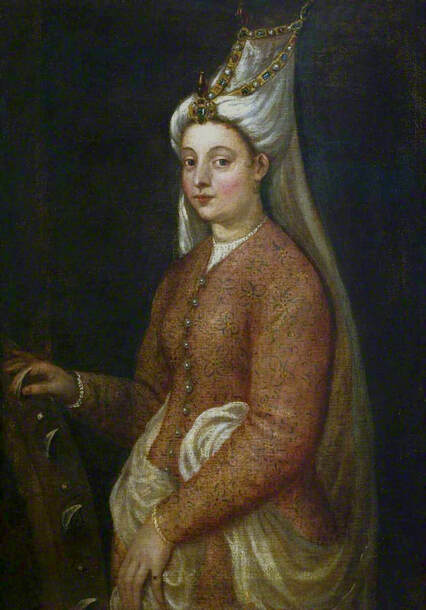
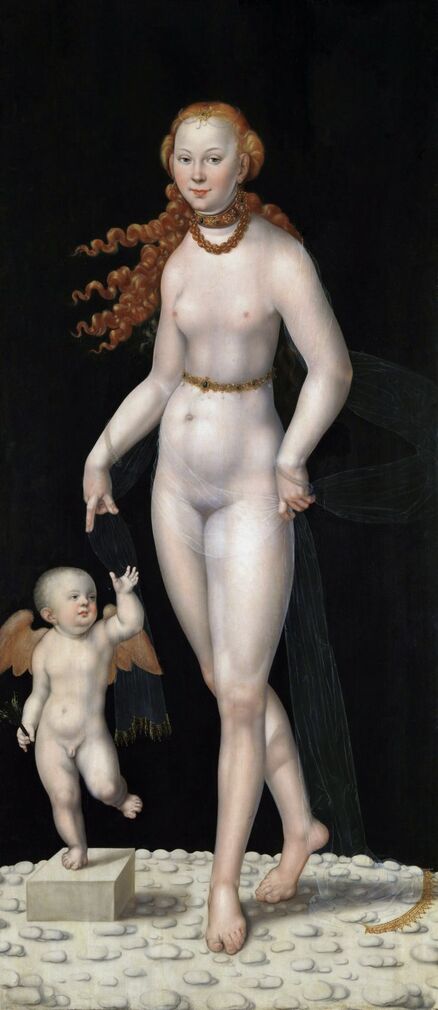
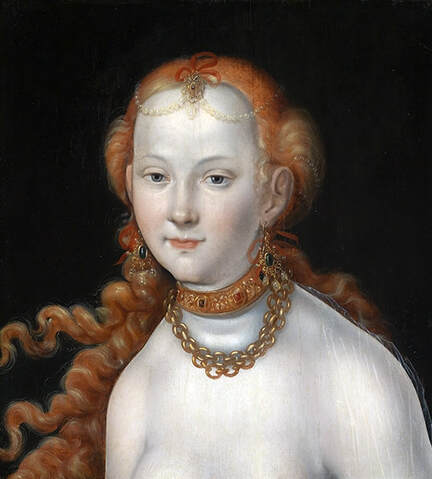
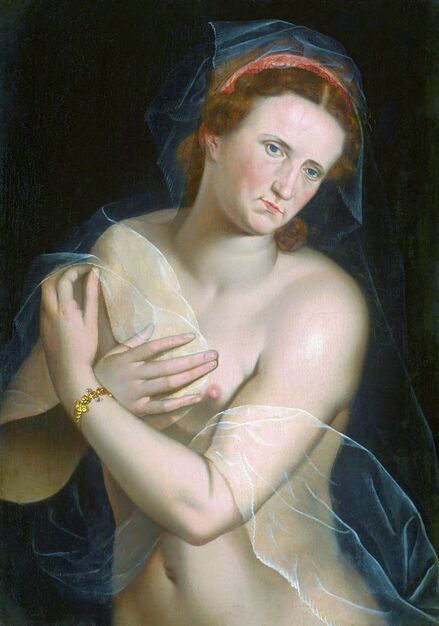
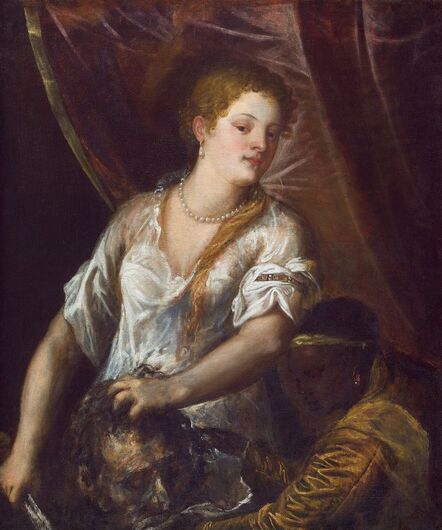
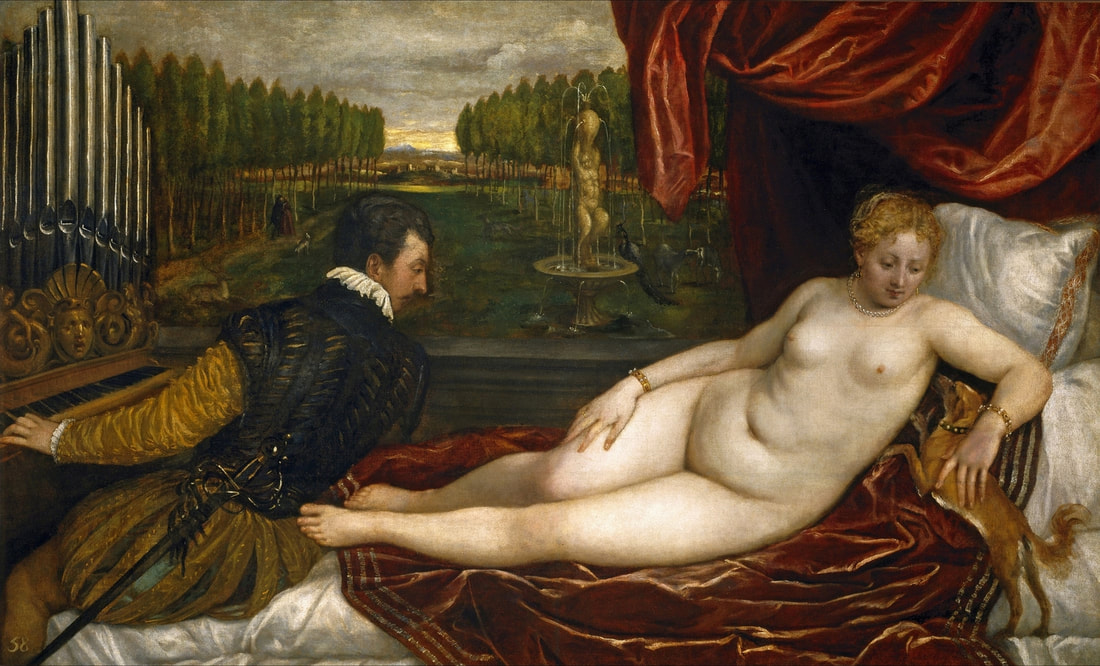
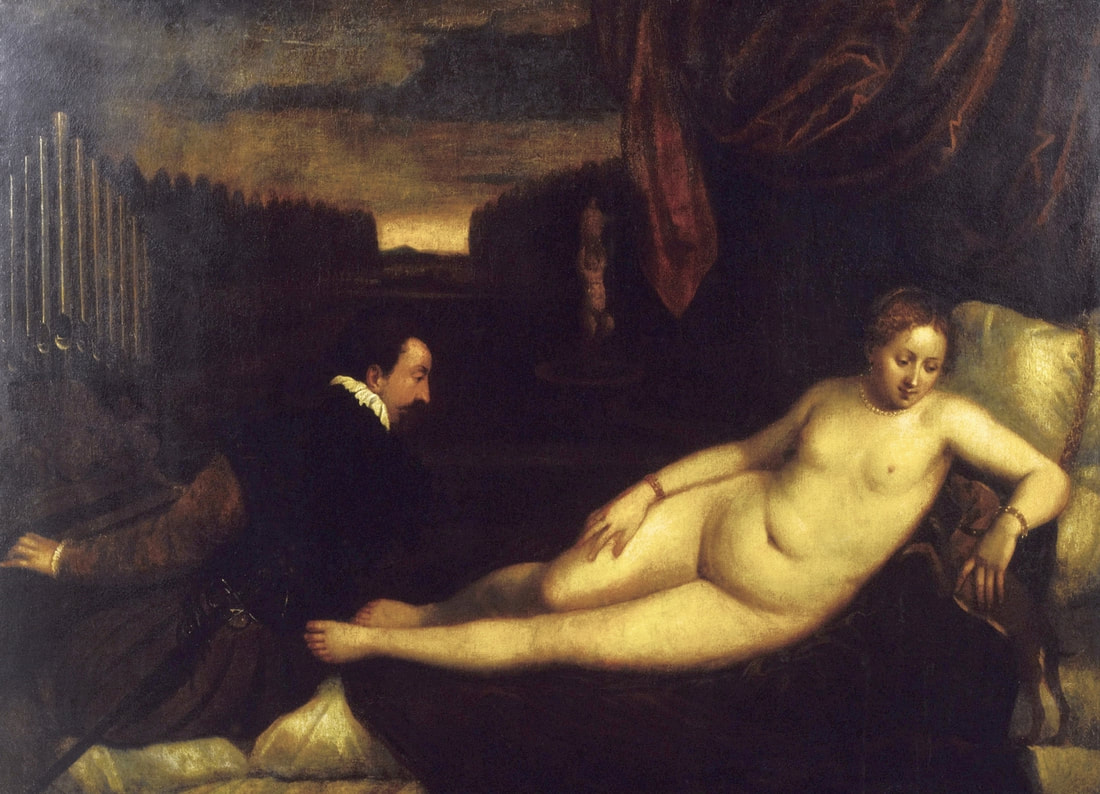
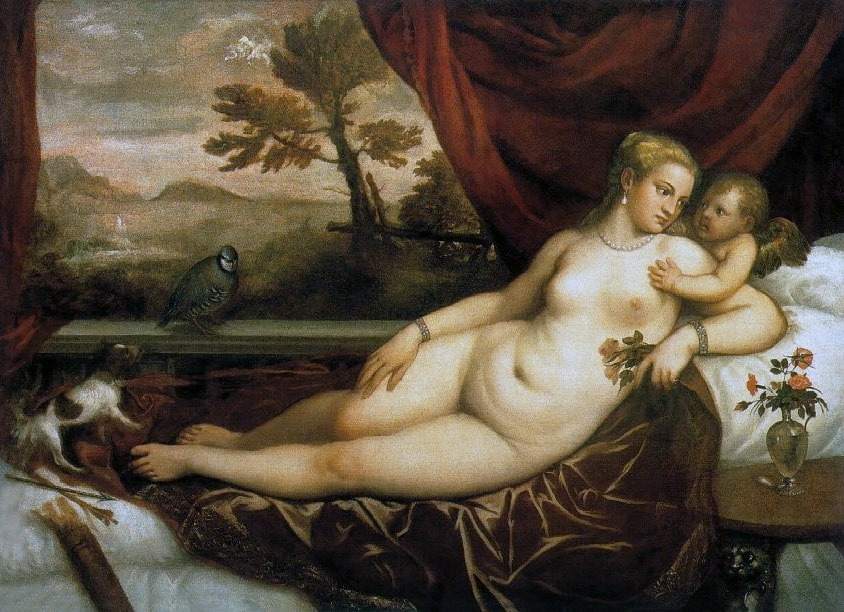
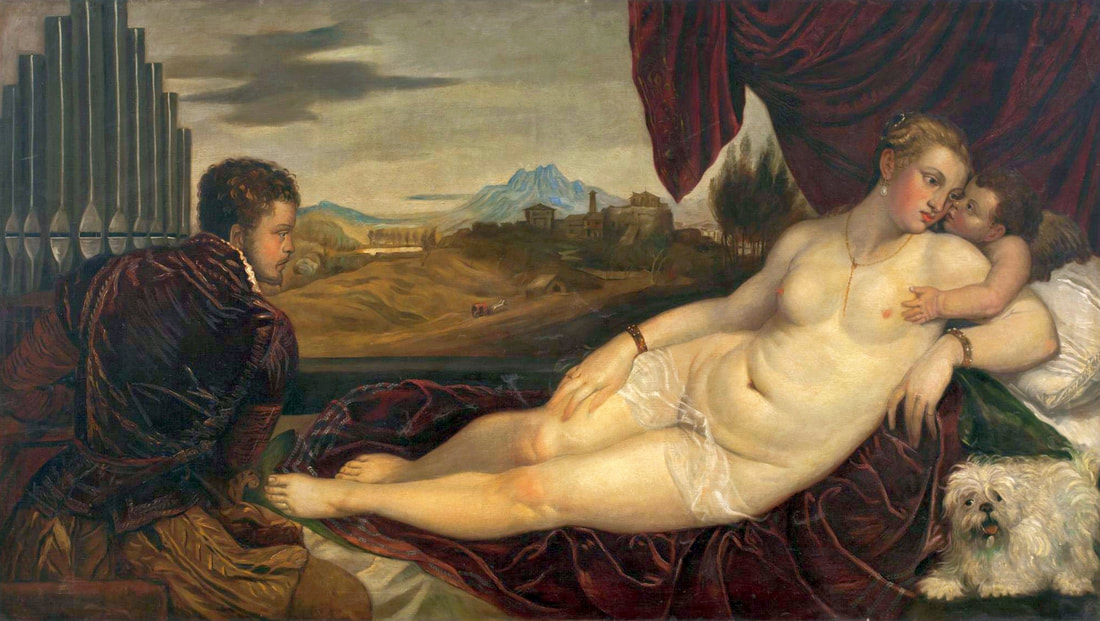
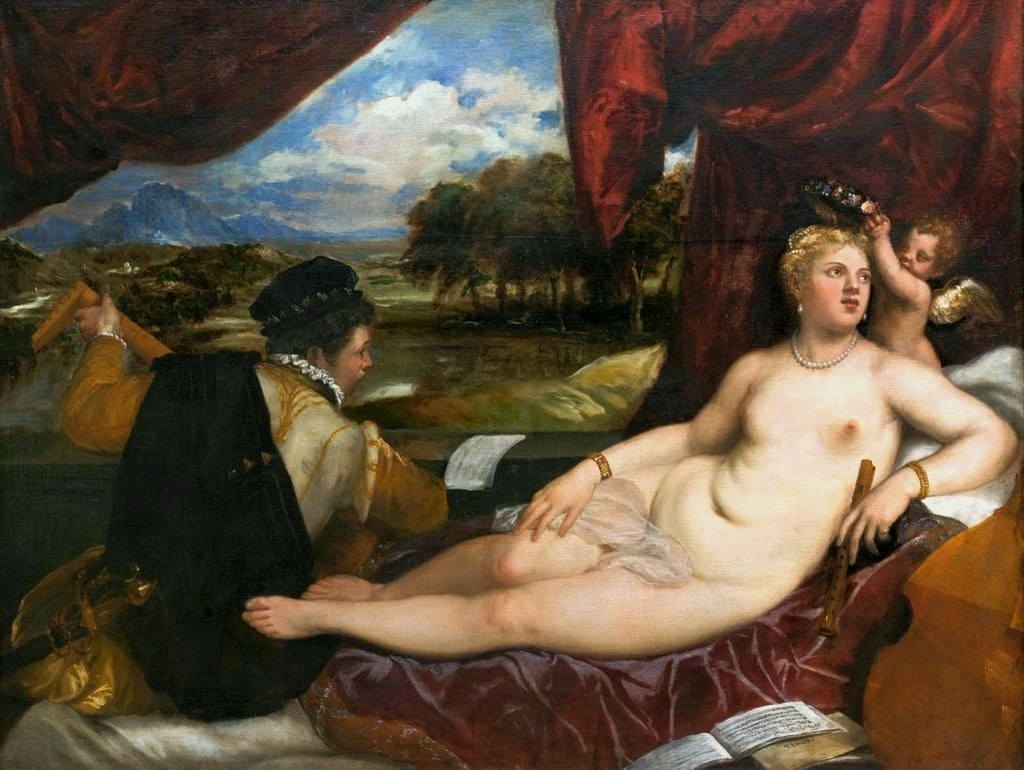
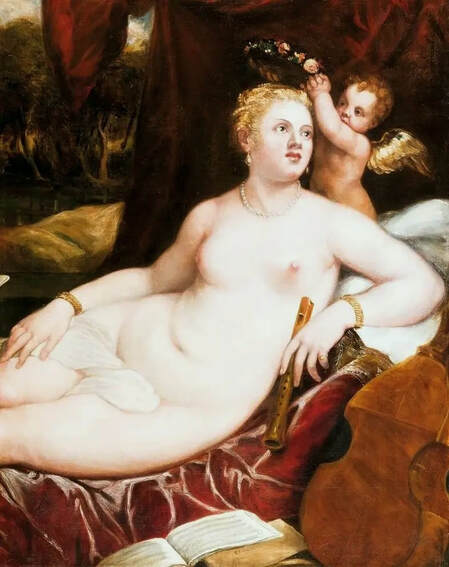
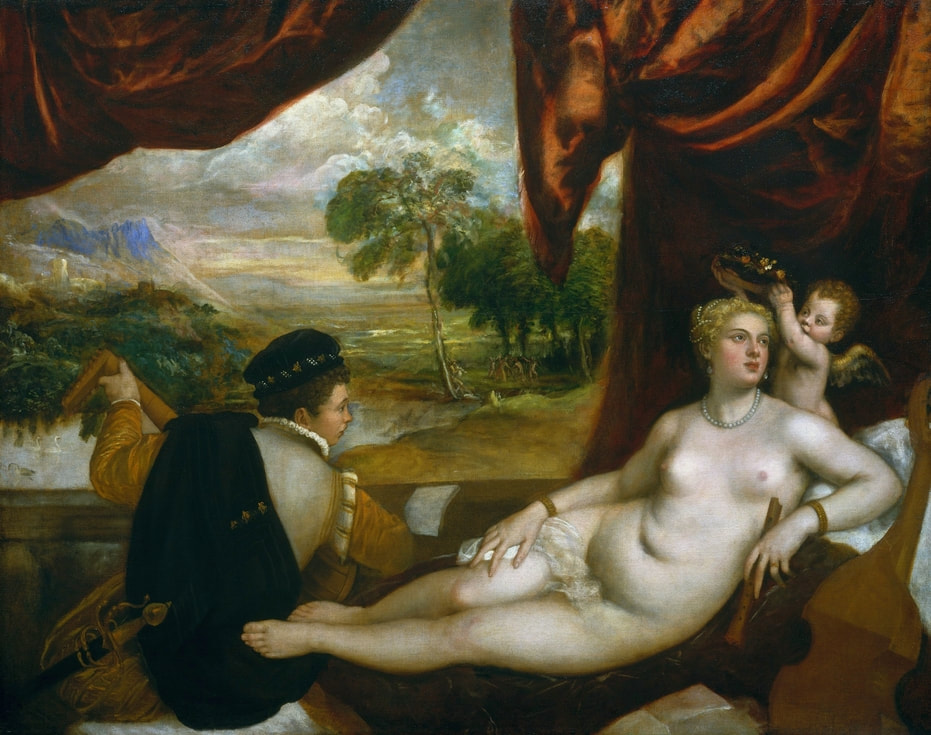
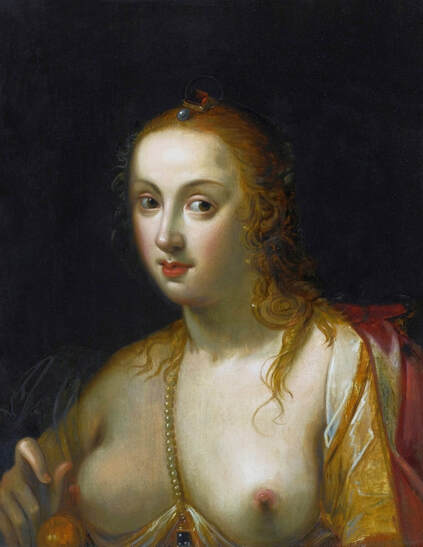
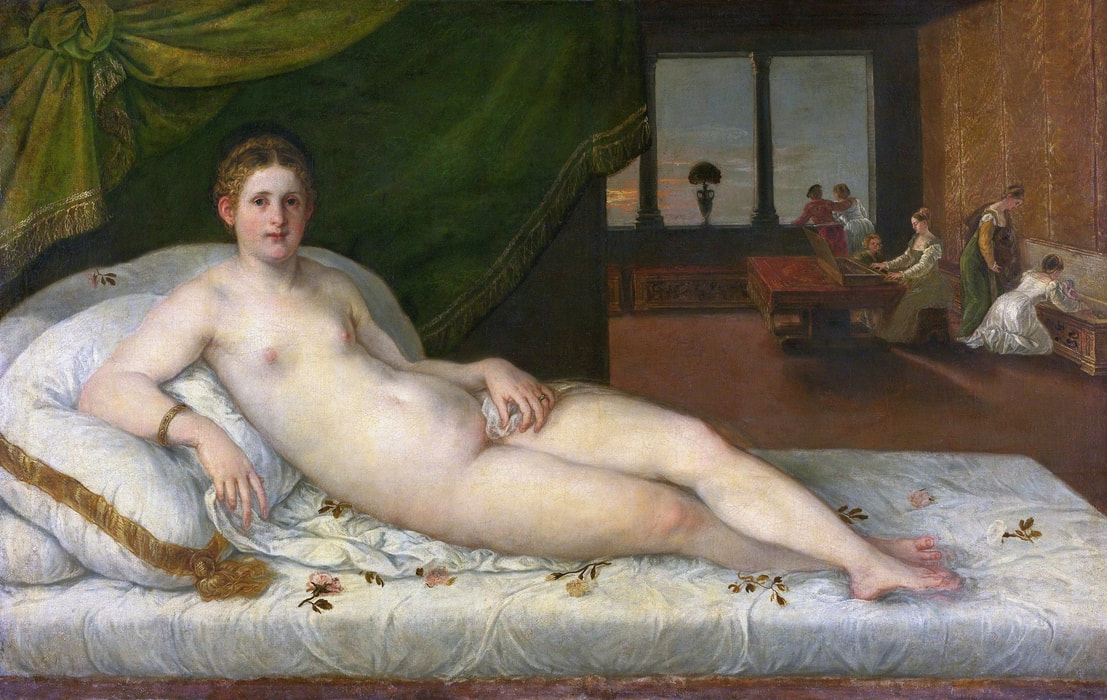
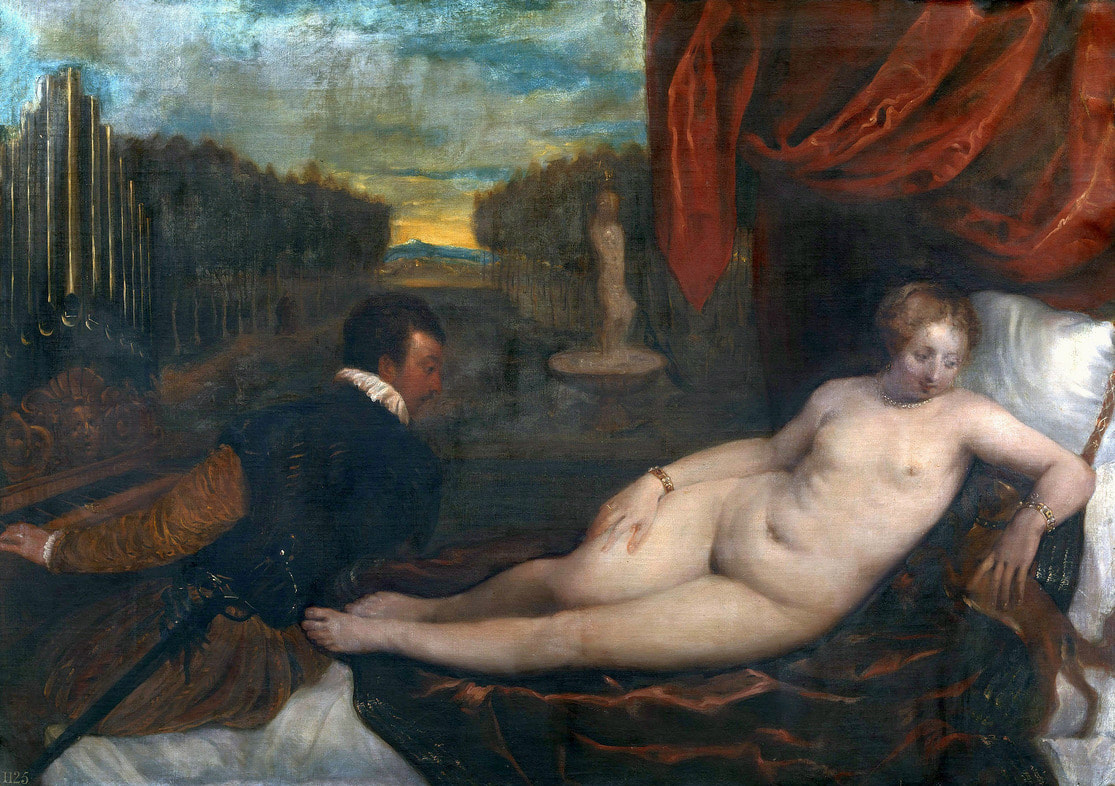
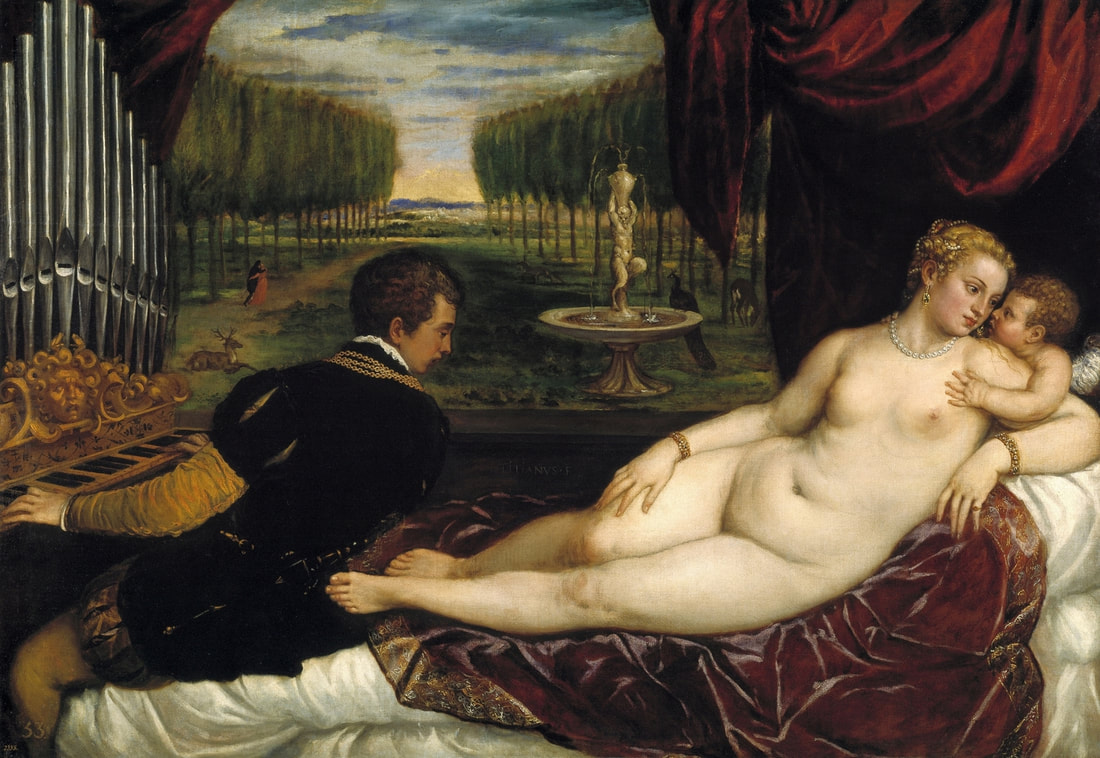
Hurrem, "the joyful one" in Persian, is known to Europeans as Roxelana - from Roxolania, Ptolemy's name for Ruthenia (especially Ukraine), then part of Poland-Lithuania. According to Samuel Twardowski's "Important legation" (Przeważna legacya iaśnie oświeconego książęcia Krzysztopha Zbaraskiego ...), published in 1633 in Kraków, she was a daughter of Ukrainian Orthodox priest from Rohatyn and she was taken prisoner by the Tatars (z Rochatyna popa była córa, / Oddana niewolnicą do szaraju). She conquered the heart of the sultan, who in 1526 conquered Buda, the capital of Hungary, ending the rule of the Jagiellons in this part of Europe. Twardowski claim that the captive reportedly resorted to witchcraft: "And thus he will make her free / And allow her to his private rooms and his bed; But it was not enough for cunning Ruthenian girl / Using an old Karaite woman for this, / Through stealth toss and hot spells / She put the venom in Soliman's bones, / That the old man's love revived". Breaking the Ottoman tradition, he married Roxelana around 1533, making her his legal wife, and she was the first imperial consort to receive the title Haseki Sultan. In response to the criticism of Suleiman's subjects that he took "a sordid slave" (niewolnice podłej) as his wife, according to Twardowski, her husband claimed that she was "from the Polish country, from the royal blood comes and genus" and that she was a sister of king Sigismund (Że ją siostrą Soliman królewską nazywa [...] Ztąd Zygmunta naszego szwagrem swym mianował). It is tempting to believe that Queen Bona, who was managing Rohatyn from 1534/1535 as part of the royal domain, was behind all this and that these two women prevented further invasion of Central Europe by the Ottoman Empire. "War not to the detriment of the kingdom, but rather for defense" (Woyna nie ku skazie królestwa, ale raczey ku obronie) was the official state doctrine of "The Realm of Venus, goddess of love" - Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth under the rule of elected Queen Anna Jagiellon, daughter of Bona Sforza, though within the Kingdom itself there were men desirous of breaking it. It was published in 1594 in Kraków in Stanisław Sarnicki's "Statutes and records of Crown privileges" (Statuta y metrika przywileiow Koronnych) under an effigy of Jan Zamoyski, Great Hetman of the Crown. Hurrem Sultan had four sons named Mehmed (1521), Selim (1524), Bayezid (1525) and Cihangir (1531) and a daughter Mihrimah Sultan (1522). There was also a son Abdullah, but he died at the age of 3. As a sultana (Italian word for wife or female relative of a sultan), Roxelana exerted a very strong influence on the state policy and she supported peaceful relations with Poland-Lithuania. Apart from Sigismund Augustus (letters of 1548 and 1549), she also corresponded with his sister Isabella, Queen of Hungary (1543) and his mother Queen Bona. Jan Kierdej alias Said Beg, who was captured by the Turks during the siege of his family castle in Pomoriany in Red Ruthenia in 1498, when he was eight, traveled to Poland three times as an Ottoman envoy (1531, 1538 and 1543). When in January 1543, Kierdej came with the embassy from the sultan to Sigismund the Old, he also brought the sultana's words to Queen Bona. Both women wanted to postpone or prevent the marriage of Sigismund Augustus with archduchess Elizabeth of Austria. The Queen of Poland, known for her outstanding artistic taste, acquired works of art and jewels in many places, including Turkey (after "Klejnoty w Polsce ..." by Ewa Letkiewicz, p. 57). The direct contacts of Roxelana with the rulers of the Venetian republic are not documented, but it is in Venice that most of her fictitious or faithful liknesses were created. It can be assumed that a large part of this "production" of portraits was intended for the Polish-Lithuanian market. Many Venetians lived in Poland-Lithuania and in Turkey and many Poles were undoubtedly interested in the life of the "Ruthenian Sultana". Roxelana's son Sultan Selim II (1524-1574), known as Selim "the blond" due to his fair complexion and blond hair, took as concubine Nurbanu Sultan (Cecilia Venier Baffo), a member of a well-known Venetian patrician family, and legally married her in about 1571. Ten letters written by Nurbanu between 1578 and 1583 to several ambassadors and to the Doge preserved in Venice. According to Vasari the Venetian painter Titian, although he never visited Istanbul, was commissioned by Suleiman the Magnificent to paint his wife Roxelana (Sultana Rossa) and their daughter Mihrimah (Cameria) (after "Images on the Page ..." by Sanda Miller, p. 84). Titian's portrait of Cameria and her mother was also recorded by Ridolfi. He and his famous workshop also painted the sultan and copies of these effigies are in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna and in private collection. To create the paintings, Titian had to use drawings or miniatures sent from Turkey. After World War II, only one known painted image of Queen Bona Sforza, created during her lifetime or close to it, has survived in the former territories of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. It is a miniature from a cycle depicting the Jagiellon family (today in the Czartoryski Museum), made by workshop of Lucas Cranach the Younger (1515-1586) in Wittenberg, Germany in about 1553 basing on a drawing or another miniature sent from Poland-Lithuania. Interestingly, also two effigies of Ottoman Sultanas survived, one is a portrait traditionally identified as Roxelana in the Lviv Historical Museum in Ukraine and the other is a likeness of her daughter Mihrimah in the Masovian Museum in Płock in Poland. Both were creted in the 16th century and come from historical collections of the former Commonwealth. The portrait in Lviv is small painting on wood (38 x 26 cm) and comes from the collection of the Ossolineum, which received it in 1837 from Stanisław Wronowski. The effigy of Mihrimah in Płock was also painted on wood (93 x 69.7 cm) and comes from the collection of the Ślizień family deposited by them with the Radziwills in Zegrze near Warsaw during World War I. Before World War II in the Red Salon of the Zamoyski Palace in Warsaw there was a portrait of the "Turkish Sultana", burnt in 1939 along with all the furnishings of the palace (after "Ars Auro Prior" by Juliusz Chrościcki, p. 285). Such portraits are also documented in Poland-Lithuania much earlier. The 1633 inventory of Radziwill Castle in Lubcha in Belarus (Central Archives of Historical Records in Warsaw, 1/354/0/26/45) lists "A painting of a lady with the inscription Favorita del gran turcho" (36). The inscription in Italian indicates that the painting was most likely made in Italy. The inventory of paintings from the collection of princess Louise Charlotte Radziwill (1667-1695), drawn up in 1671, lists the following depictions of Turkish women, some of which may be by Titian: "Turkini in a turban plays the viola" (295), "A young Turkish woman with a feather" (315), "A young woman from Turkey" (316), "Turkini in a turban and in sables, a woman by her side" (418) (after "Inwentarz galerii obrazów Radziwiłłów z XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska). Some effigies previously considered to represent Catherine Cornaro are now identified as portraits of Roxelana, like the painting in Florence with attributes of Saint Catherine of Alexandria - breaking wheel and halo (Uffizi Gallery, Inv. 1890, 909). It entered the Gallery in 1773 with the attribution to Veronese, but later the Latin inscription Titiani opus - 1542 was found on the back. A very similar portrait inscribed in French ROSSA FEMME DE SOLIMAN EMPEREUR DES TURCS (Rosa, Consort of Suleiman, Emperor of the Turks) is in the Royal Collection at Kensington Palace (RCIN 406152). Her costume is also distinctly Ottoman. Another version of this painting was before 1866 in the Manfrin collection in Venice and Samuelle Levi Pollaco created an etching of the painting with inscription: CATTERINA CORNARO REGINA DI CIPRO. Her outfit is slightly different, and we can see three pyramids in the background, most probably the three main pyramids at Giza in Egypt, at that time a province of the Ottoman Empire (Egypt was conquered by the Ottoman Turks in 1517). Eastern Orthodox Monastery of Saint Catherine of Alexandria, built by order of Byzantine emperor Justinian I at the site where Moses is supposed to have seen the burning bush, sacred to Christianity, Islam, and Judaism, is also in Egypt (Sinai Peninsula). Roxelana was a daughter of an Orthodox priest, hence this monastery was undoubtedly of particular importance to her throughout the Ottoman Empire. A reduced copy of this effigy attributed to studio of Titian was sold as "Portrait of Caterina Cornaro" (Christie's London, July 9, 2021, lot 214). Other bust-length version of this portrait by follower of Titian is in Knole House, Kent (NT 129882). The painter used the same face in his famous Venus with a mirror, today in the National Gallery of Art in Washington (inventory number 1937.1.34). This painting remained in the possession of the artist until his death, where it might have inspired visitors to commission similar paintings for themselves, or it might have served as a model for members of the workshop to reproduce. It is also possible that he wanted to have an effigy of this beautiful woman, one of his best clients. The painting is usually dated to about 1555, however, it it possible that it was painted much earlier, because "Titian's style and pictorial technique were never uniform and could vary from one work to another, as well as from one decade to another", as noted by Peter Humfrey in the Gallery's Entry for the painting (March 21, 2019). The 1971 X-ray reveals that Titian reused a canvas that once depicted two three-quarter figures standing side by side, possibly work not accepted by a client, and he rotated the canvas 90 degrees. Fern Rusk Shapley compared the double portrait with the so-called Allegory of Alfonso d'Avalos from around 1532 (Louvre in Paris). The portrait of Alfonso d'Avalos with a page, once owned by King John III Sobieski and King Stanislaus Augustus Poniatowski (J. Paul Getty Museum, inventory number 2003.486), is dated to about 1533. Giorgio Tagliaferro suggested that the double portrait was started by the young Paris Bordone while he was an assistant in Titian's studio (probably around 1516 for two years). In the mirror held by a cupid, she doesn't seem to see herself, but someone who is looking at her, most likely a man, her husband. Another cupid crowns her head with a wreath. This work is considered the finest surviving version of a composition executed in many variants by Titian and his workshop, some of the best of which are in the State Hermitage Museum, acquired in 1814 from the collection of Empress Josephine in Malmaison near Paris (inventory number ГЭ-1524), and in the Gemäldegalerie in Dresden (inventory number Gal.-Nr. 178). A version which was owned by the king of Spain (lost) was copied by Peter Paul Rubens (Thyssen-Bornemisza National Museum Madrid, 350 (1957.5)). The same woman, in similar pose and costume to the work in Florence was depicted in a painting attributed to workshop of Titian, today in the John and Mable Ringling Museum of Art in Sarasota, Florida (inventory number SN58). It comes from the Riccardi collection in Florence, sold to Lucien Bonaparte (1775-1840), younger brother of Napoleon Bonaparte, exactly like the "Portrait of the Duchess Sforza" (Portrait of Queen Bona Sforza) by Titian. Therfore both portraits - of the Queen of Poland and the Sultana of the Ottoman Empire were most probably created at the same time in Venice and sent to Florence. She is holding a little pet, most probably a mink or a weasel, a talisman for fertility. The flower in her décolletage might indicate, that she is a bride or newly wed woman. Slighly different version of this painting is in private collection. She was also depicted in another portrait by Titian (National Gallery of Art, Washington, 1939.1.292), wearing a similar green dress, a color being symbolic of fertility. She cradles an apple in her hands, which in art often connotes female sexuality. This painting was probably owned by Michel Particelli d'Hémery (1596-1650) in Paris, France. The Franco-Ottoman Alliance, one of the longest-lasting and most important foreign alliances of France, was formed in 1536 between the King of France Francis I and the Sultan Suleiman I. Beyond doubt, the French king had likenesses of the sultan and his influential wife. Numerous variants and copies of this portrait exist. In a similar portrait from private collection in Veneto (sold at Dorotheum in Vienna, 17.10.2017, lot 233) her Ottoman dress is pink, a symbol of marriage, and she is preparing her bridal wreath (similar to that visible on her head in the Washington version). The style of this painting is particularly close to Giovanni Cariani. It would be rather unusual if a Christian noblewoman from Venice would be dressed in Ottoman attire for her wedding. Therefore, through these portraits, the "Ruthenian girl" wanted to announce to the world that she is not a concubine, but the legal wife of the Sultan. After 1543 a follower of Titian, most probably Alessandro Varotari (1588-1649), known as Il Padovanino, copied other version of this painting with model holding an empty vase (Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden, Gal.-Nr. 173). The portrait identified as Roxelana from the collection of Sir Richard Worsley in Appuldurcumbe House, Isle of Wight (1804, as by 'Gentile Bellino') by follower of Titian depicts her holding an empty vase. Together with Latin inscription on the column "all is vanity" (OMNIA VANITAS) it might symbolize a great loss. On 7 November 1543 the eldest son of Hurrem Sultan, Prince Mehmed, died in Manisa, probably of smallpox. The sultana most probably knew Latin, as the Roman Catholic community was present in Rohatyn since the Middle Ages. Her large turban and face resemble the Lviv portrait. The style of this painting is also close to Giovanni Cariani. Similar to the Lviv likeness, also the effigy of Mihrimah (Cameria) in Płock has a counterpart made by workshop of Titian, today in the Courtauld Gallery in London, a copy of a lost original by Titian. It comes from the collection of Count Antoine Seilern (1901-1978), an Anglo-Austrian art collector and art historian. Like her mother, she was depicted with a spiked wheel, used to identify Saint Catherine of Alexandria. A study for this portrait by Titian or his workshop is in the Albertina in Vienna (inventory number 1492). The portrait of Cameria in the Musée Fabre in Montpellier (inventory number 65.2.1) was created by Sofonisba Anguissola (signature: PINXIT SOPHONISBE ANGUSSOLA VIRGO CRE. XIII SUCC). Like Queen Bona, who successfully ruled in the world dominated by men, the "Ruthenian girl" was well aware of the power of the image and conveyed the splendor of her reign through paintings created by the Venetian workshop of Titian.
Portrait of Hurrem Sultan (Roxelana, ca. 1504-1558) as a bride by workshop of Titian, ca. 1533, John and Mable Ringling Museum of Art in Sarasota.
Portrait of Hurrem Sultan (Roxelana, ca. 1504-1558) as a bride by workshop of Titian, ca. 1533, Private collection.
Portrait of Hurrem Sultan (Roxelana, ca. 1504-1558) as a bride holding an apple by Titian, ca. 1533, National Gallery of Art in Washington.
Portrait of Hurrem Sultan (Roxelana, ca. 1504-1558) as a bride holding her bridal wreath by workshop of Titian or Giovanni Cariani, ca. 1533, Private collection.
Portrait of Hurrem Sultan (Roxelana, ca. 1504-1558) holding an empty vase by follower of Titian, most probably Alessandro Varotari, after 1543, Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden.
Portrait of Hurrem Sultan (Roxelana, ca. 1504-1558) as Venus with a mirror by Titian, ca. 1533 or after, National Gallery of Art in Washington.
Portrait of Hurrem Sultan (Roxelana, ca. 1504-1558) as Venus with a mirror by workshop of Titian, ca. 1533 or after, The State Hermitage Museum.
Portrait of Hurrem Sultan (Roxelana, ca. 1504-1558) as Venus with a mirror by workshop of Titian, ca. 1533 or after, Gemäldegalerie in Dresden.
Portrait of Hurrem Sultan (Roxelana, ca. 1504-1558) with pyramids by Titian, ca. 1542, Private collection.
Portrait of Hurrem Sultan (Roxelana, ca. 1504-1558) as Saint Catherine of Alexandria by workshop of Titian, 1542, Uffizi Gallery.
Portrait of Hurrem Sultan (Roxelana, ca. 1504-1558) by workshop of Titian, ca. 1542, Private collection.
Portrait of Hurrem Sultan (Roxelana, ca. 1504-1558) by follower of Titian, ca. 1542, Knole House.
Portrait of Hurrem Sultan (Roxelana, ca. 1504-1558) holding an empty vase by follower of Titian or Giovanni Cariani, ca. 1543, Private collection.
Preparatory drawing for a portrait of Mihrimah Sultan (Cameria, 1522-1578) by Titian or workshop, after 1541, Albertina in Vienna.
Portrait of Mihrimah Sultan (Cameria, 1522-1578) as Saint Catherine of Alexandria by workshop of Titian, after 1541, Courtauld Gallery in London.
Portrait of Mihrimah Sultan (Cameria, 1522-1578) by unknown painter after Titian, after 1541, Masovian Museum in Płock.
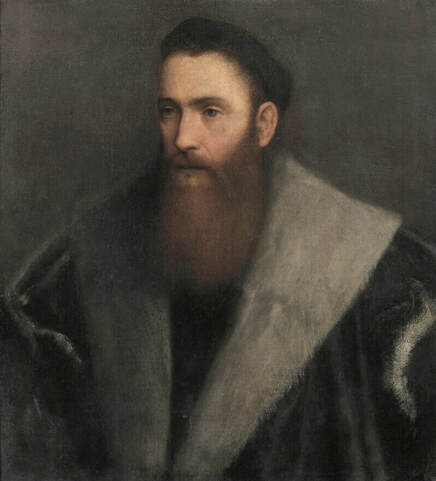
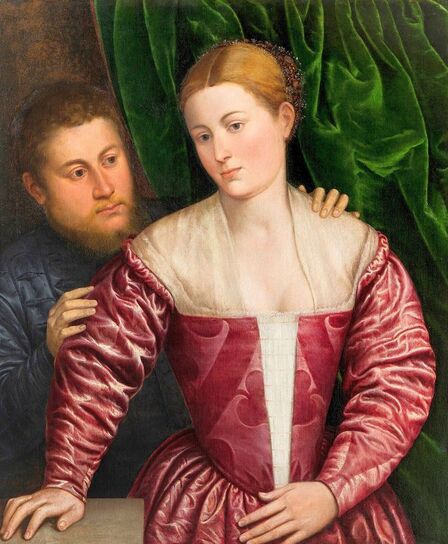
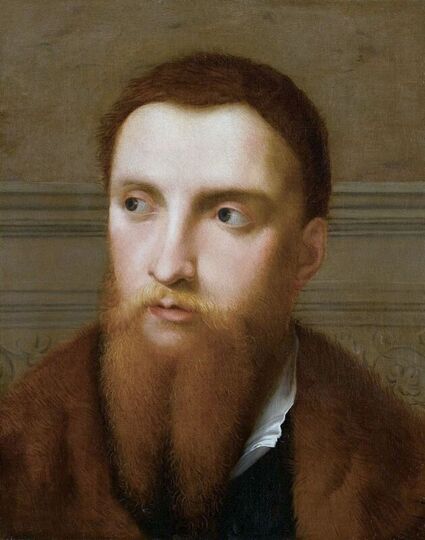
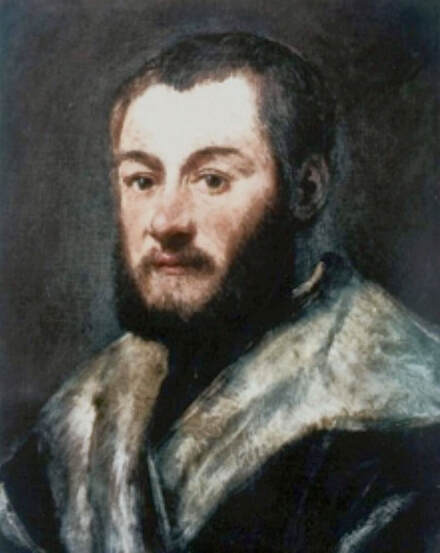
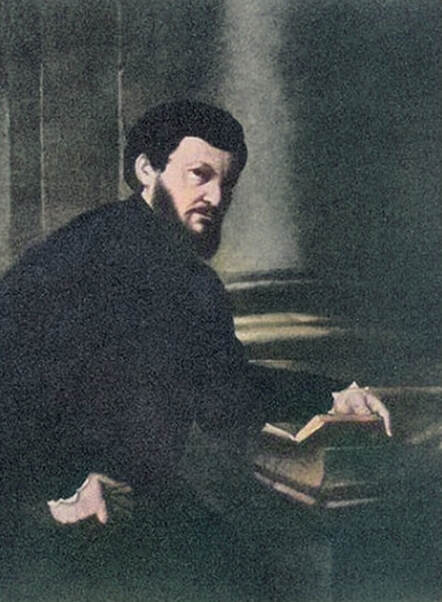
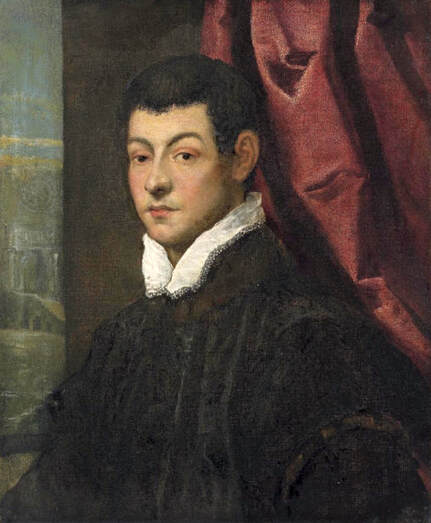
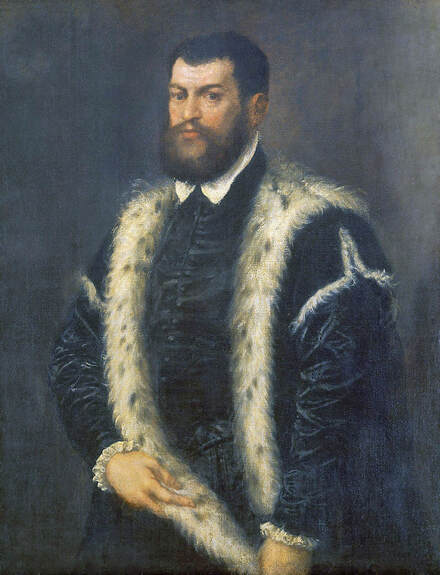
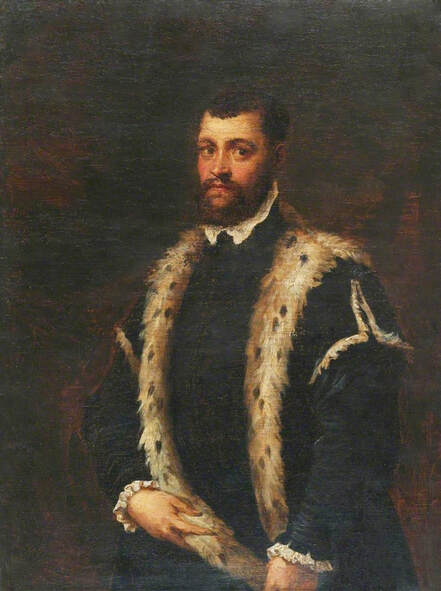
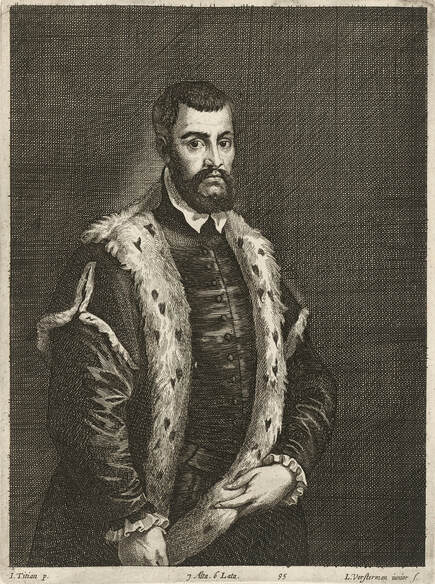
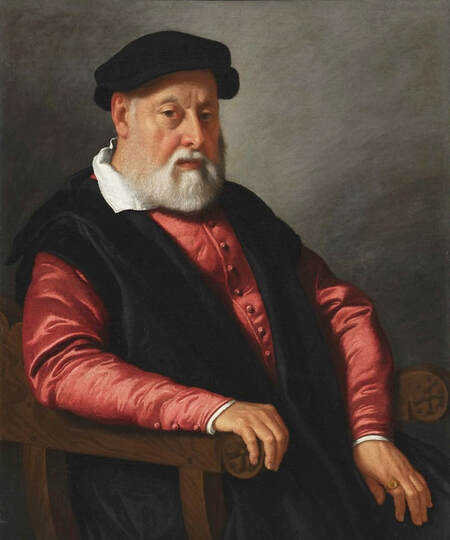
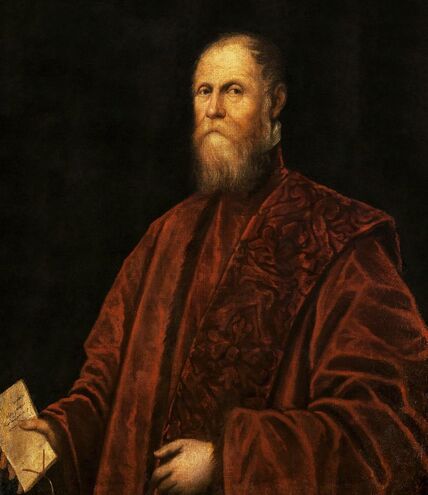
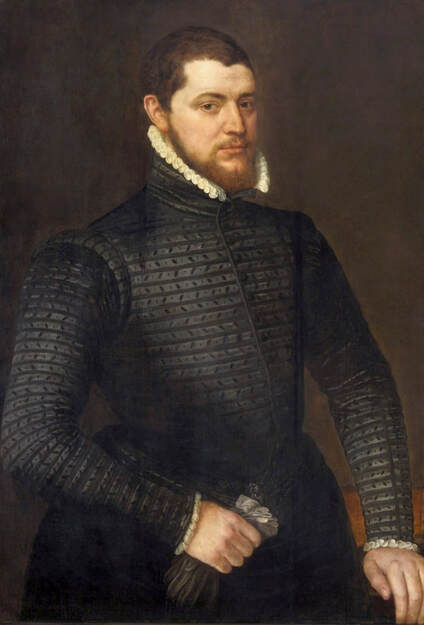
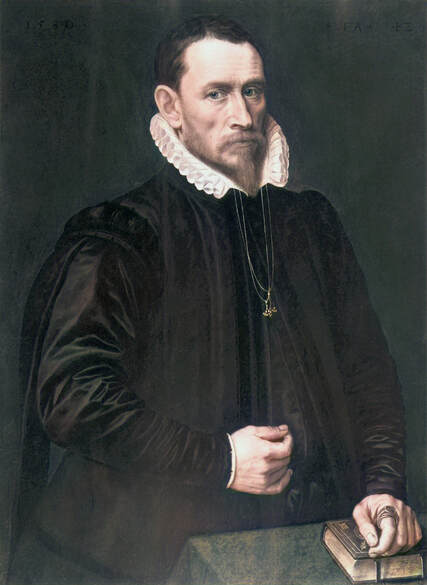
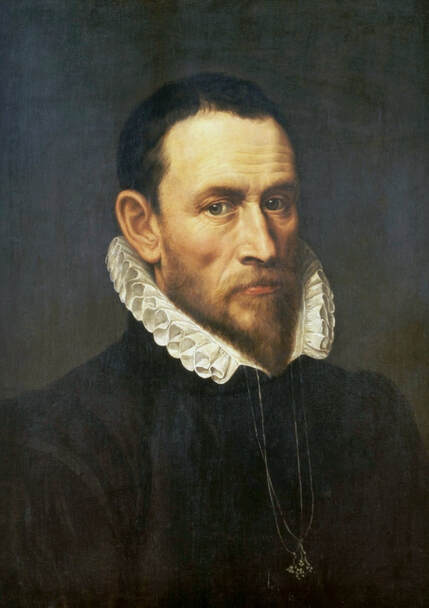
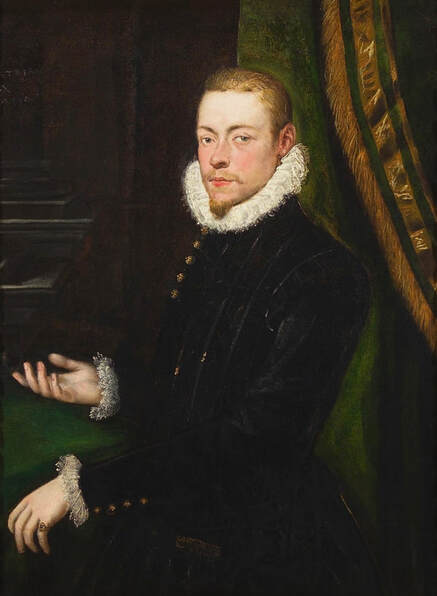
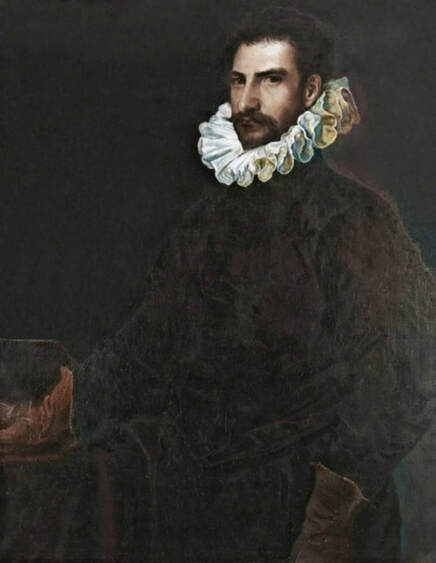
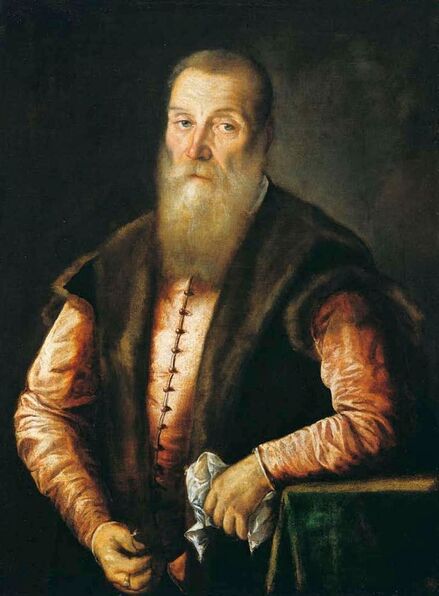
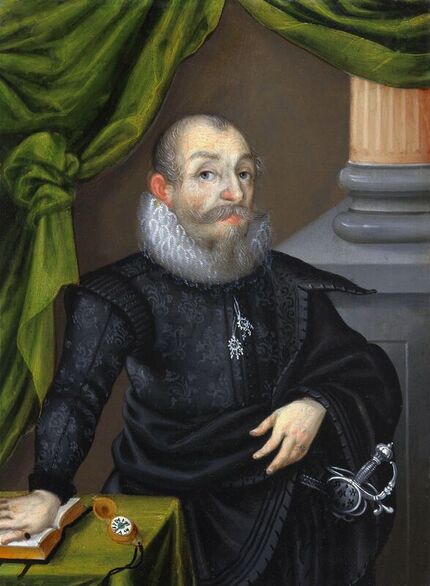
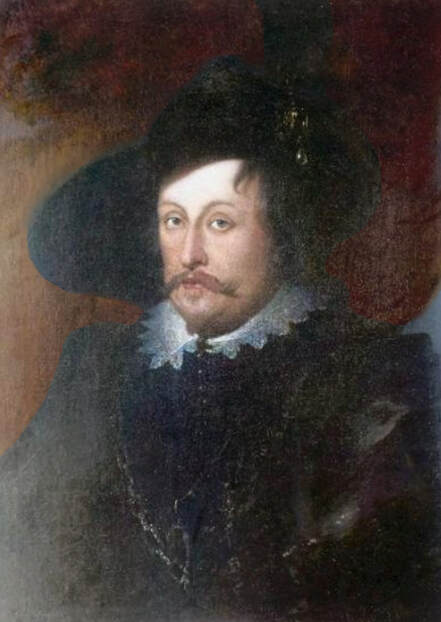
Portrait of royal courtier Jan Krzysztoporski by Bernardino Licinio
The interpretation of classical architecture by Venetian architect Andrea Palladio (1508-1580), known as Palladianism, revived by early 18th century British architects, become the dominant architectural style until the end of the century. The work of the architect and his effigies become highly demanded goods.
That is why an owner of a portrait of an unkown nobleman by Bernardino Licinio, possibly a painter, decided to turn it into a portrait of the famous architect. He added an inscription in Latin (ANDREAS. PALADIO. A.) and a set-square and a compass in sitter's right hand to make his "forgery" even more probable. The portrait, today in Kensington Palace, was acquired in 1762 by king George III from Joseph Smith, British Consul in Venice. Wooden attributes of a simple architect contrast sharply with opulent costume of the sitter, crimson doublet of Venetian silk, gold rings with precious stones and a coat lined with expensive Eastern fur. Also the man depicted is more Eastern type than an Italian. Such expensive, usually metal instrument, as compass is clearly exposed in the portraits of architects by Lorenzo Lotto, while in Licinio's portrait is barely visible. The little finger is a proof that the attributes were added later, as its appearance is anatomically impossible to hold a set-square and a compass. According to original inscription (ANNOR. XXIII. M.DXLI) the sitter was 23 in 1541, exactly as Jan Krzysztoporski (1518-1585), a nobleman of Nowina coat of arms from central Poland. Between 1537-1539 he studied in Lutheran Wittenberg, under the direction of Philip Melanchthon, recommended to him by "the father of Polish democracy" Andrzej Frycz Modrzewski. Then he went for further studies to Padua (entred as loannes Christophorinus), where on May 4, 1540, he was elected a counselor of the Polish nation. In January 1541, he welcomed in Treviso, close to Venice, the Chancellor Jan Ocieski (1501-1563) on his way to Rome. After returning to Poland, he was admitted to the royal court on 2 July 1545 and in 1551 he was made the royal secretary. He was an envoy of king Sigismund Augustus to Pope Julius III in 1551, to Joachim II Hector, Elector of Brandenburg in 1552 and to Isabella Jagiellon, Queen of Hungary in 1553. As a follower of Calvinism, he founded a congregation of this religion in his estate in Bogdanów, near Piotrków Trybunalski. He also had a large library in his brick fortified manor in Wola Krzysztoporska, which he built, destroyed during subsequent wars.
Portrait of royal courtier Jan Krzysztoporski (1518-1585) by Bernardino Licinio, 1541, Kensington Palace.
Portraits of Jan Krzysztoporski, Jan Turobińczyk and Wandula von Schaumberg by Hans Mielich
Around 1536, a German painter Hans Mielich (also Milich, Muelich or Müelich), born in Munich, went to Regensburg, where he worked under the influence of Albrecht Altdorfer and the Danube School. He stayed there till 1540, when he returned to Munich. At that time, from 1539 to 1541, Regensburg was a place of meetings between representatives of the various Christian communities and debates between Catholics and Protestants, climaxing in the Regensburg Colloquy, also known as Diet of Regensburg (1541). Among the people vividly interested in the debates were Jan Łaski (Johannes a Lasco, 1499-1560), a Polish Calvinist reformer, later involved in translation project of the Radziwill Bible, who studied in Mainz in the winter of 1539/40, and Wandula von Schaumberg (1482-1545), the Princess-abbess of the Imperial Obermünster Abbey in Regensburg from 1536, who had a seat and vote in the Imperial Diet. In 1536 Mielich created a painting of Crucifixion of Christ with his monogram, date and coat of arms of the von Schaumberg family, today in the Landesmuseum in Hannover, most probably commissioned by Wandula.
A portrait of a wealthy old woman in a black dress, white cap and a wimple by Hans Mielich in the Museu Nacional d'Art de Catalunya in Barcelona, deposit of the Thyssen-Bornemisza collection, comes from the collection of a mysterious Count J. S. Tryszkiewicz in his French castle of Birre. No such person and castle are confirmed in sources, however Count Jan Tyszkiewicz, who died in Paris on June 9, 1901, was owner of the Birzai Castle in Lithuania and a son of renowned art collector, Michał Tyszkiewicz. Both the family as well as the castle were known differently in different languages of the multicultural nation, hence the mistake is justified. Before the Tyszkiewicz family, Birzai Castle was the main seat of the Calvinist branch of the Radziwill family. According to inscription in German, the woman in the painting was 57 in 1539 (MEINES ALTERS IM . 57 . IAR . / 1539 / HM), exactly as Wandula von Schaumberg, who like the Radziwills was the Imperial Princess. In 1541 the artist went to Rome, probably at the instigation of Duke William IV of Bavaria. He remained in Italy till at least 1543 and after his return, on 11 July 1543 he was admitted to the Munich painters' guild. Hans was a court painter of the next Duke, Albert V of Bavaria and his wife Anna of Austria (1528-1590), daughter of Anna Jagellonica (1503-1547) and younger sister of Elizabeth of Austria (1526-1545), first wife of Sigismund II Augustus. Albert and Anna were married on 4 July 1546 in Regensburg. On his way to Rome, Mielich most probably stopped in Padua, where in 1541 Andreas Hertwig (1513-1575), a member of patrician family from Wrocław, obtained the degree of doctor of both laws at the age of 28. Hertwig commissioned his portrait, today in the National Museum in Warsaw. On December 10, 1540 Jan Ocieski of the Jastrzębiec coat of arms (1501-1563), secretary of king Sigismund I set off on a diplomatic mission from Kraków. It is possible that he was accompanied by Jan Turobińczyk (Joannes Turobinus, 1511-1575), an expert on Cicero and Ovid, who after studies in Kraków in 1538 became the secretary of the bishop of Płock and other secretary of the king, Jakub Buczacki, and for two years he moved to the bishop's court in Pułtusk. When Buczacki died on 6 May 1541, he lost his protector and moved to Kraków, where he decided to continue his studies. Jan was later ordained a priest in about 1545, he lectured on Roman law and he was elected rector of the Kraków Academy in 1561. A portrait of a man holding gloves in the Germanisches Nationalmuseum in Nuremberg is very similar to the portrait of Andreas Hertwig in Warsaw. According to inscription on the back, the man depicted is also Andreas Hertwig, hence the portrait is attributed to so-called Master of the Andreas Hertwig Portrait. Facial features, however, do not match and according to original inscription in Latin the man was 30 on 8 May 1541 (M D XXXXI / D VIII MAI / AETATIS XXX), exactly as Jan Turobińczyk when the news of the death of his protector could reach him in Italy and when he could decide to change his life and return to studies. Another similar portrait to the effigy of Andreas Hertwig in Warsaw is in private collection. The young man in a rich costume was depicted against a green background. According to inscription in Latin he was 25 on 22 November 1543 (M. D. XLIII. DE. XX. NOVEMBE / .AETATIS. XXV), exactly as Jan Krzysztoporski, who around that time was still in Italy. His facial features are similar to the portrait by Bernardino Licinio created just two years earlier, in 1541 (Kensington Palace). The difference in eye color is probably due to technique and style of painting. Rings on his finger are almost identical on both paintings and coat of arms on the signet ring visible on the portrait from 1543 is very similar to Nowina coat of arms as shown in the 15th century Armorial de l'Europe et de la Toison d'or (Bibliothèque nationale de France). The letters on the signet can be read as IK (Ioannes Krzysztoporski). At the beginning of the 17th century, the court painter of the Polish-Lithuanian Vasas was Christian Melich, who, according to some sources, came from Antwerp. This, however, does not exclude the possibility that he was a relative of Hans Mielich. He created one of the oldest views of Warsaw, now in Munich, most probably from the dowry of Anna Catherine Constance Vasa.
Portrait of Princess-abbess Wandula von Schaumberg (1482-1545) aged 57, from the Radziwill Castle in Birzai by Hans Mielich, 1539, Museu Nacional d'Art de Catalunya.
Portrait of Jan Turobińczyk (1511-1575) aged 30 by Hans Mielich, 1541, Germanisches Nationalmuseum in Nuremberg.
Portrait of Jan Krzysztoporski (1518-1585) aged 25 by Hans Mielich, 1543, Private collection.
Portraits of Françoise de Luxembourg-Ligny by Hans Besser and workshop of Lucas Cranach the Younger
Streets, houses, temples, public baths and other edifices of Antient Greece and Rome were full of statues, frescoes and mosacis showing naked gods and rulers. Surely in such temperatures in the south of Europe, where Bona Sforza was raised, it was easier to undress than to get dressed. More to the north the situation was quite opposite, to protect from cold, people dressed up and rarely could see any nudity, thus become more prudish in this regard. Renaissance redisovered the nude statues and paintings of the ancient and today some televison programs reinvented the concept that is good to see a potential partner naked before any engagement, at least for some people.
In 1549 Emperor Charles V (1500-1558) commissioned a bronze statue of himself as a naked ancient god and the detachable armour, so the statue could be dressed. The sculpture, created in Milan by Italian sculptors Leone and Pompeo Leoni, was presented to the Emperor in Brussels in 1556 and later transported to Madrid, today in the Prado Museum (inventory number E000273). In 1535 Françoise de Luxembourg-Ligny, a daughter of Count Charles I of Ligny and Charlotte d'Estouteville, married Bernhard III, Margrave of Baden-Baden. Françoise was a Countess of Brienne and Ligny and heiress of the County of Roussy. She was about 15 years old and the groom 61 at the time of their marriage. Almost a year after the wedding she bore her husband a son Philibert, born on 22 January 1536. Bernhard died on 29 June 1536 and their second son Christopher was born on 26 February 1537, posthumously. Next years were filled with disputes over the custody of the children, which was claimed by their uncle Ernest, Margrave of Baden-Durlach who favored Lutheranism and Duke William IV of Bavaria, husband of Bernhard's niece Marie Jakobaea of Baden-Sponheim, a staunch Catholic. In agreement with Françoise, her eldest son Philibert spent part of his youth at the court of Duke William IV in Munich. Françoise remarried on 19 April 1543 to Count Adolf IV of Nassau-Idstein (1518-1556), who was more of her age, and she bore him three children. In 1549 Hans Besser, court painter of Frederick II, Elector Palatine created a series of portraits of Françoise's eldest sons Philibert and Christopher (in Munich, from the collections of the Dukes of Bavaria and in Vienna, from the Habsburg collection). In 1531 Frederick of Palatine was a candidate to the hand of Princess Hedwig Jagiellon, he must have received her portrait, most probably in the popular "guise" of Venus and Cupid. A painting showing Venus and Cupid in the Alte Pinakothek in Munich from about 1540 is painted in the form typical for Cranach's Venuses. Its style, however, is not typical for Cranach and his workshop, hence this painting is also attributed to a Cranach's copist from the early 17th century Heinrich Bollandt. The painting was acquired in 1812 from Bayreuth Palace. In 1541, a grandson of Sophia Jagiellon, sister of king Sigismund I of Poland, Albert Alcibiades, Margrave of Brandenburg-Kulmbach received Bayreuth. He assisted Emperor Charles V in his war with France in 1543 but soon deserted Charles, and joined the league which proposed to overthrow the Emperor by an alliance with French king Henry II. He spent the last years of his life in Pforzheim with the family of his sister Kunigunde, who was married to Charles II of Baden, nephew of Bernhard III. Albert Alcibiades was unmarried, so the match with a widowed Margravine of Baden, and a French noble, would be perfect for him. Slightly different and somewhat smaller repetition of the motif in Munich was sold in Brussels on November 7, 2000. Similar painting, from the Rastatt Palace, was cut into pieces before 1772 and preserved fragments are now in the Staatliche Kunsthalle Karlsruhe (Venus with a tiara and Cupid with an arrow). The Rastatt Palace was built between 1700 and 1707 by an Italian architect for Margrave Louis William of Baden-Baden, a direct descendant of Françoise de Luxembourg-Ligny. The same woman as in the above mentioned paintings was also depicted in a series of portraits by workshop of Lucas Cranach the Younger. Most probaly all depicted her as Salome and some of them were cut later, so that the upper part could be sold as a portrait and the lower part as Saint John the Baptist. Basing on the woman's outfit they should be dated to late 1530s or early 1540s, however one of these portraits from the old collection of the Friedenstein Palace in Gotha, where there is an effigy of Hedwig Jagiellon as the Virgin, is dated 1549. A copy of the latter painting from the collection of the Dukes of Brunswick is in the Herzog Anton Ulrich Museum. The portrait now in the State Gallery in Johannisburg Palace in Aschaffenburg, comes from the art collection of Hermann Goering and other, sold in 2012, was in the collection of Prince Serge Koudacheff in St. Petersburg, before 1902. Another, signed with monogram HVK, was before 1930 in the inventory of Veste Coburg. There is also a version as Judith with the head of Holofernes in the Sanssouci Palace in Potsdam and several paintings where the woman was depicted in the satirical scene of the ill-matched couple, some of which are attributed to another 17th century copist of Cranach, Christian Richter. Facial features in all these effigies greatly resemble portraits of sons of Françoise de Luxembourg-Ligny by Hans Besser and stylistically some of these works are very close to portraits by this court painter.
Portrait of Françoise de Luxembourg-Ligny (d. 1566), Margravine of Baden-Baden as Venus and Cupid by Hans Besser or workshop of Lucas Cranach the Younger, ca. 1540, Alte Pinakothek in Munich.
Portrait of Françoise de Luxembourg-Ligny (d. 1566), Margravine of Baden-Baden as Venus with a tiara by Hans Besser or workshop of Lucas Cranach the Younger, ca. 1540, Staatliche Kunsthalle Karlsruhe.
Portrait of Françoise de Luxembourg-Ligny (d. 1566), Margravine of Baden-Baden by workshop of Lucas Cranach the Younger, 1535-1549, Johannisburg Palace in Aschaffenburg.
Portrait of Françoise de Luxembourg-Ligny (d. 1566), Margravine of Baden-Baden by workshop of Lucas Cranach the Younger, 1535-1549, Private collection.
Portrait of Françoise de Luxembourg-Ligny (d. 1566), Margravine of Baden-Baden by monogramist HVK, 1535-1549, Private collection.
Portrait of Françoise de Luxembourg-Ligny (d. 1566), Margravine of Baden-Baden as Salome by workshop of Lucas Cranach the Younger, 1549, Friedenstein Palace in Gotha.
Ill-Matched Couple, caricature of Françoise de Luxembourg-Ligny (d. 1566), Margravine of Baden-Baden and her husband by workshop of Lucas Cranach the Younger or Christian Richter, 1535-1566 or early 17th century, Private collection.
Portraits of Barnim IX of Pomerania-Szczecin, his wife and his three daughters by Lucas Cranach the Elder, his son and workshop
In 1543 three daughters of Barnim IX, Duke of Pomerania-Szczecin and his wife Anna of Brunswick-Lüneburg, Maria (1527-1554), Dorothea (1528-1558) and Anna (1531-1592), reached the legal age of marriage (12). That same year on May 6, 1543, Barnim's young cousin, king Sigismund Augustus of Poland married Elizabeth of Austria (1526-1545).
Three of Sigismund Augustus' sisters Sophia, Anna and Catherine were also unmarried and Barnim's uncle Sigismund I hoped to find a suitable husband for each of them. Due to the kinship of the ruling families of Poland-Lithuania and Pomerania, they undoubtedly exchanged some effigies. Almost a year later on July 16, 1544 Maria, the eldest daughter of Barnim, married Count Otto IV of Holstein-Schaumburg-Pineberg (1517-1576). Dorothea had to wait ten years more to marry Count John I of Mansfeld-Hinterort (d. 1567) on July 8, 1554 and Anna married three times, first to Prince Charles I of Anhalt-Zerbst (1534-1561) in 1557, then to Burgrave Henry VI of Plauen (1536-1572) in 1566 and then to Count Jobst II of Barby-Mühlingen (1544-1609) in 1576. A small painting of Hercules and Omphale by Lucas Cranach the Elder and workshop in the National Museum in Warsaw is very similar to the painting from the Mielżyński collection in Poznań, showing the family of Sigismund I in 1537. Dimensions (48.7 x 74.8 cm / 48 x 73 cm), the composition, even the poses and costumes are very similar. This painting was most probably transferred during the World War II to the Nazi German Art Repository in Kamenz (Kamieniec Ząbkowicki), possibly from the Silesian Museum of Fine Arts in Wrocław. Around 1543 the ruler of nearby Legnica was Frederick II, like Barnim a strong supporter of the Reformation and his distant relative. Both dukes had close ties with nearby Poland-Lithuania. Frederick's younger son George, future George II of Legnica-Brzeg, was unmarried at that time. It cannot be excluded that the ruling family of Legnica received this fashionable portrait of Barnim's family in guise of mythological heroes. The work match perfectly the ruling house of Pomerania-Szczecin in about 1543 and face features of Hercules and Omphale are very similar to other portraits of Barnim IX and his wife. The above described painting is a reduced version of a larger composition which was in the Stemmler collection in Cologne, now in private collection. It is very similar to the portrait of Barnim's family as Hercules and Omphale from 1532 in Berlin (lost). The effigy of Maria of Pomerania-Szczecin with a duck above her, a symbol of marital fidelity and intelligence, is almost identical with the effigy of her mother Anna of Brunswick-Lüneburg from the earlier painting. The whole composition is based on a preparatory drawing that preserved in the Museum of Prints and Drawings in Berlin (Kupferstichkabinett, inventory number 13712), signed with a monogram L.G., most probably created by Cranach's pupil who was sent to Szczecin or Barnim's court painter. All of Barnim's daughters, including the youngest Sibylla, born in 1541, were depicted in a large painting created by Cornelius Krommeny in 1598 and showing the Family tree of the House of Pomerania, today in the National Museum in Szczecin. A portrait of a young lady as Salome in the bridal crown on her head in the Museum of Fine Arts in Budapest, is almost identical with the effigy of Maria of Pomerania-Szczecin in both of mentioned paintings of Hercules and Omphale. This portrait was recorded in 1770 in the Bratislava Castle, the formal seat of the kings of Hungary, and later transferred to the imperial collections in Vienna. The same woman was depicted as Lucretia in the painting by workshop of Lucas Cranach the Elder, which was before 1929 in private collection in Amsterdam, today in the Alte Pinakothek in Munich and as Venus with Cupid as the honey thief from the collection of the Princes of Liechtenstein in Vienna, today in the Kröller-Müller Museum in Otterlo. A portrait of a lady as Judith in green dress in the National Gallery of Ireland in Dublin, purchased in 1879 from the collection of Mr. Cox in London, match perfectly the effigy of Dorothea of Pomerania-Szczecin in described paintings. Her pose and outfit is very similar to that of Dorothea's mother in both paintings of Hercules and Omphale. Two representations of Lucretia attributed to Lucas Cranach the Younger, one from the Galerie Attems in Gorizia, today in the Eggenberg Palace in Graz and the other purchased in 1934 by the Kunstmuseum Basel, are also very similar to the effigy of Dorothea. Salome with the head of Saint John the Baptist in the bridal crown, which was formerly in the collection of the King of Württemberg, now in the Bob Jones University Museum and Gallery in Greenville is identical with the effigy of the youngest daughter of Barnim in the Warsaw's painting. The painter evidently used the same template drawing to create both miniatures. Another very similar Salome, attributed to Cranach the Younger, comes from the collection of the Ambras Castle built by Archduke Ferdinand II of Austria (1529-1595), the second son of Anna Jagellonica and Emperor Ferdinand I. It was offered in 1930 by Gustaf Werner to the Gothenburg Museum of Art. The painter added a fantastic landscape in the background. Finally there is a painting of Venus and Cupid as the honey thief from the same period in the Germanisches Nationalmuseum in Nuremberg, also atrributed to Cranach the Younger. Venus' face is identical with the portrait of Anna of Pomerania-Szczecin in the painting from Stemmler collection. The painting comes from the residence of the Catholic Bishops of Freising, where it was known as Saint Juliana. It cannot be excluded that it was originally in the Polish-Lithuanian royal collection and was transferred to nearby Neuburg an der Donau with the collection of Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa or brought by some other eminent Polish-Lithuanian lady. In the National Museum in Warsaw there is also a painting showing a moralistic subject of the ill-matched couple by workshop of Lucas Cranach the Elder or his son from the third quarter of the 16th century. It was aquired by the Museum in 1865 from the collection of Henryk Bahré. The woman has slipped her hand inside the old man's purse, which leaves no doubt as to the basis of this relationship. Her face and costume is based on the same set of template drawings which were used to create portraits of Anna of Pomerania-Szczecin. The painting is of a high quality, therefore the patron who commissioned it was wealthy. While Georgia of Pomerania (1531-1573), daughter of George I, brother of Barnim, married in 1563 a Polish nobleman and a Lutheran, Stanisław Latalski (1535-1598), starost of Inowrocław and Człuchów, her cousin Anna opted for titular and hereditary German princes in her subsequent marriages. It is therefore possible that this painting was commissioned by the royal court or a magnate from Poland-Lithuania.
Preparatory drawing for a portrait of Barnim IX of Pomerania-Szczecin, his wife and his three daughters as Hercules and Omphale's maids by Monogrammist L.G. or workshop of Lucas Cranach the Elder, ca. 1543, Museum of Prints and Drawings in Berlin.
Portrait of Barnim IX of Pomerania-Szczecin, his wife and his three daughters as Hercules and Omphale's maids by Lucas Cranach the Elder and workshop, ca. 1543, Private collection.
Portrait of Barnim IX of Pomerania-Szczecin, his wife and his three daughters as Hercules and Omphale's maids by Lucas Cranach the Elder and workshop, ca. 1543, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Maria of Pomerania-Szczecin (1527-1554) as Salome with the head of Saint John the Baptist by Lucas Cranach the Elder, ca. 1539-1543, Museum of Fine Arts in Budapest.
Portrait of Maria of Pomerania-Szczecin (1527-1554) as Lucretia by workshop of Lucas Cranach the Elder, ca. 1543, Alte Pinakothek in Munich.
Portrait of Maria of Pomerania-Szczecin (1527-1554) as Venus with Cupid as the honey thief by Lucas Cranach the Elder or his son, ca. 1543, Kröller-Müller Museum in Otterlo.
Portrait of Dorothea of Pomerania-Szczecin (1528-1558) as Judith with the head of Holofernes by workshop of Lucas Cranach the Elder, ca. 1543-1550, National Gallery of Ireland.
Portrait of Dorothea of Pomerania-Szczecin (1528-1558) as Lucretia by Lucas Cranach the Younger, ca. 1543-1550, Eggenberg Palace in Graz.
Portrait of Dorothea of Pomerania-Szczecin (1528-1558) as Lucretia by Lucas Cranach the Younger, ca. 1543-1550, Kunstmuseum Basel.
Portrait of Anna of Pomerania-Szczecin (1531-1592) as Salome with the head of Saint John the Baptist by Lucas Cranach the Elder, ca. 1543, Bob Jones University Museum and Gallery in Greenville.
Portrait of Anna of Pomerania-Szczecin (1531-1592) as Salome with the head of Saint John the Baptist by Lucas Cranach the Younger, ca. 1543-1550, Gothenburg Museum of Art.
Portrait of Anna of Pomerania-Szczecin (1531-1592) as Venus and Cupid as the honey thief by Lucas Cranach the Younger, ca. 1543-1550, Germanisches Nationalmuseum.
Ill-matched couple, caricature of Anna of Pomerania-Szczecin (1531-1592) by workshop of Lucas Cranach the Elder or his son, third quarter of the 16th century, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Sigismund Augustus in armour by Giovanni Cariani
"Come poor people with joy and drink without charge the water that Bona, Queen of Poland provided" (Pauperes sitientes venite cum laetitia et sine argento. Bibite aquas, quas Bona regina Poloniae preparavit) is the Latin inscription on one of the two cisterns which is still near the Bari Cathedral, the other, of which there are no traces today, was located in the area of the Church of San Domenico and only the inscription is known (Bona regina Poloniae preparavit piscinas. Pauperes sitientes venite cum laetitia et sine argento). The queen was a great benefactress to this archiepiscopal city and, among other timely gifts, increased the number of public fountains. From Poland she directed many interventions in her duchy to improve the life and the prosperity of the inhabitants, building canals, wells, aided churches with donations.
Bona also tried to expand her possessions in Italy. In 1536 she bought the city of Capurso and in 1542 she also bought the county of Noia and Triggiano. To reach the amount necessary for the purchase of the county (68,000 ducats) she imposed new taxes, and on this occasion the municipality of Bari complained that Modugno near Bari is "praised and loved more than this city (Bari) from Y.M. (Your Majesty)" (laudata e amata più di questa città (Bari) dalla M.V. (maestà vostra)). The queen cared very much about her hereditary principalities of Bari and Rossano and wanted her son to inherit them. Among the many Italians at the Polish-Lithuanian royal court, many came from Bari. In the 1530s and 1540s, there were two physicians from Bari at the court - Giacomo Zofo (Jacobus Zophus Bariensis), who was called Sacrae Mtis phisicus in 1537, and Giacomo Ferdinando da Bari (Jacobus Ferdinandus Bariensis), who published two treatises in Kraków (De foelici connubio serenissimi Ungariae regis Joannis et S. Isabellae Poloniae regis filiae, 1539 and De regimine a peste praeservativo tractatus, 1543). In 1537 there were also Scipio Scholaris Barensis Italus, royal secretary and provost of Sandomierz, Cleofa, sub-cantor of the Cathedral of St. Nicholas in Bari (Cleophas Succantor Ecclac S. Nicolai, Barensis) who was the brother of Sigismondo, the royal chef, Teodoro de Capittelis and Sabino de Saracenis. On Bona's recommendation, in 1545, the lawyer Vincenzo Massilla (or Massilio, 1499-1580) developed the Bari code of customary law (Commentarii super consuetudinibus praeclarae civitatis Bari) written in Kraków during the years of residence at the Polish court and completed in Padua, first published in 1550 by Giacomo Fabriano and then by Bernardino Basa in Venice in 1596. Massilla was a well-known jurist and become advisor of the queen. In 1538 he held the position of governor of Rossano and moved to Kraków as auditor general for the feudal states held by Bona Sforza in southern Italy. She also sought permission to appoint the bishops of Bari and Rossano, but the pope refused. In 1543 Queen Bona returned to her plan of the sale of the Duchy of Rossano and for this purpose the representative of the city of Rossano - Felice Brillo (Britio) came to Poland. Few years later, on August 30, 1549, Luigi Zifando from Bari (Siphandus Loisius hortulanus Italus Barensis) was admitted as the royal gardener. Several people from Modugno near Bari were in service of the queen and later of her son Sigismund Augustus, like Girolamo Cornale, who died in Warsaw, and priests Vito Pascale and mentioned Scipione Scolaro or Scolare (Scholaris). When in Poland, in 1550, Pascale built himself a palace in Modugno (Palazzo Pascale-Scarli), the architecture of which is attributed to the influence of the Florentine architect Bartolomeo Berecci working in Poland. The court of Bona's son Sigismund Augustus in Vilnius was also dominated by Italians, like two singers of the queen, Erasmo and Silvester, incisor gemmarum Jacopo Caraglio, pharmacist Floro Carbosto, locksmith - Domenico, builders - Gasparus and Martinus, sculptor Bartholomeo, musician Sebaldus, harper Franciscus, caretaker of the Italian royal stallions Marino, goldsmiths: Antonio, Vincentino, Christoforus and Bartholomeo, tailor Pietro and the bricklayer Benedictus. The king favored the Italian style in his attire, and he usually wear a short Italian caftan of black silk or a German one of black cloth from Vicenza over the shirt. The most expensive part of his outfit was a sable cap, a germak coat made of black damask, lined with dormouse fur, and an Italian, gilded, sword, "a gift from Bari". Among the expensive furnishings of his three-room apartment in the new Vilnius Castle were Venetian mirrors - one of them in precious frames decorated with pearls and silver. Venetian glass was delivered to the court by Vilnius merchants, Morsztyn and Łojek (after "Zygmunt August: Wielki Książę Litwy do roku 1548" by Ludwik Kolankowski, p. 329, 332). In the Parmeggiani Gallery in Reggio Emilia (Musei Civici) there is a "Portrait of a warrior", attributed to Giovanni Cariani, who died in Venice in 1547 (oil on canvas, 95 x 77 cm, inventory number 76). It comes from the collection of Luigi Francesco Giovanni Parmeggiani (1860-1945), an Italian anarchist, forger, art dealer and collector, who before inaugurating his gallery in 1928 in his hometown, lived mainly in Brussels, London and Paris. The young man is holding his hand on a helmet. His expensive suit of armour indicates that he is a member of the aristocracy, a knight, and the landscape behind him undoubtedly represents his castle. Only one tower is visible and a church to the right. This layout and shape of the towers correspond with the Bari Castle (Castello Normanno-Svevo, Ciastello) and Bari Cathedral (Arciuescouato) as seen from the "Royal Gate" (Porta Reale) and depicted in an early 18th century print by Michele Luigi Muzio (structures C, A and H). The man's face is very reminiscent of the images of the young Sigismund Augustus, who at that time was considered as a successor of his mother in the Duchy of Bari. The paintings of the Venetian school are among the most valuable linked to Bari or the region - Saint Peter the Martyr from the Santa Maria la Nova Church in Monopoli by Giovanni Bellini, Throning Madonna and Child with Saint Henry of Uppsala and Saint Anthony of Padua by Paris Bordone or the Virgin and Child with Saint Catherine of Alexandria and Saint Ursula with a donor from Ardizzone family from the Bari Cathedral by Paolo Veronese (Pinacoteca metropolitana di Bari).
Portrait of Sigismund II Augustus in armour against the view of the castle in Bari by Giovanni Cariani, ca. 1543, Parmeggiani Gallery in Reggio Emilia.
Portrait of Barbara Radziwill, Elizabeth of Austria and Sigismund Augustus as Flora, Juno and Jupiter by Paris Bordone
Ovid in Fasti V relates the story of Juno, queen of the gods, who annoyed with her husband Jupiter for producing Minerva from his own head by the stroke of Vulcan's axe, complained to Flora, goddess of fertility and blossoming plants. Flora, gave her secretly a flower, by only touching which women immediately became mothers. It was by this means that Juno gave birth to the god Mars. The Renaissance represented Flora under two aspects, Flora Primavera, embodiment of genuine marital love, and Flora Meretrix, prostitute and courtesan whom Hercules won for a night in a wager.
Because Hercules' mother was mortal, Jupiter put him to the breast of his wife, knowing that Hercules would acquire immortality through her milk and according to the myth the droplets of milk crystallized to form the Milky Way. As Juno Lucina (Juno the light-bringer) she watched over pregnancy, childbirth, and mothers and as Juno Regina (Juno the Queen) she was the patron goddess of Rome and the Roman Empire. The great popularity of Ovid's works in Poland-Lithuania-Ruthenia, poetically called Sarmatia, left its mark on the character of the decorations of many buildings across the country, including royal residences, which were undoubtedly filled with many Ovidian motifs. Those created after the Deluge, in the 1680s, preserved in the Wilanów Palace and the Lubomirski bathing pavilion in Warsaw (based on the engravings by Abraham van Diepenbeeck). "In the 16th century, Ovid's links with Sarmatia gave rise to the legend that he had lived in Poland, had learned to speak the Polish language, and had died and been buried near the Black Sea, that is, within the borders of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. It was claimed that Ovid was the first Polish poet, and his 'naturalisation' and the 'discovery of his grave' shaped the consciousness of the ruling classes and the elites of the Commonwealth" (after "Ovidius inter Sarmatas" by Barbara Hryszko, p. 453, 455). His famous "Metamorphoses" dealt with the transformation of human beings into other entities and the deification of the descendants of Venus, goddess of love. Latin works of Andrzej Krzycki (Andreas Cricius, 1482-1537), secretary to Queen Bona, were openly inspired by the Ovid's oeuvre and Piotr Wężyk Widawski in his paraphrase of a fragment of "Metamorphoses" entitled "Philomela [...] Under the image of the goddess Venus" (Philomela. Morale. To iest S. Ksiąg rozmáitych Autorow wykład obycżáyny. Pod Obraz Boginiey Wenery), published in Kraków in 1586, "wrote not only that Ovid was very popular and widely known in Poland but also expressed his belief that Ovid had come to Poland, where he had learned the Polish language and had become a Pole". In the painting by Paris Bordone in the Hermitage Museum (oil on canvas, 108 x 129 cm, inventory number ГЭ-163), Flora receives flowers and herbs from Cupid, the god of desire and erotic love and son of Mars and Venus. Cupid is also crowning the head of Juno with a wreath. The queen of the gods is taking the herbs from the hand of Flora, hoping she was unnoticed by her husband Jupiter Dolichenus, the "oriental" king of the gods holding an axe, who stands behind her. The painting comes from the collection of Sir Robert Walpole at Houghton Hall, sold to Empress Catherine II of Russia in 1779. The message of the painting is clear, thanks to the mistress the queen is fertile. The protagonists are therfore "oriental" king Sigismund Augustus as Jupiter, his first wife queen Elizabeth of Austria, daughter of King of the Romans as Juno, and Sigismund Augustus' mistress Barbara Radziwill as Flora.
Portrait of Barbara Radziwill, Elizabeth of Austria and Sigismund Augustus as Flora, Juno and Jupiter by Paris Bordone, 1543-1551, The State Hermitage Museum.
Portraits of Barbara Radziwill and her mother as Venus Pudica by Vincent Sellaer and circle of Michiel Coxie
Before 1550, King Sigismund Augustus ordered fabrics from the best weaving workshops in Brussels. The preserved tapestries of this rich collection, now housed in the Wawel Royal Castle and other museums, depict biblical stories, a lush world of exotic plants and animals, the monogram of the king SA in a rich Renaissance setting and the coats of arms of Poland and Lithuania. The designs for the figurative tapestries were created by the Flemish painter Michiel Coxie (1499-1592), "much celebrated among the Flemish craftsmen" (molto fra gli artefici fiamminghi celebrato), according to Giorgio Vasari. Nicknamed the Flemish Raphael, Coxie was the court painter to Emperor Charles V and his son King Philip II of Spain, although he probably never visited Spain. He frequently drew inspiration or copied Italian masters such as Raphael, Michelangelo, Titian or Sebastiano del Piombo, but also from classical Antiquity. His Moral Fall of Humanity (Abduction of human wives by the sons of the gods) with a naked woman in the center of the composition, produced by the workshop of Jan de Kempeneer between 1548 and 1553 (Royal Castle in Warsaw, ZKW/511), is the best example.
Coxie was also a renowned portrait painter. He created the effigy of Christina of Denmark (Allen Memorial Art Museum, inventory number 1953.270) and his self-portrait as Saint George, wearing the same armor as Emperor Charles V during the Battle of Mühlberg in 1548 in a painting by Titian (Prado Museum, P00410, noticed by Roel Renmans, Flickr, February 23, 2015), in the left wing of the triptych of Saint George (Royal Museum of Fine Arts, Antwerp, 373). He probably also created a copy of the mentioned equestrian portrait of the Emperor by Titian. In the National Museum in Warsaw there is an intriguing painting of a naked woman, created by Michiel Coxie's entourage, perhaps his workshop (oil on panel, 60 x 49 cm, M.Ob.2158 MNW). The style of this work is the same as the portrait of Queen Barbara Radziwill as Madonna with sleeping Child sold in 2020 (oil on panel, 95 x 76 cm, Sotheby's London, September 23, 2020, lot 33). The face is also the same, as if the painter used the same set of study drawings to create both works. It is said to represent the penitent Saint Mary Magdalene, because in some copies the woman was depicted with the typical attribute of this saint - an alabaster box of ointment (Wadsworth Atheneum Museum of Art). The painting was aquired before 1979. Some copies are attributed to Bernaert de Ryckere (private collection, 70 x 50 cm) or, more idealized, to Florentine school (private collection, 62 x 52 cm). The version in the Louvre, acquired from unknown collection in Nice in 1946 (oil on panel, 73 x 55 cm, RF 1946 9), is attributed to Flemish painter. The female figure in paintings is interpreted differently as Mary Magdalene, Bathsheba, Lucretia or Cleopatra. In some cases this is supported by the corresponding attributes, but in other cases the figure appears without other explanatory objects. Researchers generally attribute the works to Frans Floris, Michiel Coxie or Vincent Sellaer and their workshops. It is possible that the original was made by an Italian or more precisely Venetian painter, because Flemish painters copied or were inspired by their works. A copy of the Allegory of Love (Naked woman and a man with mirrors) by workshop of Titian (original in National Gallery of Art, Washington), identified as disguised portraits of Alfonso I d'Este and Laura Dianti or Federico Gonzaga and Isabella Boschetti, sold in 1992, is attributed to Michiel Coxie (Dorotheum Vienna, March 18, 1992, lot 64). A very similar mirror composition was sold in Berlin in 2020 (oil on panel, 45.5 x 32 cm, Galerie Bassenge, November 26, 2020, lot 6003). But the woman's face is different. She is also much older than the woman in the Warsaw painting. There are no attributes, which is why the image is interpreted as a representation of Venus - an aging Venus in the posture of the chaste Venus Pudica. This would ultimately mean that the work could be interpreted as a hidden allegory of vanity. It is difficult to determine today which version might be original, but assuming that both painters created copies of the same composition, we would have to conclude that the paintings depict mother and daughter. The younger woman in the Warsaw painting looks at her mother, who in turn looks at the viewer. Therefore, the older woman is the mother of Queen Barbara and the she resembles the effigies of Barbara Kolanka (d. 1550) by Lucas Cranach the Elder. Such depictions were popular in the mid-16th century and frequently a general resemblance and context are enough to determine the model, as in the case of the portrait of Diane de Poitiers (1499-1566), favorite of King Henry II of France as half-naked Pax, goddess of peace (Allegory of Peace), by School of Fontainebleau (Museo Nazionale del Bargello in Florence). Other examples include several "disguised" nude portraits by Agnolo Bronzino, such as the portrait of Cosimo I de' Medici (1519-1574), Grand Duke of Tuscany as Orpheus (Philadelphia Museum of Art), portrait of Andrea Doria (1466-1560) as Neptune (Pinacoteca di Brera in Milan), Descent of Christ into Limbo with several contemporary portraits (Basilica of Santa Croce in Florence) and portrait of sixteen-year-old cardinal Giovanni de' Medici the Younger (1543-1562) as Saint John the Baptist (Galleria Borghese in Rome). Since the 17th century, many paintings from the Radziwill collection have been transferred to Berlin by different means. The inventory of paintings from the collection of Princess Louise Charlotte Radziwill (1667-1695), who lived in Berlin, Königsberg and Heidelberg, drawn up in 1671, lists numerous representations of this type, such as a large panel with a naked woman (794) and several effigies of Saint Mary Magdalene (357, 369, 531, 792, 855, 867) (after "Inwentarz galerii obrazów Radziwiłłów z XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska). In the context of known comments about Barbara Radziwill and her mother, while likely exaggerated, these effigies also appear accurate. Stanisław Orzechowski, wrote that Sigismund Augustus "wants to seek his strength and courage from his wife in the service of Venus" and stated, among other things, that Barbara "had a mother about whom people always said bad things because of her lechery, her immodesty, poisoning and witchcraft" and the royal courtier Stanisław Bojanowski added that Barbara "continued to rouging her face to deceive us until [her] last breath", even when it was clear that the illness could not be cured (after "Nieprzyzwoite małżeństwo" by Anna Odrzywolska, p. 69).
Portrait of Barbara Kolanka as Venus Pudica by Vincent Sellaer, ca. 1545-1550, Private collection.
Portrait of Barbara Radziwill as Venus Pudica by circle of Michiel Coxie, ca. 1545-1550, National Museum in Warsaw.
Judgment of Paris with portraits of Hedwig Jagiellon and members of her family by workshop Lucas Cranach the Elder or Lucas Cranach the Younger
On February 15, 1545 the double wedding was celebrated with great splendor in Berlin. Princess Sophie of Legnica (1525-1546), the daughter of Frederick II (1480-1547), Duke of Legnica, Brzeg, and Wołów, and his second wife, Sophia of Brandenburg-Ansbach (1485-1537), married John George of Brandenburg (1525-1598), son of Magdalena of Saxony (1507-1534) and Joachim II Hector (1505-1571), Elector of Brandenburg, while the sister of John George, Barbara (1527-1595), married George (1523-1586), brother of Sophie of Legnica. The marriage cemented the alliance of the Silesian Piasts and the Hohenzollerns concluded on October 18, 1537 in Legnica with the betrothal of the princely children.
The two brides, Sophie (granddaughter of Sophia Jagiellon, Margravine of Brandenburg-Ansbach) and Barbara (granddaughter of Barbara Jagiellon, Duchess of Saxony), and the incumbent Electress of Brandenburg - Hedwig Jagiellon (1513-1573) were related. Hedwig was the second wife of Joachim II Hector and they had six children - their first son, Sigismund (1538-1566), future Bishop of Magdeburg and Halberstadt, was named after Hedwig's father. After Joachim II introduced the evangelical faith in the electorate, the electress continued to be Catholic. At the beginning of 1551 (according to other sources in autumn of 1549), Joachim II and Hedwig traveled to the forest of Schorfheide near Berlin for a boar hunt. The electoral couple lived at Grimnitz hunting lodge. On January 7, 1551, when they went for a walk on the upper floor in the morning, the rotten floor collapsed beneath them and Hedwig fell into the room below. She allegedly refused medical treatment out of modesty. Although the electress recovered, her pelvis, feet and hips were so badly injured that she had to use crutches for the rest of her life. Joachim, who hung between two beams, on which he leaned with his hands and arms, was saved from falling by a servant. He became disgusted with his crippled wife, and he took concubines. The electress reconciled with her husband nine years later, in 1560, when the celebration of the silver wedding coincided with the marriage of their second daughter, Hedwig (1540-1602), to Julius of Brunswick-Lüneburg (1528-1589), stepson of Sophia Jagiellon (1522-1575), Duchess of Brunswick. Instead of Christian compassion, mean people were spreading rumors about God's punishment, because the electress was Catholic and foreigner, not speaking German (at least at the beginning). The elector's younger brother, Margrave Hans von Küstrin (1513-1571), a staunch Lutheran, even claimed that this terrible accident happened after two images of the Virgin Mary made of gold or silver from the Treasury of Berlin Cathedral (possibly Ruthenian or Byzantine icons of the Virgin Hodegetria) were brought to Hedwig and she and her court ladies fell down with the images. He described the accident in a letter to Andrzej I Górka (1500-1551), castellan of Poznań, which was in the Archives of the Prussian Royal Family in Berlin (after "Jagiellonki polskie w XVI wieku", Volume 3, p. 282). He also added that "the floor was not rotten or damaged anywhere, not even where it had collapsed" and that "two or three days before the accident, a great light appeared in the sky above the Grimnitz house" (Es ist aber sonsten der Boden an diesem gebew an keinem ort verstockt, verfault und schadhafft gewesen, auch an den enden nicht do er eingangen. Item ein zwen oder drey tage zuvor, ehe denn diese Ding gescheen, bey der nacht, hatt sich ueber dem hause Grimnitz, so weit sich allein desselben Vmbkreiss erstreckt, ein grosser luchter glanz um Himmell erhoben). According to other legend, it was not an accident but an attempt on the life of the elector prepared by Hedwig's lover, a Polish nobleman, guest of the princely couple. He had maliciously sawed the floorboards in order to eliminate his rival. Seized with remorse after an unexpected result of his action, he becomes a hermit (after "Allgemeine Encyklopädie der Wissenschaften und Künste" from 1871, Volume 1, Issue 91, p. 352). In Grimnitz, Joachim II met the beautiful wife of the gun and bell foundry master, who was therefore known as the "beautiful foundrywoman" (Die Schöne Gießerin), Anna Dieterich née Sydow, and made her his mistress. Her husband, Michael Dieterich, who died in 1561, was the last manager of the electoral foundry in Grimnitz. Anna Sydow lived for many years in the Grunewald hunting lodge, which Joachim built in 1542-1543, and bore him two children. The affair with her allegedly started after the accident, although there is no clear evidence for this, so they could meet much earlier. Very little is known about Hedwig's life. As a Polish-Lithuanian, woman and Catholic she was not highly esteemed in Brandenburg's historiography. She accompanied her husband to the Imperial Diets - in 1541 in Regensburg, and in 1547 in Augsburg. She corresponded with her half-sister Isabella, Queen of Hungary and her half-brother Sigismund Augustus. In a letter dated Warsaw, September 17, 1571 (today at the Wawel Royal Castle), written in ink with particles of gold, Sigismund Augustus called her the "Infanta of the Kingdom of Poland, Marchioness of Brandenburg" (Illvstrissimæ Principi dominæ Heduigi, Dei gratia Infanti Regni Poloniæ Marchionisæ Brandemburgensi ...). In her last known portrait she is very obese, little more than her husband, probably because of the difficulty in walking. It was created in 1562 by Italian painter Giovanni Battista Perini (Parine) as a counterpart to the portrait of Joachim II (Berlin City Museum, VII 60/642x), however, it is known from a later copy made in 1620 by Heinrich Bollandt (Berlin Palace, Berliner Schloss), which was lost during World War II. As for the brides of the 1545 double wedding, Sophie of Legnica died a few days after the birth of her son Joachim Frederick (1546-1608), his father's successor as Elector of Brandenburg. Barbara become the Duchess of Brzeg in 1547. She bore her husband seven children, five daughters ad two sons, and when George II died in 1586, after forty-one years of marriage, he left the Duchy of Brzeg to his wife as her dower with the full sovereignty over this land until her own death. George II's fascination with the Italianate court of the Jagiellons is reflected in the architecture of the "Silesian Wawel" - the Piast Castle in Brzeg. Arcaded courtyard of the castle was built between 1547 and 1560 by Giovanni Battista de Pario and his son Francesco, while the main gate was adorned with effigies of Silesian Piasts. Sculptors Andreas Walther and Jakob Warter created busts of George II's ancestors and the coat of arms of the Kingdom of Poland that crown the gate - although George II was a vassal of the Habsburgs, he opposed their absolutist policy in Silesia. They also carved the full-length effigies of the Duke and his wife above the portal (1551-1553). The tapestries that George and Barbara commissioned between 1567 and 1586 resemble the famous Jagiellonian tapestries (Wawel Arrases) and indicate that in the field of arts and patronage almost everything in Brzeg was like in Kraków. In the Grunewald hunting lodge in Berlin there is a large painting by workshop Lucas Cranach the Elder or Lucas Cranach the Younger, depicting the Judgment of Paris (oil on panel, 209.5 x 107.2 cm, GK I 1185). It is similar to allegorical portraits of Dukes of Legnica-Brzeg, Ziębice-Oleśnica and Lubin in the scene of the Judgement of Paris from the 1520s, identified by me, however, it was created much later - dated variably between 1540-1545. The painting is one of four panels, which belonged to Elector Joachim II and were in 1793 in the Berlin Palace. The woman in the center of the composition is the goddess Venus, the most beautiful of the goddesses that Paris will judge. She looks at the viewer. This is undoubtedly a "disguised portrait" of a woman, who, most likely, commissioned this painting. She knows perfectly well who will win this contest, however, she puts her hand on the armour of a man portrayed as Paris as if to say stop, you should follow your heart and choose someone else. The old man behind her represents Mercury, a messenger of the gods. He raises his staff with which he strikes Paris on the chest, warning him of female seduction with a loud cry and urging him to make a careful decision. Cupid, god of affection and desire, points his arrow at the young woman near Mercury. Venus in this painting has the features of Electress Hedwig Jagiellon, as in the painting by Hans Krell in the same collection or in many paintings by Lucas Cranach the Elder and his workshop. Consequently Mercury is Duke Frederick II of Legnica-Brzeg, who in earlier painings was depicted as Paris, the second goddess is his daughter Sophie of Legnica and Paris is her husband John George of Brandenburg - his features match his effigy by Lucas Cranach the Younger in Dresden (Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister, inventory number 1949). The third goddess is Barbara of Brandenburg, John George's sister and future Duchess of Brzeg. This painting is therefore a commemoration of the double marriage and alliance with the Piasts of Silesia. Similar Judgement of Paris by follower of Lucas Cranach the Elder was also in Berlin (oil on panel, 50.5 x 34 cm, private collection before 2009), however, only Hedwig is identifiable on the right. Other people are different. Paris looks at Venus-Hedwig and another woman holds her hand on his arm and points to his heart, while Cupid points his arrow to her heart. So this is most likely Hedwig's husband Elector Joachim II and his new mistress and the painting was commissioned to sanction this new relationship. The third woman in the scene is most likely Sophie of Legnica, as a very similar effigy can be seen in another large panel from the mentioned series from the Berlin Palace. She is holding the shoes of Bathsheba in the scene of Bathsheba at the bath (oil on panel, 208 x 106 cm, GK I 1186), similar to the painting by Cranach from 1526, most likely from Hedwig's dowry, depicting her father Sigismund I, his wife Bona and mistress Katarzyna Telniczanka in the same scene (Gemäldegalerie in Berlin). Bathsheba could be therefore a portrait of Joachim's mistress - Anna Sydow, while he was portrayed as the biblical King David. Barbara of Brandenburg was also depicted in other painting by Cranach. Lucretia from the collection of Hans Grisebach in Berlin, attributed to Lucas Cranach the Elder or his son Cranach the Younger, has her features, similar to the painting from the Berlin Palace and her statue from the Brzeg Castle. It was inspired by the iconic image of Bona Sforza, Queen of Poland created a decade earlier, which was praised by Andrzej Krzycki (1482-1537), Archbishop of Gniezno in his epigram "On Lucretia depicted more lasciviously" (In Lucretiam lascivius depictam). Also in the field of portraiture, the dukes of Legnica-Brzeg inspired strongly by the Polish royal court. Protestantism opposed such "lasciviousness", so most likely in the second half of the 16th century, as the style indicates, she was dressed. This overpaint (dress) was removed after 1974.
Judgment of Paris with portraits of Hedwig Jagiellon (1513-1573), Sophie of Legnica (1525-1546), Barbara of Brandenburg (1527-1595), Frederick II of Legnica-Brzeg (1480-1547) and John George of Brandenburg (1525-1598) by workshop Lucas Cranach the Elder or Lucas Cranach the Younger, ca. 1545, Grunewald hunting lodge.
Judgment of Paris with portraits of Hedwig Jagiellon (1513-1573) and members of her family by follower of Lucas Cranach the Elder, ca. 1545-1550, Private collection.
Bathsheba at the bath with portraits of Sophie of Legnica (1525-1546), Joachim II Hector (1505-1571) and, most probably, Anna Sydow by workshop Lucas Cranach the Elder or Lucas Cranach the Younger, ca. 1545-1550, Grunewald hunting lodge.
Portrait of Barbara of Brandenburg (1527-1595), Duchess of Brzeg as Lucretia by workshop Lucas Cranach the Elder or Lucas Cranach the Younger, ca. 1545-1550, Private collection.
Portrait of Electress Hedwig Jagiellon (1513-1573) by Heinrich Bollandt after Giovanni Battista Perini, 1620 after original from 1562, Berlin Palace, lost during World War II. Virtual reconstruction, © Marcin Latka
Portrait of Stanisław Orzechowski by Giovanni Cariani
"My homeland is Ruthenia, located on the Tyras River, which the inhabitants of the coastal area call the Dniester, at the foot of the Carpathian Mountains, the range of which separates Sarmatia from Hungary", begins his autobiography Stanisław Orzechowski or Stanislaus Orichovius (1513-1566), a nobleman of Oksza coat of arms. He wrote these words in 1564 at the request of Giovanni Francesco Commendone (1523-1584), Venetian bishop and papal legate to Poland (letter of December 10, 1564 from Radymno). In a letter of August 15, 1549 from Przemyśl (Datae Premisliae, oppido Russiae, die Assumptionis beatae Virginis, anno Christi Dei nostri 1549) to Paolo Ramusio (Paulus Rhamnusius), secretary of the Council of Ten in Venice, he adds that "my country, harsh and uncouth, which has always worshiped Mars, but has only recently begun to worship Minerva. For Ruthenia previously did not differ much in lineage and customs from the Scythians with whom it borders, however, having relations with the Greeks, from whom it adopted the confession and faith, it abandoned its Scythian harshness and savagery, and now it is gentle, calm and fertile, it is very fond of Latin and Greek literature" (after "Orichoviana ..." by Józef Korzeniowski, Volume 1, pp. 281, 587).
Educated at the universities of Kraków (1526), Vienna (1527), Wittenberg (1529), Padua (1532), Bologna (1540) and continuing his studies in Rome and Venice, Orzechowski was a typical representative of Polish-Lithuanian diversity. He was born on November 11, 1513, in Przemyśl or nearby Orzechowce. Stanisław was very proud of his Ruthenian origins and described himself as gente Roxolani, natione vero Poloni (of Ruthenian/Roxolanian origin, Polish nationality), however, he wrote mainly in Latin. On July 5, 1525, at the age of 12, he was ordained a Catholic priest and became a canon of Przemyśl. In 1543, shortly after return to Poland, he was excommunicated by Bishop Stanisław Tarło for having many incompatible benefices and for his absence at the diocesan synod. A few years later, in 1547, the new bishop of Przemyśl, Jan Dziaduski, accused Orzechowski, who had offspring with his concubine Anna Zaparcianka (Anuchna z Brzozowa), of maintaining a scandalous life. In 1550 Stanisław arranged a wedding for a Catholic priest Marcin Krowicki and Magdalena Pobiedzińska in Urzejowice. A year later, in 1551, he himself married in Lścin with a 16-year-old noblewoman, Magdalena Chełmska, for which Bishop Dziaduski excommunicated Orzechowski. He corresponded frequently with King Sigismund Augusus, Nicolaus "the Black" Radziwill, Jan Amor Tarnowski and his son Jan Krzysztof, Piotr Kmita, Jakub Uchański and wrote letters to Cardinal Alessandro Farnese (letters dated May 1, 1549 and January 15, 1566 from Przemyśl), Pope Julius III (letter dated May 11, 1551 from Przemyśl) and King Ferdinand (letter dated September 7, 1553 from Kraków). Orzechowski's speech at the funeral of King Sigismund I was published in Kraków in 1548 (Funebris oratio: habita a Stanislao Orichovio ...) and then in the same year in Venice with coat of arms of Queen Bona Sforza on the title page (Stanilai Orichouii Rhuteni Ornata et copiosa oratio ...), printed by Paolo Ramusio and republished in 1559 also in Venice, in the collection Orationes clarorum virorum. In a letter from Venice of 1548, Ramusio asked Orzechowski to send him his other works through Bona's secretary, Vitto Paschalis (Reverendi Domini Vitti Paschalis Serenissimae Reginae Bonae a secretis). No effigy of Orzechowski made during his lifetime is known. The portrait published in Starożytności Galicyjskie in Lviv in 1840 (lithography by Teofil Żychowicz) depicts a man in mid-17th century costume, thus almost a century after his death (1566). In 2022 a portrait of a bearded man holding his right hand on a helmet and left hand on a sword, attributed to circle of Titian, was sold in Paris (oil on canvas, 94 x 75 cm, Hotel Drouot, June 17, 2022, lot 18). The painting comes from the collection of Achille Chiesa in Milan (sold at American Art Galleries in New York, 22-23 November 1927, lot 117, as Portrait of a Warrior) and already in 1927 it was not in a very good state of preservation. At the top right-hand corner is the name of the personage the portrait represents, but unfortunately no longer legible. His face was slightly altered during the restoration, however, the style of the portrait, particularly the way the hands were painted, allows the painting to be attributed to Giovanni Cariani (d. 1547), also known as Giovanni Busi or Il Cariani, active in Venice and Bergamo near Milan. According to the Latin dates visible on some old reproductions, the man was 32 years old in 1545 (ÆTAT SVÆ ANNO / XXXII / MD.XLV), exactly like Stanisław Orzechowski, who a year earlier, in 1544, published in Kraków his two important works - the "Baptism of the Ruthenians. Bull on not rebaptizing Ruthenians" (Baptismus Ruthenorum. Bulla de non rebaptisandis Ruthenis) and Ad Sigismundum Poloniae Regem Turcica Secunda calling for solidarity from Christian Europe against the Ottoman Empire. In 1545, Orzechowski was accused of beating to death a subject of bishop Dziaduski from Przysieczna and the nobleman in the painting has a pose as if ready to defend himself by any means. His helmet, although generally resembling some Renaissance burgonets, is very unusual, and the closest analogy can be found with the helmets discovered in Scythian burial mounds (compare "The Scythians 700–300 BC" by E.V. Cernenko). The man holds it because it was probably found near his place of origin, it is therefore a precious memento of the ancient inhabitants of this land and an important symbol.
Portrait of Stanisław Orzechowski (1513-1566), aged 32 by Giovanni Cariani, 1545, Private collection.
Portrait of Stanisław Karnkowski by Jacopo Tintoretto
Stanisław Karnkowski of Junosza coat of arms was born on May 10, 1520 in Karnkowo near Włocławek, as a son of Tadeusz vel Dadźbog, heir of Karnków and Elżbieta Olszewska from Kanigów. As a young man, he left his family home and went to his uncle, the bishop of Włocławek, Jan Karnkowski (1472-1537). It was him who owes Karnkowski his early education.
In 1539 he began studies at the Kraków Academy. After graduating, in 1545, he went to Italy for further education - first to Perugia, and then to Padua, where he completed his studies with a doctorate utriusque iuris. He also studied in Wittenberg, where he became acquainted with the teachings of Luther. After returning from studies in 1550, he became the secretary of the bishop of Chełmno and then of Jan Drohojowski, bishop of Włocławek. In 1555 he became the secretary of King Sigismund Augustus, from 1558 he was the Grand Referendary of the Crown and in 1563 he became the Grand Secretary, and later Bishop of Kuyavia from 1567, Archbishop of Gniezno and Primate of Poland from 1581. He served as regent of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth (Interrex) in 1586-1587, after death of king Stephen Bathory. Karnkowski amassed one of the wealthiest Polish libraries in the late 16th and early 17th century, comprising according to some estimates 322 books, some of which he acquired during his studies abroad, like Consilia Ludouici Romani by Lodovico Pontano, published in 1545 (Archdiocese Archives in Gniezno). The portrait of young man in a black costume buttoned to a high collar and holding his right forearm on a column-base, was first recorded in the Great Cabinet at Kensington Palace in 1720 as Titian. It is now thought to be Tintoretto's earliest dated work. According to inscription in Latin on a column-base the man was 25 years old in 1545 (AN XXV / 1545), exactly as Stanisław Karnkowski, when he began his studies in Italy. He resemble greatly Karnkowski from his portrait when bishop of Włocławek, created between 1567-1570 by unknown painter (Higher Seminary in Włocławek), and as Primate of Poland in green cassock (Archbishop's Palace in Gniezno), painted in 1600 by Monogrammist I.S. In private collection in Switzerland, there is reduced copy of this effigy also attributed to Jacopo Tintoretto.
Portrait of Stanisław Karnkowski (1520-1603), aged 25 by Jacopo Tintoretto, 1545, Kensington Palace.
Portrait of Stanisław Karnkowski (1520-1603), aged 25 by Jacopo Tintoretto, ca. 1545, Private collection.
Portraits of Stanisław Spytek Tarnowski by Tintoretto
"Stanislaus Count of Tarnów, a man of the most perfect gifts of mind, body and fortune, born in the first noble family, having traveled through Hungary, Moesia, Macedonia, Greece, Syria, Judea, Arabia, Egypt, Italy, and Germany as a youth, and having received the insignia of the holy service from the Pontiff and the Emperor and the excellent honors from Christian and Turkish princes, he returned home and he was decorated with the highest honors by King Sigismund" (Stanislao Comiti a Tarnow viri animi corporis et fortunae dotibus absolutissimo, qui primaria ortus familia, adolescens Hungaria, Moesia, Macedonia, Graecia, Syria, Judaea, Arabia, Aegypto, Italia, Germania peragratis, ac utriusque sanctae militiae insignis a Pontifice et Imperatore acceptis praeclarisque honorariis Principibus tam Christianis quam Turcicis onustus domum rediens, a rego Sigismundo summis honoribus est exornatus) is a fragment of a Latin inscription, which was in the upper part of the tomb monument of Stanisław Spytek Tarnowski (1514-1568), voivode of Sandomierz in the church in Chroberz between Kraków and Kielce.
This magnificent monument, considered one of the best in Poland, was founded in 1569 by Stanisław's wife, Barbara Drzewicka (Barbara de Drzewicza), niece of primate Maciej Drzewicki (1467-1535). The inscription in lower part commemorates the foundation and informs that Stanisław lived 53 years and nearly seven months and died in the castle in Krzeszów nad Sanem on April 6, 1568, third hour of the following night (Vixit annos LIII menses fere septem obyt in arce Krzessow [...] MDLXVIII sexta aprilis hora tertia noctis seqventis). The deceased was portrayed in the fashionable "Sansovino pose", sleeping above the sarcophagus in richly decorated renaissance armour. Behind the figure of the voivode, the center of the arcade is filled with a cartouche with his coats of arms including the cross of the Knights of the Holy Sepulchre and the attributes of Saint Catherine of Alexandria, commemorating his pilgrimage to the Holy Land and Saint Catherine's Monastery on Mount Sinai. On both sides of the arcade there are panoplies (armours, breatplates, helmets, pistols, lances, kettledrums), and above them niches with sculptures of St. Michael the Archangel and Samson tearing the lion's mouth. The latter statue is the most unusual among many sculptures in this monument and it is also identified with Benaiah, son of Jehoiada, captain of King David's guard, who supported Solomon and became commander of his army (after "Nagrobki w Chrobrzu ..." by Witold Kieszkowski, p. 123). His Roman costume with anatomical armour (lorica musculata) of a centurion, also make him close to Hercules slaying the Nemean lion. The monument is attributed to the most eminent sculptor of the Polish Renaissance - Jan Michałowicz of Urzędów or his workshop. Stanisław was a son of Jan Spytek Tarnowski and Barbara Szydłowiecka, niece of Krzysztof, Great Chancellor of the Crown. In the 1530s, perhaps together with his father, he undertook a pilgrimage to the Holy Land. In 1537, he was appointed the Sword-bearer of the Crown, starost of Sieradz and the castellan of Zawichost in 1547. He became the Great Treasurer of the Crown in 1555 and in 1561 voivode of Sandomierz. Before 1538 he married Barbara and they have seven children - six daughters and one son. Around 1552, he bought Chroberz and Kozubów for 70,000 florins from the Tęczyński family and founded the church in Chroberz. The rich medieval castles of Chroberz and Krzeszów, which he undoubtedly rebuilt in Renaissance style, like all similar magnates of the time, were both destroyed. In 2017, during the 7th Beijing International Art Biennale at the National Art Museum of China, a "Commander in ancient armour" by Jacopo Tintoretto (oil on canvas, 220 x 120 cm) from a private collection was exhibited. Earlier, in 2015, it was also part of the "Images of a Genius. The Face of Leonardo" exhibition at Huashan Creative Park in Taipei, Taiwan. At that time the arrangement of his left foot was modified by the restorers. The man wears rich Roman-style armour, the heroic anatomical cuirass, designed to mimic an idealized male human physique, and caligae sandals. His golden cassis helmet is decorated with rich reliefs. His sword however is not a typical gladius of a Roman soldier, it is more of an oriental saber, so he is more of an Eastern warrior, like the Sarmatians, the legendary invaders of Slavic lands in antiquity and the alleged ancestors of nobles of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. This portrait is dated 1545 in the catalogues and according to the Latin inscription the model was 31 years old when it was painted (ÆTATIS SVÆ / AÑ XXXI), exactly like Stanisław Spytek Tarnowski, who according to some sources was born in October 1514 (after "Hetman Jan Tarnowski ..." by Włodzimierz Dworzaczek, p. 375). As a pilgrim to the Holy Land, like many other pilgrims from Poland-Lithuania, he undoubtedly embarked on a ship in Venice. It is possible that he visited the city in 1545, but it is more likely that he commissioned his portrait in the Republic of Venice based on study drawings sent from Poland. The same man was also depicted in another portrait by Tintoretto, bust-length, in a black coat lined with fur (oil on canvas, 50.2 x 35 cm). It was sold in 2002 (Christie's New York, January 25, 2002, lot 27) and comes from the collection of Prince Adam Jerzy Czartoryski (1770-1861) in Paris. The collections of the Czartoryski family, dispersed after the insurrection of 1830, were secretly taken to Paris, where Adam's wife, Zofia Anna Sapieha, purchased the Hôtel Lambert in 1843. He also figures in another portrait by Tintoretto, now in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna (oil on canvas, 73 x 65 cm, GG 11). This painting is dated around 1547/1548 and is identifiable in the Imperial collection in Vienna in 1816. After the Partitions of Poland (1772-1795), when Vienna became the new capital for nobles in southern Poland, many moved their art collections there. It is also possible that the portrait was sent to Vienna already in the 16th century - in 1547 Stanisław Spytek become the castellan of Zawichost near Sandomierz and his relative, Jan Amor Tarnowski (1488-1561), obtained from the emperor the title of count related to the possession in southern Poland. Despite huge losses to Polish art collections due to wars, invasions and the subsequent impoverishment of the country, some works by Venetian painters, including Tintoretto, survived destruction, confiscations and evacuations. One such painting is Narcissus by Tintoretto from around 1560, acquired in 2017 by the National Museum in Wrocław from a private collector. In the 19th century it was a property of Otto Hausner (1827-1890) in Lviv. Although the Galician art collector could acquire this painting during his travels in Western Europe and especially in Italy, he more likely bought it in Poland or Ukraine. Lviv, capital of the Ruthenian Voivodeship, was an important economic center of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, with significant Italian influences and community, and wealthy nobles and patricians frequently commissioned and purchased such paintings from abroad. When it comes to portraiture, secular art and European Old Masters, many art historians want to see pre-19th century Poland as an artistic desert, but surviving inventories and other documents from the 16th, 17th and 18th centuries prove that this was not the case.
Portrait of Stanisław Spytek Tarnowski (1514-1568), aged 31, in ancient armour by Tintoretto, 1545, Private collection.
Portrait of Stanisław Spytek Tarnowski (1514-1568) from the Czartoryski collection by Tintoretto, ca. 1545, Private collection.
Portrait of Stanisław Spytek Tarnowski (1514-1568) by Tintoretto, 1547/1548, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Narcissus from Hausner collection in Lviv by Tintoretto, ca. 1560, National Museum in Wrocław.
Portraits of Erazm Kretkowski by Lucas Cranach the Younger and Giovanni Cariani
"Here lies Kretkowski, where fate has led you, When you explored all the lands and all the seas around you, Without tiring your limbs with toil, You traversed the swift Ganges and the icy waves of Borysthenes [Dniester River], The Tagus and the Rhine, the two-armed Istria And the seven twin gates of the Nile. Now you will see the great Olympus And the ethereal houses, where, mingled with the gods, you laugh At the cares and hopes and lamentations of men" (HIC TE CRETCOVI MORS ET TVA FATA MANEBANT / CVM TERRAS OMNES ET CVM MARIA OMNIA CIRCVM / LVSTRARES NVLLO DEFESSVS MEMBRA LABORE / TE RAPIDVS GANGES GELIDÆQ. BORISTENSIS VNDÆ / TE TAGVS ET RHÆNVS TE RIPA BINOMINIS ISTRI / ET SEPTAGEMINI NOVERVNT OSTIA NILI / NVNC CONCESSISTI MAGNVM VISVRVS OLYMPVM / ÆTHEREASQ. DOMOS VBI DIIS IMMISTVS INANES / ET CVRAS ET SPES HOMINVM LAMENTAQ. RIDES.), reads the so-called Epitaphium Cretcovii in the Basilica of St. Anthony in Padua - Latin epitaph written by poet Jan Kochanowski and dedicated to Erazm Kretkowski (1508-1558). It is one of the first known poetic texts of the poet who, in the spring of 1558, traveled for the third time to Italy.
Kretkowski, castellan of Gniezno, died in Padua in the Republic of Venice on May 16, 1558 at the age of 50, according to the first part of the inscription on his epitaph (ANN. ÆTAT. SVÆ QVINQVAG. OBIIT PATAV. DIE MAII XVI M D L VIII), at the beginning of another longer journey. His beautiful epitaph with bronze bust was probably made by Francesco Segala (ca. 1535-1592), a sculptor active in Venice and Padua, who served the court of Guglielmo Gonzaga in Mantua, or Agostino Zoppo (d. 1572), active in Padua and Venice. It was created before 1560 and probably founded by his cousin, Jerzy Rokitnicki. His bust depicts a relatively young man, around 30 or 40 years old, so it was based on an earlier effigy, miniature, drawing, portrait or less likely a statue also by a Venetian artist, for in 1538, at the age 30 years old, Kretkowski was a Polish-Lithuanian envoy to the Ottoman Empire and he undoubtedly visited Venice. In 1538 he also became castellan of Brześć Kujawski and his hairstyle is typical of the late 1530s - e.g. portrait of a young groom from the Rava family by Lucas Cranach the Elder, dated '1539' (Museu de Arte de São Paulo). Besides being a traveler and an explorer, as mentioned in his epitaph, Erazm, son of Mikołaj Kretkowski, voivode of Inowrocław, and Anna Pampowska, daughter of Ambroży, voivode of Sieradz, was like his father a courtier at the royal court of Sigismund I and Bona Sforza. In 1534 he was engaged to Queen Bona's lady-in-waiting, Zuzanna Myszkowska, daughter of Marcin, castellan of Wieluń. However, the prenuptial agreement was broken by the bride's parents and Kretkowski remained unmarried until the end of his life. Thanks to the support of Queen Bona, Kretkowski received lucrative offices and dignities from the king. In 1545 he was nominated for the voivode of Brześć Kujawski, however, this nomination was annulled, and from 1546 he was the starost of Pyzdry. He was the superior of Greater Poland customs (1547) and from 1551 he held the office of castellan of Gniezno. Soon, however, Kretkowski found himself in opposition to Queen Bona, because with a group of magnates he supported the marriage of the young king Sigismund Augustus with his mistress Barbara Radziwill (after "Pomnik Erazma Kretkowskiego ..." by Jerzy Kowalczyk, p. 56). In 1551 he was one of the commissioners for the Congress of Głogów to meet the commissioners of King Ferdinand of Austria and in 1555, together with Jan Drohojowski, Bishop of Włocławek, he was sent to Henry V, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg, regarding his marriage to Princess Sophia Jagiellon. He therefore had good relations and connections in Germany. It is not known exactly when he visited India, Egypt or Istria in the Venetian Republic, however, he must have started his journey by boarding a ship in Venice. In the National Museum in Warsaw there is a portrait of a bearded man in a grey-black coat, attributed to Lucas Cranach the Younger (oil on panel, 64.5 x 49 cm, M.Ob.836). It comes from the collection of Carl Daniel Friedrich Bach (1756-1829), a German painter, draftsman and art teacher, who bequeathed the painting to the Silesian Society for Patriotic Culture in Wrocław. After 1945 the painting was moved to Warsaw from the Nazi German Art Repository in Kamenz (Kamieniec Ząbkowicki) and earlier it was in the Silesian Museum of Fine Arts in Wrocław (inventory number 1284). It is not known where and how Bach acquired the painting, but from 1780 he was a painter in the service of Count Józef Maksymilian Ossoliński, a wealthy landowner, politician and historian, in Warsaw. In 1784 he accompanied Count Jan Potocki, an explorer, historian, novelist and diplomat, on his journey to the Netherlands, France and Italy and between 1786-1792, at Potocki's expense, he studied, initially in Rome and later in Portici. He stayed in Paris, Venice, Vienna and Berlin. According to the Latin inscription in the upper left corner of the painting, the man in the portrait was 38 years old in 1546, when the painting was created (1546 / ANNO ÆTATIS SVÆ. XXXVIII), exactly like Kretkowski when he became the starost of Pyzdry. He celebrated important events in his life with portraiture, as evidenced by the prototype of his bronze bust. However, in such a portrait for private use or for his family or close friends, he does not need to recall that he was a nobleman of the Dołęga coat of arms and starost of Pyzdry, as in the epitaph for the general public. The reminder of the date of creation and his age was sufficient. The man in the portrait closely resembles the features depicted in his bust. A study drawing to this or another portrait of the starost of Pyzdry is in the Museum of Fine Arts in Reims (distemper on paper, 36.5 x 24.7 cm, 795.1.276). It was acquired in 1752 by the City of Reims, together with a set of other study drawings by Cranach and his studio, including the effigy of Philip I, Duke of Pomerania from around 1541 (795.1.266). The man has the same expression on his lips, although his beard is shorter. The same man, with a longer beard and wearing a black cap was depicted in another painting, which was sold in 2012 in Boston (oil on canvas, 75.5 x 63.5 cm, sold at Bonhams Skinner, May 18, 2012, lot 202), as by Italian school. The painting was purchased from Harris & Holt Antiques, West Yorkshire in England and was previously attributed to Titian or his circle. The style of the painting is closest to that of Giovanni Busi il Cariani, who died in Venice in 1547. The man wears a similar grey-black coat, as in painting by Cranach, but in this version it is lined with expensive fur. Although it is likely that Kretkowski visited both workshops, in Wittenberg and Venice, it is more likely that, like Queen Bona, he was painted by a member of the workshop sent to Poland to prepare study drawings.
Preparatory drawing for a portrait of Erazm Kretkowski (1508-1558), starost of Pyzdry by Lucas Cranach the Younger or workshop, ca. 1546, Museum of Fine Arts in Reims.
Portrait of Erazm Kretkowski (1508-1558), starost of Pyzdry, aged 38 by Lucas Cranach the Younger, 1546, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Erazm Kretkowski (1508-1558), starost of Pyzdry by Giovanni Cariani, ca. 1546, Private collection.
Portrait of Barbara Radziwill in a blue dress, known as La Bella by Titian
In May 1543 22-year-old king Sigismund Augustus married his 16-year-old cousin Elizabeth of Austria. During the entry into Kraków for her coronation, the lords and knights of the Kingdom were dressed in all sorts of costumes including Italian, French and Venetian. The young Queen died just two years later failing to produce an heir to the throne. Sigismund Augustus commissioned for her a magnificent marble tomb monument from Paduan sculptor trainded in Venice, Giovanni Maria Mosca called Padovano. The king was hoping that his mistress, Barbara Radziwill, whom he intended to marry, would give him a child.
Portrait of a lady in a blue dress by Titian, known as La Bella is very similar to effigies of Barbara Radziwill, especially her portrait in Washington. The gold buckles on her dress in the form of decorative bows, although painted less diligently, are almost identical. Her garments are epitome of the 16th century luxury - a dress of Venetian velvet dyed with costly indigo blue, embroidered with gold thread and lined with sables, of which Poland-Lithuania was one of the leading exporters at that time. She holds her thick gold chain and pointing at weasel pelt, a zibellino, also known as flea-fur or fur tippet, on her hand, a popular accessory for brides as a talisman for fertility. Contemporary bestiaries indicate that the female weasel conceived through the ear and gave birth through the mouth. "This 'miraculous' method of conception was thought to parallel the Annunciation of Christ, who was conceived when God's angel whispered into the ear of the Virgin Mary" (after "Sexy weasels in Renaissance art" by Chelsea Nichols). Inclusion of the zibellino represents the hope that the woman would be blessed with good fertility and bore many healthy children to her husband. This symbolism excludes the possibility that the portrait represents a Venetian courtesan ("woman wearing the blue dress"), secretly painted by Titian for Francesco Maria I della Rovere, Duke of Urbino, who was already married and had three daughters and two sons, in about 1535. As early as 1545 Pope Paul III wanted to marry his granddaughter Vittoria Farnese to widowed Sigismund Augustus, whom however wed in secret his mistress sometime between 1545 and 1547 (according to some sources they were married since 25 November 1545). Vittoria finally married on 29 June 1547, Guidobaldo II della Rovere, Duke of Urbino (son of Francesco Maria), who at this time was in the service of the Republic of Venice. It is highly probable that the Duke or Vittoria received a portrait of the royal mistress, which was later transferred to Florence. A copy of the portrait by Titan's workshop, most probably by Lambert Sustris, painted with cheaper pigments without highly expensive ultramarine, is a proof that as in case of portraits of Empress Isabella of Portugal the sitter was not in the painter's atelier and the portrait was one of a series. There were also mistakes and inadequacies, her gold buckles were repleaced with simple red ribbons. Comparison with portraits of Empress Isabella confirms that Titian loved proportions and classical beauty. Just by making the eyes slightly bigger and more visible and harmonizing their features, he achieved what his clients expected of him, to be beautiful in their portraits, close to the gods from their Greek and Roman statues, it was renaissance. The miniature by unknown miniaturist Krause, probably an amateur, from the late 18th or early 19th century in the Royal Castle in Warsaw, indicate that a version of the painting was also in Poland, possibly in the collection of king Stanislaus Augustus Poniatowski. From 1545 the young king Sigismund Augustus spared no money for his mistress. Jewish and Florentine merchants Abraham Czech, Symon Lippi and Kasper Gucci (or Guzzi) were delivering to the royal court enormous quantities of expensive fabrics and furs. Between 1544-1546, the young king emloyed many new jewelers at his court in Kraków and Vilnius, like Antonio Gatti from Venice, Vincenzo Palumbo (Vincentius Palumba), Bartolo Battista, Italian Christophorus, Giovanni Evangelista from Florence, Hannus (Hans) Gunthe, German Erazm Prettner and Hannus Czigan, Franciszek and Stanisław Merlicz, Stanisław Wojt - Gostyński, Marcin Sibenburg from Transilvania, etc. Not to mention Giovanni Jacopo Caraglio, who in about 1550 created a cameo with Barbara's divinely beautiful profile. In just one year, 1545, the king bought as many as 15 gold rings with precious stones from Vilnius and Kraków goldsmiths. In 1547 Girolamo Mazzola Bedoli, a painter from Lombardy, created a painting of Adoration of the Magi for the Certosa Sancta Maria Schola Dei in Parma, today in the Galleria nazionale di Parma (inventory number GN145). A man depicted as one of the Magi has a costume clearly inspired by the costume of a Polish-Lithuanian nobleman. His oriental sabre and colors - crimson and white, the national colors of Poland, also indicate that it is a man from Poland-Lithuania, most likely inspired by the increased presence of their envoys in artistic circles in Italy at that time. According to sources Barbara was a beauty, hence the title in Italian, La Bella, is fully deserved. "The composition of her body and face made her so beautiful that people out of jealousy disparaged her innocence", she was "gloriously wonderful, like a second Helen [Helen of Troy]" as was written in a panegyric, she had white alabaster skin, "sweet eyes, gentleness of speech, slowness of movements".
Portrait of Barbara Radziwill in a blue dress, known as La Bella by Titian, 1545-1547, Pitti Palace in Florence.
Portrait of Barbara Radziwill, known as La Bella by workshop of Titian, most probably by Lambert Sustris, 1545-1547, Private collection.
Portrait of Barbara Radziwill in French costume
On 15 June 1545 died Elizabeth of Austria, first wife of Sigismund II Augustus, who continued his affair with his mistress Barbara Radziwill, whom he met in 1543. Already in September 1546 rumors were circulating in Kraków that Sigismund was going to marry "a private woman of the worst opinion". To prevent this and to strengthen the pro-Turkish alliance (the eldest daughter of Bona, Isabella Jagiellon, was established by Sultan Suleiman as a regent of Hungary on behalf of her infant son), it was decided to marry Sigismund to Anna d'Este (1531-1607), daughter of the Duke of Ferrara and related to the French ruling house.
The miniature of a lady in Italian costume, said to be Bona Sforza d'Aragona from the 1540s, which was in the Czartoryski collection, cannot depict Bona as the woman is much younger and features are different, it is very similar though to effigies of Barbara Radziwill. The features of this lady, on the other hand, are very similar to these visible in a portrait of a lady holding a chalice and a book in the National Museum in Warsaw, once in the collection of art dealer Victor Modrzewski in Amsterdam, therefore most probably originating from some magnate collection in Poland. The latter painting is attributed to circle of Master of the Female Half-Lengths, a Flemish or French court master painter who frequently depicted ladies in guise of their patron saints and who also worked for other European courts (e.g. portrait of Isabella of Portugal in Lisbon). The woman is dressed according to French fashion, very similar to the outfit in the portrait of Catherine de' Medici, Queen of France from about 1547 in the Uffizi (Inv. 1890: inv. 2448). She is holding a prayer book and a chalice, an attribute of Saint Barbara, who was considered to provide protection against sudden and violent death (the scene on the chalice shows a man killing other man) and patron saint of pregnant women (together with Saint Margaret of Antioch). Both paintings are most probably workshop copies from a larger commission of state portraits, but the resemblance is still visible.
Portrait of Barbara Radziwill in French costume by circle of Master of the Female Half-Lengths, ca. 1546-1547, National Museum in Warsaw.
Miniature of Barbara Radziwill by circle of Jan van Calcar, ca. 1546-1547, Czartoryski Museum (?), published in Aleksander Przeździecki's "Jagiellonki polskie" (1868).
Miniature of Bona Sforza d'Aragona by Jan van Calcar, ca. 1546, Uffizi Gallery in Florence.
Portrait of Thomas Howard, Duke of Norfolk by Giovanni Cariani or Bernardino Licinio
In February 1546 arrived to London the envoy of Poland-Lithuania Stanisław Lasota (Stanislaus Lassota) of Rawicz coat of arms (ca. 1515-1561), courtier of Queen Bona Sforza (aulicus Bonae Reginae), valet, diplomatic agent and royal secretary. He presented Henry VIII with enticing proposals of cooperation with Poland and assured the English monarch that Poland did not intend to stop supplying grain to England which at that time was at war with France, and needed a constant supply of grain to the country and to the front.
Lasota, trusted by the royals, was used for discreet missions. He also presented a project (without an official authorization) of marrying Sigismund Augustus to Princess Mary Tudor (1516-1558). Henry VIII rewarded Lasota with a golden chain and appointed him a golden knight (eques auratus) in front of the entire court. There is even a document in the files of the Privy Council, which shows that the Council paid on "Aprilis 1546. To Cornelys, the goldsmith, for makeng a coler of esses for the gentilman of Polonia". Lasota set out from Vilnius in 1545 and before he reached England, he also went to Vienna, Munich and Spain. In March 1546 Stanisław leaves London and arrives in Paris, where, in turn, he proposes the marriage of Sigismund Augustus with Princess Margaret of Valois (1523-1574), daughter of King Francis I. A year later Lasota went to England again with an official embassy (after "Polska w oczach Anglików XIV-XVI w." by Henryk Zins, p. 70-71). Precious gifts were part of diplomacy at that time and Lasota undoubtedly also brought many valuable gifts. In 1546 Sigismund I offered Ercole II d'Este, Duke of Ferrara a gold chain worth 150 Hungarian gold florins. His wife Queen Bona, like her son later, had a special affinity for jewelery. In 1543 she gave her son 40 silver cups, many gold chains and other valuables. Exquisite jewels were ordered by the queen or for her from the best goldsmiths in Poland-Lithuania and abroad. At the beginning of 1526 a gold chain was ordered in Nuremberg for Bona and in 1546 Seweryn Boner paid 300 florins to Nuremberg goldsmith Nicolaus Nonarth for making necklaces for her daughters. Pearls were bought for huge sums in Venice and in Gdańsk and ready-made gems were purchased in Nuremberg and Turkey (after "Klejnoty w Polsce ..." by Ewa Letkiewicz, p. 57). In 1545 the court embroiderer Sebald Linck received Venetian gold and some other type of gold, which in the bills is described as aurum panniculare, to adorn the ceremonial robe of Sigismund I. In 1554 envoy of the Queen purchased in Antwerp "goldsmith's work to the amount of 6,000, to give to the Queen of England", as reported Venetian ambassador to the Imperial Court Marc'Antonio Damula and two years later Pietro Vanni (often Anglicised as Peter Vannes), Latin secretary to King Henry VIII, describing Bona's departure from Poland and her stay in Venice, wrote that "she has conveyed out of the country, by divers secret ways, an infinite quantity of treasure and jewels" (to the Council, March 7, 1556, in Venice). Portrait paintings were also an integral part of diplomacy. The rulers exchanged their likenesses, portraits of potential brides, family members, important personalities and famous people. In June 1529 a portrait of Duke of Mantua, Federico II Gonzaga (1500-1540), was brought to Bona by his emissary and in 1530 a diplomat in service of Sigismund and Bona Jan Dantyszek sent to Krzysztof Szydłowiecki, Great Chancellor of the Crown, the portrait of the Spanish conquistador Hernán Cortés. In Warsaw preserved one of the best portraits of Henry VIII by circle of Hans Holbein the Younger, most probably painted by Lucas Horenbout (National Museum in Warsaw, oil on oak wood, 106 x 79 cm, inventory number 128165). The portrait is a version of king's effigy created by Holbein the Younger in 1537 as part of a mural in the Whitehall Palace. It was earlier in the collection of Jakub Ksawery Aleksander Potocki (1863-1934) and Leon Sapieha (inscription verso: L. Sapieha) and in 1831 "Henry VIII of England by Holbeyn on wood in a gilded frame" is mentioned in a register of paintings of Ludwik Michał Pac by Antoni Blank (February 1, 1831, Ossolineum, Wrocław). Another catalogue by Blank, of the Radziwill collection in Nieborów near Łódź, published in 1835, lists five paintings by Holbein (items 426, 427, 458, 503, 505). The portrait of Gdańsk merchant Georg Gisze (1497-1562), knighted by the Polish King Sigismund I in 1519, was created by Hans Holbein the Younger in 1532 in London to be sent to his brother Tiedemann Giese, secretary to the King of Poland (today in the Gemäldegalerie in Berlin). In the private collection in Hamburg, Germany, there is a portrait of a wealthy nobleman. His facial features and costume are strikingly similar to these in the effigies of Thomas Howard (1473-1554), Third Duke of Norfolk, Earl Marshal and Lord High Treasurer, uncle of two of the wives of King Henry VIII, Anne Boleyn and Catherine Howard, and one of the most powerful nobles in the country. Hans Holbein the Younger and his workshop created a series of portraits of the Duke of Norfolk (Windsor Castle, Castle Howard and private collection) aged 66, therefore created at the peak of his power in 1539. Although favored by Henry VIII for most of his life, his position became unstable after the execution of his niece Catherine Howard in 1542 and again in 1546 when he and his son were arrested for treason (December 12). This leading Catholic politician under Henry VIII and Mary Tudor was described by Venetian ambassador Ludovico Falieri in 1531: "[he] has very great experience in political government, discusses the affairs of the world admirably, aspires to greater elevation, and bears ill-will to foreigners, especially to our Venetian nation. He is fifty-eight years old, small and spare in person". The mentioned portrait in Hamburg shows an older man in his 60s or 70s in a costume from the 1540s. The shape of his gold sleeve buckles is reminiscent of a Tudor rose and he holds his right hand on the closed helmet of his Italian/French-style armour. In June 1543, Howard declared war on France in the King's name during the Italian War of 1542-1546. He was appointed Lieutenant-General of the army and commanded the English troops during the unsuccessful siege of Montreuil. On 7 June 1546, the Treaty of Ardres was signed with France. Everything indicates that it is a portrait of Howard, except for gold chain around his neck. In all portraits by Holbein and workshop he wears the Order of the Garter, an important order of chivalry related to the English crown. If we would consider the portrait as effigy of the Duke of Norfolk, therefore this different chain was a part of diplomatic efforts of the commander, who complained about the inadequate supply of his army during the French campaign. So it's like a message to someone, 'I like your gift, we could be allies'. Another intriguing thing about this portrait is its author. The painting was created by Italian painter in the style close to Giovanni Cariani and Bernardino Licinio. Federico Zeri attributed the work in 1982 to Cariani, who died in Venice in 1547, or to 16th century school of Ferrara. In 1546 Queen Bona commissioned a series of paintings for the Kraków Cathedral in Venice and contacts with Ferrara were increased due planned marriage of Sigismund Augustus with Anna d'Este (the portrait of the bride was supposedly sent via Venice by Carlo Foresta, one of the agents of the Kraków merchant Gaspare Gucci). Concluding, the portrait in Hamburg was commissioned in Venice for or by the Polish-Lithuanian court, basing on a drawing or miniature sent from England. Despite their great wealth, the match with a distant, elective monarchy of Poland-Lithuania was not considered to be advantageous to the hereditary kings of England, especially when the war with France was over and they did not need an increased supply of grain and Sigismund Augustus decided to marry his mistress Barbara Radziwill.
Portrait of Georg Gisze (1497-1562), Gdańsk merchant by Hans Holbein the Younger, 1532, Gemäldegalerie in Berlin.
Portrait of Henry VIII of England by circle of Hans Holbein the Younger, most probably Lucas Horenbout, 1537-1546, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Thomas Howard (1473-1554), Third Duke of Norfolk by Giovanni Cariani or Bernardino Licinio, 1542-1546, Private collection.
Portrait of Catherine Willoughby, Duchess of Suffolk by workshop of Hans Holbein the Younger
It is said that Catherine Willoughby (1519-1580) was considered a candidate to marry Sigismund Augustus after the Polish ambassador failed to obtain the hand of Princess Mary Tudor in 1546, and between 1557 and 1559 she and her husband were "placed honourably in the earldom of the said king of Poland, in Sanogelia [Samogitia in Lithuania], called Crozen [Kražiai]" (after "Chronicles of the House of Willoughby de Eresby", p. 98). Catherine was a daughter and heiress of William Willoughby, 11th Baron Willoughby de Eresby, by his second wife, María de Salinas, maid-of-honour to Queen Catherine of Aragon. She and her second husband Richard Bertie (1516-1582) were of the Protestant faith and in 1555 they were forced to flee England due to the Catholic rule of Queen Mary I and only returned to England under the Protestant Queen Elizabeth I.
Her first husband was Charles Brandon, 1st Duke of Suffolk, whom she married on 7 September 1533, at th age of 14. They had two sons, both of whom died young in 1551 - Henry (b. 1535) and Charles (b. 1537). In the Metropolitan Museum of Art there is a portrait of a girl aged 17 (Latin: ANNO ETATIS·SVÆ XVII) by workshop of Hans Holbein the Younger, also identified as effigy of Catherine Howard, Queen of England from 1540 until 1542, hence dated to about 1540 (oil on panel, 28.3 x 23.2 cm, inventory number 49.7.30). The painting was at the beginning of the 19th century in the collection of Prince Józef Antoni Poniatowski (1763-1813), a nephew of king Stanislaus Augustus, who inherited many paintings from his collection and consequently also from historical royal collections. The main feature of her face is a chrchteristic upper lip, also visible in the picture of a painting before conservation when retouching were removed. A similar lip is seen in portraits identified as depicting children of Catherine Willoughby - Henry Brandon, 2nd Duke of Suffolk (1535-1551) by Hans Holbein the Younger (Royal Collection, RCIN 422294) and Susan Bertie (b. 1554) by unknown painter (Beaney House of Art and Knowledge). Her face and pose also resemble those seen in the portrait drawing of the Duchess of Suffolk by Hans Holbein the Younger, created between 1532-1543 (Windsor Castle, RCIN 912194). The resemblance of a woman from the picture to the later image of Catherine's daughter is surprising. A cameo brooch on her bust with two heads could be Castor and Pollux, the astronomical Gemini, interpreted by Renaissance mythographers in terms of shared immortality and the bond that unites two people even after death (after "Castor and Pollux", Cengage, Encyclopedia.com).
Portrait of Catherine Willoughby (1519-1580), Duchess of Suffolk, aged 17 by workshop of Hans Holbein the Younger, ca. 1536, Metropolitan Museum of Art.
Portrait of Zofia Firlejowa as Venus by workshop of Giovanni Cariani
In 1546 or at the beginning of 1547, Jan Firlej (1521-1574) of Lewart coat of arms, later Grand Marshal of the Crown, voivode of Kraków and the head of the Calvinist camp, married the incredibly wealthy Zofia Bonerówna, daughter of royal banker Seweryn Boner (1486-1549), receiving a huge dowry of 47,000 florins and the Boner property near Ogrodzieniec Castle. Jan was the eldest son of Piotr Firlej (d. 1553), voivode of Ruthenia from 1545 and a trusted adviser of Queen Bona Sforza and King Sigismund Augustus, and Katarzyna Tęczyńska. Concluded on the initiative of his father, who used the money from Jan's wife's dowry to pay off his debts, this marriage turned out to be very beneficial from the point of view of the family's interests.
Piotr was a patron of arts, he extended his Janowiec Castle and built a Renaissance palace in Lubartów. At his expense a beautiful tombstone was created in about 1553 by Giovanni Maria Mosca, called il Padovano in the Dominican church in Lublin. In his great estates in Dąbrowica, a village a mile from Lublin, he had a magnificent palace, whose stairs carved in marble were admired by poet Jan Kochanowski. Zofia's parents were also renowned patrons of arts. Bronze tomb sculpture of Seweryn and his wife Zofia née Bethman was created between 1532-1538 by Hans Vischer in Nuremberg and transported to Kraków. Between 1530-1547 Seweryn rebuilt and extended Ogrodzieniec Castle, transforming the medieval stronghold into a Renaissance castle - it was called "little Wawel". The Boners furnished it with beautiful furniture, tapestries and other most valuable items imported from abroad. In 1655, the castle was partially burnt down by the Swedish army, which was stationed there for almost two years, ruining a large part of the buildings. Similar to the royal court, many such items were also commissioned or acquired in Venice. In 1546 a Venetian Aloisio received a fur coat and several dozen thalers for the total amount of 78 zlotys 10 groszy for various instruments which he brought from Venice to Kraków on the king's order. As the Governor of the royal estates Zofia's father Seweryn, who kept the books of accounts for the court, brokered many such purchases. In 1553 two Jews from Kazimierz, Jonasz, the elder of the Kazimierz community, and Izak, the son of the second senior of this community and royal supplier Izrael Niger, took part in a trade mission sent by the king to Vienna and Venice to purchase goods for the royal court, receiving an advance payment of 840 Hungarian florins in gold. A few months later (April 11, 1553) Izak Izraelowicz Niger (Schwarz) was sent back to Venice in order to purchase wedding gifts for the third wife of Sigismund Augustus, Catherine of Austria, receiving 400 Hungarian florins in gold (after "Biuletyn Żydowskiego Instytutu Historycznego", Issues 153-160, p. 7). Inhabitants of the royal city of Kraków were connoisseurs of art and had important collections of paintings and portraits. In 1540 Katarzyna, widow of Paul Kaufman, a merchant of Kraków, residing in the convent of St. Andrew, left her portraits in her last will to the convent (Omes imagines suas dat, donat se defuncta, Conventui huic s. Andrere, ad Ecclesiam et etiam sororibus monialibus) and in 1542 in the list of paintings of the late Melchior Czyżowski, Vice-Procurator of the Kraków Castle (Viceprocuratori Castri Cracoviensis), there were two of his portraits (Duæ imagines Dni Melchioris C ...), a painting of Herodias (Tabula pieta, Herodiadis), possibly by workshop of Cranach, the woman taken in adultery (Figura de muliere deprehensa in adulterio), possibly by Venetian painter, the twelve labors of Hercules (Duodecem labores Herculis), a view of Venice (Cortena in qua depicta est Venetia), a painting of Judith and Herodias, painted on both sides (Tabula Judith et Herodiadis, ex utraque parte depicta), painting of Thisbe and another of Judith (Figura Thisbe, Fig. Judith), Nativity of Christ (Nativitatis Christi) and Mary Magdalene (Mariæ Magdalenæ), most likely by Venetian school, and other religious paintings. Over half a century later, in about 1607, other representative of the family, Hieronim Czyżowski, recorded in books of the Polish Nation 15 years earlier, in 1592, ordered a painting by the Venetian painter Pietro Malombra with his portrait as donor (Resurrection of Knight Piotrawin by Saint Stanislaus) for the altar of the Polish Nation in the Basilica of Saint Anthony in Padua. In the Scottish National Gallery there is a preparatory study for this painting (inventory number RSA 221), in which however the donor is not present in the composition, indicating that his portrait was added later, possibly based on a drawing sent from Poland. Bonerówna married Jan Firlej shortly before or after his return from diplomatic mission at the court of Ferdinand I of Austria and most likely to the court of Ferrara. She bore him two daughters Jadwiga and Zofia and four sons Mikołaj, Andrzej, Jan and Piotr. Zofia died in or after 1563 and Jan married secondly Zofia Dzikówna (died after 1566) and later Barbara Mniszech (died 1580). The couple probably had another daughter, Elżbieta, however, she died at the young age in 1580. Her tombstone behind the main altar of the church in Bejsce near Kraków was founded by her brother Mikołaj Firlej (d. 1600), voivode of Kraków, who has a magnificent burial chapel in the same church, modeled on the Sigismund Chapel. This monument to the Polish virgin, according to Latin inscription (ELIZABETHAE / IOAN(NIS) FIRLEII A DAMBROWICA PALAT(INI) ET CAPIT(ANEI) CRACOVIEN(SIS) / ATQVE MARSALCI REGNI F(ILIAE) / VIRGINI NATALIB(VS) ILLVSTRI. FORMA INSIGNI AETATE FLORE(N)TI / VITA PVDICISSIMAE [...] NICOL(AVS) FIRLEIVS A DAMBROWICA IO(ANNES) F(IRLEIVS) - CASTELL(ANVS) BIECEN(SIS) / SORORI INCOMPARABILI E DOLORIS ET AMORIS FRATERNI / MOERENS POS(VIT) / OBIIT AN(N)O D(OMI)NI : M.D.LXXX), is considered a rarity and attributed to workshop of Girolamo Canavesi. She was depicted sleeping, half-recumbent, in a pose reminiscent of the Birth of Venus, a Roman fresco from the House of Venus in Pompeii, created in the 1st century AD, or Venus from cassone with scenes of the Battle of Greeks and Amazons before the walls of Troy by workshop of Paolo Uccello, painted in about 1460 (Yale University Art Gallery, New Haven). Elżbieta's tombstone is crowned with coat of arms of the Firlejs - Lewart, a rampant leopard. In 2014 an unframed painting of recumbent Venus and Cupid by workshop of Giovanni Cariani (d. 1547) was sold in London (oil on canvas, 102 x 172.2 cm, Bonhams, 9 July 2014, lot 35). Cupid points his arrow at the heart of the lying woman, symbolizing love. In the right corner of the canvas, on the tree, there is a shield with coat of arms showing a rampant leopard on red background, very similar to the one visible in the monument to Elżbieta Firlejówna in Bejsce, as well as many other depictions of coat of arms of the Firlej family. In the background, there is a gothic cathedral, very similar to view of St. Stephen's Cathedral in the Panorama of Vienna (Vienna, Citta Capitale dell' Austria), created by Italian engraver in about 1618 (Wien Museum, inventory number 34786). The painting recall the erotic plaques from cupboard-cabinet by Peter Flötner or Wenzel Jamnitzer from the Zamoyski Estate in Warsaw (lost during World War II). The cabinet was adorned with 26 bronze plaques with nude lying female figures. It was most probably created in Augsburg or in Nuremberg and could come from a royal or a magnate commission. Flötner created several exquisite items for Sigismund I in the 1530s, including silver altar for the Sigismund Chapel and casket of Hedwig Jagiellon (Saint Petersburg). If this painting of Jan Firlej's wife as Venus was painted by Cariani's workshop shortly before the artist's death, this would explain why Firlej decided to order his portrait from young Jacopo Tintoretto in 1547 (Kröller-Müller Museum). A manuscript in the Ossolineum (number 2232) from the 1650s, lists a great number of jewels, furniture, paintings, books, clothes, fabrics with Lewart coat of arms and relics from Firlej estates in Dąbrowica, Ogrodzieniec and Bejsce. It also includes many imported goods and portraits, like "foreign fans", "pictures of deceased ancestors and many various arts, very expensive and elaborate", "great Persian and home-made rugs", "two paintings: one in French costume, the other in Polish, and the third started, in French style", "many old pictures from Ogrodziniec and Dąbrowica, one with a dwarf with a great son; costly, pious pictures on copper, many on canvas", "costly glass, buried in a cellar in Dąbrowica from the enemy, Jarosz Kossowski dug it", most likely Venetian glass saved during the Deluge (1655-1660), "the Bonarowski chalice, three gold stamps, folded into one, by elaborate work", most probably from dowry of Zofia Bonerówna, "various foreign spectacles of copper, foreign jetons" and other items.
Portrait of Zofia Firlejowa née Bonerówna (d. 1563) as Venus and Cupid with Lewart coat of arms by workshop of Giovanni Cariani, 1546-1547, Private collection.
Portrait of Jan Firlej by Jacopo Tintoretto
Thanks to his father's efforts, Jan Firlej (1521-1574) received an education at the highest level. He studied at the University of Leipzig for two years, then continued his education at the University of Padua for the next two years. From there with his relative count Stanisław Gabriel Tęczyński (1514-1561), chamberlain of Sandomierz, and Stanisław Czerny, starost of Dobczyce, he went to the Holy Land, visited Egypt and Palestine. They set off on a journey from Venice in the second half of 1541 - on June 16 that year he participated in the solemn procession in Venice, as the Lord of Dąbrowica (dominus de Dambrouicza) among the group of pilgrims of Jerusalem (peregrinorum Hierosolimitanorum). He also traveled to Rome. Around 1543, he returned to Poland, and in 1545, he entered the service of King Sigismund I. In the same year, he was sent on a mission to Emperor Charles V at the Diet of the Holy Roman Empire in Worms. According to Stanisław Hozjusz (Hosius, Op. I, 459) in 1547, as an envoy, he participated in diplomatic activities at the court of Ferdinand I of Austria, possibly concernig the king's marriage with Barbara Radziwill or the plans to marry him to Anna d'Este (1531-1607), daughter of the Duke of Ferrara.
In January 1546, Giovanni Andrea Valentino (de Valentinis) the court physician of Sigismund the Old and Queen Bona, was sent from Kraków with a confidential mission to Sigismund Augustus residing in Lithuania, concerning the marriage with Anna d'Este. Around that time, a separate letter was sent by the envoy of Duke of Ferrara, Antonio Valentino, staying in Poland from August 30, 1545 to September 1546, to Bartolomeo Prospero, the secretary of Duke Ercole II, to speed up the delivery of the bride's portrait. "He recommended that the parcel be exported to Venice not by royal mail, but by a private route in the hands of Carlo Foresta, one of the agents of Gaspare Gucci from Florence, a merchant in Kraków" (after Danuta Quirini-Popławska's "Działalność Włochów w Polsce w I połowie XVI wieku", p. 87). It possible that the portrait mentioned in the letter was created in Venice, as Dukes of Ferrara also commissioned ther effigies there, e.g. portrait of Alfonso II d'Este (1533-1597) by Titian or workshop in Arolsen Castle, identified by me. In 1909 in the collection of Prince Andrzej Lubomirski in Przeworsk there was a small painting (oil on tin plate, 26 x 35 cm) attributed to 16th century Venetian school depicting "Madonna and Child surrounded by people who, according to tradition, represent the family of princes d'Este; the golden-haired woman depicts probably the famous Eleonora d'Este" (after "Katalog wystawy obrazów malarzy dawnych i współczesnych urządzonej staraniem Andrzejowej Księżny Lubomirskiej" by Mieczysław Treter, item 36, p. 11). In 1547 a painter Pietro Veneziano (Petrus Venetus), created a painting to the main altar of the Wawel Cathedral and Titian was summoned to paint Charles V and others in Augsburg. The painting in the Kröller-Müller Museum in Otterlo attributed to Jacopo Tintoretto, shows a wealty nobleman in a black coat lined with tremendously expensive lynx fur. His proud pose and gloves also indicate his position. This painting was acquired by Helene Kröller-Müller in 1921 and earlier it was in the collection of Count of Balbi in Venice and possibly in the Giustinian-Lolin collection in Venice. According to inscription in lower left corner, the man was 26 years of age in 1547 (ANN·XXVI·MEN·VI·/·MD·XL·VII·), exactly as Jan Firlej, when he was sent on a mission to Austria and possibly to Venice and Ferrara.
Portrait of Jan Firlej (1521-1574) aged 26 by Jacopo Tintoretto, 1547, Kröller-Müller Museum.
Portrait of Nicolaus "the Red" Radziwill by workshop of Giovanni Cariani
In 1547 Nicolaus III Radziwill (1512-1584), Great Royal Deputy Cup-bearer of Lithuania, the son of Grand Hetman of Lithuania George "Hercules" Radziwill and Barbara Kolanka, received the title of Prince of the Roman Empire in Birzai and Dubingiai from the Emperor Charles V. He received it together with his cousin Nicholas (1515-1565), then the Grand Marshal of Lithuania, who become the Prince in Nesvizh and Olyka. In order not to confuse him with his namesake, the cousins were given the nicknames on account of the color of their hair. Nicolaus III is best known as "the Red" and his cousin as "the Black".
About the same year king Sigismund II Augustus married secretly Nicolaus' younger sister Barbara, thinking she was pregnant. Nicolaus "the Red" was henceforth brother-in-law and confidant of the king. Thanks to the king's protection he became a Lithuanian Master of the Hunt in 1545 and from 1550 he was a voivode of Trakai. Nicolaus was a famous military leader, he participated in the war with Muscovy between 1534-1537, including in the siege of Starodub in 1535. The portrait of a member of the Radziwill family, said to be John Radziwill (d. 1522), nicknamed "the Bearded", father of Nicolaus "the Black", in the National Art Museum of Belarus in Minsk, comes from the gallery of portraits in the Radziwill castle in Nesvizh. Due to the style of the costume and technique, this work is generally dated to the beginning of the 17th century. It is, however, stylistically very close to another portrait from the same collection, the portrait of of Prince Nicolaus II Radziwill (1470-1521) by Giovanni Cariani, created in about 1520. The sitter's face was created in Cariani's style, most probably by the master himself, the rest, less elaborate, was undoubtedly completed by painter's pupil. Cariani, though he worked often in Bergamo near Milan, died in Venice. The date of the artist's death is not known, his last presence is documented on November 26, 1547 in the will of his daughter Pierina, making his death coincide in the following year. The man's pose and sash is very similar to the effigy of Nicolaus III Radziwill in the Hermitage Museum (ОР-45840) signed in Polish/Latin: "Nicolaus Prince in Birzai, Voivode of Vilnius, Chancellor and Hetman / Evangelical, called the Red" (Mikołay Xże na Birżach, Wda Wilenski, Kanclerz y Hetman / Evangelik, cognomento Rufus), from the first half of the 17th century. The man is holding a military baton. His black armor is almost identical with the black armor of Nicolaus III Radziwill in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna. This armor, created by an Italian workshop in about 1545, was offered to Ferdinand II (1529-1595), Archduke of Further Austria, son of Anna Jagellonica, in 1580 by Nicolaus himself. The sword swinging from his belt is similar to golden rapier of Archduke Maximilian, the eldest son of Anna Jagellonica, created by Antonio Piccinino in Milan and by Spanish workshop in about 1550 (Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna). The man bears finally a resemblance to the effigy of Nicolaus' mother Barbara Kolanka by Cranach (Wartburg-Stiftung in Eisenach) and his sister Barbara-La Bella by Titian (Pitti Palace in Florence).
Portrait of Nicolaus "the Red" Radziwill (1512-1584) by workshop of Giovanni Cariani, ca. 1547, National Art Museum of Belarus in Minsk.
Portraits of members of the Radziwill family by Giampietro Silvio and Paris Bordone
John Radziwill (1516-1551), together with his elder brother Nicolaus "the Black" Radziwill (1515-1565), grew up at the court of King Sigismund the Old. As a royal courtier, equipped with letters of recommendation from King Sigismund I and Queen Bona, he traveled to Italy in 1542 - he certainly visited Ferrara, Padua and Venice. Both during the trip to Italy and on the way back, he stopped in Vienna at the court of Ferdinand, king of Bohemia and Hungary. He returned to Kraków in September 1542. It was probably during this trip that John became acquainted with the Reformation and returned to the country as a Lutheran (after "Archiva temporum testes ..." by Grzegorz Bujak, Tomasz Nowicki, Piotr Siwicki, p. 218).
He was the first Radziwill to die in the Evangelical faith, as evidenced by the funeral speeches by Wenceslaus Agrippa and Philip Melanchthon - Oratio Fvnebris de Illvstrissimi Principis et Domini Domini Iohannis Radzivili ..., published in Wittenberg in 1553. In 1544, he became a the Great Carver of Lithuania (krajczy, incisor Lithuaniae). He was also the starost of Tykocin. He corresponded with Duke Albert of Prussia, as several letters from the Duke to John dating from 1546 have preserved. On December 24, 1547, thanks to the efforts of his elder brother, he received the title of Prince of the Holy Roman Empire and that year he probably married Elżbieta Herburt from Felsztyn. He died childless on September 27, 1551. It was most likely John, Barbara's cousin and confidant of the young king, who facilitated their meeting (after "Przeglad polski ..." by Stanisław Koźmian, Volumes 9-12, p. 7). He participated in splendid feasts and masquerades in Vilnius, during which "only sluts or widows known of prostitution and philandering, before all other respectable women, are welcomed. Each one, because riches are only valued in our country, considers herself quite honest when she travels in a magnificent carriage drawn by many horses, or when she is decked out in gold, scarlet [fabrics] and pearls, and presents herself to people's eyes in all the market squares and crossroads", lamented Calvinist theologian Andrzej Wolan (Andreas Volanus), royal secretary (text published in 1569). During one of these parties, John Radziwill became obsessed with a woman and left his wife (after "Najsłynniejsze miłości królów polskich" by Jerzy Besala, pp. 111-114). "Augustus fell in love with Barbara Radziwill, a woman of a famous family in Lithuania [...] who always paid more attention to other matters than fame [i.e. good opinion]. Having lost her virginity with many, the king, deceived by them, glorifying form and body and easy debauchery, was first led to her" - wrote the secretary of the papal nuncio, Antonio Maria Graziani (Gratiani). They probably knew each other since childhood, as Sigismund Augustus often spent time in Lithuania with his parents and the Radziwill manor was adjacent to the Grand Ducal Castle in Vilnius. Perhaps the next meeting took place in Hieraniony (Gieranony) in Belarus in October 1543. Shortly after the death of Sigismund Augustus' first wife, many people were talking about a possible marriage. Soon, very unpleasant comments began to circulate about the king's favorite. Canon Stanisław Górski (d. 1572), secretary of Queen Bona between 1535-1548, counted thirty-eight of her lovers, called her "a great whore" (wiborna kurwa) or magna meretrix and claimed that she did not show any grief over the loss of her first husband, nor did she wear widow's mourning. Stanisław Orzechowski (1513-1566), canon of Przemyśl, an opponent of celibacy, wrote in 1548 that: "When she grew up and was given to her previous husband, she conducted herself in such a way that she either equaled or surpassed her mother in disgrace, and was marked by many blemishes of lust and immodesty". He also wrote that "There are people here and there who were rolling around lasciviously with this Thaïs [a repentant courtesan]". Later, even her cousin Nicolaus "the Black" spoke unfavorably about her: "After all, she was married to Gostautas, and in this house ex usu et natura crescebat illa diabolica symulatio [diabolical simulation grew out of practice and nature]," and that she "indulged in devilish practices out of necessity and nature." Such rumors were likely fueled by Queen Bona, as marrying a subject was not favored in the majority of highly hierarchical countries of the Western Europe, including her native Italy (in Poland-Lithuania the monarch was elected and there were no hereditary titles apart from those granted by the emperor thus seeking supporters). She expressed her concerns in a letter to the mayor of Gdańsk, Johann von Werden (1495-1554). Many renowned authors were involved in this campaign to disgrace the king's mistress, it is therefore difficult today to determine to what extent this was true. Barbara's brother, Nicolaus "the Red", and her cousin Nicolaus "the Black", after consulting her mother Barbara Kolanka, asked the king to stop visiting their house because his relations with Barbara brought shame to the entire family. Shortly after, the king secretly married his mistress. When Barbara became queen, her brother Nicolaus "the Red" was the superior of the guard surrounding the queen in Lithuania. The king sent him numerous letters (kept in the Imperial Library in St. Petersburg). Sigismund Augustus was afraid of Barbara being poisoned. There are detailed warnings about how the queen should drink and who should prepare her drink and he prefers that men, not women, give her a drink. The queen would also like to comply in everything with her husband's wishes. Once she asks what clothes to wear to greet him. The king replies that she should wear "a black dress of Italian fabric" (after "Biblioteka warszawska", Volume 4, p. 631). In the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, there is a portrait of a man holding a letter (oil on canvas, 82 x 66 cm, GG 1537). The painting comes from the the collection of Archduke Leopold Wilhelm of Austria and was recorded in Theatrum Pictorium (number 54), before two paintings depicting Andrzej Frycz Modrzewski and King Sigismund I (numbers 56, 57), identified by me. According to an inscription in the Theatrum Pictorium, the original painting was painted by Titian (I. Titian p.), while the canvas in Vienna is signed by another Venetian painter Giampietro Silvio (1495-1552), indicating that the signature was probably not known before. The portrait is clearly inspired by some effigies of Martin Luther and Philipp Melanchthon by Lucas Cranach and studio and the man resembles a Protestant preacher. However, his black coat of shiny silk and rich ring on his finger indicate that he is more of an aristocrat. According to the mentioned signature of the painter on the right above his shoulder, the painting was made in 1542 (Jo.pe.S. 1542), when John Radziwill visited the Republic of Venice and Vienna. The same man was depicted in another painting by Silvio, today in the Gemäldegalerie in Berlin (oil on canvas, 102 x 144 cm, inventory number 196). The painting was purchased in 1815 in Paris from the Giustiniani collection by Frederick William III (1770-1840), King of Prussia, with nearly 160 other works and transferred to Berlin. The collection was transferred to Paris in 1807 from Rome, where it was kept in the Giustiniani Palace built at the beginning of the 17th century and probably corresponds to the painting mentioned in the inventory of the collection of 1638 with attribution to Giorgione. The man wears a red coat of a starost or similar to the crimson żupan of the Polish-Lithuanian nobility, it was thus created after 1544. The scene depicts Christ and the Adulteress (The Adulteress Brought before Christ), illustrating the passage from the New Testament in which a group of scribes and Pharisees confront Jesus, interrupting his teaching. They bring in a woman, accusing her of committing adultery. They tell Jesus that the punishment for someone like her should be stoning, as prescribed by the Mosaic law. He declares that the one who is without sin is the one who should cast the first stone at her. The effigy of the adulteress is believed to be a disguised portrait of a famous and "magnificent courtesan" (somtuosa meretrize) Julia Lombardo, who owned such a painting before her death in 1542 in Venice. It is not known how the painting arrived in Rome in the collection of the Genoese banker Vincenzo Giustiniani (1564-1637). Most likely, it was sent to the Eternal City shortly after its creation. The woman resembles the effigy of Queen Barbara by the workshop of Paris Bordone at Knole House, Kent (NT 129951) and other portraits of the queen, while the face of Christ closely resembles the effigy of the brother of Barbara, Nicolaus "the Red", by workshop of Giovanni Cariani at the National Art Museum of Belarus in Minsk. He has dark hair because Christ could not have red hair, according to the known iconography. Another version of this painting can be found in Vilnius. It comes from the collection of Dr Pranas Kiznis exhibited at the Palace of the Grand Dukes of Lithuania. The collection includes the portrait of Pope Leo X by Jacopino del Conte and Susanna and the Elders by Palma il Giovane. The precise provenance is not specified, however, even if the painting was acquired in Italy, where it was most likely also created, this does not exclude the identification of the same protagonists as disguised portraits of Barbara Radziwill and her brother. This painting had important political significance and therefore may have been intended for family or friends in Italy. Very little is known about Silvio, who died in Venice in 1551, probably born on Venetian territory around 1495 and who signed some of his works Joannes Petrus Silvius Venetus, thus defining himself as a Venetian. Perhaps his stay in Poland-Lithuania is yet to be discovered. Such representations in the scene of Christ and the Adulteress were popular in 16th-century Europe, especially in this context of well known "adultery". Georg Vischer's painting from the Electoral Gallery in Munich (Alte Pinakothek, inventory number 1411), dated 1637, is most likely a copy of a lost original by Albrecht Dürer from around 1520. Dürer represented himself as Christ and the adulterous woman bears the features of a mistress of Alfonso d'Este (1476-1534), Duke of Ferrara (a relative of Queen Bona Sforza) - Laura Dianti (d. 1573), called Eustochia. Laura was frequently depicted in many biblical disguises, like Madonna and Child with the Infant Saint John the Baptist (Uffizi Gallery in Florence and Musée Fesch in Ajaccio), Saint Mary Magdalene (private collection), Salome (private collection), all by Titian and followers and also in the scene of Jesus preaching to Laura Dianti and her great-grandson Alfonso III d'Este, Duke of Modena and Reggio by circle of Sante Peranda (Château de Chenonceau). Similar to the Berlin painting where John Radziwill was depicted in the upper left corner as a donor, such effigy is also in the painting by Vischer (a man in a green cap looking at the viewer). In 1642, in a dispute with the d'Este family, lawyers of the Holy See even referred to the way Duke Francesco I's grandmother was depicted in a portrait from many years ago (a painting of Laura depicted like an exotic courtesan by Titian). The lack of regalia and the free convention of an "indecent" woman were, in their opinion, proof that the ruler was born out of wedlock (after "Prawna ochrona królewskich wizerunków" by Jacek Żukowski). This is why many "indecent" effigies were destroyed during the Counter-Reformation, including very probably the original by Dürer. Another similar scene with portraits is in the Schloss Johannisburg in Aschaffenburg (inventory number 6246). It comes from the Zweibrücken gallery and may have once been in Halle Cathedral, remodeled around 1520 by Cardinal Albert of Brandenburg (1490-1545). In this painting, attributed to workshop or circle of Lucas Cranach the Elder (possibly Hans Abel), Albert was depicted in the guise of Christ and his concubine Elisabeth (Leys) Schütz (d. 1527) as the adulteress. The cardinal was also frequently depicted in other religious disguises, such as Saint Jerome, Saint Erasmus and Saint Martin and his concubine as Saint Ursula. The same woman and man were also depicted together in another painting. This portrait is attributed to Paris Bordone, but its style reveals great similarities with certain works of Giovanni Cariani, such as the mentioned effigy of Nicolaus "the Red" in Minsk. Bordone probably copied a painting by Cariani and was inspired by his style. The painting is now in the Nivaagaard Museum in Nivå, Denmark (oil on canvas, 84.5 x 71 cm, 0009NMK) and was purchased on September 11, 1906 from Lesser, London by Danish businessman Johannes Hage (1842-1923). The dress of a young woman is very similar to that seen in a Portrait of a Young Woman by Bordone in the National Gallery, London, dated around 1545 (NG674), in a Portrait of a Lady from the Pitti Palace in Florence, dated between 1545 and 1555 (Palatina 109, 1912) or Women at their Toilet from around 1545 in the National Galleries Scotland (NG 10). The woman holds her hand on her womb as if to say that she remains chaste and the rumors are false. The man standing behind her resemble her and he is holding his hands on her arms in supportive gesture, he is obviously her brother. The same man is depicted in another painting by Bordone in which his pose and features also resemble those of his cousin John Radziwill from a painting by Silvio in Berlin. He is holding a letter and the painting can be compared to the portrait of the royal jeweler Giovanni Jacopo Caraglio at the Wawel Royal Castle dating between 1547 and 1553. This painting comes from the collection of Graf von Galen at Haus Assen in Lippborg in northern Germany. Since the early 17th century, the Radziwill family had significant connections and properties in Germany. It was sold in 2004 in London (oil on canvas, 92.4 x 74 cm, Sotheby's, July 08, 2004, lot 300). Among the paintings belonging to the "Victorious King" John III Sobieski (1629-1696), which could come from earlier royal collections and mentioned in the inventory of the Wilanów Palace from 1696, we find "A painting of mulieris in adulterio a Iudaeis deprehensae [a woman caught in adultery by the Jews] in gilded and carved frames" (Obraz mulieris in adulterio a Iudaeis deprehensae wramach złocistych rzniętych, No. 70). In addition to an expensive frame, this painting hung in a representative interior of the King's Antechamber, next to "A painting of Christ the Lord with the Pharisees [Christ among the doctors] in a gilded frame by Raphael" (Obraz Chrystusa Pana z Farazeuszami wramach złocistych Rafaela, No. 69). The inventory of paintings from the collection of Princess Louise Charlotte Radziwill (1667-1695), that survived the Deluge (1655-1660), drawn up in 1671, in addition to portraits of Queen Barbara and her husband, lists the following portraits of members of the family: Nicolaus Radziwił Dux in Ołyka et Nieśwież Palatinus Vilnen. (10), Joanes Radziwil Dux in Muszniki Archicamer. M.D.L. (15), Joanes Radziwił Dux in Olika et Nieśwież Etatis Sue 35 (17), Nicolaus Radziwił Dux Birzarum et Dubincorum, Palaitinus Vilnen. Gnalis Dux Exercitum M.D.L. (21) and many other unspecified portraits like "A person in black costume in German style, yellow hair" (271). The inventory also includes paintings such as "Lucifer with devils, painting on a sheet metal" (579).
Portrait of John Radziwill (1516-1551) holding a letter by Giampietro Silvio, 1542, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Portrait of John Radziwill (1516-1551) from the Theatrum Pictorium (54) by Jan van Troyen, 1660, Princely Court Library Waldeck.
Christ and the Adulteress with portraits of Barbara Radziwill (1520/23-1551), her brother Nicolaus "the Red" Radziwill (1512-1584) and cousin John Radziwill (1516-1551) by Giampietro Silvio, ca. 1545-1547, Gemäldegalerie in Berlin.
Christ and the Adulteress with portraits of Barbara Radziwill (1520/23-1551) and her brother Nicolaus "the Red" Radziwill (1512-1584) by Giampietro Silvio, ca. 1545-1547, Palace of the Grand Dukes of Lithuania in Vilnius.
Portrait of Barbara Radziwill (1520/23-1551) and her brother Nicolaus "the Red" Radziwill (1512-1584) by Paris Bordone, ca. 1545-1547, Nivaagaard Museum in Nivå.
Portrait of Nicolaus "the Red" Radziwill (1512-1584) holding a letter by Paris Bordone, ca. 1550, Private collection.
Portraits of pregnant Barbara Radziwill
In a letter of 26 November 1547, Stanisław Andrejewicz Dowojno (d. 1566) reported to king Sigismund Augustus about miscarriage of Barbara Radziwill, whom he wed secretly sometime in 1547. Having a large number of mistresses before, during and after being married, the king remained childless. At some time the parliament was willing to legitimize and acknowledge as his successor any male heir who might be born to him.
The portrait of a lady with a servant by Jan van Calcar from the collection of Prince Leon Sapieha, sold in 1904 in Paris, was said to depict pregnant Barbara Radziwill (possibly lost during World War II). It shows a woman in red dress in Italian style with emerald pendant on her chest accompanied by a midwife. The bill of a royal embroiderer, who charged the treasury for "a robe of red velvet" that he embroidered in 1549 for Queen Barbara with pearls and gold thread for 100 florins, confirms that similar dresses were in her possesion. The portrait by Calcar is very similar in comosition to the portrait known as effigy of Sidonia von Borcke (Sidonia the Sorceress) (1548-1620) and attributed to workshop of Lucas Cranach the Elder. This portrait was before World War II in the Von Borcke Palace in Starogard (destroyed), owned by a wealthy Pomeranian family of Slavic origin, along the effigy of Sophia Jagiellon (1522-1575) and her husband. The sitter costume is in German style and similar to costume of Sigismund Augustus' relative Anna of Brunswick-Lüneburg (1502-1568) (as a wife of Barnim XI of Pomerania) from about 1545 or a portrait of Agnes von Hayn from 1543, both by Cranach or his workshop, hence it cannot be Sidonia, who was born in 1548. The woman in the painting is holding a chalice, an allusion to her patron, Saint Barbara, as in a triptych by Cranach from 1506 in Dresden (the hand is almost identical). Title page of "Inscription on the tomb of the noble Queen Barbara Radziwill" (Napis nad grobem zacney Krolowey Barbary Radziwiłowny), a dirge (song of mourning) praising the king's beloved wife, published in Kraków in 1558, is decorated with a beautiful woodcut depicting Saint Barbara with the towers of the castle in the background. Both paintings, by Calcar and by workshop of Cranach, were undoubtedly then a part of Jagiellonian propaganda to legitimize the royal mistress as the Queen of Poland.
Portrait of pregnant Barbara Radziwill with a midwife by workshop of Lucas Cranach the Elder, 1546-1547, Von Borcke Palace in Starogard, most probably destroyed during World War II.
Portrait of pregnant Barbara Radziwill with a midwife by Jan van Calcar or circle, 1546-1547, collection of Prince Leon Sapieha, sold in 1904 in Paris, possibly lost during World War II.
Portrait of Barbara Radziwill by Moretto da Brescia or Jan van Calcar
The portrait of unkown lady in white in the National Gallery of Art in Washington (oil on canvas, 106.4 x 87.6 cm, 1939.1.230), attributed to Moretto da Brescia, a painter from the Republic of Venice who may have apprenticed with Titian, can be compared with a portrait by Jan Stephan van Calcar, a pupil of Titian, from the Sapieha collection in Paris. The latter painting, most probably lost during World War II, was said to depict pregnant second wife of Sigismund Augustus, Barbara Radziwill. Both face features as well as costume style and details are very much alike. The sitter's dress in Moretto's painting is also very similar to that visible in a miniature of a lady with a pearl necklace, wich can be identified as effigy of Bona Sforza d'Aragona, Queen of Poland, from the second half of the 1540s (Uffizi, Inv. 1890, 9005).
The bill of a royal embroiderer of Sigismund Augustus, who charged the treasury for "a robe of white tabinet" that he embroidered in 1549 for Queen Barbara "with a wide row of goldcloth and green velvet" for 15 florins, confirms that similar dresses were in her possesion. The Queen's taylor was an Italian Francesco, who was admitted to her service in Vilnius on 2 May 1548 with annual salary of gr. 30 fl. 30. In May 1543 during entry to Kraków for coronation of Elizabeth of Austria, the lords and knights of the Kingdom were dressed in all sorts of costumes, including Italian, French and Spanish, while the young king Sigismund Augustus was dressed in German style, probably as a courtesy for Elizabeth. The inventory of dowry of Sigismund Augustus' sister Catherine Jagiellon from 1562 includes 13 French and Spanish robes. The painting in Washington comes from the collection of Count Alessandro Contini Bonacossi (1878-1955) in Rome and Florence, who also owned the portrait of Sigismund Augustus by Francesco Salviati (Mint Museum of Art, 39.1) and portraits of the king and his third wife by Tintoretto or Titian (Uffizi Gallery and National Museum of Serbia), sold in 1936 to the Samuel H. Kress Foundation. A portrait of Queen Barbara (item 19) is mentioned among the Italian paintings in the collection of Prince Boguslaus Radziwill (1620-1669) in 1657 (Central Archives of Historical Records in Warsaw - AGAD, 1/354/0/26/79.2).
Portrait of Barbara Radziwill (1520/23-1551) in white by Moretto da Brescia or Jan van Calcar, ca. 1546-1548, National Gallery of Art, Washington.
Portraits of Sigismund II Augustus by Jan van Calcar or Moretto da Brescia
Sometime in 1547, in spite of his mother's disapproval and nobility's animosity, Sigismund Augustus, King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania secretly wed his mistress Barbara Radziwill, a Lithuanian noblewoman whom he met in 1543.
The portrait attributed to Jan van Calcar (oil on canvas, 125.5 x 92 cm, sold at Dorotheum in Vienna, April 14, 2005, lot 12), shows a young man (Sigismund Augustus was 26 in 1546). He stands against ancient buildings similar to a reconstruction of the Mausoleum of Emperor Augustus in Rome published in 1575 (the king born on 1 August was named after the first Roman Emperor Gaius Octavius Augustus) and the king's castrum doloris in Rome in 1572 or obelisk visible in the portrait of royal jeweller Giovanni Jacopo Caraglio from about 1553. The painting comes from the collection of John Rushout, 2nd Baron Northwick (1770-1859), an avid collector of works of art, antiques and coins, most likely acquired in Italy in 1790. In the "Catalogue of the pictures, works of art, &c. at Northwick Park" from 1864, it was listed with attribution to Parmigianino as "Portrait of Cosmo de Medici" (No. 34). The presumed author Jan van Calcar, a pupil of Titian in Venice, moved to Naples in about 1543, where he died before 1550. Sigismund's mother Bona Sforza was a granddaughter of Alfonso II, King of Naples and from 1524 she was a Duchess of nearby Bari and Rossano. According to the accounts of Sigismund Augustus by a courtier Stanisław Wlossek from 1545 to 1548, the king had "robes lined with lynx, short Italian", robes of black velvet and stockings of "black ermestno silk", black suede shoes, etc. The register of his clothes from 1572 includes Italian, German and Persian robes valued at 5351 zlotys. The portrait could be a pendant to a portrait of Barbara Radziwill in similar dimensions attributed to Moretto da Brescia (National Gallery of Art, 1939.1.230), which could also be attributed to Calcar, just as previously the portrait of the man described here was attributed to Moretto da Brescia, and inversely. The man is holding in his right hand a red carnation flower, a symbol of passion, love, affection and betrothal. The same sitter is also depicted in the portrait in Vienna (Kunsthistorisches Museum, oil on canvas, 86.5 x 59 cm, inventory number GG 79), signed by Calcar (. eapolis f. / Stephanus / Calcarius), and in the painting attributed to Francesco Salviati, who stayed for a brief time in Venice, in the Mint Museum (oil on panel, 109.2 x 82.9 cm, 39.1). According to the inscription, the Vienna painting was painted in Naples and was evidenced in the Imperial Gallery in 1772, so it was probably a gift to the Habsburgs. While the painting by Salviati comes from the collection of Count Alessandro Contini Bonacossi (1878-1955) in Rome and Florence, who also owned the mentioned portrait of the king's second wife Barbara Radziwill and portraits of Sigismund Augustus and his third wife by Tintoretto or Titian (Uffizi Gallery and National Museum of Serbia), sold to Samuel Henry Kress on 1 Septemeber 1939. Gold medal of Sigismund II Augustus on the occasion of birthday anniversary and coronation with bust and coat of arms of the young king was made by less known medalier Domenico Veneziano (Dominicus Venetus, Dominic of Venice) in 1548 - inscription "Sigismund Augustus, King of Poland, Grand Duke of Lithuania, aged 29" (SIGIS[mundus] AVG[ustus] REX POLO[niae] MG[magnus] DVX LIT[huaniae] AET[atis] S[uae] XXIX), today in the Ossolineum in Wrocław (inventory number G 1611). He signed his work on the reverse around the Polish Eagle: "Domenico Veneziano made [me] in the year of Our Lord 1548" (ANO D[omini] NRI[nostri] M.D.XLVIII. DOMINICVS VENETVS FECIT.).
Portrait of Sigismund II Augustus (1520-1572) by Jan van Calcar or Moretto da Brescia, ca. 1546-1548, Private collection.
Portrait of Sigismund II Augustus (1520-1572) with gloves by Jan van Calcar, 1540s, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Portrait of Sigismund II Augustus (1520-1572) with gloves, attributed to Francesco Salviati, 1540s, Mint Museum of Art, Charlotte.
Portraits of Sigismund Augustus and royal jeweller Giovanni Jacopo Caraglio by Paris Bordone and workshop
In 1972 the portrait of royal jeweller Giovanni Jacopo Caraglio was offered to the Wawel Royal Castle in Kraków by Julian Godlewski. After 1795, when Poland lost its independence, the castle, which was consumed by destructive fire in 1702 and ransacked several times by different invaders, was converted into barracks and a military hospital and almost no traces of the former royal splendor have been preserved in it. Before 1664 the painting was in the Muselli collection in Verona.
Caraglio was born in Verona in the Venetian Republic around 1500 or 1505. He was active in his hometown, as well as in Rome and Venice. In Italy he was known mainly as a copper engraver and medalist. He came to Kraków around 1538 as a recognized artist. After arriving at the Jagiellonian court, he probably parted with graphic art and devoted himself exclusively to goldsmithing and jewellery, making mainly gems with images of members of the royal family. In recognition of his merits, Sigismund Augustus ennobled him in 1552. Caraglio was also a citizen of the capital city of Kraków, and together with his wife, Katarzyna, born there, he lived in a house he bought outside the city walls - in Czarna Wieś. He had a son Ludwik and a daughter Katarzyna. During his long stay in Poland, the artist certainly made many trips to Italy. This is evidenced, among other things, by Vasari's fairly good knowledge of his life and work. We learn about one of his trips to Italy - probably on business - from the accounts prepared by Justus Decius. The bill from April 1553, apart from listing the expenses for the ores by Caraglio, contains inter alia, the entry referring to him: pro viatico itineris in Italiam (provision for a journey to Italy) (after "Caraglio w Polsce" by Jerzy Wojciechowski, p. 29). The portrait of Caraglio was in the 17th century attributed to Titian and later to Bordone, who lived in Venice from October 1552 and earlier in Milan between 1548-1552. Caraglio receives or humbly offers a medallion with king's effigy (probably made by himself) to the Polish Royal Eagle with monogram SA of Sigismund Augustus on his chest. The eagle is standing on a gold helmet among other works and utensils necessary to the goldsmith. In 1552 Caraglio went to Vilnius to make a gilded shield for the king encircled with golden roses with a cross in red enamel and three other silver shields decorated with an ornament of eagles' heads (Exposita pro ornandis scutis S.M.R. per Ioannem Iacobum Caralium Italum 1553), together with three other goldsmiths Gaspare da Castiglione, Grzegorz of Stradom and Łukasz Susski. In the background there is an obelisk and Roman amphitheatre, identified as symbol of Verona - Arena di Verona. According to the inscription in Latin on the base of the column, he was 47 years of age (ATATIS / SVAE / ANN[O] / ХХХХ / VII) at the time when the painting was created, however his face seems to be much younger. Based on this inscription, it is generally believed that the painting was painted between 1547-1553, possibly during his confirmed stay in Italy in 1553, however, it cannot be ruled out that it was based on a drawing or miniature sent from Poland. Caraglio probably gave this portrait to his sister Margherita, who lived in Verona. In the vicinity of Parma, in the town of Sancti Buseti, the artist bought a house with land and vineyards. Caraglio intended to leave the court of Sigismund Augustus in his old age and return to Italy. However, he did not fulfill his intentions, he died in Kraków around August 26, 1565 and was buried in the Carmelite Church of the Visitation, which was largely destroyed during the Deluge (1655-1660). He bequeathed the house in Verona to Elisabetta, his sister's granddaughter. The artist's wife, Katarzyna, remarried to an Italian shoemaker, Scipio de Grandis. The same man as in the Wawel painting was depicted in the work sold in Vienna in 2012 (Dorotheum, 13.12.2012, Lot 12, oil on canvas, 61.5 x 53 cm). He wears similar costume, there is a similar column behind him and the fabric in the background and the style of whole painting is very close to Paris Bordone and his workshop, comparable to portrait of a man in the Louvre, identified as effigy of Thomas Stahel, which is dated '1540'. The portrait was sold in Austria, while Caraglio travelled to nearby Slovakia in 1557, where he stayed at the court of Olbracht Łaski (1536-1604), a Polish nobleman, alchemist and courtier, in Kežmarok. At the age of twelve, Łaski was sent to the court of Emperor Charles V, who recommended him to his brother Ferdinand of Austria. He returned to Poland in 1551 and in 1553 he went to Vienna, where he became the secretary of Catherine of Austria, who became the third wife of King Sigismund Augustus. In 1556 he visited Poland again, where he met the rich widow Katarzyna Seredy née Buczyńska. Their wedding took place in 1558 in Kežmarok. It is possible that either Łaski or the Habsburgs received a portrait of the famous jeweller of the Polish king. Caraglio undoubtedly also acted as an intermediary in commissions for effigies of his patron king Sigismund Augustus. In 2011 a small portrait of a bearded man from the collection of Château de Gourdon near Nice in southern France was sold at auction in Paris (oil on canvas, 39.8 x 31.5 cm, Christie's, 30 March 2011, lot 487). It was initally attributed to follower of Moretto da Brescia, and later to Paris Bordone, and dated to the 1550s. Its previous provenance is not known. Collections of the medieval Gourdon Castle were spared during the French Revolution. Extanded by the Lombards in the 17th century, the castle was bequeathed by Jean Paul II de Lombard to his nephew the Marquis de Villeneuve-Bargemon, whose heirs sold the residence in 1918 to an American, Miss Noris, who opened a museum in 1938. Occupied during the Second World War by the Germans, then restored by Countess Zalewska, it was later acquired by French businessman Laurent Negro (1929-1996). It is therefore possible that the painting was sent from Venice to France already in the 16th century or brought from Poland by Countess Zalewska or her ancestors. Bordone painted a second, slightly larger version of this portrait (oil on canvas, 57.2 × 41.9 cm) which was in the collection of Marquess of Ailesbury in England and later with the Hallsborough Gallery in London. "The dress of both figures is understated but clearly luxurious, and conveys the sitters' importance without the need for opulence" (after Sphinx Fine Art catalogue entry). The man's facial features, red beard and dark hair correspond perfectly with other other effigies of king Sigismund Augustus by Bordone, Moretto da Brescia or Jan van Calcar, Francesco Salviati and Tintoretto, identified by me. Like in the case of portrait of Anna of Brunswick-Lüneburg (1502-1568), wife of Barnim XI of Pomerania by Lucas Cranach the Elder and portrait of John III Sobieski with the Order of the Holy Spirit by Prosper Henricus Lankrink, the artist may not have seen the model at all, but with detailed drawings with descriptions of colors and fabrics, he was able to produce a work with a great deal of craftsmanship and resemblance.
Portrait of Sigismund II Augustus (1520-1572), from the Château de Gourdon, by Paris Bordone, 1547-1553, Private collection.
Portrait of Sigismund II Augustus (1520-1572), from the Ailesbury collection, by Paris Bordone, 1547-1553, Private collection.
Portrait of royal jeweller Giovanni Jacopo Caraglio (1500/1505-1565) by workshop of Paris Bordone, 1547-1553, Private collection.
Portraits of Barbara Radziwill and Sigismund Augustus by circle of Titian
In the 18th century, with the growing popularity of the story of Mary, Queen of Scots, the portrait of an unknown lady, so-called Carleton Portrait in Chatsworth House, was identified as her effigy due to great similarity with a print by Hieronymus Cock from about 1556 and history of the Chatsworth House. Numerous prints and copies of this portrait were made. Today, however, researchers reject this identification.
The style of the painting is close to the circle of Titian and Venetian portrait painting as well as composition with a chair (Savonarola chair), a window and rich fabrics, Venetian velvet and gold cloth. The costume however, a mixture of French, Italian, Spanish and German patterns from the 1540s is not typical for Venice. Also the sitter is not a typical, a bit plump "Venetian beauty". In 1572 the royal embroiderer charged the royal treasury for dresses he embroidered for Queen Barbara in 1549 including one, the most expensive, for which he charged 100 florins: "I embroidered a robe of red velvet, bodice, sleeves and three rows at the bottom with pearls and gold". Similar puffed sleeves at the shoulders are visible in portraits of Barbara by Moretto da Brescia (Washington), Jan van Calcar (Paris, lost) and by circle of Lucas Cranach the Younger (Kraków). In February 1548 a long battle begun to recognize Barbara as Sigismund Augustus' wife and crown her as Queen of Poland. Almost since her wedding in 1547 Barbara's health began to decline. Sigismund Augustus personally tended to his sick wife. He also possibly seek a help from the only possible ally - Edward VI of England, a boy king, who like Sigismund was crowned at the age of 10 and a son of Henry VIII, who broke with the Catholic Church to marry his mistress Anne Boleyn. In 1545 to cure his first wife Elizabeth of Austria from epilepsy, Sigismund wanted to obtain a coronation ring of the English king, that supposedly was to be an effective antidote. In 1549 arrived to London Jan Łaski (John à Lasco), a Polish Calvinist reformer, secretary of king Sigismund I and a friend of the Radziwlls (Barbara's brother converted to Calvinism in 1564) to became Superintendent of the Strangers' Church. He undoubtedly mediate with the king of England in personal affairs of Sigismund Augustus and possilby brought to England a portrait of his wife. The octagonal tower in the portrait is very similar to the main landmark of the 16th century Vilnius, the medieval Cathedral Bell Tower, rebuilt in Renaissance style during the reign of Sigismund Augustus after 1544 (and later due to fires and invasions) and close to Barbara's residence, Palace of the Grand Dukes of Lithuania. The woman is holding two roses, white and red - "white roses became symbols of purity, red roses of redeeming blood, and both colors, together with the green of their leaves, also represented the three cardinal virtues faith, hope, and love" (after Colum Hourihane's "The Routledge Companion to Medieval Iconography", 2016, p. 459). The portrait of a man sitting by a window with "a Northern town beyond" is very similar to other effigies of Sigismund Augustus, while the landscape behind him is almost identical with that visible in the Carleton portrait. It is almost like if the king was sitting in the same chair in the room at the Vilnius Castle beside his beloved wife. This portrait comes from a private collection in London and was sold in 1997 with attribution to Jacopo Robusti, called Tintoretto (oil on canvas, 103.5 x 86.5 cm, sold at Christie's London, April 18, 1997, live auction 5778, lot 159). In this likeness the monarch's nose is more hooked than in other portraits by Venetian painters identified by me, however in two woodcuts with the portrait of Sigismund Augustus, published in Kraków in 1570 in the "Statutes and privileges of the Crown translated from Latin into Polish" (Statuta y przywileie koronne z łacińskiego ięzyka na polskie przełożone) by Jan Herburt, his nose is different on both of them. The strange, rather unnatural appearance of his finger also indicates that the portrait is most likely a copy of another effigy or based solely on study drawings. The portrait of a general by Titian in Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Kassel is identified by Iryna Lavrovskaya as the effigy of influential cousin of Barbara Radziwill, Nicholas "The Black" Radziwill (Heritage, N. 2, 1993. pp. 82-84). The establishment of the portrait gallery in Nesvizh is associated with Radziwill "the Black", who commissioned images abroad, including in Strasbourg (after "Monumenta variis Radivillorum ..." by Tadeusz Bernatowicz, p. 20). Similar to king Sigismund II Augustus - armours in the Royal Armoury in Stockholm, Kremlin Museum and the Polish Army Museum in Warsaw, he ordered his set of armour and barding from Kunz Lochner in Nuremberg (Kunsthistorisches Museum, some elements are in the Metropolitan Museum of Art). In one of the letters, the longing father instructed his son Nicolaus Christopher "the Orphan", who was studying abroad, to commission a portrait and send it to Lithuania. The portrait, sent from Strasbourg, aroused dissatisfaction and at the same time biting remarks about his son's clothes. The voivode ordered a new life-size portrait of his son to be made so that he could see how tall he was. He also ordered a chain with the image of the king to be painted on his son's chest (after "Tylem się w Strazburku nauczył ... " by Zdzisław Pietrzyk, p. 164).
Portrait of Barbara Radziwill (1520/23-1551) by circle of Titian, ca. 1549, Chatsworth House.
Portrait of Sigismund II Augustus (1520-1572) by circle of Titian, ca. 1547-1549, Private collection.
Portrait of Nicholas "The Black" Radziwill (1515-1565) by Titian, 1550-1552, Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Kassel.
Portraits of Barbara Radziwill by Flemish painters
The effigy, previously identified as Anne de Pisseleu, Duchesse d'Etampes (modern scholars today reject this identification), is very similar in facial features and costume style to the Carleton Portrait at Chatsworth and to the portrait of Barbara Radziwill by Moretto da Brescia in Washington. It is known only through 19th century copies, as original from about 1550 (or 1549) from the French royal collection, most probably by a Flemish painter, is considered to be lost.
Anne de Pisseleu, was a chief mistress of Francis I, king of France and a staunch Calvinist, who counseled Francis on toleration for Huguenots. Even after her deposition, following Francis' death in March 1547, she was one of the most influential and wealthy Protestants in France. It cannot be excluded, that Sigismund Augustus and the Radziwills approached her with their cause - coronation of Barbara as a queen and her recognition internationally, and that the copy of effigy of Barbara offered to her was after the French Revolution mistaken for her portrait. Around the year of 1548 or 1549, Sigismund Augustus commissioned in the Spanish Netherlands (Flanders) the first set of new tapestries for his residences (known as Jagiellonian tapestries or Wawel Arrasses). It is highly probable that as earlier his father in 1536, he also ordered some paintings there. Also the details of sitter's garments find its confirmation in the bill of the royal embroiderer who charged the royal treasury for garments he embroidered for Queen Barbara in 1549: "I embroidered a red velvet beret with pearls; I earned from it fl. 6". The portrait of a lady in Spanish-like costume, said to be Anne Boleyn from the Musée Condé and created in about 1550, is astonishingly similar to the series of portraits of Sigismund Augustus' eldest unmarried sister at that time, Sophia Jagiellon. It's almost like a pendant to Sophia's portrait, the costume is very similar and the portraits were undoubtedly created in the same workshop. It's largely idealized, like some portraits of Margaret of Parma after original by Antonio Moro, nevertheless the resemblance to Barbara's appearance is strong. Through his mother, Bona Sforza d'Aragona, Barbara's husband had claims to Kingdom of Naples and Duchy of Milan, both part of the Spanish Empire. Likewise the previous portrait, black robes are also included in the same bill of the royal embroiderer for 1549: "a robe of black teletta, I embroidered a bodice and sleeves with pearls; I earned from this robe fl. 40." or "I embroidered a robe of black velvet, two pearl rows at the bottom; I earned from it fl. 60." The portrait of a mysterious lady from the Picker Art Gallery in Hamilton was undobtedly painted by some Netherlandish master and is very close to a bit caricatural style of Joos van Cleve and his son Cornelis (e.g. portraits of Henry VIII of England). The woman however wears an Italian costume from the 1540s, similar to portrait of a lady with a book of music from the Getty Center. The jewel on her necklace has also adequate symbolic meaning, ruby is a symbol of both royalty and love, sapphire a symbol of purity and the Kingdom of God and a pearl was a symbol of fidelity. Aprat from resemblance to other portraits of Barbara, whose husband was very fond of Italian fashion, and her taylor was an Italian, this is another indicator that this is also her portrait.
Portrait of Barbara Radziwill in a pearl beret, 1849 engraving after lost original by Flemish painter from about 1549, Private collection.
Portrait of Barbara Radziwill in a pearl beret, 19th century after lost original by Flemish painter from about 1549, Victoria and Albert Museum.
Portrait of Barbara Radziwill in Spanish costume by Flemish painter, ca. 1550, Musée Condé.
Portrait of Barbara Radziwill in Italian costume by Flemish painter, possibly Cornelis van Cleve, 1545-1550, Picker Art Gallery in Hamilton.
Portrait of Queen Bona Sforza by Lucas Cranach the Younger
Portrait of an old woman by Lucas Cranach the Younger from the Museum of Fine Arts in Boston bears strong similarity with contemporary effigies of Bona Sforza, Queen of Poland. The Queen started to wear her distinctive outfit of a widowed elder lady in about 1548, after death of Sigismund I.
As for eye color and features the comparison with portraits of Emperor Charles V, her portraits by Bernardino Licinio and her daughter, proofs that different workshops differently interpreted royal effigies and as natural ultramarine (deep blue color) was an expensive pigment in the 16th century, cheaper pigments were used to make a copy (eye color). In a letter of 31 August 1538, Bona Sforza says about two portraits of her daughter Isabella, and complain that her features in the portrait that she has are not very accurate. Like the Venetian painters, to meet the high demand for his works, Cranach developed a large workshop and "style of painting that depended on shortcut solutions and an extensive use of easily copied patterns and rote methods of producing decorative detail that could be successfully replicated by assistants". An epithet "the fastest painter" (pictor celerrimus), may still be read on his tomb in the city church in Weimar (after "German Paintings in the Metropolitan Museum of Art, 1350-1600", p. 77). Despite tremendous losses during many wars and invasions Cranach's name or paintings in his style appear in many books and inventories concerning historical collections of paintings in Poland-Lithuania. Before his accession to the throne as a sole ruler Sigismund Augustus, through his cousin Duke Albert of Prussia, tries to obtain portraits of German princes painted by Lucas Cranach the Elder (after "Malarstwo polskie: Gotyk, renesans, wczesny manieryzm" by Michał Walicki, p. 36). Paintings were sent in February 1547 trough Piotr Wojanowski, tenant of Grudziądz and were hung in the royal gallery that was being created in Vilnius (after "Zygmunt August : Wielki Książę Litwy do roku 1548" by Ludwik Kolankowski, p. 329). The painting of Madonna and Child with two angels against the landscape by follower of Lucas Cranach the Elder, was probably offered to the Corpus Christi Church in Kraków by king Sigismund II Augustus. The first mention of the painting dates back to 1571 and was later reported by the chronicler of the monastery, Stefan Ranotowicz (1617-1694) in his Casimiriae civitatis, urbi Cracoviensi confrontatae, origo. Ranotowicz states that "we have a German painting in the pallatium from the royal donation representing Beatae Mariae Virginis" (after "Madonna z Dzieciątkiem w krakowskim klasztorze kanoników regularnych ..." by Zbigniew Jakubowski, p. 130). Nicolaus "the Black" Radziwill, cousin of the king's second wife Barbara, had a German tapestry based on Cranach's painting and in 1535, a Pomeranian, Antoni Wida, probably a student of Cranach, resides in Kraków and in 1557 he is recorded as a court painter of Sigismund Augustus in Vilnius (partially after "Dwa nieznane obrazy Łukasza Cranacha Starszego" by Wanda Drecka, p. 625). Inventories drawn up in 1671 in Königsberg list the huge fortune inherited by the princess Louise Charlotte Radziwill (1667-1695) from her father Boguslaus Radziwill (1620-1669), whose estates were compared by contemporaries to "Mantua, Modena and other smaller states in Italy". Among over 900 paintings in the inventory, there were portraits, mythological and biblical scenes by Lucas Cranach (24 items) along "The Face of Jesus by Albert Duer", i.e. Albrecht Dürer, and a "painting of Pawel Caliaro", that is Paolo Caliari known as Veronese, about 25 Italian paintings, several portraits of unknown Italian, German, and French ladies and gentlemen, paintings with "naked" and "half-naked" women, Ruthenian and Russian icons, a Greek altar and one "Spanish Fantasy". Portraits of members of the Radziwill family, Polish kings from John I Albert (1459-1501), more than 20 effigies of the Vasas and their families, German emperors, kings of Sweden, France, England and Spain and various foreign personalities, collected over several generations, constituted the dominant part of over 300 pieces in the inventory (after "Galerie obrazów i "Gabinety Sztuki" Radziwiłłów w XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska, p. 90). The inventory also lists many paintings that may be by Cranach the Elder and his son or 16th-century Venetian or Netherlandish painters: A lady in a white robe, with jewels, a crown on her head (71), A lady in a lynx coat in black, a dog by her side (72), A lady in a czamara, a diamond crown on her head with pearls, holding gloves (73), A beautiful lady in a pearl dress and a robe embroidered with pearls (80), A woman who stabbed herself with a knife (292), A woman, semi-circular picture at the top (293), A man of this shape, perhaps the husband of this woman (294), Dido who stabbed herself with a knife (417), A large image of Venice (472), Lucretia who stabbed herself, golden frames (690), A naked lady who stabbed herself, golden frames (691), A well-dressed lady with a child, on panel (692), A lady in a red robe who stabbed herself (693), Small picture: a German with a naked woman (embracing, naked boys serve) (737), A person with a long beard, in black, inscription An° 1553 etatis 47 (753), A lady under the tent showed her breast (840), Venus with Cupid bitten by bees (763), two portraits of Barbara Radziwill, Queen of Poland (79 and 115) and a portrait of King Sigismund Augustus of Poland, on panel (595) (after "Inwentarz galerii obrazów Radziwiłłów z XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska). The inventory also includes several nude and erotic paintings and this is only a part of splendid collections of the Radziwlls that survived the Deluge (1655-1660). Perhaps the paintings owned by a citizen of Kraków Melchior Czyżewski (d. 1542): Tabula Judith et Herodiadis ex utraque parte depicta and by Kraków councilor Jan Pavioli in 1655: "bathing Bathsheba", "Judith", "portrait of Christian, king of Denmark", "the duke of Saxony", had something in common with the Wittenberg workshop. In the collection of King John II Casimir Vasa, Bona Sforza's grandson, sold at an auction in Paris in 1672, there was Cranach's Madonna and Child (Une Vierge avec un petit Christ, peint sur bois. Original de Lucas Cronus), possibly bearing features of his famous grandmother. King Stanislaus Augustus (1732-1798), had 6 paintings by Cranach and his workshop, one of St. Jerome, the other five on mythological subjects: Venus et l'Amour sur bois (no. 941), Pyrame et Thisbe (no. 912), Venus Couchee (no. 913), Venus surprise avec Mars (no. 914), Venus et Mars (no. 915). Many Venetian, Italian and German paintings were exhibited in Warsaw in the Bruhl Palace in 1880, some of these may have originally been in the royal collection: Lucas Cranach - Old man with a young girl (35, Museum), Jacopo Bassano - Vulcan forging the arrows (43, Museum), Moretto da Brescia - Madonna with Saint Roch and Saint Anne (51, Museum), Gentile Bellini - Christ after being taken down from the cross, surrounded by saints (66, Museum), Tintoretto - Baptism of Christ (71, 81, Museum), School of Paolo Veronese - Temptation of Saint Anthony (84, Museum), Jacopo Bassano - Adoration of the Shepherds, property of Countess Kossakowska (4, room D), School of Titian - Baptism of Christ, property of Countess Maria Łubieńska (6, room D), Giovanni Bellini - Madonna, property of Count Stanisław Plater-Zyberk (75, room D), Bernardo Luini - Christ and Saint John, property of Mrs. Chrapowicka (76, room D), Bassano - Bible scene, property of Mrs. Rusiecka (19, room E), Venetian school - Historical Item: Feast of the Kings, property of Jan Sulatycki (2, room F), Lucas Cranach - Reclining Nymph, property of Jan Sulatycki (35, room F) (after "Katalog obrazów starożytnych …" by Józef Unger). Other important paintings by Cranach and his workshop related to Poland and most likely the royal court include Stigmatisation of Saint Francis, created in about 1502-1503, today in the Belvedere in Vienna (inventory number 1273), in Poland, probably already in the 16th century and in the 19th century in the collection of the Szembek family in Zawada near Myślenice, comparable to paintings by Italian masters Gentile da Fabriano (Magnani-Rocca Foundation) or Lorenzo di Credi (Musée Fesch), the Massacre of the Innocents in the National Museum in Warsaw (M.Ob.587), which was in about 1850 in the Regulski collection in Warsaw, portrait of Princess Sibylle of Cleves (1512-1554) as a bride from the Skórzewski collection, signed with artist's insignia and dated '1526' (National Museum in Poznań, lost), portrait of George the Bearded, Duke of Saxony, husband of Barbara Jagiellon (Polish Academy of Learning in Kraków, lost), alleged portrait of Henry IV the Pious, Duke of Saxony (Frąckiewicz collection, lost), miniature portrait of Katharina von Bora "the Lutheress" (collection of Leandro Marconi in Warsaw, destroyed in 1944) (paritally after "Polskie Cranachiana" by Wanda Drecka).
Portrait of Queen Bona Sforza by Lucas Cranach the Younger, 1549, Museum of Fine Arts, Boston.
Portrait of Sigismund Augustus with a construction of a bridge in Warsaw by Tintoretto
"Sigismund Augustus built a wooden bridge over the Vistula River, 1150 feet long, which was almost unmatched in terms of both length and magnificence in the whole of Europe, causing universal admiration", states Georg Braun, in his work Theatri praecipuarum totius mundi urbium (Review of major cities around the world) published in Cologne in 1617.
In 1549, to facilitate communication with Grand Duchy of Lithuania, where Barbara resided, Sigismund Augustus decided to finance the construction of a permanent bridge in Warsaw. In 1549 he bought from Stanisław Jeżowski, a land writer from Warsaw, the hereditary privilege of transport across the Vistula River, giving him in return "two villages, a mill and a half of a second mill, 40 forest voloks and 200 florins." The portrait of a man with a "Northern landscape" beyond showing a construction of a wooden bridge in The National Gallery of Art in Washington, created by Jacopo Tintoretto, is very similar to other effigies of Sigismund Augustus. It was purchased in 1839 in Bologna by William Buchanan. The city of Bologna was famous for its university, architects and engineers, like Giacomo da Vignola (1507-1573), who began his career as an architect there and where in 1548 he built three locks or Sebastiano Serlio (1475-1554), an outstanding architect and theoretician of architecture, born in Bologna. In 1547 Queen Bona, wanted to involve Serlio, married to her lady-in-waiting Francesca Palladia, at her court. Since Serlio had already a position in France, he offered Bona his students. In a letter to Ercole d'Este, Bona asked for a builder who could build anything and in 1549 the Queen settled in Warsaw. From 1548 the court physician of the king was Piotr from Poznań, who received his doctorate in Bologna and in 1549, a Spaniard educated in Bologna, Pedro Ruiz de Moros (Piotr Roizjusz), became a courtier of Sigismund Augustus and a court legal advisor (iuris consultus), thanks to recommendation of his colleague from the studies in Bologna, royal secretary Marcin Kromer. From 4 June to 24 September 1547, master carpenter Maciej, called Mathias Molendinator, with his helpers, led the construction of a wooden bridge on brick supports covered with a shingle roof, which led through Vilnia River in Vilnius from the royal palace to the royal stables. It is uncertain if the construction was actually started in 1549 or the portrait was only one of a series of materials intended for propaganda purposes, confirming the creativity and innovation of the Jagiellonian state. It is possible that due to the problems to find a suitable engeneer to help with the costruction of the largest bridge of the 16th century Europe, that the project was postponed. Only after 19 years, on 25 June 1568, ten years after the start of the regular Polish post (Kraków - Venice), the tapping of the first pile was initiated. The bridge was opened to public on 5 April 1573, a few months after the death of its founder, accomplished by his sister Anna Jagiellon, who also built the Bridge Tower in 1582 to protect the construction. The 500 meters long bridge was the first permanent crossing over the Vistula River in Warsaw, the longest wooden crossing in Europe at that time and a technical novelty. It was made of oak wood and iron and equipped with a suspension system. The bridge was costructed by "Erasmus Cziotko, fabrikator pontis Varszoviensis" (Erazm z Zakroczymia), who according to some researchers was an Italian and his real name was Giotto, a surname carried by a family of Florentine builders.
Portrait of Sigismund Augustus with a construction of a bridge in Warsaw by Tintoretto, ca. 1549, National Gallery of Art, Washington.
Portrait of Sigismund Augustus by Tintoretto or workshop, 1540s, Private collection.
Portraits of Sigismund Augustus in armour and in a black hat by Tintoretto
In the beginnig of 1549 Barbara Radziwill arrived from Vilnius via royal Radom (September 1548) to Nowy Korczyn near Kraków for her coronation and ceremonial entry into the city as the new queen. Eight times a year, large grain fairs were held in the city of Nowy Korczyn. The grain purchased there was floated down the Vistula to Gdańsk in large barges, similar to galleys, as visible in the View of Warsaw from about 1625. The lords of the Kingdom arrived to greet Barbara in Korczyn and on 12 February 1549 she embarked on a journey to the capital.
The river journey from or to Korczyn would be the easiest, however the sources does not confirm it. The accounts from 1535 inform nevertheless about boats owned by Sigismund I and his son Sigismund Augustus. The statue on the ship, visible in the painting, is clearly Saint Chrisopher a patron saint of travelers, hence it is not likely a battleship. The effigy is in Vienna and Austrian Habsburgs were Sigismund Augustus' relatives through Anna Jagellonica, two of his wives were her daughters and portraits were often commissioned to be sent to distant relatives. The portrait which could be dated to 1550, although idealized, bears a resemblance to other effigies of the king by Tintoretto and has an inscription ANOR XXX (year 30) on the base of the column. Sigismund Augustus reached his 30th year of age on 1 August 1550 and his beloved wife was crowned on 7 December 1550. Finally his mother was described as a lovely light blonde, "when (oddly enough) her eyelashes and eyebrows are completely black", so was the anomaly in hair color inherited from her? The same sitter was also depicted wearing a black hat in a portrait from private collection by Tintoretto and a workshop copy of it in the Musée des Beaux-Arts in Rouen.
Portrait of Sigismund II Augustus (1520-1572) with a royal galley by Tintoretto, ca. 1550, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Portrait of Sigismund II Augustus (1520-1572) in armour by circle of Tintoretto, ca. 1550, Private collection.
Portrait of Sigismund Augustus in a black hat by Tintoretto, 1545-1550, Private collection.
Sigismund Augustus and Barbara Radziwill as Jupiter and Io by Paris Bordone
In Ovid's "Metamorphoses" Jupiter, King of the Gods noticed Io, a mortal woman and a priestess of his wife Juno, Queen of the Gods. He lusted after her and seduced her. The painting by Paris Bordone in Gothenburg shows the moment when the god discovers that his jealous wife is approaching and he raises his green cloak to hide his mistress. The myth fits perfectly the story of romance of Sigismund Augustus and his mistress Barbara Radziwill, a Lithuanian noblewoman whom he met in 1543, when he was married to Elizabeth of Austria (1526-1545), and whom he secretly married despite the disapproval of his mother, the powerful Queen Bona.
According to Vasari, Bordone created two versions of the composition. One for Cardinal Jean de Lorraine (1498-1550) in 1538, when he went to the court of Francis I of France at Fontainebleau, and the other "Jupiter and a nymph" for the King of Poland. Researchers pointed out that stylistically the canvas should be dated to the 1550s, therefore it cannot be the painting created for Cardinal de Lorraine. The painting was allegedly brought to Sweden by Louis Masreliez (1748-1810), a French painter, hence it cannot be excluded that it was taken to France by John Casimir Vasa, great-grandson of Bona, after his abdiction in 1668, that Masreliez acquired in Italy a copy of painting prepared for the Polish king, possibly a modello or a ricordo, or that it was captured by the Swedish army during the Deluge (1655-1660) and purchased by Masreliez in Sweden. The effigy of Io is not so "statuesque" as other effigies of the goddesses by Bordone, could be a courtesan, but could also be the royal mistress and can be compared with effigies of Barbara, while Jupiter with these of Sigismund Augustus. The painting should be then considered as a part of Jagiellonian propaganda to legitimize the royal mistress as the Queen of Poland.
Sigismund Augustus and Barbara Radziwill as Jupiter and Io by Paris Bordone, 1550s, Gothenburg Museum of Art.
Sigismund Augustus in guise of Christ as The Light of the World by Paris Bordone
The particluar taste of queen Bona for paintings in guise of the Virgin Mary and her son as Jesus, biblical figures and saints is confirmed by her effigies by Francesco Bissolo and Lucas Cranach. Such portraits were popular throughout Europe since the Middle Ages.
Examples include the effigy of Agnès Sorel, mistress of King Charles VII of France, as Madonna Lactans by Jean Fouquet from the 1450s, Giulia Farnese, mistress of Pope Alexander VI as the Virgin Mary ("la signora Giulia Farnese nel volto d'una Nostra Donna" according to Vasari) and his daughter Lucrezia Borgia as Saint Catherine by Pinturicchio from the 1490s, Mary of Burgundy in the guise of Mary Magdalene created in about 1500, Francis I of France as Saint John the Baptist by Jean Clouet from about 1518, Catherine of Austria, Queen of Portugal as Saint Catherine by Domingo Carvalho from about 1530, Albrecht Dürer's self-portraits as the Saviour or Leonardo's Salvator Mundi, possibly a self-portrait or effigies of his lover Salaì as Saint John the Baptist and numerous other. Marble tondos decorating Sigismund's Chapel at the Wawel Cathedral, created by Bartolommeo Berrecci between 1519-1533 as a funerary chapel for the last members of the Jagiellonian Dynasty, shows king Sigismund I the Old as biblical king Solomon and king David (or his banker Jan Boner). The print published in Nicolas Gueudeville's "Le grand theatre historique, ou nouvelle histoire universelle" in Leiden in 1703, after original drawing from 1548, depict king Sigismund I the Old on his deathbed giving a blessing to his sucessor Sigismund Augustus having long hair. In February 1556, Bona departed Poland to her native Italy trough Venice with treasures she had accumulated over 38 years loaded on 12 wagons, drawn by six horses. She udoubtedly took with her some religious paintings, portraits of members of the royal family and of her beloved son Augustus. She settled in Bari near Naples, inherited from her mother, where she arrived on 13 May 1556. Bona died just one year later on 19 November 1557, at the age of 63. She was poisoned by her courtier Gian Lorenzo Pappacoda, who falsified her last will and stole her treasures. The paining showing Christ as The Light of the World (Lux mundi) in the the National Gallery in London (a copy in the Accademia Carrara in Bergamo) bears a strong resemblance to known effigies of Sigismund Augustus. It was given to the National Gallery in 1901 by the heirs of the surgeon, who in turn was offered the painting by a member of the Embassy of the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies, formed when the Kingdom of Sicily merged with the Kingdom of Naples in 1816, in thanks for his kindness to a Sicilian lady in 1819. According to museum description "paintings of this type were kept in houses, especially in bedrooms", so has Bona had it at her deathbed in Bari? This convention of historié portrait was undoubtedly well known to the Queen through portraits of Lorenzo de' Medici (1492-1519), Duke of Urbino by Venetian painters, depicted as Christ the Redeemer of the World (Salvator Mundi). Some sacred images in Poland-Lithuania are also considered as effigies of the monarchs, like Our Lady of the Gate of Dawn in Vilnius, allegedly depicting Barbara Radziwill, mistress and later wife of Sigismund Augustus, or portrait of Queen Marie Casimire Sobieska (1641-1716) as Saint Barbara in the Bydgoszcz Cathedral. It is believed that the painting in Vilnius was commissioned as one of two paintings, one depicting Christ the Saviour (Salvator Mundi), and the other the Virgin Mary. Other versions and workshop copies of the painting in London are today in the Accademia Carrara in Bergamo (offered in 1908), legacy of Countess Maria Ricotti Caleppio, widow of the Ancona patrician Raimondo Ricotti who died in his villa in Rome, in the Abbey of San Benedetto in Polirone near Mantua, possibly from the Gonzaga collection, and in the Musée Rolin in Autun in France, transferred from the Louvre, most probably from the French royal collection. Another reduced variant (61 x 50.5 cm) from private collection was sold in New York (Sotheby's, November 2, 2000, Lot 68). It is therefore highly probable that effigies of the king of Poland in guise of the Saviour were sent to different royal and princely courts in Europe shortly after creation in Venetian workshop of Paris Bordone, to Rome, Mantua and France, among others. In one of the side altars of the Church of the Assumption in Kraśnik there is painting of Salvator Mundi by workshop of Paris Bordone from the mid-16th century. It is possible that it was offered to the temple by Stanisław Gabriel Tęczyński (1514-1561) or his son Jan Baptysta Tęczyński (1540-1563), owners of Kraśnik, and that it was originally given to one of them by the king.
Sigismund Augustus in guise of Christ as The Light of the World by Paris Bordone, 1548-1550, National Gallery, London.
Sigismund Augustus in guise of Christ as The Light of the World by Paris Bordone, 1548-1550, Accademia Carrara in Bergamo.
Sigismund Augustus in guise of Christ as The Light of the World by workshop of Paris Bordone, 1548-1550, Abbey of San Benedetto in Polirone.
Sigismund Augustus in guise of Christ the Saviour (Salvator Mundi) by workshop of Paris Bordone, 1548-1550, Private collection.
Christ as the Redeemer of the World (Salvator Mundi) by workshop of Paris Bordone, mid-16th century, Church of the Assumption in Kraśnik.
Portraits of Queen Barbara Radziwill by Cornelis van Cleve
In interwar Poland, attention was drawn to the similarity of the face of the Madonna of the Gate of Dawn, the prominent Christian icon of the Virgin Mary venerated in Vilnius, Lithuania, with the effigies of the noble Lithuanian lady Barbara Radziwill, who became Queen of Poland. This hypothesis was presented by Zbigniew Kuchowicz in his book "Images of unusual women of Old Poland in the 16th to 18th century" (Wizerunki niepospolitych niewiast staropolskich XVI-XVIII wieku), where he claimed that the fact of the similarity of the Madonna of Vilnius with the queen was noticed by Polish historians in Catholic circles. Juliusz Kłos, a professor at Vilnius University, wrote in a Vilnius guidebook that this painting could be classified as belonging to the Italian school of the mid-16th century, and he also saw a striking similarity of the face of the Virgin Mary with the portraits of Barbara Radziwill. The resemblance was also pointed out by priest Piotr Śledziewski, according to whom "the type of the Madonna of the Gate of Dawn is strikingly similar to the portrait of Queen Barbara Radziwill [...] The same nose, the same chin and mouth, the same eyes and eye edges, the same body structure". Ultimately, it was established that the painting was created not in the times when Barbara lived, but much later. However, this does not rule out the fact that its creator could have used one of the queen's portraits as an inspiration (after "Duchy Kresów Wschodnich" by Alicja Łukawska, p. 35).
The painting of Our Lady of the Gate of Dawn was probably painted in Vilnius in the 1620s by an unknown painter. Before the appearance of the chapel in 1671, this large painting (200 x 165 cm), painted on oak boards, hung in a small niche on the inside of the city gate. In the niche of the exterior wall of the gate, as a pair to the image of the Madonna, hung an image of Christ the Redeemer (Salvator Mundi), also painted on oak boards, now in the Church Heritage Museum in Vilnius (repainted in the 18th and late 19th centuries). The cult of the image of the Our Lady began after the disastrous Deluge, after 1655. According to some authors, the originals were works of the Flemish painter Maerten de Vos from the end of the 16th century, however, given the identification of the features of the Virgin, the original painting used to paint her face was made around the middle of the 16th century. The same face was used in another painting of the Madonna, now kept in the the convent of the Poor Clares in Kraków. This small painting was founded by Father Adam Opatowiusz (Opatowczyk or Opatovius, 1574-1647), canon of Kraków and seven times rector of the Academy of Kraków, doctor of philosophy (1598) and theology (1619), educated in Padua and Rome. He is depicted as a donor holding the Child's foot in the lower part of the painting, with Saint Francis of Assisi on the left, whose effigy, according to Michał Walicki, was inspired by the works of 13th-century Italian painters Margaritone d'Arezzo or Bonaventura Berlinghieri (after "Zloty widnokrąg", p. 107). The portrait of Opatowiusz with a Crucifix is also found in the same convent, so the effigy of Saint Francis was probably modeled on an imported medieval Italian painting. The image of the Virgin and sleeping Child of Opatowiusz is directly inspired by a painting now kept at the Royal château of Blois (oil on panel, 81.2 x 64.8 cm, inventory number 869.2.20, earlier IP 57). This painting, dated by experts to around 1550, comes from the collection of Pauline Fourès, née Marguerite-Pauline Bellisle, Madame de Ranchoup - the Countess of Ranchoup, as she liked to call her, lover of Napoleon Bonaparte, offered in 1869. It was originally attributed to Lambert Lombard and now to Cornelis van Cleve, who most likely painted the portrait of Queen Barbara in a red dress (Picker Art Gallery in Hamilton). Many copies of this painting exist. Good quality versions can be found at the Musée Magnin in Dijon (oil on panel, 81.5 x 66.6 cm, 1938E183) and at the Gemäldegalerie in Berlin (oil on panel, 80 x 65 cm, 653). Two other versions from private collections were sold in 2012 (oil on panel, 84 x 70 cm, Bonhams London, December 5, 2012, lot 86) and in 2020 (oil on panel, 95 x 76 cm, Sotheby's London, September 23, 2020, lot 33). In the latter painting, attributed to follower of Cornelis van Cleve, a marble column was added to the background. The style of this painting is closest to the nude portrait of Queen Barbara kept in the National Museum in Warsaw (M.Ob.2158 MNW), attributed to circle of Michiel Coxie. The face of the Madonna surprisingly resembles the effigies of Barbara Radziwill by Paris Bordone (Nivaagaard Museum in Nivå) and Giampietro Silvio (Palace of the Grand Dukes of Lithuania in Vilnius), identified by me. The Madonna of Opatowiusz also has a crown, just to underline her royal status. A similar Madonna can also be seen in a composition depicting the Adoration of the Magi by Cornelis van Cleve. Many such compositions were created by the painter and his workshop, but one of them, kept in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna (oil on panel, 125.1 x 96.1 cm, GG 1703), is very specific. It was painted in the manner of Cornelis van Cleve and signed with monogram CAVB. Very young age of Saint Joseph, who was usually depicted as an old man, and great similarity of the effigy of the kneeling Saint Melchior, the oldest of the Magi, with the effigy of King Sigismund I in a similar scene by Joos van Cleve (Gemäldegalerie Berlin), as well as others portraits of the king, notably as a donor by workshop of Michel Sittow (private collection) and Hans von Kulmbach (Gołuchów Castle), indicate that it is more of a political allegory than a religious scene. Although the old king, who died in 1548, before Barbara's coronation, condemned in a few letters the marriage of his son to his mistress, it is generally considered that he treated his daughter-in-law well, which is why Queen Bona, who later claimed that the scandal contributed to her husband's death, may have been the instigator of the mentioned letters. The three men surrounding Madonna-Barbara should therefore be identified as her brother Nicolaus "the Red" as Saint Joseph and her cousin Nicolaus "the Black" as Saint Caspar and King Sigismund I, wearing the Order of the Golden Fleece, as Saint Melchior and it is comparable to the similar scene with the disguised portrait of Emperor Frederick III by Joos van Cleve (National Museum in Poznań and Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden). The painting was evidenced in the gallery in 1783, so it could be a gift from the Radziwills to the emperor to sanction the marriage of Sigismund Augustus.
Portrait of Queen Barbara Radziwill as Madonna with sleeping Child by Cornelis van Cleve, ca. 1550, Royal château of Blois.
Portrait of Queen Barbara Radziwill as Madonna with sleeping Child by Cornelis van Cleve, ca. 1550, Musée Magnin in Dijon.
Portrait of Queen Barbara Radziwill as Madonna with sleeping Child by Cornelis van Cleve, ca. 1550, Private collection.
Portrait of Queen Barbara Radziwill as Madonna with sleeping Child by Cornelis van Cleve, ca. 1550, Gemäldegalerie in Berlin.
Portrait of Queen Barbara Radziwill as Madonna with sleeping Child by circle of Michiel Coxie, ca. 1550, Private collection.
Madonna with sleeping Child with Saint Francis of Assisi and Father Adam Opatowiusz by unknown painter, second quarter of the 17th century, Convent of the Poor Clares in Kraków.
Adoration of the Magi with portraits of Sigismund I, Barbara Radziwill, Nicolaus "the Black" and Nicolaus "the Red" Radziwill by Cornelis van Cleve, ca. 1550, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Portraits of Franciszek Krasiński and Piotr Dunin-Wolski by Lambert Sustris or workshop
Franciszek Krasiński, a nobleman of Ślepowron coat of arms, was born on April 10, 1525, probably in the village of Krasne in Masovia, north of Warsaw, in the family of Jan Andrzej Krasiński, Pantler of Ciechanów, and Katarzyna Mrokowska. He received his primary education at the Protestant gymnasium in Zgorzelec in Silesia (part of Bohemia), then studied under Philip Melanchthon at the University of Wittenberg, from where, on the advice of Bishop Mikołaj Dzierzgowski, he resigned. In 1541, he entered the University of Kraków, later went to Italy, where he studied at the University of Bologna, and on June 4, 1551, at the University of Rome, he became a doctor of both laws. After returning to Poland, he was most probaly ordained a priest and became a secretary of his distant relative, Primate Mikołaj Dzieżgowski, who helped him obtain several church benefits: the Kalisz archdeaconry and the canon of Łuck, Łowicz and Kraków. In 1560, Franciszek became the secretary of king Sigismund Augustus under the patronage of Primate Jan Przerębski. He performed diplomatic functions, in particular in Vienna, where he was an ambassador at the Imperial court between 1565-1568. He was later crown vice - chancellor between 1569-1574 and bishop of Kraków between 1572-1577. Being sick with tuberculosis, he often stayed in the castle of the Kraków Bishops in Bodzentyn. He died there on March 16, 1577 and according to his will, he was buried in the local church, where his marble tomb monument was created by Girolamo Canavesi's workshop in Kraków.
Facial features of a man wearing an elaborately embroidered doublet and a fur-trimmed black cape in a portrait attributed to Lambert Sustris are very similar to known effigies of Franciszek Krasiński, especially to his portrait by anonymous painter which was before World War II in the collection of Ludwika Czartoryska née Krasińska in Krasne, lost. Also the pose is very similar. The painting in Krasne was dated in upper right corner Ao 1576, however, it might possibly be a later addition as on this portrait he is much younger then on other known effigies (e.g. portrait in the Franciscan Monastery in Kraków from about 1572). The painting attributed to Sustris was sold in New York in 1989 and was painted on panel. According to inscription in Latin in lower right corner, the man was 25 years old in 1550 (.ET TATIS SVE../.ANNVS./.XXV./.P./MDL), exactly as Franciszek Krasiński, when he studied in Bologna and Rome. At the Colonna Gallery in Rome there is a portrait of a man holding gloves (oil on canvas, 88 x 65 cm, inventory number Fid. n. 1477), who also resemble greatly Franciszek Krasiński from the portrait in Krasne and described effigy attributed to Sustris. It was earlier attributed to Lorenzo Lotto, Nicolas Neufchatel or Dirck Barendsz (rejected attributions) and now to anonymous painter from the Southern Netherlands. Previous attributions and style of this painting match perfectly paintings by Sustris, a Dutch painter who worked in Titian's studio and incorporated Italian Renaissance elements in his work. The costume of the man and the style is also very similar to the painting dated 1550. The date when Krasiński was ordained a priest is unknown. He was a canon of Gniezno from 1556, however, like Copernicus or Jan Dantyszek, he might not have been ordained a priest. The sitter's costume and pose can be compared with effigies of Antoine Perrenot de Granvelle (1517-1586), a leading minister of the Spanish Habsburgs, who become a canon of Besançon and prothonotary Apostolic in 1529, when he was only 12 years old, later, in November 1538, aged only twenty-one, he was appointed bishop of Arras and took holy orders two years later (after "Les Granvelle et les anciens Pays-Bas" by Krista de Jonge, Gustaaf Janssens, p. 20). Granvelle also became the archbishop of Malines (1560) and a cardinal (1561), yet in majority of his portraits, like the one created by Frans Floris in about 1541, with blue eyes, by Titian in 1548, by Antonis Mor in 1549 and in about 1560, by Lambertus Suavius in 1556, all with dark eyes, there is no explicit reference to his priesthood. A number of preserved portraits of Polish-Lithuanian "princes of the Church" are official effigies dedicated to churches, where the patron was depicted in pontifical vestments. In private images, they could allow themselves, like Granvelle, to be depicted in less formal attire, more typical of a nobleman than a priest. According to Latin inscription at upper left, the man was 37 years old in 1562 (A° 1562 / AETATIS. 37), exacly as royal secretary Franciszek Krasiński. He could have ordered this likeness in Venice and then send it to Rome, although it is also possible that in 1562 he was in Italy. Another portrait attributed to Lambert Sustris or his workshop shows a bearded man in black costume with a black hat, holiding a book and seated in a chair. This painting was sold in London in 2005. It bears inscription and date Roma Ano 1564 Etatis Mae 33 (Rome Year 1564 of My Age 33) above the man's head, as well as three other inscriptions in Greek (or Armenian), Hebrew and Italian. The inscription in Italian Non ognuno che mi dice signor / Signore entrata nel regno de cieli: / ma colui che fa la volunta del / padre mio che e ne' cieli (Not everyone who says to me, Lord, Lord, will enter the kingdom of heaven, but only the one who does the will of my Father who is in heaven) are verses of the seventh chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament, part of the Sermon on the Mount, on True and False Disciples. The age of a man match perfectly the age of Piotr Dunin-Wolski (1531-1590), the son of Paweł Dunin-Wolski, Great Crown Chancellor, and Dorota Wiewiecka of Jastrzębiec coat of arms, who after his initial studies at the Lubrański Academy in Poznań went to Bologna and Padua to complete his studies. In Bologna in 1554 he is mentioned as a student of Sebastiano Corrado (Sebastianus Corradus), professor of Greek and Latin, who translated Plato into Latin. He was a canon of Poznań since 1545 and after returning from Italy, he stayed at the court of king Sigismund Augustus, where he proved to be a man especially gifted in foreign languages and in diplomacy. He was threfore sent to Madrid in Spain in 1560 where he stayed for more than 10 years, trying to regain the so-called Neapolitan sums for the king. His stay in Rome in 1564 is not mentioned in the sources, however his letters from Barcelona of March 4 to cardinal Stanisław Hozjusz and from Madrid of September 23 to bishop Marcin Kromer might indicate such journey. He returned to Poland in 1573. He was a collector of antiquities and collected a large library, which he donated to the Kraków Academy (approx. 1000 volumes) and the library of the Płock Chapter (130 books). Dunin-Wolski died in Płock on August 20, 1590 and was buried in the cathedral church, where his tombstone has been preserved to this day as well as a portrait. This effigy, created after his death in the 17th or 18th century by a local painter, was undeniably copied from another effigy of the Bishop of Płock (since 1577), and it is astonishingly similar to the described painting by Sustris or his workshop.
Portrait of Franciszek Krasiński (1525-1577), aged 25, in embroidered doublet by Lambert Sustris, 1550, Private collection.
Portrait of royal secretary Franciszek Krasiński (1525-1577), aged 37, holding gloves by Lambert Sustris, 1562, Colonna Gallery in Rome.
Portrait of canon Piotr Dunin-Wolski (1531-1590), aged 33 by Lambert Sustris or workshop, 1564, Private collection.
Portraits of Queen Barbara Radziwill and her father by workshop of Paris Bordone
"They say that Queen Bona, who previously cared little about divine things, is beginning to be attracted to innovations in religion. Because she is reading Italian books by a certain Bernardino Ochino, once a monk in Italy and the founder of the new Capuchin Congregation, but who changed his faith and now teaches in England. They assure that she would like to bring in a similar type of teachers, i.e. preachers. A strange change in this woman's mind! She was also reconciled with Queen Barbara. Through her envoy and her confessor, Franciszek Lismaninus of Corcyra [Francesco Lismanini of Corfu], Bona called Barbara her most beloved daughter-in-law, recommended herself and her daughters to her in the most flattering terms and sent small gifts. Many claim that she did it deceitfully, not for Barbara's sake, but to enslave the king her son, who is so attached to his wife that he hates those who persecute her with hatred, and that it was all the easier for her because she knew that Queen Barbara will not live long. Queen Bona's confessor himself, whom I mentioned above, solemnly assured me that this consent was real and a divine decree. And that is a noteworthy mind shift", reported in a letter of March 9, 1551, Doctor Johannes Lang, envoy of King Ferdinand I of Austria.
This letter illustrates not only the family relationships within the Jagiellonian dynasty around the mid-16th century, but also the popularity of Italian culture and new ideas and trends at the royal court. In an earlier letter dated January 4, 1551 from Świdnica (Swidniciae) to the king, Doctor Lang adds about religious reforms in Poland-Lithuania: "I have already written to Your Royal Majesty about a marriage concluded by a priest in Pinczów, a town fourteen miles away from Kraków. Now they tell me that a new liturgy has been introduced there after the expulsion of the monks; they sing the mass in Polish and condemn communion under one species in the Eucharist. Strange crowds of nobility come there, brazenly trampling on old church rites. As far as I can predict, I see that, despite the opposition of some men, Poland will forcibly obtain priestly marriage and communion under both kinds. There will be a strange change in church things there" (after "Jagiellonki polskie ..." by Aleksander Przezdziecki, Volume 5, pp. LXVIII-LXX). At Knole House, Kent, England, there is another portrait of an unknown lady, called Mary, Queen of Scots, three-quarter length (oil on canvas, 107 x 89 cm, NT 129951), similar to the so-called Carleton portrait at Chatsworth House. The young woman wears an ivory dress embroidered in gold with blue undersleeves. Her hair is decorated with pearls and red carnation flowers, symbols of love and passion. Due to earlier identification, the portrait is attributed to the French or Flemish school. In the 18th and 19th centuries the romantic legend and tragic death of the Queen of Scots contributed to this phenomenon and even the daughter of Mary's adversary - Sir Francis Walsingham (died 1590), Frances Walsingham (1567-1633), Lady Sidney became Mary, Queen of Scots. Possibly in the 19th century the inscription on the small trompe l'oeil label, or cartellino, visible in the upper left corner, in a fine portrait of Frances attributed to Robert Peake (Fine Arts Museums of San Francisco, 1954.75), was changed to Latin: MARIA REGINA SCOTIAE. Using new technology, restorers discovered the original lettering: "The Ladie Sidney daughter to Secretarye Walsingham" (after "Who's That Lady? ..." by Elise Effmann Clifford). Similar was the case with the portrait of Princess Sophia Jagiellon (1522-1575) in Spanish costume (Czartoryski Museum, MNK XII-296) or portrait of Cardinal John Albert Vasa (1612-1634) by Venetian school (most probably Tommaso Dolabella, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw, Wil.1240), which, according to a later inscription depict Cardinal Andrew Bathory (1562-1599). The lady's features resemble those in the Carleton portrait and miniature of Queen Barbara by workshop of Lucas Cranach the Younger (Czartoryski Museum, MNK IV-V-1433), as well as other portraits of the queen. The style of this painting resembles the full-length effigy of Queen Barbara's father - George Radziwill (1480-1541), nicknamed "Hercules" in the National Art Museum of Belarus in Minsk (oil on canvas, 210 x 122 cm). It can be compared to the portraits of Sigismund Augustus in the guise of Christ as Light of the World produced by the workshop of Paris Bordone (Accademia Carrara in Bergamo and Abbey of San Benedetto in Polirone) as well as to the double portrait, attributed to Bordone (Nivaagaard Museum, 0009NMK) and portrait of a man in Paris (Louvre, INV 126; MR 74). According to the Latin inscription in the upper left corner, George Radziwill was painted in 1541 at the age of 55 (GEORGIVS RADZIWIL CASTELLANVS VILENSIS [...] AÑO DNI. M.D.XXXXI. ÆTATIS VERO SVÆ LV.). The inventory of paintings from the collection of Princess Louise Charlotte Radziwill (1667-1695), drawn up in 1671, lists some of the effigies that survived the Deluge (1655-1660). Among these portraits, many were made in 1550, such as Nicolaus Radziwil Cognomento, 2dus Dux in Gonidz Palatinus Vilne[n]sis Cancelarius M.D.L. (1), Georius Radziwił Castelanus Vilnens. Gnalis dux Exercitum M.D.L. (9), Joanes Radziwił Dux in Muszniki Archicamer. M.D.L. (15) and Nicolaus Radziwił Dux Birzarum et Dubincorum, Palaitinus Vilnen. Gnalis Dux Exercitum M.D.L. (21). The creation of such a gallery of ancestors and other family members was probably linked to the coronation of Queen Barbara on December 7, 1550.
Portrait of Queen Barbara Radziwill by workshop of Paris Bordone, ca. 1549-1551, Knole House.
Portrait of George "Hercules" Radziwill, castellan of Vilnius by workshop of Paris Bordone, ca. 1549-1551, National Art Museum of Belarus in Minsk.
Portraits of Sophia Jagiellon in Spanish costume
Daughters of Bona Sforza d'Aragona, Queen of Poland, Grand Duchess of Lithuania and Duchess of Bari and Rossano by her own right were descendants of Alfonso V, King of Aragon, Sicily and Naples.
Contacts with Spain intensified after 1550. In 1550 and 1553, Gian Lorenzo Pappacoda (1541-1576), a courtier of Queen Bona, was sent to the emperor with unknown instructions given to him by the queen. In March 1554, he also went to London and Brussels. Pappacoda's task was to convince the emperor and king of Spain to intervene on Bona's behalf at the court of Sigismund Augustus in order to facilitate her leaving Poland, and to obtain for her the position of viceroy of Naples, vacant since 1553 after the death of Pedro Álvarez de Toledo y Zúñiga (after "Odrodzenie i reformacja w Polsce", Volume 44, p. 201). In a letter dated May 11, 1550 from Valladolid, Juan Alonso de Gámiz, secretary of Charles V, informed King Ferdinand I of the arrival of the "secretary of the King of Poland with letters and gifts" (secretario del rey de Polonia con letras y presentes para sus altezas), including six horses with velvet tacks richly embroidered with royal emblems (seys cavallos portantes concubiertas de terciopelo morado y la devisa del rey bordada), as well as sable, ermine and wolf pelts for the king and queen (after "Urkunden und Regesten ..." by Hans von Voltelini, p. L-LI). The portrait of a blond lady in Spanish costume from the 1550s which exists in a number of copies, although idealized, bears a strong resemblance to the portrait of Sophia in French/German costume in Kassel by circle of Titian and her miniature in German/Polish dress by Cranach. At least two paintings are preserved in Poland (one in Kraków and the other in Warsaw) and one of inferior quality, most probably lost during World War II, was traditionally identified as Sophia (also similar to the very idealized portrait of Barbara Radziwill at the Musée Condé, known as "Anne Boleyn", inventory number PE 564). The Kraków painting was purchased between 1789 and 1791 by Princess Izabela Czartoryska in Edinburgh as a portrait of Mary, Queen of Scots, hence the inscription in French: MARIE STUART REYNE D'ESCOSSE, added in the 17th or 18th century (Czartoryski Museum, oil on panel, 22 x 17 cm, MNK XII-296). An almost exact copy of this effigy, attributed to circle of Jean Clouet, was sold in Zurich in 2011 (oil on panel, 23.3 x 18.2 cm, sold at Koller Auctions, April 1, 2011, lot 3012). The Warsaw version is slightly different and was purchased in 1972 from the Radziwill collection (National Museum in Warsaw, oil on panel, 24.5 x 19 cm, M.Ob.654). After marriage of Isabella Jagiellon in 1539, Sophia was the eldest daughter of Bona still unmarried. Three of Bona's younger daughters dressed identically, as evidenced by their miniatures by workshop of Lucas Cranach the Younger from about 1553 and inventory of dowry of the youngest Catherine includes many Spanish garments, like a black velvet coat with "53 Spanish buckles of 270 thalers worth", "buckles on (thirteen) French and Spanish robes", or "a robe of black velvet at the throat in Spanish style" with 198 buckles, etc. The fashion was udobtedly used in complex Jagiellonian politics and the portraits could be commissioned in the Spanish Netherlands and Italy. A portrait from the private collection in Sweden (oil on panel, 26 x 19 cm, sold at Metropol Auktioner in Stockholm, January 26, 2015, nr 938 5124), possibly taken from Poland-Lithuania during the Deluge (1655-1660), and created by the same workshop, showns Sophia in similar Spanish/French costume.
Portrait of Sophia Jagiellon (1522-1575) in Spanish costume by Flemish painter, 1550-1556, Czartoryski Museum in Kraków.
Portrait of Sophia Jagiellon (1522-1575) in Spanish costume by Flemish painter, 1550-1556, Private collection.
Portrait of Sophia Jagiellon (1522-1575) in Spanish costume by Flemish or Italian painter, 1550-1556, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Sophia Jagiellon (1522-1575) in Spanish/French costume by Flemish painter, 1550-1556, Private collection.
Portraits of Sigismund Augustus and Catherine of Austria as Adam and Eve from the Paradise Bliss tapestry
"Adam and Eve, the parents of calamity, stood both painted according to true image and the word all over the tapestries woven with gold. And since those portraits of the first parents, in addition to the other things to be seen, were of admirable material and workmanship, I will show them like Cebetis, so that from thence the work itself of an excellent artist, as well as the genius of the best king, may be perceived [...]. In the first tapestry, at the head of the nuptial bed, we saw the bliss in the faces of our parents; in which, when they were happy, they were not ashamed to be naked. Moreover, the nakedness of both of them so moved the spirits, especially that of Eve's husband, that lascivious girls would smile at Adam as they entered. For when the man's womb was opened, the sex of a woman is fulfilled" (calamitatis parentes Adam et Eva ad effigiem veritatis stabant textu picti ambo per omnes Cortinas, auro praetextati. Et quoniam illae primorum parentum effigies praeter caeteras res visendas, admirabili fuerunt materia et opere, eas ad Cebetis instar demonstrabo, ut inde cum opus ipsum praeclari artificis, tum vero ingenium optimi regis pernoscatis [...]. In prima Cortina, ad caput genialis lecti, parentum nostrorum contextu expressa felicitatis cernebatur effigies; in qua felices illi cum essent, non erubescebant nudi. Porro utriusque nuditas ita commovebat animos, ut viri Evae, Adamo vero lascivae introingressae arriderent puellae. Aperta enim pube ille viri, haec foeminae sexum sinu ostendebant pleno), thus praises the veracity of effigies of the figures of Adam and Eve in the tapestry commissioned by king Sigismund II Augustus, Stanisław Orzechowski (1513-1566) in his "Nuptial Panegyric of Sigismund Augustus, King of Poland" (Panagyricus Nuptiarum Sigimundi Augusti Poloniae Regis), published in Kraków in 1553.
Orzechowski (Stanislao Orichovio Roxolano or Stanislaus Orichovius Ruthenus), a Ruthenian Catholic priest, born in or near Przemyśl, educated in Kraków, Vienna, Wittenberg, Padua, Bologna, Rome and Venice and married to a noblewoman Magdalena Chełmska, described the festivities and decorations of the Wawel Royal Castle in Kraków during king's wedding celebrated on July 30, 1553. The bride was a sister of Sigismund Augustus first wife and widow of the Duke of Mantua, Catherine of Austria, daughter of Anna Jagellonica (1503-1547). Wedding chambers were adorned with tapestries from the series of the Story of Adam and Eve, created in Brussels by workshop of Jan de Kempeneer after cartoons by Michiel I Coxcie, most probably on this occasion, including the described Paradise Bliss. The author emphasizes that they were depicted naked, while both Eve and Adam's womb on this tapestry are today covered with vine branches. "A closer look at the technique of the fabric in these places reveals that the vine covering Eve's womb, and the other vine covering Adam's womb, are woven or embroidered separately and applied to the fabric itself", states Mieczysław Gębarowicz and Tadeusz Mańkowski in their publication from 1937 ("Arasy Zygmunta Agusta", p. 23). Vine branches were probably added in 1670 when the tapestry was transported to Jasna Góra Monastery for the wedding of king Michael Korybut Wiśniowiecki. Another intriguing aspect is the veracity of the images so underlined by Orzechowski. It is about the true image of the legendary first parents, a woman and a man or, most likely, the bride and groom? Adam's facial features are very reminiscent of images of king Sigismund Augustus, especially the portrait by Jan van Calcar against the Mausoleum of Empeor Augustus in Rome (private collection), while the face of Eve is very similar to that of Queen Catherine of Austria, depicted as Venus with the lute player by Titian (Metropolitan Museum of Art). These two effigies can be compared to the naked effigies of French monarchs from their tombs in the Basilica of Saint-Denis - tomb of Louis XII and Anne of Brittany (1515-1531), tomb of Francis I and Claude of France (1548-1570), and especially the tomb of Henry II and Catherine de' Medici (1560-1573), all inspired by Italian art.
Portrait of King Sigismund Augustus (1520-1572) as Adam from the Paradise Bliss tapestry by workshop of Jan de Kempeneer after design by Michiel I Coxcie, ca. 1553, Wawel Royal Castle.
Portrait of Queen Catherine of Austria (1533-1572) as Eve from the Paradise Bliss tapestry by workshop of Jan de Kempeneer after design by Michiel I Coxcie, ca. 1553, Wawel Royal Castle.
Tapestry with Paradise Bliss by workshop of Jan de Kempeneer after design by Michiel I Coxcie, ca. 1553, Wawel Royal Castle.
Portraits of Sophia Jagiellon and Catherine of Austria by Titian and workshop
"My heart moves me to tell of forms changed into new bodies" (In nova fert animus mutatas dicere formas corpora), states Ovid in the opening lines of his "Metamorphoses" (Transformations). If gods could turn into humans, why humans (and especially royals) could not turn into gods? At least in paintings.
When in June 1553 Sigismund II Augustus married his distant cousin Catherine of Austria, widowed duchess of Mantua, his three younger sisters Sophia, Anna and Catherine were not married. At the same time Catherine's cousin, Philip of Spain (1527-1598), Duke of Milan from 1540, son of Emperor Charles V, was unmarried after death of his first wife Maria Manuela (1527-1545), Princess of Portugal. Philip undeniably received a portrait of his distant relative Princess Sophia Jagiellon (1522-1575), the eldest of Bona Sforza's daughters, unmarried at that time. At the end of 1553 Philip's wedding to his second aunt, the Queen of England, Mary I (1516-1558), was announced. It turned out, however, that Philip was only a duke and there could be no marriage between the queen and someone of lower rank. Charles V solved the inconvenience by renouncing the Kingdom of Naples in favor of his son, so that he would be king. On July 25, 1554 Philip married the Queen of England. Painting of Salome with the head of John the Baptist by Titian in the Prado Museum in Madrid is dated to about 1550. Many authors underline an erotic dimension of the scene. The work was inventoried as part of the royal collection in the Alcazar of Madrid between 1666 and 1734, possibly acquired from the collection of the 1st Marquess of Leganés, between 1652-1655, who probaly bought it at the auction of collection Charles I of England. According to other sources "Salome, by Titian, painted around 1550, appears in an early inventory of the Lerma collection. In 1623 Philip IV gave it to the Prince of Wales, later Charles of England" (after "Enciclopedia del Museo del Prado", Volume 3, p. 805). Titian's workshop created several replicas of this painting transforming Salome into a girl holding a tray of fruit, most probably representing Pomona, a goddess of fruitful abundance and the wife of the god Vertumnus (Voltumnus), the supreme god of the Etruscan pantheon. According to Ovid's "Metamorphoses" (XIV), Vertumnus, after several unsuccessful advances, tricked Pomona into talking to him by disguising himself as an old woman and gaining entry to her orchard. The best version of this painting, acquired in 1832 from the Abate Luigi Celotti collection in Florence, is today in the Gemäldegalerie in Berlin. In both paintings the girl is wearing a rich jewelled tiara, so she is definitely a princess and the main fruit on her tray is a quince (or Cydonian apple), similar to that visible in watercolour paintings by Joris Hoefnagel from about 1595, one with Venus disarming Amor (National Gallery of Denmark), or less probably a lemon, a symbol of fidelity in love associated with Virgin Mary. A yellow lemon- or pear-shaped fruit, evocative of the female body, was sacred to Venus, herself often represented holding it in her right hand, as being the emblem of love, happiness, and faithfulness. "Both the Greeks and Romans used quince boughs and fruit to decorate the nuptial bedchamber. The fruit became an integral part of marriage ceremonies with the bride and groom partaking of honeyed quince. Eating the fruit was symbolic of consummating the marriage" (after Sandra Kynes' "Tree Magic: Connecting with the Spirit & Wisdom of Trees"). According to Columella (4 - ca. 70 AD), a prominent writer on agriculture in the Roman Empire, "Quinces not only yield pleasure, but health". "Romans would serve quince to their loved ones to encourage fidelity and those newly married would share a quince to ensure a happy marriage" (after Rachel Patterson's "A Kitchen Witch's World of Magical Food"). Around that time Titian's workshop created another version of this composition, which was before 1916 in the Volpi collection in Florence (hence both Pomonas were possibly initially in the Medici collection). The woman's face and pose is identical as in the Raczyński Herodias, which is the effigy of Queen Catherine of Austria. The face of the princess in the Prado painting bears great resemblance to effigies of Princess Sophia Jagiellon by Cranach and in Spanish costume by Flemish painter. Some of the copies of this Salome and Pomona were created by Titian's workshop, such as the Knebworth House copy, sold in 2003, or a reduced version, sold in 2020 (Bonhams London, October 21, 2020, lot 3), which also indicate that she was an important person. In another variant of Salome/Pomona by Titian's studio, the princess "metamorphoses" into another femme fatale - Pandora, now holding a rich jewelled box on her tray, like in later paintings by James Smetham (ca. 1865), Dante Gabriel Rossetti (1871), John William Waterhouse (1896) or Odilon Redon (1910/1912). Pandora was to be created by Hephaestus (Vulcan) on the order of Zeus (Jupiter), as the first human woman, to whom each of the gods gave some special gifts - Athena (Minerva) gave her intelligence, talent and manners and Aphrodite (Venus), beauty of a goddess, and she was also given a box containing all the evils that could afflict humanity, with a warning never to open it. In modern times, Pandora and her vessel have become, among other things, a symbol of the seductive power of women. This painting, from the French royal collection, mentioned among the paintings of Philippe II, Duke of Orléans (1674-1723), who was regent of the kingdom of France from 1715 to 1723, is today in a private collection in Milan. In the 19th and 20th centuries, many paintings returned to their place of origin, although this does not at all mean that the model was Italian (however, it is worth mentioning that through her mother, Princess Sophia was Italian). The fingers of her right hand, originally supporting larger tray in initial version (Salome) in this painting of Pandora, are eerily raised so that the girl is holding a heavy silver tray and a much heavier casket just by part of her hand. This is another proof that the painting was not taken from life, but based on study drawings sent from Poland-Lithuania, and it cannot be Titian's daughter posing for it, otherwise she would hurt herself holding these heavy objects like that. A version of a painting entitled "A Useless Moral Lesson" (allegorical subject of the loss of virginity and dangers of love) by Godfried Schalcken from 1690 (Mauritshuis) was sold in the United Kingdom in December 2020 as Pandora. Some copies of the painting by Titian's studio were sold as "Pandora's Box" (Manner of Guido Reni, 2014 and British School, 19th century, 2010) and Helena Tekla Lubomirska née Ossolińska (d. 1687), daughter of Chancellor Jerzy Ossoliński (1595-1650) was depicted in guise of Pandora, holding a bronze vase bearing the Lubomirski coat of arms - Szreniawa and inscription in Italian SPENTO E IE [IL] LUME / NON L'ADORE (the light is out, not the ardor), which is a paraphrase of a line from the poem Adone ("Adonis", 1623) by Giambattista Marino (attributed to Claude Callot and circle, National Museum and Wilanów Palace in Warsaw). Helena Tekla particularly liked different disguises in her effigies. In her portrait by Nicolas Mignard, thus ordered and created in France, she is depicted as Flora, Roman goddess of flowers and spring (inscribed on verso: Capitane Lubomirski / par Nic. Mignard., National Museum in Warsaw, M.Ob.1253 MNW) and inventory of Wiśnicz Castle from 1661 lists "a portrait of Her Highness, in the guise of Saint Helena" and "a full-length portrait of Her Highness, in the guise of Diana with greyhounds". Wanda Drecka interprets this representation of the widowed Princess Lubomirska "as the guardian of all virtues or Pandora who gives everything" (after "Dwa portrety księżnej na Wiśniczu", p. 386). It was not just a 17th century invention and such representations were known much earlier (Pandora from the French royal collection was considered to be the portrait of Titian's daughter Lavinia), also in Poland-Lithuania where Italian influences were so strong in the 16th century. Unfortunately, in Poland-Lithuania, the losses of cultural heritage during the Deluge (1655-1660) and the subsequent invasions were so great that everything was forgotten.
Portrait of Princess Sophia Jagiellon (1522-1575) as Salome by Titian, 1550-1553, Prado Museum in Madrid.
Portrait of Princess Sophia Jagiellon (1522-1575) as Pomona by workshop of Titian, 1550-1553, Gemäldegalerie in Berlin.
Portrait of Princess Sophia Jagiellon (1522-1575) as Pandora by workshop of Titian, 1550-1553, Private collection.
Portrait of Princess Sophia Jagiellon (1522-1575) by follower of Titian, after 1553, Private collection.
Portrait of Queen Catherine of Austria (1533-1572) as Pomona by workshop of Titian, 1553-1565, Private collection.
Allegorical portraits of Queen Catherine of Austria by workshop of Titian
Another version of the Pomona in Berlin by workshop of Titian was before 1970 in private collection in Vienna, Austria (oil on canvas, 99 × 82.5 cm), however, her facial features are slightly different, the face is more elongated and the lower lip is more protruding, as in most of the portraits of Catherine of Austria's relatives in Vienna. Her features are very similar to Saint Catherine of Alexandria in the Prado (inventory number P000447) and in the Raczyński Herodias. The same face and pose was copied in a painting of a nymph and a satyr which was before 1889 in James E. Scripps collection in Detroit (oil on canvas, 99 × 80.6 cm), attributed to follower of Titian, possibly by his student Girolamo Dente. The nymph playfully tugs at the ear of the satyr, who probably has the features of a court dwarf. Satyrs were nature deities and part of Bacchus's retinue. They were considered symbols of natural fertility or virility and were frequently portrayed chasing nymphs, symbolizing chastity.
Similar paintings were in royal and magnate collections in Poland-Lithuania. Inventory of the Kunstkammer of the Radziwill Castle in Lubcha from 1647 lists a painting of a "Naked lady with a satyr" offered by king John II Casimir Vasa and in 1633 a painting of "Diana with her maidens, the fauns laugh at" presented by his predecessor Ladislaus IV (after "Galerie obrazów i "Gabinety Sztuki" Radziwiłłów w XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska, p. 96). Inventory of paintings from the collection of princess Louise Charlotte Radziwill (1667-1695), drawn up in 1671, lists many nude and erotic paintings, some of which may be works by Titian: A lady half naked in sables (297, possibly a copy of a Girl in a fur by Titian in Vienna), Naked woman sleeps and two men watch (351), A naked woman sleeps and a lute and a flask with a drink is beside her and a man watches (370), A filthy image, Cupids and many naked people (371), Bacchanalia (372), Adonis wrestle with Venus (374, possibly a copy of Venus and Adonis by Titian in Madrid), A lady in flowers (375) and A lady with flowers (419, possibly a copy of Flora by Titian in Florence), Two naked women, one combs herself (420), A woman lying holding a glass, a man in front of her and Cupid embracing her (430), Three nymphs and Cupid (431), Two pictures on silver plates, one of Cupid with Venus, and the other with lustitia (628-629), Venus between two Cupids. A special image (762, most likely a painting from Bernardino Luini's workshop in the Wilanów Palace or a copy), A woman, naked, covered herself with cotton cloth, on a large panel (794, possibly a copy of a portrait of Beatrice of Naples as Venus by Lorenzo Costa in Budapest), Susanna and two old men, a large painting on canvas (815), Picture: a naked lady is sleeping and a satyr is next to her, this painting was given by King John Casimir (820), Three nymphs and Cupid (826), A lady with satyr, filthy (842), A lady lying. Small painting, golden frames (843), Naked lady with a swan, stone painting (844, possibly Leda by Alessandro Turchi, a pupil of Carlo Cagliari in Venice), A naked person in a red coat (863, possibly a copy of "Titian's Mistress" in Apsley House) (after "Inwentarz galerii obrazów Radziwiłłów z XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska). The inventory also includes several paintings which could be identified as Lucretia or Salome by Cranach and this is only a part of splendid collections of the Radziwlls that survived the Deluge (1655-1660). "The Goddess Diana with the God Pan / That chaste breast, which perpetually / Had made itself a shelter of modesty / And fled the consortium of people / To avoid some illicit act" (la Dea Diana col Dio Pan / Quel casto petto, che perpetuamente / S'era di pudicitia albergo fatto / E fuggiva il consortio de la gente / Per non venir a qualche illecito atto) is the inscription in Italian under an erotic (even obscene by some standards) print with Jupiter transformed into Satyr and Diana from the series of 15 sheets depicting the Loves of the gods (Gli amori degli dei). The version in the National Gallery of Denmark (Statens Museum for Kunst) in Copenhagen is attributed to Jacopo Caraglio, court goldsmith and medallist of King Sigismund II Augustus (inventory number KKSgb7584). Between 1527 and 1537 Caraglio was in Venice and from about 1539 in Poland-Lithuania, where he worked until his death on August 26, 1565.
Portrait of Queen Catherine of Austria (1533-1572) as Pomona by workshop of Titian, 1553-1565, Private collection.
Portrait of Queen Catherine of Austria (1533-1572) as a nymph with a satyr by follower of Titian, possibly Girolamo Dente, 1553-1565, Private collection.
Erotic print with Jupiter transformed into Satyr and Diana by Jacopo Caraglio, second quarter of the 16th century, National Gallery of Denmark.
Portrait of Sophia Jagiellon by circle of Titian
The portrait of Sophia Jagiellon (1522-1575), Duchess of Brunswick-Lüneburg from the Von Borcke Palace in Starogard, which was lost during World War II, was most probably the only signed effigy showing her features the most accurately. It bears a strong resemblance to the features of a lady by a Venetian painter from the circle of Titian in Kassel.
The portrait in Kassel is tentatively identified as effigy of Sophia's cousin Archduchess Eleanor of Austria (1534-1594), Duchess of Mantua (daughter of Anna Jagellonica, Queen of Germany, Bohemia, and Hungary), and a wife of Guglielmo Gonzaga, due to great similarity of garments and location, the Gonzagas of Mantua frequently commissioned their effigies in nearby Venice. However the face lacks an important feature, the notorious habsburg lip, allegedly stemming from Cymburgis of Masovia, a hallmark of prestige in the 16th century and inherited by Eleanor from her father, the Holy Roman Emperor Ferdinand I. The sitter's costume and features are very similar to these visible in a miniature showing Sophia's mother Bona Sforza (in the Czartoryski Museum in Kraków), who visited Venice in 1556, the year of Sophia's marriage with the 66-year-old Duke Henry V of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel. It is highly possible that the painting was commissioned in Venice by Sophia's brother, king Sigismund II Augustus or her mother. In the same collection in Kassel, there are also two other portraits from the same period by Venetian painters, which are linked to Jagiellons, a portrait of Sophia's sister Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596) and a portrait of a general, which according to Iryna Lavrovskaya, could be an effigy of influential cousin of Barbara Radziwill (second wife of Sophia's brother), Nicholas "The Black" Radziwill (Heritage, N. 2, 1993. pp. 82-84). The marriage of a 34-year-old princess with an old man was mocked in a painting, created by workshop or follower of Lucas Cranach the Elder, preserved in the National Gallery in Prague. The work was acquired in 1945 from the Nostitz picture collection in Prague (first probable record 1738, definite record 1818). The painter used earlier effigies of the Princess in the popular subject of the "grotesque marriage", dating back to antiquity when Plautus, a Roman comic poet from the 3rd century BC, cautioned elderly men against courting younger ladies. The inscription SMVST.A. on her bonnet should be therefore interpreted as a satirical anagram.
Portrait of Sophia Jagiellon (1522-1575) in a black dress by circle of Titian, ca. 1553-1565, Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Kassel.
Portrait of Sophia Jagiellon (1522-1575) in black dress by circle of Titian, most probably Lambert Sustris, ca. 1553-1565, Memphis Brooks Museum of Art.
Ill-Matched Lovers, caricature of Sophia Jagiellon (1522-1575) and her husband Henry V of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel (1489-1568) by follower of Lucas Cranach the Elder, ca. 1556, National Gallery in Prague.
Portraits of Zofia Tarnowska by Lambert Sustris and workshop of Titian
On January 18, 1553 the Sejm began in Kraków, but the proceedings were suspended immediately, as most of the deputies and senators went to Tarnów for the wedding of the nineteen-year-old daughter of Voivode of Kraków and Grand Hetman of the Crown. Zofia Tarnowska (1534-1570), the only daughter of Jan Amor Tarnowski and Zofia Szydłowiecka was marrying Constantine Vasily (1526-1608), son of Constantine, Prince of Ostroh and his wife Alexandra Olelkovich-Slutska.
In 1550, the twenty-five-year-old Constantine Vasily received from King Sigismund II Augustus the office of marshal of Volhynia. A year later he participated in the fight against the Tatars, who burned down the town and the castle in Bratslav, and probably met the Grand Hetman, Jan Amor Tarnowski, who came to the city with Polish reinforcements. Since the groom was Orthodox and the bride Catholic, the couple was blessed by priests of both rites. The celebrations must have been very impressive since Tarnowski borrowed 10,000 Hungarian zlotys from Queen Bona for this occasion or the wedding of his son just two years later. Emericus Colosvarinus (Imre Kolozsvár) from Cluj-Napoca, wrote a special speech, entitled De Tarnoviensibus nuptiis oratio, published in Kraków (he also published a speech on the occasion of the third marriage of King Sigismund Augustus that year). Taking Zofia Tarnowska as his wife, Constantine Vasily became the son-in-law of the highest secular dignitary of the Kingdom of Poland, the largest landowner, and a renowned military commander and military theoretician. Immediately after the wedding, Constantine Vasily and his wife went to his castle in Dubno in Volhynia. A year later, in 1554, Zofia gave birth to a son in Tarnów, who was named Janusz. Zofia's younger brother, Jan Krzysztof Tarnowski (1537-1567), become formal successor of his father, just few months after birth, after death of his brother Jan Amor (1516-1537). At the age of eleven, he was sent to Augsburg with his tutor Jakub Niemieczkowski, canon of Tarnów, where during the Diet of Augsburg on 25 February 1548, he witnessed the grand ceremony of inauguration of Duke Maurice (1521-1553) as Elector of Saxony. That same year also Titian and Lambert Sustris arrived to Augsburg. In December that year the young Tarnowski went to Vienna to continue his education at the court of King Ferdinand I. A year later, in November 1549, his father Hetman Jan Tarnowski bought Roudnice nad Labem estate in Bohemia for him. Between 1550-1556 Jan Krzysztof built the Renaissance eastern wing with arcades of the Roudnice nad Labem Castle. In 1553 he set off on another educational journey, which, according to Stanisław Orzechowski, was to cost his father a huge sum of 100,000 zlotys. He visited Germany, Brussels, where he was introduced to Emperor Charles V, and London. Then he went to Basel and to Italy, where he met a poet Jan Kochanowski. In Rome, he was a guest of Pope Julius III and in Parma of the Farnese princes. On April 22, 1551, died Zofia Szydłowiecka and she was buried in the collegiate church in Opatów. Peter a Rothis published in Vienna a panegyric on the deceased. A painting of a nude woman attributed to Lambert Sustris in the Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam is very similar to the portrait of Princess Isabella Jagiellon (Venus of Urbino), created few years earlier. In 1854 the painting, as by Titian, was in the collection of Joseph Neeld (1789-1856) in Grittleton House, near Chippenham. As in Venus of Urbino, all alludes to the qualities of a bride and the purpose of the painting. The pose of the woman, although inspired by Titian's painting, find its source in ancient Roman sculpture (e.g. statue of a young Roman lady from the Flavian period in the Vatican Museums). This pose was repeated in tomb monument of Barbara Tarnowska née Tęczyńska (d. 1521), first wife of Jan Amor in the Tarnów Cathedral, most probably created by Giovanni Maria Padovano in 1536 or earlier, monument to Urszula Leżeńska in the Church in Brzeziny by Jan Michałowicz of Urzędów, created between 1563-1568, and in the tomb monument of Zofia Tarnowska, Princess of Ostroh, daughter of Jan Amor, also in the Tarnów Cathedral, sculpted by Wojciech Kuszczyc, a collaborator of Padovano, after 1570. The face of a young woman with protruding ears greatly resemble the effigy of Zofia Tarnowska, Princess of Ostroh, most likely a 19th century copy of an original from the late 1550s (Museum of the Ostroh Academy), and portrait of Zofia's brother, mother and father. Jan Amor Tarnowski, a world man, who on July 4, 1518 sailed from Venice to Jerusalem, who on February 20, 1536 organized a grand wedding in Kraków for Krystyna Szydłowiecka, a younger sister of his second wife, who was getting married to Duke of Ziębice-Oleśnica and who on July 10, 1537 hosted at his castle in Tarnów the king and queen Bona, he could be planning an international marriage for his only daughter. A copy of this painting by workshop or circle of Titian, from the Byström collection, possibly taken from Poland during the Deluge (1655-1660), is in the Nationalmuseum in Stockholm. Another copy is in the Borghese Gallery in Rome, where there is also a portrait of Queen Anna Jagellonica (1503-1547) as Venus by Lucas Cranach the Elder. According to 1650 inventory of the Borghese collection it was one of a pair of similar paintings of Venus located in the same room (the small gallery, now room XI). The inventory of 1693 records them as two overdoor paintings in the same room (the sixth) as "a horizontal large painting of a naked woman on a bed with flowers on it with five other figures one that plays the cimbolo and the other that looks inside a chest" (un quadro bislongo grande una Donna Nuda sopra un letto con fiori sopra il letto con cinque altre figurine una che sona il Cimbolo e l'altra che guarda dentro un Cassa, number 333) and "a large painting of a naked Venus on a bed with a little dog sleeping with two other figures with her hand between thighs, 5 hand-palms high" (un quadro grande di una Venere nuda sopra il letto con un Cagnolino che dorme con due altre figure con la mano tra le coscie alto di 5 palmi, number 322), which was another version of Venus of Urbino - portrait of Isabella Jagiellon. Two other versions of this painting, both on a black background, were sold one in London - "A lady as Venus, reclining on a bed by follower of Titian" (Christie's, 11 July 2003, auction 9665, lot 199) and the other in Rome - "Venus, manner of Lambert Sustris" (Finarte Auctions, 28 November 2017, auction 144/145, lot 62). The same woman was also depicted in similar composition, this time more mythological due to presence of the god of war Mars and the god of desire Cupid, the son of the love goddess Venus and Mars, and a dove. "Romans sacrificed doves to Venus, goddess of love, whom Ovid and other writers represented as riding in a dove-drawn chariot". A white dove is a symbol of monogamy and enduring love, but also the regenerating and fertile powers of the goddess "arose from the conspicuous courtship and prolific breeding of the birds" (after Dean Miller's "Animals and Animal Symbols in World Culture", p. 54). It is known from at least three different versions, one by circle of Titian, is in the royal Wilanów Palace in Warsaw. The painting was most probably purchased by Stanisław Kostka Potocki before 1798 as the work of Agostino Carracci, although it cannot be ruled out that it was added to the collection much earlier. A smaller version in the style of Lambert Sustris is in the Hermitage in Saint Petersburg since 1792 and it comes from the collection of Prince Grigory Potemkin, who during his career acquired lands in the Kiev region and the Bratslav region, provinces belonging to the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. A miniature copy of the Hermitage version, painted on copper, was in private collection in Italy before 2015. Another two versions, also attributed to Sustris or his circle, are in private collections in Florence and in Rome, the version in Florence being close to the style of Bernardino Licinio (d. 1565). The shape of the castle in the distant background matches the layout of the Tarnowski Castle at the Saint Martin's Peak in Tarnów. She was also depicted in a series of paintings depicting the biblical heroine Judith, exemplary in virtue and in guarding her chastity. In a version from private collection in Italy, she is depicted in a green dress with the raised sword in a composition close to the effigy of Zofia Szydłowiecka as Judith by workshop Lucas Cranach the Elder. Another version of this Judith was in private collection in Mönchengladbach in Germany. A version from the Cobbe Collection at Hatchlands Park shows her in a blue dress before the naked body of Holofernes. It was recorded in the posthumous inventory of the collection of a Swedish businessman born in Stockholm, Henrik Wilhelm Peill (1730-1797), as "Italian, Judith with the head of Holofernes". In a version from the Palais des Beaux-Arts de Lille she is depicted in a red dress and accompanied by a servant. This painting was acquired by Louis XIV, in 1662, from a banker and collector Everhard Jabach, born in Cologne. A lower quality copy of the version in Lille is in the Münsterschwarzach Abbey. During the Middle Ages its influence reached as far north as Bremen and in the south to Lambach, near Linz in present-day Austria. Between 1631 and 1634 the abbot of Münsterschwarzach lived in exile in Austria, it is possible that he acquired the paining there from the collection of Queen of Poland, Catherine of Austria, who died in Linz on February 28, 1572. Finally she was also depicted as another biblical heroine Susanna, epitome of female virtue and chastity, unjustly accused of sexual transgression. This painting was purchased in 1961 by the Museo de Arte de Ponce from the collection of the family Trolle-Bonde in the Trolleholm Castle in southern Sweden. The painter evidently used the same set of preparatory drawings to create the face of Susanna and Judith in Lille. The popularity of "obscene" images in Poland-Lithuana before the Deluge (1655-1660) was apparently so great that some authors urged against them. "Lascivious paintings and statues, speeches and songs full of obscenity [...], whom will they not lead to all kinds of debauchery?" (Picturae & statuae lascivae, sermones & cantilenae obscoenitatis plenae [...], quam aetatem quem sexum non contaminant?), wrote in his treatise "Commentaries on the Improvement of Commonwealth" (Commentariorvm de rep[vblica] emendanda) dedicated to king Sigismund Augustus and published in Kraków in 1551, his secretary Andrzej Frycz Modrzewski (1503-1572). Half a century later Sebastian Petrycy, professor of the Kraków Academy in his commentaries to Aristotle's Oeconomicum libri duo (Oekonomiki Aristotelesowey To Iest Rządu Domowego z dokładem Księgi Dwoie), published in Kraków in 1601, wrote that children and young ladies "looking at the painted naked people will easily learn to be shameful" and confirmed his opinion in a gloss to "Politics" by Aristotle (published in 1605), writing that "indecent images are to be hidden from the youth [...] so that young people would not be scandalized" (partially after "Ksiądz Stanisław Orzechowski i swawolne dziewczęta" by Marcin Fabiański, p. 57-58). The same Sebastian Petrycy also complains about the patricians, who in their newly built houses "put expensive pictures", depicting Vulcan, Jupiter, Mars, Venus and Cupid. According to Wanda Drecka, this "expensiveness" of the images would indicate imported paintings. The inventories of the collection of Boguslaus Radziwill from 1656 and 1657 include such paintings as "Cupid, Venus and Pallas", "Venus and Hercules" and "Venus and Cupid" (after "Polskie Cranachiana" by Wanda Drecka, p. 26-27) by Cranach or Venetian painters.
Portrait of Zofia Tarnowska (1534-1570) nude (Reclining Venus) by Lambert Sustris, 1550-1553, Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam.
Portrait of Zofia Tarnowska (1534-1570) nude (Reclining Venus) by workshop or circle of Titian, 1550-1553, Nationalmuseum in Stockholm.
Portrait of Zofia Tarnowska (1534-1570) nude (Reclining Venus) by circle of Lambert Sustris, 1550-1553, Borghese Gallery in Rome.
Portrait of Zofia Tarnowska (1534-1570) nude (Reclining Venus) by Lambert Sustris, 1550-1553, Private collection.
Portrait of Zofia Tarnowska (1534-1570) as Venus with a dove by circle of Titian, 1550-1553, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
Portrait of Zofia Tarnowska (1534-1570) as Venus with a dove by Lambert Sustris, 1550-1553, The State Hermitage Museum.
Portrait of Zofia Tarnowska (1534-1570) as Venus with a dove by Lambert Sustris, 1550-1553, Private collection.
Portrait of Zofia Tarnowska (1534-1570) as Venus with a dove by circle of Lambert Sustris, 1550-1553, Private collection in Rome.
Portrait of Zofia Tarnowska (1534-1570) as Venus with a dove by circle of Lambert Sustris or Bernardino Licinio, 1550-1553, Private collection in Florence.
Portrait of Zofia Tarnowska (1534-1570) as Judith with the head of Holofernes by Lambert Sustris, 1550s, Private collection.
Portrait of Zofia Tarnowska (1534-1570) as Judith with the head of Holofernes by Lambert Sustris, 1550s, Private collection.
Portrait of Zofia Tarnowska (1534-1570) as Judith with the head of Holofernes by Lambert Sustris, 1550s, The Cobbe Collection at Hatchlands Park.
Portrait of Zofia Tarnowska (1534-1570) as Judith with the head of Holofernes by Lambert Sustris, 1550s, Palais des Beaux-Arts de Lille.
Portrait of Zofia Tarnowska (1534-1570) as Judith with the head of Holofernes by Lambert Sustris, 1550s, Münsterschwarzach Abbey.
Portrait of Zofia Tarnowska (1534-1570) as Susanna by Lambert Sustris, 1550s, Museo de Arte de Ponce.
Portraits of Catherine of Austria and Zofia Tarnowska by Titian
Family events that took place in 1553 brought a great revival in the monotonous existence of the Jagiellons. In the spring, Queen Isabella arrived to Warsaw with her 13-year-old son, John Sigismund Zapolya, to live with her mother and sisters. Soon, Sigismund Augustus also visited Warsaw, and in June the whole family went to Kraków for his wedding with Catherine of Austria, widowed Duchess of Mantua. The dynastic marriage of the king with a daughter of Ferdinand I, just few months after the wedding of the only daughter of Hetman Jan Amor Tarnowski, was decided to prevent the threat of an alliance of Tsar Ivan the Terrible with the Habsburgs against Poland-Lithuania. In July, Catherine's brother, Archduke Ferdinand, governor of Bohemia, escorted her to Kraków. The ceremony was attended by Duke Albert of Prussia, the Silesian dukes of Cieszyn, Legnica-Brzeg and Oleśnica, the papal legate Marcantonio Maffei from Bergamo (Republic of Venice), many foreign envoys and Polish magnates. The ceremonial entry to Kraków took place on July 29 and the coronation the next day. During the procession, Jan Amor Tarnowski, carried the royal crown.
During his visit the Archduke demanded that the Habsburgs should be granted succession in Poland-Lithuania in the event of king's death without a male heir. Sigismund Augustus seemed willing to agree to this request, however the senators, inspired by Tarnowski, were to answer him that this would not happen, because the king had no right to do so. The same year, Francesco Lismanini, a preacher and confessor of Sigismund Augustus, was sent to Venice to procure books for his library. Before his return in 1556, he also visited Moravia, Padua, Milan, Lyon, Paris, Geneva, Zurich, Strasbourg and Stuttgart, while among books published in this period were two dedicated to Hetman Tarnowski, both by Italian physician Giovanni Battista Monte (Johannes Baptista Montanus), Explicationes, published in Padua in 1553 and In quartam fen primi canonis Avicennae Lectiones, published in Venice in 1556. In about 1553 died Giovanni Alantsee from Venice, a pharmacist from Płock, initially a supplier of the Dukes of Masovia and later of the court of Sigismund I, who remained in Bona's service (sent by her in 1537 on a secret mission to Vienna). One of the Italian envoys who traveled permanently to Venice on the orders of the Polish royal court was a certain Tamburino. On April 30, 1549, he received 1 ducat for an unspecified order. Before her departure for Italy, the Queen deposited in Venetian banks, and also borrowed at interest, her great income from Masovia, Lithuania and Bari. In November 1555 Queen Bona wrote to Hetman's wife, Zofia Tarnowska née Szydłowiecka, asking her to arrange for a mature lady (matronam antiquam) to accompany her daughter Sophia to her husband in Germany. In 1559 Sigismund Augustus admitted to his service in Vilnius two goldsmiths from Venice, Antonio Gattis and Pietro Fontana. If Philip II could commission paintings in Titian's Venetian workshop, the same could the king of Poland and Polish magnates. Kraków and Tarnów are closer to Venice by land then Madrid. Also some contacts of Princes of Ostroh with Venice and Italy are confirmed in sources. The teacher of Constantine Vasily's sons was, among others, a Greek, Eustachy Nathanael, from Crete. He was probably educated, like many Greeks from Crete, in Italy, probably in Venice. Other Greek, Emanuel Moschopulos, educated in Collegium Germanicum in Rome also settled in Ostroh. According to letters of Germanico Malaspina (ca. 1550-1604) from 1595, papal nuncio in Poland, Constantine Vasily even asked the Catholic patriarch in Venice to come to Poland: a riformare il suo dominio (to reform his domain). Herodias with the head of Saint John the Baptist, also known as Salome, by Titian is known from several versions. The best, the so-called Raczyński Herodias, was in the 19th century in the possession of the noble Raczyński family, according to the label on the back (after Nicholas Hall's "Nemesis: Titian's Fatal Women", p. 19). The woman's face is identical with the face of Venus with the lute player by Titian in the Metropolitan Museum of Art and Saint Catherine by Titian in the Prado Museum in Madrid, she is therefore Queen Catherine of Austria, third wife of Sigismund Augustus, in guise of the biblical temptress. A copy of this painting by Titian and workshop, which was by 1649 in the royal collection in England (Hampton Court), is today in the National Museum of Western Art in Tokyo. Another copy by workshop or follower of Titian from private collection in Germany was sold in Cologne (oil on canvas, 106 x 93.5 cm, Van Ham Kunstauktionen, May 19, 2022, lot 517). Also Parrasio Micheli (ca. 1516-1578), a painter profoundly influenced by Titian who belonged to the patrician Michiel family in Venice, copied this painting. It was owned by a Venetian family (oil on canvas, 104 x 93 cm, sold at Babuino Auction House, March 28, 2023, lot 18). There is also another similar painting by Titian of other biblical heroine, Judith, in identical pose. This painting was by 1677 in Florence in the collection of Marchese Carlo Gerini (1616-1673), today in the Detroit Institute of Arts. According to X-ray examination it was painted upon other unfinished portrait of a monarch holding an orb and sceptre (after Nicholas Hall's "Nemesis: Titian’s Fatal Women", p. 18), possibly Sigismund Augustus. The woman depicted bears gret resemblance to other effigies of Zofia Tarnowska (1534-1570), Princess of Ostroh by Lambert Sustris and workshop of Titian, especially her effigies as Judith.
Portrait of Queen Catherine of Austria (1533-1572) as Herodias (or Salome) with the head of Saint John the Baptist and servants (Raczyński Herodias) by Titian, 1553-1565, Private collection.
Portrait of Queen Catherine of Austria (1533-1572) as Salome with the head of Saint John the Baptist and servants by Titian, 1553-1565, National Museum of Western Art in Tokyo.
Portrait of Queen Catherine of Austria (1533-1572) as Salome with the head of Saint John the Baptist and servants by workshop or follower of Titian, 1553-1565, Private collection.
Portrait of Queen Catherine of Austria (1533-1572) as Salome with the head of Saint John the Baptist and a servant by Parrasio Micheli after Titian, 1553-1565, Private collection.
Portrait of Zofia Tarnowska (1534-1570), Princess of Ostroh as Judith with the head of Holofernes and a servant by Titian, 1553-1565, Detroit Institute of Arts.
Portrait of Constantine Vasily, Prince of Ostroh by Jacopo Tintoretto
The man in a black costume lined with white fur in a portrait by Jacopo Tintoretto in the National Galleries of Scotland in Edinburgh, on loan to the Gallery since 1947, bears a strong resemblance to effigies of Constantine Vasily (1526-1608), Prince of Ostroh, including that visible in a gold medal with his portrait (treasury of the Pechersk Lavra and the Hermitage), and his mother Alexandra Olelkovich-Slutska from paintings by Cranach and his workshop. It is dated to about 1550-1555, the time when in 1553, at the age of 27, Constantine Vasily married Zofia Tarnowska. The painting comes from William Coningham's collection in London, exaclty as the portrait of Queen Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596) with a dog by Francesco Montemezzano in the Metropolitan Museum of Art.
In 1559 Constantine Vasily became the voivode of Kiev. The economic power of his estates and his considerable political influence quickly earned him the title of "uncrowned king of Ruthenia". In 1574, he moved the princely residence from Dubno to Ostroh, where the reconstruction of Ostroh Castle began under the Italian architect Pietro Sperendio from Breno near Lugano. Cristoforo Bozzano (Krzysztof Bodzan) from Ferrara, called incola Russiae (resident of Ruthenia), who reconstructed the Ternopil Castle in 1566 for Jan Krzysztof Tarnowski, also most probably worked for Constantine Vasily.
Portrait of Constantine Vasily (1526-1608), Prince of Ostroh by Jacopo Tintoretto, 1553-1565, National Galleries of Scotland.
Portraits of Thomas Stafford, ambassador of the King of Poland by Giovanni Battista Moroni and workshop
The portrait of a man by Giovanni Battista Moroni presenting a letter dated in Italian September 20, 1553 (Di Settembre alli XX del M.D.LIII), is known from at least three versions. His left hand, holding another document, is very similar to Moroni's famous tailor in the National Gallery in London. One vesion, sold in 2015 in London, comes from the collection of Marquise de Brissac in France, the other in the Honolulu Museum of Art, was before 1821 in the collection of Edward Solly (1776-1844) in London and another from Scandinavian private collection, showing just the man's head, was auctioned in London (Sotheby's, 09.12.2003, lot 326). Two versions were painted on canvas and the smallest, attributed to Italian School early 17th century, was painted on wood.
Apart from the date and abbreviation D V S, which could be Dominationis Vestrae Servitor (Your Lordship's Servant) in Latin or Di Vostra Signoria (of Your Lordship) in Italian, the rest is illegible and could be either in Italian or in Latin. The man is therefore showing his letter, most probably a response, to someone very important. On July 9, 1553, Mary Tudor, the eldest daughter of Henry VIII of England, proclaimed herself Queen of England. On August 3, she triumphantly entered London with her sister Elizabeth, and ceremonially took possession of the Tower. On September 27, she and Elizabeth moved into the Tower, as was the custom just before the coronation of a new monarch and on October 1, 1553, Mary was crowned in Westminster Abbey. While in a letter, in Portuguese, dated in Lisbon, September 20, 1553, king John III of Portugal announces the despatch of Lorenzo Piz de Tavora, a member of his council, as his ambassador to congratulate her Majesty on succeeding to the throne, Sigismund Augustus, king of Poland, sends a letter, in Latin, dated in Kraków, October 1, 1553, addressed to queen Mary. He despatches to Her Majesty's presence Thomas Stafford, grandson of the Most Noble Edward Stafford, late Duke of Buckingham, for that purpose. He prays the Queen to place unhesitating confidence in the said Stafford, of whom he speaks in the highest terms of praise, especially with regard to his cultivated and gracefully modest manners (Lat. State Paper Office, Royal Letters, vol. XVI. p. 9). Also king's newly wed wife, Queen Catherine of Austria, sends a letter on October 1, 1553 to queen Mary, congratulating her upon her accession, speaking in terms of high commendation of Thomas Stafford, and earnestly requests that he may be restored to the honours and possessions formerly possessed by his ancestors (Lat. State Paper Office, Royal Letters, vol. XVI. p. 11). Shortly after Jan Łaski's departure from England, Hieronim Makowiecki came to London at the end of 1553 as an envoy of the Polish king, and in the following year Leonrad Górecki attended Mary's wedding to Philip II of Spain. According to a letter of Marc'Antonio Damula, Venetian ambassador to the Imperial Court, to the Doge and Senate, dated in Brussels, August 12, 1554: "It is being treated about, to give the government of the kingdom of Naples to the Queen of Poland [Bona Sforza], together with a council, and the Emperor has already said that he is content with this; and they are endeavouring to obtain the consent of the King of England, who is expected to give it readily, the kingdom of Naples being now weary and depressed by the many wrongs endured at the hands of the Spanish governors. The ambassador of the Queen aforesaid has purchased an organ at Antwerp for 3,000 crowns, as also goldsmith's work to the amount of 6,000, to give to the Queen of England, and will go thither to endeavour to arrange this business, which is supposed to be very near conclusion". Thomas Stafford (ca. 1533-1557) was the ninth child and second surviving son of Henry Stafford, 1st Baron Stafford and Ursula Pole. His maternal grandmother was Margaret Pole, Countess of Salisbury and the last direct descendant of the Plantagenets. This lineage made Thomas and his family particularly close to the throne of England. In 1550 he went to Rome, where his uncle Cardinal Reginald Pole (1500-1558) was nearly elected a pope in the papal conclave convened after the death of Pope Paul III, and where he remained for three years. He was resident in Venice in May of 1553 when the Signory permitted him to view the jewels of Saint Mark and to bear arms in the territories of the Republic. He arrived to Poland during the summer of 1553 when Sigismund Augustus was celebrating his third marriage with Catherine, daughter of Anna Jagiellonica. It was most likely on her initiative that Stafford became an envoy of Poland-Lithuania to England. The king's recommendation to restore him to the Dukedom of Buckingham appeared to have no effect, as in January 1554 he joined the rebellion, directed against Mary's plans to become the wife of Philip II. The rebels were defeated, Stafford was captured, but was able to escape to France, where he announced his claims to the crown of England. He returned to England in April 1557, but he was arrested and sentenced to death as a traitor. He was beheaded on May 28, 1557 on Tower Hill in London. The date on a letter in mentioned portraits match perfectly the time when Stafford could receive an ambassadorial nomination and send a response expressing his appreciation to the king of Poland. Also previous locations of the works match Stafford's journeys - one was in England, one in France and one in Scandinavia, possibly taken from Poland during the Deluge. The sitter bears a strong resemblance to effigies of Thomas' uncle Cardinal Reginald Pole by Sebastiano del Piombo and workshop, in the Museum of Fine Arts in Budapest and in the Hermitage Museum, and by unknown artist, in the Trinity College of the University of Cambridge.
Portrait of Thomas Stafford (ca. 1533-1557), ambassador of the King of Poland by Giovanni Battista Moroni, 1553, Private collection.
Portrait of Thomas Stafford (ca. 1533-1557), ambassador of the King of Poland by Giovanni Battista Moroni or workshop, 1553, Honolulu Museum of Art.
Portrait of Thomas Stafford (ca. 1533-1557), ambassador of the King of Poland by workshop of Giovanni Battista Moroni, ca. 1553, Private collection.
Portrait of Abraham Zbąski by Jacopo Tintoretto
In 1553 died Stanisław Zbąski, castellan of Lublin, the father of Abraham and Stanisław (1540-1585), and on the basis of his last will written in the Lublin town book, Abraham was to receive Kurów estate with a stonghold near Płonki, and Stanisław the town of Kurów and compensation of 1000 florins. The same year the Catholic church in Kurów was turned into a Protestant temple.
The castellan of Lublin, himself educated in Leipzig (1513/1514) and most probably in Italy, send his eldest son to a Protestant university in Wittenberg in February 1544, together with another Abraham Zbąski (D. Abrahamus / D. Abrahamus de Sbanski / poloni), identified as the son of Piotr Zbąski (d. 1543) from Greater Poland, the owner of Zbąszyń, who was most likely the same age as his friend Marcin Czechowic (born in November 1532) and the son of Stanisław. One Abraham Zbąski also studied in Królewiec (Königsberg) in Ducal Prussia in 1547 (as Abrahamus Esbonski. Polonus) and in Basel from May 1551. On November 30, 1550, Abraham Zbąski (the one from Kurów or from Zbąszyń) join the court of King Sigismund Augustus. Perhaps under Abraham Zbąski's influence Celio Secondo Curione (Caelius Secundus Curio), an Italian humanist, dedicated to King Sigismund Augustus his work De amplitudine beati regni Dei, published in Basel in 1554 - on December 1, 1552, in a letter to Zbąski, he asked about the title of the Polish king, as he intended to dedicate his book to him. Celio dedicated to Abraham his Selectarum epistolarum librer II, published in 1553, and his handwritten dedication to Zbąski preserved in a volume of his M. Tullii Ciceronis Philippicae orationes XIIII, published in 1551 (Poznań University Library). This Abraham Zbąski frequently travelled to Italy, mainly to Bologna, in 1553/1554, in 1558/1559 and between 1560 and 1564. "I heard that this Abram, who recently arrived from Italy, could be quite a gem in this family" (Jakoż słyszę ten Abram, nowo z Włoch nastały, Że to może w tym domu klenot być niemały), wrote about the Zbąski family in his Bestiary (Zwierziniec/Zwierzyniec), published in 1562, the Polish poet and prose writer Mikołaj Rej. In 1554 he continued his studies at the University of Leipzig, where he enrolled for winter semester (as Abrahamus Sbansky) with Marcin Czechowic (Martinus Czechowicz), a Protestant thinker and a leading representative of Polish Unitarianism, and Stanisław Zbąski of Lublin (Stanislaus Sboxsky Lubelensis), his brother or cousin. The portrait of a young man by Jacopo Tintoretto in the Barber Institute of Fine Arts in Birmingham was acquired in 1937 from the collection of Francis Drey (1885-1952) in London, who recalled that the portrait was previously in a French private collection. Basing on this, together with the style of the costume, it was suggested that the sitter is a Frenchman. His rich costume, more northern, sword and gloves indicate that he is a wealthy nobleman, like the Zbąskis of the Nałęcz coat of arms. According to Latin inscription in upper right corner, in the month of March (or May) 1554, the man was 22 years old (ANNO 1554 MENSE MA / AETATIS SUAE 22). This date and age match the age of one of the Zbąskis (both born in about 1531 or 1532), who was in Italy in 1553/1554 and in winter of 1554 enrolled at the University of Leipzig, further north of Venice. The man bear a resemblance to effigy of Stanisław Zbąski (1540-1585), from his tomb monument in Kurów, created by Italian sculptor Santi Gucci or his workshop, and to the distant descendant of the Zbąskis, bishop Jan Stanisław Zbąski (1629-1697) from his portrait in the Skokloster Castle in Sweden.
Portrait of Abraham Zbąski aged 22 by Jacopo Tintoretto, 1554, The Barber Institute of Fine Arts.
Portraits of Halszka Ostrogska by Bernardino Licinio and workshop of Tintoretto
"What's happening to me? where I was taken? To France, or to Italy, or elsewhere? And after all, a neighbor invited me to his wedding, and I see a strange dress in this circle of female gender, and I don't see any Polish woman here, I don't know who I honor and welcome. This one sits, I see, she's from the domain of Venice, and this one in this robe, from the land of Spain. This one is supposedly French, and the other wears a Netherlandish outfit, or it's Florentine?", describes the great diversity of women's fashion in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in his satire "Reprimand of Women's Extravagant Attire" (Przygana wymyślnym strojom białogłowskim), published in Kraków in 1600, Piotr Zbylitowski (1569-1649), a poet and courtier.
From 1585, Zbylitowski was a courtier of Stanisław Górka (1538-1592), voivode of Poznań, then, in 1593, he participated in the Czarnkowski embassy to King Sigismund III, who was staying in Sweden. After returning to Poland, he married Barbara Słupska and settled in the village of Marcinkowice near Sącz in Southern Poland. In addition to the diversity of dress, which has been confirmed in Poland-Lithuania since at least the sumptuous wedding ceremonies of Sigismund II Augustus in 1543, in this work, which he dedicated to his patroness starościna Zofia Czarnkowska née Herburt (d. 1631), he also criticize the great opulence of clothing and jewelry. Extravagant headdresses, crowns and ruffs on heads, pearls and rubies, necklaces of precious diamonds, dresses with "six sleeves" adorned with pearls and precious stones, Spanish and French farthingale (portugał jak się na niej koli), conical caps similar to Turkish kiwior, robes embroidered with gold, lead him to scathing remarks - "it's a pity that she doesn't hang anything on her nose either", "how the neck will not tear from these severe ruffs" of Flemish lace, "it would be hard for her to go to work" or "it is difficult to recognize them in such clothes". The women of Poland-Lithuania dressed according to the latest fashion from Italy, Spain and France, because due the high price of Polish grain "it is not expensive" and such a rich dress can be made just "for a heap of rye". To their conservative husbands wanting them to wear more modest or Polish clothes, the wives responded angrily: "I am your companion, not your handmaid, I am allowed as you, I am not a slave". The Synod of Protestants in Poznań convened in 1570, enacted a rule of reprimanding and punishing the "licentious clothes", which generally did not bring the desired results (after "Reformacja w Polsce" by Henryk Barycz, Volume 4, p. 39). This opulence of costume was as in Italy, Spain and France undoubtedly reflected in portraiture, however, someone checking the portraits of women from Poland-Lithuania before the Delugue (1655-1660), and this article, will unmistakably have the impression that it was a poor country of old nuns. This would be correct because the majority of the portraits that survived the destruction during the wars and the subsequent impoverishment of the country were created by less skilled local artists for churches and monasteries. Such portraits were commissioned by wealthy women in their old age for the temples they founded or supported. Thus, they were depicted in a black outfit covering the whole body, a white bonnet covering the hair and ears and holding a rosary. A large number of these portraits have survived because either they were not of high artistic class, or they were created for provincial churches, far from the major economic centers of the country, which were destroyed, or both. Over a century of portraiture in Poland-Lithuania of mainly young women, disappeared almost completely. In 1551, the richest bride in Poland-Lithuania - Elizabeth (1539-1582), Princess of Ostroh also known as Halszka Ostrogska (illustri virgini Elisabetae Duci Ostroviensi, Kxięzna Helska Ilijna Ostroska, Hałżbieta Ilinaja Kniażna Ostroskaja), reached the legal age of marriage (12) and the battle for her hand began. She was the only child of Beata Kościelecka (1515-1576), the illegitimate daughter of king Sigismund I and protegee of Queen Bona, and her husband Illia (1510-1539), Prince of Ostroh. Halszka's huge fortune aroused so much interest that in 1551 the Sejm in Vilnius adopted a special resolution stating that "the widow [Beata] may not marry her daughter without the consent of close relatives", including guardians, her uncle Prince Constantine Vasily (1526-1608) and king Sigismund II Augustus. Two years later, in 1553, Constantine Vasily decided to marry Halszka to Prince Dmytro Sangushko (1530-1554), a hero of the defense of Zhytomyr from the attack of the Tatars and the eldest son of her other guardian Prince Fyodor Sangushko (d. 1547). Dmytro received written consent from Constantin Vasily and the mother for the marriage, however, when the king objected, the mother withdrew her consent. At the beginning of September 1553, Constantin Vasily and Dmytro arrived in Ostroh, where the widow lived with her daughter and stormed the castle. During the forced marriage ceremony on September 6, 1553, Halszka was silent and her uncle answered for her. Beata wrote a complaint to the king that the marriage took place without her consent and Sigismund II Augustus deprived Sangushko of the post of the starost and ordered him to appear in January 1554 in Knyszyn at the royal court. Despite the intervention of Ferdinand I of Austria, King of the Romans and future Emperor, who was constantly intriguing against the Jagiellons, in a letter dated December 11, 1553, blaming the incident on Halszka's mother, who "began to appropriate her daughter and, without her uncle's permission and consent, wanted to marry her off as she wished", Prince Constantine Vasily was deprived of the rights of guardian by the king and Dmytro was sentenced to infamy for failure to appear at the court, expulsion from the state, confiscation of property and an obligation to return Halszka to her mother. On January 20, 1554, a reward of 200 złotys was announced for Sangushko's head. Dmytro and Halszka, disguised as a servant, fled to Bohemia, hoping to take refuge in the Roudnice castle, which belonged to the hetman Jan Amor Tarnowski, father-in-law of Prince Constantine Vasily. They were pursued by the Voivode of Kalisz Marcin Zborowski, who captured them at Lysá nad Labem near Prague and fearing that Ferdinand I would release Dmytro ordered his servants to kill him on the night of February 3 at Jaroměř near the Silesian border. For murder on the territory of a foreign state, Zborowski was arrested and imprisoned, however, thanks to the intercession of king Sigismund II Augustus, the Czech king soon ordered his release. Zborowski took Halszka to Poznań to her relatives, the Kościelecki and Górka families. On March 15, 1554, she saw her mother again, who arrived to Poznań. The beauty and wealth of a young 14-year-old widow again attracted numerous suitors, including the sons of Marcin Zborowski, Piotr and Marcin, Calvinists. Beata opted for Orthodox Prince Semen Olelkovich-Slutsky (d. 1560). The king, however, decided to marry her to his loyal supporter count Łukasz III Górka (d. 1573), a Lutheran, which was announced in May 1555. With the support of Queen Bona, Beata and her daughter strongly opposed the will of the monarch and Halszka even wrote to Górka that she would rather die than marry him. However, with Bona's departure for Italy in 1556, the situation for them became increasingly difficult. Eventually the king lost his patience and decided to force the marriage. The wedding took place on February 16, 1559 at the Royal Castle in Warsaw, however, the marriage remained unconsummated (non consummatum). When the royal court moved to Vilnius, Princess Beata and her daughter fled secretly to Lviv, where they found refuge in a fortified male Dominican monastery. The king ordered Halszka to be separated from her mother and taken to her husband. Royal forces besieged the monastery but the women only gave up after their water supply was cut off. To the surprise of the Lviv starost who entered the monastery by order of the king, Beata announced that her daughter had just been married to Prince Olelkovich-Slutsky, who entered the monastery disguised as a beggar, and the marriage was consummated, so Górka would no longer be entitled to Halszka. The young princess was delivered to Warsaw, where the king declared all agreements made with Prince Olelkovich-Slutsky to be null and void and she was handed over to Łukasz Górka, who, despite her resistance, soon brought her to his residence in Szamotuły. She often accompanied her husband, always dressed in black. When he died suddenly at the beginning of 1573, she intended to marry Jan Ostroróg, but her uncle Constantin Vasily did not allow her to do so. She returned to Ruthenia, where she died in Dubno in 1582 at the age of 43. No signed effigy of Halszka preserved. In 1996, a Ukrainian artist created her imaginative portrait and depicted her like a nun holding a prayer book. In the Galerie Canesso in Paris, there is a painting depicting the "Young Lady and her Suitor", attributed to Bernardino Licinio, who died in Venice around 1565 (oil on panel, 81.3 x 114.3 cm). This painter made portraits of Halszka's mother, Beata, identified by me. It was sold in 2012 (Sotheby's New York, 26 January 2012, lot 21) and comes from the collection of Caroline Murat (1782-1839), Queen of Naples, sold in 1822, while she was in exile at the castle of Frohsdorf in Austria. She therefore probably acquired it in Austria, where resided king Ferdinand I or Naples, where collections of Queen Bona were moved after her death in Bari. It cannot be excluded that one of them received this painting as a gift. The young lady with loose blond hair wears a green cloak, a color being symbolic of fertility. Her white linen chemise has fallen from her shoulder to reveal her breast. The bas relief behind her, showing a warrior in ancient armour, connotes mythology. It could depict Odysseus leaving Penelope, but at the later stage of the painting's creation, it was painted over and uncovered during a recent restoration of the work after 2012. The woman turns her face away while glancing at her suitor. In response, he places his right hand on her wrist and his left on his heart in a gesture imploring amorous passion and future promise. Echoing the beauties of Palma Vecchio and Titian, the painting is dated to around 1520, however, the costume of the suitor indicate that it was created much later. His crimson satin doublet and regularly slashed jerkin are almost identical to those seen in a portrait of Lodovico Capponi by Agnolo Bronzino (The Frick Collection, 1915.1.19), which is generally dated to around 1550-1555. His pose and his hat are reminiscent of King Edward VI holding a flower by William Scrots (National Portrait Gallery and Compton Verney), generally dated to around 1547-1550. A workshop copy or by an unknown 17th century copyist, such as Alessandro Varotari (1588-1649), of this painting was put up for sale in 2023 in Mosta, Malta (oil on canvas, 112 x 87 cm, Belgravia Auction Gallery, December 9, 2023, lot 512). The same woman was depicted in another painting attributed to Licinio. It was confiscated during World War II from the collection of Van Rinckhuyzen in the Netherlands for Hitler's Führermuseum in Linz (oil on canvas, 80.5 x 81 cm). This painting is usually dated around 1514, but in this case the dating is also not very adequate because her black dress most closely resembles that seen in portrait of a poetess Laura Battiferri, also by Bronzino (Palazzo Vecchio in Florence), dated around 1555-1560. She is holding a feather fan, similar to that in the portrait of Catherine of Medici (1519-1589), Queen of France by Germain Le Mannier (Palazzo Pitti in Florence, inv. 1890, n. 2448), created between 1547-1559. She was also represented in a painting by workshop of Jacopo Tintoretto, today in the Montreal Museum of Fine Arts (oil on canvas, 102.9 x 86.4 cm, inventory number 180) from the 1550s. In all of mentioned effigies the model's face resemble the effigies of Halszka's mother and father by Bernardino Licinio, identified by me. Consequently the suitor in the Paris painting could be Dmytro Sangushko, Semen Olelkovich-Slutsky or Łukasz III Górka.
Portrait of Elizabeth (1539-1582), Princess of Ostroh (Halszka Ostrogska) and her suitor by Bernardino Licinio, ca. 1554-1555, Galerie Canesso in Paris.
Portrait of Elizabeth (1539-1582), Princess of Ostroh (Halszka Ostrogska) and her suitor by follower of Bernardino Licinio, after 1554 (17th century?), Private collection.
Portrait of Elizabeth (1539-1582), Princess of Ostroh (Halszka Ostrogska) holding a feather fan by workshop of Bernardino Licinio, ca. 1555-1560, Private collection.
Portrait of Elizabeth (1539-1582), Princess of Ostroh (Halszka Ostrogska) by workshop of Tintoretto, 1550s, Montreal Museum of Fine Arts.
Portrait of Adam Konarski by Jacopo Tintoretto
In 1552, a brilliant diplomatic career of a young nobleman from Greater Poland, Adam Konarski (1526-1574), began. King Sigismund Augustus sent him to Rome as an envoy to Pope Julius III. Perhaps the effect of this mission was the sending of the first apostolic nuncio to Poland in 1555, Bishop Luigi Lippomano.
Adam was a son of voivode of Kalisz Jerzy Konarski and Agnieszka Kobylińska. He studied at the Lubrański Academy in Poznań, then in Frankfurt an der Oder, from 1542 in Wittenberg and later in Padua, from where he returned to his homeland in 1547. He decided to devote himself to a career in the church as a priest, but as a result of refusal to receive the office of coadjutor of Poznań, he decided, upon the advice of his father, to pursue a secular career. In 1548 he became the secretary of King Sigismund Augustus and in 1551 he was appointed chamberlain of Poznań, the official responsible for supervising the servants and the courtiers of the king. In the same year, he finally received the Poznań provostry, but he did not quit his job at the royal chancellery. On the occasion of the king's wedding with Catherine of Austria, he went to Kraków in June 1553 together with the nuncio Marco Antonio Maffei (1521-1583), Archbishop of Chieti (born in Bergamo in the Venetian Republic) and returned to Rome in November to stay there until April 1555 (after Emanuele Kanceff, Richard Casimir Lewanski "Viaggiatori polacchi in Italia", p. 119). Upon his return, he received the post of canon of Kraków and scholastic of Łęczyca. He was again sent to Rome in 1557 after the death of Queen Bona and in 1560, also to Naples, regarding the inheritance of the Queen. In 1562, for his services to the king, he received the office of the bishop of Poznań, which he took upon his return to Poland in 1564. In 1563 Girolamo Maggi (ca. 1523-1572), an Italian scholar, jurist and poet, also known by his Latin name Hieronymus Magius, dedicated to Konarski his Variarvm lectionvm seu Miscalleneorum libri IIII, published in Venice (Venetiis : ex officina Iordani Zileti). In 1566-1567 Adam travelled to Padua. Bishop Konarski died on December 2, 1574 in Ciążeń and was buried in the Poznań Cathedral. His beautiful tomb monument there (in the Holy Trinity chapel) was created by royal sculptor (mentioned in the documents of the royal court in 1562), Gerolamo Canavesi, who, according to his signature, created it in his workshop at St. Florian's Street in Kraków (Opus Ieronimi Canavesi qui manet Cracoviae in platea Sancti Floriani). It was transported and installed in Poznań in about 1575. The portrait of a bearded man holding gloves by Jacopo Tintoretto in the National Gallery of Ireland in Dublin was purchased at Christie's, London, in 1866. According to Latin inscription the man was 29 years old in 1555 (1555 / AETATIS.29), exactly as Adam Konarski when he was returning from his mission to Italy, undeniably through the Republic of Venice, to Poland-Lithuania. The man bears great resemblance to the effigy of Bishop Adam Konarski in the National Museum in Poznań and his tomb sculpture in the Poznań Cathedral.
Portrait of royal secretary Adam Konarski (1526-1574), aged 29 by Jacopo Tintoretto, 1555, National Gallery of Ireland.
Self-portraits and portraits of Sigismund Augustus and Barbara Radziwill by Lucia Anguissola
Provenance of a portrait of a lady sitting in a chair from the collection of the royal Wilanów Palace in Warsaw (inventory number Wil. 1602) is unknown. It was suggested that it comes from the collection of Aleksander Potocki or his parents - Aleksandra née Lubomirska and Stanisław Kostka Potocki, however it cannot be excluded that it comes from the royal collection. It may be tantamount to "The picture in which the Seated Lady" (No. 247. Obraz na ktorym Dama Siedzi), mentioned in the inventory of the Wilanów Palace from 1696 in the part concerning paintings brought from various royal residencies to Marywil Palace in Warsaw (Connotacya Obrazow, w Maryamwil, zostaiących, ktore zroznych Mieysc Comportowane były, items 242-303). The painting in Wilanów was attributed to Agnolo Bronzino and Scipione Pulzone.
The woman was also depicted in other similar portrait in quarter-length, which is in Galleria Spada in Rome. This painting is attributed to Sofonisba Anguissola, while the costume is similar to that visible in Lucia Anguissola's self-portrait in the Castello Sforzesco in Milan. The latter painting is more a miniature (28 x 20 cm) and was signed and dated '1557' by the author (MD / LVII / LVCIA / ANGUISOLA / VIRGO AMILCA / RIS FILIA SE IP / SA PINX.IT). Lucia was Sofonisba's younger sister and was initiated into painting by Sofonisba and perhaps she perfected herself in Bernardino Campi's studio. Just two years earlier, in 1555, Lucia and her two other sisters Europa and Minerva were portrayed by Sofonisba in her famous Game of Chess, signed and dated on the edge of the chessboard (SOPHONISBA ANGUSSOLA VIRGO AMILCARIS FILIA EX VERA EFFIGIE TRES SUAS SORORES ET ANCILLAM PINXIT MDLV). The Game of Chess was acquired in Paris in 1823 by Atanazy Raczyński and today forms part of the collection of the National Museum in Poznań. The effigy of Lucia in the Game of Chess is very similar to mentioned two portraits in Wilanów and Galleria Spada. A copy of the portrait from Galleria Spada, in green dress, is in private collection. It was identified as effigy of Bianca Cappello, Grand Duchess of Tuscany and attributed to Alessandro di Cristofano Allori or as Sofonisba's self-portrait. Also another portrait is similar to mentioned two works in Wilanów and Rome, a portrait of a lady as Saint Lucy, half-length, in a red embroidered dress and brown mantle, attributed to circle of Sofonisba Anguissola, which was sold in December 2012 (Christie's, lot 171). It was painted more from above, like a self potrait looking in the mirror above sitter's head, therefore the silhouette is more slender and the head bigger. She holds attributes of Saint Lucy (Latin Sancta Lucia, Italian Santa Lucia) - the palm branch, symbol of martyrdom and eyes, which were miraculously restored to her. The style of all these three larger effigies, in Wilanów, Galleria Spada and as Saint Lucy, is very similar to the best known work of Lucia Anguissola, the portrait of a physician from Cremona Pietro Manna holding the staff of Asclepius, today in the Prado Museum in Madrid. This work was also signed (LVCIA ANGVISOLA AMILCARIS / F[ilia] · ADOLESCENS · F[ecit]) and was probably sent to King Philip II of Spain to win the royal favor. Portrait of king Sigismund II Augustus in armour in full-length in the Alte Pinakothek in Munich, discovered by me in August 2017, is stylistically very similar to the portrait in Wilanów described above. In this portrait, however, the king has unnaturally big eyes, that were to become the hallmark of the Sofonisba's self-portraits and portrait miniatures by her hand. We can therefore assume that Lucia sent her self-portrait to Warsaw in order to enjoy royal favour and created some effigies of the royal family basing on miniatures created by her sister. On November 29, 2017 another portrait attributed to Lucia Anguissola was sold at an auction (Wannenes Art Auctions, lot 657). This work is similar to Lucia's self-portrait in Castello Sforzesco, however her costume and coiffure are almost identical with the so-called Carleton Portrait in Chatsworth House, the portrait of Sigismund Augustus' second wife Barbara Radziwill (1520/23-1551) by circle of Titian. If not the style and the frame of this small effigy painted on copper, it could be considered as another 18th century copy of Carleton Portrait. It cannot be excluded that Lucia, like Sofonisba, created her own effigy in the costume of Queen of Poland while working on a larger portrait of the Queen. The face features are also very similar to the portrait of Barbara by Flemish painter in Musée Condé.
The Game of Chess by Sofonisba Anguissola, 1555, National Museum in Poznań.
Self-portrait in a dress of gold cloth by Lucia Anguissola, ca. 1555-1560, Galleria Spada in Rome.
Self-portrait in a green dress by Lucia Anguissola, ca. 1555-1560, Private collection.
Self-portrait sitting in a chair by Lucia Anguissola, ca. 1555-1560, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
Self-portrait as Saint Lucy by Lucia Anguissola, ca. 1555-1560, Private collection.
Portrait of King Sigismund II Augustus by Lucia Anguissola, ca. 1555-1560, Alte Pinakothek in Munich.
Portrait of Queen Barbara Radziwill by circle of Sofonisba or Lucia Anguissola, 1550s, Private collection.
Portraits of the Jagiellons and Dukes of Pomerania by Giovanni Battista Perini and workshop
"The most illustrious prince, a very dear friend. Not so long ago Johannes Perinus, our distinguished and faithful painter, complained to us, although the inheritance of his uncle the late Johannes Perinus had passed to himself and his brothers by a legitimate line of succession as the closest relatives, yet they discovered Franciscus Taurellus and his consorts, who from the donation they would contend that the same inheritance belonged to them" (Illustrissime princeps, amice plurimum dilecte. Conquestus est apud nos non ita pridem Johannes Perinus, pictor insignis ac fidelis noster, etsi haereditas patrui quondam Johannis Perini ad se fratresque suos legitimo successionis tramite tanquam ad proximos agnatos ab intestato devoluta esset, repertos tamen Franciscum Taurellum et consortes eius, qui (quod) ex donatione eandem haereditatem ad se pertinere contenderent), wrote Duke John Frederick of Pomerania (1542-1600) in a letter dated June 10, 1578 from Szczecin to Francesco I de' Medici (1541-1587), Grand Duke of Tuscany.
The duke intervened in favor of the Italian painter Giovanni Battista Perini (Parine) from Florence, his court painter. Before he become the "Princely Pomeranian portrait painter" (fürstlich-pommerischen Contrafaitmaler), he worked for the Electoral court in Berlin and in about 1562 he created the portrait of Electress Hedwig Jagiellon (1513-1573), known from a copy by Heinrich Bollandt (Berlin Palace, lost during World War II), and the portrait of her husband Joachim II (Berlin City Museum, VII 60/642 x). He probably became Joachim's court painter in 1524, as a certain painter Johann Baptista was mentioned as such at that date, and he was considered "the best painter of all in the Margraviate [of Brandenburg]" (der beste Maler überhaupt in der Mark). As he worked for the Electress and as it was customary in the 16th century to lend painters to other royal and princely courts, he probably also worked for the Jagiellons. A certain Giovanni Battista Perini, son of Piero, is mentioned in Florence in 1561 and 1563, but the profession is not specified. If he was the painter of Joachim II, then either he returned to his homeland, or he worked on the orders of the Elector from Florence. We generally think of "remote work" as a 21st century invention, however, already in the 16th century or even earlier many artists were working remotely. Cranach thus worked for several of his clients, as well as many Venetian painters, in particular Titian, copying other paintings and study drawings. For Charles V, in 1548 he painted his wife Isabella of Portugal, who died in 1539, using a mediocre painting as a reference. The Roman sculptor Bernini thus worked for Cardinal Richelieu of France and King of England. The so-called "Book of Effigies" (Visierungsbuch), lost during the World War II, was full of various preparatory drawings for the effigies of the Pomeranian dukes, mainly by Cranach's workshop, including the portraits of John Frederick and his brother Ernest Louis from 1553. They were most likely rendered by the painters with the ready-made portraits. The scenario that the Elector's lack of payment prompted Perini to leave Florence to personally claim his due and when he did not receive it he decided to enter the service of the Duke of Pomerania, is also possible. Joachim II died in 1571 and that year he painted the Electress Catharine (in a letter to the same, he asked 110 thalers for it, while she only wanted to give him 80 thalers), and passed at this period much of his time at Kostrzyn (Cüstrin), where he painted the celebrated Leonhard Thurneysser, as appears from one of his letters. Thurneysser paid him 20 thalers for it (after "Berliner Kunstblatt" by Ernst Heinrich Toelken, Volume 1, p. 143). Perini was employed by the ducal house of Pomerania as early as 1575, because on September 6, 1575, the dowager Duchess Maria of Saxony (1515-1583) wrote in a letter from Wolgast to her eldest son, Duke John Frederick, that the painter complained to her about his salary which was not paid by the elector of Brandenburg (after "Baltische Studien", Volume 36, p. 66). In 1577 he created the retable for the ducal chapel in Szczecin, rebuilt in the Renaissance style between 1575-1577 and decorated with Italianate frescoes (destroyed during air raids in 1944). He undoubtedly made many portraits, however, only one mention, in the inventory of the estate of Duke Barnim X/XII (1549-1603), is known: "full-length effigy of the late Duke John Frederick and of his wife by Johann Baptist" (hochseligen Herzog Johann Friedrichs F. G. und derselben Gemahlin Contrafei per Johannem Baptistam ganzer Gestalt). He died on April 6, 1584 in Szczecin. Duke John Frederick's contacts with his "very dear friend" Grand Duke Francesco were certainly not limited to a single letter. Monarchs of this era frequently exchanged their effigies and precious gifts and Francesco was a renowned patron of the arts. In 1560, one of the most productive medalists of the Italian Renaissance, Pastorino de' Pastorini (1508-1592), who four years earlier (in 1556) created a medal with a bust of Queen Bona Sforza, made a medal with bust of Grand Duke Francesco (Metropolitan Museum of Art, 1974.167). On the obverse it shows the profile of the duke and on the reverse Tiberinus, the genius of the Tiber, and the inscription Felicitati Temporum S.P.Q.R. in Latin. Twelve years later, in 1572, he created another medal of the Duke and in 1579 a medal of his wife Bianca Cappello (Museo del Bargello and British Museum). Perhaps Francesco recommended Pastorini to Duke John Frederick because the gold medal with his bust was clearly created in Pastorini's style (Münzkabinett in Dresden, BRA4086). Stylistically it is particularly similar to the medals of Gianfrancesco Boniperti and Massimiano Gonzaga, Marquis of Luzzara from the 1550s (both in the Metropolitan Museum of Art) and the medal of Ercole II d'Este, Duke of Ferrara, from about 1534 (National Gallery of Art, Washington). According to the date in Latin it was minted in 1573 (M.D.LXXIII). His age is also in Latin (Æ XXXII), his name, however, and the title abbreviation are in German (Hans Friderich H[erzog] Z[u] S[tettin] P[ommern]). Medal with bust of Gracia Nasi the Younger (la Chica) by Pastorini from about 1558 bears the name of the sitter in Hebrew characters and her age in Latin, therefore, such mixtures of languages were not new to Pastorini. Two shaking hands and the inscription "Remember Me" (Memento Me) on the back of John Frederick's medal suggest that it was a gift to his relatives in Saxony. Between 1971 and 1984, the Royal Castle in Warsaw was rebuilt with funds collected by civil society committees organized throughout Poland and in many foreign countries with large Polish communities. The building, which was the seat of the Polish kings and parliament, was bombed by the Germans in September 1939. During the following years of German occupation, the castle was methodically robbed and looted by the occupier and deliberately left unrestored to cause further damage. In September 1944, shortly before the end of World War II, the Germans blew up the building. In 1977, the government of the Federal Republic of Germany donated three full-length portraits of the Jagiellons - Sigismund I, his second wife Bona Sforza and his eldest daughter Isabella Jagiellon, Queen of Hungary, to the rebuilt Royal Castle (oil on canvas, 203.5 x 108, 210.5 x 111, 203.5 x 111.5 cm, inventory number ZKW/59, ZKW/60, ZKW/61). The paintings come from the Wittelsbach collection in Munich and may have been part of the dowry of Anna Catherine Constance Vasa, the great-granddaughter of Sigismund and Bona. The painter evidently used the same or similar set of preparatory drawings as the studio of Lucas Cranach the Younger to create miniatures of the Jagiellon family, dated variably between 1553 and 1565 (Czartoryski Museum). These miniatures were bought in London before the mid-19th century by a Polish collector, Adolf Cichowski and purchased by Władysław Czartoryski in Paris in 1859 at the auction of his collection. The provenance of Cranach's set in England is not known. Miniatures commissioned by Polish monarchs from a foreign artist in the 16th century were again purchased abroad in the 19th century. At that time, Cranach's workshop created several full-length portraits, such as the effigy of Augustus, Elector of Saxony and his wife Anna of Denmark from around 1564 (Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna), from the imperial collection of the Stallburg in Vienna, therefore very probably a gift to the Habsburgs, or portraits of Joachim Ernest, Prince of Anhalt and his first wife Agnes of Barby-Mühlingen, painted in 1563 (Georgium in Dessau). Thus the paintings of the Jagiellons could be part of a large order for the effigies of the royal family from different painters, including Cranach. Because of this general similarity to miniatures, the Warsaw full-length portraits are attributed to a German or Polish painter, but their style and technique indicate Italian influences. The set in the Czartoryski Museum is made up of 10 miniature portraits, so at least 7 effigies from the Warsaw cycle are missing, assuming it reflected the Cranach miniatures. The portrait of Princess Catherine Jagiellon in the Germanisches Nationalmuseum in Nuremberg (oil on canvas, 201 x 99 cm, Gm 622), destroyed during the Second World War, was probably part of this series as well as two other paintings from this museum - portraits of two wives of Sigismund II Augustus, Elizabeth of Austria (1526-1545) and Catherine of Austria (1533-1572), daughters of Anna Jagellonica (1503-1547). The composition of the two latter is slightly different from the four paintings described above. They have similar measurements (oil on canvas, 200 x 103 cm, Gm617 and 195.5 x 101.5 cm, Gm623), however, these two have inscriptions in German and in Latin, so either they were from another set or these two alone were made and sent to the sister of the two queens Anna of Austria (1528-1590), Duchess of Bavaria. Both paintings depicting the wives of Sigismund Augustus have a similar monogram PF, which is identified as the painter's monogram, but his identity remains unknown, hence he is called the Monogramist PF. The style of the two paintings resembles that of the portrait of Joachim II by Perini in Berlin. His portrait is unsigned and bears a Latin inscription, but its style indicates that the author was a German court painter. It is possible that in the portraits of two queens of Poland the inscription was also added later, and the monogram could be the abbreviation of Perini fecit in Latin, that is, made by Perini. Possibly also the full-length portrait of Sigismund II Augustus in armor by Lucia Anguissola, discovered by me in 2017 (oil on canvas, 200 x 118 cm, Alte Pinakothek in Munich, 7128), belonged to this or a similar cycle, although its composition is different and the painter does not copy the same effigy as Cranach in the Czartoryski series. Another portrait that could be from the same workshop is the portrait of a bearded man in the Palace of Versailles (oil on paper mounted on canvas, 96 x 77 cm, 893 (M.R.B. 172)). It is generally dated to the 17th century, but its style and sitter's costume indicate that it dates from the mid-16th century. The man bears a strong resemblance to the effigy of King Sigismund II Augustus by Venetian painter Battista Franco Veneziano from around 1561 (print, Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, RP-P-OB-105.261). Another possible author of this painting could be Giovanni del Monte, who was court painter to the king around 1557, however no signed work by this painter is known. The only known portrait of Pomeranian rulers attributed to Giovanni Battista Perini was the effigy of Duke John Frederick in the Pomeranian Museum in Szczecin, which was lost during World War II. According to the Latin inscription, it was painted in 1571 (ANNO DOMINI 1571), four years before Perini is generally thought to have entered the Duke's service. Italianate portrait of Duke John Frederick and his wife Erdmuthe of Brandenburg as donors under the crucifix in the main altar of the Church of St. Hyacinth in Słupsk, was undoubtedly created in Perini's milieu. It was most probably founded by Erdmuthe and most likely painted by Jakob Funck in 1602, a painter and carpenter from Kołobrzeg, who signed it with a monogram I.F.F. (Jacobus Funck fecit) on the cross. He may have been trained in Perini's workshop. In the Nationalmuseum in Stockholm there is a similar small portrait of a princely couple, also close to the style of Perini, although attributed to Lucas Cranach the Younger (oil on panel, 32 x 52 cm, NMGrh 94). It comes from the Gripsholm Castle and according to the 18th century Swedish inscription it depicts Christian IV of Denmark (1577-1648) and his wife Anne Catherine of Brandenburg (1575-1612), which is obviously incorrect as the couple is dressed in costumes from the 1590s, but when they married in 1597, Christian and Anne Catherine were in their twenties while the couple in the painting is much older and effigies do not match other portraits of the King of Denmark and his wife. It can also be compared to the portrait of John Frederick's younger brother Bogislaw XIII and his wife Anna of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg from 1600 and the effigy of a woman closely resembles the model medal with bust of Erdmuthe by Tobias Wolff from 1600 (Münzkabinett in Berlin). The man's face, apart from the mentioned portrait in Słupsk, also resembles the face of Duke John Frederick from his 1594 silver thaler (Münzkabinett in Berlin). Therefore, the painting was most likely transported to Sweden after 1630 during the Swedish occupation of Pomerania.
Portrait of King Sigismund I (1467-1548) by workshop of Giovanni Battista Perini, 1550s or 1560s, Royal Castle in Warsaw.
Portrait of Queen Bona Sforza (1494-1557) by workshop of Giovanni Battista Perini, 1550s or 1560s, Royal Castle in Warsaw.
Portrait of Isabella Jagiellon (1519-1559), Queen of Hungary by workshop of Giovanni Battista Perini, 1550s or 1560s, Royal Castle in Warsaw.
Portrait of Crown Princess Catherine Jagiellon (1526-1583) by workshop of Giovanni Battista Perini, 1550s or 1560s, Germanisches Nationalmuseum in Nuremberg, lost.
Portrait of Queen Elizabeth of Austria (1526-1545), aged 16 by Giovanni Battista Perini, 1542 or after, Germanisches Nationalmuseum in Nuremberg.
Portrait of Queen Catherine of Austria (1533-1572), aged 24 by Giovanni Battista Perini, 1557 or after, Germanisches Nationalmuseum in Nuremberg.
Portrait of King Sigismund II Augustus (1520-1572) by Giovanni Battista Perini or Giovanni del Monte, ca. 1560, Palace of Versailles.
Gold medal with bust of Duke John Frederick of Pomerania (1542-1600), aged 32 by Pastorino de' Pastorini, 1573, Münzkabinett in Dresden (Photo: © SKD).
Portrait of Duke John Frederick of Pomerania (1542-1600) and his wife Erdmuthe of Brandenburg (1561-1623) by circle of Giovanni Battista Perini, possibly Jakob Funck, 1590s, Gripsholm Castle.
Portraits of Sigismund Augustus and his third wife by Tintoretto and Lambert Sustris
After Sigismund I's marriage to Bona Sforza in 1518, the presence of Italian artists in Poland-Lithuania gradually increased.
In 1547 a painter Pietro Veneziano (Petrus Venetus), most probably in Kraków, created a painting to the main altar of the Wawel Cathedral. Ten years later, on March 10, 1557 in Vilnius, King Sigismund Augustus issues a passport to the Venetian painter Giovanni del Monte to go to Italy, and according to Vasari, Paris Bordone has "sent to the King of Poland a painting which was held very beautiful, in which was Jupiter and a nymph" (Mandò al Re di Polonia un quadro che fu tenuto cosa bellissima, nel quale era Giove con una ninfa). The latter also created an allegorical portrait of royal jeweller Giovanni Jacopo Caraglio, receiving medallion with king's effigy as a proof of his nobilitation and royal patronage of Sigismund Augustus. Giovanni Battista Ferri (Ferro) from Padua in the Venetian Republic worked in Warsaw in about 1548 and the royal accounts from 1563 provide information about the payment of over one hundred thalers to Rochio Marconio, pictori Veneciano for eight paintings made for the king. Portrait of Sigismund the Old from around 1547 from the collection of the Morstins in Pławowice, today at the Wawel Castle (inventory number ZKWawel 3239), is considered by Michał Walicki as a very definite manifestation of the Venetian tradition (after "Malarstwo polskie: Gotyk, renesans, wczesny manieryzm", p. 33). It is possible that this paining, which is sometimes attributed to German painter Andreas Jungholz, was actually created by Pietro Veneziano or his circle. Contacts with the Venetian milieu of Titian have very probably further intensified when in 1553 Sigismund Augustus married his cousin Catherine of Austria, widowed Duchess of Mantua as a wife of Francesco III Gonzaga. The high demand for paintings in the Venetian workshops required painters to complete their work quickly. This involved a change in technique which uses a series of fast brushstrokes to create the impression of faces and objects. For many prominent patrons, speed was very important as they required several copies of the same image to be sent to different relatives, like effigies of the Habsburgs by Titian. In a letter of 1548, Andrea Calmo eulogised Tintoretto's ability to capture a likeness from nature in a mere half hour and according to Vasari he worked so fast that he had usually finished while the others were just thinking about starting. On 18 December 1565 in Florence, Francesco I de' Medici, who since 1564 was regent of the Grand Duchy of Tuscany in place of his father, married Joanna of Austria, the youngest daughter of Anna Jagellonica (1503-1547), Queen of Germany, Bohemia, and Hungary, and sister of Catherine of Austria, Queen of Poland. According to preserved letters, that year Sigismund Augustus sent at least two envoys to Florence: letter of March 10, 1565 notifying Francesco about sending of the envoy Piotr Barzi (from a family of Italian origin), castellan of Przemyśl and two letters of October 2 and 6, 1565 about sending the envoy Piotr Kłoczowski, royal secretary, to attend the wedding (after "Archeion", Volumes 53-56, p. 158). Around that time Florentine painter Alessandro Allori and his workshop created several portraits of young Francesco I de' Medici holding a miniature of his wife Joanna, which were undoubtedly meant to be sent to different European royal and princely courts. It is possible that also king of Poland, who sent his envoy for Francesco's wedding, received a copy and the version which was acquired before 1826 by Gustav Adolf von Ingenheim (1789-1855), later transported to Rysiowice in Silesia and today in the Wawel Royal Castle (inventory number 2175), may possibly be considered as such. Also the princes of Tuscany undoubtedly had images of the Polish-Lithuanian royal couple. Portrait of a man in a fur coat, attributed to Tintoretto, in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence (inventory number Contini Bonacossi 33), was acquired in 1969 from the Contini Bonacossi collection in their Villa Vittoria in Florence. According to museum's description of the painting the relationships with Titian's portraiture appear evident in this work. A man with a long beard in his forties or fifties wears expensive fur coat, which were imported to Western Europe mainly from the eastern part of the continent. Poland and Lithuania at that time were considered as one on the largest exporters of pelts of various animals: "the total number of hides exported from Poland in the second half of the 16th century amounted to about 150,000" (Acta Poloniae Historica, 1968, Volumes 18 - 20, p. 203). In 1560 Berardo Bongiovanni, Bishop of Camerino reported that, "The king [Sigismund Augustus] dresses simply, but has all kinds of clothes, Hungarian, Italian, of gold cloth, silk, summer and winter attires lined with sables, wolves, lynxes, black foxes, worth over 80,000 gold scudi". Five years later, in 1565, Flavio Ruggieri described the king: "He is 45 years old, of fairly good height, mediocre, great sweetness of character, more inclined to peace than war, speaks Italian by the memory of his mother, he loves horses and he has more than three thousand of them in his stable, he likes jewels of which he has more than a million red zlotys worth, he dresses simply, although he has rich robes, namely furs of great value". The man bear a great resemblance to preserved effigies of Sigismund Augustus, especially a minaiture by Lucas Cranach the Younger in the Czartoryski Museum in Kraków (inventory number XII-538), created between 1553-1565. The same facial features were also captured in two other portraits attributed to Jacopo Tintoretto or his workshop, both in private collection. In one of them the man, much younger then in the version from the Contini Bonacossi collection, resemble greatly Sigismund Augustus from his effigy created by Marcello Bacciarelli (considered as the effigy of Jogaila of Lithuania), from the Marble Room at the Royal Castle in Warsaw, created between 1768 and 1771 (inventory number ZKW/2713). A companion to the portrait in Uffizi is undoubtedly another portrait from the Contini Bonacossi collection with similar dimensions (109 × 91 cm / 110 × 83 cm) and composition, showing the man's wife, now in Belgrade (National Museum of Serbia). Federico Zeri (1921-1998), noticed the great similarity of this portrait to minaiture of Catherine of Austria in the Czartoryski Museum (Fondazione Federico Zeri, card number 43428), created, like the effigy of Sigismund Augustus, by Lucas Cranach the Younger in his workshop in Wittenberg. However, the portrait is identified as depicting Christina of Denmark (1521-1590), despite bearing no resemblance to any confirmed effigy of widowed Duchess of Milan and Duchess of Lorraine, who dressed more according to French/Netherlandish fashion and not Central European, like the woman in the described portrait. She is holding a compass in her left hand and her right hand on a celestial globe. Catherine's interest in cartography is confirmed by support to cartographer Stanisław Pachołowiecki, who was in her service between 1563-1566 (after "Słownik biograficzny historii Polski: L-Ż" by Janina Chodera, Feliks Kiryk, p. 1104). She was depicted in a black dress, most probably a mourning dress after death of her father Emperor Ferdinand I (died 25 July 1564), therefore the portrait should be dated to about 1564 or 1565, shortly before her departure to Vienna (October 1566). A copy of the painting in Belgrade, painted on oak panel, is in Kassel (Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister, inventory number SM 1.1.940), where there are also several other portraits of the Polish-Lithuanian Jagiellons, identified by me. The style of the painting in Kassel is more Netherlandish and can be attributed to Lambert Sustris, a Dutch painter, presumably a student of Jan van Scorel, active mainly in Venice where he worked in Titian's studio. King Sigismund Augustus established a permanent postal connection between Kraków and Venice. "The tasks of the post office included taking orders in the markets, sending very expensive and light goods [like paintings on canvas] and bullion coin" (after "Historia gospodarcza Polski do 1989 roku: zarys problematyki" by Mirosław Krajewski, p. 82). Merchants importing luxury goods, like Tucci, Bianchi, Montelupi, Pinozzo family, coming from Venice, Battista Fontanini, Giulio del Pace, Alberto de Fin, Paolo Cellari, Battista Cecchi, Blenci and many others, used it frequently. It was organized on the Italian model and for many years it was operated mainly by Italians. From 1558 it was run by Prospero Provano, then, from 1562, by Christopher de Taxis, former Augsburg postmaster and imperial court postmaster, from 1564 by Pietro Maffon, a native of Brescia in the Venetian Republic, and after him from 1568 by Sebastiano Montelupi, a Florentine merchant, who received an annual salary of 1,300 thalers. In 1562, a shipment from Kraków through Vienna to Venice took about 10 days, and from Kraków to Vilnius through Warsaw - 7 days. Royal mail was free of charge, private senders paid according to the agreed rate. Montelupi was obliged to carry royal and diplomatic mail, so he sent horse messengers every week. The royal post was under the management of the Montelupi family for nearly 100 years and they maintained the line between Kraków and Venice until 1662.
Portrait of king Sigismund II Augustus wearing a black fur trimmed coat by Tintoretto, 1550s, Private collection.
Portrait of king Sigismund II Augustus (1520-1572) by Tintoretto, 1550s, Private collection.
Portrait of king Sigismund II Augustus (1520-1572) in a fur coat by Tintoretto, ca. 1565, Uffizi Gallery.
Portrait of queen Catherine of Austria (1533-1572) with a globe and a compass by Tintoretto or Titian, ca. 1565, National Museum of Serbia in Belgrade.
Portrait of queen Catherine of Austria (1533-1572) with a globe and a compass by Lambert Sustris, ca. 1565, Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Kassel.
Portrait of Francesco de' Medici (1541-1587) by Alessandro Allori, ca. 1565, Wawel Royal Castle.
Portaits of Sigismund Augustus, Catherine of Austria and court dwarf Estanislao by Venetian painters
In 1553 Sigismund II Augustus decided to marry for the third time with a widowed Duchess of Mantua and his cousin Catherine of Austria. The wedding celebrations lasted 10 days and Catherine brought as a dowry 100,000 florins as well as 500 grzywnas of silver, 48 expensive dresses, and about 800 jewels. Somewhat distant marriage continued for a few years and Catherine became close with two yet-unmarried sisters of Sigismund, Anna and Catherine Jagiellon.
The royal court travelled frequently from Kraków through Warsaw to Vilnius. In October 1558 the queen became seriously ill. Sigismund was convinced that it was epilepsy, the same disease that tormented his first wife and Catherine's sister. For this reason, the marriage has become even more distant and the king sought to obtain annulment. It was a matter of international importance, Catherine's father Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor ruled vast territories to the west and south of Poland-Lithuania and assisted Tsar Ivan the Terrible in expanding his empire on eastern border of Sigismund's realm, while Catherine's cousin King Philip II of Spain was the most powerful man in Europe, ruler of half the known world from whom Sigismund was claiming the inheritance of his mother Bona. The queen become attached to her new homeland and her family used their influence to not allow the divorce. The arch-Catholic king of Spain undeniably received portraits of the couple. The portrait of a lady in a dress of green damask attributed to Titian from the Spanish royal collection is very similar to Catherine's portrait by the same painter in the Voigtsberg Castle and to her portrait in Belgrade. It is recorded in the inventory of the Buen Retiro Palace in Madrid of 1794 as a companion to a portrait of a soldier, now attributed to Giovanni Battista Moroni, a painter trained under Moretto da Brescia and Titian: "No. 383. Another [painting] by Titian: Portrait of a Madam: a yard and a quarter long and a yard wide, companion to 402. gilt frame" (Otra [pintura] de Tiziano: Retrato de una madama: de vara y quarta de largo y una de ancho, compañera del 402. marco dorado) and "No. 402. Another [painting] by Titian: half-length portrait of a man, a yard and a half high and a yard wide, with gilt frame" (Otra [pintura] de Tiziano: retrato de medio cuerpo de un hombre, de vara y media de alto y vara de ancho, con marco dorado). The effigy of "a soldier" bears great resemblance to portraits of the king and his costume is in similar style to that visible in a miniature by Cranach the Younger in the Czartoryski Museum. The portraits of Sigismund Augustus (most likely) and his third wife were in the collection of the favorite residence of King Philip II - the Royal Palace of El Pardo near Madrid, among the paintings by Titian - "In another box was the portrait of the king of Poland, in armor and without a helmet, on canvas" (En otra caja metido el retrato del rey de Polonia, armado e sin morrion, en lienzo) and "Catherine, wife of Sigismund Augustus, king of Poland" (Catalina, muger de Sigismundo Augusto, rey de Polonia) (compare "Archivo español de arte", Volume 64, p. 279 and "Unveröffentlichte Beiträge zur Geschichte ..." by Manuel Remón Zarco del Valle, p. 236). Both paintings have similar dimensions (119 x 91 cm / 117 x 92 cm, inventory number P000262, P000487) and matching compostion, just as portraits of Pietro Maria Rossi, Count of San Secondo and his wife Camilla Gonzaga by Parmigianino in the same collection (Prado Museum), with the wife's portrait painted with "cheaper", simple dark background. The portraits of Sigismund and Catherine from Contini Bonacossi collection, although very similar, differ slightly in style, one is closer to Tintoretto, the other to Titian, therefore it cannot be excluded that just as in case of Sigismund's famous Flemish tapestries his large commission for a series of portraits was realized by different cooperating workshops from the Venetian Republic. A smaller version (22 x 17 cm) of the portrait of a woman from Prado, today in the Museo Correr in Venice (inventory number Cl. I n. 0091), is attributed to Domenico Tintoretto (1560-1635). Sigismund Augustus reunited with his wife in October 1562 at the wedding of Catherine Jagiellon in Vilnius. The king's sisters and his wife dressed similarly and similar Venetian style dress to that visible in the portrait of queen Catherine is included in the inventory of Catherine Jagiellon's dowry: "Damask (4 pieces). A long green damask robe, on it the embroidery of gold cloth with red silk, wide at the bottom, covered with patterned green velvet, trimmed with gold lace on it with green silk. The bodice and sleeves along embroidered with the same embroidery." Sigismund Augustus had his ambassadors in Spain, Wojciech Kryski, between 1559 and 1562 and Piotr Wolski in 1561. He sent letters to the king of Spain and to his secretary Gonzalo Pérez (like on 1 January 1561, Estado, leg. 650, f. 178). He also had his informal envoys in Spain, dwarves Domingo de Polonia el Mico, who appears in the house of Don Carlos between 1559 and 1565, and Estanislao (Stanisław, d. 1579), who was at the court of Philip II between 1553 and 1562, and whom Covarrubias cited as "smooth and well proportioned in all his limbs" and other sources described as a skillful, well educated and sensible person (after Carl Justi's "Velázquez y su siglo", p. 621). Estanislao is recorded back in Poland between 1563-1571. Apart from being a skilled huntsman he was also most probably a skilled diplomat, just as Jan Krasowski, called Domino, a Polish dwarf of Catherine de' Medici, Queen of France or Dorothea Ostrelska, also known as Dosieczka, female dwarf of Sigismund's sister Catherine Jagiellon, queen of Sweden. Queen Catherine of Austria sent Polish dwarves to her brother Ferdinand II (1529-1595), Archduke of Austria, and to her brother-in-law Albert V (1528-1579), Duke of Bavaria. In the gallery of Archduke Ferdinand II in Ambras, there was a portrait of a "great Pole" (gross Polackh) in a yellow coat with the inscription DER GROS POLAC, probably copied by Anton Boys from an original, mentioned in the inventory of 1621 (Aber ain pildnus aines Tartarn oder Polln mit ainem gelben röckhl, f. 358), while the inventory of the ducal art chamber (Kunstkammer) in Munich of 1598 by Johann Baptist Fickler mentions a portrait of a Polish dwarf Gregorij Brafskofski (Conterfeht des zwergen Gregorij Brafskofski so ain Poläckh, 3299/3268) (after "Die Porträtsammlung des Erzherzogs ..." by Friedrich Kenner, item 159). In 1563 the king of Spain placed two portraits of Estanislao, one showing him in Polish costume of crimson damask, both by Titian, among the portraits of the royal family in his palace El Pardo in Madrid (included in the inventory of the palace of 1614-1617, number 1060 and 1070). It is also very probable that the king of Poland had his portrait. The portrait of unknown dwarf in Kassel attributed to Anthonis Mor (oil on panel, 105 x 82.2 cm, inventory number GK 39), although stylistically also close to Venetian school, seems to fit perfectly. In the same collection in Kassel there are also other portraits linked to Jagiellons. A pensive monkey in this painting is clearly more a symbol connected to deep knowledge and intelligence than joyfulness. A drawing by Federico Zuccaro (Zuccari) in Cerralbo Museum in Madrid (inventory number 04705) shows a monarch receiving an emissary with a cardinal and figures in Polish costumes. The effigy of the monarch is similar to portrait of King Sigismund II Augustus in coronation robes from the thesis of Gabriel Kilian Ligęza (1628) and other effigies of the king. In the National Gallery of Ireland, there is another drawing by Zuccaro, showing king's mother Bona Sforza (inventory number NGI.3247). Between 1563 and 1565, the painter was active in Venice with the Grimani family of Santa Maria Formosa. It is highly probable that he was also employed on some large order from the king of Poland. It is possible that Prado portraits were executed by Sofonisba Anguissola, born in Cremona in the Duchy of Milan, who in the winter of 1559-1560 arrived in Madrid to serve as a court painter and lady-in-waiting of Queen of Spain.
Portrait of king Sigismund Augustus in crimson costume by Giovanni Battista Moroni or circle of Titian, possibly Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1560, Prado Museum in Madrid.
Portrait of queen Catherine of Austria in a dress of green damask by Giovanni Battista Moroni or circle of Titian, possibly Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1560, Prado Museum in Madrid.
Portrait of queen Catherine of Austria holding a book by Venetian painter, ca. 1560, Museo Correr in Venice.
Portrait of court dwarf Estanislao (Stanisław, d. 1579) by Anthonis Mor or circle of Titian, ca. 1560, Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Kassel.
Sigismund II Augustus receiving an emissary, with a cardinal and figures in Polish costumes by Federico Zuccaro, 1563-1565, Cerralbo Museum in Madrid.
Bona Sforza, Queen of Poland by Federico Zuccaro, 1563-1565, National Gallery of Ireland.
Portrait of Marco Antonio Savelli by workshop of Giovanni Battista Moroni or Moretto da Brescia
The portrait of a gentleman, attributed to Moretto da Brescia, from the Potocki collection in Łańcut Castle, which was exhibited in 1940 in New York (catalogue "For Peace and Freedom. Old masters: a collection of Polish-owned works of art ...", page 25 , pic. 24), present whereabouts unknown, shows a man holding an open book on a stone pedestal. This painting is a copy of larger composition, today in the Calouste Gulbenkian Museum in Lisbon, acquired in Amsterdam in 1925, and originally most probably in the Uggeri collection in Brescia. According to Latin inscription on marble pedestal, the man was a member of a rich and influential Roman aristocratic family Savelli (· M · A · SAVELL[i] / EX FAM[ilia] · ROMAN[a]) and his name was most probably Marco Antonio Savelli. The portrait is attributed to Giovanni Battista Moroni and can be dated to the mid-16th century.
The most powerful member of the Savelli family around that time was cardinal Giacomo Savelli (1523-1587), who officially replaced Alessandro Farnese (1520-1589), Cardinal Protector of Poland (from 1544) during his absence from Rome from June 1562. From mid-1562 the royal chancellery more and more often turned with requests in Polish matters not only to the protector and vice-chancellor, but also to cardinal Charles Borromeo, protonotary apostolic, and to cardinals Giacomo Savelli and Otto Truchsess von Waldburg. It is possible that this unknown Marco Antonio Savelli, was sent by his relative the cardinal on a mission first to the Republic of Venice and then to Poland-Lithuania.
Portrait of Marco Antonio Savelli from the Łańcut Castle by workshop of Giovanni Battista Moroni or Moretto da Brescia, mid-16th century, present whereabouts unknown.
Portraits of Krzysztof Warszewicki by Paolo Veronese and Jacopo Tintoretto
Krzysztof Warszewicki (Christophorus Varsavitius or Varsevitius in Latin), a nobleman of the Kuszaba coat of arms, was born in Warszewice near Warsaw as the son of Jan Warszewicki, castellan of Liw (1544-1554), and later castellan of Warsaw (1555-1556), and his second wife Elżbieta Parysówna. He was born in the first months of 1543, and the year of his birth was certainly determined by Teodor Wierzbowski on the basis of a note by Vincenzo Laureo (Lauro), bishop of Mondovì, papal nuncio in Poland-Lithuania. Describing the Warsaw Convention of 1574, Laureo mentions the attacks and accusations that Warszewicki received from opponents for his previous conduct, especially for the reckless act he committed in Italy fifteen years ago, in 1559, "at the age of sixteen". In his speech to King James I of England in the spring of 1603, Warszewicki states that he is "over sixty years old" (mihi-ultra quam sexagenario).
The old father and the young mother indulged his whims. They send him to the court of King Ferdinand I in Prague and Vienna, where little Krzysztof was admitted as a page. From there the eleven-year-old boy, probably with Ferdinand's envoys, was sent to London for the marriage of Philip of Spain to Mary Tudor, Queen of England. The splendid entry of the Spanish prince into the capital of England on July 25, 1554, despite Krzysztof's young age, already made a strong impression on him and contributed to his sympathies with the Habsburg dynasty. Returning from London to Poland, Krzysztof probably stayed at the court of Jan Tarnowski, castellan of Kraków, or at the court of Jan Tęczyński, voivode of Sandomierz, with whose family Krzysztof's grandfather and father had close relations. He also stayed in his parent's house. Piotr Myszkowski, having met his father at the Piotrków Sejm in 1555, persuaded him to send his son abroad, where he could receive a better education. The castellan decided to send his son to Germany. At the end of April 1556 Krzysztof, together with Franciszek Zabłocki and Jan Głoskowski, came to Leipzig and enrolled as students of the "Polish nation" for the summer term, but after two months they left Leipzig for Wittenberg, where they also enrolled at the university in July of that year. Then Krzysztof went to Prague and Vienna, probably because there he could get letters of recommendation needed for Italy. Leaving Vienna, he took money and a horse from an Italian, but he was caught in Villach and forced to return the stolen things, as Mikołaj Dłuski claimed eighteen years later. 14 years old Warszewicki went Bologna, where he spent over two years studying at the University until the autumn of 1559. The natural stop on his journey from Vienna was Venice, although the precise dates of his stay are not known. In a speech given in Venice in March 1602, he says "after forty years I returned to you" (post quadragesimum annum ad Vos appuli). He also visted Naples, Rome, Florence and Ferrara. Certain aspects of his stay in Italy were discussed at the Convention of Warsaw on September 2, 1574 before the parliament, when he was chosen as envoy from Masovia. Abraham Zbąski and Piotr Kłoczewski, starost of Małogoszcz accused Warszewicki of stealing a gold chain from Krzysztof Lwowski in Naples, that he borrowed money in many Italian towns, escaped and was condemned in absentia, while the Poles lost their reputation with the Italians because of this, and indecency "by debauching with men in a dishonorable way". From Venice he returned via Vienna to Poland and in the spring of 1561 he was in Warsaw. He returned to Italy in 1567 and 1571 with Bishop Adam Konarski (1526-1574), as his courtier and secretary. He became a priest in 1598 and thanks to the grant of 150 zlotys from the Kraków chapter and 100 ducats from the council of Gdańsk in October 1600, he returned to Italy again, passing through Prague, Munich, Augsburg and Innsbruck. He visits Mantua, Rome, Genoa, Bologna and stays more than four months in Venice accompanied by Giovanni Delfino (1545-1622), procurator of San Marco (after "Krzysztof Warszewicki 1543-1603 i jego dzieła ...", pp. 56-64, 129). Krzysztof's half-brother Stanisław (d. 1591), who studied in Kraków, Wittenberg (under Philip Melanchthon) and Padua, was secretary to King Sigismund II Augustus from 1556. Warszewicki was one of the most vocal critics of the elective system in Poland-Lithuania, although he acknowledged that it was rooted in old Polish customs. His fascination with the Queen of the Adriatic is best reflected in his first major work, a narrative poem "Venice" (Venecia/Wenecia), first released in 1572 in Kraków, and later in 1587 also in Kraków. The poem applied the convention of a lament uttered by personified Venice, which painted a panoramic view of the relations between the Republic of Venice and the Ottoman Porte (after "Venice in Polish Literature ..." by Michał Kuran, p. 24). In the Museum Boijmans Van Beuningen in Rotterdam, there is a portrait of a boy attributed to Paolo Veronese (oil on canvas, 30.5 x 21.7 cm, inventory number 2570 (OK)). In 1928 the painting was in the collection of Jacques Goudstikker (1897-1940) in Amsterdam (after "Paolo Veronese ..." by Adolfo Venturi, p. 120) and it was purchased by the museum in 1958. The significantly reinforced inscription in the upper part dates the work to 1558 (Anno 1558), when the painter worked on the decoration of the Marciana Library in Venice, painted frescoes in the Palazzo Trevisan in Murano and between 1560 and 1561 he was called to decorate Villa Barbaro in Maser. The inscription may have been added after it left the artist's studio and the boy was 15 or 13 years old (Aetatis 15[3]) because the last number is not clearly visible. At that time, wealthy Venetians preferred larger effigies, full-length or group portraits and frescoes (portraits of Francesco Franceschini, Iseppo da Porto and his son, Livia da Porto Thiene and hier daughter, Giustinia Giustiniani on the balcony), so this small effigy, easy to transport and sent to other places, is quite unusual. Around 1558, when he was 15, Jan, Krzysztof's father, died and it is not known if he returned to Poland from Bologna, if so, he traveled through Venice or the vicinity. Such a small painting would be a good gift for his worried mother. The same man, although older, is depicted in another painting from the Venetian school. This larger, half-length portrait by a red curtain was created by Jacopo Tintoretto (oil on canvas, 70.3 x 58 cm, sold at Christie's London on December 7, 2007, live auction 7448, lot 195). It comes from the collection of Oskar Ernst Karl von Sperling (1814-1872), a German major general in the Prussian Army, who stationed in Wrocław and died in Dresden (sold at the Kunstsalon Paul Cassirer in Berlin on September 1, 1931). Its earlier history is unknown. The landscape behind him shows an imaginative waterside temple with large stairs, a triumphal arch-shaped doorway and a rose window. This is probably the temple of Apollo at Delphi on which the ancients had placed the inscription "Know thyself" (Gnothi seauton). "Let the diplomat, then, as instructed by Apollo of Delphi, and with my advice previously given, strive to know himself", advises Warszewicki in his De legato et legatione from 1595 (after "O pośle i poselstwach" by Jerzy Życki). In this work he also makes frequent reference to Venice. Early in 1567 he left for Rome. On March 21, 1567, he was in Padua and most likely returned to Poland with a letter of March 8, 1570 from Pope Pius V to the Infanta Anna Jagiellon. His letters to Konarski are addressed from Padua - May 18 and August 10, 1571. In both cases, the only direct link to Venice is the painter, but that does not mean that the model was also Venetian.
Portrait of Krzysztof Warszewicki (1543-1603) at the age of 15 by Paolo Veronese, 1558, Museum Boijmans Van Beuningen.
Portrait of Krzysztof Warszewicki (1543-1603) by Jacopo Tintoretto, ca. 1571, Private collection.
Portraits of Princess Elizabeth Radziwill by Lambert Sustris and Frans Floris
In 1554 the construction of a large fortess in Berezhany in western Ukraine, called the "Eastern Wawel", was accomplished and its founder Mikołaj Sieniawski (1489-1569), voivode of Ruthenia commemorated it on a stone plaque with Latin inscription above the southern gate. The architect of the building is unknown, however, the Renaissance decor suggests that he was Italian.
Descended from a noble family from Sieniawa in southeastern Poland, he raised the Sieniawski name to great power and importance. Under hetman Jan Amor Tarnowski, of the same clan crest of Leliwa, Sieniawski took part in the battle of Obertyn in 1531 and in as many as 20 other war campaigns. In 1539 with Tarnowski's intercession, he become the Field Hetman of the Crown and received from King Sigismund I the Medzhybizh Fortress, which he rebuilt in Renaissance style. Around 1518, he married Katarzyna Kolanka (d. after 1544), daughter of the Field Hetman of the Crown Jan Koła (d. 1543) and a niece of Barbara Kolanka (d. 1550), wife of George Radziwill (1480-1541), nicknamed "Hercules". Sieniawski was a Calvinist and raised his children as Protestants. Nevertheless his eldest son Hieronim (1519-1582), who became a courtier of the king Sigismund Augustus in 1548, married a Catholic, Princess Elizabeth Radziwill (d. 1565). The religion was unsurpassable obstacle in many countries of divided Europe at that time, but apparenly not in the 16th century Poland-Lithuania, the "Realm of Venus", godess of love. Hieronim and Elizabeth were married before May 30, 1558 as on this date Sieniawski bequeathed to his wife "for eternity" the estates, including Waniewo, which she had previously granted him "and bequeathed to him by particular Polish laws" (after "Podlaska siedziba Radziwiłłów w Waniewie z początku XVI wieku ..." by Wojciech Bis). Elizabeth, Princess of Goniądz and Medele (Myadzyel), was the youngest of three daughters of John Radziwill (d. 1542) and Anna Kostewicz of Leliwa coat of arms. As John had no son, the Goniądz-Medele line of the Radziwill family became extinct, and his domains were divided between his daughters, Anna, born in 1525, Petronella, born in 1526, and Elizabeth. On June 5, 1559, king Sigismund Augustus, orders Piotr Falczewski, Knyszyn leaseholder and Piotr Koniński, governor of Belz, to settle the matter between the royal subjects of the Tykocin Castle and the Kamieniec chamberlain Hieronim Sieniawski and his wife Elizabeth Radziwill. After Elizabeth's death her estates were inherited by her husband, who in 1577 sold Waniewo to the Princes Olelkovich-Slutsky. In the 18th century, the Berezhany Castle was famous for its collection of paintings parts of which are now kept in various museums of Ukraine. In 1762, the collection was located in 14 halls, other rooms and a library. The walls were covered with historical pictures. On the plafonds of two large halls there were battle compositions and the Great Hall was decorated with 48 portraits of the kings of Poland. In the "Viennese" halls, one with a large canvas on the ceiling showing the Relief of Vienna in 1683 and walls covered with red-gold brocade, there were portraits of Queen Jadwiga and Tsar Peter I, the other with Venetian style gilded ceiling and walls covered with green-red brocade was also hung with portraits. In the room with walls covered with Persian fabric with gold and silver, there were portraits of Hieronim Sieniawski, King Sigismund Augustus, Potocki, voivode of Kiev and a landscape painting. In the next room covered with green-red brocade and red portiere tapestries, there were Italian religious paintings. The gilded wooden ceiling of one of the rooms was decoarated with planets and carved human heads, most probably similar to the orginal coffered ceiling in the Chamber of Deputies at the Wawel Castle. There was a large pyramid-shaped chandelier there and several portraits of family members. Next was the library with other paintings and a room with gilded ceiling with 11 paintings showing the episodes from the Battle of Khotyn (1621) and several other portraits. In the fourth upper room there was a gilded ceiling filled with portraits (after "Brzeżany w czasach Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej: monografia historyczna" by Maurycy Maciszewski, p. 33-34). From 1772, after the First Partition of Poland, Berezhany belonged to Austria, while the descendants of the Sieniawski family were based in Russian partition. The abandoned castle gradually fell into disrepair. Many valuable items were sold at auction on August 16, 1784. When princess Lubomirska won the trial in Vienna against the Austrian government to recover the portraits of the Sieniawski family painted on silver and other valuables from the family tombs, it turned out that they were melted for coinage. Paintings and portraits were moved to the outbuildings, where they were rotting and crumbling to dust (after "Brzeżany w czasach Rzeczypospolitej ...", p. 54). The author of an article, published in Dziennik Literacki from 1860 (nr 49) recalled: "Today I will only add that there were very expensive Italian paintings in the chapel and castle halls in Berezhany. There are still people who remembered them. For some of these paintings, the Sieniawskis paid several thousand ducats. Years ago, when I asked the guardian of the chapel and the castle, a simple peasant, where are the paintings, he replied that the smaller ones were dismantled and stolen, and the larger canvases were cut into sacks on the order of the officialists. It happened 30 years ago. There were many historical portraits among the paintings, namely of the Sieniawski family". The deed of destruction was accomplished during the First and Second World War. The "Realm of Mars", god of war, left only ruins in Berezhany. The portrait of lady in the Museum of Western and Eastern Art in Odessa, Ukraine (inventory number ЗЖ-112) was acquired in 1950 from Alexandra Mitrofanovna Alekseeva Bukovetskaya (d. 1956), wife of Ukrainian painter Evgeny Iosifovich Bukovetsky (1866-1948). In 1891 Bukovetsky made a trip to western Europe, returning to Odessa in the same year. In Paris he attended the Académie Julian and worked for some time in Munich. Nevertheless, he or his wife, most likely acquired the painting later in Ukraine. The effigy is considered the work of a 16th-century Venetian artist and dated between 1550 and 1560. In 1954, on the back of the main canvas, a piece of another canvas was found with the inscription: restavrir 1877. Interestingly, between 1876-1878 Stanisław Potocki started renovation and restoration works in Berezhany. The costume of depicted woman is very similar to that visible in the effigy of Queen Catherine of Austria (1533-1572) in unknown collection (published on livejournal.com on June 2 2017). The portrait of the Queen is inscribed in Latin: CHATARINA.REGINA.POLONIE.ARCHI: / AVSTRIE, therefore should be dated to between 1553-1565, before the Queen's departure from Poland. It is also closely related to a portrait of an unknown lady wearing a red velvet gown with a V-shaped white lace front from the 1550s in the Apsley House. Another similar costume and pose of the sitter is visible in the portrait of a lady in red dress by Giovanni Battista Moroni in the Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister, dated to about 1560. The woman wears a heavy gold earrings with cameos with female busts and a belt with a large cameo with sitting goddess Minerva holding on her right hand a figure, the personification of victory. Similar cameos were set on the casket of Hedwig Jagiellon, created in 1533 (The State Hermitage Museum) and the casket of Queen Bona Sforza, created in or after 1518 (Czartoryski Museum, lost during World War II). A certain similarity can also be indicated with the cameo with bust of Queen Barbara Radziwill by Jacopo Caraglio, created in about 1550 (State Coin Collection in Munich). The style of the mentioned portrait in Odessa is very close to the portrait of Veronika Vöhlin, created in 1552 and to the portrait of Charles V seated, created in 1548, both in the Alte Pinakothek in Munich and both attributed to Lambert Sustris, the same painter who created several effigies of Zofia Tarnowska (1534-1570), the only daughter of hetman Jan Amor Tarnowski. The same woman was also depicted in another painting attributed to Sustris or his circle, and showing Venus and Cupid with the view of the evening landscape. It was painted on canvas (88 x 111 cm) and is today in the private collection in Germany. A smaller version of this composition (29.5 x 42 cm), painted on panel is today in the Hallwyl Museum in Stockholm. It was acquired in 1919 in Berlin, where before 1869 there was a Radziwill Palace (later Reich Chancellery). Basing on signature (F.F.) and style it is attributed to the Flemish painter Frans Floris, who traveled to Italy probably as early as 1541 or 1542. He spent several years there with his brother Cornelis. From 1547 until his death he lived in Antwerp, where he managed a large studio with many pupils. In 1549 Cornelis Floris was commissioned to make a funerary monument for Dorothea, wife of Albert, Duke of Prussia, cousin of King Sigismund II Augustus, in Königsberg Cathedral. Design for several tapestries with monogram of Sigismund Augustus (Wawel Royal Castle), created in about 1555, is attributed to Cornelis Floris. Until his death in 1575 he worked on an impressive series of sculptures at home and abroad, including the tomb for Duke Albert in Königsberg, carved in 1570. Königsberg, known as Królewiec in Polish, was the capital of Ducal Prussia, fief of Poland (till 1657) and one of the biggest cities and ports situated close to estates of the Goniądz-Medele line of the Radziwill family. Paintings by Frans Floris were imported to different countries in Europe already in the 16th century, like the Last Judgment, created in 1565, today in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, which was verifiable in Prague in 1621, and he died while working on large paintings for a Spanish client. In Poland there is an Allegory of Caritas, acquired in 1941 for the Museum in Gdańsk (inventory number M / 453 / MPG) and a portrait of a girl as Diana in the National Museum in Wrocław (inventory number VIII-2247). The Holy Kinship by Frans Floris from the Łańcut Castle, dated to about 1555, was sold in 1945 in Zurich and tin sarcophagus of Sigismund Augustus with allegories of five senses (Wawel Cathedral) was created by Flemish/Dutch sculptors (Monogrammist FVA and Wylm van Gulich) in 1572 and inspired by engravings after drawings by Frans Floris. The sitter from the described paintings by Lambert Sustris and Frans Floris, bear a resemblance to effigies of Anna Kostewicz and John Radziwill (a print and a portrait in the National Museum in Warsaw), parents of Elizabeth Radziwill. Among paintings offered in 1994 by Karolina Lanckorońska to the Wawel Royal Castle in Kraków, there is a small painting depicting the Rest on the Flight into Egypt (oil on panel, 94.5 x 69.6), painted in the style close to Lambert Sustris (inventory number ZKWawel 7954). Before 1915 it was in the Lanckoroński Palace in Rozdil (Rozdół in Polish), between Berezhany and Lviv in Ukraine, and later transported to Vienna.
Portrait of Princess Elizabeth Radziwill (d. 1565) by Lambert Sustris, 1558-1560, Museum of Western and Eastern Art in Odessa.
Portrait of Princess Elizabeth Radziwill (d. 1565) as Venus and Cupid by Lambert Sustris or circle, 1558-1560, Private collection.
Portrait of Princess Elizabeth Radziwill (d. 1565) as Venus and Cupid by Frans Floris, 1558-1560, Hallwyl Museum in Stockholm.
The Holy Kinship from the Łańcut Castle by Frans Floris, ca. 1555, Private collection.
The Rest on the Flight into Egypt by Lambert Sustris, third quarter of the 16th century, Wawel Royal Castle.
Portraits of Anna Jagiellon, Catherine Jagiellon and Catherine of Austria as Venus by Titian
In 1558 died Mary Tudor and Philip II of Spain, ruler of the half of the known world was widowed again. He decided to marry. The future wife should be fertile and bear him many healthy sons, as his only son Don Carlos was showings signs of mental instability. At the same time the contacts of the Polish court with Spain increased. It is possible that Sigismund Augustus proposed his two unmarried sisters Anna and Catherine and sent to Spain their portraits. The match with the king of Spain, apart from great prestige, would also allow Sigismund to claim the heritage of his mother and the Neapolitan sums.
In January 1558, the councilor of the king of Spain, Alonso Sánchez took possession of the goods of the late Queen of Poland Bona in the name of the Spanish Crown and sequestered everything that was in the castle in Bari. Wojciech Kryski was sent to Madrid to appeal to Philip II about Bona's inheritance. Instructions for Kryski (January 16, 1558) and a letter from Sigismund Augustus to Philip (April 17, 1558) were dated from Vilnius. A letter of Pietro Aretino to Alessandro Pesenti of Verona, musician at the royal court, dated 17 July 1539, is the earliest witness to Giovanni Jacopo Caraglio's presence in Poland. Pesenti had been the organist to Cardinal Ippolito d'Este before becoming a royal musician at the Polish court on 20 August 1521. He was Bona's favourite organist and Caraglio created a medal with his profile on obverse and muscial instruments on reverse (Münzkabinett in Berlin). There were also other eminent Italian muscicians in royal capella, like Giovanni Balli, known in Poland as Dziano or Dzianoballi, who in the 1560s was paid 25 florins quaterly and many others. Among the lute players, the favourite of the king Sigismund II Augustus was Walenty Bakwark or Greff Bakffark (1515-1576), born in Transylvania who entered his service on 12 June 1549 in Kraków. He recieved many gifts from the king and his salary increased from 150 florins in 1558 to 175 florins in 1564. In 1559 he acquired a house in Vilnius and he travelled to Gdańsk, Augsburg, Lyon, Rome and Venice. From 1552 the court organist of the king was Marcin Andreopolita of Jędrzejów and Mikołaj of Chrzanów (d. 1562), an organist and composer. Most probably before his arrival to Poland Caraglio created numerous erotic prints, including sets of Loves of the Gods, which also contain very explicit scenes. One depicting Venus and Cupid (Di Venere et amore) is signed by him (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam). In April 1552, he made a brief return trip to Italy. On October 18, 1558 in Warsaw, Sigismund Augustus issued a privilege to Prospero Provano (or Prosper Provana, d. 1584), a Piedmontese merchant, to arrange permanent post Kraków - Venice via Vienna (Ordinatio postae Cracowia Venetias et super eandem generosus Prosper Provana praeficitur). The company was subsidized by the king and Prospero was paid 1,500 thalers a year by the royal treasury. The post was to transport luggage and people. Two paintings by Titian from the Spanish royal collection and one from the Medici collection in Florence by workshop of Titian shows Venus, goddess of love. They were created at the same time and they are almost identical, the protagonists however are different. In Prado versions the musician is interrupted in the act of making music by the sight of a nude beauty. He directs his eyes to her womb. In Uffizi version a musician is replaced with a partridge, a symbol of sexual desire. As in Venus of Urbino, all alludes to the qualities of a bride and the purpose of the painting. A dog is a symbol of fidelity, donkeys refer to eternal love, a stag is the attribute of the huntress Diana, a virgin goddess and protector of childbirth and a peacock, sacred animal of Juno, queen of the gods, sitting on a fountain refer to fecundity. A statue of satyr on the fountain is a symbol of the sexuality and voluptuous love. A pair of embraced lovers are heading towards the setting sun. A copy of "older" Venus from Prado is today in the Mauritshuis in The Hague (oil on canvas, 157 x 213 cm, inventory number 343). This painting was created in the studio of Titian and at the beginning of the 19th century was in the collection of Lucien Bonaparte, the younger brother of Napoleon Bonaparte, and later, until 1839, belonged to Cardinal Joseph Fesch in Rome. Another, most probably a workshop copy and close to the works by Lambert Sustris, is in the Royal Collection in England (oil on canvas, 96.3 x 136.9 cm, RCIN 402669). It once belonged to King Charles I and it is also attributed to Spanish artist Miguel de la Cruz (Michael Cross, active 1623-1660). Paintings from the Gemäldegalerie in Berlin, the Metropolitan Museum of Art and the Fitzwilliam Museum are similar, but the women are married. The musician directs his eyes to breasts of the goddess, a symbol of maternity, or her head crowned with a wreath. Her womb is covered and in Berlin painting the goddess is departing (carriage in the background) towards the peaks of the far north - a good quality copy of this painting, possibly from Titian's 19th century copyist, is in Kaunas, Lithuania (oil on canvas, 115.5 x 202 cm, National Museum of Art, inventory number ČDM MŽ 1217). The lanscape with stags and dancing satires in paintings of crowned Venus allude to fecundity. Despite the divine beauty of two sisters of king of Poland, Anna and Catherine Jagiellon, Philip decided for more favorable match with neighbouring France and married Elizabeth of France, who was engaged with his son. The younger Catherine married Duke of Finland in 1562 in Vilnius and departed to Finland. The painting in the Gemäldegalerie in Berlin was acquired in 1918 from private collection in Vienna and the painting in the Fitzwilliam Museum was in the Imperial collection in Prague by 1621, therefore both were sent to Habsburgs. Lambert Sustris created a reduced copy of the version from the Fitzwilliam Museum without the lute player (or possibly cut later), which was sold in Rome in 2014 (Minerva Auctions, November 24, 2014, lot 18). The painting in the Metropolitan Museum of Art was described in great detail in a 1724 inventory of the Pio di Savoia collection in Rome. Cardinal Rodolfo Pio da Carpi, humanist and patron of the arts, was the favorite candidate of Philip II of Spain in the Conclave of 1559. Catherine of Austria, willing to save her marriage and give the heir to Sigismund Augustus, most probably sent her portait to Rome to get a blessing, just as her mother Anna Jagellonica in about 1531 (Borghese Gallery). The effigy of Saint Catherine of Alexandria by Titian from about 1560 in the Prado Museum is very similar to other effigies of Queen Catherine and her portraits as Venus. The slashed wheel and the sword allude to the martyrdom of the saint and difficult marital situation of the Queen. Her royal status was appropriate for a foundation such as Royal Monastery of El Escorial (recorded as far as 1593). Despite her efforts she did not managed to save her marriage. The painting of Venus in Berlin was acquired in 1918, the year when Poland regained its independance after 123 years, eliminated by neighbouring countries. Blond goddeses of European culture were rulers of the country that should not exist (in the opinion of countries that partitioned the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth), something totally inimaginable and inacceptable to many people back then.
Portrait of Princess Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596) as Venus with the organ player by Titian, ca. 1558, Prado Museum in Madrid.
Portrait of Princess Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596) as Venus with the organ player by workshop of Titian, ca. 1558, Mauritshuis in The Hague.
Portrait of Princess Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596) as Venus with the organ player by workshop or follower of Titian, possibly Lambert Sustris, ca. 1558 or after, The Royal Collection.
Portrait of Princess Catherine Jagiellon (1526-1583) as Venus with the organ player by Titian, ca. 1558, Prado Museum in Madrid.
Portrait of Princess Catherine Jagiellon (1526-1583) as Venus with a partridge (Venere della pernice) by workshop of Titian, ca. 1558, Uffizi Gallery in Florence.
Portrait of Princess Catherine Jagiellon (1526-1583) as Venus with the organ player by Titian, ca. 1562, Gemäldegalerie in Berlin.
Portrait of Princess Catherine Jagiellon (1526-1583) as Venus with the organ player by follower of Titian, first half of the 19th century, National Museum of Art in Kaunas.
Portrait of Queen Catherine of Austria (1533-1572) as Venus with the lute player by Titian, 1558-1565, Fitzwilliam Museum in Cambridge.
Portrait of Queen Catherine of Austria (1533-1572) as Venus by Lambert Sustris, 1558-1565, Private collection.
Portrait of Queen Catherine of Austria (1533-1572) as Venus with the lute player by Titian, 1558-1565, Metropolitan Museum of Art.
Portrait of Queen Catherine of Austria (1533-1572) as Saint Catherine by Titian, 1558-1565, Prado Museum in Madrid.
Venus and Cupid by Giovanni Jacopo Caraglio, mid-16th century, Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam.
Portrait of Catherine Jagiellon in red by Giovanni Battista Moroni
A young woman in the portrait of a lady, known as La Dama in Rosso (Lady in Red) by Giovanni Battista Moroni in the National Gallery in London, bears great resemblance to Catherine Jagiellon's miniature in German costume by Lucas Cranach the Younger and her portraits by Titian and his workshop.
The identification as a portrait of poetess Lucia Albani Avogadro (1534-1568) is manly based on engraved effigy of Lucia in profile, with generic resemblance, by Giovanni Fortunato Lolmo created between 1575 and 1588, therefore almost ten years after her death, and inventory of Scipione Avogadro's collection in Brescia, which describes "two portraits by Moretto [da Brescia], one of the count Faustino, standing, the other of the countess Lucia, his wife" (Due ritratti del Moretto, uno del conte Faustino in piedi, altro della contessa Lucia sua moglie). The painting was purchased from Signor Giuseppe Baslini at Milan in 1876 with other portraits from Fenaroli Avogadro collection, most probably from their villa in Rezzato, near Brescia. Its previous history is unknown, it is threfore possible that it was acquired when their villa was extened in the 18th century or that Filippo Avogadro, who greeted Queen Bona in Treviso in 1556, wanted to have a portrait of her beautiful daughter. The sitter is pointing to a simple fan of straw worked with silk, the main accessory as in the portrait by Titian in Dresden. The fan was regarded as a status symbol in ancient Rome and developed as a means of protecting the holy vessels from pollution caused by flies and other insects in the Christian Church (flabellum), thus becoming a symbol of chastity. In Venice and Padua a fan was carried by betrothed or married women. Its specific octagonal shape might be a reference to renewal and transition as eight was the number of Resurrection (after George Ferguso's "Signs & Symbols in Christian Art", 1961, p. 154), can then be interpreted as readiness to change marital status. In 1560, at the age of 34, Catherine was still unmarried and did not want be betrothed to a tirant, Tsar Ivan IV, who invaded Livonia committing horrible atrocities. This portrait would be a good information that she prefers an Italian suitor. It was commissioned around the same time as portraits of Catherine's brother and his wife by Moroni, Titian or Sofonisba Anguissola (Prado Museum).
Portrait of Catherine Jagiellon (1526-1583) in red by Giovanni Battista Moroni or Sofonisba Anguissola, 1556-1560, National Gallery in London.
Portraits of Catherine Jagiellon by circle of Titian
In the 16th century fashion was an instrument of politics and princesses of Poland-Lithuania had in their coffers Spanish, French and German robes. The inventory of dowry of Catherine Jagiellon (1526-1583), Duchess of Finland includes many items similar to these visible in the portraits identified as portraits of the Duchess of Urbino:
- "Necklaces with precious stones, 17 pieces (the most expensive 16,800 thalers)", - "Pearl caps (13 pieces). From 40 thaler. to 335", - "Buckles on (thirteen) French and Spanish robes", - 17 velvet, long underneath garments, including one crimson with 72 French buckles, and "longitudinal pontałs [jewels and ornaments sewn onto the dress, imitating embroidery] with blocks with the same white and brown-red enamel is pair 146", - 6 satin underneath garments, one robe of white satin embroidered with gold and silver with 76 buckles, and a robe of brown-red satin embroidered along the length with gold thread. The famous pendant of Catherine with her monogram C with which she was buried, was not detailed in the inventory and a similar pearl snood net was depicted on the cameo of Catherine's mother Bona Sforza and on the portrait of a daughter of Ferdinand I of Austria, most probably one of the wives of Sigismund Augustus, in the National Gallery of Ireland. Numerous jewels and a bunch of roses allude to the purity and qualities of a bride. The necklace is a jewel in which three different stones are set, each with its own precise meaning: the emerald indicates chastity, the ruby indicates charity, the sapphire indicates purity and the big pearl is finally a symbol of marriage fidelity. The monogram on French-style (?) buckles visible in the portrait, could be interpreted as interlaced CC, just as in monogram of Catherine de' Medici, Queen of France. The identification as portrait of Giulia da Varano (1523-1547) is mainly based on inventory of the Ducal Palace of Pesaro from about 1624, which says about the portrait of the Duchess in ebony frames with her coat of arms and interlaced monogram G.G. of Giulia and her husband.
Portrait of Catherine Jagiellon (1526-1583) by Venetian school, 1550s, Bardini Museum in Florence.
Portrait of Catherine Jagiellon (1526-1583) in a pearl snood net by circle of Titian, ca. 1560, Private collection.
Portrait of Catherine Jagiellon (1526-1583) as a bride by circle of Titian, before 1562, Pitti Palace in Florence.
Portrait of Jan Firlej by Titian
After his missions to Emperor Charles V in Worms in 1545 and to the court of King Ferdinand I of Austria in 1547, the brilliant career of Jan Firlej (1521-1574) continued. He was a courtier of the king (1545), secretary of the king (1554), castellan of Belz (1555), voivode of Belz (1556), voivode of Lublin (1561), grand marshal of the Crown (1563), voivode and starost of Kraków (1572) and marshal of the Sejm (1573). After 1550, he converted to Lutheranism, then to Calvinism and introduced Protestantism in his estates. He was one of the most prominent promoters of Protestantism in the Commonwealth and an ardent defender of Polish dissidents.
Before Queen Bona left for Italy in 1556, Jan was delegated by King Sigismund Augustus, together with several other castellans under the direction of Crown Chancellor Jan Ocieski, to collect important state documents from her. The description of their activities, preserved in the letter of the chancellor of January 27, 1556 from Warsaw to the king, is interesting: "When we came to receive the letters, Her Highness began with the words: Praise God that everyone should know about my business. In my lord's time no one knew what I had in my chest; now I have to open it. But I am really happy to do it, and I will gladly do it" (Laudetur Deus quod omnes debent scire res meas; tempore domini mei nemo scivit quid ego in cista mea habebam; nunc oportet me aperire. Sed vere ego sum contenta, libenter faciam). It was mainly Queen Bona's protection that helped the house of Firlej grow: "The one who ran away from us with an immeasurable catch / Cunning, greedy, lustful, Italian in a word, [...] With what she stripped from others, she dressed the Firlejs", wrote Ignacy Krasicki (1735-1801). Interestingly, this negative opinion about the queen was written by the Catholic bishop, who after the first partition of Poland became a close friend of Frederick II of Prussia, considered misogynist and homosexual (after "Dwie książki o Ignacym Krasickim" by Stefan Jerzy Buksiński, p. 62). After the death of his brother-in-law Jan Boner (1516-1562), the castle of Ogrodzieniec passed into the possession of Jan Firlej, as husband of Zofia, daughter of Seweryn Boner. Zofia's father was a royal banker and baron in Ogrodzieniec, a title received from King Ferdinand I in 1540. Firlej was also the king's envoy to Moldavia, where he received the oath of allegiance from Bogdan IV (1555-1574), prince of Moldavia (from 1568 to 1572). During the first interregnum (1572-1573), the French court sent him rich gifts through a Pole, in order to obtain his support for the candidacy of Henry, Duke of Anjou to the throne of Poland-Lithuania, but Firlej rejected the gifts and severely rebuked the messenger. He allegedly wanted the throne for himself. In the picture gallery of the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, there is portrait of a man in a coat lined with expensive lynx fur, painted by Titian (oil on canvas, 115.8 x 89 cm, GG 76). The painting comes from the the collection of Archduke Leopold Wilhelm of Austria and was recorded in Theatrum Pictorium (number 95), after two paintings depicting Roxelana (numbers 93, 94), identified by me. David Teniers the Younger, court painter of Archduke Leopold Wilhelm, created between 1650-1656 a small copy of this painting, now in the Courtauld Institute of Art (oil on panel, 22.6 x 17 cm, P.1978.PG.436). He also depicted the painting in several views of Archduke's Gallery in Brussels (Schleißheim State Gallery, 1819, 1840, 1841), however in an incorrect layout, thus probably copying the earlier version of Lucas Vorsterman's engraving or a drawing. Titian's painting was previously thought to depict Filippo di Piero Strozzi (1541-1582), a member of the Florentine Strozzi family and condottiero, who in 1557 entered the French army and fought the Calvinist Huguenots, but this identification was rejected. Strozzi's miniature, possibly by Anton Boys, is also in the Kunsthistorisches Museum. The Habsburg collections included many portrait paintings of notable figures, mostly sent as gifts, so the man in the Venetian painter's painting must have been an important international figure. This is more of an official portrait, so the man was rather not a warrior or military leader, like Strozzi portrayed in a suit of armor of an admiral. He was most likely a diplomat or politician. The painting was initially larger in its upper part, as evidenced by old photographs and copies by Teniers. His face has also been changed. Possibly it was repainted by another painter because Titian does not render the likeness well and these alterations were removed in the 20th century. The man's pose and facial features, especially in the pre-restoration versions, resemble Jacopo Tintoretto's portrait in the Kröller-Müller Museum, depicting Firlej in 1547 at the age of 26. The painting is generally dated to around 1560, when Jan obtained important posts of voivode of Lublin (1561) and grand marshal of the Crown (1563). As a Calvinist close to Queen Bona, he can generally be seen as an opponent of the Habsburgs and their policies, but as an important dignitary, good relations with him, like for the French court, were undoubtedly important. So it was good to receive his beautiful portrait, but not necessarily to remember his identity.
Portrait of Jan Firlej (1521-1574) by Titian, 1560s, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Portrait of Jan Firlej (1521-1574) by Titian, 1560s, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna (before restoration).
Portrait of Jan Firlej (1521-1574) by David Teniers the Younger after Titian, 1650s, Courtauld Gallery in London.
Portrait of Jan Firlej (1521-1574) from the Theatrum Pictorium (95) by Lucas Vorsterman the Elder after Titian, 1673, Slovak National Gallery in Bratislava.
Portrait of Catherine Jagiellon in white by Titian
In the first half of the 18th century, a Swedish painter Georg Engelhard Schröder, created copies of two portraits of Venetian ladies by Titian. These two portraits, in Gripsholm Castle near Stockholm, are undeniably a pair, pendants showing two members of the same family, sisters. They are the only two copies of Titian by Schröder in this collection, they have almost identical dimensions (99 x 80 cm / 100 x 81 cm), composition, the two women are similar and the paintings have even similar inventory number (NMGrh 187, NMGrh 186), a proof that they were always together. The woman holding a cross and a book is Anna Jagiellon, as in the painting by circle of Titian in Kassel, the other must be then her younger sister Catherine Jagiellon, Duchess of Finland from 1562 and later Queen of Sweden.
After 1715 the Gripsholm Castle was abandoned by the royal court and between 1720 and 1770, it was used as a county jail. In 1724 Schröder was made the court painter of Frederick I of Sweden, who highly valued him. It is very probable that the king ordered the painter to copy two old, damaged portraits of unknown ladies from Gripsholm, which were then thrown away, replaced with copies by Schröder. The portrait of a second lady, in white dress and holding a fan, considered to be Titian's mistress, his daughter as a bride or a Venetian courtesan, is known from several copies. The best known is that in Dresden (without a pattern on sitter's dress, which a pupil of Titian most probably forgot or didin't managed to add), acquired in 1746 from the collection of the d'Este family (Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister, oil on canvas, 102 x 86 cm, inventory number Gal.-Nr. 170), which were friends and allies of "the Milanese princess", Bona Sforza, Catherine's mother. The other, now lost, was copied by Peter Paul Rubens, most probably during his stay in Mantua between 1600-1608, tohether with a portrait of Isabella d'Este, also by Titian and also considered to be lost (both in Vienna - Kunsthistorisches Museum, oil on canvas, 96.2 x 73 cm, GG 531) and another recorded by Anton van Dyck in his Italian sketchbook (British Museum) from the 1620s. In case of a copy by Rubens, it's also highly probable that Catherine's son, Sigismund III Vasa, who ordered paintings and portraits from the Flemish painter, also commissioned a copy of a portrait of his mother in about 1628. Another copy by a Flemish painter, holding a rose, can be found in Canterbury Museums and Galleries (oil on canvas, 54 x 40 cm, CANCM:4036). The dress, as that visible in the portraits, is described among the dresses of the Duchess of Finland in the inventory of her dowry from 1562: "Satin (6 pieces). Satin white robe; on it four embroidered rows at the bottom made of woven gold thread with silver; the bodice and sleeves are also embroidered in a similar manner; buckles on them with red enamel 76". Even without Titian's idealization, Catherine, just as her mother, was considered a beautiful woman, which, unfortunately, is less visible in her portraits in German costume by Cranach the Younger. The Russian envoy reported to Tsar Ivan the Terrible in 1560 that Catherine was beautiful, but that she was crying (after Eva Mattssons' "Furstinnan : en biografi om drottning Katarina Jagellonica", 2018), unwilling to marry a man famous of his violence and cruelty. The painting in Dresden, and its copies, was most probably commissioned by Sigismund Augustus or Anna Jagiellon and sent to the Italian friends. Another version of this portrait by circle of Titian, most probably from the collection of Sophia Jagiellon (1522-1575), Duchess of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel is also in Kassel not far from Brunswick (Wilhelmshöhe Castle, oil on canvas, 99 x 79 cm, inventory number 490). The three sisters Sophia, Anna and Catherine are therefore reunited in their portraits by circle of Titian in Kassel. In 1563, King Eric XIV of Sweden imprisoned his brother John and his consort Catherine Jagiellon in the Gripsholm Castle. Few years later Catherine granted authority to her sister Anna to fight for the Italian inheritance of Queen Bona. In the Uffizi Gallery in Florence there is also a miniature by an Italian painter, possibly Sofonisba Anguissola, showing the same blond woman in a costume similar to that visible in portraits of Catherine Stenbock, Dowager Queen of Sweden from the 1560s (oil on walnut board, 13 cm, Inv. 1890, n. 3953). It depicts Catherine Jagiellon during the time of imprisonment in Gripsholm Castle between 1563 and 1567. Althought considered a compassionate and loyal queen, the religious issues made Catherine unpopular with her contemporaries in Sweden. The Catholic queen maintained close relations with Poland-Lithuania and Italy. Her agent was Paolo Ferrari from Cremona, she also had her own ambassadors in Rome, a Dutch Catholic named Petrus Rosinus, and Ture Bielke. Catherine is considered to have had an influence on her husband John III of Sweden in many areas, such as his religious attitude, foreign policy and art. The names of her daughter and son, Isabella (in honour of her grandmother Isabella d'Aragona of Naples, Duchess of Milan) and Sigismund (in honour of her father), both contrary to Swedish tradition, indicates that, like her mother Bona Sforza, she had a much greater influence on politics than is officially claimed.
Portrait of Catherine Jagiellon, Duchess of Finland in white by Titian, ca. 1562, Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden.
Portrait of Catherine Jagiellon, Duchess of Finland in white by circle of Titian, ca. 1562, Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Kassel.
Portrait of Catherine Jagiellon, Duchess of Finland in white by Peter Paul Rubens after lost original by Titian, ca. 1600-1608 or 1628, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Portrait of Catherine Jagiellon, Duchess of Finland holding a rose by Flemish painter after Titian, after 1562, Canterbury Museums and Galleries.
Portrait of Catherine Jagiellon, Duchess of Finland in white by Georg Engelhard Schröder after original by Titian, 1724-1750, Nationalmuseum in Stockholm.
Miniature portrait of Catherine Jagiellon, Duchess of Finland by Italian painter, possibly Sofonisba Anguissola, 1563-1567, Uffizi Gallery in Florence.
Portrait of king Sigismund Augustus holding a buzdygan by workshop or follower of Giovanni Battista Moroni
In 1551 Georg Joachim de Porris (1514-1574) or von Lauchen, also known as Rheticus, a mathematician and astronomer of Italian heritage, best known for his trigonometric tables and as Nicolaus Copernicus's sole pupil, lost his job at the Leipzig University following the alleged drunken homosexual assault on a young student, the son of a merchant Hans Meusel. He was sentenced to 101 years of exile from Leipzig. As a result, he would come to lose the support of many long-time benefactors including Philipp Melanchthon. Earlier rumors of homosexuality forced him to leave Wittenberg for Leipzig. Constitutio Criminalis Carolina, a comprehensive criminal code, promulgated in 1532 by Emperor Charles V and binding for the Holy Roman Empire until 1806, mandated the death penalty for homosexuality. He fled following this accusation, for a time residing in Chemnitz before eventually moving on to Prague, where he studied medicine. He then moved to Kraków. Having settled there, where he lived in the Kaufman's tenement house in the Main Square, he erects a large obelisk in Balice near Kraków with the financial and technical assistance of Jan Boner (1516-1562), the king's advisor and the leader of the Lesser Poland's Calvinists. This gnomon of 45 Roman feet high (about 15 meters) used to indicate the declination of the sun, necessary for astronomical observations and calculations, was ready in mid-July 1554 (according to letter from Rheticus to Jan Kraton, a Wrocław naturalist, July 20, 1554). The obelisk's pyramidal shape was thought to be a link between heaven and earth and a symbol of heavenly wisdom. Rheticus' obelisk become a symbol of Oficyna Łazarzowa (Officina Lazari), printing house of Łazarz Andrysowicz (died before 1577) in Kraków.
Between 1562-1563, Rheticus was closely associated with the court of king Sigismund Augustus, making rare astronomical instruments for him on the occasion of the famous August conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn in 1563. After the death of Jan Benedykt Solfa (1483-1564), the court physician of the king, Rheticus assumed his position as well as the function of court astrologer. According to accounts of Berardo Bongiovanni, Bishop of Camerino and Papal Nuncio to Poland (1560-1563), written in 1560, "the king keeps 2,000 horses in the stable, 600 of which I saw, the rest were in the villages for fodder, as well as the foals and the stud. I have also seen 20 royal armor, four of which are remarkable works, namely one with a beautiful carving and silver-clad figures, depicting all the victories of his ancestors over Moscow. It cost 6,000 scudi. There are other victories on others. [...] Finally, he has thirty saddles and horse tacks, so rich that it is impossible to see the richer elsewhere. Some are of pure gold and silver, it is not surprising, knowing that they belong to such a king, but that they are also a masterpiece of art, no one who has not seen it would not believe it. [...] In each craft, the king has skilled masters, Jacob of Verona for jewels and carving on them, several Frenchmen for casting cannons, a Venetian for woodcarving, a Hungarian expert lute player, Prospero Anacleri, a Neapolitan for dressage of horses, and then for any craftsmanship. He allows all these people to live as everyone likes, because he is so good and gracious that he would not want to cause anyone the slightest pain. I just wish he was a bit stricter in the matter of religion" (after "Relacye nuncyuszów apostolskich", Volume 1, pp. 96-100). In 1565 Flavio Ruggieri reported that, "The king has horses in Lithuania, brought from the Kingdom of Naples during the times of Queen Bona, when also many horses were brought to Italy from Poland". Another Ruggieri (or Ruggeri), Giulio, Papal Nuncio from 1565, recalled at the beginning of 1568, drew up for the Pope's information a full report, which, after the manner of the Venetian reports, stated about the king: "now he usually lives in Lithuania, most often in Knyszyn, a small castle of this province on the border of Mazovia, where he has stables with lots of beautiful horses, some of which are Neapolitan, the other Turkish, the other Spanish or Mantuan, and most Polish. This love of horses is, in a way, the reason that the king likes to live here, and maybe also that this place, being almost in the center of his countries, it is more convenient in terms of domestic administration for the king and those who have an interest, than Kraków, located on the Polish border" (after "Relacye nuncyuszów apostolskich", Volume 1, p. 182). Adam Miciński, the court equerry of the king, in his work published in Kraków in 1570 entitled O swierzopach i ograch (On mares and stallions), says that the royal herds consisted of Arab, Turkish and Persian stallions, and the Polish mares, and that Nicolaus Radziwill the Black (1515-1565), brought the king stallions from the Archipelago (Greek Islands), including from Venetian-ruled city of Candia (modern Heraklion, Crete). In 1565 Giert Hulmacher, a burgher from Gdańsk, supplied the king with two Friesian horses, bought in the Netherlands. Portrait of a man in armor in the North Carolina Museum of Art in Raleigh is signed in lower left corner with a monorgam G B M and a date '1563', thence attributed to follower of Giovanni Battista Moroni. The style of this painting is also very close to Moroni. In the early 19th century it was owned by the Lord Stalbridge in London. The man, in a partially gilded armor, is holding a gold flanged mace of Eastern origin, very popular in Poland-Lithuania in the 16th and 17th centuries and known as buzdygan. His crimson trunkhose of Venetian fabric are very similar to that visible in a portrait of Sigismund Augustus in crimson costume in the Prado Museum in Madrid. Behind the man, among antique Roman ruins, stand his white horse and an obelisk, similar to that visible in a reconstruction of the Mausoleum of Emperor Augustus in Rome published in 1575, on title page of Rheticus' Canon doctrinae triangulorum, published in Leipzig in 1551, several publications of Oficyna Łazarzowa, some sponsored or dedicated to Polish-Lithuanian monarchs, or in the portrait of royal jeweller Giovanni Jacopo Caraglio from about 1553. Facial features of a man bear a strong resemblance to effigies of king Sigismund Augustus by Tintoretto.
Portrait of king Sigismund Augustus in armor holding a buzdygan by workshop or follower of Giovanni Battista Moroni, 1563, North Carolina Museum of Art.
Portrait of King Sigismund II Augustus at the age of 43 by Tintoretto
"For the magnates, the elected ruler was only primus inter pares, to whom honor and respect were to be shown as a symbol of the state, but not necessarily obedience. Some magnates even allowed themselves to attack and ignore the monarch" (after "Obyczaje w Polsce ..." by Andrzej Chwalba, p. 203). In the great hall of his beautiful palace in Warsaw (Sandomierski Palace), among the portraits of the ancestors of Great Crown Chancellor Jerzy Ossoliński (1595-1650), there was a portrait of King Ladislaus IV Vasa with such inscription - Primus inter pares (First among equals). The term was introduced under Emperor Augustus to describe his position in the Roman state (Principate). Augustus wanted to use this designation to emphasize his subordination to the republican institutions, de facto, however, he was absolute ruler. According to Aleksander Bronikowski, the reign of Sigismund Augustus in Poland-Lithuania, a constitutional king with little power, shows the process of further limitation of monarch's prerogatives.
Such position of the Polish monarch also determined the iconography. The majority of people accustomed to the well-known effigies of Francis I, King of France and especially Henry VIII of England in rich fabrics and adorned with precious stones and jewels from head to toe, consider them an archetype of a Renaissance monarch. Despite the fact that his wardrobe was full of the most exquisite European and Oriental clothes, Sigismund Augustus usually dressed modestly, similar to the rulers of Europe's greatest power of the 16th century - Spain. In several of his portraits, Holy Roman Emperor Charles V (1500-1558) is dressed in simple black attire. If not for the distinctive features and the Order of the Golden Fleece, such portraits could be considered effigies of a mere merchant (e.g. series by workshop of Jan Cornelisz Vermeyen). Some of the portraits of the Emperor's brother and successor to the Imperial throne Ferdinand I of Austria (1503-1564), husband of Anna Jagellonica (1503-1547), by workshop and follower of Titian, were even inscribed with a standard latin inscription, indicating only the age of the model and the date (Prado Museum in Madrid and Private collection in Vienna). According to mentioned inscription Ferdinand was 46 in 1548 (MDXLVIII / ANNO ETATIS SVE / XXXXVI), which is not entirely accurate as he was born on March 10, 1503, so generally speaking should be 45 in 1548. However, the version from Fugger Castle in Babenhausen provides the titulature (FERDINANDVS. D.G. ROMA. / IMP. ANNO. 1548) and the resemblance to many other of his preserved effigies is so obvious that the identification is not disputed. What is also noticeable in the mentioned portraits of Ferdinand is the color of his hair which is different in all versions. He has the darkest hair in the versions in Spain (Prado and Convent de Las Descalzas Reales in Madrid, attributed to Anthonis Mor) and the brightest in the versions in Germany and Austria. Ferdinand commissioned his portraits from Titian's studio in Venice and one version was undoubtedly sent to Poland to a relative of his wife Sigismund II Augustus (also husband of two of Ferdinand's daughters). Around 1538 Titian and his disciples realized also a series of portraits of King Francis I of France (1494-1547), allegedly inspired by a medal engraved by Benvenuto Cellini in Fontainebleau in 1537. Two of these portraits, in the Louvre and in the Harewood House are very similar, but many details differ (hairstyle, costume, background), so it is more likely that he painted these portraits based on study drawings of the king sent from France. These portraits were gifts to various monarchs of Europe and were copied by various workshops. The portrait of Italian Duke of Savoy, Emmanuel Philibert (1528-1580), painted by circle of Antonis Mor in the Netherlands between 1555-1558, today in the Lviv National Art Gallery, could be a gift to Sigismund II Augustus. In a letter dated April 10, 1546 from Königsberg, Duke Albert of Prussia informs King Christian III of Denmark that the young King of Poland, Sigismund Augustus, had commenced building a new palace at Vilnius in Lithuania, for which he wished to have, among other things for its decoration, the portraits of the King and his family, and requesting that they should be furnished by his Majesty, whereupon the King, in a letter dated Kolding, the 6th of June, 1546, answers the Duke, that he willingly would have sent to the King of Poland the portraits wished for, but as they were not ready, and his Majesty's portraitist, Jacob Binck, whom he had some time before sent to the Duke, had not yet returned, he must rest contented until Binck came back and painted them (after "The Fine Arts Quarterly Review", Volume 2, pp. 374-375). In early 1570 a Swedish envoy arrived in Warsaw, where Sigismund Augustus settled for good from January 1570, with a portrait of Prince Sigismund (1566-1632), son of his sister Catherine. One of the few preserved, painted and inscribed effigies of "the last of the Jagiellons" is a portrait in the National Museum in Kraków (SIGISM. AUGUSTUS REX / POLONIÆ IAGELLONIDARUM / ULTIMUS, MNK I-21). It was probably created in the first half of the 17th century as a copy of a lost original by Lucas Cranach the Younger (known from a miniature from his workshop in the same museum, mirror view, Czartoryski collection, MNK XII-538). It was acquired in Sweden by a Pole Henryk Bukowski (1839-1900), who after the January Uprising settled in Stockholm and founded an antique shop. In 2022, a portrait of a gentleman by Jacopo Robusti known as Tintoretto from the Ferria Contin collection in Milan was auctioned (oil on canvas, 117 x 92 cm, Pandolfini Casa d'Aste, September 28, 2022, auction 1160, lot 21). According to inscription in Latin on the right the man was 43 in 1563 (AÑO ÆTATIS / SVÆ XXXX III / 1563), exacly as king Sigismund II Augustus (born on 1 August 1520), when workshop or follower of Giovanni Battista Moroni, realized his portrait holding a buzdygan (North Carolina Museum of Art). The man bears a striking resemblance to other effigies of the monarch by Tintoretto identified by me and his squinted eyes make him look very much like his mother in her portraits by Cranach. The same man with a similar expression on his face was depicted in another painting by Tintoretto, now in the Rollins Museum of Art in Winter Park, Florida (oil on canvas, 57.46 x 46.35, inventory number 1962.2). He is, however, much older and wears armour adorned with gold, similar to that in the portrait of Sigismund Augustus at the age of 30 with a royal galley (Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, GG 24). The face is also similar, as well as to the smaller "derivative" works of this portrait. The portrait was previously attributed to Paolo Veronese.
Portrait of King Sigismund II Augustus (1520-1572), aged 43 by Tintoretto, 1563, Private collection.
Portrait of King Sigismund II Augustus (1520-1572) in armour by Tintoretto, 1565-1570, Rollins Museum of Art.
Portrait of Georgia of Pomerania, countess Latalska by Paolo Veronese or circle
On October 24, 1563 in Wolgast, Georgia of Pomerania, granddaughter of Anna Jagiellon (1476-1503), Duchess of Pomerania, married Stanisław Latalski (1535-1598), count in Łabiszyn, starost of Inowrocław and Człuchów. On this occassion Philip I (1515-1560), Duke of Pomerania-Wolgast asked the court administration of his uncle Barnim IX in Szczecin for a larger series of tapestries to decorate the festive chambers, altogether 28 pieces.
Georgia was a posthumous daughter of George I, Duke of Pomerania and his second wife Margaret of Brandenburg (1511-1577). She was born on November 28, 1531 as the only child of the couple and named after her father. When her mother remarried in 1534, she was brought up at the court of her stepfather, prince John V of Anhalt-Zerbst (1504-1551) in Dessau. It was decided, however, that when she reached her eighth birthday, in 1539, she must be returned to Pomerania under the custody of her half-brother Philip I. Despite this, Margaret was able to have kept her daughter with her until May 1543, when she was finally sent to Wolgast. There were plans to marry her to Jaroslav of Pernstein (1528-1560), Prince Eric of Sweden (1533-1577), future Eric XIV, when she was just 10 years old and later to Otto II (1528-1603), Duke of Brunswick-Harburg. In the fall of 1562, negotiations were initiated with Stanisław Latalski, who was an envoy of Greater Poland to the Piotrków Sejm in 1562/1563. Latalski was a son of Janusz, voivode of Poznań and Barbara née Kretkowska. His father received the title of Count of the Holy Empire from Emperor Charles V in 1538 and in 1543 he was sent to Emperor Ferdinand in order to arrange a marriage of Sigismund II Augustus with Elizabeth of Austria. In 1554 young Stanisław, accompanied by Jan Krzysztof Tarnowski, son of Hetman Jan Amor, and Mikołaj Mielecki travelled to England, Switzerland and Italy. The couple lived in Łabiszyn and in Człuchów, where Georgia was visited by her mother Margaret of Brandenburg. In 1564 Stanisław went to Wittenberg, to his wife's nephews, the Pomeranian princes Ernest Louis and Barnim, who were studying there. In the same year, under Georgia's influence, he converted to Lutheranism and brought the preacher Paul Elard (or Elhard) and his brother Hans from Szczecin, giving them in 1564 the castle chapel in Człuchów, and two years later also the parish church. Most of the city's population converted to Lutheranism. He also built a wooden Lutheran church in Łabiszyn. After the birth of her first child in 1566, three years after the wedding - a daughter named Maria Anna - Georgia lost her mind and never completely regained her sanity since. She died in childbirth in late 1573 or early 1574. Portrait of a lady wearing an elaborate yellow silk dress in Kensington Palace was painted in the style close to Paolo Veronese (oil on canvas, 87.6 x 64.8 cm, RCIN 400552). It was previously attributed to Leandro Bassano and comes from the collection of the Capel family at Kew Palace in London (acquired in 1731). The coat of arms, which is unidentified, was painted in a different style, hence it is clearly a later addition. It is painted over an original inscription in Latin, which is still in part legible: AETATIS SVAE XXXII. / ANNO DNI / 1.5.6.3 / SIBI. The woman was therefore 32 years old in 1563, exacly as Georgia of Pomerania, when she married Latalski. The upper part of her dress is transparent and embroidered with white flowers of five petals, very similar to the Luther rose visible on the epitaph of Katharina von Bora (1499-1552), wife of Martin Luther, in the Marienkirche in Torgau, created in 1552. Around her neck is a string of pearls, associated with purity, chastity and innocence and a large green jewel-pendant on a long chain, a color being symbolic of fertility. She is holding a green parrot on her hand, a symbol of motherhood. The woman bear a great resemblance to half-brother of Georgia of Pomerania, Prince Joachim Ernest of Anhalt (1536-1586) in his effigies by Lucas Cranach the Younger (Georgium in Dessau and private collection) and to effigies of Georgia's mother Margaret of Brandenburg by Lucas Cranach the Elder, identified by me (Grunewald hunting lodge in Berlin and private collection).
Portrait of Georgia of Pomerania (1531-1573/74), countess Latalska, aged 32 with a parrot by Paolo Veronese or circle, 1563, Kensington Palace.
Portrait of Anna Jagiellon holding a zibellino by Tintoretto
In 1562 on the occasion of the wedding of her younger sister Catherine in Vilnius, Anna ordered for herself three gowns: "one robe of red taffeta, and two hazuka dresses of red velvet" all sewn with pearls. The sisters dressed identically, as evidenced by their miniatures by workshop of Lucas Cranach the Younger from about 1553. Inventory of Catherine's dowry includes many items similar to these visible on the portrait of a lady holding a zibellino by Tintoretto from about 1565: a golden belt set with rubies, sapphires and pearls valued at 1,700 thalers, "a black sable stitched together from two, his head and four feet are golden, set with precious stones" of 1,400 thalers worth, a chain of large round, oriental pearls of 1,000 thalers worth, a neacklace of round, oriental pearls of 985 thalers worth, velvet long, crimson robe with three rows of pearl edgings with 72 French-style enameled buckles, velvet crimson hazuka dress lined with sables, four velvet outer garments for summer, eleven white linen shirts with gold sleeves, and even "one large yellow Turkish rug for the table".
In September 1565 arrived to Cracow count Clemente Pietra to announce the marriage of Francesco I de' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany with a cousin of Sigismund Augustus and Anna, Joanna of Austria (a sister of Sigismund Augustus' first and third wife) and to ask for the hand of Anna for 16 years old Ferdinando, brother of Duke Francesco. It is highly probable that on this occasion the king commissioned in the workshop of Tintoretto in Venice a portrait of himself, his wife and his 42 years old sister, created just as earlier effigies of the Jagiellons by medalier van Herwijck or painter Cranach the Younger, basing on drawings or miniatures sent from Poland. Experts frequently point out the uniqueness of this effigy, now at the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna (oil on canvas, 98 x 75.5 cm, inventory number GG 48), not only because of the frontality of the woman's posture, but also the unusual cut of her outfit - red velvet dress. For the authors of the exhibition "Titian and the image of women in 16th century Venice" at the Royal Palace of Milan (February 23 to June 5, 2022), "she is not a Venetian gentlewoman but from the Venetian hinterland" (Il vestito fa ritenere che non si tratti di una gentildonna veneziana ma dell'entroterra veneto) and her jewelry and the oriental carpet express good taste and high social status. Similar to the effigy of the second wife of Anna's brother, Barbara Radziwill, known as "La Bella" (Pitti Palace in Florence, Inv. 1912 no. 18), a zibellino on her hand is a fertility talisman, indicating that she is an unmarried woman. Weasel pelts (zibellino) were mainly imported to Italy from Poland-Lithuania and Muscovy. This painting, sometimes also attributed to Marietta Robusti, known as Tintoretta (d. 1590), most probably comes from the collection of James Hamilton (1606-1649), 1st Duke of Hamilton, which after his death entered the collection of Archduke Leopold William of Austria in Brussels. Hamilton collected Venetian paintings through his agent, Viscount Basil Feilding, who was sent in 1634 as ambassador to Venice, where he remained for five years. It differs, however, from the work represented in the catalog of the Archduke's collection - Theatrum Pictorium (number 79). The print by Lucas Vorsterman the Younger shows a slightly larger image and fragments of architecture in the background and attributes the original painting to Titian. There is also no zibellino in this version. It is possible that the painting was modified or that it is one of the many versions belonging to the Habsburgs, relatives of Crown Princess Anna Jagiellon, who undoubtedly received her effigies. It was mentioned in the gallery in 1735. The portrait resembles Anna's miniature by workshop of Cranach from around 1553, her funerary monument from around 1584, and a portrait by Tintoretto in the Collegium Maius in Kraków.
Portrait of Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596) when Crown Princess of Poland-Lithuania holding a zibellino by Tintoretto, ca. 1565, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Portrait of Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596) when Crown Princess of Poland-Lithuania from the Theatrum Pictorium (79) by Lucas Vorsterman the Younger after Titian, 1660, Princely Court Library Waldeck.
Portraits of Queen Catherine of Austria as Venus Verticordia by Titian and workshop
"Today I came to Radom, where the queen lives, and that same evening I visited Her Highness, comforting her in the name of the Holy Father after the loss of Emperor His Higness, although three months ago I had fulfilled this obligation by one of my secretaries, whom I sent to Radom. The Queen seemed to accept this very pleasantly, and in return she kisses His Holiness' most holy feet in the most humble way. She asked me to visit her the next morning for easier conversation", wrote about his visit on December 3, 1564 to Queen Catherine of Austria, Venetian bishop and papal nuncio Giovanni Francesco Commendone (1523-1584), in his letter to Cardinal Charles Borromeo (1538-1584), future saint.
The next day this secret audience took place, a description of which we find in Commendone's next letter: "It was on it that she spoke of her unhappy condition, complaining that, apart from leaving her for no reason, there were also attempts to divorce her, and that this was the main cause of the Synod. She considered all the accusations made against her with such care, caution, and respect for the king that I do not know whether I felt more pity or admiration for her. Later she said extensively that she knew well how the ministers, especially the envoys of the courts, contribute to all this; so she begged me and beseeched me for the holy priesthood, in the name which I had until now, and for the kindness shown to me by her father, and by her brothers, and also the Bavarian prince, that I would have mercy on her; and then she opened up completely to me and said that she had been secretly informed about the efforts made with the Holy Father for divorce, and that His Holiness, with my advice and commitment, allows it. [...] She spoke all these words with bitter tears and sobbing so that I could hardly answer her. [...] I assured her, most honestly, that the king had not mentioned a word of divorce [...]. I wish and hope to convince the Queen someday that I did just the opposite; that I tried in various ways and under various appearances to dissuade from these intentions, to suppress these thoughts, and that the same is the opinion of the Holy Father. [...] At the supper (because she wanted me to dine with me) I saw her greatly comforted. Finally, bidding me farewell, she again took me aside and asked me to recommend her pious services to the Holy Father begging him to take care of her and not to forget in his holy prayers that God may console her in these worries. I understand that the Hungarian War increased the Queen's suspicions: some argue that for this divorce and for the Emperor's other practices with the Prussian Master and Moscow against the Kingdom of Poland, efforts were made to entangle him in these Transylvanian troubles. Whatever the answer to the matter of divorce, no matter how indifferent, I remind Your Majesty most humbly to write it with a key" (after Aleksander Przeździecki's "Jagiellonki polskie w XVI. wieku. Korrespondencya Polska", Volume 3, p. 104-107). Undobtedly also works of art, paintings, were part of all these secret negotiations and political efforts. In May 1562, the queen settled in Radom alone, abandoned by the king. As a widowed Duchess of Mantua, daughter of Emperor and cousin of Philip II of Spain, she knew the power of image and allegory. In the Borghese Gallery in Rome, where there is also a portrait of Catherine of Austria's mother Queen Anna Jagellonica (1503-1547) as Venus with Cupid stealing honey by Lucas Cranach the Elder, there is a painting of Venus blindfolding Cupid by Titian, dated by Adolfo Venturi to about 1565. It was probably acquired in 1608 as part of Cardinal Paolo Emilio Sfondrati's collection. According to Erwin Panofsky it shows Venus Verticordia between the blindfolded Cupid and Anteros, the one with his eyes open, symbols of contrasting aspects of love, the blind and sensuous, and the clear-sighted and virtuous, and two nymphs symbolizing Marital Affection and Chastity. The matrons of Rome, who were so renowned for good management that old Cato told the senate, "We Romans govern all the world abroad, but are ourselves governed by our wives at home," erected a temple to that Venus Verticordia, quæ maritos uxoribus reddebat benevolos (Venus the Turner of Hearts, who makes husbands well disposed to their wives), whither (if any difference happened between man and wife) they did instantly resort. There they did offer sacrifice, a white hart, Plutarch records, sine felle, without the gall (some say the like of Juno's temple), and make their prayers for conjugal peace (after Robert Burton's "The Anatomy of Melancholy", Volume 3, p. 310). Venus has the features of Queen Catherine of Austria, similar to her other effigies by Titian. The Queen probably commissioned it as a gift for the Pope or one of the cardinals. A copy of this painting was in the collection of Cornelis van der Geest and is seen in two paintings of his art gallery in the 1630s, by Willem van Haecht. In 1624 Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa, grandson of Catherine Jagiellon, visited his gallery in Antwerp. The Nationalmuseum in Stockholm has two workshop copies of this painting, out of four known previously. One, attributed to Andrea Schiavone (inventory number NM 7170), came to the Nationalmuseum with the collection of Nicola Martelli, a Rome art dealer, in 1804, the other was transferred in 1866 from the Swedish royal collection (inventory number NM 205). It is possible that some previously known copies were taken from magnate or royal residencies in Poland during the Deluge (1655-1660), or even from the Royal Castle in Radom, which was ransaced and burned in the spring of 1656. Interestingly, in the Pinacoteca Ambrosiana in Milan, there is a painting of Adoration of the Magi by Titian from this period with figures in oriental costumes, very similar to contemporary Polish-Lithuanian attire. This work comes from the collection of Cardinal Federico Borromeo (1564-1631), cousin of Saint Charles Borromeo. It cannot be excluded that it was another luxury gift from the Queen of Poland commissioned in Venice. Some time later, most probably between 1566-1570, therefore after Queen's departure to Austria, Titian created another version of this composition. At some point after the painting's completion, most likely in the mid-18th century, its right side was cut away. Before 1739 it was in the collection of Charles Jervas or Jarvis in London (his sale, at his residence, London, 11-20 March 1739, 8th day, no. 543, as by Titian). In 1950 the painting was sold to the Samuel H. Kress Foundation, New York and in 1952 offered to the National Gallery of Art in Washington. The blonde goddess seems younger and more beautiful and composition was modified. The inventories up to 1780 describe the picture as "Venus binding the eyes of Cupid, and the Graces offering a Tribute", similar to the painting in the royal Wilanów Palace in Warsaw (Wil.1548), in which Venus bears the features of Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651), granddaughter of Catherine Jagiellon, and to the painting in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, where Venus has the features of Ladislaus Vasa's first wife Cecilia Renata of Austria. The figures bear attributes of the goddess of love: apples, a dove and flowers. They could also be interpreted as assistants of Fortuna Virilis, an aspect or manifestation of the goddess Fortuna, often depicted with a cornucopia (horn of plenty) and associated with Venus Verticordia. Fortuna Virilis, according to the poet Ovid, had the power to conceal the physical imperfections of women from the eyes of men. The x-radiographs have revealed a number of alterations, especially in woman's face, which was initially less sublime and more close to the features of the Queen. It is possible that through this painting, Catherine wanted to convince Sigismund Augustus that her rightful place is at his side and that she should return to Poland.
Allegory with portrait of Queen Catherine of Austria (1533-1572) as Venus Verticordia (Turner of Hearts) by Titian, 1563-1565, Borghese Gallery in Rome.
Allegory with portrait of Queen Catherine of Austria (1533-1572) as Venus Verticordia (Turner of Hearts) by workshop of Titian, attributed to Andrea Schiavone, 1563-1565, Nationalmuseum in Stockholm.
Allegory with portrait of Queen Catherine of Austria (1533-1572) as Venus Verticordia (Turner of Hearts) by Titian or workshop, 1566-1570, National Gallery of Art in Washington.
Adoration of the Magi with figures in Polish-Lithuanian costumes by Titian, ca. 1560, Pinacoteca Ambrosiana.
Portrait of Jan Amor Tarnowski by Tintoretto
In the Prado Museum in Madrid there is an interesting portrait attributed to Jacopo Tintoretto from the Spanish royal collection (oil on canvas, 82 x 67 cm, inventory number P000366). Because the painting was obviously created by a Venetian painter and the identity of the model is unknown, it is known as a "Portrait of a Venetian admiral". The man in rich armour etched with gold is holding a baton, that is traditionally the sign of a high-ranking military officer.
This work was offered to King Philip IV of Spain (1605-1665) by Diego Felipez de Guzmán (1580-1655), 1st Marquess of Leganés, a Spanish politician and army commander, who fought during more than 20 years in the Spanish Netherlands and in 1635 was named Captain General and Governor of the Duchy of Milan. Such portraits of important military commanders were frequently exchanged in Europe at that time and sent to different places, so that Leganés could acquire the painting in Italy, but also in Flanders or Spain. The portrait is astonishingly similar in features, pose and and style of armour to the well known effigy of Jan Amor Tarnowski commissioned by king Stanislaus Augustus Poniatowski in about 1781 for his gallery of effigies of Famous Poles at the Royal Castle in Warsaw (ZKW/3409). The effigy, just as the rest, was undoubtedly based on some original portrait still preserved in the royal collection. It was painted by court painter of king Stanislaus Augustus, Marcello Bacciarelli, who also copied other effigies of famous Poles, including Copernicus (ZKW/3433). During the Great Northern War, royal residencies of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, a Venetian style republic of nobles created in 1569 with support of the last male Jagiellon, Sigismund Augustus, were ransacted and burned again by different invaders in 1702 and 1707. That is why some effigy of Sigismund Augustus, survived in the royal collection in about 1768, was confused with the effigy of the progenitor of the Polish-Lithuanian dynasty - Ladislaus Jagiello in the cycle of Polish Kings in the Marble Room at the Royal Castle in Warsaw, commissioned by Poniatowski. Jan Amor Tarnowski (1488-1561) was a renowned military commander, military theoretician, and statesman, who in 1518 became a knight of the Order of the Holy Sepulchre in Jerusalem and was accoladed by King Manuel I in Lisbon as a knight of Portugal. In the first half of the 1540s, the hetman was already well known to the Habsburgs as a military officer and politician, as evidenced by the letter King Ferdinand I sent to Juan Alonso de Gámiz. The King of Bohemia requested not only that Elizabeth of Austria reward Tarnowski, but also that "he receive a favor in the Iberian Peninsula through Her Majesty". In the account of the expedition that the maestre de campo Bernardo de Aldana made to Hungary in 1548, he is mentioned as "the very noble Count Tornoz". The hetman corresponded frequently with the court of Vienna and perhaps also with Spain with the aim of obtaining a high position in the imperial and Spanish army. In July 1554, Charles V wrote from Brussels to Prince Philip and Mary of Hungary, either in reference to Jan Amor Tarnowski or to his son Jan Krzysztof, to inform them that "the Count of Tarna, Polish (…) came here requesting that he be present at your nuptials and to then travel to Spain at the first opportunity in order to see that province. And being the person he is, and having been highly recommended to us by the King and Queen of Bohemia my children, it is only fair that he be given a warm welcome and good treatment. I kindly request you to treat him with the utmost care for the duration of his stay" (after "Jan Tarnowski and Spain" by Paweł Szadkowski, pp. 55-57). The portrait bears finally some ressemblance to effigies of Jan Amor and his son on his monumental tomb in the Tarnów Cathedral, created between 1561 and 1573 by Venetian trained sculptor Giovanni Maria Mosca called Padovano, who also created tomb monuments of two wives of Sigismund Augustus. According to the inventory, a fine parade burgonnet from the collection of the Krasiński Estate in Warsaw, belonged to Hetman Tarnowski (Polish Army Museum, 35128 MWP). It was richly decorated with engraved and embossed mythological and biblical scenes - the Rape of the Sabine women, the Romans fighting the barbarian tribes, the arrival of Judith at the camp of Holofernes, scenes of camp life and the stylized Jagiellonian eagle with the letter 'S' of King Sigismund I on its chest. It is considered a work of Parisian, Italian or Polish workshop, which indicates that the hetman commissioned the exquisite works of art from abroad. The same man was depicted in another painting attributed to circle of Jacopo Tintoretto or Titian, standing three-quarter-length, in armour with a crimson tunic and holding a baton (oil on canvas, 120.7 x 94.9 cm). This "Portrait of a Venetian officer" comes from private collection and was sold in April 2006 (Christie's New York, lot 206). His velvet tunic with embedded metal plates is similar to so-called corazzina brigandine, a form of armour made of heavy cloth lined with small steel plates, such as that from the Royal Armoury in Warsaw, most likely made in Poland or Italy around 1550, now in the Livrustkammaren in Stockholm (Swedish war booty from 1655, 23167 LRK). Hetman's father-in-law, Chancellor Krzysztof Szydłowiecki, was depicted in a similar crimson brigandine and armour, in a painting by Titian (Pinacoteca Ambrosiana in Milan). His large codpiece, a prominent addition to the full suits of armour and the affirmation of virility, was "censored" and repainted, most likely in the 19th century. During the French wars of religion, which lasted from 1562 to 1598, Catholics mocked Huguenots as impotent ébraguettés (without virility) because they would not wear the prominent codpiece (after "A Cultural History of Dress and Fashion in the Renaissance" by Elizabeth Currie, p. 70).
Portrait of Jan Amor Tarnowski (1488-1561) in armour holding a baton by Jacopo Tintoretto, 1550-1575, Prado Museum in Madrid.
Portrait of Jan Amor Tarnowski (1488-1561) in armour with a crimson brigandine, holding a baton by circle of Jacopo Tintoretto or Titian, 1550s, Private collection.
Portrait of Jerzy Jazłowiecki by Lambert Sustris
In 1563 Stefan Tomsa, a descendant of Moldavian boyars, led a successful conspiracy against the Protestant ruler Iacob Heraclid, known as Despot Voda, who after a 3-month siege of the Suceava Castle was betrayed by mercenaries and personally killed by Tomsa. As a sign of submission to Sultan Suleiman I, Stefan ordered to send the captured Ruthenian Prince Dmytro Vyshnevetsky, who was involved in Moldavian affairs, to Istanbul, where Vyshnevetsky was tortured to death. Unable obtain recognition from the High Porte and to hold on to the throne, Tomsa fled to Poland, where King Sigismund II Augustus, in order to appease the Turks, ordered Jerzy Jazłowiecki (d. 1575), castellan of Kamianets to capture him. The Prince of Moldavia was imprisoned, then sentenced to death and beheaded in Lviv on May 5, 1564.
Jazłowiecki, born in or before 1510, was the son of Mikołaj Monasterski of the Abdank coat of arms (ca. 1490-1559), castellan of Kamianets and his wife Ewa Podfilipska. He was brought up at the court of the bishop of Kraków, Piotr Tomicki (1464-1535), but soon he began his military career under the supervision of Jan Amor Tarnowski (1488-1561) and Mikołaj Sieniawski (1489-1569) and participated in many battles. Already in 1528, as an 18-year-old, he became famous as a royal cavalry captain in the battle with the Tatars near Kamianets. In 1546, under the influence of his wife Elżbieta Tarło, he converted to Calvinism, and later closed the churches on his estates and expelled the Dominican monks. In 1544, he purchased from Mikołaj Sieniawski the town and castle of Yazlovets (Polish Jazłowiec) with the surrounding villages for 6,400 zlotys. The sum was finally paid in 1546 and from 1547 he began to call himself Jazłowiecki. Between 1550-1556 Jerzy rebuilt the Medieval fortress in Yazlovets in Renaissance style to design of Italian architects from the Lviv group of Antoni, Gabriel and Kilian Quadro, brothers of Giovanni Battista di Quadro, active in Poznań (after "Sztuka polska: Renesans i manieryzm", Volume 3, p. 120). It should be noted that the style of the stone portal above the entrance to the castle is similar to the one in the Mikołaj Sieniawski's Castle in Berezhany, created in 1554. In April 1564, he was sent as royal emissary to Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent for which he received a seat in the Senate from the king Sigismund Augustus. In 1567 Jerzy become the Voivode of Podolia, in 1569 the Voivode of Ruthenia and was appointed Field Hetman of the Crown and Grand Hetman of the Crown (without a formal nomination) that year. He also reorganized the defense of the southern borders against the Tatars. During the interregnum in 1573, Jazłowiecki was nominated by the Piast party as a candidate for the Polish throne and was supported by Sultan Selim II (after "Jak w dawnej Polsce królów obierano" by Marek Borucki, p. 69). In the Staatliche Kunsthalle in Karlsruhe, there is a portrait of a general, attributed to Lambert Sustris (inventory number 418), similar in style to portrait of Princess Elizabeth Radziwill (Museum of Western and Eastern Art in Odessa), daughter-in-law of Mikołaj Sieniawski, identified by me. This painting of unknown provenance was attributed to a Venetian follower of Titian in the gallery catalogs from 1881 to 1920. The 55-year-old man, according to Latin inscription in lower left corner of the painting (ETATIS / SVE AN / LV), is holding a heavy sword. His armour, beard and shaved head are strikingly similar to the statue of Mikołaj Sieniawski from his tombstone in Berezhany (destroyed during World War II). Behind him there is a view with the same man dismounted from the horse, standing before a body of another man, whose head was cut off. The killed man is wearing an Ottoman turban with pleated red velvet part, called külah, similar to that visible in a drawing by German School from the late 16th century and depicting Wallachian and Moldavian noblemen (inscribed ... reitten die Wallachen unnd Moldauer ..., Private collection). Michael the Brave (1558-1601), Prince of Wallachia and Moldavia, was depicted in similar turban in the Feast of Herod with the Beheading of St John the Baptist by Bartholomeus Strobel, created between 1630-1633 (Prado Museum in Madrid), as well as Alexander II Mavrocordatos Firaris (1754-1819), Prince of Moldavia, who is wearing a similar turban-like headpiece in his portrait created in 1785 or after (Private collection). The standing man in the view is not holding a sword, he did not execute the other man, he just captured him. The general from the painting bear a strong resemblance to portrait of Jerzy Jazłowiecki, when Field Hetman of the Crown, known from the photograph from the collection of the historian Aleksander Czołowski (1865-1944), most probably a 17th century copy of a painting created in about 1569. He was the same age (about 54 or 55) as Jazłowiecki when he captured the Prince of Moldavia in 1564.
Portrait of Jerzy Jazłowiecki (ca. 1510-1575), castellan of Kamianets, aged 55 by Lambert Sustris, ca. 1565, Staatliche Kunsthalle in Karlsruhe.
Portraits of Mikołaj Rej by Sofonisba Anguissola and Giovanni Battista Moroni
"Let Mantua be proud of Virgil, Verona of Catullus, You, Rej, her bard, let the country of Sarmatia [Poland-Lithuania] be proud. And all the more so that the land of Italy and Greece gave birth to many, You are almost the only one in Sarmatia" (Mantua Vergilium iactet, Verona Catullum: Te Rei, vatem Sarmatis ora suum. Hocque magis, multos quoniam tulit Itala tellus Graiaque: Sarmatiae tu prope solus ades) (after Polish translation in "Wizerunk własny ...", Part 2, by Helena Kapełuś, Władysław Kuraszkiewicz, p. 97), praises the poet Mikołaj Rej, or Mikołaj Rey of Nagłowice, in his Latin dedication Petrus Roysius Maureus (i.e. Piotr Roizjusz the Moor, born Pedro Ruiz de Moros). The Spanish poet and courtier of King Sigismund II Augustus, included this short poem in Rej's "Faithful image of an honest man" (Wizerunk własny żywota człowyeka poczciwego), published in Kraków in 1558-1560 before the poet's printed effigy showing him at the age of 50 (therefore created in 1555). Under Rej's portrait there is another Latin poem by his friend Andrzej Trzecieski (Trecesius, d. 1584) in which he calls him the Polish Dante (Noster hic est Dantes).
Considered the "father of Polish literature", Rej was one of the first poets to write in Polish (and not in Latin). He was born into a noble family at Zhuravne in Ukraine in 1505. In 1518 he was enrolled as a student of the Cracow Academy and in 1525 his father sent him to the magnate court of Andrzej Tęczyński. Between 1541 and 1548 he converted to Lutheranism, then to Calvinism. Rej participated in synods, founded churches and schools on his estates. The Catholics, who reproached him for the desecration of churches, the expulsion of Catholic priests and the persecution of monks, called him the unleashed Satan, the dragon of Oksza, Sardanapalus of Nagłowice and a man without honor and faith. In 1603, as an author, he was included in the first Polish Index of Forbidden Books. He maintained close contacts with the courts of Sigismund I the Old and Sigismund II August. Rej was also the first in Polish literature to receive a substantial reward for his work. He received Temerowce from King Sigismund I, and Dziewięciele from Sigismund Augustus as a lifelong possession and two towns, one of them Rejowiec, founded by Rej in 1547. He died at Rejowiec in 1569. His grandson, Andrzej Rej, royal secretary and Calvinist, was painted by Rembrandt in December 1637, while he was visiting Amsterdam as an ambassador (possibly the painting in the National Gallery of Art in Washington). Although he praised the wisdom of Queen Bona in his "Bestiary" (Zwierzyniec, 1562 - "A woman of wisdom, that even today she is famous in Poland, and long-remembered her words. She was from the Italian nation where wisdom is born"), beauty of her daughters Anna and Catherine and dedicated his "Life of Joseph" (Żywot Józefa, 1545) to her daughter Isabella, Queen of Hungary, he is perhaps the first author in Poland to oppose strong women and their inflences. In a dialogue between Warwas and Lupus on the cunning of women, written before 1547 and most likely published anonymously, he begins with an appeal to Venus (Wenera), the patroness of females. Women do not participate in local assemblies and parliamentary sessions (Sejm), they do not sit over books, and yet they lead men by the nose. All women are cunning and laugh secretly at men who drink even out of their shoes for their health (after "Mikołaja Reja, żywot i pisma" by Michał Janik, p. 36). He frequently criticizes women, their extravagant clothing and their excessive make-up - "looks like she's wearing a mask" (iż się zda jakoby była w maskarze). In the second known effigy of the poet, published in later edition of his "Faithful image of an honest man" and in "Speculum" (Zwyerciadło), published in 1568, similar to that from 1555, he is not depicted in national costume (crimson żupan), as one would expect from the national poet of the time, but in rich foreign costume – embroidered Italian-style shirt, rich doublet, wearing a hat and several chains. In this last portrait, he is holding a book, just to remind us that he is a poet. Both portraits are woodcuts, created by an artist working for a Kraków-based printer and bookseller Maciej Wirzbięta and most likely they were created after an original painted effigy of the poet as was customary. Later, engravers began to add the relevant inscriptions, that they were authors, not a painter who created the original portrait (fecit, sculpsit, pinxit, delineavit, invenit in Latin). Educated Poles, besides books, also commissioned and acquired portraits of their favorite foreign authors. Portrait of Dante Alighieri (1265-1321) by Pontormo or workshop in the Czartoryski Museum (inventory number XII-218) was most likely brought to Poland already in the 16th century (painted around 1530). Later it was acquired by Princess Izabela Czartoryska, who placed it next to those of Torquato Tasso (423), Francesco Petrarca (424) and Beatrice Portinari (425) in the Temple of Memory at Puławy, opened in 1801. In her collection, which she also enlarged by acquisitions abroad, there were also letters by Tasso (891), Ariosto (892), as well as portraits of French Renaissance poets François Rabelais (944), Clément Marot (945) and Michel de Montaigne (946) and even chairs of Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1310) and William Shakespeare (1311) in special box-cases, included in the inventory of the collection published in 1828 (Poczet pamiątek ...). Among the paintings belonging to the "Victorious King" John III Sobieski (1629-1696), which could come from earlier royal collections or those of his father Jakub Sobieski (1591-1646) and mentioned in the inventory of the Wilanów Palace from 1696, we find "A picture of Cicero in a black frame" (Obraz Cycerona wramach czarnych, No. 223), "A pair of paintings, one of which represents Petrarch and the other, Laura, his wife, in black frames" (Obrazow para na iednym Petrarcha, na drugim Laura zona iego, wramach czarnych, No. 223) and "A picture of Laura" (Obraz na ktorym Laura, No. 246). Why then couldn't the French or the Italians have the portrait of a famous Sarmatian poet? Especially when many Polish collections were transferred to France and Italy. In the Museum of Fine Arts in Reims, in France, there is portrait of a man sitting in a chair and holding a book (oil on canvas, 115 x 96.1 cm, inventory number 910.4.1). He was interrupted while reading so he put his finger in a book so as not to miss the page. He gazes at the viewer and the romantic ruins behind him suggest he is a poet. Another book is lying on a table. The overall style of the painting suggests Giovanni Battista Moroni as a possible author, but the technique is different, so perhaps it was done by a painter from Moroni's workshop or circle. However, it can also be compared to some works by Sofonisba Anguissola, such as her self-portrait with Bernardino Campi (Pinacoteca Nazionale di Siena) and self-portrait at the easel (Łańcut Castle), both from the 1550s. His eyes also indicate that she might be the author as she frequently enlarged them in her paintings. This portrait was earlier attributed to Lorenzo Lotto, who died in Loreto in 1556/1557, and can be dated to about 1550 at the earlierst (about 1560, according to some sources). The painting was bequeathed in 1910 by French politician Louis Victor Diancourt (1825-1910), born in Reims, and its earlier provenance is unknown. Perhaps there was initially an oral tradition or documents indicating that the painting depicts a famous poet of the 16th century, so since the portrait was in France, it has been identified as depicting a French poet - François Rabelais (born between 1483 and 1494, died 1553), despite the fact that there is no resemblance to his other effigies. Rabelais was in Italy, in Turin and Rome, in 1534, 1540, 1547-1550, as a physician and secretary to Cardinal Jean du Bellay, nevertheless, as a clergyman in majority of his confirmed effigies he is depicted wearing a large biretta of the Christian clergy, thus, because of this and the lack of resemblance, the identification is now rejected and the work is referred to as a "portrait of an unknown man". The man wears a crimson tunic, typical of the Polish-Lithuanian nobility of the time (Rej was a wealthy nobleman of Oksza coat of arms), and his hat, shirt and face looks very much like in the print showing Mikołaj Rej at the age of 50. Another version of this portrait exists, this one however is by Moroni, now at the Pope John XXIII Hospital in Bergamo (oil on canvas, 86 x 71 cm, inventory number 57099). Coming from the collection of a lawyer Giacomo Bettami de-Bazini and donated to the hospital by his son Antonio, the painting was in storage at the Carrara Academy since 1879. It was probably purchased on the Bergamo market in the early 18th century. "An old man seated in an armchair, entirely titianesque, is one of the best of this painter in the Bettame house" (Un vecchio seduto sopra sedia d'appoggio tutto tizianesco è de' migliori dell'autore in casa Bettame), praised the quality of the painting Francesco Maria Tassi in 1793. It is generally dated to the 1560s and the man is much older. His pose and costume are almost identical to the Reims painting, as if the painter had used the same study drawings created for the previous painting and just changed the face. His frowning eyebrows and more hooked nose are more like in the portrait of Rej published in 1568. Mikołaj dedicated his "Faithful image" to hetman Jan Amor Tarnowski (1488-1561), one of the richest people in Poland-Lithuania, whose portraits were painted by Jacopo Tintoretto and tomb monument carved by Giammaria Mosca called Padovano. Rej's portrait, similar to that of another eminent Polish poet of the Renaissance - Jan Kochanowski (1530-1584) from 1565 (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam), was therefore most likely created by Giovanni Battista Moroni from drawings sent from Poland. The same background as in the painting in Reims was used in another portrait by workshop of Moroni, today in the National Palace of Ajuda in Lisbon (oil on canvas, 112.7 x 109 cm, inventory number 496). It represents an ecclesiastic in a black biretta, seated on a chair and holding an hourglass. His face resembles more the effigies of Rabelais, in particular his laughing portraits, than the Reims painting.
Portrait of Mikołaj Rej (1505-1569) by Sofonisba Anguissola or circle of Giovanni Battista Moroni, ca. 1555, Museum of Fine Arts in Reims.
Portrait of Mikołaj Rej (1505-1569) by Giovanni Battista Moroni, ca. 1568, Pope John XXIII Hospital in Bergamo.
Portrait of Jan Kochanowski by Giovanni Battista Moroni
Almost all old churches in former territories of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth have at least one good quality tomb monument in Italian style with effigy of deceased, but portrait paintings are very rare. Wars and invasions impoverished the nation and majority of non-religious paintings that preserved in the country, were sold by the owners.
The exact date of birth of Jan Kochanowski is unknown, however according to inscription on poet's epitaph in the church in Zwoleń near Radom, he died on August 22, 1584 at the age of 54 (Obiit anno 1584 die 22 Augusti. Aetatis 54), therefore he was born in 1530. He started his education at the Artium Faculty of the Kraków Academy in 1544. Presumably in June 1549, he left the Academy and, perhaps, went to Wrocław, where he stayed until the end of 1549. Between 1551-1552 he stayed in Królewiec (Königsberg), the capital of Ducal Prussia (fiefdom under the Polish crown). From Królewiec, he left for Padua in 1552, where he studied until 1555. Kochanowski was elected a counselor of the Polish nation at the University of Padua (presumably from June to August 2, 1554). He returned to Poland in 1555 and after several months in Królewiec and Radom, he left for Italy at the end of the summer of 1556, presumably to repair his health. He was back in Poland between 1557 and 1558 and in spring that year he left for Italy for the third time. At the end of 1558, Kochanowski went to France, and in May 1559, he finally returned to Poland. In mid-1563, Jan entered the service of Deputy Chancellor Piotr Myszkowski, thanks to which he become the royal secretary of king Sigismund Augustus, before February 1564, the office he held untill his death. In 1564, he helped his friend Andrzej Patrycy Nidecki (Andreas Patricius Nidecicus), also secretary at the traveling court and chancellery of Sigismund Augustus (Kraków - Warsaw - Vilnius). Nidecki was preparing the second fundamental edition of Cicero's "Fragments" for printing. It was published in Venice in 1565 by the printer Giordano Ziletti (Andr. Patricii Striceconis Ad Tomos IIII Fragmentorvm M. Tvllii Ciceronis ex officina Stellae Iordani Zileti), who also published many other Polish-Lithuanian authors. In October 1565 another royal secretary and Kochanowski's friend, Piotr Kłoczowski (or Kłoczewski), left for Ferrara as king's envoy to attend the wedding of Alfonso II d'Este with Sigismund Augustus' cousin Archduchess Barbara of Austria. Kłoczowski, who apparently accompanied him during his first trip to Italy, offered him a new journey: "Piotr, I don't want to take you to Italy a second time. You will get there alone: it's time for me to deal with myself. If I am to become a priest, or better a courtier, If I will live at the court or in my land", wrote the poet (Xięga IV, XII.). Jan Kochanowski, considered one of the greatest Polish poets, died in Lublin. His nephews Krzysztof (d. 1616) and Jerzy (d. 1633), founded him a marble epitaph in the family chapel in Zwoleń, created in Kraków in about 1610 by workshop of Giovanni Lucano Reitino di Lugano and transported to Zwoleń. The portrait of a man holding a letter by Giovanni Battista Moroni in the Rijksmuseum Amsterdam can be compared with poet's posthumous effigy in Zwoleń. It bears the inscription in Latin and artist's signature at the bottom of the letter: AEt. Suae. XXXV. Miii MDLXV. Giu. Bat.a Moroni (Age 35. 1565. Giovanni Battista Moroni), which match perfectly the age of Kochanowski in 1565.
Portrait of Jan Kochanowski (1530-1584) aged 35 holding a letter by Giovanni Battista Moroni, 1565, Rijksmuseum Amsterdam.
Portraits of Jan Krzysztof Tarnowski by circle of Dosso Dossi and Lambert Sustris
Wars and invasions contributed not only to the looting and destruction of works of art, including paintings, but also to the resulting chaos and impoverishment, so many preserved images as well as documents confirming the author and the identity of the sitter have been lost. Deteriorating living conditions also had an impact on art collections, as good quality and well-preserved paintings were frequently sold and neglected paintings, even by great masters, due to deterioration, had to be disposed of.
This is probably the reason why, in the 18th century, an unknown local painter made a copy of the full-length portrait of Count Jan Krzysztof Tarnowski (1537-1567), today in the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 229 x 114 cm, inventory number MP 5249 MNW). The original must have been of good Venetian work, as the painter was inspired by the blurred brushstrokes of painters from the circle of Titian, particularly visible in the upper part of the painting. The identity of the model is confirmed by a large coat of arms of the Tarnowski family - Leliwa, above his head on the right, and a lengthy inscription in Latin on the left - Joannes Christophorus Comes / In Tarnow Tarnowski ..., listing all his titles. The painting comes from the Tarnowski collection, deposited with five other portraits in the National Museum during World War II. His costume, although generally resembling the 16th century attire of Polish-Lithuanian and Hungarian nobles, which were very similar (fanciful szkofia, a hat decoration of Hungarian origin, and Polish delia coat lined with fur), is quite unusual. A similar tunic with a longer part in the back, embroidered on the front with vertical rows of buttons, is visible in the effigy of a Pole (Polognois, f. 41) from Théâtre de tous les peuples et nations de la terre by Lucas de Heere, painted in the 1570s (Universiteitsbibliotheek Gent). However, the wider sleeves, the silver color, the belt and the garters are not typical and it is possible that he wore the costume made in Lisbon in 1516 for his father Jan Amor Tarnowski, as suggested by some authors. A Polish nobleman in a Hungarian-Portuguese costume is just another confirmation of the great diversity of fashion in Poland-Lithuania of the Renaissance, confirmed by so many authors, which has been forgotten today. King Manuel I of Portugal (1469-1521) was depicted in similar tunic in a disguised portrait as Saint Alexis in the scene of Wedding of Saint Alexis by Garcia Fernandes, painted in 1541 (Museu de São Roque in Lisbon), and Tarnowski's portrait and attire can be compared to some portraits of governors of Portuguese India - Francisco de Almeida (d. 1510) and Afonso de Albuquerque (d. 1515), created after 1545, both in the Museu Nacional de Arte Antiga in Lisbon. Such diversity was not only the Polish specialty and also occurred in other countries in Europe. The full-length portrait of a Spanish noble lady Doña Policena de Ungoa (Polissena Unganada), daughter of Juan de Ungoa, Barón de Sonek y Ensek, Mayordomo del Emperador (Emperor's Steward) and Margarita Loqueren, Camarera de la Emperatriz (Maid to the Empress), governess to the children of Empress Maria of Spain (1528-1603) and wife to Don Pedro Laso de Castilla, depicts her dressed in the German/Austrian fashion of the imperial court in Prague and Vienna from the 1550s (not the Spanish fashion, like the Empress). Inscription in Italian: ILL. DONNA POLISSENA UNGANADA MOGLIE DI D. PIETRO LASSO DE CASTIGLIA ..., confirms her identity. This portrait comes from the Arrighi de Casanova collection in the Château de Courson near Paris and was variably attributed to the Italian, Spanish (circle of Alonso Sánchez Coello) and Austrian school (follower of Jakob Seisenegger). In recent literature, the identification of the model in Warsaw portrait has been questioned due to the discovery of a miniature in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna (GG 5338). According to short inscription in Latin (IOANNES / COMES / A SERIN), it depicts Count Jan Zrinský (ca. 1565-1612), a nobleman from the Zrinský (Zrínyi) family of Zrin (Serin), son of Nikola IV Zrinski (ca. 1508-1566) and Eva z Rožmberka (1537-1591). According to Jan K. Ostrowski ("Portret w dawnej Polsce", p. 34), the sitter should rather be identified as the father of Jan, famous commander Nikola IV, so this inscription is partially incorrect, therefore, its author had a vague knowledge of who was really depicted. If the first part of the inscription (IOANNES) could be incorrect, the second (A SERIN) could also be questioned and the model is not Jan Zrinský, but Jan Tarnowski. This small miniature comes from a series of almost 150 contemporary and historical portraits of rulers of Europe and members of the imperial House of Habsburg, including many Polish monarchs. Many of them were created by Flemish painter Anton Boys for Archduke Ferdinand II of Austria (1529-1595), son of Anna Jagellonica (1503-1547), after 1579, when he become his court painter. Boys copied many other effigies form the Imperial collection, representing the models on dark or brown backgound, however some mistakes happened and the effigy of Viridis Visconti (1352-1414), Duchess of Austria and a daughter of the Lord of Milan, Bernabò Visconti, is most likely the effigy of Isabella of Aragon (1470-1524), Duchess of Milan and mother of Bona Sforza as it resembles greatly her profile from the lunette in the house of the Atellani in Milan. The miniature of Count Jan is different and shows a clear influence of Flemish (colors) and Italian (blurred brushstrokes) style. Unlike other miniatures in the series, it has a distinctive background - green fabric. Not only the technique is different, but also the composition. Thus, this earlier miniature by a different painter has just been adapted to the series by adding the inscription. What is also very important for the identification of the model is which man has been depicted on a larger version with a more detailed description. Mainly the person who ordered the portrait was interested in having the full version. The larger painting depict Count Jan Krzysztof Tarnowski. Only the possible author of the miniature remained and all the given factors speak for Lambert Sustris (d. 1584 or later), a Dutch painter active mainly in Venice, who in 1552 created full-length portraits of Hans Christoph Vöhlin and of his wife Veronika von Freyberg zum Eisenberg (Alte Pinakothek), as well as many effigies of Jan Krzysztof's sister Zofia Tarnowska (1534-1570), identified by me. The same man, also against green fabric, but now in a more Italian attire, yellow doublet and embroidered shirt, was depicted in another portrait, sold in London in 2019 (oil on canvas, possibly reduced, 56.5 x 45.3 cm, Sotheby's, 5 December 2019, lot 109). It comes from the Addeo collection in Rome and it was identified as portrait of Duke Alfonso I d'Este (1476-1534) and attributed to Dosso Dossi (d. 1542). Both identification and attribution were later rejected and the painting was sold as by circle of Girolamo da Carpi (1501-1556), who collaborated with Dosso Dossi on commissions for the d'Este family. The influences of Dossi's style are visible, thus the authorship of his pupils, such as Giuseppe Mazzuoli (d. 1589) or Giovanni Francesco Surchi (d. 1590), is possible. However, the style of this painting is also very similar to the head study of a young man, possibly being a portrait of the young Tintoretto, attibuted to Lambert Sustris (Slovak National Gallery, O 5116). The characteristic feature of the children of Zofia Szydłowiecka (1514-1551), protruding ears, visible in the funerary monument of Jan Krzysztof Tarnowski by Giammaria Mosca Il Padovano in the cathedral of Tarnów, as well as in the portraits of his sister by Sustris, is noticeable in both described paintings in Vienna and from the Addeo collection. Considering the age of the man, the two effigies were most likely created shortly before the death of Jan Krzysztof, who died of tuberculosis on April 1, 1567 as the last male representative of the Tarnów line of the Tarnowski family. Jan Krzysztof received his middle name in honor of his maternal grandfather Krzysztof Szydłowiecki (1467-1532), Grand Chancellor of the Crown, whose portrait by Titian is in the Pinacoteca Ambrosiana in Milan. He received an excellent education and traveled extensively in his youth. He was imperial count and proprietor of Roudnice nad Labem in Bohemia and he visited the imperial court in Vienna in 1548. In 1554 he went to Italy. After the death of his father in 1561, the young count maintained the closest relations with Nicolaus Radziwill the Black (1515-1565), the husband of his aunt. After Radziwill's death, Jan Krzysztof managed his estates located in the Crown including Szydłowiec. He maintained a large court, and his main supplier was a Jew from Sandomierz, Jakub Szklarz, who brought goods from Gdańsk (after "Panowie na Tarnowie ..." by Krzysztof Moskal, part 9). It was probably Jan Krzysztof who commissioned the monument for his father from Padovano, modeled on the monuments of the Venetian doges, the concept of which could have been conceived by the poet Jan Kochanowski, who dedicated several of his works to Jan Krzysztof. Pedro Ruiz de Moros dedicated him his Carmen fvnebre in obitv, published in Kraków in 1561, and Stanisław Orzechowski his Panagiricus nuptiarum, published in Kraków in 1553. Inventories of Tarnów Castle, like the castle itself, have not preserved, but the last will of the court physician and secretary to Count Jan Amor Tarnowski, Stanisław Rożanka (Rosarius), may give an idea of its wealth. Rożanka was educated at the University of Padua in the Venetian Republic. In his will of 1569, which was opened after his death in 1572, Stanisław, a Calvinist and the owner of a house in Saint Florian's Street in Kraków, mentioned many of his exquisite possessions. "And besides the things described above (these are valuables, dresses, utensils, etc.), I have old Roman and Greek numismatics, books, maps, pictures, etc. Of these, my brother, Dr. Walenty, all of my books and mappas and antiqua numismatics both gold and silver, to use and keep. [...] I want my second brother Mr Jan to be given a sable-lined damask szubka [fur coat], a silver cup with a lid, four precious cups and a silver ewer, and all flasks, and armours, also pictures, a chariot &c. &c." (after "Skarbniczka naszej archeologji ..." by Ambroży Grabowski, p. 65). In 1542, Jan Amor, aged 54, the father of Jan Krzysztof, suffering from gout, traveled to Italy for treatment, probably to Abano Terme, a health resort located near Padua. He also visited the Duke of Ferrara Ercole II d'Este and returned via Vienna, where King Ferdinand was to offer him command of his army during the war with the Ottoman Empire, but he did not accept the offer because of the good relations between King Sigismund I and the Turks. Such journeys serve to describe the origins of many beautiful Italian works of art in their collections for many European museums. The collections of the counts of Tarnów were undoubtedly exquisite and comparable to those of the dukes of Ferrara, however, today no traces of this patronage are kept in Tarnów, everything has been looted, destroyed or scattered. The Tarnowskis equaled or even surpassed the Venetian doges and the kings of Poland with their funerary monument and their portraits were equally splendid.
Miniature portrait of Count Jan Krzysztof Tarnowski (1537-1567) by Lambert Sustris, ca. 1565-1567, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Portrait of Count Jan Krzysztof Tarnowski (1537-1567) by circle of Dosso Dossi or Lambert Sustris, ca. 1565-1567, Private collection.
Portrait of Wawrzyniec Goślicki by Giovanni Battista Moroni
On January 3, 1567 Wawrzyniec Grzymała Goślicki (Laurentius Grimaldius Goslicius) obtained the degree of Doctor Utruisque Juris (doctor of both laws - civil and church law) at the University of Bologna.
Goślicki was born near Płock in Masovia and after studying at Kraków's Academy he left for Italy after 1562. During his studies in Padua, in 1564, he published the Latin poem De victoria Sigismundi Augusti, which he dedicated to the victory of king Sigismund II Augustus over tsar Ivan IV the Terrible in the war of 1560. After receiving his doctorate in Bologna he visited Rome, and then Naples together with his friends. On the way back, Goślicki stopped in Rome for a while. In 1568, during his stay in Venice, he published his best-known work, De optimo senatore, also dedicated to king Sigismund Augustus. The book printed by Giordano Ziletti was later translated into English with the titles of The Counselor and The Accomplished Senator. After his return to Poland in 1569, he entered the king's service as the royal secretary. He later decided to become a priest and he was elevated to the episcopal dignity in 1577. In 1586 he was made bishop of Kamieniec Podolski and according to a document issued by Cardinal Alessandro Farnese entitled Propositio cosistorialis, he was 48 in 1586, therefore he was born in 1538. Wawrzyniec Goślicki died on October 31, 1607 in Ciążeń near Poznań as the Bishop of Poznań (from 1601) and was buried in the city's cathedral. According to his last will his tomb monument was to be modeled on the monument to his predecessor Bishop Adam Konarski, the work of Girolamo Canavesi, a sculptor from Milan, who had his workshop in Kraków. Goślicki's monument created in Kraków, most probably by workshop of Giovanni Lucano Reitino di Lugano, as Konarski's monument, was transported to Poznań after 1607. The effigy of a young man by Giovanni Battista Moroni in Accademia Carrara in Bergamo (oil on canvas, 56.9 x 44.4 cm) is very similar to Goślicki's features in his statue in Poznań. According to inscription in Latin (ANNO . AETATIS . XXIX . / M . D . LXVII) the man was 29 in 1567, exactly as Goślicki when he earned his degree at Carolus Sigonius in Bologna. Another version by workshop or follower of Moroni is in private collection in Florence (oil on canvas, 52 x 42 cm).
Portrait of Wawrzyniec Goślicki (1538-1607) aged 29 by Giovanni Battista Moroni, 1567, Accademia Carrara in Bergamo.
Portrait of Wawrzyniec Goślicki (1538-1607) by workshop or follower of Giovanni Battista Moroni, ca. 1567, Private collection.
Portrait of royal secretary Jan Zamoyski by Tintoretto
"Carissimo Signore Valerio Montelupi, I have received a letter from my Ursyn [Niedźwiedzki] from Padua. He writes that, in accordance with my instructions, he went to Venice in the affairs of a painter. He looked at the paintings almost finished. From his description, I can see two things that should be given close attention. First of all - it was my intention that only two figures should be imagined clearly and decoratively, and this is the figure of the standing Savior and the figure of St. Thomas kneeling with his hand stretched to Christ's side", writes in Italian Chancellor Jan Zamoyski (1542-1605) in a letter of 1602 regarding paintings for the Collegiate Church in Zamość, commissioned in the workshop of Domenico Tintoretto in Venice (after "Jan Zamoyski klientem Domenica Tintoretta" by Jan Białostocki, p. 60).
Zamoyski studied at the Universities of Paris and Padua, where he became Councillor of the Polish Nation and rector of the university in 1563. He also abandoned Calvinism in favor of Catholicism and discovered his love for politics. In the Archives of Venice there is a one-of-a-kind document in which the Venetian Senate congratulates the King of Poland on having such a citizen in his country, and expresses the highest appreciation for Zamoyski (Senato I Filza, 43. Terra 1565 da Marzo, a tutto Giugno): "It happened on April 7, 1565 at a session of the Senate. To the Serene King of Poland. Jan Zamoyski, the son of a noble starost of Belz, spent several years with great glory and honor at our University of Padua; last year, the most esteemed man was a gymnasiarch [the rector] [...] In this office he was doing so well and so excellently that not only the hearts of all young people who came to Padua to educate their minds with science, but also all citizens, especially our officials, he was able to win kindness in a special way. For this reason, we always welcomed him with the best will, and whenever there was an opportunity, we tried to surround him with favor and respect. There were various reasons for doing so; first of all, to your Majesty, whom we love greatly and to whom we are completely devoted, to please in the best possible way, and also, because we are deeply attached to the most noble Polish nation, finally in the conviction that Zamoyski's merits and virtues required us to do so". After returning to Poland, Zamoyski was appointed secretary to King Sigismund II Augustus and in 1567, when he was 25 years old, he acted as the king's commissar entrusted with a responsible and dangerous mission. At the head of the court armed forces, he forcibly took away the illegally seized starosties of Sambor and Drohobych from the Starzechowski family. A painting by Jacopo Tintoretto from the Fundación Banco Santander in Madrid shows a young twenty-five year old man (ANN.XXV). His high social status is accentuated with gold rings, a belt embroidered with gold and a coat lined with ermine fur. He stands proudly with his hand on the table covered with crimson fabric. His hands and the table were not painted very diligently, which may indicate that it was completed in a hurry by the artist's studio working on a large order. The man bear a great resemblance to effigies of Jan Zamoyski, especially his portrait painting, attributed to Jan Szwankowski (Olesko Castle) and engraving by Dominicus Custos after Giovanni Battista Fontana (British Museum), both created in his later years. A portrait attributed to Tintoretto or Titian from the same period is in the Odessa Museum of Western and Eastern Art. It represent Girolamo Priuli (1486-1567), who was a Doge of Venice between 1559-1567, when Zamoyski was in Venice. During the restoration of the painting, the inscriptions TIZIANO and the letters TI (over the shoulder) were discovered, however a very similar portrait in private collection and majority of larger versions are attributed to Tintoretto. The portrait of Priuli was transferred from the State Hermitage Museum in Saint Petersburg to the Odessa Museum in 1949. The painting comes from the collection of Prince Lev Viktorovich Kochubey (1810-1890), who distinguished himself in the storming of the Warsaw fortifications during the November Uprising (1830-1831), the armed rebellion in the heartland of partitioned Poland against the Russian Empire. The inventory number on the back '453' is sometimes interpreted as tantamount to an entry in the 18th century catalog of Gonzaga's collections, however, it is unknown where exactly Kochubey acquired the painting. After the collapse of the November Uprising the collections of magnates who sided with the insurgents were confiscated, e.g. painting of Madonna and Child by Francesco Francia in the State Hermitage Museum (inventory number ГЭ-199), created between 1515-1517, was confiscated in 1832 from the Sapieha collection in Dziarecyn, comprising 36 paintings of Old Masters and 72 portraits (after "Przegląd warszawski", 1923, Volumes 25-27, p. 266). In this case the thesis that Priuli's portrait was originally offered to Zamoyski or king Sigismund II Augustus is very probable.
Portrait of royal secretary Jan Zamoyski (1542-1605) aged 25 by Jacopo Tintoretto, ca. 1567, Fundación Banco Santander.
Portrait of Girolamo Priuli (1486-1567), Doge of Venice by Tintoretto or Titian, 1559-1567, Odessa Museum of Western and Eastern Art.
Portraits of Zuzanna Orłowska by Jacopo Tintoretto
"The King-Deceiver, of mixed Lithuanian and Italian blood, did not deal honestly with anyone. In repaying the shame with which he has covered me, I want to repay him bad for bad", noted the accusations made by Zuzanna (Susanna) Orłowska (or Szabinówna Charytańska, died after 1583), the mistress of King Sigismund II Augustus, historian Świętosław Orzelski (1549-1598) in his book Interregni Poloniae libri VIII (1572-1576).
The king's third marriage with his distant cousin and the Austrian Archduchess Catherine, concluded in 1553, was not happy from the very beginning. Even before his wife's departure in 1566, at the beginning of the 1560s, he allegedly had an affair with Regina Rylska, the wife of the courtier Jan Rylski. The romance of the king and Zuzanna, probably began in 1565, that is, before Queen Catherine left Poland. According to the account of the courtier of the King, Zuzanna was to be the illegitimate daughter of a canon of Kraków, other sources, however, indicate that her father was Szymon Szabin Charytański. The king and his entourage called her Orłowska (Lady of the Eagle or Mistress of the Eagle), possibly in reference to the king's coat of arms (White Eagle). Orłowska was suspected of knowing magic and together with her aunt, famous healer (or a witch-doctor) Dorota Korycka, she was to treat Sigismund Augustus, and received high remuneration for her services. With time, the feeling of the king towards Orłowska weakened, and after recovering, the king decided that "he would have no contact with demons and similar women", as he wrote in a letter to his courtier Stanisław Czarnotulski. He abandoned his mistress, and her place in the royal alcove was taken by Anna Zajączkowska, a lady of the court of Sigismund's sister Anna Jagiellon. Most likely the reason for Zuzanna's separation from the king was her betrayal. Although Orłowska herself was not faithful to him, she believed that it was the king who had disgracedly abandoned her and humiliated her. Apparently, every Thursday, "having invited the devils to a supper", according to Orzelski who knew it from the bed-chamber servant (łożniczy) of the King, Jan Wilkocki, she used magic and sprinkled peas on hot coals, saying: "Whoever has abandoned me, let him suffer so much and sizzle". When in 1569, Sigismund Augustus became seriously ill, he ordered Korycka and Orłowska to be summoned. When both women refused to help him, he promised his former lover, a thousand zlotys as a dowry when she gets married. After the king's death, Zuzanna Orłowska married the Polish nobleman Piotr Bogatko, who in 1583 bequeathed 2,400 florins to his wife as a dower and they had four sons. Jacopo Tintoretto's Bathing Susanna in the Louvre (oil on canvas, 167 x 238 cm, inventory number INV 568; MR 498) shows a moment from the Old Testament story in which biblical heroine Susanna, epitome of female virtue and chastity, unjustly accused of sexual transgression, is watched by two elderly men, acquaintances of her husband, who desire her. She sits naked in a garden beside a pool, while her maidservants are drying or brushing her hair and cutting her nails. A partridge at her feet is a symbol of sexual desire and three frogs is a symbol of fecundity and fertility. "The frog was also sacred for Venus, Roman goddess of love and fertility. Venus's yoni (female genitals) sometimes was depicted as a fleur-delis consisting of three frogs" (after Marty Crump's "Eye of Newt and Toe of Frog, Adder's Fork and Lizard's Leg: The Lore and Mythology of Amphibians and Reptiles", p. 135). "Many medieval recipes for magical and medicinal potions and ointments included frogs and/or toads as ingredients, and the animals were used in rituals intended to cure drought. In addition, medieval and Renaissance people generally thought that witches could turn themselves into frogs and toads at will. The devil too was said to sometimes take the shape of a frog or toad" (after Patricia D. Netzley's "Witchcraft", p. 114). Two ducks represent constancy and rebirth and a rabbit symbolizes fertility. The outwardly turned face of the sitter gazing at the viewer is a clear information that she is someone important. The work is an oil painting on canvas and is generally dated to the third quarter of the 16th century (1550-1575). Neoclassical frame is not original and was added in the 19th century. Bathing Susanna was acquired by King Louis XIV of France in 1684 from Marquis d'Hauterive de L'Aubespine. It is believed to have previously belonged by King Charles I of England (his sale, London June 21, 1650, no. 229), however, it could be also tantamount to "A picture painted on canvas, which shows a naked woman, without frame" (item 440) from the inventory of belongings of king John Casimir Vasa, great-grandson of Sigismund I, sold in Paris in 1673 to Mr. Bruny for 16.10 pounds. "Saint Susanna and two old men, a large painting on canvas" (815) is mentioned among the paintings from the collection of Princess Louise Charlotte Radziwill (1667-1695), inventoried in 1671 (after "Inwentarz galerii obrazów Radziwiłłów z XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska). The same woman was also depicted in a portrait painting by Tintoretto, owned by Rijksdienst voor het Cultureel Erfgoed in Amersfoort (oil on canvas, 101.5 x 77.5 cm, NK1639), which was before 1941 in the collection of Otto Lanz in Amsterdam. She is sitting in a chair, dressed in a rich Venetian style costume of orange silk. "In ancient Rome, the wives of the priests of Jupiter [king of the gods] wore a flammeum, an orange and yellow veil. The young Roman women betrothed in marriage copied this style as a symbol of hope for a long and fruitful marriage" (after Leatrice Eiseman's "Colors for Your Every Mood: Discover Your True Decorating Colors", p. 49). Based on all these facts the sitter should be identified as king's mistress Zuzanna Orłowska. Just as royal effigies, the portraits of king's mistress were created in the Republic of Venice basing on drawings or miniatures sent from Poland-Lithuania. The so-called Marshal's Book, a register of official state expenses of the court of Sigismund Augustus between 1543-1572, which was described in a publication from 1924 by Stanisław Tomkowicz ("Na dworze królewskim dwóch ostatnich Jagiellonów", pp. 31, 32, 36), is silent about court painters, as are the bills. Tomkowicz suggests that perhaps their wages were recorded separately and adds that the king often bought paintings, mostly portraits, even in batches of 16 and 20 pieces, however, "over the course of several years, one expense was recorded for the purchase of a painting depicting... a naked woman". The accounts of 1547 also mention a payment to a prostitute (meretricem) Zofia Długa (Sophia Long), who dressed in armor was to fight with Herburt and Łaszcz in a jousting tournament at the expense of the court treasury.
Portrait of Zuzanna Orłowska, mistress of King Sigismund II Augustus, as Bathing Susanna by Jacopo Tintoretto, 1565-1568, Louvre Museum.
Portrait of Zuzanna Orłowska, mistress of King Sigismund II Augustus by Jacopo Tintoretto, 1565-1568, Rijksdienst voor het Cultureel Erfgoed.
Portraits of Andreas Jerin by circle of Giovanni Battista Moroni and Gillis Claeissens
In the summer of 1566, young Andreas Jerin (also von Jerin, Gerinus or Jerinus) went to Rome to continue his philosophical-theological studies. From 1559 he studied at the University of Dillingen in Bavaria, where he earned a baccalaureate and a master's degree in 1563. As tutor to the brothers Gebhard and Christoph Truchsess von Waldburg, sons of Imperial Councilor, he continued his studies at the University of Leuven (Louvain) in the Spanish Netherlands in 1563 and was accepted as an alumne in the Collegium Germanicum et Hungaricum in Rome in October 1566 on the recommendation of Petrus Canisius, a Dutch Jesuit priest. Two years later he was ordained a priest in the sacristy of St. Peter's Basilica (December 15, 1568). He was then pastor to Swiss Guard. In 1571 he received his theological doctorate at the University of Bologna and Cardinal Otto Truchsess von Waldburg gave him the parish of Dillingen.
As early as 1570 he received a canonship at the Wrocław Cathedral of St. John the Baptist in Silesia, where he became a cathedral preacher in 1572. At the same time he was given the office of rector at the Wrocław seminary. From 1573 he was custodian of the Church of the Holy Cross (till 1538 Copernicus was a scholastic of this church). At that time Hieronim Rozdrażewski (d. 1600) was the provost of Wrocław. Rozdrażewski received the provostship in 1567, however, due to the strong resistance of the chapter, he took over it only in 1570. The provost, who in his childhood stayed with his brothers at the royal court in France and studied in Ingolstadt and Rome, become the royal secretary at the end of the reign of Sigismund Augustus. He took part in the political life of Poland and his duties in Wrocław were performed at his request by Andreas. In 1578, Rozdrażewski resigned from the provostship in favor of Jerin. On September 29, 1578 Jerin was elevated to the Bohemian nobility in Prague. For his services as an imperial envoy in Poland, Emperor Rudolf II elevated him to the imperial and hereditary Austrian nobility on February 25, 1583. After the death of Martin von Gerstmann, Bishop of Wrocław, the cathedral chapter elected Jerin, the emperor's candidate, as his successor on July 1, 1585. Despite some opposition to Jerin as a non-Silesian and of commoner background, he was consecrated on February 9, 1586. At the same time, the emperor appointed him senior governor of Silesia. Andreas celebrated important events in his life with portraiture. Two of his preserved portraits were created after his elevation to bishop of Wrocław. One, attributed to Martin Kober, is in the National Museum in Wrocław. The other showing him at the age of 47 (suae aetatis XXXX VII) and attributed to Bartholomeus Fichtenberger, was most likely offered by the bishop himself to the parish church of St. George in his hometown of Riedlingen on the river Danube in the south-west of Germany, approximately 400 km north of Bergamo and Milan. He also offered a silver chalice with his coat of arms to the church in Riedlingen (the portrait and chalice are now in the local museum). He was a patron of the sciences and arts. In 1590 he had the goldsmith Paul Nitsch (1548-1609) make a precious silver high altar for the Wrocław Cathedral, which was recently reconstructed after World War II destruction. In 1624, during his visit in the city, the altar was admired by prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (future king of Poland as Ladislaus IV). Fichtenberger painted the wings of this retable in 1591 and the bishop was depicted in the scene of the Sermon of Saint John the Baptist and as Saint Ambrose, Bishop of Milan and patron saint of this city, in the outer wings with the Fathers of the Church. In 1586 Nitsch also created a gold portable altarpiece for the bishop (Wrocław Cathedral). On March 28, 2019 a portrait of a gentleman, half-length, in a black doublet, white ruff and black hat, attributed to circle of Giovanni Battista Moroni was sold on an auction in Munich (Hampel Fine Art Auctions, oil on canvas, 68.6 x 52.7 cm, lot 1045). According to original inscription in Latin, covered because of bad condition and repeated by the restorer on the reverse, the man was 27 in 1567 (ÆTATIS. SVE. 27. / ANNO DNI 1567, upper left), exacly as Jerin when he was studying in Rome. If he traveled there from Riedlingen, where he was born in 1540, or from Leuven via Riedlingen, his possible stop before October 1566 was Bergamo in the Venetian Republic or Milan, where he could order a portrait. The most famous painting workshop in this area at that time was that of Moroni, who in 1567 created a painting of Last Supper for the church in Romano di Lombardia and the portrait of Wawrzyniec Grzymała Goślicki (Accademia Carrara in Bergamo). The man from the painting bear a strong resemblance to mentioned effigies of Andreas Jerin. Almost an exact copy of this portrait exist, three-quarter-length, which however was created by different workshop, more close to the Flemish school. It was also sold at Hampel, Munich (December 4, 2020, oil on wood, 43 x 33.5 cm, lot 1121) and comes from private collection in Paris. It is attributed to Flemish painter Gillis Claeissens (d. 1605) or his circle. Gillis, born in Bruges, was a member of a prominent family of artists and he is identified with the Monogrammist G.E.C. He was admitted as a master of the Guild of St. Luke of Bruges on 18 October 1566 and he remained in the workshop of his father Pieter Claeissens the Elder until 1570. Jerin seems to have commissioned a copy of his Italian portrait in Flanders for his friends in Leuven or elsewhere. A portrait painted in a very similar style is in Lviv, Ukraine (National Art Gallery, oil on wood, 28.8 x 21, inventory number Ж-453). It shows a young girl in prayer and her costume indicate that the painting was created in the 1570s. It is attributed to a German or Sothern Netherlandish painter and comes, most likely, from the collection of the Princes Lubomirski. Before everything was destroyed by war and hatred, the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, established by the Union of Lublin in July 1569, was a land of great prosperity for different people. Since the Middle Ages, Venetian, Genoese and other merchants coming to Lviv brought spices, silk fabrics, jewels, decorative weapons and morocco products from Kaffa, the great center of Genoese trade on the Black Sea. From there eastern goods were sent further to Kraków and Wrocław, and then to Nuremberg and as far as the port of Bruges in Flanders. Merchants in Lviv sold them cloth, amber, raw hides and herring (after "Prace Komisji Historycznej", Volume 65, p. 198). In the 14th - 15th centuries, there was a trading post of the Teutonic Order in Lviv and in 1392 Prussian amber was stored in the city in the cellar of the merchant Ebirhard Swarcze. From Lviv amber was exported to Constantinople (after "Z historii południowo-wschodniego szlaku bursztynowego" by Jarosław R. Daszkiewicz, p. 261). Trade flourished in the second half of the 16th century - two Jews from Lviv paid fifty pounds of amber to Chaim Kohen of Constantinople for wine, rice and roots (cassiae), Armenian Christopher, translator of His Highness, takes from Chaskiel Judowy wine and gives him in return tin, cloth from Lyon and Gdańsk and karazye cloth, Greek merchant Konstantinos Korniaktos (Konstanty Korniakt) takes English and Dutch cloths from the Lviv merchant Wilhelm Boger, and pays him with alum, rye and wheat. The export of grain to Gdańsk in the second half of the 16th century in Lviv was dominated by two local merchants Zebald Aichinger and Stanisław Szembek and in the second row there was a whole colony of Englishmen who had settled in the city, such as Tomasz Gorny, Wilhelm Allandt, Jan Whigt, Wilhelm Babington, Jan Pontis, Ryszard Hudson and Wilhelm Moore. One of the principal buyers of grain in Lviv at that time was a London merchant, Richard Stapper, whose agent in Lviv was Jan Pontis (after "Patrycyat i mieszczaństwo lwowskie ..." by Władysław Łoziński, p. 43, 46-47). Foreign artists, like Italian architects Pietro di Barbona (d. 1588) and Paolo Dominici Romanus (d. 1618), architect Andreas Bemer (Andrzej Bemer, died after 1626) of German or Czech origin, and Dutch sculptor Hendrik Horst (d. 1612), were active in Lviv. It is possible that the girl depicted was a daughter of a merchant and her portrait was commissioned in Bruges and sent to Lviv. During his studies, Jerin had the opportunity to meet many Poles and during his stays in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth as the imperial envoy (Lublin, 1589 and Kraków, 1592), he had the opportunity to admire some of the exquisit works of art from the royal collection, including the famous silver altar of Sigismund I in his chapel at the Wawel Cathedral, created in Nuremberg between 1531-1538, which probably inspired Andreas' foundation for the Wrocław Cathedral. On the occasion of peace negotiations with the Commonwealth in 1589 Andrzej Schoneus from Głogów (Andreas Glogoviensis), later rector of the Kraków Academy, published two odes in Kraków about "the Sarmatian peace" (De pace Sarmatica Odae II Ad Andream Gerinum), dedicated to Jerin.
Portrait of Andreas Jerin (1540-1596), aged 27 by circle of Giovanni Battista Moroni, 1567, Private collection.
Portrait of Andreas Jerin (1540-1596) in a black doublet by Gillis Claeissens, ca. 1567, Private collection.
Portrait of a young girl as donor by Gillis Claeissens, 1570s, Lviv National Art Gallery.
Portraits of Wojciech Sędziwój Czarnkowski by Adriaen Thomasz. Key
In the summer of 1568 died Jakub Ostroróg, General Starost of Greater Poland, "a man endowed with extraordinary gentleness, piety and prudence, a lover of justice and equality before the law", in the words of the chronicler of the city of Poznań. Ostroróg was a prominent magnate and politician from Poznań and one of the main leaders of the community of Bohemian Brethren. The Protestant community in the city expanded under his protection. He was appointed Starost of Poznań and General Starost by King Sigismund II Augustus in 1566.
The place of the dissident in the Poznań royal castle was taken by the Catholic Wojciech Sędziwój Czarnkowski (1527-1578), and soon the Jesuits were provided with buildings in Poznań (after "Życie codzienne w renesansowym Poznaniu, 1518-1619" by Lucyna Sieciechowiczowa, p. 91). Czarnkowski, a nobleman of Nałęcz III coat of arms, studied in Wittenberg in 1543 and Leipzig in 1545 and he became a royal courtier in 1552. He and his older brother Stanisław Sędziwój (1526-1602), Crown referendary, were strong supporters of the House of Habsburg. Stanisław, educated at German universities in Wittenberg and Leipzig, stayed at the court of Charles V and in 1564 he was an envoy to the Pomeranian dukes, and in 1568, 1570 and 1571 to Sophia Jagiellon (1522-1575), Duchess of Brunswick-Lüneburg. In 1575, the brothers signed the election of Emperor Maximilian II of Austria against the Queen Anna Jagiellon and her husband. During the next royal election in 1587 his son Adam Sędziwój (1555-1627) and brother signed the election of Archduke Maximilian III of Austria (1558-1618) against the Queen's candidate, Sigismund III Vasa. The portrait of Adam Sędziwój, created between 1605-1610 and most probably sent to the Medicis, is in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence (inventory number 2354 / 1890). Later in his life he become a supporter of king of Sigismund III Vasa, he organized a confederation in Greater Poland in defense of the king during the Zebrzydowski's rebellion and in his portrait he was depicted in national costume (crimson żupan and delia coat). In the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna there is a portrait of a man in Spanish costume attributed to Adriaen Thomasz. Key (oil on panel, 109 x 82.5 cm, inventory number GG 1034). It is identifiable in the treasury of the imperial collection in Vienna in 1773. The painting was most likely a gift to the Habsburgs. According to inscription in Latin in upper right corner of the painting the man was 41 in 1568 (A°.ÆTATIS.41 /.1568.), exaclty as Wojciech Sędziwój Czarnkowski when he become the General Starost of Greater Poland. A reduced bust-length version of this portrait in oval was most likely in a private collection, present whereabouts unknown (after "Adriaen Thomasz. Key ..." by Koenraad Jonckheere, p. 89). Netherlandish influences were increasing at that time in Poland-Lithuania, which is reflected in the architecture of cities of the former Commonwealth like Gdańsk, Elbląg, Toruń and Königsberg (at that time Duchy of Prussia was a fief of Poland). Some Netherlandish painters, like court painter Jakob Mertens from Antwerp or Isaak van den Blocke (born in Mechelen or Königsberg), also decided to settle in the Commonwealth. Others, like Tobias Fendt (Kraków, around 1576) and Hans Vredeman de Vries (active in Gdańsk between 1592-1595), went there temporarily or only took orders from customers from Poland-Lithuania. Many famous artists were unwilling to travel, especially when busy with high local demand. In order to have a marble bust made by famous Italian sculptor Gian Lorenzo Bernini, active in Rome, King Charles I of England ordered his Triple Portrait painted 1635-1636 by the Flemish artist Sir Anthony van Dyck, showing the king from three viewpoints (Royal Collection, RCIN 404420). He also ordered a similar portrait and bust of his wife Henrietta Maria in 1638. In about 1640-1642 also Cardinal Richelieu of France sent his Triple Portrait by Philippe de Champaigne to Rome (National Gallery in London, NG798) as a study for his statue by Francesco Mochi and a bust by Bernini (Louvre, MR 2165) and in August 1650, Francesco I d'Este, duke of Modena and Reggio sent paintings by Justus Sustermans and Jean Boulanger as a study for his marble bust by Bernini (Galleria Estense in Modena). In 1552 marble blocks and statues created by Giovanni Maria Mosca called Padovano and Giovanni Cini in Kraków for monuments of two wives of Sigismund II Augustus were floated down the Vistula to Gdańsk and Königsberg, then up the Nemunas and Neris rivers to the capital of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania - Vilnius, covering a total of over 1,500 km. Paintings were less heavy and easier to transport over great distances than the heavy and fragile sculptures.
Portrait of Wojciech Sędziwój Czarnkowski (1527-1578), General Starost of Greater Poland, aged 41 by Adriaen Thomasz. Key, 1568, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Portrait of Wojciech Sędziwój Czarnkowski (1527-1578), General Starost of Greater Poland by Adriaen Thomasz. Key, ca. 1568, Present whereabouts unknown.
Portrait of doctor Wojciech Oczko by Venetian painter
In 1569 doctor Wojciech Oczko (1537-1599), called Ocellus, physician, philosopher and one of the founders of Polish medicine, who studied syphilis and hot springs, returned from his studies abroad to his hometown Warsaw and newly created republic of Poland-Lithuania - the Union of Lublin, signed on 1 July 1569, created a single state, the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. He began to practice medicine at St. Martin's Hospital.
Oczko's father was the Warsaw cartwright Stanisław (d. 1572), one of his brothers Rościsław (Roslanus) was a priest, and his sister Jadwiga married the painter Maciej. He left for the Academy of Kraków around 1559 or 1560, because in 1562 he received bachelor's degree there. He then received a master's degree at the cathedral school in Warsaw and a funding from the chapter in 1565 to study medicine in Italy. Wojciech studied at the Universities of Padua, Rome and Bologna, where he earned a doctorate in medicine. He also travelled to Spain and France, where he spent time in Montpellier. In order to keep him in Warsaw, the chapter of St. Martin's Hospital gave him a house close to the hospital without any payment, provided that he lived in it himself and did the necessary repairs. Later another resolution was passed in 1571 that Oczko should treat the poor free of charge in the hospital. At that time, his fame and renown was so great in the country that he became the archiater (a chief physician) of Sigismund Augustus and the royal secretary (D. D. Sigism: Aug: Poloniae regis Archiatro ac Secretario), according to inscription on his epitaph. He then served for a time as personal physician to Franciszek Krasiński, bishop of Kraków, and from 1576-1582 (with some breaks) as the court physician to Stephen Bathory (the king and his predecessor Sigismund Augustus suffered from venereal diseases, among others). Wojciech also had literary interests and prepared the staging of Jan Kochanowski's "The Dismissal of the Greek Envoys", a play staged at the wedding of Deputy Chancellor Jan Zamoyski in the royal Ujazdów Castle in Warsaw - a note in the accounts of the Deputy Chancellor states on January 6, 1578: "I gave doctor Oczko for building, painting, etc., 151 (zlotys) for the tragedy". His major work "French court disease" (Przymiot francuski), published in Kraków in 1581, is an extensive essay on syphilis, in which he denies the false views of his contemporaries - in Russia, where it certainly came at about this time, it was called the Polish disease (after Oliver Thomson's "Short History of Human Error", p. 328). In his other essay "Hot springs" (Cieplice), published in Kraków in 1578, he speaks about the importance and benefits of mineral waters. From 1598 Oczko lived in Lublin, where he died a year later. He was buried in the Bernardine Church in Lublin, where his nephew Wincenty Oczko, canon of Gniezno, founded him an epitaph made of two-color marble. Portrait of a red-bearded man in the Städel Museum in Frankfurt am Main was acquired on April 17, 1819 from the collection of Johann Friedrich Morgenstern (1777-1844), a German landscape painter, as a work of Titian. Morgenstern most probably purchased the painting during his studies at the Dresden Academy of Fine Arts, between 1797-1798 (in the first half of the 18th century Dresden was the informal capital of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth as the main residence of the Saxon kings). The man in a courtly black costume in French/Italian style is holding his hand on books, so he must be a scholar. According to inscription in Latin on the base of the column he was 33 in 1570 ([A]NNOR[VM]. XXXIII / ANNO. MDLXX), exactly as Wojciech Oczko when he become the royal physician in Warsaw. The sign below the inscription is interpreted as showing a dragon, however it could be also Scorpio, the sign which rules the genitals, as in a German woodcut from 1512 (Homo signorum or zodiacal man) or a print created in 1484 depicting a person with syphilis. An outbreak of syphilis in November 1484 was assigned by Gaspar Torella (1452-1520), physician to Pope Alexander VI and Cesare Borgia, and Bartolomeo della Rocca known as Cocles (1467-1504 ), astrologer from Bologna, to the conjunction of the four great planets in Scorpio. Oczko's portrait could have been created by a Venetian artist active at that time at the royal court or commissioned in Venice, basing on drawings, like the royal effigies.
Portrait of doctor Wojciech Oczko (1537-1599), chief physician of king Sigismund Augustus, aged 33 by Venetian painter, 1570, Städel Museum.
Portrait of a man in eastern costume, possibly singer Krzysztof Klabon by Jacopo Tintoretto
The catalogue of Wallraf-Richartz-Museum in Cologne from 1927 ("Wegweiser durch die Gemälde-Galerie des Wallraf-Richartz-Museums", p. 70, number 516) includes a portrait painting of a man in eastern costume painted in the style of Jacopo Tintoretto, possiby lost during World War II. His long inner robe of bright silk buttoned up with gold buttons is similar to Polish żupan and his dark coat is lined with fur, he also wears a heavy gold chain. This garment resemble greatly the costume of a horseman in the Crucifixion by circle of Lucas Cranach the Elder, created in 1549 (Salzburg Museum), the attire in the portrait of Jan Opaliński (1546-1598), created in 1591 (National Museum in Poznań) or costumes in Twelve Polish and Hungarian types by Abraham de Bruyn, created in about 1581 (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam).
The inscription in Latin is only partially visible on preserved photograph, covered with a later frame: [...] VIII / [...] NTOR / [...] MNI PRIN. / [...] D. / [...] XX. Presumably the text originally read: "His age 28, the chief singer of all, in the Year of our Lord 1570" ([ÆTATIS SVÆ XX]VIII / [CA]NTOR / OMNI[VM] PRIN.[CEPS] / [A.]D. / [MDL]XX). The sitter is holding a small book, which could be a psalter, a book containing a verse translation of the Book of Psalms, meant to be sung as hymns. The man is therefore likely to be Krzysztof Klabon or Clabon (Christophorus Clabonius), who, according to some sources, came from Königsberg in what was then the Ducal Prussia, fiefdom of Poland (a note from 1604: Eruditus Christophorus Clabonius Regiomontanus S.R.M. chori musices praefectus) or he was Italian and his real name was Claboni. If he was born in 1542 (aged 28 in 1570), he could arrive to Poland in 1553 with Queen Catherine of Austria, widowed Duchess of Mantua. Prior to 1565, he belonged to a group of young singers in the royal chapel orchestra of King Sigismund II Augustus, and from 1565 to a group of instrumentalists (translatus ex pueris cantoribus ad numerum fistulatorum). On February 4, 1567, together with four other musicians, he was promoted to full wind-players (ad fistulatores maiores). Antoni Klabon, most probably Krzysztof's brother, was admitted into the king's service at court as a trumpeter in Lublin on June 25, 1569 (Antonius Klabon tubicinator. Susceptus in servitium Maiestatis Regiae Liublini die 25 Iunii 1569, habebit omnem provisionem similem reliquis). In 1576, during the reign of Stephen Bathory, Krzysztof became the bandmaster of the court band and he was replaced by Luca Marenzio in 1596, during the reign of Sigismund III Vasa. He sang at the wedding of Jan Zamoyski with Griselda Bathory (1583), with a lute at two weddings of Sigismund III and at the ceremony on the occasion of the capture of Smolensk (1611). He traveled twice with Sigismund III to Sweden (1593-1594 and 1598). Klabon was also a composer, his extant works are "Songs of the Slavic Calliope. On present victory at Byczyna" (Pieśni Kalliopy słowieńskiey. Na teraznieysze pod Byczyną zwycięstwo) for 4 mixed voices, 3 equal voices, and for solo voice with lute, published in Kraków in 1588, one sacred piece, the five-part Aliud Kyrie (Kyrie ultimum) from the lost Łowicz organ tablatures and the soprano part of one other, Officium Sancta Maria. "Numerous residences dispersed the courtiers of Sigismund Augustus. Many of them stayed away from the king. For example, in 1570 the superior of the royal band, Jerzy Jasińczyc, along with some of the musicians, lived in Kraków, while the rest were in Warsaw with the king, who, moreover, complained that there were not enough of them" (after "Barok", Volume 11, 2004, p. 23). Some famous musicians from the royal capella, like Valentin Bakfark, traveled extensively around Europe. According to accounts of the court of Albert V, Duke of Bavaria in Munich, a singer from Poland was paid 4 florins for a performance in 1570 (Ainem Sänger aus Polln so vmb diennst angehalten 4 fl. after "Beiträge zur Geschichte der bayerischen Hofkapelle", Volume 2, p. 47).
Portrait of a man in eastern costume, possibly singer Krzysztof Klabon by Jacopo Tintoretto, ca. 1570, Wallraf-Richartz-Museum.
Portraits of Sigismund Augustus with his maritime fleet and at the old age by Tintoretto
Between 1655-1660 the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, a wealthy Venetian style republic of nobles created in 1569 with support of the last male Jagiellon, Sigismund Augustus was invaded by neighbouring countries from north, south, east and west - the Deluge. Royal and magnate residencies in Warsaw, Kraków, Grodno and Vilnius and other locations were ransacted and burned which resulted in the loss of works by the greatest Venetian painters, like Paris Bordone, Tintoretto or Palma Giovane and a loss of memory of the royal effigies and their patronage.
The portrait of a "Venetian admiral" in armour from the 1570s, acquired by the National Museum in Warsaw in 1936 from the Popławski collection (oil on canvas, 81 x 68 cm, inventory number M.Ob.635, earlier 34679) bears a great resemblance to the effigies of the king from the last years of his life, notably a miniature by workshop of Dirck de Quade van Ravesteyn at the Czartoryski Museum (MNK XII-146), painted after the original from around 1570. According to Universae historiae sui temporis libri XXX (editio aucta 1581, p. 516), originally published in Venice in 1572, the king was about to set up an enormous fleet against Denmark, consisting of galleys with three, five and more rows on the Venetian model in order to protect "Sarmatia". In the spring of 1570 he entrusted the Maritime Commission with the construction of the first ship for the Polish-Lithuanian maritime fleet, while bringing in specialists Domenico Zaviazelo (Dominicus Sabioncellus) and Giacomo de Salvadore from Venice. Shortly before turning 50 in 1570, the king's health rapidly declined. Antonio Maria Graziani recalls that Sigismund was unable to keep standing without a cane when greeting Venetian Cardinal Giovanni Francesco Commendone in November 1571 who was sent by Pope Pius V to join Venice, Papal States and Spain in the interest of a crusade against the Ottoman Empire. During research carried out in 1996 at the National Museum, an x-ray revealed an unfinished portrait of another man or the same but younger, perhaps unpaid work or not accepted by the client. The painter used the earlier composition to paint a new image on it, which was a common practice in his studio. In the Popławski collection the painting was attributed to Tintoretto. Jan Żarnowski, in the 1936 collection catalog, suggested Jacopo Bassano as a possible author, however, he pointed out the resemblance of this painting among others to two portraits by Tintoretto at the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna (after "Katalog wystawy obrazów ze zbiorów dr. Jana Popławskiego", number 19, p. 48). One is a portrait of Sigismund Augustus with a royal galley (GG 24), identified by me, the other is a portrait of an old man in a fur coat and carmine tunic, similar to the Polish-Lithuanian żupan (oil on canvas, 92.4 x 59.5 cm, GG 25). The receipt issued by Princess Anna Jagiellon after the death of Sigismund Augustus to Stanisław Fogelweder, in addition to Italian, German and Persian dresses, lists numerous fur garments, such as sable coats, made of leopards, wolverines, lynxes, wolves and black foxes and traditional costumes - żupany, kopieniaki, kabaty, kolety, delie (after "Ubiory w Polsce ..." by Łukasz Gołębiowski, p. 16), which were generally crimson. The resemblance of the men in all the mentioned effigies, in Vienna and Warsaw, is striking. The image of a man in a fur coat is also dated around 1570, like the Warsaw painting, and comes from the collection of Archduke Leopold William of Austria in Brussels, included in the catalog of his collection - Theatrum Pictorium (number 103). The intensity of Poland-Lithuania's contacts with the Republic of Venice around 1570 is attested by some preserved works of art. Portrait of a Venetian senator holding a letter by Jacopo Tintoretto of unknown provenance in the National Art Museum of Belarus in Minsk, was most probably transported to the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth at that time, possibly offered to the king Sigismund II Augustus or the Radziwills. The map of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth - "The Sarmatian part of Europe, which is subject to Sigismund Augustus, the most powerful king of Poland" (Partis Sarmatiae Europae, quae Sigismundo Augusto regi Poloniae potentissimo subiacet) by Andrzej Pograbka (Andreas Pograbius), dedicated to Mikołaj Tomicki, son of the castellan of Gniezno, was published in Venice in 1570 by Nicolò Nelli. In a painting by Tintoretto from a private collection, the same man, although older, was depicted with a dark hat, very similar to those seen on many printed effigies of the last male Jagiellon - effigy by Frans Huys and Hieronymus Cock (1553-1562), at the age of 35 by Hans Sauerdumm (1554), by Battista Franco Veneziano (ca. 1561), in Jan Herburt's Statuta y przywileie koronne ... by Monogrammist WS (1570) or by Dominicus Custos (1601), as well as in the portrait painting at the age of 41, thus painted in about 1561, at the Wawel Royal Castle (inventory number 535).
Portrait of king Sigismund II Augustus (1520-1572) in armour with his maritime fleet by Tintoretto, ca. 1570, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of king Sigismund II Augustus (1520-1572) in a żupan and a fur coat by Tintoretto, ca. 1570, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Portrait of king Sigismund II Augustus (1520-1572) from the Theatrum Pictorium (103) by Lucas Vorsterman the Younger after Tintoretto, 1660, Princely Court Library Waldeck.
Portrait of king Sigismund II Augustus (1520-1572) in a hat by Tintoretto, ca. 1572, Private collection.
Portrait of a Venetian senator holding a letter by Jacopo Tintoretto, third quarter of the 16th century, National Art Museum of Belarus in Minsk.
Portraits of children of Catherine Jagiellon by Sofonisba Anguissola and Titian
In a letter of 8 January 1570 from Warsaw (in the imperial archives in Vienna), the imperial envoy, Johannes Cyrus, abbot of the Premonstratensian monastery in Wrocław, informs Baron Trautson von Sprechenstein that the king of Sweden, John III, has sent an envoy to the Polish-Lithianian court with a portrait of his son, Prince Sigismund, and that he will probably want to promote him to the throne of Poland-Lithuania. He also adds that a year earlier the Swedish monarch had received many letters from Germany (most probably from Sophia Jagiellon, Duchess of Brunswick-Lüneburg), Prussia and Poland urging him to look after his son's interests and succession in Poland-Lithuania (after "Dyarysze Sejmów koronnych 1548, 1553 i 1570 r. ..." by Józef Szujski, p. 134).
In March 1569, Sigismund Augustus agreed to meet with the emperor about the succession. Maximilian II even fixed the date of the congress in Wrocław for August 1569, but the king asked for a delay. In the end, despite the efforts of abbot Cyrus, the congress did not take place at all, because Sigismund Augustus deliberately delayed its date. Prince Sigismund, as the only son of the reigning King of Sweden, was first and foremost his successor, as Sweden was a hereditary monarchy, so the success of all these endeavors should be attributed primarily to the wife of John III, Catherine Jagiellon. With her siblings Sigismund Augustus, Sophia and Anna, she was most likely willing to create a peaceful union of different countries of Europe under one king, thus expanding the idea of the Commonwealth (Res publica), established by the Union of Lublin in July 1569. A very innovative project in 16th century Europe, when many people thought it was noble to invade other nations, kill people, loot, destroy, subjugate others and thus create primitive empires. Unfortunately, such peaceful coexistence never had a reliable chance in Europe before the tragedy of World War II. Catherine ruled Sweden similarly to her mother Bona in Poland-Lithuania, in a way described by Mikołaj Rej in his dialogue between Warwas and Lupus, thus many of her decisions are attributed or signed by her husband. In many cultures, it is said that the man is the head, but the woman is the neck and she can turn the head any way she wants. It was therefore she who had her son's portrait painted and sent with official legation to Poland-Lithuania. The symbolism of this portrait must have been obvious to everyone in the country, so it can be assumed that, like the other effigies of the Jagiellons, it was commissioned from a renowned foreign workshop and that the prince was dressed in the national costume. No other document concerning this painting has been preserved, like probably the effigy itself. However, such portraits were frequently created in series for different notables. It cannot be the full-length portrait of the 2-year-old prince, attributed to the Dutch painter Johan Baptista van Uther (Wawel Royal Castle, inventory number 3221, from the collection of the Polish Academy of Arts and Sciences in Kraków), because according to the inscription it was created two years earlier, in 1568, when the prince had actually 2 years (ÆTATIS SVÆ 2 / 1568). What's more the more German or Flemish costume of a boy with a ruff, would not please the supporters of the national cause. In the Zamość Museum there is a small oval portrait of a boy with a feathered hat, which at first glance may resemble the works by the great Polish painter Olga Boznańska (1865-1940), who was inspired by the works of Diego Velázquez (1599-1660) and also painted children, or a 19th century pastiche of portraits of the Spanish infantes by Velázquez, such as effigies of Philip Prospero, Prince of Asturias (1657-1661), however, according to museum experts, the painting is by the Italian school and it was created at the beginning of the 17th century. It was recently included in the exhibition in late 16th century interiors above another importation from Italy, an oriental-style chest of drawers inlaid with mother-of-pearl, ivory and silver, the so-called Certosina technique, from the beginning of the 18th century. Many of the oldest paintings in the museum, such as the Putto with a tambourine by circle of Titian or Lorenzo Lotto from the first half of the 16th century, a copy of the original attributed to Titian from around 1510 (Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna), comes from the collection of the Zamoyski estate in Warsaw. In addition to purchasing the Italian paintings, the Zamoyskis also received them as gifts, such as in 1599 when Papal Nuncio Claudio Rangoni, Bishop of Reggio, gave Chancellor Jan Zamoyski and his wife a copy of the miraculous image of Our Lady of Reggio and in 1603 the same Rangoni also sent a portrait of Pope Clement VIII to Zamoyski. The 1583 inventory mentions two religious paintings of Mary Magdalene and Christ carrying the cross (after "Kultura i ideologia Jana Zamoyskiego" by Jerzy Kowalczyk, p. 97-98), possibly disguise portraits by Italian school. The 1604 print with effigy of Jan Zamoyski (British Museum) was created by the Roman engraver Giacomo Lauro (Iacobus Laurus Romanus) most likely from a study drawing or a miniature sent from Poland. The boy's crimson outfit and characteristic hat are typical of the national fashion of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth at the turn of the 16th and 17th centuries. We can find similar costume in many works of art depicting Polish-Lithuanian nobles like miniature with Polish horsemen from the Kriegsordnung (Military ordinance) of Albert of Prussia from 1555 (State Library of Berlin), a copy of which most likely belonged to his cousin and overlord Sigismund Augustus, or a Polish-Lithuanian nobleman (Polacho) from Habiti Antichi Et Moderni di tutto il Mondo ... by Cesare Vecellio, published in Venice in 1598 (Czartoryski Library in Kraków). A similar crimson costume and hat can also be seen in the effigy of a Pole (Polognois) from Lucas de Heere's Théâtre de tous les peuples et nations de la terre, painted in the 1570s (Universiteitsbibliotheek Gent), images of Polish-Lithuanian nobles in Theatrum virtutum ac meritorum D. Stanislai Hosii by Tomasz Treter, painted between 1595-1600 (National Library of Poland) or in a much later fragment of the Commonwealth's map (Poloniae Nova et Acvrata Descriptio) by Jan Janssonius, published in Amsterdam in 1675 (National Library of Poland). The broad, blurry brushstrokes of Zamość's painting are characteristic of a one painter living near the beginning of the 17th century - Titian. He was one of the first to leave such visible stains of paint created through dynamic short brushstrokes, thus providing inspiration for many later artists, Velázquez and Rembrandt among them. A large number of orders required him to be quick and to simplify the painting technique. It is particularly noticeable in his late paintings, made between 1565 and 1576 - Boy with dogs in a landscape (Museum Boijmans Van Beuningen), Saint Jerome (Thyssen-Bornemisza Museum) and the Crowning with thorns (Alte Pinakothek). The portrait of a boy was painted on cedar wood, a precious wood particularly appreciated by cabinetmakers, imported to Venice from Lebanon, Cyprus and Syria in the 16th and 17th centuries. Titian and his workshop are usually associated with canvas as the primary material, however, some of the master's smaller exquisite paintings for royal patrons were done on more expensive wood or even marble, such as Mater Dolorosa with clasped hands from 1554 (oil on panel, 68 x 61 cm, Prado Museum, P000443) and Mater Dolorosa with her hands apart from 1555 (oil on marble, 68 x 53 cm, Prado Museum, P000444), both commissioned by Emperor Charles V, and also the Penitent Magdalene, probably painted for Francesco Maria della Rovere, Duke of Urbino, between 1533 and 1535 (oil on panel, 85.8 x 69.5 cm, Pitti Palace, Palatina 67) or portrait of Pope Julius II, painted between 1545-1546, from the collection of Vittoria della Rovere (oil on panel, 100 x 82.5 cm, Pitti Palace, Palatina 79). The boy in the painting may be three or four years old, as Prince Sigismund, born June 20, 1566, and the effigy resemble the earlier painting and the portrait of Sigismund's sister, Princess Elizabeth "Isabella" Vasa (1564-1566), at Wawel Castle (oil on canvas, 94.8 x 54.7 cm, 3934). The latter portrait is another intriguing aspect of the patronage of the Queen of Sweden. The style of the painting is obviously Italian and due to the inscription ISABEL in Spanish (medieval Spanish form of Elizabeth) it was initially believed to represent Catherine's older sister, Isabella Jagiellon (1519-1559) and dated about 1525. This painting comes from the collection of the Sapieha family in Krasiczyn. The costume of the young girl with a small ruff is much later and the effigy resembles the statue of Princess Isabella as depicted on the sarcophagus of her tomb sculpted by Willem Boy, carved around 1570 (Strängnäs Cathedral). As the eldest daughter of Catherine, she received the name in honor of her famous great-grandmother Isabella of Aragon (1470-1524), Duchess of Milan and suo jure Duchess of Bari. The style of this effigy most closely resembles the paintings attributed to Sofonisba Anguissola, who was court painter and lady-in-waiting to Elisabeth of Valois (Isabel de Francia, Isabelle de Valois), Queen of Spain, from 1560 until queen's death in 1568, and lived at the Spanish court in Madrid. Among the closest analogous paintings are the self-portrait with Bernardino Campi from the 1550s (Pinacoteca Nazionale di Siena), the double portrait of the two young girls from around 1570 (Royal Palace of Genoa) and the portrait of a young woman from around 1580 (Lázaro Galdiano Museum). To be painted by the court painter of the Queen of Spain was a great prestige in the 16th century, moreover on the maternal side Catherine was a descendant of some Aragonese monarchs. Very wealthy Jagiellons could easily afford such "extravagance". The style of this painting both in composition and technique resembles the series of paintings of children of Emperor Maximilian II (1527-1576), son of Anna Jagellonica (1503-1547), in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna - Archduchess Anna (1549-1580) (95 x 60 cm, 8148), Archduke Rudolf (1552-1612) (95 x 55.5 cm, 3369), Archduke Matthias (1557-1619) (95 x 56 cm, 3372), Archduke Maximilian (1558-1618) (95 x 55.5 cm, 3370), Archduke Albert (1559-1621) (95 x 55.5 cm, 3267) and Archduke Wenceslaus (1561-1578) (95 x 55.5 cm, 3371). They were probably commissioned in Spain, as their mother was the Spanish Infanta Maria (1528-1603), daughter of Emperor Charles V and Isabella of Portugal. Also, the dimensions and style of inscription of all these paintings are similar, so the portrait of Isabella Vasa could be one of many paintings depicting the children of Catherine Jagiellon by Anguissola or her workshop. It is also possible that the Wawel Castle painting does not depict the Vasa Princess at all, because some paintings from the Habsburg series are missing, including the effigy of Elizabeth of Austria (1554-1592), future queen of France. The style of the princess's portrait can also be compared to Sofonisba's self-portrait at the easel (Łańcut Castle), which was probably an advertisement of her talent or a gift to a generous client sent to Poland. Catherine most likely commissioned the effigies of her children through her envoys, such as Ture Bielke (1548-1600), who visited Szczecin in 1570 and later went to Venice or Count Olivero di Arco, who entered into relations with the royal court of Sweden after the autumn of 1568 and in the summer of 1570 presented himself in Venice as official ambassador of the Swedish monarch (after "Le Saint-Siège et la Suède ..." by Henry Biaudet, p. 208). In November 1569, Venetian Cardinal Giovanni Francesco Commendone, papal legate to Poland, wrote to Princess Anna asking if it was possible for Anna's sister, as the new queen of Sweden, to influence the country's politics, while Catherine corresponded at the same time with the pope (e.g. letter from Pius V to Catherine Jagiellon, March 8, 1570). Intermediaries at the Spanish court could have been the Polish ambassadors, Piotr Dunin-Wolski (1531-1590), representing Commonwealth's interests between 1561-1573, or Piotr Barzy, starost of Lviv, sent in 1566 to Madrid, where he died in 1569. Also the mentioned painting of a boy with dogs in a landscape (oil on canvas, 99.5 x 117 cm, Museum Boijmans Van Beuningen), could be related to Poland-Lithuania. Because the artist used the same study drawing of a dog as in a portrait of a general in the Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Kassel, painted between 1550 and 1552, it is thought to have been commissioned by the same client or his family. According to Iryna Lavrovskaya, the portrait of a general could be an effigy of Nicholas "The Black" Radziwill (Heritage, N. 2, 1993. pp. 82-84). The effigy of a boy embracing the dog who looks at a second dog suckling two puppies on the left recalls the story of abandoned Romulus and Remus (Capitoline Wolf), the founders of the city of Rome and the children of the god of war Mars and the priestess Rhea Silvia. Interestingly enough, the eldest son of Nicholas "The Black", Nicolaus Christopher (1549-1616) is said to have received the nickname "the Orphan" when King Sigismund Augustus found the child left unattended in one of the rooms of the royal palace. After his studies in Strasbourg, in mid-1566, the young 17-year-old Radziwill went through Basel and Zurich to Italy. He stayed longer in Venice, Padua and Bologna, he also visited Florence, Rome and Naples and, as he himself wrote, "everything worth seeing". He returned to the country in 1569 (after "Polski słownik biograficzny", 1935, Volume 24, p. 301). After the death of his mother in 1562 and his father in 1565, at this time in his life he could really feel like an orphan, so an allegorical painting reminiscent of his father would be a good souvenir from Venice.
Portrait of Princess Elizabeth "Isabella" Vasa (1564-1566), daughter of Catherine Jagiellon or Elizabeth of Austria (1554-1592), granddaughter of Anna Jagellonica (1503-1547) by Sofonisba Anguissola, 1560s, Wawel Royal Castle.
Portrait of Prince Sigismund Vasa (1566-1632), son of Catherine Jagiellon, in Polish-Lithuanian costume by Titian, ca. 1570, Zamość Museum.
Boy with dogs in a landscape, most probably allegorical portrait of Nicolaus Christopher "the Orphan" Radziwill (1549-1616) by Titian, 1565-1576, Museum Boijmans Van Beuningen.
Portrait of Infanta Juana de Austria with court dwarf Ana de Polonia by Sofonisba Anguissola
"We have a great joy with them (...) each day this gift becomes more pleasant to us, for which we also offer our grateful appreciation to Vostrae Serenitati" wrote emperor Charles V on May 11, 1544 to Queen Bona Sforza, who sent him two dwarfs raised at her court, Kornel and Katarzyna.
Dwarfs were present at the Polish court since the Middle Ages, however it was during the reign of Sigismund I and Bona that their presence was significantly strengthened. As servants of Osiris and their association with other Egyptian gods of fertility and creation, like Bes, Hathor, Ptah, dwarfs were also symbols of fertility, revival and abundance in Ancient Roman World and one fresco from Pompeii near Naples is a very special example of it (after "The meaning of Dwarfs in Nilotic scenes" in: "Nile into Tiber: Egypt in the Roman World", Paul G.P. Meyboom and Miguel John Versluys, 2007, p. 205). To secure the endurance of the dynasty in the times when child mortality was very high, fertility was very important to Bona, granddaughter of Alfonso II, King of Naples. There were Spanish dwarfs at the Polish court, like Sebastian Guzman, who was paid 100 florins, a cubit of Lyonian cloth and damask and Polish monarchs sent their dwarfs to Spain, like Domingo de Polonia el Mico, who appears in the house of Don Carlos between 1559-1565. The presence of Polish dwarfs was also significant at the French court. In 1556 Sigismund Augustus sent to Catherine de Medicis, Queen of France two dwarfs, called grand Pollacre and le petit nain Pollacre and in 1579 a dwarf Majoski (or Majosky) was even studying at her cost. A lot of female dwarfs were at the court of the Jagiellons, like a certain Maryna, an old dwarf of Queen Bona, who was paid salary by king Stephen Bathory or Jagnieszka (Agnieszka), female dwarf of Princess Sophia Jagiellon, who was her secretary. Queen Barbara Radziwill, had at her court a dwarf Okula (or Okuliński) and she received two female dwarfs from the wife of voivode of Novogrudok. After her mother left for her native Italy, when all her sisters were married and her brother was occupied with affairs of state and his mistresses, Anna Jagiellon spent time on embroidery, raising her foster children and dwarfs. A portrait showing a little girl hiding under protective arm of a woman by Sofonisba Anguissola in Boston (Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum, oil on canvas, 194 x 108.3 cm, P26w15), due to appearance of her ruff can be dated to the late 1560s or early 1570s. The woman is Infanta Doña Juana de Austria (Joan of Austria), widowed Princess of Portugal, sister of king Philip II of Spain, ruler of one half of the world and mother of king Sebastian of Portugal, ruler of the second half of the world (according to Treaty of Tordesillas, 1494), sister of Holy Roman Empress Maria of Austria, as well as Archduchess of Austria, princess of Burgundy, a friend of Ignatius of Loyola, founder of the Society of Jesus (Jesuits), one of the most influential religious orders of the Catholic Reformation, and whose confessor was her cousin Francis Borgia, third Superior General of the Jesuits. She was the most influential and powerful woman in Europe. The portrait which is said to depict Catherine Stenbock (1535-1621), Queen of Sweden from the Stenbock Palace in Kolga (Kolk) in Estonia, now in private collection (oil on canvas, 63 x 50 cm, sold at Bukowskis in Stockholm, Sale 621, December 11, 2019, lot 414), is de facto a copy or a version of Juana de Austria's portrait by Alonso Sánchez Coello from 1557 (Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna), most probably created by Sofonisba in about 1560. Kolga Palace was once owned by Swedish soldier Gustaf Otto Stenbock (1614-1685), who during the invasion of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth was promoted to field marshal. The painting, once sent to Sigismund Augustus or his sister Anna by Juana, was therefore taken from one of the royal residences during the Deluge (1655-1660) and this unknown lady was later identified as a Queen of Sweden from the Stenbock family. The portrait in Boston is also very similar to the portrait in the Basque Museum in Bayonne by workshop of Sofonisba or Juan Pantoja de la Cruz (oil on canvas, 170 x 120 cm, inventory number G 2). It depicts Isabel de Francia (Elisabeth of Valois, 1545-1568), Queen of Spain, daughter of Catherine de Medicis and third wife of Philip II, with a little girl, which could be her French female dwarf Doña Luisa. It was a portrait of Queen Isabel that Sofonisba sent to the Pope Pius IV in 1561: "I heard from the most reverend Nuncio of your Holiness, that you desired a portrait, from my hands, of her Majesty the Queen, my mistress", according to Sofonisba's letter dated Madrid, September 16, 1561 and "We have received the portrait of the most serene Queen of Spain, our dearest daughter, that you have sent us" according to Pope's letter dated Rome, October 15, 1561. The girl in Boston portrait is holding in her hand three roses. The association of the rose with love is too common to require elaboration, it was the flower of Venus, goddess of love in ancient Rome. Three flowers symbolize also Christian teological virtues, faith, hope and love, with love pointed as "the greatest of these" by Paul the Apostle (1 Corinthians 13). She is therefore a foreigner at the Spanish court and the painting is a message: I am safe, I have a powerful protector, do not worry about me, I love you, I remember about you and I miss you. It is a message to someone very important to the girl, but also important to Juana. We can assume with a high degree of probability that it is a message to the girl's foster mother Anna Jagiellon, who to strengthen her chances to the crown after death of her brother, assumed the unprecedented but politically important Spanish title of Infanta: Anna Infans Poloniae (Anna, Infanta of Poland, e.g her letter to cardinal Stanisław Hozjusz, from Łomża, 16 November 1572). In the 16th century Spanish portraiture even members of the same family were rarely depicted together. Suffocating court etiquette made exception only to dwarfs and court jesters, like in the portrait of infanta Isabella Clara Eugenia with a female dwarf Magdalena Ruiz by Alonso Sánchez Coello from about 1585 (Prado Museum) or in the portrait of pregnant youger sister of Anna of Austria (1573-1598), Queen of Poland - Margaret, Queen of Spain with a female dwarf Doña Sofía (her name might indicate Eastern origin) from about 1601 by Juan Pantoja de la Cruz or Bartolomé González (Kunsthistorisches Museum). Blood connections and family ties were very important to Spanish Habsburgs, Ana de Austria (Anna of Austria, 1549-1580), fourth wife of Philip II, was his niece (her mother Maria was his sister and her father was his cousin). Spanish sources mentions that in 1578 died Doña Ana de Polonia, court dwarf of Queen Ana de Austria (after "Ana de Austria (1549-1580) y su coleccion artistica", in: "Portuguese Studies Review", Almudena Perez de Tudela, 2007, p. 199), most probably the same mentioned in 1578 in Cuentas de Mercaderes (Merchant Accounts), M. 4, granting her a skirt and other clothing. If this girl is the same with that in the portrait of Juana, and after death of Juana in 1573 she joned the court of a foreign queen who arrived to Spain in autumn of 1570, this lovely green-eyed girl was probably someone more than an agreeable court dwarf. Her name might indicate, apart from the country of her origin, also her family, like Doña Juana de Austria (Joan of Austria, Joan from the House of Austria, the Habsburgs), who was born in Madrid and never visited Austria, hence Doña Ana de Polonia (Anna of Poland, Anna from the House of Poland, the Jagiellons). So was this girl an illegitimate daughter of Sigismund Augustus, who after death of Barbara in 1551 was desperate to have a child or his sister Anna, a vigorous (gagliarda di cervello) spinster? Such a bold hypothesis cannot be excluded due to its nature that rather should be concealed and kept secret, and lack of sources (in Poland apart from paintings, also many archives were destroyed during wars). The preserved sources, especially from the last years of reign of Sigismund Augustus are controversial. Imperial envoy, Johannes Cyrus, Abbot of the Premonstratensian monastery in Wrocław, in a letter dated March 3, 1571 states that "The king would even marry a beggar, if she only gave him a son" and Świętosław Orzelski, Sejm deputy and Lutheran activist, in his diary that "in the same castle [Royal Castle in Warsaw], where Infanta Anna lived, Zuzanna was lying in one bed, Giżanka in the second, third at Mniszek's, the fourth in the room of the royal chamberlain Kniaźnik, fifth at Jaszowski's" about "the falcons" (Zuzanna Orłowska, Anna Zajączkowska and Barbara Giżanka among others), mistresses of the king. He also allegedly had illegitimate daughters with them. Maybe a research in Spanish archives will allow to confirm or exclude the hypothesis that Ana de Polonia was a daughter of Sigismund or of his sister Anna and was sent to distant Spain. The painting was purchased by Isabella Stewart Gardner in 1897 from the collection of Marchese Fabrizio Paolucci di Calboli in Forli. Its earlier history is unknown. It was most probably aquired in Poland by cardinal Camillo Paolucci, born in Forli, who was a papal nuncio in Poland between 1727-1738. Also earlier provenance is possible through cardinal Alessandro Riario Sforza, a distant relative of Anna from the branch of the family who were lords of Forli and Imola, who was named papal legate in Spain in 1580, just two years after death of Ana de Polonia, and who could acquire a copy of painting made for the Queen of Poland.
Portrait of Infanta Juana de Austria (Joan of Austria) from the Stenbock Palace by Sofonisba Anguissola or workshop, ca. 1560, Private collection.
Portrait of Queen Isabel de Francia (Elisabeth of Valois) with a female dwarf by Sofonisba Anguissola or workshop, 1565-1568, Basque Museum in Bayonne.
Portrait of Infanta Juana de Austria (Joan of Austria) with female dwarf Ana de Polonia by Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1572, Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum in Boston.
Portrait of Stanisław Reszka by Adriaen Thomasz. Key
In 1569 Stanisław Reszka (Rescius), secretary of cardinal Stanisław Hozjusz went with him to Rome. During his stay there, he assisted the cardinal in his public activities in the Roman Curia and during the conclave in 1572. That year he was also an envoy in his name to the Viceroy of Naples, Cardinal Granvelle ("On the third day after the election of Pope Gregory XIII, I left with the most eminent Cardinal Granvelle for Naples", wrote Reszka in a letter), and the following year to King-elect Henry of Valois. He helped the cardinal with organization during his journey and stay in the Eternal City. He was also increasingly active in the cultural and literary field. Rescius assisted in the publication of the works of Cardinal Hozjusz (Paris 1562, Antwerp 1566 and 1571, Cologne 1584). Opera qvae hactenus extitervnt omnia ... was published in Antwerp by the publishing house of the widow and heir of Joannes Steelsius (Antverpiae : in aedibus viduae et haeredum Ioannis Stelsij), shortly after Hozjusz's return to Poland after the 1565-6 papal conclave (20 December - 7 January) and Opera omnia was published by the same publishing house in 1571, hence the work was prepared and directed from Rome. The full-length portrait of Cardinal Hozjusz, offered by Pope John Paul II in 1987 to the reconstructed Royal Castle in Warsaw (inventory number ZKW/2207/ab, previously in the Vatican Library), was painted in 1575 by Flemish painter Giulio (Julius) della Croce, called Giulio Fiammingo. Reszka himself published in Rome portraits with biographies of popes (1580), Roman emperors (1583), Cardinal Hozjusz (1588) and Polish kings (1591) (after "Vademecum malarstwa polskiego" by Stanisław Jordanowski, p. 44).
Stanisław, educated at the Lubrański Academy (Collegium Lubranscianum) in Poznań, in Frankfurt an der Oder as well as in Wittenberg and Leipzig, came from a bourgeois family. He was born in Buk in Greater Poland on September 14, 1544. He obtained his doctorate in Perugia and in 1559 he became the secretary of Bishop Stanisław Hozjusz. In 1565 he was ordained a deacon in Rome and in 1571 he became a canon of Warmia. Two years later, in 1573 he was appointed by King Henry of Valois as the royal secretary and in 1575 he was ordained priest by Hozjusz in the church of St. Clement in Rome. From 1592 he stayed in Naples as an envoy of the Commonwealth. One of Reszka's greatest achievements in Rome was the founding of the Polish College. He recommended many Poles and Prussians to Marcin Kromer, Prince-Bishop of Warmia, like Leonard Neuman, an Olsztyn resident, who was not admitted to the Collegium Germanicum in Rome (after "Działalność polonijna Stanisława Reszki ..." by Aleksander Rudziński, p. 70, 72). As a diplomatic agent in Rome, distinguished by his artistic taste, Rescius also becomes an artistic agent of the monarchs of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. He was an important supplier of works of art for Sigismund III Vasa, who purchased them in Naples, Rome and Venice, along with Tomasz Treter, Jan Andrzej Próchnicki, Bartłomiej Powsiński, Spanish and Italian envoys and magnates traveling abroad (after "Malarstwo europejskie w zbiorach polskich, 1300-1800" by Jan Białostocki, Michał Walicki, p. 19). He also corresponded with Queen Anna Jagiellon, to whom he sent from Rome on January 19, 1584 "the Indian stone". In the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna there is a portrait of a man with a reddish beard by Adriaen Thomasz. Key (oil in panel, 85 x 63 cm, inventory number GG 3679, signed top left with the monogram: AK). This painting is verifiable in the imperial collection Prague in 1685 and was transferred to Vienna in 1876. Key, a Calvinist painter active in Antwerp in the Spanish Netherlands, painted in 1579 several versions of effigy of William the Silent, the leader of the Dutch revolt, however some portrait paintings of William's opponent Don Fernando Álvarez de Toledo, 3rd Duke of Alba, are also attributed to him, in collaboration with Willem Key (in Palacio de Liria in Madrid and in Museum Prinsenhof in Delft), as well as portraits of Margaret of Parma (1522-1586), Catholic Regent of the Netherlands (Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, GG 768 and Museum Prinsenhof in Delft). The man with a reddish beard is holding gloves in his right hand and his black costume and pose resemble the portraits of Antoine Perrenot de Granvelle (1517-1586), when bishop of Arras, especially the painting by Antwerp painter Antonis Mor in the Kunsthistorisches Museum, created in 1549 (GG 1035) or a similar portrait of future cardinal by Titian, created a year earlier (Nelson-Atkins Museum of Art, 30-15). According to Latin inscription in upper part of the painting the man was 28 in 1572 (1572 / Æ T A. 28), exacly as Rescius, when he accompanied Cardinal Granvelle to Naples. The diplomat died there in 1600.
Portrait of Stanisław Reszka (1544-1600), aged 28 by Adriaen Thomasz. Key, 1572, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Portraits of Don Joseph Nasi, Duke of Naxos by Lorenzo Sabatini and circle
"While Selim was staying in Kütahya as the governor of the sultan, Don Joseph Nasi had just arrived at the sultan's court, and by his skilful manners, polite conversation and, above all, his riches, he captured the sultan's heart so much that he wrote a letter to Ercole II, Duke of Ferrara, asking him to allow Don Joseph's relative move with his property to Turkey, which also happened in 1558", writes Aleksander Kraushar in his "History of Jews in Poland", published in Warsaw in 1865 (Historya Żydów w Polsce, Volumes 1-2, p. 314).
The author is referring to Prince Selim (1524-1574), son of Hurrem Sultan (Roxelana), wife of Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent, who after death of his mother in 1558 engaged in an open struggle with his brother Bayezid for the throne. Prince Selim, who had the support of his father, emerged victorious and Bayezid escaped to the Safavid Empire with his sons and a small army. Don Joseph Nasi (ca. 1524-1579), mentioned in this fragment, was a Jewish diplomat, banker and financial advisor at the court of the Ottoman Sultans Suleiman I and his son Selim II. In his eventful life he went by different names: Portuguese João Miques in Portugal, Italian Giovanni Miches in Venice, Castilian Juan Miguez in Spain and Flanders and Joseph Nasi or Jusuff Nassy in Constantinople (Istanbul) and many variations of these names. He was born around 1524 in Portugal, where the family had fled from persecution in Castile. Joseph's father, Agostinho, was a doctor who taught at the University of Lisbon and his aunt was Gracia Mendes Nasi (1510-1569), also known by her Christianized name Beatrice de Luna Miques, wife of Don Francisco Mendes. The latter, in partnership with his brother Diogo, built a veritable commercial empire by trading mainly in spices. In the 1530s, following the establishment of the Inquisition in Portugal and the death of Don Francisco, Joseph fled with his aunt Dona Gracia, who took over the management of her husband's banking operations, to Antwerp. The enormous wealth enabled her to influence kings and popes. In about 1545 the family moved to Venice and from there to the more tolerant Ferrara. During this time, they more openly returned to Judaism. In 1553 a Judaeo-Spanish translation of the Hebrew Bible, one dedicated to Duke Ercole II d'Este (1508-1559), and one for the Jewish public dedicated to Gracia Nasi, was published in Ferrara - the Ferrara Bible. Soon, after disputes over control of the family properties with her sister Brianda and an agreement reached in 1552, ratified before the Senate of Venice, Gracia moved with her daughter Ana, who had adopted the name of Reyna, and her court to Istanbul, where she settled in the European quarter of Galata in 1553. In January that year, Joseph abducted his wealthy cousin Beatrice (Gracia la Chica, Little Gracia), Brianda's daughter, from Venice and married her in Ravenna. He was caught and permanently banned from Venetian territory, including all Mediterranean possessions of the Republic. Nasi then traveled to Rome to get the Pope to lift the ban and to have his wife and her fortune restored to him. His aunt sent a ship from Ragusa to Ancona to fetch him and his brother Samuel (Bernardo), and they embarked for Istanbul in November 1553. A few months after his arrival in Constantinople, he openly professed the Jewish religion and had himself circumcised, married his cousin Reyna (Ana) according to the Jewish rite and moved into a magnificent palace with her and his aunt, the Belvedere with a view of the Bosphorus. Nasi's political career began in the service of the Ottoman Sultan, Suleiman the Magnificent, who, in addition to his wealth, also appreciated his excellent economic and political connections throughout Europe and his familiarity with the mentality of the Christian empires. According to one report "There are few persons of account in Spain, Italy, or Flanders who are not personally acquainted with him". German merchant, Hans Dernschwam, who participated in the embassy of Ferdinand I to Constantinople (1553-1555), described Nasi and his family in his diary: "The aforementioned scoundrel arrived in Constantinople in 1554, with about twenty well-dressed servants, who follow him as though he were a prince. He wears silk clothing, with sable lining". Dernschwam criticizes his lavish lifestyle, his following the fashion of the European nobility, arranging tournaments and theatrical performances in his garden (after "The Long Journey of Gracia Mendes" by Marianna D. Birnbaum). In the meantime, in Italy, when Brianda and her daughter declared their intention to confess openly to Judaism, the Council and the Doge decided that the women should leave Venice. They moved to Ferrara, where in 1558 Gracia la Chica (Beatrice) was engaged to Samuel (Bernardo) Nasi, Joseph's brother. Nasi, through the sultan's emissaries, successfully negotiated the safe conduct of his brother and his former wife in Christian rite to join their family in Constantinople, after approval granted by the Duke of Ferrara on March 6, 1558 and by Venice in May that year (after "Italia judaica ...", p. 177). Around that time or after the arrival in Istanbul, a bronze medal with the bust of Gracia la Chica at the age of 18 (A AE XVIII), commemorating the marriage or the engagement, was commissioned from an Italian medalist, active mainly in Florence and in nearby Siena - Pastorino de' Pastorini (British Museum, 1923,0611.23). Although it is claimed that he traveled extensively in Italy to create his medals, it is more likely that the majority of them were created from drawings sent from different places. Also Queen Bona ordered a medal with her bust, created in 1556 (National Museum in Kraków, MNK VII-Md-70), most probably commissioned from Bari. Joseph obtained the favor of Prince Selim who made him a member of his honor guard. When Pope Paul IV sentenced a group of converts in Ancona in the Papal States in 1556 to be burned at the stake, Gracia and Joseph organized a trade embargo of the port. Then Gracia signed a long-term lease agreement with Sultan Suleiman for the region of Tiberias in the Galilee. Starting in 1561 Joseph had the city walls rebuilt and encouraged the immigration of Jewish artisans from Venice and the Papal States. When Pope Pius V published the bull of February 26 , 1569 expelling the Jews from his state, many went to the Nasi fief. After the death of Sultan Suleiman I in 1566 and the ascension of Selim II to the Sultanate, he rewarded Joseph with the Duchy of Naxos and the Cyclades for his services which he ruled through his governor Francesco Coronello, a Spanish Jew. Joseph was at the peak of his economic and political power. He supported the war with the Republic of Venice, at the end of which Venice lost the island of Cyprus. Nasi primarily ruled the duchy from his Belvedere Palace, where he also maintained his own Hebrew printing press, which was kept by his wife, Dona Reyna, after Joseph's death. As an influential figure in the Ottoman Empire he corresponded with the most important monarchs of Europe and their representatives, including Sigismund II Augustus. He was introduced to the monarch of Poland-Lithuania in 1562 by Sultan Suleiman himself, in these words: "a gentleman worthy of all honor, faithful and favored by Us" (after "History of the Turkish Jews ... " by Elli Kohen, p. 74). According to some surviving letters, the two corresponded in Latin and Italian - "To Joseph Nasi the Jew. Brisk, grateful, dear to us" (Josepho Nasi Judaeo. Strenue, grate, nobis dilecte), wrote the king in Latin recommending his ambassador to the High Porte in 1567 the Calvinist Piotr Zborowski (d. 1580), castellan of Wojnicz. "Sacred Majesty! [...] I greatly desire to serve Your Majesty not only in this case of good and great value, but in every other thing that you commands me" (Sacra Magesta! [...] Essendo io desideratissimo servir Vestra Magesta non solo in questo si bene e di tanto valore, ma in ogni altera cosa che quella mi commandi), replied Nasi in Italian regarding friendly relations with Selim. In a letter of February 25, 1570 from Warsaw (Varsaviae, die XXV Februari) "To the Jew Nasi, King Sigismund Augustus: Distinguished sir, our beloved friend!" (Judaeo Nasi Sigismundus Augustus rex: Excelens domine amice Nr. dilecte), the king refers to a secret affair (negotii), probably a plan to buy the Principality of Wallachia from the sultan, "about which you will learn in detail from Our envoy Wancimulius, to whom we have orally entrusted this matter for security". This envoy was Zuane Vancimuglio of Vicenza (Joannes Vancimulius Vincentinus), who previously, as a spy for the Inquisition, tracked heretics in the Venetian possessions. Nasi sent him to Poland to let the king know that the Turks were ready to provide military support to obtain Bari and Rossano from Spain (after "Zuane Vancimuglio, agent wioski Zygmunta Augusta" by Stanisław Cynarski, p. 361). In September 1569 he was the king's envoy to Rome and after return to Poland he was sent to Turkey. In June 1570, Vancimuglio was in Poland and in the late autumn of that year he returned to Rome and was imprisoned there on charges of homosexuality (de Venere vetita) with a "boy who was already publicly flogged in Rome" (Chłopcza thego, quo abusus esse dicitur yuz chwostano publice po Rzimye), probably a male prostitute, and spying for Turkey, as informed Jerzy of Tyczyn (Georgius Ticinius), king's secretary, in a letter of December 2, 1570 to Bishop Marcin Kromer. The last mention of him comes from a letter of very reluctant to him Cardinal Stanisław Hozjusz to the king of March 31, 1571, in which he writes that "Vancimuglio has already received his reward" (Vancimulius iam accepit mercedem suam). In a letter of March 7, 1570, also from Warsaw (Datum Varsaviae, die VII martii anno MDLXX), recommending his ambassador Jędrzej (Andrzej) Tarnowski, the king calls Nasi "Illustrious prince, our beloved friend" (Illustris Princeps amice noster dilecte) and assures him that "Your Illustriousness may be convinced that We are also ready to provide you with similar services whenever the opportunity arises". As a result of the special relations that developed between Don Joseph and Polish kings, especially Sigismund Augustus, several of his agents settled in Lviv, and the city served as a base for Polish-Turkish trade (after "Jewish history quarterly", Issues 1-4, 2004, p. 8). He also obtained commercial privileges from the king. Sigismund Augustus undoubtedly had a painted effigy of the Duke of Naxos and Joseph had a portrait of the Polish-Lithuanian monarch in his Belvedere Palace, as was customary in the 16th century for such important figures. Similar to the medal with the profile of his cousin Gracia la Chica, such effigies were commissioned in Italy, but probably not in Venice, since the relations of the Nasi family with the "Queen of the Adriatic" were not friendly. The opulent residences of Polish-Lithuanian kings and magnates, like the Koniecpolski Castle in Pidhirtsi (Podhorce) near Lviv in western Ukraine, were filled with the most exquisite works of art created by local, European and Oriental artists (paintings, sculptures, tapestries, silverware, parade weapons, horse tacks, carpets, Turkish and Persian jewelry, etc.). Elected king Stanislaus Augustus Poniatowski (1732-1798), commissioned portraits of Chajka and Elia, two Jewish women from Zhvanets (National Museum in Warsaw), and from the time of Esterka, the Jewish mistress of king Casimir the Great, who reigned between 1333 and 1370, the Jews were close to the royal court as physicians, suppliers and bankers, so many portraits of them were also in the royal collection, unfortunately everything was looted, destroyed and dispersed. In 1567 Joseph made public his attachment to Spain. That year, negotiations for a truce between the Ottoman Empire and the Holy Roman Empire began, while Nasi began importing wool and merino sheep (for wool) from Spain and mulberry trees (for silkworms) from France, with the intention of starting a textile industry. In 1570, Joseph even asked for safe conduct for himself and his entire household to return to Spain. He asked to be pardoned for following Jewish law. It is not known if he was serious in this admission and his intentions are not clearly known (after "Joseph Nasi, Friend of Spain" by Norman Rosenblatt, p. 331). After the defeat suffered by the Ottoman forces at the Battle of Lepanto (October 7, 1571), Joseph's influence at court gradually diminished. Selim II's death in 1574 caused him to retire from court, he was nevertheless allowed to retain his titles and income. Nasi died on August 2, 1579, leaving no descendants. In 2017 a portrait of an old bearded man in a rich coat lined with fur, "probably Hercules II of Este, Duke of Ferrara and Modena", was sold in Barcelona, Spain (oil on canvas, 112.6 x 100.6 cm, Balclis, May 31, 2017, lot 1393). The painting is attributed to Italian school from the second half of the 16th century. It represents an old man sitting in a chair, and near a table covered with a red carpet. The man bears no resemblance to the Duke of Ferrara from his effigies, such as the Pastorini medal of about 1534 (National Gallery of Art, Washington), so this identification must be rejected. He is holding a letter and pointing to the recipient "To Ercole II, Duke of Ferrara and Modena, 1558" (A / Hercole II. / Duca di Ferrara e Modena / 1558). Dates were usually not added in the addressee field, so the letter and the portrait itself commemorate an important event in the sitter's life. In 1558 the sultan at the request of Joseph Nasi corresponded with Ercole II regarding the relocation of his relatives from Ferrara. An almost exact copy (or original) of this painting exists. It is now in the Galleria Estense in Modena (oil on canvas, 115 x 92 cm, inventory number R.C.G.E. 12) and before 1784 it was in the collection of the Dukes of Modena in their palace (Palazzo Ducale). This painting is of better quality, so the one from Spain could be a workshop copy. It is dated to around 1570-1576 and unanimously attributed to Lorenzo Sabatini (died August 2, 1576), a painter from Bologna in the Papal States, who moved to Rome in 1573 to work under Vasari in the Vatican. The recipient of the man's letter is different. It is addressed to Quaranta Malvasia of Bologna, treasurer of Romagna (All Ill.re Sig.r mio prone oss.mo Il / sig.r Quaranta Malvasia Thes.ro di Romagna / Bologna), identified with a certain Cornelio Malvasia who was a member of the Council of forty senators (Consiglio dei Quaranta), which governed the city of Bologna. Sabatini worked for the Malvasia family in Bologna (around 1565 he painted the altarpiece and the frescoes in their chapel in the church of San Giacomo Maggiore, and he was the author of portraits mentioned in their house), however, why Quaranta Malvasia commissioned a portrait in which he points to his name on the letter? If this would be his portrait, he would prefer to hold a letter from the Pope, the Emperor, King of Poland or even the Sultan. He rather commissioned or received a portrait of a famous man holding a letter to him, which would be a sign of great respect. The man was most likely an important contractor to the treasurer of Romagna (Papal States, including the Duchies of Ferrara and Modena) and the letter concerned financial matters or the safe conduct of Jews from the Papal States. The man is therefore Don Joseph Nasi, who was around 52 in 1576 (born in 1524 or before) and died exactly 3 years after Sabatini.
Portrait of Don Joseph Nasi (ca. 1524-1579), Duke of Naxos holding a letter to Ercole II, Duke of Ferrara by circle of Lorenzo Sabatini, ca. 1570-1576, Private collection.
Portrait of Don Joseph Nasi (ca. 1524-1579), Duke of Naxos holding a letter to Quaranta Malvasia of Bologna, treasurer of Romagna by Lorenzo Sabatini, ca. 1570-1576, Galleria Estense in Modena.
Portraits of Anna Jagiellon by Tintoretto and circle of Titian
"The Queen is fresh and in such good health that I would not consider it a miracle if she were to become pregnant", reported from Warsaw on 29 January 1579, Giovanni Andrea Caligari (1527-1613), papal nuncio in Poland, about 56 years old Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596), elected co-ruler of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth.
"In the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries, overweightness and obesity were considered symbols of sexual attractiveness and well-being" (Naheed Ali's "The Obesity Reality: A Comprehensive Approach to a Growing Problem", 2012, p. 7) and Anna's mother Bona Sforza, who visited Venice in 1556, was obese in her 40s and 50s, as visible in the cameo in the Metropolitan Museum of Art (inv. 17.190.869). At the end of November 1575 Austrian legation arrived in Warsaw, officially promising the infanta marriage to Archduke Ernest of Austria (1553-1592), the son of Emperor Maximilian II and Maria of Spain, and her relative as a grandson of Anna Jagellonica (1503-1547). But the offer was accepted very restrainedly and cautiously, even coldly. Anna was to reply modestly that she depended on the entire Republic and would only do what custom and the general will would require of her, and that she "entrusted her orphanage to God's holy protection" (after "Anna Jagiellonka" by Maria Bogucka, p. 118). The young Archduke, 30 years younger than the potential bride, undoubtedly received her effigy. News coming mainly from Vienna and Venice informed the general public about the course of 1575 royal election in the Commonwealth. The Fuggers, a prominent group of European bankers, learned about the election of Emperor Maximilian as king of Poland from reports sent from Vienna on December 16, 1575, and then from Venice (newspaper of 30 December) (after "Z dziejów obiegu informacji w Europie XVI wieku" by Jan Pirożyński, p. 141). In the Jagiellonian University Museum in Kraków there is a painting attributed to Tintorretto from about 1575 (after "Muzeum Uniwersytetu Jagiellońskiego" by Karol Estreicher, p. 100). This painting was offered to the Cracow Academy by Franciszek Karol Rogawski (1819-1888) in 1881 (oil on canvas, 110 x 96 cm, inventory number 2526). According to Rogawski's record, the portrait features the queen of Cyprus, Caterina Cornaro (1454-1510), and was acquired at Sedelmayer's auction in Vienna. It had earlier belonged to the Viennese gallery of Joseph Daniel Böhm (1794-1865) and was also attributed to Paolo Veronese, Battista Zelloti and circle of Bernardino Licinio (after "Foreign Painting in the Collections of the Collegium Maius" by Anna Jasińska, p. 146). The crown on her head alludes to a royal dignity, however, the woman's costume does not resemble well known effigies of the queen of Cyprus by Gentile Bellini and can be compered to the dress of La Belle Nani by Paolo Veronese (Louvre Museum), dated to about 1560, or to the costume of a lady from The Madonna of the Cuccina Family (Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden), also by Veronese, painted around 1571. Her face has the appearance of not being taken live, as points out Enrico Maria Dal Pozzolo ("Un Michele da Verona e uno Jacopo Tintoretto a Cracovia", p. 104), who also attribute the canvas to Tintorretto. Therefore the painting was created after another effigy, a drawing or a miniature. The same woman was also depicted holding a cross and a book in a painting in the Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Kassel (inventory number GK 491), a copy of which was in the Swedish royal collection (18th century copy of lost original is in the Gripsholm Castle, inventory number NMGrh 187). The painting in Kassel is attributed to circle of Titian or specifically to his pupil Girolamo di Tiziano, also known as Girolamo Dante, and was acquired before 1749. This effigy is a pendant to portrait of Catherine Jagiellon, Duchess of Finland in white by Titian, identified by me. The woman bears strong resemblance to effigies of Anna Jagiellon, especially the miniature by Lucas Cranach the Younger in the Czartoryski Museum and her tomb sculpture at the Wawel Cathedral. Polish-Lithuanian magnates owned a number of paintings by Titian and Tintorretto, like Michał Hieronim Radziwiłł, who according to the Catalogue of his picture gallery, published in 1835 (Katalog galeryi obrazow sławnych mistrzów z różnych szkół zebranych przez ś. p. Michała Hieronima xięcia Radziwiłła wojew. wil. teraz w Królikarni pod Warszawą wystawionych), had a copy of Venus of Urbino by Titian (Portrait of Princess Isabella Jagiellon nude, identified by me), item 439 of the Catalogue, or "Portrait of a lady in a dark green dress trimmed with gold braid. She takes a flower from the basket with her right hand, and leaning, holds a crimson scarf with her left hand. Painting well preserved. - Painted on canvas. Height: elbow: 1, inch 16.5, width: elbow: 1, inch 10" (Portret damy, w sukni ciemno-zielonej, galonem złotym obszytej. Prawą ręką bierze z koszyka kwiatek, lewą oparta, trzyma szal karmazynowy. Obraz dobrze zachowany. - Mal. na płót. Wys. łok. 1 cali 16 1/2, szer. łok. 1 cali 10, item 33, p. 13), a landscape with staffage (item 213, p. 64) and an Italian landscape with a tree (item 273, p. 83), all attributed to Titian or Saint Paul and Anthony in the desert, painted on wood, attributed to Tintorretto (item 365, p. 108). In 1574 Anna decided to reactivate the postal service between Poland and Venice, suspended in 1572 after death of her brother, and to do so at her own expense (after "Viaggiatori polacchi in Italia" by Emanuele Kanceff, p. 106). The Queen, heiress of the Neapolitan sums, used Montelupi's postal facilities, who through their own agents, maintained close contact with the bankers in Naples, who sent them sums of money with great frequency (after "Saeculum Christianum", Vol. 1-2, p. 36). "In fact, we demand Y.L. [Your Lordship] as far as things or needs of our own are concerned, to pay no heed to our expense, because we will gladly cover it everywhere. But whatever may be sent through cursores ordinarios [ordinary messengers], please send through cursores, who may also go as far as Venice. And with the merchants goods, everything comes to us fast and at great cost. As for the other things, another time we will answer to Y.L. With this we wish Y.L. to be well. Dated Varsoviae, die 10 Novembris A. D. 1573. Kind to Y.L. Miss Anna Polish Princess", wrote the Infanta to cardinal Stanisław Hozjusz (after "Starożytności Historyczne Polskie ..." by Ambroży Grabowski, p. 21). Anna was a well known benefactor of the Cracow Academy (now Jagiellonian University) and she visted it twice on 20 July 1576 and on 24 April 1584. Three days after her last visit she sent the doctors of the Academy a mug of pure gold and a few beautifully bound books. If Elizabeth I (1533-1603), hereditary Queen of England, favoured the French fashion, especially "when the Anjou marriage negotiation were at their height" in about 1579 (Janet Arnold's "Queen Elizabeth's Wardrobe Unlock'd", 2020, p. 188), the elected Queen of the Polish-Lithuanian Republic, could prefer the fashion of the Venetian Serenissima.
Portrait of Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596), elected co-ruler of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth by Jacopo Tintoretto, ca. 1575, Jagiellonian University Museum in Kraków.
Portrait of Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596) holding a cross and a book by circle of Titian, 1560-1578, Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Kassel.
Portrait of Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596) holding a cross and a book by Georg Engelhard Schröder after original by circle of Titian, 1724-1750, Nationalmuseum in Stockholm.
Portrait of Henry of Valois by workshop of Tintoretto
After the death of Sigismund II Augustus in 1572, Catherine of Medici, Queen of France, willing to make her favourite son Henry of Valois, Duke of Anjou the king of Poland, sent her court dwarf Jan Krasowski, called Domino to the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. Under the guise of visiting his family in his homeland, he was to make some inquiries and explore the mood in the Commonwealth. Catherine used all her power to offer the crown to her son by influencing the noble electors.
In order to be more agreeable to the Ottoman Empire and strengthen a Polish-Ottoman alliance, on 16 May 1573, Polish-Lithuanian nobles chose Henry as the first elected monarch of the Commonwealth. He was officially crowned on 21 February 1574. Expecting that Henry will marry her and she will become a Queen, Infanta Anna Jagiellon the wealthiest woman in the country and a sister of his predecessor, ordered French lilies to be embroidered on her dresses. Already in 1572, the Infanta was accused of wanting the crown for herself or to impose her candidate against the will of the council and the lords of the kingdom. "We already see that Y[our] H[ighness] is doing something without our will, with great anger. We see that you want this crown for you, but you will not elect us the lord", Anna cited the accusations made by the council in a letter of December 18, 1572 from Warsaw to her sister Sophia Jagiellon, Duchess of Brunswick-Lüneburg. She was also accused of attempts to poison opposition leaders, including Franciszek Krasiński, Bishop of Kraków and Calvinist Jan Firlej, Voivode of Kraków - according to letter from Wawrzyniec Rylski, courtier of Catherine Jagiellon, to Duchess Sophia dated February 2, 1573 from Warsaw (after "Jagiellonki polskie ..." by Alexander Przezdziecki, Volume 4, pp. 12, 30). Despite the fact that he arrived to Poland with a large retinue of his young male lovers, known as the mignons (French for "the darlings"), including René de Villequier, François d'O and his brother Jean, Louis de Béranger du Guast and especially his beloved Jacques de Lévis, comte de Caylus (or Quélus), and that "he even flattered the Polish lords by cleverly adopting their attire", as wrote Venetian envoy Girolamo Lippomano, he was not feeling well in the unknown country. After death of his brother Charles IX, Catherine urged him to return to France. During the night of 18/19 June 1574, Henry secretly fled the Commonwealth. The portrait of a man in black hat by workshop of Tintoretto from private collection in Milan is almost identical with the portrait of Henry depicted against the wall hanging with his coat of arms as King of Poland in the Museum of Fine Arts in Budapest by Italian painter (inventory 52.602) and his portrait holding a crown in the Doge's Palace in Venice (Sala degli Stucchi) by workshop of Tintoretto. It bears no distinction, no reference to his royal status, as in mentioned two portraits in Budapest and Venice, he is depicted as a simple nobleman. It is higly probable then that it was one of a series of state portraits commissioned by Anna in Venice before Henry's coronation, as a clear signal that he should marry her before becoming a king. The Infanta was most probably well aware of his inclination towards men, as apart from Krasowski, there were also other Polish dwarfs at the French court. Raised at the multicultural court of the Jagiellons, where people spoke Latin, Italian, Ruthenian, Polish and German, they were perfect diplomats. In 1572 king Sigismund Augustus sent to Charles IX, four dwarfs and in October that year, Claude La Loue brought another three dwarfs from Poland as a gift from Emperor Maximilian II, father of Charles IX's wife Elisabeth of Austria (after Auguste Jal's "Dictionnaire critique de biographie et d'histoire", 1867, p. 896). A portrait, said to be Mariana of Austria with a female dwarf wearing a wimple from a private collection in Spain, lost, is very similar to the portrait of Elisabeth of Austria in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, which is attributed to Giacomo de Monte (Netherlandish Jakob de Monte, according to some sources). Painter of similar name, Giovanni del Monte, possibly Giacomo's brother, is mentioned as a court painter of Sigismund Augustus before 1557. It is therefore highly probable that the portrait of Queen of France with her dwarf was created for or at the initiative of the Polish-Lithuanian court. On April 28, 2021 a portrait of a young woman wearing an embroidered dress and a pearl necklace by North Italian School was sold on an auction in London (oil on canvas, 25 x 18.5 cm, Sotheby's, lot 317). On other auction her dress was identified as Spanish court dress (Neumeister in Munich, July 15, 2020, auction 388, lot 141). Her costume and style of this painting resembles the portrait of Elisabeth of Valois, Queen of Spain with a female dwarf by Sofonisba Anguissola or her workshop (Basque Museum in Bayonne), the painter who joins the two mentioned terms (North Italian School and Spanish court). The woman in the portrait strongly resembles the effigies of Elisabeth of Austria, especially her best-known portrait by François Clouet in the Louvre, mentioned likeness in Vienna by de Monte and her face from the effigy by Jooris van der Straaten in the Convent of Las Descalzas Reales in Madrid, dated to about 1573. The portrait of Elisabeth's sister Anne, Queen of Spain by Sofonisba is also dated to about 1573 (Prado Museum, P001284). In several portraits, Elisabeth has blond hair, while in this one as well as in the portrait by de Monte, her hair is dark, which could indicate that at some point she lightened her hair or that painters copying effigies from general drawings were unaware of her true hair color. The style of this small portrait is also very similar to another signed work of Sofonisba - portrait of Cameria in the Musée Fabre in Montpellier (inventory number 65.2.1). Elisabeth, like her sister Anne, Queen of Spain, were both granddaughters on the paternal side of Anna Jagellonica (1503-1547), and as in the case of dynastic relations, the links between artists and patrons from different countries of Europe, including Poland-Lithuania, were also strong. Due to the still small number of medalists in the country, the royal court usually commissioned images of this kind abroad, in Vienna or Prague. Only once, during the short reign of Henry of Valois, did the court order two coronation medals from Parisian artists (after "Dzieje sztuki medalierskiej w Polsce" By Adam Więcek, p. 85). Medals of Henry of Valois on the election as King of Poland, attributed to French sculptor Germain Pilon, are in the National Museum in Kraków (inventory number MNK VII-Md-97) and in the Royal Castle in Warsaw (ZKW.N.830/2511). Similar was the case for portrait paintings, and Venice was the nearest center with a large number of painting workshops.
Portrait of Henry of Valois, elected monarch of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth by workshop of Tintoretto, ca. 1573, Private collection.
Portrait of Elisabeth of Austria, Queen of France by workshop of Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1573, Private collection.
Portrait of Elisabeth of Austria, wife of Charles IX as a widow with a female dwarf wearing a wimple by Jakob de Monte, after 1574, Private collection, lost.
Portraits of Joachim Frederick of Brzeg by Adriaen Thomasz. Key
In 1574 Joachim Frederick (1550-1602), the eldest son of George II the Pious, Duke of Brzeg-Oława-Wołów, arrived to Kraków. He was sent there by his uncle Elector John George as a representative of Brandenburg during the coronation of the newly elected King of Poland, French Prince Henry of Valois. During his youth, Joachim Frederick spent several years at the court of his uncle. The next year, in 1575, he attended the coronation of Rudolf II as king of the Romans in Regensburg.
Joachim Frederick was a representative of the Silesian Piasts, descendants of the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. Also Emperor Maximilian II, whose son Archduke Ernest of Austria was a candidate for the throne in the free election of 1573, sent a delegation to the royal coronation entrusting it to another Piast - Wenceslaus III Adam, Duke of Cieszyn. Despite the disappointment of his son's defeat, it was necessary to strive to maintain good relations with Poland, mainly due to concerns about Silesia. "Towards the King of Poland he cannot help and his Majesty is filled with regret, seeing him occupy that office, which he designated for his son, [...], and also because this king, besides being powerful and bordering on a great distance, can lay claim to Silesia, a very important province", a Venetian envoy Giovanni Correr reported on May 30, 1574 (finally drawn up on August 29, 1578). Oratio Malaspina wrote from Prague to Cardinal Como on July 10, 1579, that the Polish envoy "came to renew the ancient confederations between the Kingdom of Poland and the province of Silesia" and Bishop Giovanni Andrea Caligari wrote to the same Cardinal Como from Vilnius on August 10, 1579 that "In addition to the things in Hungary, the king could easily take Silesia and Moravia from the emperor, and he would have help from all those German princes who do not love the house of Austria, and there are many of them" (after "Księstwo legnickie ..." by Ludwik Bazylow, p. 482). Abraham de Bruyn (d. 1587), a Flemish engraver from Antwerp, who established himself at Cologne about the year 1577, created several depictions of Polish-Lithuanian noblemen, however, only three engravings of people from other social spheres related to the territory of today's Poland are known. They represent the inhabitants of Gdańsk (four patricians from Gdańsk and nine women of different classes) and two Silesian women, which clearly indicate the main areas of Netherlandish presence in this part of Europe. While Martin Kober, a Silesian painter born in Wrocław become around 1583 the court painter of the Polish king Stephen Bathory, the leading artists working in Silesia in the second half of the 16th century were a Dutch painter Tobias Fendt (d. 1576), educated in the studio of Lambert Lombard in Liège and active in Wrocław since 1565, and sculptor Gerhard Hendrik (1559-1615) from Amsterdam, who between 1578-1585 lived in Gdańsk and after traveling to France, Italy and Germany, he settled in Wrocław in 1587. On May 19, 1577, Joachim Frederick married Anna Maria of Anhalt. After the death of his father in 1586, he received the Duchy of Brzeg to which, however, his mother Barbara of Brandenburg (1527-1595) was entitled to as a widow. In the National Museum in Warsaw there is a portrait of a young man in French costume - black satin doublet and a ruff (oil on panel, 47 x 33 cm, inventory number M.Ob.819 MNW, earlier 186634). It comes from the collecting point of the Ministry of Culture and Art Paulinum in Jelenia Góra, Silesia and was acquired as a result of the so-called restitution campaign in 1945 (after "Early Netherlandish, Dutch, Flemish and Belgian Paintings 1494–1983" by Hanna Benesz and Maria Kluk, item 351). It is attributed to Adriaen Thomasz. Key, a Flemish painter active in Antwerp, who adopted the Key family name after taking over the workshop of his master Willem Key in 1567. Adriaen specialized in portraiture and worked successfully for wealthy merchants and the court. He was a Calvinist, but continued to live in the city after the Fall of Antwerp in 1585, when all Protestants were given four years to settle their affairs and leave the city. He died in Antwerp in or after 1589. According to inscription in upper part of the painting the man was 24 in 1574 (1574 / Æ T A 24), exactly as Joachim Frederick, born September 29, 1550 in Brzeg, when he arrived to Kraków for the coronation of French Prince Henry of Valois as King of Poland. The same man, in similar costume, was depicted in another painting attributed to Key, today in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna (Gemäldegalerie, oil on panel, 98.5 x 71 cm, inventory number 808), verifiable in the gallery in 1720, therefore most probably coming from the old collections of the House of Habsburg. Because of similar dimensions, this portrait is considered to be a counterpart to the portrait of a lady dated '1575' (Gemäldegalerie, oil on panel, 99.5 x 70.8, inventory number 811), however, the composition is not matching. The woman is much larger when comparing the pictures, which is very unusual for a European portraiture, even if she was actually taller. As the numbers indicate, they were not included in the inventory at the same time and therefore were not previously considered a pair. Small differences in these images (in Warsaw and Vienna) are noticeable, such as the color of the eyes, but a comparison with the portraits of Philip II, King of Spain by Anthonis Mor and workshop, proves that even the same workshop interpreted the same image differently. The man bear a strong resemblance to Barbara of Brandenburg, Joachim Frederick's mother, from her statue above the main gate of the Brzeg Castle (created by Andreas Walther and Jakob Warter, between 1551-1553) and his grandmother Magdalena of Saxony (1507-1534), daughter of Barbara Jagiellon (1478-1534), Duchess of Saxony. In portraits by Lucas Cranach the Elder and his workshop (Art Institute of Chicago, Grunewald hunting lodge in Berlin), the color of Magdalena's eyes is different (brown/blue). The shape of the nose is especially characteristic in these family members.
Portrait of Joachim Frederick of Brzeg (1550-1602), aged 24 by Adriaen Thomasz. Key, 1574, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Joachim Frederick of Brzeg (1550-1602) by Adriaen Thomasz. Key, ca. 1575, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Portrait of Sophia Jagiellon and Sidonia von Borcke by Adriaen Thomasz. Key
Two paintings by German school in the Von Borcke Palace in Starogard, north of Szczecin, both lost during World War II, depicted members of the Jagiellonian dynasty. One, created by workshop of Lucas Cranach the Elder and representing pregnant Barbara Radziwill with a midwife, was traditionally identified as the most famous member of the Von Borcke family - Sidonia the Sorceress (1548-1620), the other was a signed effigy of Sophia Jagiellon (1522-1575), Duchess of Brunswick-Lüneburg.
Von Borcke, a Pomeranian noble family of Slavic origin, originally known as Borek or z Borku and having two red wolves in their coat of arms, were owners of the large estates in Pomerania with several towns, including Łobez, Resko, Strzmiele, Węgorzyno and Pęzino Castle. Since the times of Maćko Bork (Matzko von Borck), who died in about 1426, the family had some ties to the Jagiellons and Poland. His great-granddaughter, mentioned Sidonia, lived at the court of Duke Philip I in Wolgast and became a lady-in-waiting to his daughter princess Amelia of Pomerania (1547-1580). In 1569 the Polish court planned to marry Amelia to Albert Frederick, Duke of Prussia and Polish vassal. The son of Philip I, Prince Ernest Louis (1545-1592), fall in love with Sidonia and promised her marriage. However, the wedding did not take place, as the prince, under pressure from his family, withdrew from his promise and in 1577 he married Sophia Hedwig of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel (1561-1631), granddaughter of Hedwig Jagiellon (1513-1573), Electress of Brandenburg, daughter of Sigismund I. In 1556 Sophia Hedwig's grandfather, Henry V (II) of Brunswick-Lüneburg (1489-1568), married a daughter of Sigismund I - Sophia Jagiellon. In 1619 in Wolfenbüttel, grandson of Duke Philip I, Duke Ulrich of Pomerania (1589-1622) married a great-granddaughter of Hedwig Jagiellon and Henry V, Princess Hedwig of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel (1595-1650). The family ties between the ruling families of Poland-Lithuania, Pomerania and Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel were therefore pretty strong at that time. Two known portraits of Hedwig of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel in French costume and large cartwheel farthingale (in the Royal Collection, RCIN 407222 and in the Gymnasium in Szczecinek, lost during World War II) were painted by a Netherlandish painter, attributed to Jacob van Doordt, Marcus Gheeraerts the Younger, Daniël Mijtens or Paulus Moreelse. The Dukes of Pomerania frequently commissioned their effigies from the best foreign artists and the so-called "Book of effigies" (Visierungsbuch) of Duke Philip II of Pomerania (Pomeranian State Museum in Szczecin, lost during World War II) was a collection of their likenesses, some of which were attributed to circle of Albrecht Dürer and Lucas Cranach the Elder. The so-called Croy tapestry in the Pommersches Landesmuseum representing the Duke Philip I with his family as well as the family of his wife Maria of Saxony was made in 1554 by Peter Heymans, a Dutch weaver, in Szczecin. The composition of the tapestry was based on the graphics by Lucas Cranach the Elder and it is possible that Cranach's workshop in Wittenberg created the cartoon to this work. The painting of Madonna and Child with cherries by circle of the Netherlandish painter Quentin Matsys was acquired by Duke Bogislaw X (Pomeranian State Museum in Greifswald), some jewels of the Dukes of Pomerania from the late 16th and early 17th century are attributed to Jacob Mores the Elder, active in Hamburg (National Museum in Szczecin), a cup in the shape of a peacock, created by Joachim Hiller in Wrocław in Silesia and a crystal bowl made in Paris and framed in Szczecin, both owned by Erdmuthe of Brandenburg, Duchess of Pomerania are in Green Vault in Dresden. The dukes also commissioned and purchased many exquisite objects from the center of European goldsmithing - Augsburg, like the famous Pomeranian Art Cabinet of Duke Philip II, silver plaques by Zacharias Lencker from Darłowo Altar or ivory veneered and painted box with exotic parrots, fish, and other animals and coat of arms of Philip II of Pomerania and his wife (Courtauld Institute of Art). Some contacts with Italy and Italian artists in this part of Europe are also documented. In 1496 Duke Bogislaw X went on a pilgrimage to the Holy Land, leaving his duchy under the regency of his wife Anna Jagiellon (1476-1503), sister of Sigismund I. He traveled to Venice and he was received in Rome by the Pope Alexander VI Borgia, who presented him with a ceremonial sword (nowdays in the collection of the Hohenzollern Castle, scabbard, in the Monbijou Palace in Berlin, was lost during World War II). Mannerist west wing of the Castle in Szczecin was built between 1573 and 1582 by Italian architects Wilhelm Zachariasz Italus and Antonio Guglielmo (Antonius Wilhelm) for Duke John Frederick (1542-1600) and Giovanni Battista Perini (Parine) from Florence created the painting to the ducal chapel and duke's portrait. Portrait of Duke Boguslaus XIV (1580-1637) is in the Villa di Poggio a Caiano, one of the most famous Medici villas near Florence. In 1576 de Hane (d'Anna) family from Brabant, settled in Lübeck in Germany, about 290 km west of Szczecin, ordered a painting in Venice for the St. Catherine's Church in Lübeck. This large canvas depicting the Raising of Lazarus (140 x 104 cm) and representing some members of the family in the background, was painted by Tintoretto (signed and dated: IACO TINTORE / VENETIS F. / 1576). Around 1575 other Venetian painter Parrasio Micheli created a large painting depicting Allegory of the birth of the Infante Ferdinand, son of Philip II of Spain, today in the Prado Museum in Madrid (oil on canvas, 182 x 223 cm, inventory number P000479). The work was created in Venice with a portrait of Infante's mother Anna of Austria (1549-1580), Queen of Spain, granddaughter of Anna Jagellonica (1503-1547), Queen of Germany, Bohemia, and Hungary. The painting was sent by Micheli to Philip II without a commission, to win the favor of the monarch. Spanish monarchs also sent similar gifts to relatives, mostly in Vienna. A large painting by Alonso Sánchez Coello depicting King Philip II of Spain banqueting with his family and courtiers (The Royal feast), created in 1596 (signed and dated: ASC ANNO 1596), purchased by the National Museum in Warsaw in 1928 from Antoni Kolasiński's collection (oil on canvas, 110 x 202 cm, inventory number M.Ob.295, earlier 73635) was perhaps such a gift sent to the Polish-Lithuanian royal family. Micheli also painted the Dead Christ venerated by Pope Pius V, which could be another gift to powerful King of Spain ordered in Venice, this time from the Pope (Prado Museum, P000284). Netherlandish painters created effigies of both Philip II and his wife. A small portrait of the King of Spain from private collection (oil on panel, 46.4 x 35.6 cm), identified by me, is attributed to Adriaen Thomasz. Key, a portrait of Anna of Austria in Alte Pinakothek in Munich (inventory number 4859) was created by Flemish painter (attributed to Justus van Egmont) and very similar preparatory drawing in Albertina Museum in Vienna (inventory number 14269) is also attributed to Key (also to Antonis Mor or Peter Candid, similar to signed portrait painting by Alonso Sánchez Coello in the Kunsthistorisches Museum, inventory number 1733). In her last years the Duchess of Brunswick-Lüneburg, Sophia Jagiellon, retired to the families residence in Schöningen, where she laid out the famous pleasure garden, which no longer exists today. She remodelled her residencies at Schöningen and Jerxheim in Renaissance style, according to the taste of the time. Her husband Henry V died in 1568 and two years later, in the spring of 1570, Sophia converted to Lutheranism. Most likely around that time a tombstone of Henry V, his two sons, killed in the Battle of Sievershausen in 1553, was created in Marienkirche in Wolfenbüttel. The tombstone is attributed to Jürgen Spinnrad and after the Duchess' death Adam Lecuir (Liquier Beaumont), a sculptor trained in Antwerp, created her relief sculpture basing on an effigy from the time of her marriage (1556). When her stepson tried to limit her authority as a widow, she appealed to Emperor Maximilian II and promised him to support Archduke Ernest's candidacy for the Polish throne and his marriage to her sister Anna. However, Stanisław Sędziwoj Czarnkowski, a supporter of the emperor's son, complained in a letter to Sophia that he tried to persuade Anna to accept the portrait of Archduke Ernest, "which Her Majesty by any mean whatever didn't want to" and further reports that "for four Sundays a picture of a French prince hung at her place". Earlier, in April 1570, Sophia's brother Sigismund II Augustus sent Czarnkowski as his envoy for arbitration in affairs with her stepson, Henry's successor, Julius (1528-1589). The Duchess was fluent in Polish, Italian, Latin and German, and she left a lively correspondence with more than 184 correspondents. She proved herself to be a good financial manager. Sophia had a reputation as a very rich woman with a large amount of cash and borrowing money at interest. The cities of Leipzig - 20,000 thalers, and Magdeburg - 30,000 thalers, took the largest 5% loans from the Duchess, as well as the Elector of Brandenburg, John George - 20,000 thalers and her stepsister Hedwig - 1,000 thalers. Her regular customer-debtor was her stepson, Julius, who often borrowed large sums (e.g. 15,000 thalers in November 1572). She also invested money in various goods, both movable and immovable (after "Zofia Jagiellonka ..." by Jan Pirożyński, p. 70). In her last will, she left Stanisław Sędziwój and his brother Wojciech Sędziwój Czarnkowski (his portrait by Adriaen Thomasz. Key is in Vienna) 500 ducats each. Duke Julius studied in Leuven (Louvain) in the Habsburg Netherlands and visited France in 1550. Under his rule many Netherlandish artists, architects and engineers were employed by the ducal court of Wolfenbüttel, like Willem de Raet from 's-Hertogenbosch (1574–1576), entrusted with the modernisation of the waterways, recruited for Duke Julius by his compatriot, painter Willem Remmers, or a painter Hans Vredeman de Vries (1587–1591), who created a portrait of Sophia's niece Hedwig of Brandenburg (1540-1602), Duchess of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel and who later moved to Gdańsk (1592-1595). Ruprecht Lobri from the Low Countries become the personal valet of the duke. After discovery of the deposits of decorative stones (marble and alabaster) in his territory in the early 1570s Julius contracted stone cutters from Mechelen: Hendrick van den Broecke, Augustin Adriaens and Jan Eskens. The duke offered alabaster portals to his stepmother Sophia Jagiellon, and the magistrates of Gdańsk and Bremen and sent letters with samples, such as tabletops and dishes, to Duke Henry XI of Legnica and Duke Albert Frederick of Prussia (after "Netherlandish artists and craftsmen ..." by Aleksandra Lipinska), both having close ties with the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. Sophia bequeathed half of her inheritance to her sisters and the other half to the Commonwealth institutions. Among other things, she decreed that marble tombs should be built in the Wawel Cathedral and that a marble slab engraved with the genealogy of the Jagiellons should be placed in the Chapel of the Holy Cross. The 1575 inventories of the collection of the Duchess of Brunswick list more than 100 paintings and 31 portraits, including images of Sigismund Augustus, the children of her sister Catherine Jagiellon - Sigismund and Anna Vasa, and king Henry of Valois, as well as one historical painting depicting the beheading in 1568 of Lamoral of Egmont and Philip de Montmorency, Count of Horn, the leaders of the anti-Spanish opposition in the Low Countries, most probably by Flemish painter. Her book collection consisted of about 500 items, many of which had beautiful, luxurious bindings. The Map of Poland (Poloniae Recens Descriptio. Polonia Sarmatie Europee quondam pars fuit ...) in the Herzog August Bibliothek in Wolfenbüttel, created in 1562 by Hieronymus Cock in Antwerp, was most likely commissioned by Sophia Jagiellon. In the National Museum in Warsaw there is a portrait of a woman with a gold chain around the waist, attributed to Adriaen Thomasz. Key (oil on panel, 74 x 52.5 cm, inventory number M.Ob.822 MNW, earlier 34666). It was purchased in 1935 from the collection of Jan Popławski and in the 19th century it was in the Shchukin collection in Moscow. Her costume resembles the one seen in the portrait of Ermgart von Bemmelsberg by Westphalian school, painted in 1574 (private collection), portrait of a woman by Adriaen Thomasz. Key, dated '1578' (Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, 1036), and costumes of women of Brabant and Gdańsk from Omnium pene Europae ... by Flemish engraver Abraham de Bruyn, published in 1581. Her ruff is similar to the one visible in the mentioned portrait of Queen of Spain by Flemish painter in Munich and in the effigy of Joachim Frederick of Brzeg (1550-1602) by Adriaen Thomasz. Key, dated '1574' (National Museum in Warsaw, M.Ob.819). Her face and pose resemble other effigies of the Duchess of Brunswick-Lüneburg, identified by me, especially the portrait by circle of Titian in Kassel. A portrait of a lady in similar costume, also attributed to Key, is in private collection (oil on panel, 96.5 x 65.1 cm, sold Christie's London, April 20, 2005, lot 17), earlier, presumably, by descent at Studley Royal, Yorkshire. The woman wear a red coral bracelet, a fertility symbol in ancient Rome, as in portraits of young brides by Florentine painter Domenico Ghirlandaio, also believed to be a love talisman and perhaps even an aphrodisiac. According to Latin inscription: AN DNI 1576 (upper left) and ÆTATIS · SVÆ 28 (upper right), the woman was 28 in 1576, exacly as Sidonia von Borcke, born in the Wolf's Nest (Wulfsberg or Vulversberg - Strzmiele Castle) in 1548, when she was a lady-in-waiting to princess Amelia of Pomerania and Prince Ernest Louis fall in love with her.
Portrait of Sophia Jagiellon (1522-1575), Duchess of Brunswick-Lüneburg by Adriaen Thomasz. Key, ca. 1574, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Sidonia von Borcke (1548-1620), aged 28 by Adriaen Thomasz. Key, 1576, Private collection.
Portraits of Clara of Brunswick-Lüneburg, Duchess of Pomerania and Dianora di Toledo by Giovanni Battista Moroni
On October 15, 1595, at the age of 22, Prince Philip (1573-1618), the eldest son of Bogislaw (Boguslaus) XIII (1544-1606), Duke of Pomerania and his first wife Clara of Brunswick-Lüneburg (1550-1598), embarks on an educational journey through Italy and France.
He was accompanied by several people appointed by his father and traveled under the name of Christianus von Sehe. Through Meissen, Nuremberg and Augsburg, Philip reached Venice. Then he visited the whole of Italy and go as far south as Naples and Salerno. On the way, he stopped for a long time in Rome. The next stop of the journey was Florence, where he stayed for over three months. From there he set out again for Venice, from which he left for the ancient city of Forum Iulii (most probably Cividale del Friuli), to the cities of Styria and Carinthia. He also visited two powerful Venetian fortresses: Palma and Gradisca, which defended the Republic against the invasion of the Turks. From Milan he set out across Lake Como, where he admired the collections of Paolo Giovio, to Constance, where he found the place of the martyrdom of Jan Hus. The news of his mother's illness prevented him from further expanding his journey to the Netherlands, France and England. The prince, waiting for further news from his father, set off only to Besançon, and then to Lorraine, where he visited Nancy, and when more favorable news came from Pomerania - he set off through Alsace to Bohemia, to the court of Emperor Rudolf II. In Prague, he saw the relics of St. Wenceslaus and met Vincenzo Gonzaga, Duke of Mantua, a major patron of the arts and sciences. He returned home via Bohemia and Silesia, where in Legnica he met his relatives, and via Dresden arrived back in Barth at the end of November 1597 after over two years of journey. Soon, however, on January 26, 1598, after a short illness, the mother of Philip - Clara died at the castle in Franzburg. The 48-year-old Duchess probably died from the plague. As a child and adolescent, Philip enjoyed the education of a late Renaissance prince, as was customary at the time, but his artistic and scientific interests soon went beyond the ordinary. At the age of twelve he already had his own collection of books and paintings. He wrote his first scientific treatises at the age of 17 - Philippi II Pomeraniae Ducis De duarum in mediatore naturarum necessitate oratio, published in his father's printing house in Barth in 1590, and at the age of 18 he wrote: "It is my pleasure to collect the best, exquisite books, portraits from a master's hand and old coins of all kinds. From them I learn how to improve myself and at the same time how to be useful to the community" (Hoc est genus voluptatis meas, ut bonos selectissimos libros et artificiosas imagines et vetera omnis generis numismata maxime quaeram ex quibus me ipsum non solum corrigam, sed etiam, ut publice prodesse discam) (after "Die Kunst am Hofe der pommerschen Herzöge" by Hellmuth Bethe, p. 70). In order to give his numerous treasures an appropriate space, Philip commissioned his own art chamber, which was to be housed in the outer west wing of the Szczecin Castle and his library had approx. 3,500 volumes and was arranged like the great library in Florence. In exchange for the portraits of the Pomeranian dukes, he received such paintings for the Szczecin museum as the portrait of Charlemagne or Frederick Barbarossa. The bonds he forged during his travels and correspondence benefited in the many gifts he received and exchanged. In 1617, Philip's wife Sophia, received birthday gifts from friendly rulers, from Duke Wilhelm of Bavaria - a gold chain, and from Grand Duchess of Tuscany - a crystal mirror decorated with precious stones and an embroidered scarf to cover it. An important memento of the friendly relations of the Lutheran rulers of Pomerania with the Catholic Grand Dukes of Tuscany is a portrait of Philip's younger brother Bogislaw XIV (1580-1637), Duke of Pomerania from 1625, in the Villa di Poggio a Caiano, one of the most famous Medici villas (inventory number OdA Poggio a Caiano 234), identified by me. This portrait was created in about 1630 as the duke wears a miniature of Gustavus Adolphus, King of Sweden, who invaded Pomerania in August 1630 and forced Bogislaw into an alliance. However, the relations of the ruling house of Pomerania with Florence and Venice had been important since the time of Duke Bogislaw X who visited Italy between 1496 and 1498. In the archives of Florence preserved a letter from Duke Bogislaw to the Signoria of Florence sent from Viterbo in 1498 (Ex Viterbio 1498). Consequently, the Pomeranian Griffin dynasty and the Medici, without a doubt, frequently exchanged their effigies. In the Uffizi Gallery in Florence there is a miniature portrait of a lady in a ruff from the late 16th century (oil on copper, 7.5 x 5.5 cm, Inv. 1890, 1117). The miniature was identified with the one described in the inventory drawn up after the death of Ferdinando de' Medici (1663-1713), Grand Prince of Tuscany as: "a similar (copper oval) painted by the hand of Pietro Purbos the portrait of a woman with a ruff collar, dressed in the Flemish style" (un simile (aovatino in rame) dipintovi di mano di Pietro Purbos il ritratto di una donna con collare a lattughe, vestita alla fiamminga), thus attributed to Frans Pourbus the Younger (1569-1622), although the authorship of his father Pieter Jansz. Pourbus (circa 1523-1584) or his workshop is also likely. A replica of this effigy, in the Walters Art Museum in Baltimore (oil on copper, inventory number 38.204, gift of the Abraham Jay Fink Foundation), is also attributed to Flemish painter. The sitter's costume with a larger ruff and hairstyle indicates about 1590 as a possible date of creation - similar to some effigies of Margherita Gonzaga (1564-1618), Duchess of Ferrara, portrait of Anna Caterina Gonzaga (1566-1621), Archduchess of Austria from 1587, portrait of Anne Knollys from 1582 or portrait of Anna of Austria (1573-1598), Queen of Poland from about 1592 (Royal Castle in Warsaw). The same woman was depicted in a portrait by Giovanni Battista Moroni, holding a fan of a newly married woman, now in the Rijksmuseum Amsterdam (oil on canvas, 73.5 x 65 cm, SK-A-3036). This painting is dated between 1560-1578 and was purchased in 1925 from the Grand Ducal Picture Gallery in Oldenburg (mentioned between 1804-1918). The earliest mention of this painting dates from 1682, when the work was listed in the collection of Gaspar Méndez de Haro (1629-1687), Viceroy of Naples: "841 Portrait of a woman holding a fan adorned with pearls by the hand of Lorenzo Lotti", confirmed by the initials "DGH, 841" on the reverse of the canvas (after "Giovanni Battista Moroni" by Simone Facchinetti and Arturo Galansino, p. 134). She wears a rich red dress and she places her right hand on a pendant representing an allegory of fidelity (a female figure on a throne with two dogs beside her). A copy of this portrait by workshop or follower of Moroni was sold in Vienna in 2015 (oil on canvas, 72 x 64.5 cm, Dorotheum, 10.12.2015, lot 58). The provenance and geographical location of all the effigies indicate that the woman was an important international figure, a consort of an European ruler. Erdmuthe of Brandenburg (1561-1623) wife of John Frederick of Pomerania (1542-1600) was depicted in similar red dress in a large painting depicting the Family tree of the House of Pomerania, painted by a Dutch painter Cornelius Krommeny in 1598 (National Museum in Szczecin). Krommeny most likely created his work in Güstrow where he worked as court painter to Ulrich III, Duke of Mecklenburg and his wife Anna of Pomerania, from some study drawings, as no other works for the Pomeranian dukes are known, his stay in Pomerania is unconfirmed and resemblance to the living dukes is very general. Erdmuthe was also depicted in very similar dress in a painting by Andreas Riehl the Younger, created around 1590, lost in World War II. It was however not Erdmuthe who ensured the continuity of the dynasty. She married John Frederick on February 17, 1577 in Szczecin, however, their marriage remained childless. It was the first wife of John Frederick's co-regent Bogislaw XIII, Clara of Brunswick-Lüneburg, who gave birth to all male and female successors of the Dukes of Pomerania. In a painting by Krommeny she is also depicted in a red dress, but more German-style and no other effigy of her is known. The Dukes and Duchesses of Pomerania dressed similarly, as confirmed by the effigy of John Frederick and Erdmuthe as donors by Jakob Funck, painted in 1602 (Saint Hyacinth Church in Słupsk) and a similar portrait of Bogislaw XIII and his second wife Anna of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg by an unknown painter from 1600. Clara's eldest son, Philip II, born July 29, 1573, is depicted in a red doublet and hose in Krommeny's painting. Clara and Bogislaw were married on September 8, 1572 after the death of her first husband on March 1, 1570, which matches the general dating of the painting in Amsterdam. The couple had eleven children. After the wedding with the rich widow Bogislaw commissions the construction of a representative Renaissance palace in Neuenkamp named Franzburg in honor of his father-in-law Duke Francis of Brunswick-Lüneburg. He also established a city based on the model of Venice, a Venetian-like aristocratic republic with a thriving trade, especially with grain and beer, crafts and an academy to compete with the neighboring Hanseatic Stralsund (after "Von der Rückkehr Bogislavs X ..." by Friedrich Wilhelm Barthold, p. 423). This fascination for the Venetian Serenissima was undoubtedly also reflected in fashion and art. The woman from the mentioned effigies bear great resemblance to daughters of Clara of Brunswick-Lüneburg - Clara Maria (1574-1623) and Anna (1590-1660). Portraits of the Duchess of Pomerania were commissioned in the Republic of Venice and in Flanders, being the most important commercial, artistic and craft centers of Renaissance Europe. Another similar portrait of a wealthy aristocrat by Moroni from the same period is now in the Frick Collection in New York (oil on canvas, 51.8 x 41.4 cm, inventory number 2022.1.01, acquired in 2022). The provenance of the painting was little known until relatively recently. In 1928 it appeared in a sale of antiques from the collection of Prince Gagarin of Saint Petersburg, thus provenance from the Ducal collection of Pomerania or the Polish royal collection is possible. The woman bears a striking resemblance to Eleonora di Garzia di Toledo or Leonor Álvarez de Toledo Osorio (1553-1576), more often known as "Leonora" or "Dianora", from her signed effigy (DIANORA DI TOLEDO) by unkown Florentine painter, now in the Medici Villa of Cerreto Guidi near Empoli. The villa was built between 1564 and 1567. On 15 July 1576 Isabella de' Medici (1542-1576), daughter of Cosimo I de' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany, and Eleanor of Toledo (Eleonora di Toledo), was murdered in the villa by her husband Paolo Giordano I Orsini in punishment of her alleged infidelity ("strangled at midday" by her husband in the presence of several servants, according to Ferrarese ambassador Ercole Cortile). A year earlier, in 1575, Orsini, who was a grandson of Felice della Rovere (illegitimate daughter of Pope Julius II) and Costanza Farnese (an illegitimate daughter of Pope Paul III) was depicted as a saint in a disguised portrait of the members of the Medici family by Giovanni Maria Butteri (Museum of the Last Supper of Andrea del Sarto). Dianora was Isabella's cousin and close friend and died of a similar "accident" only a few days before, on July 11, 1576, strangled with a dog leash by her husband and first cousin, Don Pietro de' Medici (1554-1604), in the Villa Medici at Cafaggiolo. The resemblance of facial features and hairstyle to another signed effigy of Dianora (LEONORA / VXOR / DI PIERO / MEDIC / CE), in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, can also be mentioned, as well as to portraits of her famous aunt Eleanor of Toledo, elongated nose, shape of the lips, whose features differ in the paintings by different painters and their workshops (Agnolo Bronzino, Alessandro Allori). In the spring of 1575, Dianora's husband was sent to Venice to meet Bianca Cappello, the mistress and future wife of his older brother, Francesco I, the new Grand Duke of Tuscany. This trip was the prince's first diplomatic mission and the date of his stay in the Republic of Venice corresponds to the general dating of the Moroni painting. A series of portrait paintings by a famous painter and his workshop, as was a practice for members of the ruling houses, would be a good gift for his young wife, known for her fine artistic taste, friends and relatives, hence a miniature or drawing was probably used to make it. In 1560 Moroni painted Gabriel de la Cueva, 5th Duke of Alburquerque, a Spanish nobleman who was appointed Viceroy of Navarre in 1560 and later Governor of the Duchy of Milan in 1564, a position that he held until his own death in 1571 (Gemäldegalerie in Berlin, 79.1). The painting was signed and dated in Latin "1560 / Giovanni Battista Moroni painted" (M.D.LX. / Io: Bap. Moronus. p.) and bears the original inscription in Spanish. How and when he and Moroni met is unknown, perhaps they did not meet at all and Moroni just copied facial features and pose from a painting by Spanish court painter, like Antonis Mor from Utrecht in the Netherlands, made on the occasion of becoming Viceroy of Navarre. After her tragic death, many people were undoubtedly keenly interested that Dianora and her effigies would be forgotten.
Portrait of Clara of Brunswick-Lüneburg (1550-1598), Duchess of Pomerania by Giovanni Battista Moroni, ca. 1572-1575, Rijksmuseum Amsterdam.
Portrait of Clara of Brunswick-Lüneburg (1550-1598), Duchess of Pomerania by workshop or follower of Giovanni Battista Moroni, ca. 1572-1575, Private collection.
Portrait miniature of Clara of Brunswick-Lüneburg (1550-1598), Duchess of Pomerania by workshop of Pieter Jansz. Pourbus or Frans Pourbus the Younger, ca. 1590, Uffizi Gallery in Florence.
Portrait miniature of Clara of Brunswick-Lüneburg (1550-1598), Duchess of Pomerania by Netherlandish painter, ca. 1590, Walters Art Museum in Baltimore.
Portrait of Dianora di Toledo (1553-1576) by Giovanni Battista Moroni, ca. 1575, Frick Collection in New York.
Portrait of Bogislaw XIV (1580-1637), Duke of Pomerania with a miniature of King of Sweden by unknown painter, ca. 1630, Medici Villa of Poggio a Caiano.
Miniature portrait of George Radziwill by workshop of the Bassanos or Sofonisba Anguissola
"In the name of the Lord, in the year 1575. On the 11th of October, which then fell on Tuesday, I left Buivydiškės. I left there my sick brother, the great court marshal of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Nicolaus Christopher, and went to Italy with my younger brother, Albert", wrote in Latin in a diary of his journey George Radziwill (1556-1600), future cardinal (after "Dziennik podróży do Włoch Jerzego Radziwiłła w 1575 roku" by Angelika Modlińska-Piekarz).
Born in Italian style villa of his father in Lukiškės in Vilnius, George was raised and educated as a Calvinist. After his mother's death, in 1562, he spent some time at the royal court (perhaps as a page). Between 1571-1573, together with his brothers Albert and Stanislaus, he studied in Leipzig. In the summer of 1573, he accompanied his brother Nicolaus Christopher "the Orphan" to France and after his return, together with his younger brothers, he converted to Catholicism on April 11, 1574. Through Warsaw (October, 24-26), where he spent time with Infanta Anna Jagiellon, and Vienna (November, 12-20), where he met Emperor Maximilian II and his sons and where he saw "a beast of strange size, an elephant, sent as a gift to the emperor by Philip, king of Spain" on December 3 or 4 he arrived to Venice, the city "which, because of its beauty and its location, undoubtedly holds the priority palm among the cities of the whole world". He went to stay at the Magnificent White Lion, a German inn. He left the city in a hurry two days later, because of the suspicion of the plague, but during his brief stay he admired the St. Mark's Basilica, the Doge's Palace and the Arsenal. "After leaving the arsenal, I was driven around the city for two hours, where I saw many magnificent and very beautiful buildings, especially in the great street that stretches the entire width of the city, in colloquial language it is called the Grand Canal, the beauty of which I could never get enough of". He did not specify which places he visited, it is possible that he was also taken to the famous Venetian painting workshops. George commissioned works of art in Italy for himself and his brother, like in 1579, when one of the Roman painters made an altar for Nicolaus Christopher "the Orphan" (after "Zagraniczna edukacja Radziwiłłów: od początku XVI do połowy XVII wieku" by Marian Chachaj, p. 97). From Venice he went to Padua and then via Florence further to Rome to study philosophy and theology. In the years 1575-1581 he stayed in Italy, Spain and Portugal. In 1581, already as a bishop (from 1579), he was strongly condemned by King Stephen Bathory for the incident with the confiscation and burning of Protestant books in Vilnius. That same year, in 1581 he was again in Venice, together with his elder brother Nicolaus Christopher (after "Ateneum Wilenskie", Volume 11, p. 158). Two years later, in 1583, he was ordained a priest (April 10), consecrated a bishop (December 26), and received the cardinal's beret in Vilnius on April 4, 1584. In March 1586 he set out for Rome, where on June 26 he received the cardinal's hat from Pope Sixtus V. A two sided miniature in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence (inventory number 1890, 4051, oil on copper, 10.2 cm) is on one side a reduced and simplified version of portrait of Nicolaus Christopher Radziwill "the Orphan" by Francesco Bassano the Younger or workshop, created between 1580-1586, identified by me. The composition of the miniatures is not similar, so they were probably not created at the same time. Both portraits, although close to miniatures by the Bassanos in the Uffizi (1890, 4072, 9053, 9026), also relate to works of Sofonisba Anguissola, who moved to Sicily (1573), and later Pisa (1579) and Genoa (1581) and who could copy the paintings by the Bassanos. The young man in a ruff is presenting a ring on his finger, comparable to that visible in portraits of cardinal George Radziwill, possibly a souvenir of conversion, and his face resemble other effigies of the cardinal. According to Silvia Meloni, a copy of the recto of this miniature is kept in Udine, noth of Venice, which presents on the back the eagle testing its children in the sun. Eagle was a symbol of the Radziwills and cardinal George used it in his coat of arms, like the one published in 1598 in Krzysztof Koryciński's In felicem ad vrbem reditvm [...] Georgii S. R. E. cardinalis Radziwil nvncvpati [...]. All travelers returning from Venice to Poland or going to Rome from Poland trough Venice had to drive close to Udine. According to George's diary he was in San Daniele del Friuli near Udine in 1575. Funeral speech with biography of Cardinal George Radziwill by Daniel Niger and Jan Andrzej Próchnicki under the title In funere Georgii Radzivili S. R. E. Cardinalis Ampliss was published in Venice in 1600 in printing and publishing house of Giorgio Angelieri.
Miniature portrait of George Radziwill (1556-1600) by workshop of the Bassanos or Sofonisba Anguissola, 1575-1581, Uffizi Gallery.
Portraits of Anna Jagiellon by Francesco Bassano and circle of Veronese
On 15 December 1575, in Wola near Warsaw, infanta Anna Jagiellon and her husband Stephen Bathory, Voivode of Transylvania were elected as monarchs of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth.
Since the end of the 1570s Anna's court was bursting with life and she kept lively correspondence with many Italian princes, like Francesco I de Medici and his mistress Bianca Cappello, the daughter of Venetian nobleman Bartolomeo Cappello, exchanging news on politics and fashion, sending and receiving gifts (cosmetics, medicaments, crystal bowls and cups, luxury fancy goods, small pieces of furniture e.g. marble tables, silver incrusted boxes etc.) and even courtiers. "From February of 1581 to December of that year, several letters from the agent of Bianca Cappello [...] Alberto Bolognetti, described the perfect female dwarf he found for Cappello in Warsaw; the nana is described as having great "proportions" and being "very beautiful." The nana's travels through Cracow and Vienna were fully documented [...]" (Touba Ghadessi's "Portraits of Human Monsters in the Renaissance", p. 63). The portrait of a lady by circle of Paolo Veronese from the 1570s, traditionally identified as effigy of Catherine Cornaro (1454-1510), Queen of Cyprus, and known in at least three variants (in Vienna, Montauban and private collection), bears a strong resemblance to the miniature of Anna when a princess of Poland-Lithuania from about 1553. Also the gold cross pendant set with diamonds, visible on the portrait, is very similar to the one depicted on the print in the Hermitage Museum showing Anna (inventory ОР-45839). The picture in Vienna (Kunsthistorisches Museum, inventory number GG 33) was painted in the same period and in the same style as the portrait of a bearded man with hourglass and astrolabe attributed to Francesco Bassano (Kunsthistorisches Museum, inventory number 5775), identified by me as the portrait of king Stephen Bathory, Anna's husband. The portrait of the king was most probably offered before 1582 to Ferdinand II, Archduke of Austria for his collection in the Ambras Castle in Innsbruck, while the "portrait of the Queen of Cyprus" was initially installed at the Stallburg, where various holdings of the Habsburg family were brought together and displayed, and later transferred to the Belvedere in Vienna (after "Wien. Fremdenführer durch die Kaiserstadt und Umgebung" by Dr. J. Spetau, p. 122). Like in the case of the Queen's likeness in her widowhood by Martin Kober, acquired from the Imperial collection in Vienna in 1936 (Wawel Royal Castle), her Habsburg relatives undoubtedly also received other effigies from different periods of her life. The Queen also sent them other valuable gifts, like oriental fabrics, also visble in described portaits by Francesco Bassano. The 1619 inventory of the estate of Emperor Matthias lists several textiles of Ottoman and Safavid manufacture offered by Anna to either Matthias or his brother Emperor Rudolf II, veils and handkerchiefs (after "Objects of Prestige and Spoils of War" by Barbara Karl, p. 136). The portrait of a woman from Barbini-Breganze collection in Venice, today in Stuttgart (Staatsgalerie, inventory number 126, acquired in 1852), bears a strong resemblance to the portrait of Anna by Tintoretto in the Jagiellonian University (pose and features) and to her effigy in Vienna holding a zibellino (features and garments), also by Tintoretto. This painting is attributed to Parrasio Micheli, who died in Venice on April 1578. Discovery of a letter of August 20, 1575 in the General Archive of Simancas (Estado, 1336. fol. 233) from the painter to king Philip II, allowed to attribute to him one of his major works as well as assign the subject - Allegory of the birth of the Infante Ferdinand (Prado Museum in Madrid, inventory number P000479). Infante's mother Anna of Austria (1549-1580), Queen of Spain, granddaughter of Anna Jagellonica (1503-1547), was depicted as bare-chested Venus, while her midwives attend to the mythological child Cupid - "The World celebrates that Venus has given birth" (CELEBRIS MUNDI VENERIS PARTUS), according to inscription in Latin in upper part of the paiting. The painting in Prado was formerly attributed to Carlo Caliari, known as Carletto, the youngest son of Paolo Veronese and believed to represent the birth of Charles V, in his letter, however, Micheli explained all the allegories (after "Ein unbekannter Brief des malers Parrasio Michele" by Constance Jocelyn Ffoulkes, pp. 429-430). In the Stuttgart painting, the queen has a zibellino (weasel skin) on her belt, a popular accessory for brides as a fertility talisman. Therefore, the work must be dated shortly before or after his marriage to Bathory. Anna's strong familial and intellectual connections to Italy and a reputation as an advocate for women's educational pursuits within the scientific disciplines, persuaded Camilla Erculiani, an Italian apothecary, writer and natural philosopher from Padua in the Venetian Republic, to dedicate her work "Letters on Natural Philosophy" (Lettere di philosophia naturale), published in Kraków in 1584, to Anna. The Queen was also known for promoting education of girls at her court (after "Daughters of Alchemy: Women and Scientific Culture in Early Modern Italy" by Meredith K. Ray, p. 118). One of the finest book illuminations related to Anna was probably also made in Italy. It is her coat of arms with a crown supported by two angels and the inscription ANNA REGINA POLONIÆ in handwritten treatise of Francesco Pifferi of Pisa from 1579 (Delle cagioni dalle quali mossi alcuni heretici sono tornati alla fede catolica), dedicated to the queen (ALLA SERENISSIMA ET SACRA MAESTA ANNA REGI/NA DI Polonia, Wawel Royal Castle, ZKnW-PZS 6046)
Portrait of Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596), elected co-ruler of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth by Francesco Bassano, ca. 1580, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Portrait of Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596), elected co-ruler of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth by workshop of Francesco Bassano, ca. 1580, Private collection.
Portrait of Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596), elected co-ruler of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth by workshop of Francesco Bassano, ca. 1580, Musée Ingres in Montauban.
Portrait of Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596), elected co-ruler of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in a robe of pink damask over a patterned brocade dress by Parrasio Micheli, 1575-1578, Staatsgalerie Stuttgart.
Allegorical portrait of Anna Jagiellon by Francesco Montemezzano
In July 1572 died Sigismund II Augustus, leaving the throne vacant and all the wealth of the Jagiellon dynasty to his three sisters. Anna, the only member of the dynasty present in the Commonwealth, received only a small portion of inheritance, but still became a very rich woman. Sigismund's death changed her status from a neglected spinster to the heiress of the Jagiellon dynasty.
In June 1574 an unexpected turn of events made her one of the favorites in the second election, after Henry of Valois left Poland and headed back to France. Jan Zamoyski reconciled different camps promoting Anna to the crown. On December 15, 1575, Anna was hailed the King of Poland in the Old Town Square in Warsaw. Jan Kostka and Jan Zamoyski, representing the parliament, came to her to ask for her consent. It was then that Anna was supposed to utter the phrase that she "would rather be a queen than a king's wife". A day later, the nobility recognized her definitively as the "Piast" king and Stephen Báthory, Voivode of Transylvania, was proposed as her husband. The painting identified as allegory of Pomona from the old collection of the Czartoryski Museum bears a great resemblance to other effigies of Anna. A woman in rich costume is being offered a basket with apples, denoted as symbol of the royal power and a symbol of the bride in ancient Greek thought, and pink roses, which represented innocence and first love - Báthory was the first husband to the 52 years old queen. In the catalogue of the Czartoryski Museum from 1914 by Henryk Ochenkowski (Galerja obrazów: katalog tymczasowy), this painting was attributed to "probably Parrasio Micheli" (item 188) and listed together with another painting by the 16th century Venetian School and depicting "Death of the Doge? Three ladies at the bedside. In the background the dogaressa, dictating a letter" (oil on canvas, 101 x 75 cm, item 187), which was most probably lost during World War II. This description fits perfectly with the facts known about the last moments of king Sigismund I the Old, who died in his Wawel residence in Kraków on April 1, 1548, at the age of eighty-one. On February 3, the young king Sigismund Augustus left for Lithuania and the old king was in Kraków with his wife Bona and three daughters Sophia, Anna and Catherine. According to Stanisław Orzechowski the young king who arrived from Vilnius on May 24, was welcomed by his mother "with her three daughters, and with a company of noble matrons" (Bona mater cum filiabus tribus ac cum matronarum nobilium turba adventantem regem expectabat) (after "Zgon króla Zygmunta I ..." by Marek Janicki, p. 92-93). Bona undoubtedly wrote a letter urging him to return and either she or her daughter Anna could commission a painting commemorating the event. However, this description may not have been accurate, because this painting is identified in today's catalogs with a horizontal (and not vertical) work from the first quarter of the 17th century (oil on canvas, 113 x 179 cm, inventory number MNK XII-231).
Allegorical portrait of Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596), elected co-ruler of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth by Francesco Montemezzano, 1575-1585, Czartoryski Museum in Kraków.
Portraits of Anna Jagiellon by workshop of Tintoretto and Francesco Montemezzano
"There is a bridge across the Vistula near Warsaw, built at a great cost of Queen Anna, sister of King Sigismund Augustus, famous all over the Crown", wrote Venetian-born Polish writer Alessandro Guagnini dei Rizzoni (Aleksander Gwagnin) in his book Sarmatiae Europeae descriptio (Description of Sarmatian Europe), printed in Kraków in 1578.
On 5 April 1573, during the Royal Election after death of king Sigismund Augustus, the longest bridge of Renaissance Europe was opened to the public. The construction cost 100,000 florins, and Anna Jagiellon, willing to become a Queen, also allocated her own funds for this purpose. It was a great achievement and major political success praised by many poets like Jan Kochanowski, Sebastian Klonowic, Andrzej Zbylitowski and Stanisław Grochowski. The bridge, built of huge oaks and pines brought from Lithuania, was 500 meters long, 6 meters wide, it consisted of 22 spans and stood on 15 supports/towers that protected the construction. The construction, however, required constant renovations and was partially broken several times by ice floes on the Vistula River. It was severely damaged after Anna's coronation (1 May 1576) and in his letters from 15 August 1576 to the starosts, King Stephen Bathory recommended the delivery of wood for repair. Again in 1578 and the renovation was managed by Franciszek Wolski, voit of Tykocin. The wood material was floated from the San river. The works were completed in 1582 and "Anna Jagiellon, Queen of Poland, spouse, sister and daughter of grand kings, ordered the construction of this brick fortified tower", according to inscription on bronze plaque in Museum of Warsaw commemorating the fortified Bridge Gate. Anna, as her brother, undeniably ordered some portraits to commemorate her role in construction and maintenance of the bridge. The portrait from private collection in Milan, attributed to Tintoretto or Veronese and depicting a blond woman in a crown against the view of a bridge, fit perfectly. Her facial features resemble greatly the portrait by Tintoretto in the Jagiellonian University Museum. The painter depicted the bridge only symbolically in a small window. The recipients of the painting should know what it is about, there was no need to change the convention of Venetian portrait painting to show the whole construction. On her gown there is a symbol of six pointed star, in use since ancient times as a reference to the Creation and in Christian theology - star of Bethlehem. The star, was symbolic of light and of the preaching of Saint Dominic, who was the first to teach the Rosary as a form of meditative prayer, and become an attribute of Virgin Mary, as Queen of Heaven and as Stella Maris. The title, Stella Maris (Star of the Sea), is one of the oldest and most widespread titles applied to Virgin Mary. It came to be seen as allegorical of Mary's role as "guiding star" on the way to Christ. The crown of stars is visible in a painting by Tintoretto in the Gemäldegalerie in Berlin (acquired from Francesco Pajaro in Venice in 1841), created in about 1570 showing Madonna and Child venerated by St. Marc and St. Luke, and in a painting of Madonna of the Rosary from Sandomierz, created by Polish painter in 1599 in which old Queen Anna was depicted with other members of her family and Saint Dominic. Thanks to Queen Anna's efforts the rosary confraternities, which mainly existed in Kraków were extended to all of Poland on 6 January 1577 and the annual feast of rosary was solemnly celebrated throughout the Commonwealth. She also donated, among other things, a few precious jewels and necklaces with which the image of Black Madonna of Częstochowa was adorned. In 1587 the Queen received the Golden Rose from Pope Sixtus V, which she offered to the collegiate church of St. John in Warsaw, lost. The same woman in similar pose and in similar gown was depicted in painting by Francesco Montemezzano from William Coningham's collection in London, now in The Metropolitan Museum of Art.
Portrait of Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596), elected co-ruler of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth with a symbolic view of the bridge in Warsaw by workshop of Tintoretto, 1576-1582, Private collection.
Portrait of Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596), elected co-ruler of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth by workshop of Tintoretto, 1576-1582, Private collection.
Portrait of Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596), elected co-ruler of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth with a dog by Francesco Montemezzano, ca. 1582, The Metropolitan Museum of Art.
Mystical marriage of Saint Catherine with a portrait of queen Anna Jagiellon by Venetian painter
In 1556 having ambitions of becoming a Viceroy of Naples, Bona Sforza d'Aragona, Anna's mother, agreed to lend to her distant relative king Philip II of Spain a huge sum of 430,000 ducats at 10% annual interest, so-called "Neapolitan sums". Even when paid, the interest payment was late and according to some people the loan was one of the reasons why Bona was poisoned by her trusted courtier Gian Lorenzo Pappacoda.
On November 10, 1573, and November 15, 1574 Catherine Jagiellon, Queen of Sweden, who had the right to a part of the Neapolitan sums in her dowry (50,000 ducats) agreed to renounce and cede it to her sister Anna, as the dispute deteriorated Polish-Swedish relations. The Commonwealth had bad experiences with a "foreign" candidate, Henry of Valois, who fled the country through Venice just few monts after election, therefore the only possible succesors of over 50 years old queen were children of her sister Catherine, Sigismund born in 1566 (elected as Commonwealth's monarch in 1587) and Anna born in 1568. The painting in Madrid is very similar in style to two portraits of Anna from the same period (in Vienna and Kassel). The lady in her 40s or 50s depicted as the Virgin Mary, Queen of Heaven is a clear indication that the scene has no purely religious meaning and it is very similar to other effigies of Anna, especially to the portrait by Tintoretto in Kraków. According to the researchers the canvas should be attributed to Palma il Giovane, who created paintings for Anna's nephew and sucessor, Sigismund III Vasa (Psyche cycle and a painting for the St. John's Cathedral in Warsaw, destroyed during World War II) or Domenico Tintoretto, who painted several paintings for Anna's Chancellor, Jan Zamoyski. In the collection of the Royal Wilanów Palace in Warsaw there is a painting representing highly erotic subject of Leda and the swan by Palma il Giovane or his workshop from the last quarter of the 16th century. It is uncertain how it found its way there, so the option that it was commissioned by Anna, who, as her mother Bona, was strongly engaged in maintaining good relation with her husband Stephen Bathory, is very probable. The mystical marriage of Saint Catherine, a symbol of spiritual grace, should be interprated then that Catherine's children still have claims to the Neapolitan sums and the crown. Its history before 1746 is unknown, therefore it cannot be excluded that the painting was sent to the Spanish Habsburgs, just as her portrait in Vienna, personally by the queen. In November 1575, hence shortly before her election, Anna sent to Spain her envoy Stanisław Fogelweder, who was her ambassador there until 1587. She also had her informal envoys in Spain, dwarves Ana de Polonia (Anna of Poland, died 1578) and Estanislao (Stanislaus, died 1579).
Mystical marriage of Saint Catherine with a portrait of queen Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596) by Venetian painter, possibly Palma il Giovane or Domenico Tintoretto, 1576-1586, Prado Museum in Madrid.
Leda and the swan by Palma il Giovane or workshop, fourth quarter of the 16th century, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
The Banquet of Cleopatra with portraits of Anna Jagiellon, Stephen Bathory and Jan Zamoyski by Leandro Bassano
On 1 May 1576, then 52 years old Infanta Anna Jagiellon married ten years younger Voivode of Transylvania Stephen Bathory and was crowned as co-ruler of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. Soon after the wedding the king started to avoid his elderly wife. He dedicated her just three wedding nights and didn't look into her bedroom afterward. The papal nuncio in Poland, Giovanni Andrea Caligari, reported in August 1578, that the king does not trust her, that he is afraid of being poisoned by her, an art her mother, Bona, was well acquainted with, and he adds in a letter of February 1579, that she is haughty and vigorous (altera e gagliarda di cervello). One night, Anna wanted to visit Bathory, but he escaped. Many people witnessed this event, the Queen developed a fever and was subjected to phlebotomy.
King Stephen reportedly never held a great attraction for the marriage state and women in general, and he married Anna only to do a nice thing for the nation, she however was under the illusion that she would keep her husband with her and seduce him with boisterous balls and feasts. Primate Jan Tarnowski wrote in a letter to a Lithuanian magnate that "as she caught up a man, she carries her mouth high and proud". The Queen had a grudge against Chancellor Jan Zamoyski, who according to Bartosz Paprocki "wanting to be a lord in Masovia, he sowed disagreement between the king and the queen" and "caused that the king did not live with the queen". Some "distasteful" rumors were also spread during the expedition to Polotsk in 1578, when the king slept in the same hut with Gaspar Bekes, his trusted friend (after Jerzy Besala's "Wstręt króla do królowej"). When Stephen left his wife in 1576, he did not see her, with some breaks, until 1583. She resided in Warsaw in Masovia where in a spacious and richly furnished wooden mansion in Jazdów (Ujazdów), built by her mother Queen Bona, she often held festivities and court games, he in Grodno (in todays Belarus). In January 1578 she organized in Jazdów famous wedding celebrations for Jan Zamoyski and his Calvinist second wife Kristina Radziwill, which lasted for several days. In February 1579, the Queen prepared a court ball, awaiting Stephen's arrival. In the evening, the Warsaw Castle was illuminated, and the inhabitants were waiting for the king's arrival. Unfortunately, only the messenger with the letter arrived. The king wrote in it that due to the preparations for the war expedition, he would spend the whole year in Lithuania. The disappointed queen "ordered the lights to be turned off and the instruments to be taken out, and with great anger she retreated to her chambers", wrote the nuncio in a letter of February 26. The courtiers rumored that he wanted to divorce her. The King and Queen reunited in June 1583 in Kraków for the opulent wedding celebrations of Zamoyski with his third wife and a king's niece, Griselda Bathory. The wedding feast was held in the chambers of Queen Anna at the Wawel Castle. The lavish tournaments and a procession of masks was illustrated by an Italian artist in a "Tournois magnifique tenu en Pologne", today in the National Library of Sweden. Rich Venetian fabrics, like these used in chasubles founded by Anna and her husband (Cathedral Museum in Kraków) or vessels, like enamelled basin with her coat of arms and monogram (Czartoryski Museum), acquired by Anna in Venice, were undoubtedly used during the feasts. The sources confirm that allegorical paintings were brought to the Polish court from Venice for Sigismund III Vasa, Anna's sucessor, like Psyche cycle by Palma il Giovane or Diana and Caliosto by Antonio Vassilacchi. "You subjects learned this riding from your king", snapped resentful Anna in 1583, when someone from her court set off on a journey. The Banquet of Cleopatra by Leandro Bassano in Stockholm shows an episode described by both Pliny's's Natural History (9.58.119-121) and Plutarch's Lives (Antony 25.36.1), in which the spartan Roman warrior Antony being seduced by the sensual opulence of Cleopatra. The Queen of Egypt takes an expensive pearl, reputed to have aphrodisiac qualities, because of an association between pearls and Venus, the goddess of love, and dissolves it in her wine, which she then drinks. It is a culmination of a wager between Cleopatra and Mark Antony as to which one could provide the most expensive feast, which Cleopatra won. Lucius Munatius Plancus, a Roman senator had been asked to judge the wager. The three protagonists are clearly Anna Jagiellon as Cleopatra, her husband Stephen Bathory as Mark Antony and his friend Jan Zamoyski as Lucius and the painting was commissioned by the Queen to one of her residences, most probably Jazdów. It is recorded in the Swedish royal collection as far as 1739, therefore, most probably, it was taken from Poland during the Deluge (1655-1660), like the marble lions from Ujazdów Castle, or during the Great Northern War (1700-1721). In 1578 with the support of Queen Anna the brotherhood of Saint Anne was founded in Warsaw at the Bernardine Church of Saint Anne, and approved by the Pope with the bull Ex incumbenti in 1579. The first member and guardian of this fraternity was Jan Zamoyski, chancellor and great hetman of the Crown. The painting by the same author, Leandro Bassano, from the Swedish royal collection, showing Saint Anne and the infant Virgin Mary was also undeniably created for Anna Jagiellon around the same time as the Banquet of Cleopatra. In 1760 this Catholic painting with Bernardine nuns was in the collection of Louisa Ulrika of Prussia, who freely converted from Calvinism to Lutheran when she moved to Sweden. It is another indication that this painting also was taken from Poland during the Deluge by Swedish or Prussian (Brandenburgian) forces. Also other paintings by Bassano family and their workshop in Poland were created for partrons in Poland, like the Forge of Vulcan by Francesco Bassano the Younger in the National Museum in Warsaw. It was aquired in 1880 from Wojciech Kolasiński. Taking into consideration that other versions of this painting are in royal collections of "friendly" countries (Prado Museum in Madrid, inventory P005120, recorded as far as 1746 and Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, inventory 5737, recorded in Ambras collection in 1663), it is highly possible that it was commissioned or aquired by Bathory or Anna's successor Sigismund III. Another painting shows Adoration of the Magi with a man in Polish costume (almost idedntical as in the effigy of a Polish nobleman in the Bayerische Staatsbibliothek) as one of the Magi.
The Banquet of Cleopatra with portraits of Anna Jagiellon, Stephen Bathory and Jan Zamoyski by Leandro Bassano, 1578-1586, Nationalmuseum in Stockholm.
Saint Anne and the infant Virgin Mary by Leandro Bassano, 1578-1586, Nationalmuseum in Stockholm.
Forge of Vulcan by Francesco Bassano the Younger, 4th quarter of the 16th century, National Museum in Warsaw.
Adoration of the Magi with a Polish nobleman by Francesco Bassano the Younger, 4th quarter of the 16th century, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Pope Gregory XIII and portrait of Constantine Vasily, Prince of Ostroh by workshop of Francesco or Leandro Bassano
Despite huge losses during the wars, other conflicts and fires Venetian painting is particularly richly represented in the National Art Gallery in Lviv in Ukraine. During the 16th and 17th centuries, Lviv, the second largest city in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, with a population of around 30,000, was the capital of the Ruthenian Voivodeship.
Among the notable works, one could distinguish the Sleeping Venus by Palma Vecchio, portrait of an old man by Titian, identified as effigy of Antonio Grimani (1434-1523), Doge of Venice (oil on canvas, 94 x 79.8, signed in upper right corner: Titianus P[inxit]), offered by professor Florian Singer in 1858, portrait of Francis I (1494-1547), King of France by circle of Titian after original by Joos van Cleve (oil on copper, 16.5 x 12.5 cm, inventory number Ж-41), from the collection of count Leon Piniński, Saint John the Baptist in the wilderness by workshop of Jacopo Bassano (oil on wood, 51 x 67 cm, Ж-287), a copy of work created in 1558 for the altar of the family Testa di San Giovanni in the church of San Francesco in Bassano, Madonna and Child as the Queen of Heaven with Saints by workshop of Jacopo Tintoretto (oil on canvas, 46 x 53 cm, inventory number Ж-755), from the collection of Wiktor Baworowski (1826-1894), David with a sword, presumably a fragment of a larger composition by Venetian painter (oil on canvas, 67 x 78 cm, Ж-1377), from the Lubomirski collection and Saint Veronica wiping the face of Christ on the road to Calvary by Palma il Giovane, until 1940 in the collection of Major Kündl. Given the extensive economic and artistic contacts of the Commonwealth with the Venetian Republic at that time, we should assume that at least two-thirds of these paintings originally found their way into the Commonwealth already at the time of creation by different means (purchases or gifts). Among interesting portraits of the Italian school in the gallery, there is a portrait of Pope Sixtus V (1521-1590) from the collection of the Ossolineum in Lviv (oil on canvas, 116 x 95 cm, Ж-4947). In 1586, in the bull issued on October 10, Sixtus, who was a pope from 1585 to his death in 1590, confirmed the brotherhood of Saint Anne, founded in Warsaw by Queen Anna Jagiellon in 1578. The establishment of the brotherhood was approved by Pope Gregory XIII (1502-1585) in 1579 and confirmed in 1581 by his nuncio to Poland Giovanni Andrea Caligari (1527-1613), bishop of Bertinoro and again in 1584 by another nuncio of Gregory XIII Alberto Bolognetti (1538-1585), who before coming to Poland served as nuncio in the Republic of Venice (1578-1581). In the Commonwealth, Bolognetti was confronted with the advance of Protestantism and the spread of indifferentism. Numbers of both high and low clergy had gone over to Protestantism, some even to atheism. Presentation for church posts at all levels was under the control of local magnates or the king and selection had more to do with loyalty than religious views or vocation. He emphasized to king Stephen Bathory the necessity of appointing only Catholics to office, but with limited success. He also reported to Rome about the trade with Flanders, the port of Gdańsk, where the English heretics had considerable influence, and activities of Spanish agents in Poland, buying grain and other commodities. On May 1, 1584 Pope Gregory XIII declares the feast of St. Anne. The Pope sent the queen a gift of Agnus Dei through Stanisław Hozjusz, which he had consecrated, supported her during the royal elections and with her efforts at the Spanish court concerning the Neapolitan sums. With the help of the queen and her sister Catherine, Queen of Sweden, he secretly sent several priests and Jesuits to Sweden. In 1580, Paweł Uchański delivered a sacred sword (Wawel Royal Castle) and a hat from Gregory XIII to Anna's husband Stephen Bathory in Vilnius and in about 1578 the pope offered the king the coral rosary (Museum of Applied Arts in Budapest, E 65.76). Gregory also established a personal correspondence with Constantine Vasily (1526-1608), Prince of Ostroh, a leder and a promoter of Eastern Christian culture in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. On June 6, 1583 the Pope granted his son Janusz (1554-1620), who after education at the court of the Holy Roman Emperor in Vienna converted from Orthodoxy to Roman Catholicism in 1579, the privilege of a portable altar. In a letter of July 8, 1583, Prince Constantine Vasily wrote to the Pope that he met the nuncio Bolognetti in Kraków and discussed with him the problem of "some people who with all zeal seek only disagreement" (after "Unia Brzeska z perspektywy czterech stuleci" by Jan Sergiusz Gajek, Stanisław Nabywaniec, p. 33) and he sent to the Pope "Chyzycen, the archbishop of the Greek rites; asking him for a copy of the bible, written in Slavic language, which he could reprint for the benefit of the people of the Greek religion". Constantine Vasily also favored the introduction of the Gregorian calendar (introduced in 1582 by Pope Gregory XIII), however the Patriarch of Constantinople "severely reprimanded the Prince of Ostroh for recommending the change of the calendar to the Ruthenian people". Numerous portraits of the ruling popes undoubtedly belonged to Queen Anna Jagiellon and the catholic magnates of the Commonwealth. Nicolaus Christopher Radziwill "the Orphan" (1549-1616) had oil portraits of Popes Sixtus V and Paul V and Cardinals Francesco Sforza, Charles Borromeo and Alessandro Farnese (after "Monumenta variis Radivillorum ..." by Tadeusz Bernatowicz, p. 18) and according to Latin poem "Paintings in the hall in Zamość" (Imagines diaetae Zamoscianae) by Szymon Szymonowic (Simon Simonides), published in Zamość in 1604, Hetman Jan Zamoyski had a portrait of Sixtus V (To Sykstus Piąty - chlubny z tego miana). The portrait of Pope Clement VIII (Ippolito Aldobrandini) in the National Museum in Kielce, painted in about 1592 by circle of Giuseppe Cesari, could be a gift to Anna Jagiellon or her nephew Sigismund III Vasa. It is highly possible that the portrait in Lviv also comes from magnate or royal collection. The sitter is identified as Sixtus V, however, he resemble more the effigies of his predecessor Gregory XIII - portrait by Bartolomeo Passarotti (Friedenstein Palace in Gotha), a small portrait with inscription GREGORIVS. XIII P. M. (The Antique Guild), engraving with inscription GREGORIVS. XIII. PAPA. BONONIEN. (Fototeca Gilardi) and especially a portrait attributed to Scipione Pulzone. The features, pose and costume are very similar, the only noticeable difference is only the color of the eyes, however Anna Jagiellon also has a different eye color in her portraits by workshop of Cranach (Czartoryski Museum) and Kober (Wilanów Palace). Also the style of this portrait is very interesting and close to that of Venetian painters Francesco and Leandro Bassano. The painter simplified the composition, probably intentionally he omitted the back of the Pope's chair, which indicate that the portrait was part of a series of similar portraits, some of which were intended for the Polish-Lithuanian market. The portrait of Constantine Vasily, Prince of Ostroh with a crucifix (unknown location, possibly lost during World War II) from the 1590s, was painted in the same style.
Portrait of Pope Gregory XIII (1502-1585) by workshop of Francesco or Leandro Bassano, 1572-1585, Lviv National Art Gallery.
Portrait of Constantine Vasily (1526-1608), Prince of Ostroh with a crucifix by Leandro Bassano or follower, 1590s, location unknown, possibly lost during World War II.
Portraits of Jadwiga Sieniawska, Voivodess of Ruthenia by the Bassano workshop and Jacopo Tintoretto
"You equated the state with the shy Diana, / You equated the face with the rosy Venus. [...] / Adornment of the earth! happy, happy, / To whom God has appointed you kind, / To whom Hymenaios in the steady words / And with eternal torches joined you", wrote in his poem entitled "To Miss Jadwiga Tarłówna, (later voivodess of Ruthenia)", a Polish poet of the late Renaissance Mikołaj Sęp Szarzyński (ca. 1550 - ca. 1581). It is considered an epithalamium, a wedding song for the wedding with the lord of Berezhany (Brzeżany), Hieronim Sieniawski (1519-1582), who married Tarłówna in 1575.
Jadwiga was the fifth child of Jan Tarło, standard-bearer of Lviv, and Regina Malczycka. She came from the ancient Tarło family from Szczekarzowice. Her parents owned Chapli (Czaple nad Strwiążęm) near Sambir (Sambor) and a part of Khyriv (Chyrów) in the Ruthenian Voivodeship (Ukraine). "Lords of Hungary and Wallachia" wanted to marry her and King Sigismund Augustus promised her hand to Bogdan IV (1555-1574), Prince of Moldavia in 1572, but he was deposed that year (after "Brzeżany w czasach Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej: monografia historyczna" by Maurycy Maciszewski, p. 78-80). After death of her father (died in 1570 or 1572) and before marriage, she most probably lived at the very Italianized court of king's sister, Infanta Anna Jagiellon. Jadwiga received from father as a dowry only 3,000 zlotys and 1,500 zlotys in jewels, and from her mother 2,000 zlotys. It was a considerable amount for those times, but far from being a magnate's fortune. In June 1574, Hieronim buried his third wife, Anna née Maciejowska, and ordered a beautiful marble tombstone for her. Just few months later, in 1575, at the age of 56, he married Jadwiga who was about 25 years old (born in about 1550). The bridegroom bequeathed 14,000 zlotys to her as a dower. The next year (1576), she gave birth to Hieronim's only son, Adam Hieronim. Her husband died in 1582 and was buried in the family chapel in Berezhany. The young widow founded a beautiful tomb monument for him and his father and dedicated herself to raising her only son and did not remarry. She was glorified on a marble plaque in the castle church in Berezhany for restoring the weakened fortune to good condition after her husband's death: "These monuments were laid to her father-in-law and to her sweet husband by Jadwiga née Tarło, both with her powerful virtue, which she shines in her homeland, and with the sharpness of her mind. May our ages produce more of likewise matrons here and everywhere! The Republic would flourish if each of them would restore lost goods in this way after her husband's death" (Haec socero et dulci posait monumenta marito / Tarlonum Hedvigis progenerata domo, / Virtate omnigena patrio quae claret in orbe, / Nec minus ingenii dexteritate sui. / O utinam similes illi praesentia plures / Saecula matronas hic et ubique ferant ! / Publica res floreret abi post fata mariti / Quaelibet amissas sic repararet opes). According to the sculptor's monogram (H.H.Z.) hidden behind the statue of Hieronim, the monument was created by Hendrik Horst (d. 1612), a Dutch sculptor from Groningen, active in Lviv since 1573. The overall design of this tomb monument, destroyed during World War II, resemble the monument to King Sigismund II Augustus in the Wawel Cathedral, founded by Queen Anna Jagiellon and created between 1574-1575 by Santi Gucci, and monument to Doge Francesco Venier (1489-1556) by Jacopo Sansovino and Alessandro Vittoria in San Salvador in Venice, created between 1556-1561. Until 1939 in the armoury of the Berezhany Castle in the western tower, there was a large painting depicting the funeral procession of Mikołaj Sieniawski (ca. 1489-1569), Jadwiga's father-in-law, in Lublin in 1569 with king Sigismund Augustus and lords of the kingdom. The deathbed conversion of Hieronim Sieniawski, a definitive Calvinist, was also influenced by his fourth wife, Tarłówna, a zealous Catholic according to papal nuncio, with the aid of Benedictus Herbestus Neapolitanus (Benedykt Zieliński or Benedykt Herbest), educated in Rome. Also Hieronim's sisters converted shortly after his death, closing numerous Calvinist churches on their estates (after "Calvinism in the Polish Lithuanian Commonwealth 1548-1648" by Kazimierz Bem, p. 181). In 1584 she issued a location privilege for the new town of Adamówka, named in honor of her son, later a suburb of Berezhany and most probably founded the Church of the Nativity of the Virgin Mary. Her only son, who most probably, like all his three sons later, studied in Padua before 1593, employed at his court Venetian engineer and architect Andrea dell'Aqua. A painting by workshop of Jacopo Bassano (1515-1592) of unknown provenance in the Odessa Museum of Western and Eastern Art, shows a wealthy lady in the mythological scene of Abduction of Europa. In the same museum there is also a portrait of Princess Elizabeth Radziwill (d. 1565) by Lambert Sustris, identified and attributed by me. In the 1560s Jacopo Bassano created several versions of Adoration of the Magi (Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, The Barber Institute of Fine Arts, The State Hermitage Museum) with a man in a costume of a Polish-Lithuanian nobleman depicted as Melchior, the old man of the three Magi, comparable to effigies of Constantine (ca. 1460-1530), Prince of Ostroh by Lucas Cranach the Elder. He wears a green kaftan with sweeping floor-length sleeves and a fur collar, very similar to those visible in the effigy of a Polish horseman by Abraham de Bruyn, published in 1577 (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam) or in his Twelve Polish and Hungarian types, published in 1581 (also in the Rijksmuseum) or in the picture of a Polish-Lithuanian noble in "Theatrum virtutum ac meritorum D. Stanislai Hosii" by Thomas Treter, created between 1595-1600 (National Library in Warsaw). The effigy of the old man represented as Melchior, possibly intentionally or unintentionally, bear a resemblance to the effigy of Jadwiga's father-in-law, Mikołaj Sieniawski, Voivode of Ruthenia (and a Calvinist), from the tomb monument founded by her. According to some sources Mikołaj also converted to the Catholic faith shortly before his death (died in 1569), therefore he could commisson a series of his effigies as one of the Magi, or the painter just inspired by the images of Mikołaj commissioned in his studio. In the myth, the god Zeus (Jupiter) assumed the form of a bull and enticed Europa to climb onto his back. The bull carried her to Crete, where Europa became the first Queen and had three children with Zeus. Unlike the earlier, very erotic version of the scene painted between 1560-1562 by Titian for King Philip II of Spain (Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum in Boston) with Europa sprawled helplessly in open-legged posture and her face not visible, in Bassano's painting the woman's face is clearly visible. This portrait-like historié picture was therefore commissioned by this woman. In the 17th century Margaret Cavendish (1623-1673), Duchess of Newcastle-upon-Tyne in a large painting attributed to Jan Mijtens (La Suite Subastas in Barcelona, May 26, 2023, lot 26) and Madame de Montespan (1640-1707), chief royal mistress (maîtresse-en-titre) of King Louis XIV of France, and her children, in another large composition from the studio of Pierre Mignard (Kurpfälzisches Museum Heidelberg, L39), were represented in such historié paintings in the guise of Europa. In the foreground there is a rabbit as an allegory of fertility, a duck, associated with Penelope, queen of Ithaca, as a symbol of marital fidelity, and a small dog, allegory of fidelity and devotion. A Cupid sitting on a tree in the upper right corner is prepared to aim an arrow at her heart. The island of Crete is visible in the far background, but the landscape around is similar to topography of Berezhany as depicted on the Austrian map of 1779-1783. There is a large lake (regulated in the 18th century) and two hills, which were depicted by the painter as rocky Alpine hills. Another, horizontal (96 x 120 cm) version of this composition, from private collection in Rome and attributed to circle of Francesco Bassano (1549-1592), was sold in 2021 (Finarte Auctions, 16.11.2021, lot 73). In both paintings the woman has a fashionable hairstyle from the late 1570s or early 1580s and the painting in Rome was most probably sent as a gift to the Pope or one of the cardinals (this woman managed to convert to Catholicism the Voivode of Ruthenia!). A number of paintings by Francesco Bassano and his workshop are also in Poland (Adoration of the Magi with a Polish nobleman and Forge of Vulcan in the National Museum in Warsaw, Forge of Vulcan in the National Museum in Poznań or Annunciation to the shepherds in the Wawel Royal Castle and another in the Museum of the Warsaw Archdiocese). The same woman was also depicted in a portrait of a lady in a green dress (a color being symbolic of fertility), attributed variously to Jacopo and Leandro Bassano, in the Norton Simon Museum in Pasadena, California. The picture was previously in the Edward Cheney collections in Badger Hall in Badger, near Wolverhampton, England (demolished in 1952). A pendant on a gold chain around her neck is a jewel in which two different stones and a pearl are set, each with its own precise meaning: the ruby indicates charity, the emerald indicates chastity, and a pearl is a symbol of marriage fidelity. The woman's dress and hairstyle are very simular to those visible in a self-portrait with madrigal by Marietta Robusti in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence, dated to about 1578 (inventory 1890 n. 1898). A signed painting by Leandro Bassano (signature: Leandro) from Jan Gwalbert Pawlikowski collection is in the Wawel Royal Castle and Lamentation of Christ, attributed to him is in the Vereshchagin Art Museum in Mykolaiv, close to Odessa. Resurrection of Lazarus from the altar of the Mocenigo family in the church of Santa Maria della Carità in Venice (today in the Gallerie dell'Accademia in Venice), another signed work by Leandro Bassano (LEANDER/ BASSANE.is/ F.), dated to between 1592-1596, shows a man in a costume of a Polish-Lithuanian noble. She was also depicted as a widow in a portrait by Jacopo Tintoretto in the Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden. This painting was probably acquired in Venice by Duke Francesco I d'Este (1610-1658) and listed as "Portrait of a woman dressed in black - Titian" (Ritratto di donna vestita de nero - Tiziano) in the inventory of 1744 of the Galleria Estense in Modena, then sold to Augustus III of Poland-Lithuania-Saxony in 1746 (as portrait of Caterina Cornaro). This portrait is dated to early 1550s, however similar costume of a Venetian widow (Vidua Veneta / Vefue Venetiene) is visible in an engraving representing Ten women dressed according to Italian fashion by Abraham de Bruyn, created in about 1581 (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam). The style of this picture can be compared with portrait of the Procurator Alessandro Gritti in the Museu Nacional d'Art de Catalunya, dated to between 1581-1582, and portrait of Piotr Krajewski (1547-1598), żupnik of Zakroczym in the Masovian Museum in Płock, dated '1583'. The latter painting is generally attributed to circle of Martin Kober, however the man's face is painted in the same style as the widow in Dresden. Krajewski, a nobleman of Leliwa coat of arms, was the owner of villages Mochty and Smoszewo and a manager (żupnik) which oversaw the salt storehouse in Zakroczym near Warsaw, the seat of Infanta Anna Jagiellon. His portrait was most probably commissioned in Venice and a court painter in Warsaw added coat of arms and inscription (painted in different style). A miniature copy of this portrait was photographed around 1880 by Edward Trzemeski in the Yellow Room of Pidhirtsi (Podhorce) Castle near Lviv, opposite another miniature, a copy of portrait of Catherine Jagiellon, Duchess of Finland in white. Due to the layout, both were probably copies of prints by Pierre-François Basan based on the original paintings, published in the Recueil d'Estampes d'après les plus célèbres Tableaux de la Galerie Royale de Dresde in 1753 (number 11 and 12), when the two paintings were attributed to Titian, however, this selection and placement above the door might suggest that in the 18th century there were still clues to the identity of the two women and their connection to Poland-Lithuania. In the Zhytomyr Region History Museumin Ukraine there is a portrait of Giovanni Francesco Sagredo (1571-1620), a Venetian mathematician and close friend of Galileo, painted by Gerolamo Bassano. The painting comes from the nationalized collections of barons de Chaudoir (the family may come from a line of French Protestant emigrants who fled in 1685 from Belgium and one de Chaudoire worked at the court of King Stanislaus Augustus). In the 1590s Sagredo studied privately with Galileo in Padua and in 1596 at the age of 25 he became a member of the Great Council of Venice. His portrait attributed to Gerolamo Bassano in the Ashmolean Museum depict him in the robes of the a Procurator of Saint Mark, therefore the portrait from Zhytomyr like the effigy from private collection, attributed to circle of Domenico Tintoretto, should be dated to before 1596, therefore could be acquired by Adam Hieronim during his potential studies in Italy. Sagredo was depicted in a crimson tunic similar to Polish-Lithuanian żupan. It is possible that all mentioned paintings by Venetian painting workshops, in Odessa, Mykolaiv and Zhytomyr, originate from the same collection - "the Eastern Wawel": Berezhany Castle, dispersed among several museums in Ukraine. Despite that no signed likenesses of Jadwiga Sieniawska née Tarło or her close relatives have preserved, basing on all these facts the mentioned potraits should be indentified as her effigies.
Abduction of Europa with portrait of Jadwiga Sieniawska née Tarło, Voivodess of Ruthenia by workshop of Jacopo Bassano, 1578-1582, Odessa Museum of Western and Eastern Art.
Abduction of Europa with portrait of Jadwiga Sieniawska née Tarło, Voivodess of Ruthenia by workshop of Francesco Bassano, 1578-1582, Private collection.
Portrait of Jadwiga Sieniawska née Tarło, Voivodess of Ruthenia in a green dress by Jacopo or Leandro Bassano, ca. 1578, Norton Simon Museum.
Lamentation of Christ by Leandro Bassano, late 16th century, Vereshchagin Art Museum in Mykolaiv.
Portrait of Jadwiga Sieniawska née Tarło, Voivodess of Ruthenia in mourning by Jacopo Tintoretto, ca. 1582, Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden.
Portrait of Piotr Krajewski (1547-1598), żupnik of Zakroczym by workshop of Jacopo Tintoretto, 1583, Masovian Museum in Płock.
Portrait of Giovanni Francesco Sagredo (1571-1620) by Gerolamo Bassano, 1590s, Zhytomyr Region History Museum.
Portraits of king Stephen Bathory by Venetian painters
Official portraiture showed Bathory as he should look like and as he was perceived, imagined by average and less educated subjects, i.e. a strong, powerful, masculine monarch in rich national costume, a man capable to protect the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth from Tsar Ivan the Terrible, a brutal tyrant, who used terror and cruelty as a method of controlling his country and who invaded the Commonwealth during the second royal election after Henry of Valois's sudden return to France in mid-June 1574 through Venice. The Tsar had captured Pärnu on 9 July 1575, took as many as 40 thousand captives (according to Świętosław Orzelski) and devastated much of central Livonia. Anna Jagiellon and Bathory were elected just few months later on December 15.
In private effigies or these dedicated to his European colleagues Bathory could allow himself to be depicted as educated in Padua lover of astronomy, in a cloak of a simple soldier in his army or as an old, tired man. The portrait by Tintoretto from the Spanish royal collection, shows Bathory in a toga-like attire similar to the costume of a Venetian magistrate. It is a kopieniak a sleeveless raincoat of Turkish origin (kepenek), popular at that time in Hungary (köpenyeg). According to Stanisław Sarnicki's "Księgi hetmańskie", published in 1577-1578, kopieniak was a sort of Gabina (gabìno), a toga in ancient Rome, while according to "Encyklopedja powszechna" (Universal encyclopedia, vol. 15 from 1864, p. 446) in Poland the attire and a word were popularized by Bathory, "who used the kopieniak in hunting and during war expeditions". After king's death some of his robes valued at 5351 zlotys were given to his courtiers. The inventory made in Grodno on 15 December 1586 includes many kopieniaks, made by his Hungarian tailor Andrasz, like the most valuable "scarlet kopieniak lined with sables with one silk button and a loop, 1548 zlotys worth", "12 navy blue half-kopieniaks lined with sables, with gold buttons" or "4 kopieniaks of different colors". The portrait of a bearded man with hourglass and astrolabe by Francesco Bassano from Ambras Castle in Innsbruck is very similar in style and composition to the portrait of Anna Jagiellon in Vienna. Before 1 February 1582 Bathory offered to Ferdinand II, Archduke of Austria many items captured during the Siege of Pskov to his large collection of armaments in Ambras, including his armor accompanied by a portrait and resume. On March 10, 2020, a "portrait of King Ladislav VI of Hungary", whose style resembles works from the workshop or circle of Jacopo Bassano, was auctioned (oil on canvas, 65 x 47.5 cm, attributed to Italian school, inscription in Latin: LADISLAVS VNG. BOE / REX.). This portrait is almost a direct transposition of a print by Venetian printmaker Gaspare Oselli (Osello) after a drawing by Francesco Terzio from Bergamo, a pupil of Giovanni Battista Moroni, representing Ladislaus the Posthumous (1440-1457), King of Hungary, Croatia and Bohemia and Duke of Austria. This engraving, created in 1569, was a part of a series of 58 prints with portraits of 74 members of the House of Austria, dedicated to Ferdinand II, who was a son of Anna Jagellonica (1503-1547), Queen of Hungary, Bohemia and Croatia. Among the things given in deposit to king's courtier Mr Franciszek Wesselini (Ferenc Wesseleny´i de Hadad) in the inventory of king's belongings, there were "A gold carriage chest with the coat of arms of His Highness Augustus, in which there are various small things. Golden saddle of the deceased king Sigismund Augustus. A casket with small things and crane feathers" and also "A leaky watch (water hourglass)" and "Large old Turkish carpets, which were brought by Mr. Grudziński from Hungary from Machmet Basha", most probably offered by Sokollu Mehmed Pasha, Grand Vizier of the Ottoman Empire. The inventory does not include any Western, black costumes, however since the king used many items of his predecessor Sigismund Augustus, he undoubtedly had access to his extensive black Italian wardrobe. Curiously the black Italian hose with protruding codpiece were at that time in Poland considered by simple people as more effeminate than dress-like żupan of colorful Venetian fabric. "The nation is effeminate [...] Franca [syphilis], musk, lettuce, with them it came, These puffed hose, stockings, mostardas, The Italian haughty nation has recently brought here" (269, 272-274), wrote in his satire "Conversation of the New Prophets, Two Rams with One Head" (Rozmowa nowych proroków, dwu baranów o jednej głowie) published in 1566/1567, Marcin Bielski. His interest in astronomy is confirmed by his support to the sorcerer Wawrzyniec Gradowski from Gradów and with a sojourn at his court of John Dee, an English mathematician, astronomer and astrologer and Edward Kelley, an occultist and scryer in March 1583 and April 1585, who were paid 800 florins by the king. He also transformed the Jesuit gymnasium in Vilnius into an academy (1578), where astronomy, poetry and theology were taught. Leaving Transylvania for Poland in 1576, he consulted astrologers, with whom he also set the date of his wedding with Anna Jagiellon. Therefore Bathory was maybe more effeminate in his private life then in his public appearance, he was however one of the most eminent monarchs of this part of Europe, a wise and brave king who led the Polish-Lithuanian Republic to its greatest glory and power. After 50 his health rapidly declined. As Sigismund Augustus, Bathory most probably suffered from syphilis, treated by his Italian physicians Niccolò Buccella and Simone Simoni. "The king his grace had on his right leg two fingers below the knee, up to the ankle, a kind of rash, in which there were sometimes shallow, flowing wounds. On that leg, lower than the knee, he had an apertura [ulcer]: and when little was leaking from it, he had no appetite, the nights were restless and sleepless." The portrait in Budapest by Leandro Bassano, which is very similar to other effigies of Bathory, undeniably show him in the last year of his life.
Portrait of king Stephen Bathory in kopieniak coat by Tintoretto, ca. 1576, Prado Museum in Madrid.
Portrait of king Stephen Bathory with hourglass and astrolabe by Francesco Bassano, ca. 1580, Ambras Castle in Innsbruck.
Portrait of king Stephen Bathory sitting in a chair by Leandro Bassano, ca. 1586, Museum of Fine Arts in Budapest.
Portrait of Primate Jakub Uchański by Jacopo Tintoretto
In the 14th century BC, Akhenaten, the pharaoh of the 18th dynasty of Egypt and his wife and co-ruler Nefertiti closed the temples of the gods of Egypt introducing monotheism by promulgating the worship of a single universal deity, the solar god Aten. They decided to found a new capital Akhetaten (horizon of the Aten) near present-day Amarna. The strong position of women in ancient Egypt was increased under Akhenaten and Amarna period is considered as one of the finest in the art of Ancient Egypt. Not long after Akhenaten's death, his successors reopened the state temples to other Egyptian gods and the name of the "heretic pharaoh" was removed from all of his statues and monuments. His radical move destabilised the social and economical system of Egypt. Temples were key centers of economic activity and charity and continue to uphold maat, the divine order of the universe, a principle that embraced diverse peoples with conflicting interests. People were expected to act with honor and truth in matters that involve family, the community, the nation, the environment, and the gods. Local courts known as Houses of Judgment were associated with local temples and resolved disputes at the gates of the temples.
As in Jerusalem and Mesopotamia, temples cared for the needy or marginalized in society, including the poor, widows, orphans, elderly and homeless, provided hospitality, food, and asylum (after "Mending Bodies, Saving Souls" by Guenter B. Risse, p. 45). Similar was the role of the Roman church in Poland-Lithuania during Renaissance. Catholic hierarchs understood the need for tolerance in a multi-religious country, especially during Reformation, which was often misunderstood abroad, and they were frequently accused of indifferentism. They also understood the role of institutions, social order and hierarchy inherited from medieval times when a single religion dominated in certain regions, financed through taxes and tithes. The bishop of Kraków, Andrzej Zebrzydowski (1496-1560), a student of Erasmus of Rotterdam, also educated in Paris and in Padua, was then attributed with a saying: "You can believe even in a goat if you like, so long as you pay the tithes". His episcopate took place during the mass conversion of the nobility to Calvinism and the bourgeoisie to Lutheranism. In 1556 Zebrzydowski also stood before an ecclesiastical court together with Bishop Jan Drohojowski after rumors of heresy. Papal nuncio Luigi Lippomano headed this investigation. He was charged with maintaining a friendship with Jan Łaski, a well-known Protestant leader, possessing heretical books and inappropriate conduct, including maintaining a relationship with a young Jewess (after "Sinners on Trial" by Magda Teter, p. 145). The Counter-Reformation and foreign invasions changed everything in Poland. After partitions of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth by the Habsburg monarchy, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Russian Empire, the Catholic church was one of the few public institutions where people could speak Polish freely (after "November 1918" by Janusz Żarnowski, p. 31) and some Russian writers from the late 18th century stressed degeneration of Catholic Poland and the need to "civilize" it by its neighbors (after "The Russo-Polish Historical Confrontation" by Andrzej Nowak). In the spring of 1578 Paweł Uchański (d. 1590), beloved nephew of other "heretic" hierarch of the Catholic church in the Commonwealth, advocating religious tolerance, Jakub Uchański (1502-1581), archbishop of Gniezno and primate of Poland, was sent on a mission to the Pope in Rome and to the Spanish Viceroy of Naples. It was customary in Catholic countries that each new monarch, after his accession to the throne, sends an envoy to the Pope with a declaration of obedience to the head of the Church. Uchański received this mission from king Stephen Bathory in 1577, but under various pretexts he delayed the journey. The embassy reached Venice on September 23, and stayed there until November 28, 1578, under the pretext of seeking permission to travel to Rome. Then the legation arrived in Padua. It was only at the beginning of February of the following year that it was decided to return to Venice and go by sea to Ancona, to reach Rome via Loreto. After a month's stay there, they went to Naples for a month, then returned to Rome for the next six months. Like all the missions in Naples, this one also had a lot to do with the inheritance of Queen Bona, mother of Queen Anna Jagiellon and a loan made by Bona to Philip II of Spain, which was never repaid. In the first days of March 1580, Paweł was in Łowicz received by the archbishop, who lend him 30,000 zlotys to pay off debts incurred in Italy. According to Giovanni Andrea Caligari (1527-1613), papal nuncio to Poland, "as always malicious towards the Uchańskis", Paweł borrowed 10 thousand in Rome and 6 thousand in Padua. He offered and received gifts, he gave Cardinal Farnese his own horses brought from Poland together with the carriage and he received a gold chain worth 500 ducats from the signoria of Venice, and 6,000 ducats from the pope. He probably also bought and ordered many luxury goods in Italy. The debt was so great that it was not yet repaid in 1586 (money borrowed from the Duke of Tuscany). The creditors claimed their dues in various ways, they even disturbed the secretary of state in Rome, so in March 1583 Paweł delegated a certain Jerzy Polit to settle the matter and buy the silverware and other items pledged in Rome (after "Uchańsciana seu collectio documentorum ..." by Teodor Wierzbowski, p. 49). In 1575 Primate Uchański, who was Archbishop of Gniezno from 1562 and interrex, a short-term regent, of the Commonwealth twice (1572-1573, 1575-1576), joined the pro-Habsburg camp and together with other senators proclaimed Emperor Maximilian II, cousin and brother-in-law of Philip II of Spain, the king. Due to the opposition of many other nobles, Maximilian lost, and Anna and her husband become the co-rulers of the Commonwealth. The Primate was a patron of arts and in 1573 at the archbishops' castle in Łowicz he began the construction of a magnificent Renaissance palace worthy of a king. From 1580 or possibly earlier he employed an eminent mannerist sculptor for the decoration of his residence, Jan Michałowicz of Urzędów (d. 1583), who also created the archbishop's mausoleum at the Łowicz cathedral. The palace was completed in 1585 after death of Uchański and Michałowicz by Primate Stanisław Karnkowski (blown up by retreating Swedish forces in 1657). Alabaster tomb monument of Uchański in the Łowicz Cathedral, created by Michałowicz between 1580-1583 in the Italian style (rebuilt between 1782-1783), and marble tombstone of Calvinist Piotr Tarnowski (died before 1597), father of Primate Jan Tarnowski, by Willem van den Blocke in the style of the Netherlandish mannerism in the same temple, were made from imported Belgian limestones and English alabaster. Similar to tomb monuments of the Tarnowski family by Giovanni Maria Padovano and to the Ostrogski family by Willem van den Blocke in the Tarnów Cathedral, they perfectly illustrate the main influences of art in Poland at that time and great diversity. D. Basilii Magni [...] De moribvs orationes XXIIII [...] by Stanisław Iłowski (Ilovius), dedicated to Primate Jakub Uchański, was published by Giordano Ziletti and Giovanni Griffio in Venice in 1564. Uchański sent a volunteer group to the war with Moscow, and ordered full armours for his soldiers from Brunswick craftsmen through Sophia Jagiellon, Duchess of Brunswick-Lüneburg (after "W służbie polskiego króla ... " by Marek Plewczyński, p. 288). In the Prado Museum in Madrid, there is a portait of an archbishop (El arzobispo Pedro) by Jacopo Tintoretto from the second half of the 16th century (oil on canvas, 71 x 54cm, inventory number P000369). It comes from the royal collection, mentioned in the collection of Queen Elisabeth Farnese (1692-1766) in the palace of La Granja (fireplace room, 1746, no. 523), most likely sent to Spain already in the 16th century. According to inscription in Latin it depicts Archbishop Peter (PETRVS. / ARCHI EPVS). The characteristic tilde above v in EPVS, could indicate that the inscription was added much later in Spain and that the person who added the inscription had vague knowledge of who was depicted. From the times of Saint Lawrence Justinian (Lorenzo Giustiniani, 1381-1456), Catholic bishops of the Archdiocese of Venice are known as Patriarchs (Latin: Patriarcha Venetiarum) and the only Peter in the second half of the 16th century, Pietro Francesco Contarini (1502-1555), died after just a few months in the office. Among the Archbishops of Seville and Archbishops of Toledo there is no Pedro in the second half of the 16th century and their effigies are not similar to the described portrait. The portrait of Gaspar de Quiroga (1512-1594), Archbishop of Toledo, created cardinal in 1578, in Prado (P000401) is attributed to follower of Tintoretto, however it is also close to the style of the Bassanos. It was ordered in Venice from Spain and the sitter was identified mainly basing on "his unquestionable resemblance to the portrait that Luis de Velasco painted of him in 1594 for the chapter house of the Toledo Cathedral" (after "The artistic relations of Cardinal Quiroga with Italy" by Cloe Cavero de Carondelet). The portrait of king Stephen Bathory by Tintoretto in the same collection (P000374) is stylistically very close to the effigy of the "Archbishop Peter", the two portraits were therefore probably created around the same time. The archbishop from the Prado painting resemble greatly the effigies of Primate Uchański, especially the lithography in the catalogue of archbishops of Gniezno by Julian Bartoszewicz (Arcybiskupi gnieźnieńscy ...), published in 1864 and his statue in Łowicz. Philip II of Spain was unquestionably interested in having a portrait of Primate of Poland and Archbishop of Gniezno who ruled the Commonwealth during the interregnum and proclaimed his cousin Maximilian the king.
Portrait of Primate Jakub Uchański (1502-1581), Archbishop of Gniezno by Jacopo Tintoretto, 1562-1580, Prado Museum in Madrid.
Portrait of Cardinal Gaspar de Quiroga (1512-1594), Archbishop of Toledo by workshop of the Bassanos, after 1578, Prado Museum in Madrid.
Portrait of Cardinal Henry I, King of Portugal by Domenico Tintoretto
In 1579 brothers of Nicolaus Christopher Radziwill "the Orphan" (1549-1616), George (1556-1600), future cardinal, and Stanislaus (1559-1599), arrived in the capital of Portugal. "The coadjutor of Vilnius Radziwll, wrote to me from Lisbon on April 3 that he greeted the king dressed in cardinal's robes, but holding pleasantly a scepter in his old and weakened hand", wrote in a letter from Rome on June 6, 1579 the royal secretary Stanisław Reszka (1544-1600) about the audience before Cardinal Henry I (1512-1580), King of Portugal (after "Z dworu Stanisława Hozjusza: listy Stanisława Reszki do Marcina Kromera, 1568-1582" by Jadwiga Kalinowska, p. 221). Then, via Turin and Milan, the Radziwill brothers arrived in Venice in September 1579. From there they set off via Vienna to Poland and finally reached Kraków by the end of the year (after "Radziwiłłowie: obrazy literackie, biografie, świadectwa historyczne" by Krzysztof Stępnik, p. 298).
In 2022 the portrait of Cardinal-King of Portugal from private collection, created in Venice, Italy, was sold at the auction in Munich, Germany (Hampel Auctions, December 8, 2022, lot 238). It was painted by Domenico Tintoretto in 1579 as according to Latin inscription it depict the Cardinal-King at the age of 67 (HENR.S CARD.S / REX. PORTV / GALIAE. ETCZ [...] /. AETATIS / SVAE. LXVII.). Cardinal Henry, born in Lisbon on January 31, 1512, become the king of Portugal at the age of 66 (coronation in Lisbon on August 28, 1578) after death of his great-nephew King Sebastian, who died without an heir in the Battle of Alcácer Quibir that took place in 1578. In January 1579 Jerónimo Osório da Fonseca (Hieronymus Osorius, 1506-1580), Bishop of the Algarve, Portuguese historian and polemicist, wrote a letter in Latin to "to the invincible Stephen Bathory, king of Poland" (inuictissimo Stephano Bathorio regi Poloniae) expressing his gratitude for reading his books (scripta namque mea tibi usque adeo probari ut in castris etiam, quotiens esset otium, otium illud te libenter in libris meis assidue uersandis consumere) (after "Opera Omnia. Tomo II. Epistolografia" by Sebastião Pinho, p. 214). Osório was a member of the royal council (Mesa da Consciência e Ordens), who advised the Cardinal-King on political matters. It cannot be excluded that the portrait of the Cardinal-King was commissioned in Venice by the Radziwill brothers, or by the Cardinal-King through their intermediary, as a gift to the royal couple of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Queen Anna Jagiellon and her husband Stephen Bathory. The painting was acquired by the National Museum of Ancient Art in Lisbon (inventory number 2224 pint).
Portrait of Cardinal Henry I (1512-1580), King of Portugal, aged 67 by Domenico Tintoretto, 1579, National Museum of Ancient Art in Lisbon.
Portrait of Stanislaus Radziwill by Alessandro Maganza
The younger of the two Radziwill brothers who visited Portugal in 1579, Stanislaus (1559-1599), was considered a very religious person, hence his later nickname Pius, meaning pious in Latin. He was a thoroughly educated person and, apart from Lithuanian, he knew several foreign languages. He translated from Greek into Polish part of the work of the Patriarch of Constantinople Gennadius Scholarius, which was published in 1586. He was also the author of a work on the main truths of the faith entitled "The Spiritual Arms of the Rightful Christian Knight" (Oręże duchowne prawowiernego rycerza chrześcijańskiego), published in Kraków in 1591.
Although the capital of Spain, Madrid, did not impress the prince ("here in Madril, apart from the royal court, there is nothing to see, a vile and filthy village", wrote Stanislaus to one of his brothers in the country), during this half-year stay on the Iberian Peninsula he and his brother were undoubtedly deeply marked by the highly religious and chivalric culture of the 16th century Spain and Portugal. The Orders of chivalry - Santiago, Calatrava, Alcántara, and Montesa in Spain and Order of Christ and Order of Avis in Portugal, originally dedicated to the warrior knights of the crusade against the Moors, served to create an elite of specially favoured nobles. Admission to these aristocratic military brotherhoods was restricted and required purity of noble blood as well as the support of former noble members, thus all Spanish and Portuguese nobles proudly display the characteristic crosses of the great chivalric orders on their portraits. Foreigners were admitted to the order as honorary knights, however they were not subject to the statutes and were excluded from the participation in the revenues (after "The British herald, or Cabinet of armorial bearings ..." by Thomas Robson, p. 88). They were not permanent members of the order, therefore, for example in the Catalog of Knights of the Order of Christ (Catálogo dos cavaleiros da ordem, published in "La bibliografía de la Orden Militar de Cristo ..." by Juan de Ávila Gijón) between 1579-1631, there is no foreign name. From Madrid, the Lithuanian travelers and their companions went on foot to Santiago de Compostela (one hundred Spanish miles), a major place of Catholic pilgrimage. Although there is no confirmation of this in the available sources, the reception of two Radziwill brothers by the King of Portugal was undoubtedly accompanied by an exchange of gifts and foreign noble guests were often honored in a special way, such as Jan Amor Tarnowski, knighted by King Manuel in Lisbon in 1516, together with two Polish companions (after "Jan Tarnowski ..." by Zdzisław Spieralski, p. 82). Stanislaus died in Passau in Germany, in 1599, during his pilgrimage to Loreto in Italy. According to his last will, he was buried in the Bernardine Church in Vilnius. His tombstone was however created much later, between 1618-1623, most likely in the workshop of the Flemish sculptor Willem van den Blocke, who worked in Gdańsk. His funerary statue was therefore based on some earlier effigies sent to Gdańsk. This tombstone was heavily damaged during the Deluge (1655-1660), when Vilnius was occupied by Russian forces, who burned down the church and killed the monks and civilians hiding in the monastery. In the National Museum of Art in Kaunas in Lithuania there is a portrait of a man with a cross of a chivalric order on his chest (oil on canvas, 61 x 48.5 cm, inventory number ČDM MŽ 139). His costume clearly dates from the 1570s and resembles some effigies of King Henry of Valois, elected monarach of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and his courtiers - tall black hat with a feather and a ruff, thus the portrait was initially considered to be his likeness. A similar cross is seen on a leaf from the Book of scriptures of the Order of Christ (Livro das escrituras da Ordem de Cristo) with the crowned coat of arms of King Sebastian of Portugal, created between 1560-1568 (Convent of Christ in Tomar) and closely resemble the badge of the order, the motto of which was "the Christian army" (Militia Christiana), gold and enamelled cross, today in the National Palace of Ajuda in Lisbon (inventory number 5190). Very similar crosses were depicted in several portraits, notably the portrait of a knight of the Order of Christ, presumed to be Vasco da Gama (1469-1524) by Portuguese or Flemish painter (Corneille de Lyon?), from the second quarter of the 16th century, and another by Portuguese painter from the second quarter of the 17th century, both in the National Museum of Ancient Art in Lisbon (697 Pint, 71 Min). The painting can be attributed to the Flemish, Spanish or German school, however, its style is strikingly similar to the portrait of Marie de' Medici (1575-1642), Queen of France by Alessandro Maganza (1556-1632) in the Lithuanian National Museum of Art in Vilnius (LNDM T 4018), identified by me. Similarities with the likeness of Bianca Cappello (1548-1587), Grand Duchess of Tuscany (private collection) and the Virgin and Child with Saints (Nationalmuseum in Stockholm) by Maganza, can also be indicated. Like the portrait of the Queen of France, the portrait of a knight in Kaunas probably also comes from the Radziwill collection, a powerful family with extensive possessions in many countries of the former Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. In 1572, Maganza moved to Venice, following the advice of his friend the sculptor Alessandro Vittoria. After his marriage in 1576 he returned to Vicenza, between Padua and Verona in the Venetian Republic. Assisted by his flourishing family workshop - in which his four children were employed - he worked for clients in the Venetian cities including Verona, Brescia and Padua and in Florence - portrait of a man with his son, from the collection of Leopoldo de' Medici (1617-1675) where it was attributed to Tintoretto (1588, Uffizi Gallery, inventory 1890, n. 940) or the Feast of Herod (Pitti Palace, Palatina 387). Based on all these facts, the portrait could be identified as an effigy of a Portuguese knight by Maganza, if not a striking resemblance of the sitter to the portrait of Stanislaus Radziwll in the Wilanów Palace in Warsaw (Wil.1222). This portrait is an 18th century copy of an earlier effigy that has not been preserved, possibly by a Venetian painter, and was signed in Latin (STANISLAVS RADZIWILL D.G.DVX IN OŁIKA ET NIESWIEZ ...). He was depicted in a ruff and armor engraved with gold, as in his other known likenesses - a drawing in the State Hermitage Museum (ОР-45854) from the mid-17th century and a painting in the Lviv Historical Museum from the late 18th century. The painting was most likely created or commissioned in Vicenza in 1579 during Stanislaus' trip from Milan to Venice. If from that date Maganza and his workshop worked mainly for customers from Poland-Lithuania, many of his works were destroyed due to the wars and invasions that the country experienced in the following eras.
Portrait of Stanislaus Radziwill (1559-1599) with the cross of the Portuguese Order of Christ by Alessandro Maganza, ca. 1579, National Museum of Art in Kaunas.
Portraits of Katarzyna Tęczyńska by Francesco Montemezzano and workshop of Alessandro Maganza
Another portrait of the member of the Radziwill family close to the style of Alessandro Maganza (before 1556-1632) is now in the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 133 x 88.5 cm, 128854 MNW). It depict Katarzyna (Catherine) Tęczyńska (1544/5-1592), daughter of Stanisław Gabriel Tęczyński, voivode of Kraków, and Anna Bogusz. The family of Count Tęczyński was one of the most influential and wealthy families of the Polish kingdom (Imperial counts from 1527). At the age of 14 or 15, in May 1558, she married Ruthenian Prince Yuri Olelkovich-Slutsky (ca. 1531-1578). Yuri was Orthodox, and Katarzyna, although Catholic, was well versed in Orthodox worship, as her mother was also Orthodox. Faith was not an obstacle in Poland-Lithuania before the Counter-Reformation. She received a rich dowry of 20,000 zlotys including silverware, pearls and jewelry worth 13,000 zlotys and 10,000 in cash. She bore 3 sons to her husband and when he died in 1578 she managed principalities and many estates until her sons come of age. In addition, she received additional lands from the king.
Three years later, in 1581, Katarzyna remarried. The wealthy widow chose younger Christopher Nicolaus Radziwill (1547-1603), nicknamed "the Thunderbolt", Field Hetman of Lithuania. She became his third wife and gave birth to two of his children. She died on March 19, 1592. The Warsaw painting most likely comes from Tęczyn (Tenczyn) Castle and, like other portraits of members of the Tęczyński family kept in the same museum (128851, 128850, 139537), it passed after 1816 to the Potocki collection in Krzeszowice where it was enlarged and repainted. These modifications were removed during the conservation of the painting in 1986-1991. The painting was attributed to local painters from Slutsk (anonymous) or Kraków (Martin Kober) or an unknown Polish-Lithuanian workshop, but its style with blurred lines is evidently Venetian and closest to Maganza. It is not as elaborate as other paintings by the master, indicating that it was probably from a series of paintings commissioned from his workshop. Stylistically, it can be compared to the work signed by Alessandro's son, Giovanni Battista the Younger (IO: BAPT. MAGAN. / P.) in the church of Santa Corona in Vicenza, depicting the League against the Turks in 1571. It was painted in the late 16th century or early 17th century, hence the portraits of King Philip II of Spain, Pope Pius V and Doge Alvise Mocenigo were modeled on other effigies. Tęczyńska is dressed as a widow in a Polish-style black dress with white sleeves and a transparent veil called rańtuch or rąbek. She also wears a ruff, very similar to that in the portrait of Queen Anna Jagiellon in Amsterdam (Rijksmuseum, SK-A-3891). The large Latin inscription above her head: "In the year of the Lord 1580. Catherine, Countess of Tęczyn, by the grace of God, Princess of Slutsk, 35 years old" (ANNO DOMINI M.DL XXX. / CATHERINA COMES A THENCZN DEI / GRATIA DVCISSA SLVCENSIS ÆTATIS / SVÆ XXXV AÑO.) and the coat of arms were probably added later. The painting was most likely commissioned by the widow as a gift for her relatives. Although in the majority of her surviving effigies she is dressed as a widow (a drawing in the Hermitage Museum, ОР-45851 and a print from Icones familiæ ducalis Radivilianæ ...), similar to some effigies of Queen Bona Sforza and of Queen Anna Jagiellon, this does not mean that she was always a widow or that she always dressed as such. The list of jewels of Princess Olelkovich-Slutska written on April 16, 1580 in Slutsk (AGAD, 1/354/0/26/949), lists many of her jewels such as six necklaces, including "a necklace in which rubies twenty eight, diamonds seven, pearls twenty" and 21 pendant crosses set with precious stones. She undoubtedly also had more exquisite dresses. Some surviving inventories of the Radziwill family indicate that they possessed the most elaborate works of art created in Europe and imported from the Orient. Silverware, weapons and fabrics prevail as the most valuable, but sometimes female dresses and paintings are mentioned. Register of armours and jewels belonging to Katarzyna's second husband Christopher Nicolaus Radziwill from 1584 (Central Archives of Historical Records in Warsaw - AGAD, 1/354/0/26/5) contains only one portrait - the image of his third wife Katarzyna Tęczyńska (Obraz Jey Mći), as well as 10 large Venetian tapestries (Opon weneczkich wielkich iedwabnych - Dziesieć) and 12 tapestries "with faces", made in Poland-Lithuania (Opon s twarzami domowey roboty - dwanaseci). It also includes the dresses of two of his deceased wives Katarzyna Sobek - 4 black velvet dresses, one embroidered with silver thread (snurkiem srebrnym obwiedziony) and many other exquisite dresses of his second wife Katarzyna Ostrogska, daughter of Zofia Tarnowska, including a red velvet dress (Hazuka Axamitna wzorzysta czyrwona), Spanish dress of red gold cloth (Hazuka Hiszpanska złotogłowowa czyrwona), a Spanish robe of red gold cloth with a smaller pattern and 52 gold clasps (Szata czyrwonego złotogłowu drobnieyszego Hispanska ... w niey feretow zlotych piecdziesiat dwa) and 7 for summer, one of white satin embroidered with gold thread (Lietnik Atłassowy biały z bramami drobnemi ... złotym snurkiem obwiedzione) and two of silver and gold cloth - blue and dark brown (Lietnik srebrogłowowy blekitny czałowity, Lietnik złotogłowowy bronatny czałowity). Register of a part of belongings of the same Christopher Nicolaus, made in 1600 (AGAD, 1/354/0/26/7), lists 2 large Venetian tapestries (Opon weneckich wielkich II) and 3 small tapestries made in Poland-Lithuania (oponek domowey roboty ... 3), several old tapestries "with faces" (opon staroswieckich stwarzami) and female dresses (Szaty białogłowskie). Register of property of Prince Boguslaus Radziwill (1620-1669) from 1657 (AGAD, 1/354/0/26/79.2), lists many paintings from his collection including several by Cranach, Italian and Dutch paintings and Ruthenian icons (Siedm obrazow ruskich). The mentions about the paintings are very general which confirms their lesser value: "Two Paintings of Saints on Copper", "23. Long Drawer with a picture of Susanna, a picture of a naked woman, the second picture also of a woman", "24. A drawer with different paintings in frames 28 pieces ...", "33. A drawer with five paintings", "34. A drawer with a battle painted on copper", "25. A drawer with a large painting of a woman on canvas, ebony frame", "19. A drawer with ten Italian paintings in frames and one of Queen Barbara [Radziwill], nine various paintings without frames", "45. A drawer with two small old paintings", "53. A drawer with six paintings of women without frames, one of a male Radziwill without frame, four paintings with frames", "57. A drawer with thirteen Italian paintings", "58. A drawer with fourteen different paintings", "Two images", "Nine pictures" ... etc. An effigy of "Katarzyna Tęczyńska, wife of Prince Christopher" (111) is mentioned among the paintings from the collection of Princess Louise Charlotte Radziwill (1667-1695), inventoried in 1671 (after "Inwentarz galerii obrazów Radziwiłłów z XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska). Tęczyńska's face can also be identified in another painting from the Venetian school. She has larger lips as in the Icones familiæ ducalis Radivilianæ ..., but the general resemblance of the face to the Warsaw painting is striking. She is dressed in a Venetian summer dress of very expensive gold cloth and holds a small dog, a symbol of marital fidelity. The landscape behind her probably symbolizes her vast lands. This painting, now in the Harvard Art Museums - Fogg Museum in Cambridge, Massachusetts (oil on canvas, 125.5 x 105.8 cm, inventory number 1917.220), was donated in 1917 by Edward Waldo Forbes (1873- 1969), American art historian and the director of the Fogg Art Museum at Harvard University from 1909 to 1944. Its earlier history is unknown. The work is dated around 1580 and was previously attributed to Antonio Badile (1516-1560), Paolo Caliari, called Veronese (1528-1588) and now to Francesco Montemezzano (1555 - after 1602), who painted the portraits of Queen Anna Jagiellon, identified by me. The same workshops (Maganza and Montemezzano) also painted the effigies of Princess Elizabeth Euphemia Radziwill née Vyshnevetska (1569-1596).
Portrait of Katarzyna Tęczyńska (d. 1592), Princess of Slutsk, aged 35 by workshop of Alessandro Maganza, 1580, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Katarzyna Tęczyńska (d. 1592), Princess of Slutsk with a dog by Francesco Montemezzano, ca. 1580-1584, Harvard Art Museums.
Portraits of Count Stanisław Górka by Anthonis Mor and Adriaen Thomasz. Key
On February 14, 1580 a synod of the Protestants was held in Poznań, presided over by Count Stanisław Górka (1538-1592), voivode of Poznań (Stanislaus Comes a Gorka Palatinus Posnanienis - according to inscription on his tomb monument), one of the leaders of the Lutherans in Greater Poland. German Paulus Gericius and Polish Jan Enoch, ministers of the Lutheran church in Poznań, opposed the merger and any unity with the Bohemian Brethren, the so-called Sandomierz Consensus (Consensus Sendomiriensis), an agreement reached in 1570 between a number of Protestant groups in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. At the synod, the Sandomierz Consensus was confirmed again, and the voivode rebuked the troublemakers (after "Wiadomość historyczna o Dyssydentach ..." by Józef Łukaszewicz, p. 103).
Stanisław was a son of Barbara Kurozwęcka (d. 1545) and Andrzej I Górka (1500-1551), an envoy who has studied and traveled abroad and made a close friendship with Duke Albert of Prussia (1490-1568), who visited him in Poznań during his meeting with Duke Frederick II of Legnica (1480-1547). The Górkas were Imperial counts (title granted by Emperor Charles V in 1520 or 1534). Between 1554-1555 Stanisław studied at the University of Wittenberg. In 1557 he participated in the campaign of the Polish-Lithuanian army against the Livonian Order and in 1565 he took part in the Livonian War. After death of Sigismund II Augustus in 1572 he supported the candidacy of the High Burgrave of Bohemia William of Rožmberk and then the French prince Henry of Valois during the royal election. In 1573, after the death of his elder brother Łukasz III (d. 1573), Stanisław received the post of voivode of Poznań. In 1574 he met Henry of Valois on the border of the Commonwealth and he entertained him in Kórnik. He initially stongly opposed the the camp of "Cezarians" (imperial supporters), and sided with the nobles shouting that they prefer the devil to a Habsburg (after "Infuły i szyszaki ..." by Amelia Lączyńska, p. 188), but eventually he sided with them (from about 1578) and in 1588 he fought at Byczyna against Jan Zamoyski. From then on, he was in opposition to the king until the end of his life. His marriage to Jadwiga Sobocka remained childless and as a result the Górka family died out in the male line. His huge estates together with Kórnik became the property of his nephew Jan Czarnkowski (d. 1618/19). Stanisław maintained contacts with leaders of the Lutheran community, like Philip Melanchthon and Duke Albert of Prussia and during the second interregnum, he was even considered as a candidate for the throne. In 1573, he came into conflict with the chapter of the Poznań cathedral. It was about refusing the burial of his brother Łukasz III, an ardent Lutheran, in the family chapel in the Poznań cathedral. He decided to build a new chapel in the family seat in Kórnik, a Protestant mausoleum modelled on royal Sigismund Chapel in Kraków (after "Rezydencja Stanisława Górki ..." by Katarzyna Janicka, pp. 93, 103, 105). Eight years before his death, in 1584, he signed a contract with Dutch sculptor Hendrik Horst (d. 1612), active in Lviv, to whom he commissioned the execution of marble-alabaster tombstones for himself and his brothers Łukasz (d. 1573) and Andrzej II (d. 1583) and an alabaster crucifix. At that time, Horst and his workshop also worked on tombstones of voivodes of Ruthenia in Berezhany (1582-1586). Large quantities of Lviv alabaster were imported to Poznań and Kórnik - only in 1592 three coachmen from Skierniewice delivered to "Stheinszneider [stone cutter] Henryk [Hendrik Horst]" 30 pieces of "Ruthenian marble" for the mausoleum (after "Mauzoleum Górków w Kórniku" by Jan Harasimowicz, p. 290). This commission, completed after the death of Stanisław Górka by his nephew Jan Czarnkowski, has not survived in its original form as Kórnik suffered particularly severely during the Deluge (1655-1660), when the army of the Elector of Brandenburg stationed there. Later the mausoleum was transformed into a Marian chapel between 1735-1737. The count was one of the richest men of that time in the Commonwealth. His fortune consisted of the property of the Górkas in Greater Poland, Lesser Poland and in Ruthenia. Stanisław and his brother Andrzej also actively participated in the grain trade in the 1570s by sending transports to Pomerania (after "Studia z dziejów Ziemi lubuskiej" by Władysław Korcz, p. 116). Almost throughout the 16th century, Poland enjoyed an excellent grain boom, therefore Venice and the Duchy of Tuscany, affected by crop failures and famine in the western Mediterranean, became directly interested in import of Polish grain, however, the transport was organized by the Dutch (after "Ceny, płace i koszty utrzymania ..." by Antoni Mączak, p. 763), who also controlled the grain trade in Pomerania. Much of the grain also went to the Netherlands, so luxury goods were acquired and ordered there. Already in the Middle Ages, wealthy patrons from Poland recognized the quality of Netherlandish craftsmanship. Janusz Suchywilk (d. 1382), Chancellor and Archbishop of Gniezno and Andrzej Bniński (1396-1479), Bishop of Poznań, ordered their tomb slabs in Flanders (after "Polskie nagrobki gotyckie" by Przemysław Mrozowski, pp. 47, 90). The monument to Andrzej I and Barbara Górka née Kurozwęcka in Poznań Cathedral, founded by Andrzej II, was created in Kraków by Girolamo Canavesi from Milan and transported to Poznań. The Latin inscription on the cornice at eye level is an advertisement of his workshop in Kraków - "The work of Girolamo Canavesi, who lives in Kraków at St. Florian's Street, in the year of the Lord 1574" (Opus Hieronimi Canavexi qui manet Cracoviae in platea S. Floriani A.D. 1574). The residences of the Górkas in Poznań and Kórnik were also filled with exquisite works of art. "The house was decorated with so much gold, silver, and [Flemish?] tapestries that it would not easily be inferior to any prince's [abode] in all its ornamentation", describes the Górka Palace in Poznań a chronicler after the meeting concerning the situation of Protestants in Prussia, Germany, Greater Poland and Silesia in November 1543. Following the example of the kings, Stanisław maintained his own music band and his house in Poznań was called "the house of weddings and music" (dom godów i muzyki). German composer Hermann Finck (1527-1558) dedicated his five volumes of Practica Mvsica on musical theory and the performance of vocal music, published in Wittenberg in 1556, to Górka brothers (DOMINIS COMITIBVS A GORCA MAGNIFICO DOMINO LVCAE PALATINO BRZESTENSI, ANDREAE & Stanislao Buscensibus ...) and addressed a separate dedication to Stanisław (Fuit eximia erga me quoque liberalitas Celsitudinis tuae, Ilustris Domine Stanislæ). In the Royal Museums of Fine Arts of Belgium in Brussels, there is a portrait of a man by Adriaen Thomasz. Key (oil on panel, 86 x 63 cm, inventory number 3621). It was signed by the painter (monogram on the book: ATK) and comes from the bequest of painter Paul Hamman, purchased from Thomas Agnew & Sons gallery in London in 1902. The man in a strict pose and attire, like a judge, holds his hand on a book, possibly a bible, as if indicating that what is written in it is the most important. There are several rings on a pointing finger of his left hand one of which is clearly a signet ring with his coat of arms (indistinct), so the man is a wealthy aristocrat. According to Latin inscription in upper part of the painting he was 42 in 1580 (1580. / ÆTA.42.), exaclty as Count Stanisław Górka, when he presided the synod of the Protestants in Poznań. Exact, reduced copy of this painting was sold in New York in 2003 (oil on paper on panel, 82 x 48.5 cm, sold at Christie's on January 24, 2003, lot 52). The same man was depicted in a "Portrait of a gentleman" (Retrato de caballero) in a Dutch-style frame in carved, ebonized and polychromed wood imitating tortoiseshell, sold in Seville (oil on canvas, 44 x 33 cm, Isbilya Subastas, June 22, 2022, lot 80). The shape of his small ruff is typical of Western European fashion in the 1560s, similar to that seen in a portrait of a gentleman with a hunting dog by Anthonis Mor dated '1569' (signed upper left: Antonius mor pingebat a. 1569, National Gallery of Art in Washington, 1937.1.52). The painting is attributed to the Italian school of the 17th century, however, stylistically the closest is the portrait of Martín de Gurrea y Aragón (1526-1581), Duke of Villahermosa and count of Ribagorza, attributed to circle of Anthonis Mor, which was before 1935 in Vienna (Nationalmuseum in Stockholm, NM 3233). Similar soft brushstrokes are also seen in other works attributed to Mor - portrait of Giovanni Battista di Castaldo (Thyssen-Bornemisza Museum) and portrait of Alfonso d'Avalos (Czartoryski Museum). The shape of the man's ear from the Seville portrait is slightly different from Key's paintings, however comparison with the portraits of King Philip II by Mor and his studio indicates that even the same painter and his entourage were not so strict in this regard. The portrait sold in Seville is in fact a copy of a painting attributed to Mor, the existence of which was notified to me by ArteDelToro on February 2, 2024. This "Portrait of a Gentleman, bust-length, in a dark slashed doublet and ruff" was sold in 1998 in London (oil on panel, 42.5 x 32.4 cm, Christie's, auction 5944, April 24, 1998, lot 44). The monogram incised on the reverse testifies that it belonged to Don Gaspar Méndez de Haro (1629-1687), 7th Marquis of Carpio. The marquis, who died in Naples, was an important art collector and acquired many splendid paintings in Italy, including several works by Tintoretto, Christ Crowned with Thorns by Antonello da Messina (Metropolitan Museum of Art, 32.100.82) or the Adoration of the Child by Lorenzo Lotto with disguised portrait of Catherine Cornaro, Queen of Cyprus as Saint Catherine (National Museum in Kraków, MNK XII-A-639). He also owned the portrait of John Sigismund Zapolya, King of Hungary by Tintoretto and the portrait of Clara of Brunswick-Lüneburg (1550-1598), Duchess of Pomerania by Giovanni Battista Moroni, identified by me. Anthonis traveled widely and painted the most important monarchs and aristocrats of Western Europe. Perhaps his visit to Poland or Stanisław Górka's stay in Antwerp are yet to be discovered, but as with many of his portraits of monarchs, the painter and his studio had to rely heavily on preparatory drawings, similar to sculptors creating tombstones with carvings of the deceased. Wanting and expecting high quality, the count could send drawings by local or court artists, similar to Clouet's crayons, to Antwerp or painting workshops to sent their pupils to different places (including to Poznań), as Cranach and most likely Canavesi did, to create initial drawings. The man in the described portraits bears a strong resemblance to the voivode of Poznań from his funerary monument in Kórnik, effigy of his great-grandfather Andrzej Szamotulski (d. 1511), voivode of Poznań as a donor (Virgin and Child with Saint Anne, Saint Andrew and Saint Jerome, ca. 1521, Collegiate Church in Szamotuły) and his grandfather Łukasz II Górka (1482-1542), general starost of Greater Poland as a donor (Annunciation by Master of Szamotuły, 1529, Kórnik Castle, founded by Łukasz II to the Górka Chapel at the Poznań Cathedral).
Portrait of Count Stanisław Górka (1538-1592) by Anthonis Mor, 1560s, Private collection.
Portrait of Count Stanisław Górka (1538-1592) by circle of Anthonis Mor, 1560s, Private collection.
Portrait of Count Stanisław Górka (1538-1592), voivode of Poznań, aged 42 by Adriaen Thomasz. Key, 1580, Royal Museums of Fine Arts of Belgium in Brussels.
Portrait of Count Stanisław Górka (1538-1592), voivode of Poznań by Adriaen Thomasz. Key, ca. 1580, Private collection.
Portraits of Nicolaus Christopher Radziwill "the Orphan" by Domenico Tintoretto and Francesco Bassano
Around 1550 in Lukiškės, a part of the city of Vilnius, located to the west and southwest of the Old Town, Nicolaus "the Black" Radziwill (1515-1565), cousin of Queen Barbara, built a magnificent renaissance villa or a summer manor house, beautifully located in the bend of the Neris river, surrounded by the steep banks of the river and a pine forest. The estate was owned by the Radziwill family from 1522 and called Radziwill Lukiškės, later Vingis in Lithuanian or Zakręt in Polish, both meaning a bend or a curve.
Lukiškės (Łukiszki in Polish) took its name from the name of a merchant, Łuka Pietrowicz, most probably a Ruthenian, who founded a settlement here in the 14th century in the land given to him by Vytautas the Great. It was also here that Vytautas settled the Tatars, who had their mosque in Lukiškės, and in the 15th century the district was also called Tatar Lukiškės (after "Przewodnik po Wilnie" by Władysław Zahorski, p.83). Nicolaus "the Black", the strongest supporter of the Reformation in Lithuania, arranged a chapel for the Calvinists in one of the rooms. Protestants were active in the manor in the years 1553-1561, and the estate became the cradle of the Reformation in Lithuania. "In a room covered with a pall, in front of a table on which there were branched candlesticks with three Graces of Greek mythology, Czechowicz with Wędrychowski, Catholic priests in the past, taught from the pulpit the Lithuanian nobility", wrote Teodor Narbutt in his work published in Vilnius in 1856 ("Pomniejsze pisma historyczne szczególnie do historyi Litwy odnoszące się", p. 66). In 1558 a reformed school also started operating in the palace. Nicolaus "the Black" died in Lukiškės in May 28/29, 1565 and the estate was inherited by his sons. The eldest, Nicolaus Christopher Radziwill "the Orphan" (1549-1616), received his primary education in Lukiškės in the Protestant gymnasium founded by his father. "In the 1550s and the 1560s the palace in Lukiškės was one of the most important centers of political, religious and cultural life of the then Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth" (after "Miles Christianus et peregrinus: fundacje Mikołaja Radziwiłła "Sierotki" w ordynacji nieświeskiej" by Tadeusz Bernatowicz, p. 139). Between 1566-1574, the sons of Nicolaus "the Black" converted from Calvinism to Catholicism. According to legend, Nicolaus Christopher received the nickname "the Orphan" in early childhood. Allegedly, once the King Sigismund Augustus found the child left unattended in one of the rooms of the royal palace, he caressed the child saying: "poor orphan". On June 20, 1569 he was granted the post of Court Marshal of Lithuania. Soon "the Orphan" became close to the king and carried out his personal assignments until his death. In 1567, Nicolaus Christopher "the Orphan" inherited his father's estate and became the guardian of his younger brothers and sisters. He was a capable diplomat and in 1573, he headed the embassy to Paris to Henry of Valois. The journey at the turn of 1573 and 1574 lasted six months. After returning to the Commonwealth, he fell seriously ill and vowed to make a pilgrimage to the Holy Land as soon as his health allowed. It is believed that Nicolaus Christopher was ill with gout and some kind of venereal disease. He set out in the autumn of 1580 and after treatment near Padua and Lucca, he spent the entire spring of 1581 in Venice, also visiting Padua and Bologna. There was a plague in the Middle East at that time, so "the Orphan" changed his plans and returned the Commonwealth in April 1581. In 1582 he again left for Italy, from where in 1583 he went to the Holy Land. Together with his brothers Albert (1558-1592) and Stanislaus (1559-1599), he created the Nesvizh, Kletsk and Olyka entails in 1586, becoming the first Nesvizh ordynat. He was also Grand Marshal of Lithuania from 1579 and castellan of Trakai from 1586. In 1584 Stanislaus, nicknamed "the Pious", first ordynat of Olyka, offered part of the Lukiškės estate to the Jesuits and in 1593 he also donated the remaining part of the Lukiškės estate with the palace and other buildings. Jesuit Lukiškės became the intellectual and cultural center of Vilnius at that time. In the years 1593-1774, traditional ceremonies of conferring academic degrees were held there. From 1646, there was a garden of medicinal herbs, and tinctures and mixtures were sold in the Jesuit Academic Pharmacy. In March 1647 the Jesuits offered a sumptuous feast in the villa in Lukiškės to the royal couple, Ladislaus IV and Marie Louise Gonzaga, who visited the academy. Between 1655 and 1660, during the Deluge, like much of the capital of Lithuania, Lukiškės and Tatar estates were destroyed. In the place of a manor house or near to it, in the years 1757-1761, the Jesuits built a baroque three-story palace to design by Johann Christoph Glaubitz. According to Teodor Narbutt ("Pomniejsze pisma historyczne szczególnie do historyi Litwy odnoszące się", p. 66-67), in the chapel in the left wing of the palace there was a beautiful painting of the "Three Marys going to the tomb of the Savior, painted by the Italian school", possibly from the Radziwill collection, lost after 1793. During his stays in Venice in 1580 or 1582 "the Orphan" commissioned a marble altar of the Holy Cross, created in 1583, which was originally intended for the parish church in Nesvizh, built in the years 1581-1584, later moved to the new Corpus Christi Church, constructed between 1587-1593 by Gian Maria Bernardoni. The altar is attributed to Girolamo Campagna (1549-1625), a sculptor from Verona and a pupil of Jacopo Sansovino, and a signature of his collaborator Cesare Franco (Franchi, Francus, Francho) from Padua is visible on the base: CESARE DE FRANCHI PATAVINO OPVS FEC ... /...CHI LAPICIDA VENETIIS 1583. The sculptures were probably transported to Nievizh in 1586, and the permit issued by the Doge of Venice, Pasquale Cicogna (1509-1595), for the transport of marbles probably concerns the altar of the Holy Cross (after "Rzeźby Campagni i Franco w Nieświeżu a wczesny barok" by Tadeusz Bernatowicz, p. 31) or other sculptures commissioned in Venice. Marble bust of a painter Francesco Bassano the Younger (1549-1592), the eldest son of Jacopo and brother of Leandro, from his tombstone in the church of San Francesco in Bassano (today in the Museo Civico di Bassano del Grappa), created in about 1592, is also attributed to Campagna as well as bust of Christopher Nicolaus Radziwill (1590-1607), Nicolaus Christopher's son, in the Corpus Christi Church in Nesvizh. Letter from courtier Rafał Kos of February 1, 1594 (AGAD reference number: 1/354/0/5/7374) written from Venice, which mentions a painter named Mazzuola, confirms that paintings were imported from Venice by Nicolaus Christopher "the Orphan" (after "W poszukiwaniu utraconej tożsamości" by Jolanta Meder-Kois, Izabella Wiercińska). Portrait of young man in a black coat lined with lynx fur and with a landscape visible in the distance through a window, was acquired by the Pushkin Museum in Moscow in the 1930s from an unknown source as the work of the painter from the Bassano circle (inventory number 2842). It is today attributed to Domenico Tintoretto (1560-1635), the eldest son of Jacopo, who from 1578 was already involved in Tintoretto's Gonzaga cycle and participated in the redecoration of the Doge's Palace between 1580 and 1584. The man presents his estate which resemble greatly the topography of the Vingis estate (Radziwill Lukiškės) in Vilnius, depicted on a map created in 1646 (collection of the Vilnius University), as well as on watercolor paintings by Seweryn Karol Smolikowski created in 1832 (National Museum in Warsaw, inventory number Rys.Pol.14339 MNW and Rys.Pol.14340 MNW), and by Marceli Januszkiewicz created in 1836 (National Museum of Lithuania). The architecture of his Italian-style villa is similar to the pavillons of the Radziwill Palace in Vilnius, the larger palace of the Calvinist branch of the family, depicted in 1653 medal by Sebastian Dadler. There is a church or a chapel far in the background with high tower, similar to that visible on 1646 map of Lukiškės (F), undoubtedly a Catholic temple. It can be assumed that it symbolizes the triumph of Catholicism over the cradle of the Reformation in Lithuania. The young man from the portrait is therefore the eldest son of Nicolaus "the Black", Nicolaus Christopher "the Orphan". He was depicted in very similar costume and in similar compositon (window, table) in a print created by Tomasz Makowski in Nesvizh in 1604 - Panegyric of the Skorulski brothers (Jan, Zachariasz and Mikołaj) on the occasion of receiving the office of voivode of Vilnius by Nicholaus Christopher (National Museum in Kraków, inventory number MNK III-ryc.-36976). The same man, in similar costume, was also represented in another painting which was attributed to Domenico Tintoretto - Portrait of a man holding his right hand on his heart. This work comes from the collection of Géza von Osmitz (1870-1967) in Bratislava (sold in Vienna, 12 March 1920, lot 68). The style of this painting is more close to the Bassanos, especially portrait of King Stephen Bathory by Francesco Bassano the Younger from the Ambras Castle, identified by me. The man from both described portraits bear a great resemblance to effigies of Nicolaus Christopher, all created in his later age, like engraving by Lukas Kilian, created in Augsburg in about 1610 (National Library in Warsaw, inventory number G.10401) or engraving by Dominicus Custos, published in 1601, after a drawing by the Veronese painter Giovanni Battista Fontana (1541-1587), who decorated the walls of the Spanish Hall at Ambras (Lithuanian Art Museum, inventory number LDKVR VR 667). A two sided miniature in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence (inventory number 1890, 4051, oil on copper, 10.2 cm) is on one side a reduced and simplified version of the painting by Bassano, showing the man in a similar pose but with a different hairstyle. Both portraits, although close to miniatures by the Bassanos in the Uffizi (1890, 4072, 9053, 9026), also relate to works of Sofonisba Anguissola, who moved to Sicily (1573), and later Pisa (1579) and Genoa (1581).
Portrait of Nicolaus Christopher Radziwill "the Orphan" (1549-1616) with a view of the Vingis estate (Radziwill Lukiškės) in Vilnius by Domenico Tintoretto, 1580-1586, Pushkin State Museum of Fine Arts in Moscow.
Portrait of Nicolaus Christopher Radziwill "the Orphan" (1549-1616) by Francesco Bassano the Younger or workshop, 1580-1586, Private collection.
Miniature portrait of Nicolaus Christopher Radziwill "the Orphan" (1549-1616) by workshop of the Bassanos or Sofonisba Anguissola, 1580-1586, Uffizi Gallery.
Portrait of Gustav Eriksson Vasa by Sofonisba Anguissola
In 1575 another inconvenient royal child was sent to be raised abroad, this time from Sweden to Poland. In August 1563 King Eric XIV of Sweden imprisoned Catherine Jagiellon, Duchess of Finland in Gripsholm Castle. She was released in 1567, but during this four-year imprisonment she gave birth to a daughter and a son, future Sigismund III. Catherine was crowned queen of Sweden in spring of 1569, when Eric was deposed. In March 1575, the Swedish Council of State decided to separate the seven-year-old boy Gustav Eriksson Vasa, the only son of Eric XIV, from his mother Karin Månsdotter, as king John III feared that the deposed Eric's followers in Sweden would use Gustav to be able to carry out their reinstatement plans. At Catherine's request her sister Anna agreed to take care of him.
He was well educated, attended the best Jesuit schools in Toruń and Vilnius and Collegium Hosianum in Braniewo. He knew many languages as well as astrology, chemistry and medicine. He travelled to Rome in 1586 and to Prague to meet Emperor Rudolf II, who learned about his chemical talent. As education and travel at that time were far more expensive than nowadays, he was not living in poverty as a prisoner or even a slave in chains in a poor and barbaric country, as some people want to believe. A small portrait of a child by Sofonisba Anguissola in profuse mannerist frame from private collection in Switzerland (oil on wood, 37 x 28 cm, sold at Van Ham Kunstauktionen in Cologne, June 2, 2021, lot 926) shows a boy wearing an elegant black velvet doublet trimmed in gold, black hose and a black cape, like an attendant of the Jesuit school. The boy's features are very similar to these known from portraits of Eric XIV, his daughter Sigrid and to the portrait of a woman from Gripsholm Castle from about 1580, which is identified as Eric's step-sister Princess Elizabeth or his wife Karin Månsdotter. His pose and costume are almost identical with these visible in portrait of king John III of Sweden, husband of Catherine Jagiellon and Gustav Eriksson's uncle, in the Nationalmuseum in Stockholm, a copy of original portrait by Johan Baptista van Uther from 1582. Anguissola's portrait can be threfore dated to 1582, a year when Gustav Eriksson reached his legal age of 14, and it was commissioned by his foster mother, proud of her boy starting education, most probably as one of a series for herself, her friends in Poland and abroad.
Portrait of Gustav Eriksson Vasa (1568-1607) by Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1582, Private collection.
Portrait of the Beautiful Nana and her husband by Sofonisba Anguissola
Another mysterious portrait by Anguissola from the 1580s was acquired in 1949 by the National Museum in Warsaw from private collection (oil on canvas, 60 x 48.5 cm, inventory number M.Ob.1079 MNW). It was previously attributed to Giovanni Battista Moroni and it shows a man with his daughter.
The girl is holding a flower with four petals, similar to a primrose considered as a symbol of true (faithful) love, just as in "The Primrose" by John Donne (1572-1631), to white Caucasian rockcress (Arabis caucasica) or myrtle, consecrated to Venus, goddess of love and used in bridal wreaths - Pliny call it the "nuptial myrtle" (Myrtus coniugalis, Natural History, XV 122). She wears a coral necklace, a fertility symbol in ancient Rome (after Gerald W. R. Ward's "The Grove Encyclopedia of Materials and Techniques in Art", 2008, p. 145), as in portraits of young brides by Florentine painter Domenico Ghirlandaio and in Polish folk costumes, and a symbol of protection, meant to bring good luck, as in portraits of court dwarf Magdalena Ruiz. The red-haired man with blue eyes holds firmly a hand of young blue-eyed blond girl, this is not her father, this is her husband. In 1581 Anna Jagiellon sent to her friend Bianca Cappello, Grand Duchess of Tuscany, one pretty, graceful female dwarf who could dance and sing. Monsignor Alberto Bolognetti, Bishop of Massa Marittima organized a travel for her from Warsaw through Kraków and Vienna. She was accompanied by "a Polish Gentleman named Mr. Giovanni Kobilmiczhi, and I [...] lingua Cobilnisczi, who is setting off in a carriage. I believe that the girl will feel comfortable, being highly recommended to the gentleman, and provided with whatever she needs to protect her from cold" (un Gentilhuomo Polaco nominato Signore Giovanni Kobilmiczhi, et mi [...] lingua Cobilnisczi, Il quale mettendo a viaggio in carozza. Mi credo che la fanciulla si condurrà comodamente, havendola lo massime al gentilhuomo molto raccomandata, et provista di qual che suo bisogno per difenderla dal freddo), according to the letter of February 15, 1581. The man was most probably Jan Kobylnicki, a courtier of king Stephen Bathory. Beautiful Nana (Italian for female dwarf) was probably married after her arrival to Florence, possibly even with Kobylnicki or other Pole, and it was probably the Queen who commissioned her portrait with her husband from Anguissola, who moved from Pisa near Florence to Genoa in 1581. Consequently a two-sided portrait miniature of a female dwarf and her husband in the Uffizi Gallery (oil on copper, 7.2 x 5.6 cm, Inv. 1890, n. 4086) painted in the style of Sofonisba from the same period, should be considered as effigy of parents of beautiful Nana.
Portrait of the Beautiful Nana and her husband by Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1581-1582, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait miniature of mother of the Beautiful Nana by Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1581-1582, Uffizi Gallery in Florence.
Portrait miniature of father of the Beautiful Nana by Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1581-1582, Uffizi Gallery in Florence.
Portrait of Cardinal Alberto Bolognetti by Lavinia Fontana or studio
In a letter dated April 12, 1581 addressed to King Stephen Bathory, Pope Gregory XIII announced the appointment of Alberto Bolognetti (1538-1585), Bishop of Massa Marittima, as nuncio to the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. Shortly after his arrival in April 1582, Bolognetti was welcomed by Queen Anna Jagiellon at her rich wooden palace of Jazdów (Ujazdów) in Warsaw, where he admired the tapestries "made of silk and gold" left to her by her brother king Sigismund Augustus, the garden with "vines and other plants that the king had brought from Hungary", and a dining room "entirely decorated with beautiful arrases with plants and animals made of gold and silk, at the top of which was a royal canopy and under it two small tables joined together and covered with the same tablecloths" (mi condusse ad una parte ornata tutta di razzi bellisimi di boscaglie et animali pur d’oro et di seta, in capo della quale era un baldachino regale et sotto quello dui tavolini congiunti insieme et coperti dalie medesime tovaglie), which he described in a letter to Cardinal Tolomeo Gallio (1527-1607).
Alberto, born and educated in Bologna, where he obtained a doctorate in law on May 23, 1562 at the university, became a clerk and professor of civil law there. In 1574, he moved to Rome and was appointed apostolic protonotary by Pope Gregory XIII. Then he was nuncio to Grand Duke Francesco I in Florence from February 25, 1576 to September 10, 1578 and in the Republic of Venice from September 10, 1578. His departure from Venice, at the end of March 1581, was quite sudden and soon after he arrived in Rome, he left for Poland. In 1582, Bolognetti persuaded King Stephen to implement the bull of Gregory XIII which established the Gregorian calendar and to found the first Jesuit house in Kraków. Pope Gregory XIII made him a cardinal during the consistory of December 12, 1583. However, he never received the red hat or a titular church since he died before he could come to Rome for the ceremonies. In its pride at the elevation of Cardinal Alberto, the Senate of Bologna granted him an annual pension of 500 gold scudi. The cardinal died of fever at Villach in Carinthia in May 1585, while returning from Poland to participate in the papal conclave of 1585. He was buried in his family tomb in the church of Santa Maria dei Servi in Bologna. In the Wilanów Palace in Warsaw there is a portrait of Cardinal Bolognetti (oil on canvas, 125 x 92 cm, Wil.6185) presenting a letter addressed to him (All Illmo. et Rev. Mons/re / Il S. Card. Bolognetti mio sig/re Oss./mo / In Polonia), most probably the letter of appointment to the cardinalate from the pope. Therefore, it must have been created in 1583 and before 1585. The painting is mentioned in the 1893 description of the palace - "Abelardus Bolognetti, cardinal and nuncio, in Poland in 1583 under Stephen Bathory" ("Willanów, Czerniaków, Morysin ..." by Wiktor Czajewski, item 807, p. 155), after a portrait of Cardinal George Radziwill (article 804). It is possible that it was initially in the collection of Queen Anna Jagiellon in Warsaw. The painting is attributed to an Italian painter. Its style most closely resembles the portrait of Raffaele Riario, which was most likely in the Riario-Sforza collection in Rome (sold at Dorotheum in Vienna, April 24, 2018, lot 52). Raffaele holds a letter from the Duke of Bavaria in his hands and the writing style is also very similar. Riario's portrait was initially attributed to the Lombard school, then to Lavinia Fontana, a painter active in Bologna and Rome, who created the miniature portrait of King Stephen Bathory (National Museum in Kraków, MNK I-290). The pose of the model and the style of the painting are also comparable to two works signed by Lavinia - portrait of a man with a book, said to be senator Orsini, from 1575, at the Musée des Beaux-Arts de Bordeaux (signed and dated: LAVINIA FONTANA DE ZAPPIS FACIEBAT MDLXXV, inventory number Bx E 197) and portrait of a young man at a table from Rohde-Hinze collection in Berlin, dated 1581 (LAVINIA FONT: DE ZAPPIS FAC. MDLXXXI). It is also similar to the unsigned work - portrait of Pope Gregory XIII with inscription GREGORIVS.XIII.PONT. OPT. MAX (sold at Christie's, May 18, 2017, lot 563). Therefore, as in the case of the portrait of King Bathory, the Bolognetti portrait was most likely painted by Fontana from study drawings sent from Poland.
Portrait of Cardinal Alberto Bolognetti (1538-1585), Apostolic Legate to the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth by Lavinia Fontana or studio, ca. 1583, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
Portraits of Tomasz Treter by Lavinia Fontana
In 1583 Tomasz Treter (1547-1610), secretary to Cardinal Stanisław Hozjusz, published in Rome his major work Romanorvm imperatorvm effigies ... with effigies and short biographies of Roman emperors ending with Rudolf II, grandson of Anna Jagiellonica (1503-1547). He dedicated his book to King Stephen Bathory (1533-1586), elected co-ruler of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth as husband of Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596). The engravings in this work, among which the magnificent coat of arms of the king, were made by Giovanni Battista de Cavalieri, very probably after drawings by Treter. He was also a poet, philologist, heraldist, engraver and translator. His prints he sent to various European monarchs, including Francesco I de' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany. He is the author of two famous engravings related to the Polish-Lithuanian monarchs - Castrum doloris of Sigismund Augustus in Rome from 1572 and Eagle with the galaxy of Polish kings also called Eagle of Treter with 44 medallions of Polish monarchs from Lech to Sigismund III, created in 1588. Together with Stanisław Pachołowiecki he developed a map of Polotsk (Descriptio Dvcatvs Polocensis), during the campaign of King Stephen Bathory in 1579, engraved by Giovanni Battista de Cavalieri (Joa. Baptista de Cauallerijs tipis aeneis incidebat Anno Domini 1580).
Treter was the son of Jakub, a bookbinder from Poznań, and Agnieszka née Różanowska and after studies in Poznań and Braniewo, he went to Rome in 1569, where he studied theology and law. Tomasz obtained a doctorate in canon law and stayed in Rome for 22 years. He was the secretary of the bishops of Warmia: Stanisław Hozjusz and Andrew Bathory. He was a canon at the Lateran and the first superior of the Polish Hospice in Rome founded by Hozjusz and between 1579-1593 he was a canon at the Basilica of Santa Maria in Trastevere in Rome and a canon in Olomouc in Moravia. In July 1584 he returned to Poland and in December 1585 he was elected canon of Warmia. In 1586 Treter become secretary to Queen Anna Jagiellon. He then returned to Rome and was responsible for the construction of the mausoleum for queen's mother Bona Sforza in Bari. In a letter of May 26, 1590, Queen Anna informed Father Tomasz that a portrait of Bona had been sent to his address, according to which the sculptors were to recreate the features of the deceased. Father Treter was also an artistic agent of the Polish-Lithuanian monarchs. Together with Stanisław Reszka and Andrzej Próchnicki, he bought paintings for the queen and the king, collected information about their prices and new painting talents that appeared in Italy (after "Zamek Królewski" by Jerzy Lileyko, p. 113). Between 1595 and 1600 he created beautifully illustrated manuscript with 105 drawings - Theatrum virtutum ac meritorum D. Stanislai Hosii, showing the episodes in the life of Cardinal Stanisław Hozjusz (National Library of Poland, Rps BOZ 130), in some of which he probably took part, like 70. Cardinal Stanisław Hozjusz dining with his courtiers (ABSTRACTIO A SENSIBVS), 76. Cardinal Stanisław Hozjusz at the Lublin Council before King Sigismund Augustus (PRAESENTIA IN COMITIIS LVBLINENSIB) or 77. Departure for Rome (PROFECTIO ROMAM SVSCEPTA). Treter died on February 11, 1610 in Frombork in Prussia. In the collection of Michelangelo Poletti in the Castello dei Manzoli in San Martino in Soverzano near Bologna there is a portrait of a man holding a letter by Bolognese painter Lavinia Fontana (oil on canvas, 98 x 82 cm), who in about 1585 created a miniature portrait of King Stephen Bathory (National Museum in Kraków, MNK I-290). The model in the black costume sits next to a desk with an inkwell, pen and clock. The Latin inscription on the chair indicates that the painting was created in 1583 (LAVINIA FONTANA DE / ZAPPIS FACIEBAT / MDLXXXIII), when Treter published his Romanorvm imperatorvm effigies ..., at the age of 36 and shortly before his return to Poland. That year, Lavinia also painted Antonietta Gonsalvus (Antonia González), daughter of Petrus Gonsalvus ("The Hairy Man"), who was staying with her family in Bologna or Rome. The same man was also depicted in another painting by the same artist, as the style indicates. This painting is now in the Lithuanian National Museum of Art in Vilnius (oil on canvas, 36.5 x 27 cm, LNDM T 3991). It is attributed to the Venetian school of the 17th century. He also wears a black outfit, but this portrait is a less formal, private, and therefore less idealized. He has an unbuttoned collar and his ruff is smaller and more comfortable. This portrait, the owner could easily take with him to the north.
Portrait of secretary Tomasz Treter (1547-1610) by Lavinia Fontana, 1580s, Lithuanian National Museum of Art.
Portrait of secretary Tomasz Treter (1547-1610) by Lavinia Fontana, 1583, Castello dei Manzoli.
Portraits of King Stephen Bathory in national costume by Italian painters
The majority of the surviving effigies of the king are attributed to the only painter (or his entourage/workshop) whose stay in Poland-Lithuania is confirmed - a Silesian Martin Kober from Wrocław, although stylistically some of them are very far from his confirmed works. Kober arrived in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in about 1583 from Magdeburg and became court painter to elected Queen Anna Jagiellon and her husband Stephen Bathory of Transylvania.
Only two signed works by Kober are known, but the late 16th century portraits of Sigismund III and his family, painted in a very distinctive style, can fairly be attributed to him. The signed works are a life-size portrait of King Stephen Bathory, signed with a monogram and date (MK / 15.83, Museum of the Missionary Fathers in Kraków) and a miniature likeness of Sigismund III from 1591, signed on the reverse in German (MARTINVS KÖBER RÖ : KEI : MAI : / VNDER- THENIGSTER BEFREITER MALER / VON BRESSLAV . VORFERTIGET / ZV WARSCHAV . DEN 30 APRILL . 1591., Wawel Royal Castle). After Bathory's death in 1586, Kober went abroad - from about 1587 he worked for Emperor Rudolf II in Prague and returned to Poland around 1589. In 1595 he went to Graz. Among the works attributed to Kober and his circle is a miniature of King Stephen Bathory in the National Museum in Kraków (oil on copper, 17.4 x 14.8 cm, MNK I-290), purchased in 1909. This undated portrait was made around 1585 because it shows the king at age of 52, according to the Latin inscription at the top left in the frame (STEPHAN[US] BATORİ DE / SCHVMLAİ ∙ REX POLO/NİÆ ∙ M:[AGNUS] DVX ∙ LITHVA/NİÆ ∙ PRİNCEPS ∙ TRAN/SİLVANİÆ ∙ ANNO ∙ÆTA/TİS Lİİ). The style of this painting is very distinctive and characteristic of Lavinia Fontana (1552-1614), a woman painter active at that time in Bologna in the Papal States and particularly close to her self-portrait in the studio, painted in 1579 (oil on copper, diameter 15.7 cm, Uffizi Gallery in Florence, inv. 1890, 4013). Even the inscriptions on both miniatures were created in the same style. Since Lavinia's stay in Poland-Lithuania is not confirmed, she probably received a miniature by Kober to copy. Another portrait of Bathory in Italian or more specifically Venetian style is in Wilanów Palace in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 108.5 x 73.8, Wil.1163, earlier 570), mentioned for the first time in an inventory from the mid-19th century. Its style is very close to the portrait of Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596) kept at the National Museum in Warsaw (MP 5323) and portrait of Bianca Cappello (1548-1587), Grand Duchess of Tuscany, a friend of Anna (sold at Capitolium Art in Brescia on October 17, 2018), both by Alessandro Maganza (before 1556-1632). Also Francesco Bassano the Younger, in 1586, the eldest son of Jacopo Bassano, who worked in the Bassano family workshop in Venice with his three brothers, received a portrait of the monarch by Kober to copy. This miniature, close in style to the earlier effigy of the monarch in Italian costume (Kunsthistorisches Museum Vienna, GG 5775) and the portrait of a Knight of Malta in the Civic Museum in Bassano del Grappa, both attributed to Francesco Bassano the Younger, was acquired by the Wawel Royal Castle in 2013 from a private collection. This painting bears the Latin inscription STEPHANVS I / REX POLONIE / ANNO / 1586 and because it reproduces the same known effigy of the monarch is it also linked to Kober or his circle. This was a universal practice and two engraved effigies of Bathory by Italian engravers were created from such effigies, most likely by Kober or another artist permanently or temporarily active in Poland-Lithuania. An engraver and goldsmith active in Venice and Padua Domenico (Zenoi) Zenoni (inscription: Stepano Battori Re di Polonia ...) and another anonymous engraver, active in Italy (inscription: Questy in 2 giornate uenuto d'Alba iulia, fece solenne entrata in Cracouia ...), received such effigy in 1576 to reproduce it in their prints.
Portrait of Stephen Bathory (1533-1586), elected co-ruler of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, in national costume by workshop of Alessandro Maganza, ca. 1583, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
Miniature portrait of Stephen Bathory (1533-1586), elected co-ruler of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, at the age of 52, in national costume by Lavinia Fontana, ca. 1585, National Museum in Kraków.
Miniature portrait of Stephen Bathory (1533-1586), elected co-ruler of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, in national costume by Francesco Bassano the Younger, 1586, Wawel Royal Castle.
Portraits of Griselda Bathory and Elżbieta Łucja Gostomska by Sofonisba Anguissola
To strengthen the influence of the Bathory family in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, king Stephen planned the marriage of his Calvinist niece Griselda (née Christine) with the widowed Grand Chancellor of the Crown, Jan Zamoyski, one of the most powerful men in the country.
They were married on June 12, 1583 at the Wawel Cathedral in Kraków. Griselda came to Kraków with a retinue of 1,100 people, including six hundred soldiers guarding the her dowry. The wedding celebration with truly royal splendor lasted ten days. After Bathory's death in 1586, Zamoyski helped Sigismund III Vasa gain the Polish throne, fighting in the brief civil war against the forces supporting the Habsburgs. Griselda died four years later on 14 March 1590 in Zamość, an ideal city designed by Venetian architect Bernardo Morando. The city was not far from the second largest city of the Commonwealth, Lviv, dominated by a Royal Castle. The portait of a young lady by Sofonisba Anguissola from the National Art Gallery in Lviv (oil on canvas, 115 x 92 cm, inventory number Ж-821) is very similar to the portrait of Anna Radziwill née Kettler from about 1586 in the National Museum in Warsaw. Anna Radziwill was a wife of a brother of first wife of Zamoyski. Their headdresses or bonnets are very much alike, as well as the dress, ruff, jewels and even the pose. The woman in Anguissola's painting is holding a zibellino, a symbol of a bride, and a small book, most probably a Protestant bible. The features of the woman's face are very similar to portraits of Griselda's uncle, cousin and brother. The painting comes from the collection of Countess Eleonora Teresa Jadwiga Lubomirska née Husarzewska (1866-1940) and was exhibited in Lviv in 1909 as "Portrait of a lady in Spanish dress" (after "Katalog ilustrowany wystawy mistrzów dawnych ..." by Mieczysław Treter, item 53, p. 19). According to the catalogs of this exhibition, the painting was signed and dated 1558 in the upper left corner (Sofonisba Angusciola F. MDLVIII.), but this date is unreliable because the model's costume is much later. A miniature in Sofonisba's style in the Uffizi Gallery (oil on copper, 6.7 x 5.1 cm, Inv. 1890, 9048, Palatina 778), shows a girl in very similar dress inspired by Spanish fashion to that in Lviv portrait. Her jewelled headdress is not Western however, it is in Eastern style and similar to Russian kokoshnik (from the Old Slavic kokosh, which means "hen" or "cockerel"). Such headdresses carried the idea of fertility and were popular in different Slavic countries. In Poland they preserved in some folk costumes (wianek, złotnica, czółko) and become dominant at the court of Queen Constance of Austria in Warsaw in the 1610s and 1620s. The girl is therefore Elżbieta Łucja Gostomska (later Sieniawska), who in about 1587 at the age of 13 (born 13 December 1573), entered the court of Anna Jagiellon and whose miniature the Queen could send to her friend Bianca Cappello in Florence. She was the child of a Calvinist Anzelm Gostomski (d. 1588), voivode of Rawa. Her mother, Zofia Szczawińska, fourth wife of Anzelm, who raised her in Sierpc was affraid that her beautiful and wealthy daughter would be abducted by suitors. In 1590, despite her aversion to marriage, she married the Calvinist Prokop Sieniawski, then the court cupbearer, whom Queen Anna and her relatives chose for her. Consequently also other portrait, depicting a lady with a pendant with Allegory of Abundance, and attributed to Spanish school (Alonso Sánchez Coello) could be a work of Anguissola and identified as a court lady of Anna Jagiellon. She could be Dorota Wielopolska, lady-in-waiting of the Queen who in May 1576 married Piotr Potulicki, Castellan of Przemyśl. The queen organized for her a lavish feast and a tournament at the Wawel Castle. The painting was aquired by the National Museum in Kraków from a private collection in Gdów near Wieliczka, which was owned by the Wielopolski family.
Portrait of Griselda Bathory (1569-1590) by Sofonisba Anguissola, 1586-1587, National Art Gallery in Lviv.
Miniature portrait of Elżbieta Łucja Gostomska (1573-1624) by Sofonisba Anguissola, 1586-1587, Uffizi Gallery in Florence.
Portrait of a young woman with a pendant with Allegory of Abundance, most probably Dorota Wielopolska by Sofonisba Anguissola, 1580s, National Museum in Kraków.
Portraits of Elizabeth Euphemia Radziwill by Francesco Montemezzano and Alessandro Maganza
Ruthenian Princess Elizaveta Yevfimiya (Elizabeth Euphemia) Vyshnevetska or Elżbieta Eufemia Wiśniowiecka, also known as Halszka, was born in 1569 in the Calvinist family of the voivode of Volhynia and starost of Lutsk, Prince Andriy Vyshnevetsky (1528-1584) and his wife Eufemia Wierzbicka (1539-1589), as the firstborn child. After her father's death, she inherited large estates near Minsk and according to her mother's decision, on November 24, 1584 in Dzieraunaja (Derewna) in present-day Belarus, she married Nicolaus Christopher Radziwill "the Orphan" (1549-1616). She was 20 years younger than Radziwill and only 15 years old. Radziwill, who had just returned from a pilgrimage to the Holy Land in 1582-1584 (via Venice), succeeded in convincing the future wife and her mother to abandon Calvinism and convert to Catholicism. A few months after the wedding, in a letter dated February 25, 1585, he personally informed Pope Gregory XIII about this fact. The formal conversion may have taken place later, since in 1587 in a letter of April 18, Cardinal Alessandro Peretti di Montalto (1571-1623), congratulates him for having made her change her faith. "The Orphan" became a staunch, not to say fanatical Catholic, when he contracted a venereal disease (probably syphilis) during his stay abroad and the intensive treatment that the prince underwent both in Poland and abroad (mainly in Italy) has proven to be effective (after "Elżbieta Eufemia z Wiśniowieckich ..." by Jerzy Flisiński, Słowo Podlasia).
Elizabeth Euphemia bore her husband 3 daughters and 6 sons and their firstborn child Elizabeth was born soon after the marriage in 1585. In the spring of 1593 the prince and his wife went to Italy for treatment in the hot springs near Padua in the Venetian Republic. The place was also symbolic as the Radziwill family claimed lineage from an ancient mythical nobleman Palemon (Publius Libon) of Colonna (Column) coat of arms, who is sometimes described as a Roman or a fugitive from the Venetian lagoons. Medical advice was also at stake, which was sought from famous doctors in Padua and Venice. After few months of treatment, in October 1593, they returned directly to the country, disappointing Cardinal Montalto, Cardinal Protector of the Kingdom of Poland (from 1589), who was expecting a visit from Radziwill and his wife in Rome. Together with her husband Elizabeth Euphemia founded many churches and monasteries, some of which were designed by an Italian architect and a Jesuit Giovanni Maria Bernardoni (1541-1605). Very little information preserved about other members of the Radziwill court or the artists. In 1604, the prince's court physician was paid 400 zlotys a year, and the equerry, the Italian Carlo Arigoni, was paid 124 zlotys a year. Another Italian Bartol Faragoi was a page in 1604. In 1597, Nicolaus Christopher wrote a letter to the city council of Riga about Cornelius de Heda, a Dutch painter (as his name suggests) brought from Italy, who was to carry out painting work in Niasviz (Nesvizh), but he fled with money not fulfilling his obligations. In his last will "the Orphan" ordered foreign craftsmen to be paid and sent away (after "Lituano-Slavica Posnaniensia", Volumes 8-10, p. 202). The most important sculptures related to Radziwill and his wife were all imported from Venice - marble altar, marble epitaphs of Nicolaus Christopher, Elizabeth Euphemia and their son Christopher Nicolaus Radziwill (1590-1607) in Corpus Christi Church in Nesvizh were all created in Venice by Girolamo Campagna and Cesare Franco. Elizabeth Euphemia died on November 9, 1596 in Biała Podlaska at the age of 27. She was buried in the church of Corpus Christi in Niasviz, in the crypt of the Radziwill family. After her death, Nicolaus Christopher decided to remain a widower for the rest of his life. In the Gösta Serlachius Museum of Fine Arts in Mänttä, Finland, there is a portrait of a noblewoman in elaborate Venetian costume (oil on canvas, 120 x 92.5 cm, inventory number 286). Based on the painting style, it was initially attributed to Giovanni Antonio Fasolo (1530-1572), a painter of the Venetian school, active in Vicenza and surroundings, thus dated to around 1572. It was believed that the woman depicted was the artist's daughter, Isabella, who married in 1572 and that the painting was a wedding portrait. New research claims that it was created around 1580 in the workshop of Paolo Veronese. The painting comes from the collection of a Finnish industrialist and art collector Gösta Michael Serlachius (1876-1942). It is not known where and when he acquired the painting. The possible location seems to be St. Petersburg, where his family owned a brewery and which at the time was the largest art market in the nearest region and where many art collections from the former Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth were transferred after the end of the 18th century. Comparison with Venetian costumes from the last quarter of the 16th century indicates that the portrait was created around the turn of the 1580s and 1590s and that this woman was a noble, as the closest similar costume was depicted in Cesare Vecellio's De gli habiti antichi, e moderni ..., published in Venice in 1590 (Spose nobili moderne, plate 310). Similar costumes were also depicted in the Book of Italian Costumes by Niclauss Kippell, painted in about 1588 (Walters Art Museum, W.477.15R) and in Pietro Bertelli's Diversarum nationum habitus, published in 1589. According to the Latin inscription in the upper right corner of the painting, the woman was 18 when the painting was created (Ao. ÆTATIS SVE. / XVIII.), exactly like Elizabeth Euphemia when her conversion was confirmed in Rome. The woman in the portrait bears a strong resemblance to Princess Radziwill from her partially imaginative portrait by the Polish-Lithuanian painter Wincenty Sleńdziński from 1884 (Mir Castle complex in Belarus), her effigy published in 1758 in Icones familiæ ducalis Radivilianæ ... as well as the facial features of her third son Albert Ladislaus Radziwill (1589-1636) from his portrait in the National Museum in Warsaw (MP 4431 MNW). The style of the painting is very similar to the portrait of Elizabeth Euphemia's brother-in-law Stanislaus Radziwill (1559-1599) in the National Museum of Art in Kaunas in Lithuania (ČDM MŽ 139) and the effigy of Bianca Cappello (1548-1587), Grand Duchess of Tuscany (private collection), attributed to Alessandro Maganza (d. 1632), a pupil of Giovanni Antonio Fasolo. Maganza obviously worked for the Radziwills and many other clients from Poland-Lithuania, as many other paintings of a similar style exist in the former territories of the Commonwealth. The same woman in a similar costume was depicted in another painting by the eminent Venetian painter Francesco Montemezzano (oil on canvas, 91.4 x 74.3 cm), who between 1575 and 1585 created Allegorical portrait of Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596), elected co-ruler of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth (Czartoryski Museum, XII-227). The painting comes from a private collection and was sold in 2019 in New York (Christie's, May 1, 2019, live auction 17467, lot 303). She wears a crown of a princess and her hair is loose like on the effigies of young brides. Like for another Radziwill Princess, Katarzyna Tęczyńska (d. 1592), the effigies of Elizabeth Euphemia were painted by Maganza and Montemezzano from sketches sent from the Commonwealth. Similar to the sculptures for their mausoleum that the Radziwills commissioned in Venice, their effigies and other paintings were therefore mostly created there as well.
Portrait of Princess Elizabeth Euphemia Radziwill née Vyshnevetska (1569-1596) as a bride in Venetian costume by Francesco Montemezzano, ca. 1584-1587, Private collection.
Portrait of Princess Elizabeth Euphemia Radziwill née Vyshnevetska (1569-1596), aged 18, in Venetian costume by Alessandro Maganza, ca. 1587, Gösta Serlachius Museum of Fine Arts in Mänttä.
Portrait of Anna Kettler by workshop of Alessandro Maganza
Another Venetian-style portrait of the member of the Radziwill family from the same period is in the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 156 x 103 cm, MP 2472, earlier 233159). It is a portrait of Anna Radziwill née Kettler (1567-1617), daughter of Gotthard Kettler, Duke of Courland and Semigallia (vassal state of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth) and Anna of Mecklenburg. On 20 January 1586, in Jelgava, she married Albert Radziwill (1558-1592), the younger brother of Nicolaus Christopher Radziwill "the Orphan". Her husband was a frequent guest at her father's court, and he also traveled frequently. In 1582 he was in Polotsk with King Bathory, at the beginning of July 1582 he left for Italy, and from January to May 1583 he stopped in Venice. In January he was in Kraków, from there he went to Kaunas and at the end of July 1584 to Lublin. In December he appeared at the royal court in Grodno and probably went to Warsaw (after "Polski słownik biograficzny", Volume 30, p. 137).
In her portait Anna is dressed in more Northern fashion and holds a small dog, a symbol of marital fidelity. The style of this painting closely resembles the portrait of Katarzyna Tęczyńska (died 1592), Princess of Slutsk in the same collection (128854 MNW), therefore it should be attributed to the workshop of Alessandro Maganza. The painting was donated in 1969 by Stanisław Lipecki and Róża Lipecka from Kraków and comes from Silesia. It was correctly identified by Janina Ruszczyc in 1975 because, according to an inscription in German, most likely dating from the end of the 18th century, it depicts the unknown Duchess Ludemilla of Legnica and Brzeg (Ludemilla! / Herzogin Vo: / Lieg: Bri: u Woh: / Mutter des Lezten / Herzog u Bau / erin der Fürsten / Gruft). The painting was probably part of the dowry of Anna's sister, Elizabeth Kettler, who on September 17, 1595 married Adam Wenceslas, Duke of Cieszyn or it was moved to Żagań in Silesia after 1786 when Peter von Biron, the last Duke of Courland and Semigallia, bought the Duchy from the Lobkowicz family. A painting from the same period and painted in the same style also bears an incorrect inscription. It comes from a private collection in England and is attributed to an English school of the 17th century (oil on canvas, 76.2 x 63.5 cm). According to mentioned inscription the man in Italian or French costume from the 1580s is Edward VI (1537-1553), King of England, portrayed in 1553 at the age of 15 (EDWarD VI ÆTATIS . SUÆ . 15 / ANNO. DOMINO . 1553). This unusual mixture of English and Latin was probably added in the late 19th or 20th century to sell the painting more profitably. The original indications of his identity, if any, have most likely been removed, so perhaps we will never know his true identity. The man could be a nobleman from Poland-Lithuania or an Italian courtier at the court of elected Queen Anna Jagiellon or the Radziwills, painted like his patrons by the Venetian workshop of Maganza.
Portrait of Anna Radziwill née Kettler (1567-1617) with a dog by workshop of Alessandro Maganza, ca. 1586-1587, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of a man in a ruff with a false inscription identifying the model as Edward VI (1537-1553), King of England by workshop of Alessandro Maganza, 1580s, Private collection.
Portraits of Duke Henry XI of Legnica by Flemish and French painters
In 1551 Frederick III, Duke of Legnica (1520-1570) visited the French and Polish royal court. The Duke joined a coalition of rebellious Protestant princes, and formed an alliance with King Henry II of France, a longtime enemy of the Habsburgs. Consequently, he was deprived of the Duchy in favor of his son Henry XI (1539-1588), who was still a minor and initially ruled under the regency of his uncle, Duke George II of Brzeg (1523-1586).
Despite being a fief of the Habsburgs, George II was in opposition to their absolutist policies in Silesia. Through his marriage to the daughter of the Elector of Brandenburg Barbara (1527-1595), granddaughter of Barbara Jagiellon (1478-1534), he was on good terms with the Electorate of Brandenburg. He also maintained friendly relations with Poland, corresponded with the Archbishop of Gniezno Jakub Uchański, King Sigismund II Augustus, and later with Stephen Bathory. Young duke Henry spent several years at the court of his uncle in Brzeg. Between 1547 and 1560 George II rebuilt the castle there in the Renaissance style. Italian architects Giovanni Battista de Pario (Johann Baptist Pahr) and his son Francesco added an arcaded courtyard, strongly inspired by the architecture of the Wawel royal castle in Kraków. Some of the tapestries that he commissioned were also inspired by famous Jagiellonian tapestries (Wawel arrases). Tapestry with Abduction of the Sabine women with coat of arms of George II and his wife, today in private collection, created between 1567-1586, is a copy of Wawel's The Moral Fall of Humanity from the series The Story of the First Parents, weaved between 1548-1553 in Brussels by Jan de Kempeneer after design by Michiel Coxie for King Sigismund Augustus. The weaver just rearranged a few figures in the composition. Two other tapestries made for the Duke of Brzeg are in the Cathedral Church of St. Paul in Detroit. Heraldic tapestry with coat of arms of George II and his wife in the National Museum in Wrocław, was created in 1564 by his court weaver (from 1556) Flemish Jacob van Husen, who worked before (for ten years) in the workshop of Peter Heymanns in Szczecin. His successor was Egidius Hohenstrasse from Brussels, active in Brzeg from the 1570s and remaining there until his death in 1621 (after "Funkcja dzieła sztuki ...", p. 203). He created the heraldic tapestry with coat of arms of Barbara of Brandenburg (Church of Saint Nicholas in Brzeg). At that time, Silesia became an important center in the European textile industry. In the first half of the 16th century Legnica merchants appeared more and more often at the Leipzig Fair, trading primarily Silesian canvas. Raw materials and ready weaving products, in particular Legnica cloth, were exported to other cities, while wool was brought to Legnica from Greater Poland. The export of Silesian linen began to be organized in the 1560s by Netherlandish merchants. It was the Flemish/Dutch merchants, who controlled about 80% of the Baltic trade at the time, who became the organizers of the export of Silesia linen to America and West Africa at the turn of the 16th and 17th centuries. According to a document of 1565 issued by King Sigismund Augustus merchants from Silesia and Moravia sold cloth in Poland. Against the competition of foreign merchants, especially the Scots, the English and the Dutch, who at the end of the 16th century began to flock to Silesia en masse, an imperial patent of August 20, 1599 was imposed, under which only local merchants could trade in Silesian products (after "Związki handlowe Śląska z Rzecząpospolitą ..." by Marian Wolański, p. 126). Painters in Venice and later in the Netherlands needed cloth for their paintings and by the 17th century canvas was imported on a large scale from Silesia to the Netherlands (after "A Corpus of Rembrandt Paintings: Volume II: 1631–1634", p. 18). In the artistic field, ties with Poland, Flanders and Dutch Republic were also strong. In 1550, the city council of Poznań pays 3 florins and 24 grossus to the council of Legnica in Silesia for a portrait of Emperor Charles V. It could have been a small likeness from the Skórzewski collection by workshop of Lucas Cranach the Elder, signed with artist's insignia and dated '1550', today in the Gołuchów Castle (National Museum in Poznań, oil on panel, 31 x 35 cm), however, this effigy could have been also by Flemish school, like the painting in Warsaw (National Museum in Warsaw, 183175 MNW) or Spanish, Flemish or Italian school after original by Titian, like the portrait in Kraków (Czartoryski Museum, MNK XII-259, purchased in Paris in 1869). The paintings were mainly imported from abroad and came from Germany, Italy and the Netherlands. In 1561 Jan Frayberger, a merchant from Wrocław in Silesia, brought to Poznań twelve dozen of painted playing cards from Flanders and "2 paintings of the Saxon Elector", Stanisław Voitt had "11 Netherlandish paintings on canvas, new" and in 1559 Jan Iwieński brought two chests of books from Italy, several everyday objects and one painting imago quedam. A well-known goldsmith from Poznań, Erazm Kamin (d. 1585), had four paintings on canvas and 14 Italian paintings and a furrier from Poznań Jan Rakwicz (d. 1571) left "10 paintings in frames, 4 paintings without frames" (after "Studia renesansowe", Volume 1, p. 369-370). According to preserved documents, the kings of Poland ordered tapestries (in 1526, 1533, between 1548-1553) and paintings (in 1536) in Flanders. The Spanish and Austrian Habsburgs commissioned tapestries with their effigies (Conquest of Tunis tapestries) and inspired by Hieronymus Bosch's works (Temptation of St. Anthony and the Haywain tapestries in Madrid), so did the rulers of France (Valois tapestries in Florence, one with Festivals for the Polish ambassadors in 1573) and Portugual (Deeds and triumphs of João de Castro, viceroy of Portuguese India in Vienna). Flemish portraitists were then considered to be among the best in Europe. Some of them were willing to travel, like Lucas de Heere, who designed tapestries for Catherine de' Medici and who created the triple profile portrait, said to be mignons (male lovers) of Henry of Valois (Milwaukee Art Museum), but others not. Today, rich people order such personalized things from very distant places like shoes, it was the same in the 16th century. According to Latin inscription in upper part of the painting sold in Paris in 2019 (oil on panel, 35.5 x 27.6 cm, Artcurial, 27.03.2019, lot 294), the man depicted was 24 in 1563 (AN° DNI - 1563 - ÆTATIS - SVE - 24 -), exaclty as Duke Henry XI of Legnica (born on February 23, 1539 at Legnica Castle), when Emperor Maximilian II arrived to Legnica for the baptism of his daughter Anna Maria, greeted with great celebration and a magnificent feast. This small painting is attributed to Gillis Claeissens (or Egidius Claeissens), a Flemish painter active in Bruges, and comes from private collection in Paris. Almost an exact copy of this painting exist, however, the face and left hand are different, as well as the inscription. The painter has just "glued" the other face into the same body. This "copy" is now in the Museum Helmond in the Netherlands (oil on panel, 35.5 x 27.5 cm, inventory number 2007-015) and the man depicted was 22 in 1563 (AN° DNI - 1563 - ÆTATIS SVE - 22 -), therefore born in 1541. There is no resemblance between the red-haired man and the dark-haired man, hence they were not members of the same family. The man from the Helmond portrait is identified as Adolf van Cortenbach, Lord of Helmond from 1578, however, Adolf was born around 1540, so he would be 23 in 1563, not 22. This sitter bear a striking resemblance to a man born in 1541 whose face is known from many effigies painted by the best European painters - Francesco de' Medici, later Grand Duke of Tuscany and regent from 1564. Prior to his marriage to Joanna of Austria, daughter of Anna Jagiellonica (1503-1547) in 1565, Francesco had spent a year (June 1562 - September 1563) at the court of King Philip II of Spain, Lord of the Seventeen Provinces of the Netherlands. Around 1587 Hans von Aachen, who from 1585 lived in Venice, created a portrait of Francesco (Pitti Palace, OdA Pitti 767), and between 1621-1625 a Flemish painter Peter Paul Rubens copied an effigy of the duke for his daughter Marie de' Medici, Queen of France (Louvre). Although in the majority of his portraits, Francesco has brown eyes, in this one, like in the painting by Alessandro Allori in the Museum Mayer van den Bergh in Antwerp (MMB.0199), his eyes are blue. The red-haired man from the Paris portrait was also depicted in another painting, today in the National Gallery of Art in Washington (oil on panel, 31.2 x 22.7 cm, inventory number 1942.16.1). He is older, his forehead is higher, he lost part of his hair and his costume and ruff in French style indicate that the painting was made in the 1570s. At the beginning of the 20th century this painting was part of the collection of art dealer Charles Albert de Burlet in Berlin, where many items from Ducal collections in Legnica and Brzeg were transported after 1740-1741. The portrait if attributed to French school and its style is very close to the portrait of Claude Catherine de Clermont, duchess of Retz in the Czartoryski Museum (MNK XII-293), attributed to follower of François Clouet, possibly Jean de Court, who died in Paris after 1585 and who in 1572 succeeded Clouet as painter to the king of France. Great similarities are also to be noted with portrait of Louis I de Bourbon, Prince of Condé (1530-1569) by workshop of François Clouet (sold at Sotheby's, sale L14037, lot 105). After the death of Sigismund II Augustus, Henry XI was a candidate to the Polish crown in the first free election in 1573, but he obtained only three votes and it was the French candidate Henry of Valois who was elected. At the beginning of 1575 he was in Poznań at the funeral of Bishop Adam Konarski and in July he went to Kraków, in order to hold talks with the local voivode, Piotr Zborowski, who was to help him in obtaining the throne. In 1576 the Duke of Legnica took part in expedition to France of the exiled Henri I de Bourbon, Prince of Condé (1552-1588), Louis' son, who fled to Alsace and rallied new Huguenot troops. Henry's conduct became more and more prodigal, he undertook numerous costly journeys to various cities, doubling the debts left by his father. In 1569, he participated in the Sejm in Lublin, where the Union of Lublin was concluded. At a meeting with Sigismund II Augustus in Lublin, he presented the Polish monarch with two lions and precious jewels and this expedition cost 24,000 thalers, while the annual income of the duke amounted to less than 12,000 thalers. During his absence, he was deposed in 1576 by Emperor Maximilian II and his brother Frederick IV, who had been co-ruling until then, exercised the power alone. Four years later, in 1580, Henry XI was allowed to rule again in Legnica, but in 1581, he came into conflict with Emperor Rudolf II and was imprisoned in Prague Castle and then transferred to Wrocław and Świdnica. In 1585, Henry XI managed to escape and fled to Poland. With the help of elected Queen Anna Jagiellon and her husband, he unsuccessfully tried to regain control of his duchy. In 1587 he went to Sweden as a personal envoy of the Queen and he accompanied the newly elected King Sigismund III Vasa to Kraków, where Henry XI died in March 1588 after a short illness. Because he was a Protestant, the Catholic clergy of Kraków refused to give Henry a burial. Eventually his body was interred in the chapel of the Carmelite Church. This Gothic church, founded in 1395 by Queen Jadwiga and her husband Jogaila of Lithuania (Ladislaus II Jagiello) was seriously damaged in 1587 during the siege of Kraków by Emperor Maximilian. It was rebuilt with the financial help of Anna Jagiellon in 1588. In the National Museum in Warsaw (deposited to Palace on the Isle) there is a portrait of a bald man with a beard from the fourth quarter of the 16th century, painted by Flemish painter (oil on panel, 44.9 x 30.3 cm, inventory number Dep 629, M.Ob.2753, earlier 158169). It was acquired between 1945-1957. This man bear a striking resemblance to the man from the portrait in Washington and to the only known so far graphic representation of Duke Henry XI of Legnica, engraving by Bartłomiej Strachowski, published in Georg Thebesius' Liegnitzische Jahr-Bücher ... in 1733, after original effigy from about 1580. The style of a portrait of a bearded man in Warsaw greatly resemble the effigy of Alessandro Farnese (1545-1592), Duke of Parma and Governor of the Spanish Netherlands, attributed to Antoon Claeissens, Gillis' brother, in the same collection (deposited to Palace on the Isle, Dep 630, M.Ob.2749). Farnese's likeness was purchased in 1950 from Czesław Domaradzki and has almost identical dimensions (oil on panel, 44.5 x 33.5 cm). In private collection, there is another portrait in similar dimensions (oil on panel, 46.4 x 35.6 cm), attributed to Adriaen Thomasz. Key (died after 1589), and similar to full-length effigy of King Philip II of Spain by Juan Pantoja de la Cruz in the El Escorial, while in the Rijksmuseum Amsterdam there is a portrait of Queen Anna Jagiellon, purchased in 1955 from the dealer Alfred Weinberger in Paris, attributed to Cologne school, close to works of a painter active in Lviv, Jan Szwankowski (d. 1602). In the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna there are two miniatures of Duchesses of Legnica (inscription D. DE LIGNIZ) from the 1570s, painted by Flemish or Italian painter, which should be identified as Anna Maria (1563-1620) and Emilia (1563-1618), daughters of Henry XI. In conclusion, the rulers of Europe frequently exchanged their effigies, which were frequently created in different places, not necessarily by the "court painters".
Portrait of Duke Henry XI of Legnica (1539-1588), aged 24 by Gillis Claeissens, 1563, Private collection.
Portrait of Francesco de' Medici (1541-1587), aged 22 by Gillis Claeissens, 1563, Museum Helmond.
Portrait of Duke Henry XI of Legnica (1539-1588) by follower of François Clouet, possibly Jean de Court, ca. 1570-1576, National Gallery of Art in Washington.
Portrait of Duke Henry XI of Legnica (1539-1588) by Antoon Claeissens, 1580s, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Alessandro Farnese (1545-1592), Duke of Parma by Antoon Claeissens, 1580s, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Queen Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596) by Jan Szwankowski or Cologne school, ca. 1590, Rijksmuseum Amsterdam.
Portrait of King Philip II of Spain (1527-1598) by Adriaen Thomasz. Key or follower, ca. 1590, Private collection.
Portrait of Jan Tomasz Drohojowski by Leandro Bassano
Jan Tomasz Drohojowski (1535-1605) from Drohojów, near Przemyśl, was a son of Krzysztof Drohojowski, a nobleman of Korczak coat of arms, and Elżbieta Fredro. He had five sisters and two brothers, Kilian and Jan Krzysztof (died before December 12, 1580), the royal secretary. He studied at the University of Wittenberg (enrolled on June 21, 1555), with his brother Kilian in Tübingen, then alone in Basel in 1560. Well educated, knowing French, Italian and Latin, he began to serve the king Sigismund Augustus. He was sent by him with a mission to Italy. According to Krzysztof Warszewicki (1543-1603), he brought the king as a gift a horse of wonderful color and virtue (equum admirabilis coloris et bonitatis Regi donavit). After return he became the royal secretary and in 1569 in this capacity he signed three privileges. At the time of the king's death, he was in Knyszyn and prevented the royal property from being looted and at the Sejm of 1573, Jan Tomasz called for a punishment of those guilty of looting royal valuables.
Shortly thereafter, Jan Tomasz went to Kraków to participate in the reception ceremony of king Henry of Valois. He stayed in Kraków, performing his duties as secretary and courtier of the king, and he even borrowed a certain amount to king Henry. Then he was sent on several ambassadorial missions, including to France. He was present at the anointing of king Henry at Reims on February 13, 1575. On March 2, 1575 in a letter from Prague to Infanta Anna Jagiellon he reported to her about the coronation of Henry and his marriage with Louise of Lorraine. The Infanta, in a letter of April 10, 1575, written from Warsaw to her sister Sophia, calls Jan Tomasz a courtier of the King. After returning from the mission in Courland in 1578, he hosted king Stephen Bathory for 5 days in Przemyśl (for which he spent 911 zlotys) and become the starost of Przemyśl. Also in 1578, he founded octagonal chapel of St. Thomas (Drohojowski Chapel) at the Przemyśl Cathedral, built in the Renaissance style. To put up one tower at the Przemyśl castle he spent 180 zlotys. At the end of January 1579 he was sent by the king to Constantinople (Istanbul). In a letter of January 13, 1581 from Warsaw to Andrzej Opaliński (1540-1593), Court Crown Marshal, Mr Bojanowski calls Jan Tomasz, Gian Tomaso in Italian. In May 1583, princess Griselda Bathory, niece of the king, stayed in Drohojowski's Palace in Voiutychi, designed in Renaissance style by Italian architect Galeazzo Appiani from Milan, with her entire retinue of 500 infantry soldiers and 78 mounted knights. In 1588 he escorted to Krasnystaw, Archduke Maximilian of Austria (1558-1618), who stood as a candidate for the throne of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, taken captive at the Battle of Byczyna (24 January). Before December 20, 1589 Jan Tomasz was appointed the crown referendary because the letter of king Sigismund III from that date already gives him this title. His career was facilitated by family ties with Jan Zamoyski, Great Hetman of the Crown, who entrusted the guardianship of his son Tomasz to him in 1589. He became friends with Mikołaj Herburt (1524-1593), castellan of Przemysl and he married his daughter, Jadwiga Herburt. From this marriage he had a son, Mikołaj Marcin Drohojowski, most probaly born in the late 1580s (he loses a trial in 1613 and in 1617 he sold Rybotycze estate to Mikołaj Wolski (1553-1630)). Jan Tomasz died in the Przemyśl castle on November 12, 1605 at the age of 70. The portrait of a nobleman in a black French style costume lined with fur by Leandro Bassano, was offered to the Nationalmuseum in Stockholm in 1917. The aristocratic tone of this portrait is accentuated by the verticality of the figure, his pose and gloves. The date in upper left corner of the canvas was not added very skillfully, therefore we can assmue that it was added later by the owner or at his request, not by the original painter. According to this inscription in Latin, the man was 53 in June 1588 (AET . SVAE . / LIII / MĒS . VI / 1588), exactly as Jan Tomasz Drohojowski. Below there is also another date in Latin: March 27 (27 mês martij), which could be the date of birth of Jan Tomasz's son Mikołaj Marcin. The man's costume and pose as well as facial features bears a striking resemblance to a portrait of Jan Tomasz's brother Jan Krzysztof (d. 1580), the royal secretary, in the Przemyśl Cathedral. This portrait, created in the first half of the 18th century, is a copy of other effigy and is a pendant to a portrait of his brother Jan Tomasz, who as a starost (capitaneus) of Przemyśl, administrative official, equivalent to the County Sheriff, was depicted in an armor and holding an axe.
Portrait of Jan Tomasz Drohojowski (1535-1605), starost of Przemyśl aged 53 by Leandro Bassano, 1588, Nationalmuseum in Stockholm.
Portrait of Sigismund III Vasa at a young age by Domenico Tintoretto
After the death of Stephen Bathory in December 1586, when 63 years old elected Queen Anna Jagiellon, could finally rule on her own, she was most probably too sick and too tired to do this. She supported the candidature of her niece Anna or her nephew Sigismund, children of her beloved sister Catherine, Queen of Sweden as candidates in next election. Sigismund was elected the ruler of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth on 19 August 1587.
Raised in Protestant Sweden, where Flemish Domenicus Verwilt and Dutch Johan Baptista van Uther with their stiff realism were chief portraitists at the court of his father and his predecessor, he found "degenerated", frivolous style of the Venetians not very appealing to him, at least initially. Although, he commissioned paintings in Venice, all most probably destroyed, no portrait is mentioned in sources. He supported Martin Kober, a Silesian painter trained in Germany, as his main court portraitist. It was therefore his aunt Anna Jagiellon, who could order a series of portraits of her protégé from Tintoretto for her and for her Italian friends. The portrait of a blond hair young man, wearing a tight black doublet in El Paso Museum of Art is very similar to other known portraits of the king, especially his effigy in Spanish costume by Jakob Troschel from about 1610 (Uffizi in Florence) and a portrait holding his hand on a sword, attributed to Philipp Holbein II, from about 1625 (Royal Castle in Warsaw). Chronologically this portrait fit perfectly known portraiture of the king: portrait as a child aged 2 from 1568 (AETATIS SVAE 2/1568), created by Johan Baptista van Uther as gift for his aunt (Wawel), as a Duke of Finland aged 18 (AETATIS SVAE XVIIII), consequently from 1585, also created by van Uther in Sweden (Uffizi), next this portrait by Domenico Tintoretto from about 1590, when he was 24 and was already in Poland and then the miniature at the age of 30 (ANNO AETATIS XXX) from about 1596 by workshop of Martin Kober or follower (Czartoryski Museum). The painting was inscribed on the column (AETATIS…X…TORET), now mostly effaced. His left hand looks like if was posed on a sword at his belt, however no object is present. It was probably less visible in a drawing or miniature sent to Tintoretto, hence he left his hand strangely in the air, a proof that the sitter was not in painter's atelier. Forgetting of such an important object in the 16th century male portraiture, could be also a result of a rush to accomplish some big royal commission. The Order of the Golden Fleece, basing on which some of Sigismund's portraits were identified, was granted to him in 1600. It is highly probable that the painting showing the Baptism of Christ by John the Baptist in the National Museum in Warsaw, created by Domenico Tintoretto around that time (after 1588) was also commissioned by Anna. It was bequeathed to the School of Fine Arts in Warsaw by Piotr Fiorentini in 1858 and later purchased by the Museum. Its earlier history is unknown, therefore Fiorentini, born in Vilnius, who later lived in Kraków and Warsaw, could have acquire it in Poland or Lithuania. Anna was engaged in embellishment of the main church of Warsaw - Cathedral of Saint John the Baptist and she also built 80-meter-long corridor (covered passage) connecting the Royal Castle with the Cathedral.
Portrait of Sigismund III Vasa at a young age by Domenico Tintoretto, ca. 1590, El Paso Museum of Art.
Baptism of Christ by Domenico Tintoretto, after 1588, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of princess Anna Vasa in Spanish costume by Domenico Tintoretto
In about 1583, after her mother's death, Anna Vasa like her aunt Sophia Jagiellon in 1570, converted to Lutheranism. Already in 1577, papal diplomacy proposed to marry her to an Austrian archduke, Matthias or Maximilian.
She arrived to Poland in Ocober 1587 to attend her brother's coronation and she stayed until 1589, when she accompanied Sigismund to meet their father John III of Sweden in Reval and then followed John to Sweden. Anna returned to Poland to attend the wedding of Sigismund with Anna of Austria in May 1592. When just few months later, on 17 November 1592, John III died, Sigismund was willing to abdicate in favor of Archduke Ernest of Austria, who was about to marry his sister Anna. This was also intended to alleviate the Habsburgs, who already lost in two royal ellections. Archduke Ernest, the son of Emperor Maximilian II and Maria of Spain, together with his brother Rudolf (Emperor from 1576), was educated at the court of his uncle Philip II in Spain. To announce this turn in country's politics, where Anna Vasa become a focal point, her aunt most probably commissioned a series of portraits of her niece. The portait by Domenico Tintoretto from the collection of Prince Chigi in Rome, now in the Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum in Boston, shows a woman in black saya, a Spanish court dress, from the 1590s, similar to that visible in the portrait of the Infanta Isabella Clara Eugenia by Sofonisba Anguissola in the Prado Museum from about 1597. However the white ruff collar, cuffs and her gold necklace are definitely not Spanish, they are more Central European and very similar to garments visible in portraits of Katarzyna Ostrogska from 1597 in the National Museum in Warsaw and in the portrait of Korona Welser by Abraham del Hele from 1592 in the private collection, they are not Venetian. The features of the woman's face are the same as in Anna Vasa's portrait from about 1605 and her miniatures from the 1590s identified by me. A book on the table beside her is therefore Protestant Bible, published in the small octavo format and landscape with rivers and wooded hills is how Tintoretto imagined her native Sweden. The portrait of a man with a red beard from the same period in the National Museum in Warsaw and attributed to Tintoretto's workshop is almost identical in composition, techinique and dimensions. He is holding a similar book. It is therefore an important royal court official. The royal secretary from 1579 and a staunch Calvinist Jan Drohojowski (d. 1601) fit perfectly. From 1588 he was also a castellan of Sanok, hence one of the most powerful protestants in the country. Drohojowski was the son of Stanisław Drohojowski, the promoter of Calvinism. His mother Ursula Gucci (d. 1554), also known as Urszula Karłowna, was also a protestant. She was a lady-in-waiting of Queen Bona and a daughter of Carlo Calvanus Gucci (d. 1551), a merchant and contractor, who arrived in Kraków in the retinue of Queen Bona and was later made Żupnik of the Ruthenian lands.
Portrait of princess Anna Vasa (1568-1625) in Spanish costume by Domenico Tintoretto, ca. 1592, Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum in Boston.
Portrait of Jan Drohojowski, castellan of Sanok by workshop of Domenico Tintoretto, ca. 1592, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portraits of Anna of Austria and Anna Vasa by Sofonisba Anguissola
In 1586, to strengthen her nephew's chances in royal election, Queen Anna Jagiellon proposed a marriage between Sigismund and Anna of Austria (1573-1598). The Habsburgs had strong influences in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and their claims to the throne were supported by part of the nobility. Due to the political instability and Maximilian of Austria's desire for the Polish crown, Anna's parents, preferred the match with Henry of Lorraine.
The plans resummed in 1590 when Anna's engagement with Duke of Lorraine was broken off. In April 1592, the betrothal was formally celebrated in the Imperial Court in Vienna. Despite the opposition of the nobles, Sigismund and 18 years old Anna were married by proxy in Vienna on 3 May 1592. She arrived to Poland with her mother Archduchess Maria Anna of Bavaria and a retinue of 431 people. The young king welcomed his wife accompanied by the "old queen" Anna Jagiellon and his sister Princess Anna Vasa in Łobzów Palace near Kraków where four tents were set up, decorated in Turkish style for the feast. The young queen received rich gifts, including "Kanak necklace with large diamonds and rubies and oriental pearls, which are called Bezars 30" from the king, "a chain of oriental pearls and a diamond necklace, and two crosses, one ruby, the other diamond" from the "old queen" and "kanak necklace with a cross of rubies and diamonds pinned on one" from Princess Anna, among others. Also "the envoy from the Lords of Venice" brought gifts valued at 12,000 florins. Anna of Austria's Spanish connections become very important soon after her arrival, when after death of his father Sigismund left for Sweden and was willing to abdicate in favor of Archduke Ernest of Austria, who was about to marry his sister Anna Vasa. Two of Anna's effigies by Martin Kober from about 1595 were later sent to dukes of Tuscany (both Francesco I and Ferdinando I were half-Spanish by birth, through their mother Eleanor of Toledo). Three miniatures and a portrait, all in Sofonisba Anguissola's style, can be dated to around that time. One minature from the Harrach collection in Rohrau Castle in Austria, possibly lost, identified as effigy of Anna of Austria, shows de facto Anna Vasa with an eagle pendant. The other in the Uffizi Gallery (oil on copper, 9.1 x 7.3 cm, Inv. 1890, 8920, Palatina 650) depict Anna Vasa in more northern costume. The latter miniature is accompanied by very similar miniature of a lady in Spanish cosume with a necklace with Imperial eagle (oil on copper, 6.4 x 4.9 cm, Inv. 1890, 8919, Palatina 649), it is an effigy of Anna of Austria, the young queen of Poland and relative of the Holy Roman Emperors and the King of Spain. The portrait by Sofonisba from private collection in Italy (oil on canvas, 61 x 50.5 cm, sold with this attribution on October 1, 2019), which shows a blond lady with a heavy gold necklace is very similar to other effigies of Queen Anna of Austria, especially her portrait in Kraków, most probably by Jan Szwankowski (Jagiellonian University Museum) and engravings by Andreas Luining (National Museum in Warsaw) and Lambert Cornelis (Czartoryski Museum in Kraków). The miniature of a man from the collection of the Dukes Infantado in Madrid (oil on copper, Archivo de Arte Español - Archivo Moreno, 01784 B), painted in Sofonisba Anguissola's style, shows a man in eastern costume. His attire is very similar to these visible in a miniature with Polish horsemen from Albert of Prussia's "Kriegsordnung" (Military ordinance), created in 1555 (Berlin State Library) and in a portrait of Sebastian Lubomirski (1546-1613), created in about 1613 (National Museum in Warsaw). The features of the man's face are similar to miniature of Sigismund III Vasa (Bayerisches Nationalmuseum) and his portrait by Martin Kober (Kunsthistorisches Museum), both created in the 1590s. In the same collection of the Dukes Infantado, there is also a miniature attributed to Jakob de Monte (Giacomo de Monte) from the same period, showing king's mother-in-law Archduchess Maria Anna of Bavaria (1551-1608), as well as her miniature by Sofonisba from around 1580 (oil on copper, 01616 B), miniature of Emperor Rudolf II (oil on panel, 01696 B) and Sofonisba's self-portrait in Spanish costume (oil on canvas, 01588 B). All miniatures probably originally belonged to the Spanish royal collection.
Portrait of Queen Anna of Austria (1573-1598) by Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1592, Private collection.
Miniature portrait of Queen Anna of Austria (1573-1598) in Spanish cosume by Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1592, Uffizi Gallery in Florence.
Miniature portrait of Princess Anna Vasa (1568-1625) by Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1592, Uffizi Gallery in Florence.
Miniature portrait of Princess Anna Vasa (1568-1625) with eagle pendant by Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1592, Rohrau Castle.
Miniature portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa in Polish costume by Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1592, collection of the Dukes of Infantado in Madrid.
Portraits of Sigismund Bathory at a young age by Domenico Tintoretto
After failed plans to cede the throne of the Commonwealth to Archduke Ernest, as no monarch could do this without approval from the Diet, the Holy See had proposed the marriage of Princess Anna Vasa to Sigismund Bathory, who both could rule the country during the absence of the king (Sigismund III left for Sweden in 1593).
Sigismund was the nephew of king Stephen Bathory, who on 1 May 1585 confirmed his legal age by dissolving the council of twelve noblemen who ruled Transylvania in his name and made János Ghyczy the sole regent. After death of his uncle in 1586, he was one of the candidates to the throne of the Commonwealth. Sigismund knew Latin and Italian and in 1592 at his court in Alba Julia he had a large group of Italian musicians like Giovanni Battista Mosto, Pietro Busto, Antonio Romanini, or Girolamo Diruta among others. In summer of 1593, he went to Kraków in disguise to start negotiations regarding his marriage with Anna Vasa. Possibly on this occasion either the Polish court or Sigismund himself ordered a series of portraits from Domenico Tintoretto. It is unknown why negotiations were eventually unsuccessful, possible reason might be his homosexuality. The elites were probably afraid of another frivolous "Valois", who will escape from the country after few months or it was Anna who refused to marry him. Three years later however, on August 1595, Sigismund married Maria Christina of Austria, a sister of Anna of Austria (1573-1598), hence becoming brother-in-law of the king of Poland. It was regarded as a major political gain, but Sigismund refused to consummate the marriage. In summer of 1596 he sent his confessor, Alfonso Carrillo, to Spain. The Jesuit asked Philip II for finacial aid, as well as the Order of the Golden Fleece for Sigismund. The king promised Carrillo, in addition to 80,000 ducats in aid and granting of high distinction, diplomatic aid to Poland. On 21 March 1599 Sigismund formally abdicated receiving the Silesian duchies of Opole and Racibórz as compensation and left Transylvania for Poland in June. On 17 August 1599 Pope Clement VIII dissolved his marriage. A young man in a ruff from the 1590s, known from a series of portraits by Domenico Tintoretto, his workshop and some Italian painter, resemble greatly Sigismund Bathory, who was 21 in 1593. One version, in Kassel, bears an inscription ANNO SALVTIS / .M.D.L.X.X.X.V. (In the year of Salvation 1585) on a letter placed on a table beside him, it is a letter from Sigismund's uncle, King Stephen of Poland confirming his rights to Transylvania and therefore his claims to King's inheritance. The other in private collection in Marburg is inscribed TODORE del SASSO / CIAMBERLANO / AETATIS SVAE XXXVI with an image of a key, therefore claiming to be Chamberlain Todore del Sasso, aged 36, however no such man is confirmed in sources, especially as a recipient of the Order of the Golden Fleece known from so many portraits, the inscription must be false. It cannot be also Francesco Maria II della Rovere, Duke of Urbino as the effigy does not match with his features and he had his exquisit court painter Federico Barocci. Another portrait from the Swedish royal collection by Domenico's workshop is in Stockholm. It was probably sent to Sigismund III, when he was in Sweden for his coronation. There is also another version, but by a different painter, in Mexico. It is attributed to Giovanni Battista Moroni or to Domenico Tintoretto, therefore stylistically close, to a painter born in Cremona, Sofonisba Anguissola, court painter of Spanish monarchs. The effigy is very similar to previous portraits, just the Spanish Order of the Golden Fleece was added. It was commissioned by Polish court or Sigismund himself in about 1596 basing on effigy from 1593. Bathory was depicted in Hungarian costume in the Habiti Antichi Et Moderni di tutto il Mondo ... by Cesare Vecellio (Habito del Prencipe di Transiluania / Dacię Principis ornatus, p. 407), published in Venice in 1598 (Czartoryski Library in Kraków), after the effigy of King Sigismund III Vasa (Rè di Polonia / Poloniæ Rex, p. 346) and Sultan Murad III (Svltan A Mvrhat, p. 358).
Portrait of Sigismund Bathory, Prince of Transylvania at a young age by Domenico Tintoretto, ca. 1593, Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Kassel.
Portrait of Sigismund Bathory, Prince of Transylvania at a young age by Domenico Tintoretto or workshop, ca. 1593, Nationalmuseum in Stockholm.
Portrait of Sigismund Bathory, Prince of Transylvania at a young age by Domenico Tintoretto or workshop, ca. 1593, Private collection.
Portrait of Sigismund Bathory, Prince of Transylvania at a young age by circle of Giovanni Battista Moroni, most probably Sofonisba Anguissola after Domenico Tintoretto, ca. 1596, Museo Nacional de San Carlos in Mexico.
Portrait of Agnieszka Tęczyńska as Saint Agnes by Francesco Montemezzano
In October 1594, when she was just 16 years old, the eldest daughter of Andrzej Tęczyński, Voivode of Kraków, and Zofia nee Dembowska, daughter of Voivode of Belz, married the widower Mikołaj Firlej, Voivode of Kraków from 1589. The wedding feast with the participation of the royal couple took place in the "Painted Manor" of the Tęczyński family in Kraków, later donated to the barefoot Carmelites (1610). The groom, brought up in Calvinism, secretly converted to Catholicism during his trip to Rome in 1569. He studied in Bologna.
Agnieszka was born in the lavish Tenczyn Castle, near Kraków on January 12, 1578 as the fourth child. Both of her parents died in 1588 and most probably then she was raised in the royal court of Queen Anna Jagiellon. In 1593 she accompanied the royal couple, Sigismund III and his wife Anna of Austria, on their trip to Sweden. For some time, Tęczyńska's confessor was the Jesuit Piotr Skarga. After her husband's death in 1601, she took up the upbringing of her children, the administration of huge assets and she became involved in philanthropic and charitable activities. Widowed, Tęczyńska fell into devotion. She died in Rogów on June 16, 1644, at the age of 67, and was buried in the crypt at the entrance to the church in Czerna, she founded. In the preserved paintings, offered to different monasteries, she is depicted in a costume of a widowed lady or in a Benedictine habit, like in a full-length portrait in the Czartoryski Museum in Kraków from about 1640, created by circle of royal court painter Peter Danckerts de Rij or in a three-quarter length portrait in the National Museum in Warsaw, created by Jan Chryzostom Proszowski in 1643. The latter portrait, very Italian in style, was most likely inspired by a portrait of Queen Anna Jagiellon by Sofonisba Anguissola. A portrait in the Museum of Fine Arts in Houston (MFAH) depicts a lady with a lamb, an attribute of Saint Agnes, a patron saint of girls, chastity and virgins. "During the Renaissance, women who were soon to be married often associated themselves with this saint because Agnes chose to die rather than marry a man she did not love", according to MFAH catalogue. She is holding a Catholic book, most probably a volume of Saint Thomas Aquinas' "On the truth of the Catholic faith" (Incipit liber primus de veritate catholicae fidei contra errores gentilium). A rose-bush is in this context a symbol of the Virgin Mary and of messianic promise of Christianity because of its thorns (after James Romaine, Linda Stratford, "ReVisioning: Critical Methods of Seeing Christianity in the History of Art", 2014, p. 111). Woman's face is very similar to the effigies of Agnieszka Tęczyńska, later Firlejowa from the last decade of her life and to the portrait of her nephew, Stanisław Tęczyński in Polish costume, created by Venetian painter active in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Tommaso Dolabella. The portrait was in von Dirksen's collection in Berlin before 1932 and stylistically is very close to portraits of Queen Anna Jagiellon by Francesco Montemezzano (died after 1602), a pupil and a follower of Paolo Veronese.
Portrait of Agnieszka Tęczyńska as Saint Agnes by Francesco Montemezzano, ca. 1592-1594, Museum of Fine Arts, Houston.
Portraits of Queen Anna Jagiellon by workshops of Alessandro Maganza and Sofonisba Anguissola
The new lifestyle came in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth with the new young king Sigismund III arriving from Sweden with his sister and his courtiers. However, at her court in Warsaw, the aged Queen Anna Jagiellon still favored the Italians and Italian culture. From around 1590 her personal physician was Vincenzo Catti (or Cotti) from Vicenza, apothecary Angelo Caborti from Otranto, called Andzioł, ennobled in 1590 and rewarded by Sigismund III with an estate in Samogitia, gardener Lorenzo Bosetto (Bozetho) and sculptor Santi Gucci. On May 5, 1594, the Queen concluded an agreement in Warsaw "with Florentine Santy Guczy, our bricklayer [...] to make the grave of King Stephen". No painters are mentioned in the sources, indicating that probably all paintings, including the portraits, were commissioned from foreign workshops or in Gdańsk, which become the main commercial center of the Commonwealth. When in August 1590 Riccardo Riccardi, the envoy of the Grand Duke of Tuscany, came to Poland, Anna welcomed him warmly and gave him letters of recommendation to the authorities of Gdańsk, to facilitate the purchase of grain for Italy (after "Anna Jagiellonka" by Maria Bogucka, p. 155).
The newcomers from Italy spread the Counter-Reformation in the tolerant Commonwealth which gained popularity at Anna's court. Once two Capuchin fathers Francesco and Camillo appeared in the country with the intention of establishing a monastery in Poland. They showed letters of introduction from Ferdinand II (1529-1595), Archduke of Further Austria and recommendations of many bishops and abbots. They claimed to belong to the first Venetian families, Cornaro and Contarina, so they were welcomed everywhere. They preached, collected contributions, and distributed relics of the Holy Cross, which they allegedly had from Cardinal Farnese, but at the same time they behaved extremely indecently and even caused public scandals. During an audience with the queen, one of them undressed to show how thin his fasting had made him, so Anna, had to turn her face away, reports Alberto Bolognetti (1538-1585), papal nuncio in the Commonwealth (from 12 April 1581 to April 1585). Bolognetti ordered them to be imprisoned and placed temporarily in the Bernardine monastery in Warsaw. They soon confessed that they fled the Venetian province. They were visited by their compatriot, the royal physician, Lutheran Niccolò Buccella, who urged them to escape (after "Sprawozdania z posiedzeń Towarzystwa Naukowego Warszawskiego ...", Volumes 28-30, p. 40). Many Italians converted in the Commonwealth, such as Friar Hieronim (Girolamo) Mazza, a Venetian priest, who gave up his habit and married a woman with whom he had two children, a son and a daughter, and became an administrator of the Royal Post of the Montelupi in Kraków (after "Przegląd Poznański ...", Volume 27, p. 205). He is the author of the poem Epithaphium Ioannis Cochanovii from 1584. Anna, like her siblings and her mother, loved luxury and the items she owned or gave as gifts were of the finest local and foreign craftsmanship. In 1573 she ordered a pendant with "a large emerald, a smaller ruby, two small diamonds, a small sapphire and a small ruby". To the Wawel Cathedral, she offered many exquisite textiles and church vestments made from rich Italian fabrics. On a picnic at her estate in Ujazdów in 1579, she rode in a rich scarlet carriage covered with gold cloth inside and eight horses with a leopard complex (according to the letter from nuncio Giovanni Andrea Caligari to cardinal Como dated May 2, 1579). To the family mausoleum - Sigismund Chapel, she offered large quantities of silver objects, such as in 1586 "a pair of silver-gilt cruets" with the Polish eagle and her monogram A, in 1588 silver candlesticks with her coat of arms, in 1589 she sent from Warsaw a silver bell with the Polish eagle and her monogram and in 1596, shortly before her death, she donated a silver lectern with the eagle and the letter A and the text around the coat of arms: Anna Jagiellonia D.G. Regina Poloniae M.D. Lituaniae. The portrait of the queen in the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 103.3 x 77.5 cm, MP 5323) was in the 19th century in the Wilanów Palace in Warsaw. It is considered to be a variant of a portrait of Anna, also from the Wilanów Palace (Wil.1160), attributed to Martin Kober, most likely created in 1595 for which he was paid 14 florins and 24 groszy on the basis of the receipt of payment for three portraits of Anna Jagiellon, Sigismund III and his wife Anna of Austria. The Queen was portrayed as a founder and protector of St. Anne's Brotherhood, established in 1578 at Warsaw's Bernardine church of Saint Anne, with a gold distinctorium of the Brotherhood (introduced in 1589 after being sancioned by Pope Sixtus V) in the form of a gold medaillion with depiction of St. Anne and inscription SANCTAE ANNAE SOCIETATIS. The style of this painting is very Venetian and resembles the effigy of Anna's husband, Stephen Bathory, at Wilanów Palace (Wil.1163) and the portrait of her friend Bianca Cappello (1548-1587), Grand Duchess of Tuscany (private collection), both by Alessandro Maganza or his studio. The portrait of the queen in the Royal Castle in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 97.5 × 87.5 cm, ZKW 64) is closest to the works attributed to Sofonisba Anguissola and her workshop, such as the "Three children with a dog" (Corsham Court in Wiltshire), portrait of Joan of Austria (1535-1573), Princess of Portugal (private collection) and especially portrait of Don Carlos, Prince of Asturias (1545-1568), son of Philip II of Spain (Museum of Fine Arts of Asturias in Oviedo). This painting comes from the collection of Schleissheim Palace near Munich in Bavaria and was donated to the castle in 1973 by the government of West Germany. In the 16th and 17th centuries, the Sarmatians did much more than have a distinctive national workshop or school of painting, they financially supported Europe's greatest artists, and their effigies adorn the world's greatest museums and collections.
Portrait of Queen Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596) as a widow by workshop of Alessandro Maganza, ca. 1595, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Queen Anna Jagiellon (1523-1596) as a widow by workshop of Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1595, Royal Castle in Warsaw.
Portrait of Andrzej Kochanowski by Sofonisba Anguissola
"To Mr. Andrzej Kochanowski, son of Dobiesław, heir of Gródek, famous for his birth and his own virtues, a man distinguished in life by God's great gifts, such as wisdom, diligence, temperance, piety towards God, kindness towards friends, immense generosity towards the poor, who, when with great sadness and pain of his relatives and noble people, at the age of 54, he ended his life in the year of the Lord 1596 on March 24, in this church, which he erected in the name and glory of God, according to the rite of the Catholic Church, whose principles he always followed in his life, he was buried. A monument, as a proof of love, was erected to him by Mr. Andrzej Kochanowski, nephew, son of Jan, vicecapitaneus of Stężyca", reads the Latin inscription on a late-Renaissance wooden epitaph in the Parish church in Gródek near Zwoleń and Radom in Masovia. The church was founded by the mentioned Andrzej from Opatki (de Opatki), son of Dobiesław, heir in Gródek and Zawada and his wife Anna Mysłowska, who completed the construction and furnished the temple. The permission to build the church was issued by cardinal George Radziwill on April 3, 1593 and the building was ready in 1595. It was consecrated by the cardinal two years after death of the founder in 1598 and the epitaph was erected in 1620. This church was plundered by the Swedes in 1657, the thieves in 1692, and again in 1707 from silver and more expensive apparatus. The second time, among other valuables, two thorns from Christ's crown were stolen, set in silver, which Cardinal Radziwill had left as a gift at the consecration. The village was burnt to the ground in 1657 (after "O rodzinie Jana Kochanowskiego … ", p. 161-168).
According to some sources Andrzej from Opatki had two sons – Eremian and Jan, according to other he died childless and as his heirs he named Kasper, Stanisław, Andrzej, Adam and Jerzy, sons of his brother. It was however not the heir in Gródek, but the brother of poet Jan Kochanowski (1530-1584), also Andrzej, who translated Virgil's Aeneid, published in 1590, and works by Plutarch (after "Wiadomość o życiu i pismach Jana Kochanowskiego" by Józef Przyborowski, p. 9-10). The younger brother of famous poet was born before 1537 and died in about 1599. In 1571 he married Zofia of Sobieszyn, daughter of Jan Sobieski, with whom he had 9 sons, one of whom, Jan from Barycz Kochanowski, was in 1591 transferred by his father from the queen's court in Warsaw to Jan Zamoyski. The village of Gródek passed to the Kochanowski family as a dowry of Anna Mysłowska, who later married Stanisław Plicht, castellan of Sochaczew and after his death Abraham Leżeński. Cardinal Radziwill's favor indicates that the couple was associated with his multicultural court in Kraków as well as the court of Queen Anna Jagiellon in nearby Warsaw. A document issued by the cardinal to Anna Kochanowska née Mysłowska in Stężyca on October 30, 1598 was signed in presence of the members of his court, some of them have Italian and even Scottish names, like Jan Fox (1566-1636), scholastic of Skalbmierz, who studied in Padua and in Rome after 1590, Kosmas Venturin, secretary, Jan Equitius Montanus, parish priest, Andrzej Taglia, canon of Sącz and Jan Chrzciciel Dominik de Perigrinis of Bononia, chaplain. Portrait of a man and two boys in the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 80 x 66.5 cm, M.Ob.2484 MNW) is inscribed in Latin in the vicinity of each head. The first inscription above the head of the man indicate that the painting was made in 1596 and his age was 54 (AETATIS. 54: / ANNO 1596.), hence he was born in 1542, the older boy to the left was 10 and he died in 1594 (AETATIS. 10: / OBIIT 1594), thus born in 1584, and the younger was 10 in 1596 (AETATIS 10: / ANNO 1596), thus born in 1586. The dates concerning the man perfectly match the age of Andrzej Kochanowski from Opatki in 1596 and his effigy resemble greatly that of his relative Jan by Giovanni Battista Moroni (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam), identified by me. Therefore, the boys are either his sons or the sons of his brother and the painting was created shortly before his death or most probably commissioned by the widow to commemorate the death of all three. The convention of this portrait is very like an epitaph, additionally underlined by the postmortem effigy of the older boy, which was created two years after his death, but he was depicted living and embracing his father or uncle. It can be compared with mentioned painted epitaph of Andrzej from Opatki, created 24 years after his death and depicted sleeping in an armor. The described painting in Warsaw was acquired from Kraków as a result of the so-called restitution campaign in 1946 and it is attributed to a Flemish painter (after "Early Netherlandish, Dutch, Flemish and Belgian Paintings 1494–1983" by Hanna Benesz and Maria Kluk, Vol. 2, p. 40, item 817). Its style, however, is very much like in a portrait of Beautiful Nana and her husband by Sofonisba Anguissola in the same museum (M.Ob.1079 MNW) and another painting attributed to the Cremonese painter - portrait of Infanta Juana de Austria with female dwarf Ana de Polonia in the Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum in Boston, both in terms of rather stiff Spanish composition and technique. We can conclude that similar to portraits of female court dwarfs of Queen Anna Jagiellon, also this portrait was created by Sofonisba, who on 24 December 1584 married sea merchant Orazio Lomellino and lived in Genoa until 1620. Lomellino's family had commercial contacts with Poland-Lithuania since the second half of the 15th century. Among the numerous names of Italian merchants who in the mid-15th century stayed temporarily or settled permanently in Lviv, capital of the Ruthenian Voivodeship, we can find the most eminent names from the history of Genoese or Venetian colonies, such as mentioned Lomellino (Lomellini), Grimaldi, Lercario and Mastropietro. The Lomellinos, one of whom was Carlo the Genoese admiral, the other Angelo Giovanni, podesta, i.e. the municipal chief of Pera, maintain relations with the Lindners in Lviv in the 1470s (after "Lwów starożytny", Vol. 1 by Władysław Łoziński, p. 126). Sofonisba's family who settled in Venice belonged to the patriciate of that city from 1499 to 1612.
Portrait of Andrzej Kochanowski (1542-1596) from Opatki and his two sons or nephews by Sofonisba Anguissola, 1596, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Queen Anna Jagiellon by Sofonisba Anguissola
In about 1550, a young Cremonese painter, Sofonisba Anguissola, created her self-portrait (private collection) in a rich dress and in a pose exactly the same as that visible in a portrait of Catherine of Austria, Duchess of Mantua and later Queen of Poland. Catherine's portrait, in Voigtsberg Castle, is attributed to Titian. Sofonisba either created this portrait, participated in its creation or saw it somewhere, as Mantua is not far from Cremona. It could be threfore Catherine, who introduced her to the Polish court, when in June 1553 she married Sigismund II Augustus. Around that time Sofonisba created her self-portrait at the easel, one of the best of her self-portraits, which she could sent to the Polish court as a sample of her talent. This portrait is now in the Łańcut Castle.
The portrait which was previously identified as effigy of Catharine Fitzgerald, Countess of Desmond and Duchess of Dorset (d. 1625) in Knole House is very similar to effigies of Anna Jagiellon by Martin Kober and his workshop in coronation robes from the Sigismund's Chapel (1587) and in widow's clothing (1595) at the Wawel Castle. It was recently identified as portrait of Sofonisba Anguissola basing on a leaf from van Dyck's Italian Sketchbook. The inscription in Italian was evidently added later, as the year 1629 is mentioned in the text (the painter was in Italy between 1621 and 1627). The drawing shows an old lady, similar to that from the Knole portrait. According to inscription it is an effigy of Sofonisba, whom the Flemish painter visited in Palermo: "Portrait of Lady Sofonisma painter made live in Palermo in the year 1629 on the 12th of July: her age 96 still having her memory and brain very prompt, very courteous" (Rittratto della Sigra. Sofonisma pittricia fatto dal vivo in Palermo l'anno 1629 li 12 di Julio: l'età di essa 96 havendo ancora la memoria et il serverllo prontissimo, cortesissima). However Sofonisba died on 16 November 1625 and according to sources she was born on 2 February 1532, hence she was 92 when she died. Van Dyck was in Palermo in 1624. If he could confuse the dates of Sofonisba's life, he could also confuse the portrait of Queen of Poland by her hand, created in about 1595, that she had, with her self-portrait (Keller Collection, 1610). He may also have seen the portrait elsewhere in Italy, or even in Flanders or England. The Knole portrait was most probably acquired from the English royal collection, therefore it is highly probable that Anna sent to Queen Elizabeth I her effigy, one from a series created by Anguissola. In July 1589, English envoy Jerome Horsey, wanting to see Anna, sneaked into her palace in Warsaw: "before the windows whereof were placed pots and ranks of great carnations, gillyflowers, province roses, sweet lilies, and other sweet herbs and strange flowers, giving most fragrant, sweet smells. [...] Her majesty sat under a white silk canopy, upon a great Turkey carpet in a chair of estate, a hard-favored queen, her maids of honor and ladies attendants at supper in the same room". Queen Anna allegedly asked him, how Queen Elizabeth could "'spill the blood of the Lord's anointed, a queen more magnificent than herself, without the trial, judgment and consent of her peers, the holy father the Pope and all the Christian princes of Europe?' 'Her subjects and parliament thought it so requisite, without her royal consent, for her more safety and quiet of her realm daily endangered.' She shook her head with dislike of my answer", reported Horsey. Anna died in Warsaw on 9 September 1596 at the age of 72. Before her death she managed to accomplish tomb monuments for herself (1584) and her husband (1595) in Kraków, created by Florentine sculptor Santi Gucci, and for her mother in Bari near Naples (1593), created by Andrea Sarti, Francesco Zaccarella and Francesco Bernucci. She was the last of the Jagiellons, a dynasty that ruled over vast territories in Central Europe since the late 14th century, when Polish nobles proposed to pagan Duke of Lithuania, Jogaila, to marry their eleven-year-old Queen Jadwiga and thus become their king. Counter-Reformation, that she supported, and foreign invasions destroyed Polish tolerance and diversity, greedy nobles destroyed Polish democracy (Liberum veto) and invaders turned much of the country's heritage into a pile of rubble. The only portrait of the Queen in the nest of the Jagiellons - Wawel Royal Castle in Kraków was acquired from the Imperial collection in Vienna in 1936, just three years before World War II broke out. It was created by Kober in about 1595 and sent to the Habsburgs.
Self-portrait at the easel by Sofonisba Anguissola, 1554-1556, Łańcut Castle.
Portrait of Queen Anna Jagiellon by Sofonisba Anguissola, or a copy by Anton van Dyck, ca. 1595 or 1620s, Knole House.
Portrait of Queen Anna Jagiellon, a drawing by Anton van Dyck after lost painting by Sofonisba Anguissola, 1620s, British Museum.
The successors of the Jagiellons, the Vasas, shifted the focus of artistic patronage north, supporting Flemish and Dutch painters and acquiring luxury goods and art in the Netherlands, but Italian influences were still strong. "The Italian nation, from which we received the religion, literature, good arts, and the equipment of the more elegant life of the Sarmatians, is the most deserved" (Natio Jtalica optime de nobis merita est, a qua religionem, literas, bonas artes, ac elegatioris vitae apparatum Sarmatae accepimus), wrote in a letter of 1601 the Grand Chancellor Jan Sariusz Zamoyski (1542-1605) to Pope Clement VIII.
The great influences of Italians and Italian culture in Poland-Lithuania have led to increased interest in the Polish-Lithuanian royal elections on the Italian peninsula, which is now largely forgotten. In 1573, Alfonso II d'Este, Duke of Ferrara dispatched the celebrated poet Giovanni Battista Guarini to Poland-Lithuania, to perorate his cause before the Diet (Sejm). Guarini failed in his mission and on his return to Ferrara was criticized for diplomatic ineptitude (after "Politics and Diplomacy in Early Modern Italy ..." by Daniela Frigo, p. 167). Other important Italian candidates in the first free election of 1573 also included Alessandro Farnese, Duke of Parma and Piacenza and Francesco I de' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany. The latter was also considered in the third free election of 1587, when son of Catherine Jagiellon Sigismund Vasa was elected, and he had strong support. Simone Gengi of Urbino, an architect and military engineer in the service of the late King Stephen Bathory, believed that among the many candidates put forward, he had a good chance of success (...et quanto ella per parere de più principali potessi più d'ogn'altro aspirare a questa corona), as he states in a letter dated January 7, 1587 from Riga (dal nuovo forte di fiume Dvina), addressed to the Grand Duke and his ambassador to the imperial court in Prague Orazio Urbani. He asked to the director of the royal post of Poland-Lithuania Sebastiano Montelupi to spare no effort and money so that the courier with letters to the Grand Duke would reach Vienna as soon as possible. It was Montelupi, who in a letter of December 18, 1586 informed the court in Ferrara about the death of Bathory. He recommended hiring a special messenger dressed in German clothes and fluent in German. From Vienna, through the Tuscan ambassador, the letters were to be sent to Florence. The candidature of the Florentine ruler was supported, among others, by Stanisław Karnkowski, Archbishop of Gniezno, Olbracht Łaski, voivode of Sieradz and by Chancellor Jan Zamoyski. At the beginning of February 1587, they sent an embassy to Florence, which included, among others, the brother-in-law of the voivode of Sieradz, Wincenty de Seve, provost of Łask, who was ordered to invite the Grand Duke to take part in the upcoming election. His candidature was supposedly presented in the Sandomierz voivodship by Chancellor Zamoyski himself, who, according to Urbani, sincerely favored Francesco. According to the Tuscan diplomat, the Dukes of Ferrara and Parma had little chance in the upcoming election as petty and insignificant rulers. The fact that the Florentine milieu in Kraków was also keenly interested in the upcoming election is evidenced by a letter of January 7, 1587, from Filippo Talducci, addressed to Marco Argimoni in Florence, in which, listing the candidates for the Polish Crown, he mentioned the Grand Duke of Tuscany, who, if he wanted to mobilize appropriate financial resources, would have a chance to be elected (il figliuolo del Re di Svetia, il Cardinale Batori, il Duca di Ferrara et il nostro Serenissimo Gran Duca, il quale se volessi attendere con li mezzi sapete, sarebbe cosa riuscibile. Dio lasci seguire il meglio). The aspirations to the Polish crown of the Dukes of Ferrara, Parma and even Savoy are mentioned in the correspondence of the Tuscan ambassadors in Madrid, Bongianni Gianfighacci and Vincenzo Alamanni (letters of February 21, March 27 and April 4, 1587) (after "Dwór medycejski i Habsburgowie ..." by Danuta Quirini-Popławska, pp. 123-126). The portrait of the Grand Duke, today kept in Wilanów Palace (Wil.1494), could refer to this candidacy. It most likely comes from a series of similar small portraits from Ros near Grodno in Belarus, attributed to the 18th century Italian school. This "portrait of a man" is considered a copy of Angelo Bronzino, but it closely resembles the portraits of Francesco made by his court painter Alessandro Allori (1535-1607). Triumphal arches for King Sigismund III Vasa's entry ceremonies into Kraków in 1587 were to be dressed in images of the Jagiellons as the ancestors of the new king. As their faces were almost totally unknown because of their antiquity (Effigies enim eorum, cum plerisque fere vetustate ignotae essent), the aforementioned Chancellor Zamoyski had them extracted from the oldest monuments (ex antiquissimis quibuscumque monumentis eruerat) and provided with them appropriate inscriptions. These inscriptions were printed separately and some are quoted by David Chytraeus in his Chronicon Saxoniae ..., published in Leipzig in 1593 (after "Listy Annibala z Kapui ..." by Aleksander Przezdziecki, p. 107). It is thanks to the efforts of later generations that the identity of many important personalities has been preserved. They added inscriptions to the paintings, created copies or published them as engravings. In the former territories of the Commonwealth, this continuity has been dramatically interrupted by wars and invasions. Italian costumes, food, gardens, music, language and books, paintings, crafts and dances were most popular in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, even the hours were still counted in Italian style under the reign of the elected monarch Sigismund III Vasa - 24 hours from sunset one day to sunset the next day. In two letters, probably from 1614 and 1615, Sigismund III expressed his gratitude to the nuncio Claudio Rangoni for the paintings he sent from Italy. Two years later, in 1617 and the following year, Rangoni again sent two paintings and "some [other] paintings" (alcuni quadri) to the king, then to the queen. According to the nuncio, the king loved paintings and willingly purchased the works of the best masters and demonstrated a passion for expensive jewelry and tapestries. The king was not only an art lover, but also an amateur artist. What is very meaningful is that during the Zebrzydowski rebellion in 1606, he was mocked by his opponents as a "Venecist/Venetian" (wenecysta), who prefers to "ride with the Italians in a gondola, paying richly for their folly, instead of mounting a horse in armor" (after "Odrodzenie w Polsce ...", Volume 5, ed. Bogusław Leśnodorski, p. 358). In his "Sejm Sermons" (Kazania sejmowe), published in 1597 in Kraków, Piotr Skarga, the court preacher of Sigismund III, metaphorically appealed to parliament not to further restrict the king's power in favor of a more Habsburg absolutism: "Good Lords! Do not make the kingdom of Poland a [free] city of the German Reich, do not make a painted king as in Venice. Because you don't have Venetian mindset and you don't live in one city" (Sermon 6). He also scolded the great wealth and luxurious life of the nobility, their expensive clothes of velvet and silk, cellars full of wine, gilded carriages: "See what abundance and riches and joyful life this mother has brought you, and how she has gilded you and granted so much that you have enough money, plenty of food, clothes so expensive, such crowds of servants, horses, carts; so much money and income multiplied everywhere" (Sermon 2), and neglecting the defence of the Commonwealth: "No one living in abundance like this watches the castles and city walls" (Sermon 8). As in the previous epoch, in the 17th century, foreign costumes were still very popular among the nobility. Franciszek Siarczyński in his "Image of the reign of Sigismund III ...", published in Poznań in 1843, claims that he "saw paintings in Kraków in which Zebrzydowski looked like a Sultan, Zborowski like a Roman knight, in Krosno Stanisław Oświęcim, has all the clothes of a Swede, Tarnowski of an armed Greek, etc. Niesiecki described the portrait in Topolno of Krzysztof Konarski, from 1589, in guise of a German knight". A nobleman in Spanish parade outfit, who took part in Prince Ladislaus Vasa's expedition to Moscow in 1612, was ridiculed by other soldiers: "[go back] to Salamanca, to Compostela, Mr. Spaniard" (after "Obraz wieku panowania Zygmunta III ...", p. 73-74). Members of different ethnic groups of Sarmatia traveled to different Western European countries, primarily for doing business, as the country was a major supplier of many important goods, but also to pursue their studies, for a better climate or for health, to make a pilgrimage or simply to visit other countries. After completing studies at the Kraków or Vilnius Academy or other important schools of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, it was customary to continue studies abroad, in Padua, Bologna, Leuven, Leiden or Ingolstadt, among others. Abroad, Sarmatians frequently adopted local costumes, which is confirmed by numerous sources, but some, decided to travel in their traditional costumes - usually a crimson żupan, delia coat and kolpak hat. These costumes were frequently captured by different artists from Italy, Flanders, the Netherlands and France in their works. Some foreigners were also depicted in Sarmatian costumes, such as the painter Martin Ryckaert in his magnificent portrait painted around 1631 by Anthony van Dyck (Prado Museum in Madrid). Nicolas Lagneau (National Library of France), Stefano della Bella, Guercino (Nationalmuseum in Stockholm) and Rembrandt left numerous drawings and engravings representing characters dressed in typical Sarmatian costumes. Such costumes can also be seen in the paintings by Mattia Preti (Capitoline Museums in Rome), Giuseppe Maria Galeppini (private collection in Sweden) and David Teniers the Younger (Louvre and Neuburg State Gallery). Johann Heinrich Schönfeld painted around 1653 his "Sarmatians at the tomb of Ovid" (Museum of Fine Arts in Budapest and Royal Collection), which could be an illustration of one of the many Renaissance accounts of tomb-finding expeditions, such as that described by Stanisław Sarnicki in 1587 (Annales, sive de origine et rebus gestis Polonorum et Lituanorum, p. 73), and Philips Wouwerman produced between 1656 and 1668 a painting representing the Polish-Lithuanian cavalry fighting the army of the "Brigand of Europe" during the Deluge (National Gallery, London). The preserved poetry, created before the Deluge, confirms the image of a wealthy Commonwealth, concerned with various social problems, and not a country ravaged by constant wars and invasions of neighbors, fighting for its independence. The collection of manuscripts by Polish poets, mainly members of the community of Polish Brethren, compiled in 1675 by Jakub Teodor Trembecki (1643-1719/1720), published in 1910-1911 by Aleksander Brückner ("Jakuba Teodora Trembeckiego wirydarz poetycki", volume I), includes the following poems by unknown poets: 27. On an Italian feast, 28. Polish prosperity, 29. Polish playfulness, 165. On foreign costumes in Poland ("Nowadays, you can barely recognize Poles, there are Italians, French, in great number at the courts"); by Jan Gawiński of Wielomowic (ca. 1622 - ca. 1684): 215. On Venus ("Displeased Venus makes no one rich; She has a naked son; pleased, when you pay her"), 262. A girl without shame ("And your beautiful nature and wonderful senses, my Lady, have been spoiled by these oddities of your costumes"), 263. Today's wives ("Among the pagans, wives died for their husbands, and today they would dance on his grave"), 325. The concept of a Ruthenian painter under the painting of Judith beheading Holofernes; by Hieronim Morsztyn (ca. 1581 - ca. 1622): 368. Court disease ("Syphilis, ulcers, buboes, were brought from France and they were accommodated in a brothel"), by Jan Andrzej Morsztyn (1621-1693): 471. To the Italian ("You, Italian, sell Venetian products and you profit greatly from it") and by Daniel Naborowski (1573-1640): 617. To one hermaphrodite ("You have a female form but you have a prick, so you are both [woman and man]"), 643. On nude images in the bathhouse ("It's decent to wash naked in the bathhouse"). For his obscene epigram about female breasts, Hieronim Morsztyn most likely took inspiration from an Italian model: "Cazzo [an Italian vulgarism for phallus], stuck in the crotch, couldn't do its job" (Cazzo w kroku pojmane nie mogło się sprawić) (after "Poeta i piersi" by Radosław Grześkowiak, p. 18). The French-born queen Marie Louise Gonzaga is generally considered to have introduced more daring, not to say inappropriate, female costumes to Poland, mainly due to the marked contrast between effigies of the queen and portraits of her predecessors from the Habsburg dynasty - Cecilia Renata of Austria, Constance of Austria and Anna of Austria. However, many authors seem to forget that these queens preferred the fashion of the imperial or Spanish court which did not allow bare breasts described by Wacław Potocki (1621-1696). The popularity of daring French, Venetian and Florentine costumes was confirmed much earlier by Piotr Zbylitowski in his "Reprimand of Women's Extravagant Attire" (Przygana wymyślnym strojom białogłowskim), published in Kraków in 1600, and Italian fashion dominated at the court of the Jagiellons. Although in fact the fashion introduced by Marie Louise "revealed" more to the public gaze. In a letter from Gdańsk dated February 15, 1646 addressed to Cardinal Jules Mazarin (1602-1661), the queen wrote that "the Polish ladies are dressed how people dressed in France fifteen years ago: hastily sewn dresses, with very short waists and very wide sleeves. They all rush as fast as they can to imitate our clothes. Their materials are extremely expensive and covered with precious stones. The daughter-in-law of Great Crown Chancellor [Katarzyna Ossolińska née Działyńska] changes her outfit every day". The French courtier Jean Le Laboureur (1621-1675) also reports that many members of the nobility dressed in French style for the queen's reception. Szymon Starowolski (1588-1656) in his "Reform of Polish Habits" (Reformacya Obyczaiow Polskich), published before 1653, laments that "almost all of Poland became French, and probably all stricken with the French disease [syphilis]" (wszytka już prawie Polska sfrancuziała, a podobno sfrancowaciała) and Krzysztof Opaliński (1609-1655) could not refrain from ridiculing exaggerated costumes and excessive use of cosmetics by the ladies in his Liryki (donkey milk to brighten the complexion, roasted almonds to darken the eyebrows, crushed corals with sea foam-sepiolite as a powder for the cheeks). "The rich ladies here are very fond of sumptuous clothes, so they order various delicate works from the nuns and pay them well", wrote one of the French nuns of the Visitation of the Virgin Mary, who visited Poland in 1654. She also adds that she saw in several monasteries wonderful silver, gold and silk embroideries, most perfectly finished, decorated with jewels with great splendor, sometimes even luxury. Queen Marie Louise, who had just left Paris, wrote in the mentioned letter to Cardinal Mazarin that: "The splendor is extraordinary [...] In short, I had no idea, despite the best thoughts that I had created to take courage during the journey. Everything exceeded my expectations, so you will have no doubt that I am very satisfied" (after "Studya historyczne" by Wiktor Czermak, p. 75-76, 98-99, 101-102, 123-125, 127). Sometimes foreign ladies also adopted something from Polish fashion. A Frenchwoman and lady-in-waiting to the queen, Marie Casimire de La Grange d'Arquien, confided in one of her letters to Jan Sobieski that she used Polish caps instead of French hairstyles and that she was already tired of the bra she had been wearing so far, and she ordered a new one to be made: "it is more Crimean style, fastened to the side" (il est un peu z krymska zapięty na bakier) with Polish words in a French letter. Although her new garment was not purely Polish, because the word "Crimean style" also indicates the original Tatar pattern. Ladislaus IV purchased and ordered many luxury fabrics from Italian merchants for himself and the queen. In 1637, the sum of 11,281 zlotys was paid to the Kraków merchant Wincenty Barsotti for silk and bed linen intended for the king's wedding and a year later, in September 1638, Ladislaus purchased, through Hieronim Pinocci in Italy, "five pieces of gold cloth" for an amount of 7,265 zlotys, and a few years later, in November 1645, he again owed 4,000 thalers to Pinocci for fabrics brought from Venice and Vienna. According to the king's letter to his treasurer dated December 7, 1634, when the envoy of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth went to Moscow, there was in his entourage a courtier with a royal commission to purchase "various and fine furs" for 20,000 zlotys. According to the registers of 1652-1653, John Casimir purchased satin, velvet, fine silk, gold lace, ribbons, etc., as well as lynx, ermine, sable and dormouse fur, mainly from Jews. In 1667, Miss Ruffini, apparently Italian or of Italian descent as her surname indicates, was paid between 2,318 and 2,528 zlotys per month for the needs of the queen's kitchen. While according to the list of debts of Ladislaus IV, he owed 39,412 zlotys for Italian, French and Hungarian wines imported from Vienna in the years 1636-1639, and 90,000 zlotys to a jeweler and John Casimir paid to the watchmaker approximately 17,500 zlotys between 1652-1653, approximately 13,000 zlotys for his clothes and 74,726 zlotys in total for the beautiful clothes for his servants, the purchase and the execution of several paintings (to Salomon Schindler for the paintings, to Father Karwat for the paintings painted in Rome, to a painter from Elbląg) resulted in an expenditure of only 2,026 zlotys between 1652 and 1653. This lower value does not mean that they were not splendid paintings. We should remember that "Old Masters" became such much later and eminent painters for whose works some are today willing to pay a fortune, sometimes found it difficult to sell their works during their lifetime or their paintings were undervalued, as in the case of El Greco, an eminent Greek-Spanish painter trained in Venice. El Greco received only 350 ducats for the Disrobing of Christ (El Expolio), completed in the spring of 1579 for the high altar of the sacristy of the cathedral of Toledo, although his own expert had valued it at 950 and the Martyrdom of Saint Maurice, painted for El Escorial in 1580 did not satisfy King Philip II. El Greco's only masterpiece in Poland, probably from the Lubomirski collection, was discovered by chance in 1964 in the parish church of Kosów Lacki, east of Warsaw, and was therefore forgotten for several centuries. It cannot be excluded that its "Venetian" style was recognized by the young Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski (1616-1667) and that it was purchased during his visit to Spain in 1634. Nuncio Mario Filonardi (1594-1644) in a letter dated July 11, 1637 to Cardinal Bartolini mentions that to decorate his palace in Ujazdów, Ladislaus IV imported from Florence a large number of bronze statues, marble tables and statuettes. These sculptures were to cost 7,000 thalers, and their installation was carried out by the architect Agostino Locci, trained in Rome. The name of the author is not mentioned, but the main sculptor active at that time in Florence was Pietro Tacca (1577-1640), who worked for Ladislaus' cousins from the Medici family and created equestrian bronze statues of king's uncle King Philip III of Spain and his son of Philip IV, both in Madrid. In 1625, during his visit to Florence or Livorno, from where the prince was to embark for Genoa, Ladislaus also had the opportunity to personally meet the sculptor. There is no trace of these statues anywhere, indicating that they were probably melted down by the invaders to make cannons. Besides the well-known large brick residences of Warsaw, Kraków, Vilnius and other major cities, the Polish-Lithuanian Vasas owned several large wooden palaces of which nothing survives today. The most important was Nieporęt, near Warsaw. The palace was built by Sigismund III and later belonged to John Casimir. It had a large courtyard, a beautiful garden and a magnificent chapel. Le Laboureur praises the splendid carpentry work of the building and writes that it had a large number of comfortable rooms, all very beautiful and that it leaves nothing to be desired except that it was made of a more durable material. There were also several wooden mansions built in Warsaw and other cities for different family members and several hunting palaces, such as the one in Białowieża Forest, built before 1639 to the design by Giovanni Battista Gisleni. Baroque poetry also referred to the position of women in society and the value of paintings. "If there were more such [women] in Poland, much more would be achieved!" (O gdyby takich w Polszcze było siła, Daleko by się więcej dokazało!), comments Wacław Potocki in his poem "Judith" (Judyta) after the defeat of the Commonwealth forces at the Battle of Pyliavtsi in September 1648, praising the wisdom, strength and courage of women and criticizing the ineptitude of male leaders. "Why do you refuse such a trivial thing?" (Czemuż mi rzeczy tak lichej żałujesz?), asks the poet, most likely Jan Andrzej Morsztyn (1621-1693) in his "On the Refused Image" (Na obraz odmowiony), commenting on his beloved's refusal to offer him her portrait. This passage confirms that painted effigies were popular and inexpensive. An anecdote from the beginning of the 17th century from an inn in Gdańsk refers to painted effigies commissioned by nobles - a certain nobleman sent a painter to his friend's house to make a portrait of his wife, famous for her beauty, but the husband chased away the painter saying that if the noble liked the portrait, he would also want to see the original every day (after "Mówią wieki", Volume 19, 1976, p. 13). The inventories of the royal collections of the Jagiellons and the Vasas of Poland-Lithuania have not been preserved in their entirety, but information preserved in the townspeople's wills, as well as in the inventories of their property, and the patronage of their successors gives an impression of quality of their collections, when the country was one of the leading countries of Europe during the Renaissance and the beginning of the Baroque. Poland-Lithuania was also one of the richest on the continent. Even the lower strata of the Commonwealth's nobility owned the finest items produced in the best local and foreign workshops - such as the silver lavabo with the Rogala coat of arms of Jan Loka, starost of Borzechowo, created in Augsburg by Balthasar Grill, hidden in the ground during the Deluge (1655-1660). The attitude towards art in Brandenburg, which was one of the invaders during the Deluge, and at the royal court of Poland-Lithuania is best illustrated by the report of Andrzej Köhne-Jaski, a Calvinist amber merchant from Gdańsk, also active in diplomacy as envoy of Sigismund III and the electors of Brandenburg. Around 1616, Jaski commented on the destruction of paintings in Brandenburg: "I didn't pay much attention to it this summer, but I remember the magnificent paintings by Albrecht Dürer and Lucas [Cranach] hanging in churches. I wish HM [His Majesty] had such [paintings]" (Ich habe dießen sommer so genaue achtung nicht darauf gegeben, aber erinnere mich, das noch schöne bilder von Albrecht Dührer und Lucas vorhanden und in der kirchen hengen. Wolte wünschen, das EM solche hätten) (after "Das Leben am Hof ..." by Walter Leitsch, p. 2358). At that time, Italian and Flemish art, not German, dominated the royal court. Patricians of the royal city of Kraków, many of whom were of Italian descent as their names suggest, owned many paintings, sometimes by excellent foreign masters, as evidenced by the extract from the will of Jan Paviola (Joannes Benedictus Savioly, d. 1653), councilor of Kraków. The list and estimate of paintings, appraised by the elders of the painters guild Marcin Klossowski and Marcin Blechowski, painters from Kraków, include many portraits and paintings which could be from Italian, Venetian, Flemish, Dutch and German schools, but the author and the origin was not indicated. The word landscape - lanczaft in Old Polish, was used in a very similar form to Landschaft in German and landschap in Netherlandish, which could indicate that these paintings were Dutch/Flemish or German. "Picture of late King Ladislaus IV; Queen Her Highness Louise Marie; Image of the imperial son; his sister; the late Lord of Kraków Koniecpolski; [Picture] in which a crowned woman gives a mug to a soldier; Four pictures, representing the four parts of the world with people; four, depicting day and night, one damaged; three representing a part of the world; Landscape with fishing; Image of Bethsheba: bathing; [Picture] depicting the destruction of the city, with the army below fighting; Four pictures of Joseph's story, very demaged, among them one is whole; Landscape with highwaymen; Judith's painting, broken; female cook with venison; 12 images of Roman Emperors; two on which fish are painted, without frames; Image of King Ladislaus IV in elk skin; Judicium Parisis [Judgement of Paris] with three goddesses; Four images representing the parts of the year with maidens; Portrait of His Majesty King Ladislaus IV in a red coat; Queen Her Highness Cecilia [Renata]; King His Highness Sigismund III; Frederick Henry, Prince of Auraniae [Orange]; King Christian of Denmark; Duke of Saxony; Emperor His Highness Ferdinand III; His wife the empress; Leopold; the old empress; An image of a man with a mug and a scull; cavaliers playing cards with a lady; Orpheus with animals; Landscape with people eating in summer; robbers, on copper, in frame; on copper, without figures, with a column or pillar; Painting on copper, three Kings [Adoration of the Magi]; washing the feet of the apostles; Picture of a garden, on copper; Judith, on copper; Esther, on copper; on copper, Melchisedech offering bread and wine to Daniel; Saint Peter leaving the prison with the angel; the Samaritan on copper; Saint Francis; Five pictures with sea foam on gumi, made with paints on parchment; Picture on panel, a scull". This long and rich list of paintings was made on February 15, 1655. A few months later, in July 1655, two Swedish armies entered Greater Poland, one of the wealthiest and most developed provinces of the Commonwealth, which for centuries had been unaffected by any military conflict. They were soon followed by other countries and the invaders were not as sensitive to art as the patricians of the Commonwealth, precious materials, copper, silver and especially gold were the most important. Paul Würtz (1612-1676), governor of Kraków during Swedish-Transilvanian occupation of the city between 1655-1657 ordered wrought iron bars, marbles, precious wainscoting and floors to be ripped out, and silver sarcophagus of Saint Stanislaus, created in Augsburg in 1630 (founded by Sigismund III), silver altar of Saint Stanislaus, created in Nuremberg in 1512 (founded by Sigismund I), as well as statues and candlesticks from the Wawel Cathedral to be melted (after "Elity polityczne Rzeczypospolitej ..." by Marceli Kosman, p. 323). The true origin of looted items was often concealed or erased like coat of arms on the marble lions in front of Drottningholm Palace near Stockholm. "The day before yesterday, news came to us that they had sacked all the churches of Kraków, and that only one chalice had been saved from which some monks were saying mass in secret", reported in a letter of December 4, 1655 from Głogów Pierre des Noyers, secretary of Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga (after "Lettres de Pierre Des Noyers secrétaire de la reine de Pologne ...", published in 1859, p. 22). The situation was similar in other cities of the Commonwealth, particularly in Vilnius and Warsaw, where during the second occupation the royal residences were subjected to systematic looting by Swedish and Brandenburgian forces. "The Warsaw townspeople had to help in transporting the looted items to the Vistula bank, under pain of confiscation of their own goods. [...] On August 11, the commandant of the capital, General von Bülow [Barthold Hartwig von Bülow (1611-1667)], received an order to transport all valuables and works of art from the Castle. At that time, over 200 paintings were taken away, including plafonds from five castle rooms, royal silverware, furniture and 33 tapestries. The Swedes had already committed truly barbaric acts, scraping gold from the gilded paneling and ceilings, "of which they made at most three or four ducats, and the damage they caused exceeded 30,000 francs" [according to mentioned letter by des Noyers]. Everything of any value was transported by water towards Toruń and Königsberg, e.g. jasper columns from the royal garden" (after "Warszawa 1656" by Mirosław Nagielski, p. 262). "They generally killed everyone in Vilna [Vilnius], both men and women, except young people and children, whom they sent to Muscovy, and put Muscovites to live there. [...] In Vilna, the Muscovites have ruined the beautiful and sumptuous chapel of Saint Casimir, which cost more than three millions; and in the big church they put their horses; it serves them as a stable", adds des Noyers in letters of November 8 and December 28, 1655 (after "Lettres ...", p. 10, 40). The next significant inventory of paintings of a councilor of Kraków, Gerhard Priami, made on July 21, 1671, so few years after the destructive Deluge (1655-1660), is not that impressive: "Portraits of King Sigismund III with the Queen [...]; Image of flagellation [of Christ] [...]; Solomon, upwards [...]; St. Joseph on panel, old-fashioned [...]; Four landscapes [...]; Landscape with a fair [...]; Image of Lot [and his daughters] [...]; Two landscapes at elbow height; Picture of Judith [...]; Three pictures of the story of Tobias; Image of the Blessed Virgin in roses; Saint John the Baptist; Jesus falling [under the cross]; Image of the Blessed Virgin majoris; Two portraits of His Lordship Ossoliński, the second of His Lordship Lubomirski; coats of arms, imperial and royal; Two courtesans, one bigger the other smaller; Portrait of the late Priami, which stays with Mr. Jerzy Priami". According to testament of Jan Pernus, councilor of Kraków, from 1672 he had a large painting of Præsentationis (Presentation), allegedly by Rubens. He collaborated with the Swedes during the invasion in the years 1655-1657 and took part in the shameful looting of the royal palace in Łobzów and the Wawel Cathedral by the occupants. Pernus looted valuable marbles from the Łobzów palace, and it is possible that he took the paintings decorating the royal residence (after "Galeria rajcy Pernusa" by Michał Rożek). "Two paintings of Roman work on copper, which are in my room, one of the Nativity of Christ, the other of the Assumption of the Virgin Mary of equal size; I want my nephew (Franciszek Pernus, heir) to offer them to His Majesty the King, the merciful Lord, from me, the lowest subject [...] To Mr. Reyneker, councilor of Kraków, my son-in-law, [...] I mark him a picture of Saint John Cantius, painted on a metal plate, from the worthy Master Strobel [Bartholomeus Strobel], asking him to accept this tiny gift as a sign of my love and as a souvenir. [...] Living in great friendship with Priest Adam Sarnowski, Canon of Warsaw and Łowicz, private scribe of His Highness, as a souvenir, I give him a painting of the Virgin Mary, of a prominent Roman craftsman. This picture is in the room in the garden, with Saint Joseph and Saint John, plus four paintings on canvas, with flowers on them, about three quarters of a cubit large, with golden frames". Four paintings with flowers of Roman work he donated to the Bielany Monastery and portraits of himself and his wife to the Pernus Chapel at the St. Mary's Basilica in Kraków (after "Skarbniczka naszej archeologji ..." by Ambroży Grabowski, pp. 61-68). Mentioned Adam Sarnowski made provisions for his possessions and paintings in his will signed in Frombork on April 15, 1693, four months before his death. One painting he left to Queen Marie Casimire Sobieska (de La Grange d'Arquien): "To the Queen Her Majesty, My Lady, the original of Three Kings [Adoration of the Magi] by Rembrandt, in black frames, which is upstairs in the hall, and another beautiful that Mr. Locci will choose" (after "Testament Adama Sarnowskiego ..." by Irena Makarczyk, p. 167). Jadwiga Martini Kacki, later Popiołkowa, in her will of 1696 says: "To Fathers Carmelites na Piasku, please give two paintings painted in Greek style on canvas, and the third one by Salwator". The 1696 property list of Kazimierz Bonifacy Kantelli (Bonifacius Casimirus Cantelli) from Carpineti in Campania, apothecary and royal secretary, who came to Kraków from Krosno, and obtained the city rights in 1625, includes a large number of paintings, mostly religious; but there are also portraits of notable people, such as king John III Sobieski, Ladislaus IV Vasa, Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga, Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria, King John Casimir, King Michael Korybut, Chancellor Ossoliński and many others. Occasionally there are also other objects of art in inventories, like "Amber effigy of King Sigismund III", mentioned in the will of Wolfowicowa, wife of the Kraków councilor in 1679. In 1647 a widow Anna Zajdlicowa née Pernus, in her last will stated: "To Mr Filip Huttini, secretary and decree scribe of the King His Majesty, Kraków councilor, I give and bequest my golden leather upholstery [cordovan], with pictures of Polish kings". There were also many paintings with mythological themes. In the register of property of councilor Kasper Gutteter (1616) there were paintings depicting Venus, Hercules and the mythical Labyrinth. The image of Mercury with Venus was in the house of Wojciech Borowski (1652). Rozalia Sorgierowa (1663) had a painting of Andromeda and the list of movables of Oktawian Bestici from 1665 contained: "Satyr on canvas", "Venus lying naked" and "Three Dianas". In the collection of Andrzej Kortyn (Andrea Cortini) there were six mythological paintings, including Venus and Cupid (after "Mecenat artystyczny mieszczaństwa krakowskiego ..." by Michał Rożek, p. 177). According to the rich inventory of May 10, 1635, the municipal scribe of Poznań Wojciech Rochowicz owned a painting of Pallas Athena, Venus and Juno, as well as 5 small paintings in frames painted on oak boards depicting "Roman people". Several erotic paintings were mentioned in the very rich gallery of Poznań burgher Piotr Chudzic, who died in 1626, like a "naked picture for appetite", "3 paintings of courtesans" and "a very small round Venetian picture on tin of a courtesan" (after "Odzież i wne̜trza domów ..." by Magdalena Bartkiewicz, p. 68 and "Inwentarze mieszczańskie Poznania", p. 407). Rochowicz in Poznań had one image of a courtesan and one of a wenetka (Venetian courtesan), Krzysztof Głuszkiewicz in Lviv had six paintings of courtesans and in Kraków paintings of courtesans were owned by: Franciszek Delpacy (1630), Anna Telani (1647), Oktawian Bestici (1655), Andrzej Cieski (1659), Gerard Priami (1671) and Stanisław Kłosowicz (1673), who had four paintings of courtesans (after "Sztuka a erotyka", ed. Teresa Hrankowska, p. 197). Hieronim Morsztyn (1581-1623), author of the "Worldly Pleasure" (1606) and many erotic poems, in his work "Actaeon. (To Polish Courtesans)" wrote that they would gladly "run naked". Nude and erotic paintings, such as "A round painting in a gilded frame, which represents the 3 Graces with the portrait of His Highness the King" (62), "A painting in a gilded and sculpted frame, representing the 3 Graces, giving the Books of Eternity with the portrait of His Majesty the King" (63) and "A painting that depicts a naked woman with a man, embracing" (65), are mentioned in the inventory of the bathing pavilion of King John III Sobieski in Zhovkva in 1690 (Regestr opisania łaźni w zamku żółkiewskim po odjeździe Króla Jmci na sejm do Warszawy in anno 1690 die 5 Januarii). The Polish Vasas, descendants of the Jagiellons on the maternal side (through Catherine Jagiellon), were renowned patrons who commissioned many beautiful paintings and other objects locally and abroad in the best workshops, such as for example a series of 6 tapestries with the story of Diana, purchased around 1611-1615 by Sigismond III Vasa in the workshop of François Spierincx in Delft. In 1624, Peter Paul Rubens painted Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (future Ladislaus IV) during his visit to Brussels. According to available sources, Rubens and Ladislaus Sigismund's father, king Sigismund III, never met in person, but the beautiful portrait of the king is undoubtedly by his hand (attribution to Rubens by Ludwig Burchard, Heinz Collection Kisters in Kreuzlingen). Although not confirmed in surviving letters or inventories, this effigy of the king was beyond doubt created from some study drawings or miniatures sent from Warsaw. Elected king John III Sobieski (from 1674) consciously organized European opinion, commissioning appropriate works, paintings and engravings in Poland and abroad, in the Netherlands, Flanders, Paris and Italy (works by Romeyn de Hooghe, Reinier de la Haye, Caspar Netscher, Prosper Henricus Lankrink, Ferdinand van Kessel, Adam Frans van der Meulen, Jan Frans van Douven, workshops of Pierre Mignard and Henri Gascar, Jacques Blondeau, Simon Thomassin, Giovanni Giacomo de Rossi, Domenico Martinelli). Exquisite sculptures were also ordered abroad, like statues by Flemish sculptors Artus Quellinus II and his son Thomas II and Bartholomeus Eggers (Wilanów Palace and Summer Garden in Saint Petersburg, taken from Warsaw in 1707), jewellery in Paris (Sobieski diamond) and silverware in Augsburg (works by Abraham II Drentwett, Albrecht Biller, Lorenz Biller II and Christoph Schmidt). The construction of his suburban residence, inspired by the Villa Doria Pamphili in Rome, Sobieski entrusted to Augustyn Wincenty Locci, son of the Italian architect Agostino Locci. The best local and foreign artists, architects and scientists participated in the decoration of the residence and the glorification of the monarch, his wife and the Commonwealth. The inventory of the Picture Gallery of the Radziwill Palace in Biała Podlaska, called Radziwiłłowska (Alba Radziviliana), from November 18, 1760, provides an interesting insight into the quality and diversity of painting collections in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. The palace was built by Alexander Louis Radziwill (1594-1654), Grand Marshal of Lithuania after 1622 on the site of old wooden mansions. The inventory lists 609 positions of mainly religious and mythological paintings of which nothing preserved in Biała: (52) Painting of Diana, painted on tin with two arrows without frames, (53) Picture of Adonis sleeping with the Goddess Hera [Venus and Adonis], painted on glass in gilded frames, (84) Painting of Diana's hunt, painted on a panel in a gilded frame, (113) Sleeping Venus lying on a bed, without frames, (117) Face of Pallas [Athena], painted on canvas without frame, (128) Venus standing in water [Birth of Venus], painted on copper in gilded frames, (157) Portrait of King Sigismund Jagiello and Grand Duke of Lithuania [Sigismund I] on tin without a frame, (158) Portrait of King Sigismund of Poland and Sweden [Sigismund III Vasa], [...], painted on tin, without frame, (165) Portrait of Henry Helesius [Henry of Valois], King of Gallia and Poland, Grand Duke of Lithuania, painted on copper in frames, (166) Portrait of King Stephen Bathory, painted on tin in black frames, (181) Diana holding a trumpet, painted on canvas in old gilded frames, (192) Story of Vulcan and Venus, painted on canvas, without frames, (193) Second story, also of Venus, also with Venus and Vulcan, large painting on canvas, without frames, (206) Male portrait, painting by Rubens, on canvas in black frames, (210) Picture of Baceba [Bathsheba] at her bath, painted on canvas without frame, (213) Painting of Lucretia, expressive, with a dagger, a fine painting painted on canvas, no frame, (217) Picture of Herodianna [Herodias] with the head of Saint John, painted on canvas without frames, (224) Picture of Hercules, painted on canvas without frame, (233) Painting of Venus descending from the clouds, a large painting on canvas, without frames, (234) Picture of Lucretia pierced with a dagger, painted on canvas, without frames, (235) Painting of nude Venus reclining with Cupid, painted on canvas, no frame, (258) Story of Venus with Adonis, large painting on canvas, without frame, (259) Portrait of a knight, full-length, Rabefso [Rubens?], on canvas without frame, (283) Painting of Bacchus, painted on canvas without frame, (284) Painting of Judith, painted on canvas, without frame, (296) Picture of Lucretia, painted on panel, without frame, (302) Half-naked person, painted on canvas, without frame, (303) Meditating Lucretia, painted on canvas, without frame, (335) Landscape with dwarfs and fruits, painted on canvas, (336) Landscape with dying Diana and the nymphs, on canvas, (348) Painting of Venus sleeping naked, painted on canvas, without frame, (349) Painting of Adonis with Venus enjoying, painted on canvas, without frame, (376) Painting of Venus with Cupid and Zefiriusz with Hetka [most likely homoerotic Zephyrus and Hyacinth], two pieces of similar measure and N°, painted on canvas, without frames, (390) Story of Dyanna on which golden rain falls [Danaë and the shower of gold, possibly by Titian or workshop], painted on canvas without frames, (391) Sleeping Venus, painted on canvas, without frames, (535) Portraits of various Lords ... thirty-six of different sizes, painted on canvas, without frames, (536) Portraits of various Lords and Kings of unequal size, painted on canvas, (544) Different portraits under one No., nineteen pieces, painted on canvas, (577) Portrait of Stephen Bathory, King of Poland, painted on canvas in black frames, (596) Story of Judith with Holofernes, painted on canvas in black frames, (597) Venus asleep on the hunt, painted on canvas, (604) Story of Saint Susanna with two Elders, painted on panel in black gilded frames, (607) Kings of Poland, fifty and one on parchment and (608) A lady with a dog, painted on panel, without frame (after "Zamek w Białej Podlaskiej ..." by Euzebiusz Łopaciński, pp. 37-47). With such a large collection, it was difficult to fully describe the identity of each effigy. The chaos of war also contributed to the forgetting of the names of models and painters. Many valuable works of art in Poland-Lithuania were looted or destroyed during the invasions of the country in the 17th, 18th, 19th and 20th centuries. The country became significantly impoverished due to the wars, so valuable and movable works of art, especially those whose history was lost, were sold. By the end of the 18th century, like the country itself, Poland-Lithuania had almost completely disappeared from the history of European art. Art collections were confiscated during the Partitions of Poland - after collapse of the Kościuszko Uprising in 1794 (especilly Polish crown jewels), November Uprising in 1830-1831 and January Uprising in 1863-1864. To secure their belongings, many aristocrats move their collections abroad, especially to France. When the Second World War broke out in 1939, the Jagiellonian tapestries commissioned in Flanders by king Sigismund II Augustus and recovered from the Soviet Union between 1922-1924, were transported through Romania, France and England to Canada and returned to Poland in 1961. The elective system of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth also favored the outflow of works of art from the country. Paintings and other valuables from the royal collection that survived the Deluge (1655-1660) were transported to France by king John II Casimir Vasa (1609-1672), who abdicated in 1668 and moved to Paris. Many valuables were inherited by Anna Gonzaga (1616-1684), Princess Palatine, who died in Paris. Queen Bona Sforza (1494-1557) moved her belongings to Bari in Italy, Queen Catherine of Austria (1533-1572) to Linz in Austria and Queen Eleonora Wiśniowiecka (1653-1697) to Vienna. French Queen Marie Casimire Sobieska and her sons transported their collections to Rome and France and elective monarchs from the Saxon dynasty in the 18th century moved many items to Dresden. The last monarch of the Commonwealth, Stanislaus II Augustus, abdicated in November 1795 and moved part of his collection to Saint Petersburg. It should also be noted that when the treasures of the Most Serene Republic (Serenissima Respublica Coronae Regni Poloniae Magnique Ducatus Lithuaniae) were plundered by different invaders, in 1683, the army of the Republic under the leadership of the elected monarch John III Sobieski saved the opulent imperial treasures from a similar fate at the gates of Vienna (Relief of Vienna or Battle of Vienna). A century later, between 1772 and 1795, Austria was one of the countries that divided the Republic (Partitions of Poland) and Poland disappeared from the maps of Europe for 123 years.
Art collection of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa, attributed to Étienne de La Hire, 1626, Royal Castle in Warsaw.
Portraits of Sigismund III Vasa and Stanisław Radziejowski by Daniël van den Queborn or follower of Frans Pourbus the Younger
In the Czartoryski Museum in Kraków there is a portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa attributed to Dutch school (oil on panel, 93 x 68 cm, inventory number MNK XII-352). The painting was purchased in 1875, together with other portraits and miniatures, from Mikołaj Wisłocki from Pogorzela. It was initially attributed to Bartholomeus van der Helst (1613-1670) and according to the printed sticker on the back of the painting it was purchased in Podbela in Belarus, near the Białowieża Forest and hung for a long time in the old larch chapel in Białowieża (Zygmunt 3o Król - na drzewie ma być roboty fan der Helsta malarza Holenderskiego - nabyty w Podbiałey, pod puszczą Białowieską - wisiał bardzo długo w Starey Modrzewiowej Kaplicy w Białowieży (gub. Grodzieńska:)).
Jagiellonian hunting mansion located in Stara Białowieża was probably used as early as 1409, and around 1594, during the reign of Sigismund III Vasa, it was moved to the center of modern Białowieża, where a mill was also built. Less than a year after his election, in 1588, in the face of the plague in Kraków, the young king left the capital and hunted in the Białowieża Forest. "The manor house in Białowieża built for His Royal Highness for passage and hunting" is mentioned in 1639 and it was destroyed during the Deluge (1655-1660) or soon after and was last mentioned in 1663. In 1597 Sigismund III orders the Court Treasurer of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Dymitr Chalecki (d. 1598), to cancel the charges against the serfs employed in digging "Our Białowieża Pond" and to "relax the heavy burdens in the works" (after "Dwór łowiecki Wazów w Białowieży ..." by Tomasz Samojlik and others, pp. 74, 76-77, 80, 84). In 1651 Sigismund's son John II Casimir empoyed a Dutch architect and engineer Peeter Willer (or Willert) for similar works in Nieporęt near Warsaw and Henry IV of France (1553-1610) brought the best Dutch engineers to dry out, drain, build polders with their canals, locks, meadows, and low farms all round the coast of France (after "The French Peasantry ..." by Pierre Goubert, p. 2). It is quite possible that Sigismund also employed specialists from the Netherlands, also those already active in Polish Prussia, to create ponds and supply plants and fish. The painter probably never saw the king in person, so the resemblance is not striking, especially to portraits by Martin Kober, which has led some authors to suggest that it was originally a portrait of somone else transformed into the king's effigy. Probably in the 17th century, as the style suggest, a Latin inscription (SIGISMVNDVS III / DEI GRA: REX POLONIÆ) and a crown were added, however taking into consideration the provenance from the royal Białowieża, tradition, general resemblance and inscriptions there is no reason to claim that this is not an original portrait of the king commissioned in the Netherlands. A similar effigy of Sigismund with a long mustache and blond hair was included in hand colored map of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth (Poloniae Amplissimi Regni Typvs Geographicvs) from Speculum Orbis Terrarum by Gerard de Jode, published in Antwerp in 1593. The likeness of the king is one of the few effigies in this publication, which could indicate that the Polish court influenced it on this particular map or that it was inspired by the increase in orders for effigies in the Netherlands at that time. The style of the painting from Białowieża is reminiscent of the two portraits unanimously attributed to Frans Pourbus the Younger (1569-1622), a Flemish painter from Antwerp (from about 1592 active in Brussels), in the Galleria nazionale di Parma, identified as Luigi Carafa and his wife Isabella Gonzaga (inventory number 297, 303), however, it is even more similar to two paintings atributed to another painter from Antwerp - Daniël van den Queborn, both in the Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam. One depict a child 18 months old in 1604, possibly Louis of Nassau, the illegitimate son of Prince Maurice of Orange (SK-A-956) and the other, dated '1601', Francisco de Mendoza, Admiral of Aragon and Marquis of Guadalest, who was mayordomo mayor (lord high steward) in the household of Albert VII, Archduke of Austria and took part in different diplomatic missions to Poland, Hungary, Styria and the Holy Roman Empire (SK-A-3912). In 1579 Daniël joined the guild of Middelburg and in 1594 he became court painter to Prince Maurice in The Hague. The style of the king's costume and ruff is very similar to that seen in Gortzius Geldorp's portraits of the 1590s - portrait of Jean Fourmenois, dated '1590' (Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam, SK-A-912) and portrait of Gottfried Houtappel, dated '1597' (The State Hermitage Museum, ГЭ-2438). Portrait of Joachim Ernst (1583-1625), Margrave of Brandenburg-Ansbach (sold at Christie's, 27 October 2004, lot 46) from the 1610s, as his costume indicate, is attributed to follower of Frans Pourbus the Younger. In 1609, Pourbus moved to Paris and Joachim Ernst's stay in France at that time is not confirmed in sources. On August 14, 1593 Sigismund III arrived in Gdańsk with his wife Anna of Austria, sister Anna Vasa and the entire court. The city was a major port of the Commonwealth where Netherlandish influences became predominant at that time in almost all aspects of life (trade, art, architecture and fashion). The river cruise from Warsaw to Gdańsk lasted 12 days and the ceremonial welcome took place at the Green Gate. On 15 August 1593 the court took part in the procession at the Dominican Church. The ceremony was presided over by the Bishop of Kuyavia, Hieronim Rozdrażewski, who purportedly commissioned a drawing illustrating the event (possibly a study for a painting), attributed to Anton Möller the Elder (Wawel Royal Castle). The king then went with the court to Wisłoujście, from where on September 16, on 56 or 57 ships, he sailed with the people accompanying him and a detachment of the Polish-Lithuanian army to Sweden. The king embarked on a ship provided by the city of Amsterdam (after "Polacy na szlakach morskich świata" by Jerzy Pertek, p. 56). It is possible that among the courtiers accompanying the king was also the young nobleman Stanisław Radziejowski (1575-1637). He was a courtier at the court of the widowed Queen Anna Jagiellon in Warsaw, where he received the title of court steward and after her death in 1596 he passed to the court of Sigismund Vasa, where he again served mainly Queen Anna of Austria and her son Ladislaus Sigismund. He later did not hold any functions at the court, but he took part in confidential missions abroad and in the Commonwealth (after "Radziejowice: fakty i zagadki" by Maria Barbasiewicz, p. 41). Stanisław studied abroad, in Würzburg in 1590. In 1598 he was sent as a peace delegate to Moscow, he become the starost of Sochaczew in 1599 and he accompanied the king during his travels (e.g. in 1634 to Gdańsk). Radziejowski often had the opportunity to host the entire royal court under his roof in his estate in Radziejowice near Warsaw. There was no foreign envoy, no apostolic nuncio who did not experience his hospitality and Queen Constance of Austria, Sigismund's second wife, willingly took a bath in Radziejowice. No effigy of Stanisław preserved in Poland, but as a courtier so close to the queen who traveled abroad, he undoubtedly dressed primarily in Western European fashion. The painting in the National Museum in Kraków (inventory number MNK I-20) depicting the Adoration of the Crucifix with King Sigismund III Vasa and his male courtiers, painted by Wojciech Maliskiewic in 1622, clearly shows the disposition of fashion at the royal court. Only a quarter of the courtiers are dressed in national costume, the others wear ruffs and fashionable hose. In 1583 Balthasar Bathory de Somlyo, nephew of King Stephen Bathory raised at his court in Kraków, was portraited by Hendrick Goltzius in French costume during his visit to the Netherlands with his friend Stanisław Sobocki. Treasurer (Jan Firlej, Grand Treasurer of the Crown) from Stanisław Sarnicki's "Statutes and records of crown privileges", published in Kraków in 1594, also wears western attire, as well as Stanisław's infamous son Hieronim (1612-1667), who was depicted dressed according to Western European fashion in a print by Jeremias Falck Polonus, created in 1652. In 2022 a portrait of a young man painted in similar style to the Białowieża portrait was sold at Dorotheum in Vienna (oil on canvas, 65.5 x 55 cm, 11.05.2022, lot 25). This painting is attributed to Frans Pourbus the Younger and comes from private collection in Uruguay (since the 1920s). The exact provenance is unknown, so it is possible that it was associated with Polish immigration to Uruguay where the first Poles arrived in the 19th century as political refugees who fled after the January Uprising (the first Polish organization in Montevideo was established in 1921). The young man is wearing a fashionable embroidered doublet and a lace ruff. According to Latin inscription in upper part of the painting it was created in Antwerp and the sitter was 18 in 1593 (ANTVE'[rpiae] ANo SAL.. / 1593 / ÆTA' SVÆ.18..), exacly as Radziejowski, when he may have finished his studies and could board a ship in Antwerp for Gdańsk or just order it from Gdańsk in Antwerp, like his grandson Cardinal Michał Stefan Radziejowski, who ordered his portrait in Paris (attributed to painter from Antwerp Jacob Ferdinand Voet, Czartoryski Museum, MNK XII-377). The family resemblance is striking with the portrait of Michał Stefan in the Museum of Warsaw (MHW 15948), and mentioned effigy of Stanisław's son, the shape of the nose, the puffiness under the eyes and a dimple in the chin being particularly similar in these family members. A painting attributed to Frans Pourbus the Younger, which may come from the collection of Sigismund III and possibly linked to Radziejowski's diplomatic activity, is in the Lithuanian National Museum of Art in Vilnius (oil on canvas, 56 x 44 cm, LNDM T 4019). This "Portrait of a woman with a red ribbon" is dated at the top right '1604' and belonged to the same gallery as "Portrait of a woman with a diadem", dated '1614' (LNDM T 4018), which is an effigy of Marie de' Medici (1575-1642), Queen of France by Alessandro Maganza, identified and attributed by me. The woman's costume is also similar to that visible in another effigy of the Queen of France, created by Thomas de Leu or circle around 1605 (Austrian National Library), while her facial features resemble those of Christina of Lorraine (1565-1637), Grand Duchess of Tuscany (wife of Marie's uncle), after a print by Thomas de Leu, produced between 1587-1590 (The Royal Collection, RCIN 615750). Her features also resemble those in Christine's other portraits, such as that by the French painter, perhaps François Quesnel, from 1588 (Uffizi Gallery in Florence, Inv. 1890, n. 4338) or a copy by the Italian painter, painted after 1589 (sold at Sotheby's New York, May 26, 2023, lot 314). Around 1604, Frans Pourbus painted Christine's future daughter-in-law - Archduchess Maria Magdalena of Austria (1587-1631) in a yellow dress (Kunsthistorisches Museum, GG 3385) and her older sister Constance (GG 3306). Several portraits of the Polish-Lithunian Vasas preserved in Florence, such as the full-length portrait of Sigismund III (Inv. 1890, n. 2270) dating from around 1610. The monarchs of the Commonwealth undoubtedly also owned numerous effigies of the sovereigns of Tuscany. Some of them may also have been brought by Radziejowski, who was in Florence in 1616 and who in 1615 gave Grand Duchess Maria Magdalena a mirror in an amber frame.
Portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa (1566-1632) by Daniël van den Queborn or follower of Frans Pourbus the Younger, 1590s, Czartoryski Museum in Kraków.
Portrait of courtier Stanisław Radziejowski (1575-1637), aged 18 by Daniël van den Queborn or follower of Frans Pourbus the Younger, 1593, Private collection.
Portrait of Christina of Lorraine (1565-1637), Grand Duchess of Tuscany in French costume by workshop of Frans Pourbus the Younger, 1604, Lithuanian National Museum of Art in Vilnius.
Portrait of Queen Anna of Austria by Jacopo Tintoretto
Italian painters, faithful to ancient Roman tradition, frequently idealized their models. On the other hand, painters of the Nordic, Netherlandish and German schools, preferred a sometimes grotesque naturalism. This is best seen in the portraits of Emperor Charles V. In the paintings by Marco Cardisco, Parmigianino, Titian, Giorgio Vasari and Francesco Terzi, he is a quite handsome man with harmonious features and large eyes, while in the paintings by Lucas Cranach, Jakob Seisenegger, Jan Cornelisz Vermeyen and Flemish painters, he sometimes looks more like a court jester than a ruler of one of the greatest empires in history.
It was also a strong Habsburg tradition to collect effigies of different rulers of Europe, especially members of their own family. The effigies of Habsburg women who became queens of Bohemia, Hungary, Portugal, France, Denmark, duchesses of Tuscany, Mantua, Savoy, Parma, Bavaria or princesses of Transylvania are richly represented in their collections in Madrid and Vienna. It is therefore quite unusual that the Polish queens from the House of Austria are almost not represented in the collections known today. Some preserved inventories prove that the effigies of Polish monarchs were in the Habsburg collections in Madrid and Vienna. For example, the inventory of certain belongings of Queen Margaret of Austria, sister-in-law of King Sigismund III Vasa, subject to her guardian of the jewels (guardajoyas) Hernando Rojas, from October 1611, lists a miniature portrait (naipe) of the son of the king of Poland (Un retrato del hijo del rey de Polonia en un naipe, item 146) and thirteen "miniature portraits of members of the queen's household, our lady" (Trece retratos de naipe de personajes de la cassa de la reyna, nuestra señora, item 151) (after "Inventare aus dem Archivo del Palacio zu Madrid" by Rudolf Beer, p. CLXXV). For Sigismund's first wife, Anna of Austria (1573-1598), the portraits of her family left in Graz and lost during the Wawel fire in 1595 were obviously of great importance. After the fire, new portraits of the family in Graz had to be painted. The mother, Archduchess Maria Anna of Bavaria, soon sent a portrait of herself, but Anna said the picture bore no resemblance to her mother. "I'm sorry that YH [Your Highness] doesn't have a painter yet. My husband gave me permission for his painter to send him out to paint everyone when he has time, so he will have plenty of work to do" (Es ist mir ye gar laid, das ED [Eure Durchlaucht] jez kain maler hat. Mein gemahel hat mir sein maler bewilligt, wan es wider ED nit wer, denselben hinauszuschigken und alle abzemalen, wann er ainmal zeit hat, dann er hat jez gar vil ze arbaiten), she wrote to her mother in a letter dated April 6, 1595 most likely about the court painter Martin Kober (after "Das Leben am Hof ..." by Walter Leitsch, p. 371, 1267-1269, 1280, 1284, 2376, 2378-2379, 2562). Some information preserved in Austria on the portraits exchanged in preparation for the king's first marriage. The beginnings of the negotiation date back to a time when both were still children, the bride was not yet eight years old and the groom was fourteen and a half years old. It is possible that a portrait of an eight-year-old girl was sent by the Habsburgs. When the affair came to light nine years later, a portrait had to be sent again. "I would like to affirm that the king, as soon as he received the Archduchess Anna's effigy, fell deeply in love with it, opened it in his chamber and, having stood in front of it for a long time, also sent a retrato [Spanish for portrait] of her to his father, the king in Sweden, who was also happy to accept such things" (wol affirmiren, das der könig, alsbald er dero erzherzogin Anna contrafee bekomben, sich stark darein verliebt, dasselbe in seiner camer aufgemacht und villmallen ein guette lange weil darvor gestanden seye, auch seinem herrn vattern, dem könig in Schweden, ein retrato darvon geschickt habe, der im solches gleichsfalls gar wol gefallen lassen), wrote Sebastian Westernacher to Archduchess Maria Anna of Bavaria on May 19, 1591. The effigy of sixteen-year-old Anna hung in the king's bedroom and she was depicted wearing "a white-silver embroidered dress" (in einem weiß silbernen gewirkten rock abconterfeyet), according to a Kraków newspaper about the wedding in May/June 1592. Contemporaries certainly knew that these portraits were often largely beautified, so that the groom had only two options if he wanted to avoid exposing himself to the unknown: send beauty spies or trust the pictures. Before his first marriage, Sigismund sent such spies, but he probably also trusted the effigies. An emissary of the king delivered his portrait to the court master (Hofmeister) of Anna's mother, representing him wearing a jewel with the monogram SA, most probably of his uncle Sigismund Augustus or the groom and bride (Sigismund and Anna), recounted Archduchess Maria Anna to Emperor Rudolf II, in a letter from Graz, dated July 8, 1591 (seines künigs contrafet in ainem tafelein von ebano, darbey auch ain gemaldes glainot an einer klainen gulden kettl an des künigs hals hangend, und darinnen dise zwen puechstaben SA zu sehen). According to some sources, Sigismund's first wife did not care much for luxury. Her confessor, Fabian Quadrantinus (1549-1605) from Starogard Gdański, educated in Rome, affirmed that: "No gold, no jewels, no precious stones were seen on her. She was dressed mostly in black". Other documents prove she did it. According to one inventory, the queen owned more than a hundred items of clothing, and according to a second inventory, more than two hundred. She ordered goods from Florence and purchased luxury goods from Gdańsk. She always ate with a gold spoon and wore jewelry, regularly a ruby and emerald ring, as well as a necklace with a sapphire. Urszula Meyerin, in a letter dated April 3, 1598, claimed that even when she was young, Anna "never respected the voluptuousness, splendor, joys or lusts of the world, but despised and rejected them" (nimmermehr der welt üppigkeit, pracht, freuden oder wollusten geachtet, sondern vielmehr verachtet und verworfen). Jan Bojanowski, however, wrote shortly after her arrival that she was far from being melancholy (krolowa pani nasza is iest pani od melancholiei daleka) and that she was always joyful, but with a gracious dignity (letter of June 22, 1592). When the king wanted to go into battle against the Tatars, the queen expressed the wish to stay close to him, "if necessary, she also wanted to become a mercenary and wear armor" (wan's sein müeste, wolt sie auch ein landsknechtin weren und das fäleisen nachtragen, letter from Ernhofer to Archduchess Maria Anna, April 5, 1595). When she was sent a new portrait of her brother who had become fat, she wrote to her mother: "That's why it seems to me that he was in his 10th month [of pregnancy]" (Darum es dunkt mich auch, ehr sei ihn 10. monat gwesen, letter of February 1, 1597). In another letter to her mother, she commented "that the good old King of Spain is really funny and that you can really enjoy him" (das der guett alt kinig von Hispania erlich paufellig ist und das man sein auch schier gnueg hatt, letter of May 3, 1597). The queen was also adventurous and repeatedly went out incognito to see something, such as the procession on January 27, 1595. Together with Anna Radziwiłłowa née Kettler (1567-1617), she went out in a sleigh "dressed like a patrician lady" (wie burgerin geklaidet). They were not recognized by Polish women and when one of them tried to force her way before the queen, Radziwiłłowa began to argue with her (letter from Ernhofer to Archduchess Maria Anna, March 6, 1595). Similar to other Polish-Lithuanian ladies who experimented with fashion, the young queen undoubtedly also wore Venetian, French, Florentine or Flemish dresses, as described by Piotr Zbylitowski in his "Reprimand of Women's Extravagant Attire" (Przygana wymyślnym strojom białogłowskim), published in Kraków in 1600. Although the queen was very pious, she was not stubbornly zealous like her mother. From August 1592 to August 1593, the young queen lived near the Italianate court of the elderly Queen Anna Jagiellon, sending letters from residences in Ujazdów and Łobzów. Relations between the two queens were probably a bit difficult for many reasons. Above all, they had no common language, as the young queen only spoke German and Spanish and understood Latin and Polish - according to Giovanni Paolo Mucante (Intende, come dicono, la lingua latina, la spagnola, la todesca et anco la polacca, ma non parla se non todesca et spagnola, letter of September 25, 1596). Anna Jagiellon spoke Latin, Polish and Italian. At the beginning there were also some difficulties with priority. During the last six months of her life, the old queen once again lived under the same roof as the young queen. Anna of Austria one day sent her mother the gifts she had received from Anna Jagiellon (letter of November 22, 1593). Young Anna also cared for the old, sick queen herself. The relationship between the two was so good that Archduchess Maria Anna became truly jealous (letter from Salome von Thurn to Archduchess Maria Anna, May 5, 1594). In the Prado Museum in Madrid there is a portrait of a young woman in a green dress sitting on a chair (oil on canvas, 114 x 100 cm, inventory number P000484). The painting comes from the Spanish Royal Collection (no. 597) and was initially attributed to Paolo Veronese (1528-1588) and now to Jacopo Tintoretto (1518-1594). The woman has flowers in her hair and her costume indicate that the painting was made in the 1590s. A similar dress can be seen in a portrait of a woman from the Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden (inventory number Gal.-Nr. 249), dated around 1590 and previously thought to represent Marie de' Medici, Queen of France. Comparison with two woodcuts from Habiti Antichi Et Moderni di tutto il Mondo ... by Cesare Vecellio (Czartoryski Library, 2434 I Cim), book published in Venice in 1598 and assembling contemporary fashion from across the world - Gentildonne ne'Regiment (p. 104) and Donne per casa (p. 108), indicates that she wears the costume of a Venetian noblewoman at home. In this book, the effigy of King Sigismund III (Rè di Polonia / Poloniæ Rex, p. 346) was published with some typical costumes of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. Her protruding lower lip and provenance of the painting indicate that she is a Habsburg. The painter beautified the effigy by making the nose and lips smaller, however, the resemblance to other effigies of the Queen of Poland is notable, in particular the portrait from the Royal Castle in Warsaw (FC ZKW 1370), her effigy in the scene of the Birth of the Virgin by Juan Pantoja de la Cruz in the Prado Museum (P001038) and her portrait by Martin Kober in the Uffizi Gallery (2392 / 1890). Idealization was common at that time. The portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa in a large hat by workshop of Philipp Holbein II, which was before 1939 in the collection of Jan Perłowski in Warsaw (lost during the World War II), is the best example of this practice, perhaps initiated by the painter, who wanted the model to conform more to his standards of beauty. The woman in this portrait also closely resembles the queen's younger sister, Constance, who a decade later would become the second wife of Sigismund III, in her idealized portrait at Wawel Royal Castle (inventory number 1783). According to inventories of Queen Anna's clothing held at the National Archives of Sweden in Stockholm (Riksarkivet, Extranea 85), probably made around 1595, the queen also owned a dress similar to the one depicted in the painting: "A green damask skirt with gold edges" (Ain grien damasten rock mit golt gebrämbt, 92).
Portrait of Queen Anna of Austria (1573-1598) in a Venetian damask dress by Jacopo Tintoretto, ca. 1592-1594, Prado Museum in Madrid.
Portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa in a large hat by workshop of Philipp Holbein II, 1610s, lost during World War II.
Portrait of Prince Jerzy Zbaraski as Saint George by Paolo Fiammingo
In 1591, after initial studies in the country, the young Zbaraski brothers Jerzy (George) or Yuriy (1574-1631) and Krzysztof (Christopher) or Kryshtof (1579-1627), descendants of Ruthenian Prince Fyodor Nesvitsky (died before 1442), went on a long trip abroad. They visited Germany, Italy and France. They studied in Padua (1592-1593) and visited Venice, Rome and Naples. In France, they went to Lyon, Bordeaux and Paris. While studying abroad, the brothers converted from Calvinism to Catholicism, however, they were supporters of religious tolerance and opponents of the enormous influence of the Jesuit Order.
They returned to the country at the turn of 1594 and 1595. In the following year (1596) they participated in the expedition to Hungary, in the Moldavian expedition and in the siege of Suceava. In 1598 Jerzy was in the retinue accompanying King Sigismund III Vasa in Sweden. Probably at the turn of 1600 and 1601, both Zbaraski brothers went to the Netherlands, where Jerzy studied Greek and history under Justus Lipsius in Louvain. Between 1602-1605, Krzysztof stayed in Italy again, where he mastered mathematical science under the supervision of Galileo. In 1616 also Jerzy returned to Padua where he enrolled at the university. In 1620, after the death of Janusz Ostrogski, Jerzy Zbaraski was appointed Castellan of Kraków. Like his yonger brother Krzysztof, he was not married and had no children. The Zbaraski brothers were the heirs of their father's enormous fortune, in addition to the estates of their mother, Duchess Anna Chetvertynska (Czetwertyńska), a member of the Ruthenian princely family, who according to Józef Wolff were descendants of Yaroslav the Wise, Grand Prince of Kiev. In the 16th century Chetvertynski family owned large estates in Ukraine and Belarus and like Zbaraski family, they had Ruthenian Pogonia, displaying Saint George defeating the dragon, in their coat of arms. Already in June 1589, in the retinue of bishop Radziwill and voivode Mikołaj Firlej, Jerzy visited the imperial court in Prague, where he had the opportunity to admire exquisite art collections of Emperor Rudolf II. From Venice, Jerzy, a great connoisseur and lover of art, brought the painting of Our Lady of Myślenice, later famous for miracles. According to "The History of the Miraculous painting of Our Lady in Myślenice", published in 1642 in Kraków, the original painting belonged to Pope Sixtus V, who left it in his will to the granddaughter of his sister, who became the abbess of a convent in Venice. When Prince Jerzy Zbaraski saw it in the convent, he wanted to have it, but the abbess did not want to give him the original, but agreed to make a copy. During the plague in Kraków in 1624, the painting was supposed to be burnt as "infected", but was spared from destruction. In 1633, the painting was transferred to the parish church in Myślenice. The image of the Virgin Mary is painted on a wood panel (50.3 x 67.8 cm) and because of some style similarities it is attributed to the Prague school from the beginning of the 17th century. The face and pose of the Virgin is however almost identical as in the painting showing Bathsheba at her bath (sold at Cambi Casa d'Aste in Genoa on 30 June 2020, lot 100), created by Paolo Fiammingo (Paul the Fleming, ca. 1540-1596). Fiammingo, born Pauwels Franck, was a Flemish painter, who, after training in Antwerp, was active in Venice for most of his life. He also possibly worked in Florence. Around 1573 he settled permanently in Venice, where he became a student of Jacopo Tintoretto. He opened a successful studio, which received commissions from all over Europe. One of his most important clients was Emperor Rudolf II and Hans Fugger, the heir of a German banking dynasty, who commissioned him in 1580 to produce several paintings to decorate the Swabian Escorial - Kirchheim Castle near Augsburg. The style of the hand of Mary in Myślenice painting is similar to that visible in the Lady revealing her breast (An honest courtesan) by Domenico Tintoretto, dated to the 1580s (Prado Museum in Madrid, inventory number P000382). The portrait of a man as Saint George in private collection, attributed to Italian or Venetian school, is also similar to Tintoretto's style. This small painting (28.7 x 21.7 cm) was painted on copper and the style of painting resemble more precisely the image entitled Profession of arms from the Munich Residence, attributed Fiammingo and created in the 1590s (Alte Pinakothek in Munich). Prince Jerzy Zbaraski was a founder of at least two churches dedicated to his patron saint, Saint George. One in the main seat of the Prince and his brother, Zbarazh in Volhynia, was the burial place of part of the Zbaraski family. The wooden church and fortified Bernardine monastery was founded in 1606, and from 1627 the new brick church was built, most probably to design by Venetian architect and engineer of His Highness King Sigismund III Vasa, Andrea or Andrzej dell'Aqua, driving nearly 1,600 piles into the marshy area. This church was destroyed in 1648. In 1630 Zbaraski also founded Saint George's church in Pilica. Between 1611-1612, Krzysztof commissioned to Vincenzo Scamozzi in Venice, a project for a fortified palace intendend for Zbarazh. In a commentary to his design, published in 1615 in his "L'Idea Della Architettura Universale", Scamozzi recalled numerous meetings and discusions on military architecture with the learned Ruthenian aristocrat. It was however a design of the Flemish military engineer Hendrik van Peene and Venetian Andrea dell'Aqua that was used to built the new Zbarazh fortress between 1626-1631. His treatise on artillery "Praxis ręczna działa" from 1630 (manuscript in the Kórnik Library), dell'Aqua dedicated to Prince Jerzy Zbaraski. In 1627 Jerzy founded the Zbaraski Chapel at the Gothic Dominican Church in Kraków, as a mausoleum for himself and his brother. It was built by the masons and sculptors Andrea and Antonio Castelli, probably according to the design of the royal architect Constantino Tencalla. In the baroque chapel there are monuments to two brothers carved in black Dębnik marble and white alabaster. Jerzy is depicted sleeping in armour and in a pose almost identical to that in the tomb monument of King Sigismund I the Old in the Sigismund's Chapel (1529-1531). His hairstyle is typical of a Polish-Lithuanian magnate from this period and he is holding his mace like if he was holding his manhood, a less subtle allusion to his virility or promiscuity. It is possible that some of the highly erotic works by Fiammingo were commissioned by Prince Zbaraski. The man depicted as Saint George resemble Jerzy Zbaraski from his tomb sculpture, his portrait painted in the 1780s after original from the 1620s (Wilanów Palace in Warsaw) and effigies of his brother Krzysztof (National Museum of the History of Ukraine and Lviv National Art Gallery). Jerzy was accused of a dissolute lifestyle and when he decided to put an end to coin counterfeiters with whom he was about to cooperate, they "persuaded one lady who visited the prince to give him a poison" (after "Niepokorni książęta" by Arkadiusz Bednarczyk, Andrzej Włusek). Despite having no children, the memory of the last Prince Zbaraski preserved in the exquisite works of art that he commissioned.
Portrait of Prince Jerzy Zbaraski (1574-1631) as Saint George by Paolo Fiammingo, 1592-1594, Private collection.
Our Lady of Myślenice by Paolo Fiammingo, 1592-1594, Saint Mary's church in Myślenice.
Portrait of royal courtier Sebastian Sobieski by Leandro Bassano
Around October 16, 1593, king Sigismund III Vasa departed from Gdańsk for his coronation as the hereditary king of Sweden. He was accompanied by his courtiers, including Sebastian Sobieski (ca. 1552-1614), third son of captain Jan Sobieski (ca. 1518-1564) and Katarzyna Gdeszyńska. Earlier that year, in February, Sebastian was sent by the King as his envoy to the Lublin Sejmik (regional assemby). It is the first confirmed important function of this royal courtier. "Instructions for the Lublin Sejmik given from His Majesty to Sebastian Sobieski, a royal courtier in Warsaw on February 16, 1593", is in the Czartoryski Library in Kraków (BCz 390).
Sobieski most probably studied at the Calvinist school in Bychawa near Lublin. On December 17, 1576, probably thanks to the intercession of the Crown Vice-Chancellor Jan Zamoyski, he was admitted, as a page, to the court of king Stephen Bathory. Then, like his brothers, due to growing influence of the Counter-Reformation movement at the royal court, he converted to Roman Catholicism. On May 1, 1584, he was transferred to the group of salatariati saeculares (lay beneficiaries) in which he was until the death of the king. He became a supporter of Zamoyski, supported the election of king Sigismund III and, apparently, he participated in the defense of Kraków against the attack of the troops of Archduke Maximilian II in 1587 and the Battle of Byczyna in 1588. From May 1596, he held the position of Standard-Bearer of the Crown and as such he was depicted in the "Entry of the wedding procession of Sigismund III Vasa into Kraków in 1605" (Royal Castle in Warsaw). Portrait of a bearded man in oriental costume from private collection in France, due some similarity to the style and, possibly, dates of his life is attributed to Hans von Aachen (1552-1615), a German painter trained in Italy. In 1592, while he was still working in Munich, von Aachen was appointed a court painter of Rudolph II, Holy Roman Emperor and moved to Prague in 1596. According to inscription in Latin in upper right corner the man was 41 years old in 1593 (ANNO 1593 / ÆTATIS 41), exacly as Hans von Aachen, but also Sebastian Sobieski, born in about 1552. The portrait is evidently not a self-portrait of imperial court painter and this wealthy nobleman was depicted in a crimson silk żupan buttoned up to with gold buttons, very similar to żupan buttons of Stanisław Piwo, deputy cup-bearer of Płock, from the second quarter of the 17th century (Skrwilno Treasure, Toruń Regional Museum). His black coat trimmed with lynx fur it is almost identical to the one shown in the portrait of Jan Opaliński (1546-1598), created in 1591 (National Museum in Poznań), or in Twelve Polish and Hungarian types by Abraham de Bruyn, created in about 1581 (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam). His lace collar is very similar to the one in the effigy of The Marshal (Stanisław Przyjemski with a marshal staff) from Stanisław Sarnicki's "Statutes and records of crown privileges" by Jörg Brückner in Kraków, created in 1594 (Czartoryski Library). Letters on the table are very important documents, most probably envoy instructions given by the king. The style of painting is identical with portrait of Doge Marino Grimani (1532-1605), created in about 1595 by Leandro Bassano, signed: LEANDER A PONTE BASS [ANO] EQVES F. (Princeton University Art Museum). The man bear a resemblance to effigies of Sebastian Sobieski's brother Marek Sobieski (ca. 1550-1605), voivode of Lublin (1862 woodcut after lost portrait from the Zamoyski collection) and his brother's descendant (Marek's grandson), king John III Sobieski (portrait painting from the 1670s in the Kórnik Castle). Mentioned portrait of Jan Opaliński in Poznań, a copy of a painting destroyed during World War I (from the burnt manor house in Rogów near Opatowiec), is considered by Michał Walicki as a very definite manifestation of the Venetian tradition "referring to the portraits of the Bassanos" (after "Malarstwo polskie: Gotyk, renesans, wczesny manieryzm", p. 33). Stilistically very similar was the painting which was before World War II in the Saint Lazarus hospital in Warsaw bearing the inscription in Latin: R. P. PETRVS SKARGA SOCIETATIS IESV. It represented the court preacher of King Sigismund III Vasa, Piotr Skarga (1536-1612), who became the first priest to hold it. The hospital was established in 1591 on his initiative for the poor and lepers and the founder was depicted sitting in his study before a table covered with an oriental carpet.
Portrait of royal courtier Sebastian Sobieski (ca. 1552-1614) aged 41 by Leandro Bassano, 1593, Private collection.
Portrait of Jan Opaliński (1546-1598) aged 45 by follower of the Bassanos, 1591, National Museum in Poznań.
Portrait of preacher Piotr Skarga (1536-1612) by follower of the Bassanos, after 1591, Saint Lazarus hospital in Warsaw, lost.
Portraits of Queen Anna of Austria and her sisters by Martin Kober and Spanish painters
The inventories of Queen Anna's clothing held at the National Archives of Sweden in Stockholm (Riksarkivet, Extranea 85) were probably made around 1595 because include many items created when she was already queen, such as pillows embroidered with the coats of arms of Poland and Lithuania. The young queen dressed primarily in black Spanish saya in the Central European version as shown in her official portraiture by Martin Kober. She also had specifically "Polish clothing" (Volgen IM polnische klaider, items 205-212) and shorter Spanish dresses (Spänische kurze jänger). In private, she wear many colorful clothes - brown, purple, leibfarb (skin color), yellow, red, white, tyrkroth (Turkish red), aschenfarb (gray), blue and others. She also had at least three green dresses: "A green gold cloth robe" (Ain grien gulden stuck, 72), "A green satin skirt with gold edges" (Ain grien atleser rock mit gulden porten, 87) and "A green damask skirt with gold edges" (Ain grien damasten rock mit golt gebrämbt, 92) (after "Das Leben am Hof ..." by Walter Leitsch, p. 1282, 2381, 2555-2562, 2569, 2571).
The green satin "skirt" (87), a symbolic color of fertility, mentioned in the inventory could be the same dress that was depicted in a portrait of Archduchess Anna at the age of 18, dated 1592 (ANNA ARCHIDVCISSA AVSTRIÆ. / ANNO ÆTATIS / XVIII. / MD / LXXXXII.) from the Bavarian State Painting Collections (on permanent loan to the Germanisches Nationalmuseum in Nuremberg, oil on canvas, 60.5 x 50.9 cm, Gm661 / 6846). This portrait, as well as other similar portraits of her mother and siblings, come from Neuburg Castle. It was therefore most likely originally part of the dowry of Constance of Austria (because her portrait is missing from this series) and later the dowry of her daughter Anna Catherine Constance Vasa. Her large golden pendant shows Jupiter and Danae. The young archduchess was therefore painted shortly before her marriage to Sigismund and the style of this painting is close to Martin Kober, who also worked for the Habsburgs - notably similar to the portrait of Anna's daughter Anna Maria Vasa (1593-1600) at the convent of Las Descalzas Reales in Madrid and portrait of Stanisław Lubomirski (1583-1649) and his sister Katarzyna (d. 1612) at the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna. All of Anna's sisters were depicted in similar dresses. Because of this and the strong family resemblance of all the sisters, it is sometimes difficult to determine the model in other series, such as that from the dowry of Archduchess Maria Magdalena of Austria, today at the Villa del Poggio Imperiale in Florence. This series is attributed to Giacomo de Monte (Jakob de Monte), although the style is also close to Kober. In the series in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, probably from Graz Castle, the portrait of Maria Christina of Austria (1574-1621), is identifed to depict Anna (inventory number GG 3238). This effigy is attributed to de Monte, who used the same set of study drawings as Kober to create the portrait from the Neuburg Castle painted in 1595, when the Archduchess was 21 years old (MARIA CRISTIERNA ARCHIDVCISSA AVSTRIÆ. / ANNO ÆTATIS XXI. / M.D. / XCV., Alte Pinakothek in Munich, oil on canvas, 60.5 x 52 cm, 6845). In the series from the Convent of the Descalzas Reales in Madrid, also attributed to Giacomo de Monte, the four sisters were transformed into Christian saints - Anna was depicted as Saint Dorothy, Maria Christina as Saint Lucy, Catherine Renata as Saint Catherine and Elizabeth as Saint Agnes. Among the portraits of the family members of Margaret of Austria, Queen of Spain, which were in the Queen's Gallery of the Royal Alcazar in Madrid in 1636, there was undoubtedly also a portrait of the Queen of Poland. These portraits were described as: "Parents and brothers of Queen Doña Margarita. Thirteen half-length portraits of the parents and brothers of Queen Doña Margarita, without frames (?), and made by Bartholome Gonçalez for El Pardo" (Padres y hermanos de la Señora Reina Doña Margarita. Treçe retratos de medio cuerpo arriba de los Padres y hermanos de la Señora Reina Doña Margarita, sin molduras, y los hiço Bartholome Gonçalez para el Pardo, Inventory of the Alcázar of 1636, pp. 185-188). Seven portraits from the series, created by the court painter Bartolomé González y Serrano (1564-1627) before 1627, were deposited in 1918 at the Spanish embassy in Lisbon and were destroyed during the fire of 1975. One of them was reproduced in 1968 in the Antemurale XII (Institutum Historicum Polonicum Romae) as a portrait of Anna of Austria (Anna Regina Poloniae, Museo del Prado). In this likeness, she wears a typical Spanish saya from the end of the 16th century. According to an article by Gloria Martínez Leiva ("El incendio de la Embajada española en Lisboa de 1975", January 16, 2018), it is not an effigy of Anna, but of her sister Archduchess Catherine Renata of Austria (1576-1599). The young girl actually resemble more the effigy of Catherine Renata in 1595, when the Archduchess was 18 years old (CATERINA RENEA ARCHIDVCISSA / AVSTRIÆ. ANNO ÆTATIS XVIII. / M.D. / XCV., Germanisches Nationalmuseum, oil on canvas, 60.6 x 50.9 cm, Gm665 / 6847) by Kober then the portrait of her elder sister from the same series. Posthumous effigies of Archduchess Maria Anna and her husband Charles II of Austria (1540-1590) by González, painted after 1608 (Prado Museum, P002434, P002433), were most likely part of the Lisbon series. Regarding the series by Kober, in which some effigies bear different dates (1590, 1592 and 1595), the painter probably created them at the same time but they show the models at different ages and dates. He most likely copied several effigies of Constance's family while working on paintings for her (or one of her sisters') dowry in 1595 in Graz. The eldest daughter of Archduchess Maria Anna was also depicted with her sisters and mother in the scene of the Birth of the Virgin by Juan Pantoja de la Cruz in the Prado Museum (oil on canvas, 260 x 172 cm, P001038). This painting, commissioned by Queen Margaret of Austria for her private oratory in the palace of Valladolid, was created in 1603 (signed and dated: Juº Pantoja Dela .+. Faciebat. / 1603). It probably commemorates the birth and death of the Infanta Maria of Spain, who died in infancy in her first month (March 1, 1603). Her grandmother, Archduchess Maria Anna, is depicted as a divine midwife accompanied by her already deceased daughters - Anna, Queen of Poland and Archduchess Catherine Renata of Austria, who died at the age of twenty-three before her marriage to Ranuccio I Farnese, Duke of Parma. That is why both of them wear more Italian dresses, because in Poland-Lithuania, Italian fashion was popular. All three look at the viewer. The young girl near Saint Anne's bed also looks at the viewer. Her Habsburg features allow her to be identified as Constance of Austria, who in 1602, with her younger sister Maria Magdalena, was considered at the court of Madrid as a candidate to marry Ferdinand I, Grand Duke of Tuscany, but ultimately married Sigismund III in 1605. Although Pantoja accompanied the royal family on journeys to Valladolid, Burgos, Lerma and El Escorial, he probably never left Spain. Archduchess Maria Anna visited Spain for her daughter Margaret's wedding, but that was in 1599. So all the effigies were created by the Spanish painter based on other portraits of family members of the queen or on study drawings, like the mentioned paintings by Bartolomé González. Archduchess Maria Anna's great attachment to her eldest daughter is demonstrated by the fact that when the Archduchess fell into panic because of the Ottoman advance, she wanted to flee to Poland to be with her daughter, and not to Munich, Prague, Brussels or Madrid. In a letter dated September 18, 1594 from Poznań, the queen assured her mother that she could come to Kraków (solang mein gmahel und ich waß haben, so sol ED auch allezeit unverlassen sein).
Portrait of Archduchess Anna of Austria (1573-1598), aged 18 in 1592, by Martin Kober, ca. 1595, Germanisches Nationalmuseum.
Portrait of Archduchess Maria Christina of Austria (1574-1621), aged 21, by Martin Kober, 1595, Alte Pinakothek in Munich.
Portrait of Archduchess Catherine Renata of Austria (1576-1599), aged 18, by Martin Kober, 1595, Germanisches Nationalmuseum.
Birth of the Virgin with portraits of Archduchess Maria Anna and her daughters by Juan Pantoja de la Cruz, 1603, Prado Museum in Madrid.
Portrait of Queen Anna of Austria (1573-1598) and her sister Archduchess Catherine Renata of Austria (1576-1599) in the scene of the Birth of the Virgin by Juan Pantoja de la Cruz, 1603, Prado Museum in Madrid.
Portrait of Archduchess Catherine Renata of Austria (1576-1599) in Spanish dress by Bartolomé González y Serrano, after 1608, Prado Museum in Madrid, destroyed.
Portraits of Queen Anna of Austria nude (Sleeping Venus) by Dirck de Quade van Ravesteyn
Queen Anna of Austria, first wife of Sigismund III, frequently exchanged effigies with members of her family in Austria. Her portraits (conterfet, conterfeit), usually small miniatures (Meiner klein conterfet schick ich ED), are frequently mentioned in her letters to her mother. In January 1595, Anna's brother, Ferdinand of Austria (1578-1637), was about to send two paintings, one for his mother, "the other for your sister, the queen" (das ander für dein schwester die kinigin), according to a letter from Archduchess Maria Anna to him dated January 3, 1595 from Graz (after "Das Leben am Hof ..." by Walter Leitsch, p. 1278, 2380, 2569).
"The reigning queen is 19 years old, slim, but of nice face, pleasant and polite" wrote the Venetian envoy, Pietro Duodo, in his 1592 report to the Venetian Senate (after "Zbiór pamiętników ..." by Julian Ursyn Niemcewicz, p. 76). Judging by the official portraits of the queen by Kober, nothing can be said about her figure, because she is completely covered by her Spanish dress and only her face is clearly visible. So was Duodo allowed to see the queen naked or admire her naked effigy? In a letter of May 19, 1591 to Archduchess Maria Anna, regarding the portrait of Anna received by Sigismund, Sebastian Westernacher reports that the king "opened it in his room" (in seiner camer aufgemacht). The fact that the king admired it in his private chamber indicates that the portrait was nude or erotic as such effigies were frequently covered. For example, the inventory of paintings from the collection of Princess Louise Charlotte Radziwill (1667-1695), drawn up in 1671, mentions "A closed filthy picture" (Obraz plugawy zamykany, item 685 / 56) (after "Inwentarz galerii obrazów Radziwiłłów z XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska, p. 279). Regarding one of her portraits, sent from Kraków to Vienna, the Queen declared in a letter that she preferred it to be destroyed rather than fall into the wrong hands (after "Sztuka i polityka ..." by Juliusz Chrościcki, p. 33-34). Such a statement clearly indicates that the effigy must have been very intimate in nature. The same statement concerns the effigies of her family which were lost in the fire of Wawel Castle in 1595. Some of the Queen's personal belongings, including jewelry, were thrown out of windows into the garden and then not all the items were found, some were stolen, including the chest with "portraits of Her Ducal Highness and all the young princes and princesses" (comterfett von ir f[irstlich] d[urchlaucht] und der ganzen jungen herschaft), according to a letter from Urszula Mayerin dated April 7, 1595. "I would prefer them to burn, instead of being stolen" (Es wer mir lieber, sie weren verbrunnen, ais das mans gestolen hat), the queen said, which also indicates that some of them could be erotic in nature. In many ways, the young queen tried to imitate or compete with the old queen Anna Jagiellon. After the fire, she regretted losing all her tiaras: "I lost all my diadems, including one of 53 very large pearls, almost as large as those on the old queen's string of pearls, and various small things" (Ich hab alle meine krenl verloren, darunder ainẞ [mit] 53 gar grosse perl, schier so groẞ alẞ der alten kinigin grosse sch[n]uer und allerlay kleine sachen) (after "Der Brand im Wawel ..." by Walter Leitsch, p. 248, 251). The marriage of all of Anna Jagiellonica's granddaughters was a highly political affair, so their cousin, Emperor Rudolf II, controlled many aspects of the marriage arrangements. Entire galleries of bridal portraits were made for the emperor during these years and Anna of Tyrol (1585-1618) and Constance of Stiria (1588-1631), the sister of Queen Anna of Austria, were also painted for Sigismund after the death of his first wife. At the end of 1603, the emperor sent the painter Hans von Aachen to Innsbruck. The painter then left for Bavaria, Savoy and Modena, when Rudolf changed his mind and thwarted the negotiations with Sigismund III regarding the marriage with Anna of Tyrol. It was even suspected that the painter would "not paint well" (nichz guttz mallen) to prevent the marriage. The effigy of Anna of Tyrol's older sister, Archduchess Maria of Austria (1584-1649) by Hans von Aachen, now kept at the National Art Gallery in Lviv (inventory number 3857), was most likely created for Sigismund in 1604 (dated upper left). The naturalism of this effigy as well as that of Constance (Kunsthistorisches Museum, GG 9452) is almost grotesque, closer to the paintings from the imperial cabinet of curiosities (Wunderkammer) than to the effigies of relatives of the emperor. The effigies of the young queen Anna of Austria sent to the Medicis preserved in Florence (a three-quarter-length portrait and a miniature - Uffizi Gallery, 2392 / 1890, Inventario Palatina, n. 624) and in Munich, offered to the Wittelsbach family (full-length portrait - Alte Pinakothek in Munich, 6992 and a miniature - Bavarian National Museum, R. 1459). As was customary at the time, the emperor had to receive images of his cousin, the Queen of Poland, but no portrait of Anna sent to her family in Vienna, Graz or Innsbruck is known. In the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna there is a painting of a reclining nude woman ("Sleeping Venus" or "Venus in repose") (oil on panel, 80 x 152 cm, GG 1104). The painting probably comes from the collection of Rudolf II, but it is clearly evidenced in the gallery in 1783 (after "Joseph Heintz ..." by Jürgen Zimmer, p. 101). The painting was thought to be identical to the painting mentioned in the inventory of the Vienna collection between 1610-1619: "Item a nude lady, painted by Joseph Hainzen" (Item ein nackhets weib von Joseph Hainzen untermahlt, No. 83) and to depict a courtesan at the court of Rudolf II in Prague or his mistress, such as Kateřina Stradová also known as Catherina Strada (ca. 1568-1629), the daughter of the painter Ottavio Strada the Elder, with whom he had six children. However, no clear evidence has ever been established. Such private and intimate effigies were not intended for the general public, as today when they can be easily seen in museums and different exhibitions, but for a narrow circle of spectators, so we would probably never find clear written confirmation of who was represented. The painting is now attributed to Dirck de Quade van Ravesteyn, a Dutch painter who, between 1589 and 1608, was painter at the court of Rudolf II in Prague, where several painters from Holland and Flanders were working at the time. He was admitted in June 1589 as a portraitist. In 1598, there is evidence that he owned a house in Prague's Malá Strana and even lent large sums of money to other people, including artists. He was inspired by the works of other painters, including two "wandering" Flemish painters Hans Vredeman de Vries and his son Paul, who came from Gdańsk to Prague in 1596. At the Museum of Fine Arts in Dijon, there is a pendant (companion piece) to this painting (oil on panel, 90 x 164 cm, CA 134). It also most likely came from the imperial collection in Vienna and, before 1809, it was in the gallery of the Belvedere Palace from where it was taken by Napoleon. There are some differences between the two paintings, such as the color of the pillow, however, both paintings depict the same woman, seen from a different angle. A recent restoration revealed the presence of gold coins at the top of the painting, so originally the composition was intended to represent the model in the mythological scene of Danae, seduced by Jupiter transformed into golden rain. A large gold pendant with the scene of Jupiter and Danae can be seen in the portrait of Archduchess Anna at the age of 18 (Germanisches Nationalmuseum, Gm661). The Vienna version was cut on the left and also indicated the presence, at the top of the composition, of gold coins. The two paintings were exhibited together at the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna during the temporary exhibition "Baselitz - Naked Masters" from March 7 to June 25, 2023. Embroidered pillows as elaborate as those depicted in the paintings were mentioned in the inventory of the queen's possessions (Riksarkivet in Stockholm, Extranea 85) - "a pillow with the Lithuanian coat of arms embroidered in silver, gold and silk" (Ain kyß mit dem litauischen wapen mit silber, golt und seyden gestickt, 213), "a pillow embroidered with silver, gold and silk with the Polish coat of arms" (Mer ain gewirkts kyß von silber, golt und seyden mit dem polnischen wapen, 214) or "a pillow embroidered with silver, gold and silk with the coat of arms of the Tęczyński family" (Mer ain gewirkt kiß von silber, golt und seyden mit dem tentschinischen wapen, 215). A work from de Quade van Ravesteyn's early period of work, dating from around 1590, showing the mystical marriage of Saint Catherine, is in the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on panel, 29.5 x 21.5 cm, M.Ob.108, earlier 235). It comes from the collection of Piotr Fiorentini in Warsaw, bequeathed to the School of Fine Arts in 1858. It is possible that it was part of the royal collection which survived the Deluge (1655-1660) and that the painter visited the Polish-Lithuanian royal court in the 1590s. Two portraits of Sigismund III are also close to the style of de Quade van Ravesteyn - a miniature in the Czartoryski Museum in Kraków showing the king at the age of 30, thus created in 1596 (inscription: SIGISMVND[US] POLONIÆ ET / SVECIÆ REX M[AGNUS] DVX LITH[UANIÆ] / ET FINLANDIÆ ANNO ÆTA / TIS XXX, oil on copper, 17.2 x 14.2 cm, MNK XII-144) and a portrait in the National Museum in Warsaw (inscription: SIGISMVNDT. D.G. REX POLONIÆ, oil on panel, 27 x 20 cm, MP 188 MNW). At the turn of the 16th and 17th centuries, numerous paintings were commissioned and purchased in Prague by the Polish-Lithuanian royal court from the artists of the imperial court of Rudolf II. Some of them or their agents also arrived in the Commonwealth. The best example of such a work, produced in Prague, Augsburg or Kraków, is the signed portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa by Joseph Heintz the Elder (J. Heintzen F. / SIGISMVNDVS ... / REX POLONIAE / & SVECIAE ...) in the Alte Pinakothek in Munich (inventory number 11885). Another example is a composition inspired by Pomarancio's fresco at Santo Stefano Rotondo in Rome - Stoning of Saint Stephen, attributed to Hans von Aachen. It was created or acquired for Saint Stephen's Church in Kraków (demolished in 1801, now in the new Saint Stephen's Church). In 1601, Andrzej Opaliński (1575-1623) acquired in Prague a portrait of Michael the Brave (1558-1601), prince of Wallachia, for the king, perhaps by Bartholomeus Spranger and a work signed by Spranger (B. SPRANGERS. ANT .F.) from the same period, depicting Vanitas (Putto with a skull), is in the Wawel Royal Castle (inventory number 935, from the Miączyński-Dzieduszycki collection). One such early import to the Commonwealth could also be Spranger's Saint Ursula with female martyrs in the Lithuanian National Museum of Art (LNDM T 3995), donated to the Vilnius Society of Friends of Science before 1937. At the National Museum in Warsaw there is also the Allegory of Fortune from the circle of Spranger (M.Ob.763 MNW) and his signed drawing depicting Original Sin (B(?) Spranger in., Rys.Ob.d.701, from the Society for the Encouragement of Fine Arts in Warsaw), as well as the portrait of Alfonso II d'Este, Duke of Ferrara close to the style of Hans von Aachen (M.Ob.1913, from the collection of Jan Popławski) and Martyrdom of Saint Sebastian, after the print by Jan Harmensz. Muller, painted by von Aachen or circle (M.Ob.812, from the post-WWII Art Repository in Kraków). Both paintings clearly reference Titian's Jagiellonian nudes, particularly the portrait of Princess Isabella Jagiellon (Venus of Urbino) and the portrait of Anna Jagiellon as Venus with an organist and a dog, copies of which undoubtedly also appeared in the royal collection before the Deluge. The woman greatly resemble Anna of Austria from her portraits by Sofonisba Anguissola (private collection) and Tintoretto (Prado Museum, P000484), identified by me. It must therefore be concluded that through these paintings, the young Queen of Poland wanted to show her cousin the Emperor, that she is not a specimen from his cabinet of curiosities, but a beautiful sovereign of the Realm of Venus.
Mystical marriage of Saint Catherine by Dirck de Quade van Ravesteyn, ca. 1590, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Queen Anna of Austria (1573-1598) nude (Sleeping Venus) by Dirck de Quade van Ravesteyn, ca. 1595, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Portrait of Queen Anna of Austria (1573-1598) nude (Sleeping Venus) by Dirck de Quade van Ravesteyn, ca. 1595, Museum of Fine Arts in Dijon.
Miniature portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa, aged 30 by workshop of Dirck de Quade van Ravesteyn, ca. 1596, Czartoryski Museum.
Portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa by workshop of Dirck de Quade van Ravesteyn, after 1596, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Archduchess Maria of Austria (1584-1649) by Hans von Aachen, 1604, Lviv National Art Gallery.
Portraits of Stanisław Lubomirski and Bianca Cappello by Alessandro Maganza
On New Year's Day 1595, at the age of about 11, Stanisław Lubomirski (1583-1649), the eldest son of count Sebastian Lubomirski (d. 1613), together with his brother Joachim (1588-1610), left Wola Justowska near Kraków for further education at the Jesuit college in Munich. He was looked after by the trusted servants of his father, Piotr Szczepanowski, and Jan Gębczyński, a graduate of the Kraków University, who kept records of all expenses incurred at that time. Lubomirski stayed in Munich until May 1597. This stay was interrupted by financial difficulties and the wedding of the eldest sister Katarzyna who was marrying Prince Janusz Ostrogski. The costs of studying at the college and the expenses incurred during the over two-year stay in Munich were quite significant, amounting to 4,921 thalers. After returning to Poland, on July 21, 1597, his father ceded to him - with the king's consent - the starosty of Nowy Sącz (after "Stanisław Lubomirski (1583-1649) ..." by priest Andrzej Bruździński, p. 93).
At the end of 1598 or at the beginning of the following year, accompanied by the poet Piotr Kochanowski (1566-1620) and the aforementioned Jan Gębczyński, he went abroad again, this time to the south – to Italy. In 1599 he enrolled at the University of Padua and he also went to France and the Netherlands. He returned in 1601 and the following year he was admitted to the royal court. King Stephen Bathory was Stanisław's godfather. As the Kraków Żupnik between 1581-1592 his father built his fortune primarily from "salt" as well as usurious loans, which was assessed negatively in the Commonwealth. In 1597 even the crown jewels were pawned with Lubomirski and in 1595 Sebastian became the count of Wiśnicz from the imperial nomination. Around that time the "travelling belongings" of magnates and nobles were carried on "treasure carts" and in "room chariots" covered with leather in chests and boxes, often of French manufacture, very sophisticated and waterproof, intended for a specific type of objects, like "a tin case for pictures", according to inventory of the Radziwill family (after "Mieszkańcy Rzeczypospolitej w podróży ... " by Urszula Augustyniak, p. 375). Stanisław, who would later become the patron of a prominent Italian architect, Matteo Trapola, also acquired and commissioned works of art abroad. One such ambiguous expense for a meeting with a painter was recorded by Gębczyński during his stay in Munich - "For the copy of Stach and with the painter" (Za kopią Stach i z malarzem), 5 zlotys 21 grosz. "Everything cannot be entrusted to paper", wrote in a letter of July 8, 1588 from Venice, diplomat Stanisław Reszka and matters which could not be discussed directly were conveyed orally by a trusted and additionally authenticated messenger, who sometimes substituted a letter, simply for lack of time to write it (after "W podróży po Europie" by Wojciech Tygielski, Anna Kalinowska, p. 14). In the Wilanów Palace in Warsaw there is a portrait of an elegant 14-year-old young man against the background of a column and a curtain by Venetian school (oil on canvas, 176 x 115 cm, inventory number Wil.1150). It comes comes from the Wiśnicz Castle and it was moved to Warsaw before 1821. The castle in Wiśnicz was purchased by Sebastian Lubomirski in 1593 and between 1615 and 1621 Trapola enlarged and rebuilt it for his son Stanisław. The original inscription in Latin: Aetatis 14, above his head confirms the model's age, while the later inscription identifying the model as Sebastian Lubomirski (Sobestian Lubomirski Wielkorządca Kr.: W: Woryniecki zmarły R. 1613) was transferred to the back of the doubled canvas. Basing on this information the painting is dated to about 1560 (Sebastian was born in about 1546) and attributed to Giovanni del Monte or de Monte, painter active at that time at the royal court of Poland-Lithuania (he left for Venice in 1557). However, as noted by Wanda Drecka ("Portrety Sebastiana Lubomirskiego ...", p. 92), the cut of his hose or trousers can only be compared with the costumes of the guards in the Entry of the wedding procession of Sigismund III Vasa into Kraków in 1605 (Royal Castle in Warsaw), so-called "Stockholm roll" because it was taken to Sweden during the Deluge (1655-1660) and returned to Poland in 1974. The boy's shoes are very similar to those depicted in the portrait of Swedish statesman Mauritz Stensson Leijonhufvud, dated '1596' (ANNO DOMINO 1596, Skokloster Castle) and the pose and costume can be compared to the portrait of Sir Walter Raleigh and his son, dated '1602' (National Portrait Gallery in London). Similar trousers and shoes can also be seen in a double portrait of two children in matching green costumes, now in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna (oil on canvas, 116 x 91 cm, GG 3299). The portrait is identified to possibly represent members of the Polish royal family and attributed to the German or Polish school. This is mainly because the girl's costume and pose are very similar to those of Stanisław's sister, most likely Krystyna in her portrait in the National Museum in Warsaw (128871). A ruff similar to that of the boy's effigy was depicted in the portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa, also in the Kunsthistorisches Museum (GG 3302) and the portraits of his children Princess Anna Maria Vasa at the age of 3 (ÆTATIS SVÆ Ao. III.) and Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa at the age of 1 (ÆTATIS SVÆ I. Ao.) in the Monastery of Las Descalzas Reales in Madrid, painted in 1596. The portraits of King Sigismund and his children were created by his court painter Martin Kober of Wrocław, who died before 1598 in Kraków or Warsaw. All were sent to king's relatives in Vienna and Spain. A copy of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund's effigy was also sent to Bavaria (Alte Pinakothek in Munich). Moreover, the mentioned portrait of two children in Vienna also resembles in style the aforementioned portraits of Kober, who in 1595 went to Graz to paint the family of Sigismund's wife, Anna of Austria (1573-1598). In the same year, on July 14, when Stanisław stayed in Munich, his father Sebastian received confirmation and recognition from Emperor Rudolf II of the hereditary title of Imperial Count of Wiśnicz, granted by Emperor Charles V on February 15, 1523 to his ancestors (after "Genealogie rodów utytułowanych ..." by Tomasz Lenczewski, p. 41). On this occasion or even earlier, the emperor most likely received the portraits of the count and his family members, including his eldest son and his sister Katarzyna. The girl in the described portrait is apparently older than the boy, exactly like Katarzyna born around 1581, who was depicted in a similar rich costume in her portrait in the National Museum in Warsaw (157500). The boy in the painting could be 7 years old, so the painting must be dated to around 1590, when Kober returned from the imperial court in Prague to Poland. The painting can be verified at the Imperial Gallery in Vienna in 1772. His satin doublet of silver color, collar and hairstyle are almost identical as in the portraits of James I(VI) Stuart, king of England and Scotland by Adrian Vanson, dated '1595' (Scottish National Gallery and private collection) and portrait of a gentleman, formerly suggested to be William Shakespeare, dated '1602' (private collection). The portrait should consequently be dated to around 1597, when 14-year-old Stanisław Lubomirski become the starost of Nowy Sącz and soon left for Italy. The boy's facial features closely resemble other effigies of Stanisław Lubomirski in the Wilanów Palace (Wil.1565, Wil.1258). The same boy was depicted in another portrait from Lubomirski collection painted in the same style, today in the Lviv National Art Gallery (oil on canvas, 67 x 78 cm, Ж-1377). It is presumably a fragment of a larger composition showing him in guise of biblical David with a sword. The style of both paintings, in Wilanów and Lviv, is very close to that of Alessandro Maganza (1556-1630), a painter born and active in Vicenza, as well as in Venice, influenced by Tintoretto, Palma the Younger and Veronese. His distinctive technique is particularly well visible in a painting dated '1590' (M.D.LXXXX), today in the Nationalmuseum in Stockholm (NM 32), representing the Virgin and Child with Saints, as well as in the portrait of a woman with pearls (sold at Capitolium Art in Brescia on October 17, 2018, oil on canvas, 40 x 53 cm). The latter effigy is a version of a portrait of Bianca Cappello (1548-1587), Venetian noblewoman who become the Grand Duchess of Tuscany, painted by Scipione Pulzone in 1584 (Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, GG 1138). The painter most likely received a drawing or miniature of the Grand Duchess to copy, as his stay in Florence is unconfirmed. It was probably the same with the effigies of the young starost of Nowy Sącz ahead of his visit to Italy. Another interesting "Portrait of a woman", painted in the same style, is in the Lithuanian National Museum of Art in Vilnius (oil on canvas, 56 x 44 cm, inventory number LNDM T 4018). It is attributed to Frans Pourbus the Younger because of a certain resemblance to his works and the woman represented is obviously Marie de' Medici (1575-1642), Queen of France. It is dated '1614' in upper right corner. Presumably in 1613 Nicolaus Christopher Radziwill of Olyka (1589-1614), went to France, from where he returned via northern Italy and in May 1614, because of his illness, he stayed in Verona, from where, on May 9, 1614, he sent a letter to his friend Ferdinand I Gonzaga (1587-1626), Duke of Mantua (after "Zagraniczna edukacja Radziwiłłów ..." by Marian Chachaj, p. 69). It could be he who commissioned this painting in the Republic of Venice, or it was commissioned by the Vasas. In 1614 the so-called "Treter Eagle" (Ordo et series regum Poloniae) with effigies of monarchs of Poland was published in Paris by Jean le Clerc, and a year later, in 1615, a niece of the Queen of Poland, the Infanta Anne of Austria (1601-1666) married Louis XIII of France, son of Marie de' Medici.
Portrait of Stanisław Lubomirski (1583-1649) and his sister Katarzyna (d. 1612) by Martin Kober, ca. 1590, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Portrait of Stanisław Lubomirski (1583-1649), starost of Nowy Sącz, aged 14 by Alessandro Maganza, ca. 1597, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
Portrait of Stanisław Lubomirski (1583-1649) holding a sword by Alessandro Maganza, ca. 1597, Lviv National Art Gallery.
Portrait of Bianca Cappello (1548-1587), Grand Duchess of Tuscany by Alessandro Maganza, ca. 1584, private collection.
Portrait of Marie de' Medici (1575-1642), Queen of France by Alessandro Maganza, 1614, Lithuanian National Museum of Art.
Portraits of Dukes of Savoy by Sofonisba Anguissola
The diplomatic contacts of Poland-Lithuania with the Duchy of Savoy in the 16th century date back with certainty to the year 1535, when Queen Bona planned to marry her eldest daughter Isabella Jagiellon with Louis (Ludovico) of Savoy (1523-1536), Prince of Piedmont, son of Charles III and Beatrice of Portugal. She wrote about this to the ambassador of King Ferdinand I, Sigismund von Herberstein, from Vilnius on December 14, 1535 and the matter was discussed earlier by her envoy Ludovico Alifio (after "Królowa Bona ..." by Władysław Pociecha, p. 206). As was customary, the portrait of the Jagiellonian princess was certainly sent to Savoy, while she received the portrait of Louis. Sadly the prince died in Madrid on November 25, 1536. Some informal contacts were much earlier, for example in February 1416 in Chambéry Janusz of Tuliszków, a knight of the Dryja coat of arms from Greater Poland and a diplomat, received the Order of the Collar (later Order of the Most Holy Annunciation) from Amadeus VIII (considered the last historical antipope). They undoubtedly increased around 1587 when the candidature of the Duke of Savoy in the third free election was discussed in Madrid (after "Dwór medycejski i Habsburgowie ..." by Danuta Quirini-Popławska, p. 123).
In the 16th and 17th centuries portraiture was part of diplomacy and monarchs of different countries in Europe frequently exchanged their effigies. Portraits were also sent to friends and family members. In 1558, Georgius Sabinus (1508-1560), a German poet and diplomat, was sent to Poland-Lithuania to win the support of Polish-Lithuanian lords, including Stanisław Ostroróg, Jan Janusz Kościelecki, Łukasz Górka, Jan Tarnowski and Jan Zborowski, to the candidacy of Sigismund of Brandenburg (1538-1566), son of Joachim II Hector, elector of Brandenburg from his second marriage with Hedwig Jagiellon (1513-1572), for the throne after his uncle Sigismund Augustus. In the name of young Prince Sigismund, he gave each of them a gold chain, from which hung the portrait of the prince. As he was only known to a few of them, he wanted to present his effigy to them "as a symbol of friendship" (als ein Symbol der Freundschaft). The Polish-Lithuanian lords reciprocated so that "hardly any other envoy sent to Poland has ever returned home with as much wealth and gifts as he does" (mit so vielem Reichtum und Gaben wie er, sei wohl kaum je ein zweiter nach Polen beordneter Gesandter heimgekehrt, after "Forschungen zur brandenburgischen und preussischen Geschichte ...", Volume 11, p. 156). The miniatures probably came from Cranach's workshop, like the portraits of Sigismund's father, although it cannot be ruled out that they were commissioned in Italy by the prince's mother Hedwig. Diplomatic missions were frequently accompanied by the exchange of valuable gifts and they generally represented the country's most valuable exports, so the Italians offered paintings, rich fabrics and luxury cosmetics and the Poles offered clocks, sables, horses and amber. Cardinal Enrico Gaetani, papal legate in Poland from April 1596 to June 1597, offered King Sigismund III Vasa some paintings by famous masters, the queen richly embroidered veils and a conch with musk set in a rich setting, all worth at least 800 scudi. The king gave the cardinal a beautiful temple-shaped clock with moving figurines showing the procession and blessing of the Holy Father worth over 3,000 scudi, and 40 sables worth 500 scudi. The Bishop of Kuyavia in Wolbórz gave the legate two horses with rich Turkish-style shabracks, and the cardinal distributed gold medals with his image to the courtiers. Boniface Vanozzi, sent from the same Cardinal Gaetani to Chancellor Jan Zamoyski, distributed beads, rosaries, medals, agnus dei, pictures on metal sheet in ebony frames and he received a horse with velvet Turkish-style shabrack, a large gold medal depicting King Stephen Bathory, an elk hoof, lots of game, vinegar, oil and sweets. To the king and queen Vanozzi presented paintings, tapestries woven in Spain (or more likely in the Spanish Netherlands), colorful gloves with scent, and musk. The king gave him very expensive sables and a clock worth 1,000 thalers and the queen, various utensils made of white amber for the chapel, a crucifix, a tray for altar cruets, a pax and a monstrance, all beautifully carved in Gdańsk. In 1597, the ambassador of the Spanish king, Don Francisco de Mendoza (1547-1623), Admiral of Aragon and Marquis of Guadalest, received from Sigismund III sables worth 2,000 scudi and his courtiers were offered golden cups (after "Domy i dwory ..." by Łukasz Gołębiowski, pp. 258-259). At that time, the elected monarch of the Commonwealth also sent his brother-in-law, the King of Spain, portraits of his children by Martin Kober, both dated '1596' (Monastery of las Descalzas Reales in Madrid) and in 1621, the Polish ambassador in London, Jerzy Ossoliński, was given portraits "att length" of the King and Prince Charles. The royal collections of the Commonwealth before 1655 were therefore comparable to those of the Spanish monarchs (Prado Museum in Madrid and El Escorial), Holy Roman Emperors (Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna and Hofburg), Dukes of Tuscany (Uffizi Gallery in Florence and Pitti Palace) or Dukes of Savoy (Galleria Sabauda in Turin and Palazzo Madama). Unfortunately very little preserved today in the former territories of the Commonwealth, including inventories and other documents. In the National Museum in Warsaw there is a portrait of two boys, attributed to circle of Dutch painter Anthonis Mor, who worked for Spanish and Portuguese monarchs (oil on canvas, 56.5 x 46 cm, inventory number M.Ob.941 MNW, earlier 231117). It was purchased in 1962 from Romuald Malangiewicz. Its earlier history is unknown, so we cannot exclude the provenance from the royal or magnate collection in Poland-Lithuania. The painting was cut from a larger group portrait painting, as a fragment of a woman's dress, most likely the mother of the two boys, is visible to the right. Such portraits were particularly popular in Italy at the turn of the 16th and 17th centuries - portrait of Maria di Cosimo Tornabuoni, a Florentine noblewoman, and her two little sons, one dressed in dominican habit, by Tiberio di Tito (Tiberio Titi) or a portrait of Bianca degli Utili Maselli surrounded by six of her children, painted by Lavinia Fontana in Rome. If the painting comes from the royal or magnate collection then the main part depicting the woman was destroyed when Commonwealth residences were ransacked and burned during the Deluge (1655-1660) or later, or it was cut into pieces to sell the picture more profitably when the country became impoverished due to wars and invasions. A portrait painted in a similar style and with a woman resembling the two boys in the Warsaw painting is now in Kensington Palace in England (oil on canvas, 42.3 x 33 cm, RCIN 402954, inscription: 305). It comes from the Royal Collection, possibly recorded in the King's Dressing Room next Paradise at Hampton Court in 1666 (number 60), and was previously thought to represent Elisabeth of Valois (1545-1568), Queen of Spain. Consequently, it was attributed to Spanish court portraitist Anthonis Mor and later to his pupil and successor under Phillip II, Alonso Sánchez Coello. It is now identifed to possibly depict Elisabeth's eldest daughter, Infanta Isabella Clara Eugenia. A companion portrait is therefore thought to possibly represent her sister Infanta Catalina Micaela of Spain (oil on canvas, 42.2 x 32.6 cm, RCIN 402957, 306). These effigies indeed resemble other effigies of the infantas, however comparing with portraits of Isabella Clara Eugenia by Coello in the Prado Museum in Madrid, painted in 1579 (P01137) and by Juan Pantoja de la Cruz from about 1599 (P000717) and signed portraits of her sister Catalina Micaela from the Castle of Racconigi (0100399544) and attributed to Sofonisba Anguissola (sold ate Christie's New York, October 14, 2021, lot 101), indicate that it should be the other way around - 305 is the portrait of Catalina Micaela and 306 of Isabella Clara Eugenia. In 1585, Catalina Micaela became Duchess of Savoy by marrying Charles Emmanuel I, Duke of Savoy in Zaragoza. A similar small portrait (oil on canvas, 55.9 x 45.7 cm) bearing the inscription: DVQUESA / DE.SAVOI, was sold at Period Oak Antiques. The style of the portrait of Catalina Micaela in the Royal Collection resembles the portrait of her mother in the Prado, attributed to Sofonisba Anguissola (P001031) and Sofonisba's self-portrait at the easel (Łańcut Castle). The composition and style of the portrait of two boys in Warsaw is in turn similar to the portrait of Infanta Juana de Austria (Joan of Austria) with female dwarf Ana de Polonia by Sofonisba (Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum in Boston, P26w15). The two boys should therefore be identified as the eldest sons of Catalina Micaela - Philip Emmanuel (1586-1605) and Victor Amadeus (1587-1637) and their known iconography matches perfectly. Both princes were frequently depicted in their youth and in many of their effigies, mostly created by the Dutch painter Jan Kraeck, known as Giovanni Caracca, they wear a similar smaller ruff (e.g. double portrait from private collection in Naples, sold at Blindarte, November 30, 2019, lot 153). Some of them were created in several versions, such as the triple portrait from 1589 (sold at Aste Bolaffi, September 25, 2013 and in Quirinale Palace in Rome). From around 1584 to 1615, Sofonisba resided in Genoa. Although in 1585 she met the Infanta Catalina Micaela on her arrival in Genoa and probably accompanied her on the way to Turin, all the portraits mentioned were probably made from sketches, study drawings or paintings by other painters, such as Kraeck. It was she who, around 1590, produced a miniature portrait of Charles Emmanuel I (sold in 2005, Christie's in London, lot 1009, as the effigy of Victor Amadeus I) and the portrait of the duke with his wife Catalina Micaela and their children (Palazzo Madama in Turin, 0611/D), as indicate the style of the two paintings. The portrait of two princes in Warsaw was therefore a gift to Sigismund III Vasa or his aunt Anna Jagiellon and was probably brought by the Spanish ambassador Mendoza or another envoy.
Portrait of Infanta Catalina Micaela (1567-1597), Duchess of Savoy by Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1590, Kensington Palace.
Portait of Victor Amadeus (1587-1637) and Philip Emmanuel (1586-1605), sons of Infanta Catalina Micaela (1567-1597), Duchess of Savoy by Sofonisba Anguissola or workshop, ca. 1596-1597, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Infanta Catalina Micaela (1567-1597), Duchess of Savoy with her sons by Sofonisba Anguissola or workshop, ca. 1596-1597. Possible layout of original painting. © Marcin Latka
Miniature portraits of the Vasas by Sofonisba Anguissola and workshop
Rich gifts accompanied all diplomatic missions. On June 14, 1592, "after the mass sung at dinner", Sigismund III, in his private room in the presence of some senators, gave audience to Pietro Duodo, orator of the Republic of Venice (Petro Dodo oratori S. Reipublicae Venetiarum), accompanied by eight Venetian nobles and seated on a bench decorated with green velvet (scamno ornato velluto viridi). He arrived to congratulate the king on his marriage to Anna. The king knighted Duodo and "presented him with a necklace worth a thousand in gold, and granted him the insignia [effigies?] of the royal family" (et donavit ei torquem millium aureorum, et concessit insignia familiae regiae). He then went to visit the queen, to whom he also gave a letter, and in the name of the Republic of Venice he presented various vessels of engraved silver, for the price of four thousand in gold (donavit S. Reginae vasa diversa argenti caelati pro pretio quatuor millium aureorum).
At that time, portraits were exchanged with Florence. In 1596, the king paid a large sum of 120 florins to the merchant Lawrence (Laurentio mercatori) "for images of Charles V, Emperor of the Romans" (pro imaginibus Caroli Quinti Caesaris Romanorum). Giovanni Paolo Mucante (d. 1617), master of ceremonies of the delegation of the papal legate, Cardinal Gaetano, wrote in a letter dated September 21, 1596 that the portrait of the late Queen Anna Jagiellon in the room was "very natural" (il suo ritratto, come dicevano, naturalissimo) and in 1601 Andrzej Opaliński (1575-1623) acquired in Prague a portrait of Michael the Brave (1558-1601), prince of Wallachia, for the king, according to a letter from nuncio Claudio Rangoni to Cardinal Pietro Aldobrandini (June 3) (after "Das Leben am Hof ..." by Walter Leitsch, p. 370, 953, 2277, 2381). Painters are sometimes mentioned, but names are missing. In 1592, before the wedding, the tailor Claudio Aubert went to Italy to get everything he needed. Among other things, he paid 96 guilders "to the painters sent to Poland to serve His Majesty" (alli pittori mandati in Polonia al servitio di SM). Much information about the wedding has been preserved, but there is no mention of Italian painters nowhere. In the accounts of 1601, there is only the following note: "Vilnius for the payment to the painters and for the repair of the tents, on August 28" (Vilnae in solutionem pictoribus et in reparationem tentoriorum, die 28 augusti, fl 110). This indicates that different workshops in Italy worked on royal commissions and sent their agents to Poland-Lithuania only to prepare the initial drawings. Besides the Venetian Redutti, who helped the king in goldsmithing work, there is evidence that Ruggiero Salomoni worked with Sigismund. He came to Poland as chaplain to the king's first wife. He was well known for his talent, because as early as 1595 he created the Easter tomb decoration for Cardinal Radziwill in Kraków Cathedral, according to a letter from Sigismundus Ernhofer to Archduchess Maria Anna dated April 5, 1595. Salomoni then acted as the king's agent in Naples around 1619, sending Italian paintings, tapestries and curiosities for the royal collection (after "The Grove Encyclopedia ...", ed. Gordon Campbell, p. 455). Luxury items were purchased in Italy, but also given to friends there. Sigismund's mother owned a silver mirror, perhaps made in Italy, and the royal courtier Stanisław Radziejowski gave Maria Maddalena of Austria, Grand Duchess of Tuscany and sister-in-law of the king an "amber mirror" (spechio di ambra), according to his letter to the Grand Duchess (June 12, 1615). The king ordered a large mirror (speculum grande cocavum) from Italy, mentioned in his letter to Salomoni (January 20, 1614). Royal envoys went to Italy, not only to acquire or order luxury goods, but also to bring renowned artists and musicians, as in December 1594, when Krzysztof Kochanowski (nephew of the poet Jan) came to Rome to recruit Italian musicians for Sigismund III or mentioned Aubert, before 1592. Around 1598, the Polish-Lithunian royal court sent numerous effigies of members of the royal family to foreign courts. The Vasas, like their ancestors the Jagiellons, and other important monarchs of Europe, commissioned their effigies from the best artists. This is why their miniature reliefs in colored wax were made by the famous workshop of Alessandro Abondio - busts of Sigismund III and his wife Anna of Austria at the Bode Museum in Berlin (inventory number 881, 882) and at the Nationalmuseum in Stockholm (NMGrh 1994, NMGrh 1995). Abondio was probably recommended to Sigismund III by his mother-in-law, Archduchess Maria Anna of Bavaria and her husband Charles II, grandson of Anna Jagiellonica (1503-1547), whose wax miniatures by Alessandro's father, Antonio, are located at Abegg-Stiftung (9.7.63). However, if we consider the enormous destruction of art in Poland-Lithuania during the Deluge (1655-1660) and other invasions, nothing can be said with certainty about this and we could also say the opposite that the Jagiellons or the Vasas recommended Abondios to the Habsburgs. At that time, the most renowned miniaturist working for the Habsburgs in Spain and Austria was Sofonisba Anguissola, who produced several of her self-portraits in miniature or small format - at the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston (60.155), Fondation Custodia in Paris (6607) or the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna (GG 285), the latter was most likely a gift for the Austrian Habsburgs. In her portrait in the Prado Museum in Madrid (P001031), recently attributed to Sofonisba, Queen Elisabeth of Valois holds in her hands a miniature of her husband King Philip II, probably also painted by Anguissola. This portrait is a sign of special recognition for the artist. Around 1575 she created a miniature of Emperor Maximilian II (1527-1576), son of Anna Jagiellonica (1503-1547), sold in Paris in 2016 (Sotheby's, June 16, 2016, lot 12, inscribed verso in Italian: Di mano / da Sofonisba / Anguisciola Cre / Monese / Dama Della Regina Isabella / di spagna moglie … / di filippo …). Sofonisba is also the author of several portrait miniatures from the collection of the Dukes of the Infantado in Madrid, which probably originally belonged to the Spanish royal collection. Among the effigies of Archduchess Maria Anna (Archivo de Arte Español - Archivo Moreno, 01616 B), Emperor Rudolf II (01696 B) and King Sigismund III in Polish costume (01784 B), there was also her self-portrait in Spanish costume (01616 B). A miniature of one of Maria Anna's daughters was also sold in Paris with attribution to the circle of Peter Paul Rubens, around 1610 (oil on panel, 8 x 6 cm, sold at the Hôtel Drouot, November 21, 2014, lot 29). This miniature probably comes from a private French collection, so the provenance from the collection of John II Casimir Vasa, who settled in France after his abdication in 1668, or from another Polish collection transferred to France in the 19th century cannot be excluded. Given this and the resemblance to the portrait in the Germanisches Nationalmuseum (Gm661), the model is most likely Anna of Austria (1573-1598), future Queen of Poland. The style of this painting also resembles greatly mentioned works by Sofonisba. Several miniatures of the Polish-Lithuanian Vasas created around 1598 are now in the Bavarian National Museum in Munich. All were probably gifts to the Wittelsbachs or came from the dowry of the Polish-Lithuanian princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa. This cycle of small paintings on brass and tin (all approximately 4.5 x 3.5 cm) includes effigies of Sigismund III (R. 1462), his first wife Anna of Austria (R. 1459, R. 1465) and their children Anna Maria Vasa (R. 1497) and Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (R. 1446). Another miniature of Queen Anna in the same style, most likely a gift to the Medicis, is in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence (oil on brass, 4.1 x 3.5, Inventario Palatina, n. 624). The miniature of Sigismund III from this cycle is particularly similar to the mentioned miniature of Emperor Maximilian II. Another miniature of Ladislaus Sigismund in the same collection (R. 1455), created around 1601, was also created in Anguissola's style. So, all miniatures were painted by the same artist and her studio. It was also Sofonisba's workshop that produced the portrait of Queen Anna at the Royal Castle in Warsaw (inscription: ANA D' AVSTRIA REG:A D' POLONIA, oil on canvas, 61 x 48 cm, FC ZKW 1370). The style of her jewelry as well as the inscription is similar to that in the portrait of Catalina Micaela of Spain (1567-1597), Duchess of Savoy, attributed to Anguissola (sold at Christie's New York, live auction 19994, October 14, 2021, lot 101). Therefore, like all mentioned Habsburg effigies, the Vasa liknesses were commissioned in the painter's workshop on the basis of other effigies or study drawings.
Miniature portrait of a daughter of Maria Anna of Bavaria (1551-1608), most probably Archduchess Anna of Austria (1573-1598), by Sofonisba Anguissola or studio, ca. 1592, Private collection.
Miniature portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa (1566-1632) by Sofonisba Anguissola or studio, ca. 1598, Bavarian National Museum in Munich.
Miniature portrait of Queen Anna of Austria (1573-1598) by Sofonisba Anguissola or studio, ca. 1598, Bavarian National Museum in Munich.
Miniature portrait of Queen Anna of Austria (1573-1598) by Sofonisba Anguissola or studio, ca. 1598, Bavarian National Museum in Munich.
Miniature portrait of Queen Anna of Austria (1573-1598) by Sofonisba Anguissola or studio, ca. 1598, Uffizi Gallery in Florence.
Miniature portrait of Princess Anna Maria Vasa (1593-1600) by workshop of Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1598, Bavarian National Museum in Munich.
Miniature portrait of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) by workshop of Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1598, Bavarian National Museum in Munich.
Portrait of Queen Anna of Austria (1573-1598) by workshop of Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1592-1598, Royal Castle in Warsaw.
Portraits of Anna Vasa and Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa by Sofonisba Anguissola
In 1594 a marriage project appeared during Anna Vasa's stay in Sweden. The candidate was John George of Brandenburg (1577-1624), the administrator of Strasbourg from 1592 and a grandson of the Brandenburg elector, who was to become the governor of Prussia, a feudal fief of the Crown of Poland. In the spring of 1596, an envoy, Paweł Arciszewski, secretary of King Sigismund III, traveled to Sweden with a portrait of John George to Anna Vasa in order to strengthen the princess's sympathy for her bridegroom (after "Das Leben am Hof ..." by Walter Leitsch, p. 2378). The painter was most likely a court painter of Sigismund III or an overseas workshop working for the Polish-Lithuanian monarchs.
Negotiations on this marriage were conducted on the Brandenburg side by the Magdeburg chancellor Wilhelm Rudolf von Meckbach and Johann von Löben who both travelled to Kraków, and on the Polish side by royal secretary Jan Skrzetuski, who travelled to Berlin, and Samuel Łaski. The date of the wedding was set for April 10, 1598 in Stockholm and Anna even received a dowry of 100,000 thalers from her brother Sigismund III Vasa, as well as jewelery, horses, furniture and 10,000 guilders as a wedding gift. Anna and her descendants were to be granted the inheritance rights to Sweden. Death of John George, Elector of Brandenburg on 8 January 1598, death of Sigismund's wife Anna of Austria (1573-1598) on 10 February and the outbreak of the uprising in Sweden made it impossible to conclude the wedding at the planned place and date. When Sigismund's uncle depose him in Sweden, these plans did not materialize. The portrait of a noblewoman and her husband in costumes from the late 1590s by Sofonisba Anguissola (oil on canvas, 123.3 x 93 cm, sold at Sotheby's London, July 11, 2002, lot 177) is very similar to other effigies of Anna Vasa. Her costume in Spanish style and pose resemble closely portrait of queen Anna of Austria by Martin Kober, created in 1595 (Bavarian State Painting Collections and Uffizi Gallery in Florence) and portrait of Archduchess Maria Anna of Bavaria (1574-1616) by Joseph Heintz the Elder, created in 1604 (Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna). The man's costume is typical for France and Protestant countries in the late 16th century. After return to Poland Sigismund made Anna starost of Brodnica on October 2, 1604, after death of Zofia Działyńska née Zamoyska and in December 1605 she attended Sigismund's wedding in Kraków, sitting in the bride's carriage. The negotiations with John George of Brandenburg were finally discontinued in 1609 and on June 3, 1610 he married Eva Christine von Württemberg (1590-1657), while Anna remained unmarried. Like her mother, Queen Catherine Jagiellon, the princess maintained a splendid and diverse court with different people as evidenced by her letter to Halszka Sapieżyna née Radziwill from Kraków, dated January 28, 1605: "We thank YL [Your Ladyship] for the female dwarf that YL brought us, and we urgently ask YL to send her with someone trusted" (Za karlice, WMci dziękujem, którąś WMć dla nas przywiozła, pilnie prosiem, abyś ją WMć przy kim pewnym sam posłała) (after "Archiwum domu Sapiehów ..." by Antoni Prochaska, p. 449). Although court dwarves of the 16th and 17th centuries are now mainly associated with Spain and their magnificent portraits by Anthonis Mor, Juan van der Hamen and especially Diego Velázquez, many paintings of this type were undoubtedly also found in Poland-Lithuania before the Deluge (1655-1660). In 1551, the painter Andreas Rul from Wrocław (Andreae Rul pictori Vratislaviensi) painted the portraits of 7 royal female dwarves, for which on March 3 he received 42 thalers, plus reimbursement of accommodation costs, and the portrait of king Sigismund Augustus, Anna's uncle, for which on March 17 he received 10 Hungarian ducats (after "Słownik artystów polskich i obcych ..." by Jolanta Maurin Białostocka, p. 355). The oval portrait in private collection in Massachusetts (oil on canvas, 65 x 52.5 cm, sold at Bonhams Skinner, November 11, 2021, lot 1036, as by school of Frans Pourbus the Younger), very similar to Anna's miniature in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence, is also stylistically close to Sofonisba as well as a miniature of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa in the Bavarian State Painting Collections (oil on tin plate, 4.4 x 3.7 cm, R. 1455).
Portrait of Princess Anna Vasa (1568-1625) in Spanish costume by Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1598, Private collection.
Portraits of Princess Anna Vasa (1568-1625) and John George of Brandenburg (1577-1624) by Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1598, Private collection.
Portrait of Princess Anna Vasa (1568-1625), starost of Brodnica by Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1605, Private collection.
Miniature of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa by Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1605, Bavarian State Painting Collections.
Portrait of Sigismund III Vasa in armour by Domenico Tintoretto
"The imago will be gratiosissima to the King. The King His Highness waits for paintings with great joy: a strange thing how he loves when he has something wonderful" (Imago będzie Królowi gratiosissima. Obrazów król Jmć czeka z wielką radością: dziwna rzecz jako się w nich kocha kiedy co cudnego ma), reveals in a letter dated July 12, 1588, written to Stanisław Reszka (1544-1600), who was in Rome, a Jesuit Bernard Gołyński (1546-1599) about the paintings commissioned by Sigismund III Vasa in Italy.
Sigismund was also a talented painter and goldsmith. According to historian Franciszek Siarczyński (1758-1829) in his "Picture of the Era of Sigismund III" (Obraz wieku panowania Zygmunta III), the king with the help of his court goldsmith, a Venetian Redutti (Reduta, Redura) made many church utensils, such as monstrances, chalices, lamps and candlesticks, which he gave to several churches. In the collection of the Alte Pinakothek in Munich there is a painting which according to Edward Rastawiecki in his "Dictionary of Polish painters" (Słownik malarzów polskich, pp. 96-97) is "another work of this kind" and it was given to king's daughter Anna Catherine Constance Vasa, "on the back, the preserved inscriptions and seals confirm the origin and authenticity of this interesting souvenir". This work is however listed in Johann Nepomuck Edler von Weizenfeld's "Description of the electoral picture gallery in Schleissheim" of 1775 as the work of Tintoretto (Jacopo Robusti, 1518-1594). Stylistically the painting is very close to this Venetian painter and his son Domenico (1560-1635). The monarch with the chain of the Order of the Golden Fleece is very similar to that visible in the study for a portrait of a king, most probably Sigismund III Vasa, in the collection of Francis Springell, attributed to Peter Paul Rubens, and to Sigismund's effigy in the Procession with St. Anianus by circle of Tommaso Dolabella in the Corpus Christi Church in Kraków. In the background, among the colonnades, there is a statue of the Madonna and Child, and in the clouds the figure which is interpreted as Saint Sigismund, patron saint of the monarchs. Heresy, depicted as an old woman, lies chained on the steps of the church. On the right are two Jesuits. Saint Sigismund has also a chain of the Order of the Golden Fleece and he bears a strong resemblance to Sigismund III's father-in-law Archduke Charles II of Austria (1540-1590), son of Anna Jagellonica. His crown is bordered with ermine like the Archducal hat (coronet). Curiously also the crown of the main monarch is bordered with ermine. It might be the painter's mistake or that Sigismund III commissioned an effigy of his brother-in-law Ferdinand II (1578-1637) who was raised by the Jesuits and dealt with heresy in his country before becoming emperor in 1619. Sigismund III received the Order of the Golden Fleece from his brother-in-law king Philip III of Spain in 1600. On this occasion he commissioned silver table service in Augsburg for 20,000 florins. The service, created by Hermann Plixen, was used for the first time during a banquet at the Castle in Warsaw on February 25, 1601. The king also commissioned other exquisite items in Augsburg, like the silver sarcophagus of Saint Stanislaus for the Wawel Cathedral in Kraków, and in other locations. Through his agent in Persia, Sefer Muratowicz, he commissioned a series of kilims with his coat of arms in 1601 and in about 1611-1615 he purchased a series of 6 tapestries in François Spierincx's workshop in Delft with the Story of Diana. On October 29, 1621 Jan Brueghel the Elder wrote to E. Bianchi about sending a lot of paintings to the King (molti pitture al Re) and the "Battle of Kircholm in 1605" by Pieter Snayers, also created for Sigismund, is today in the Château de Sassenage. In Milan, in about 1600, he commissioned a crystal lavabo (ewer and basin) with his coat of arms and monogram (Treasury of the Munich Residence) and most probably the shishak helmet offered to Feodor I of Russia (Kremlin Museum), created before 1591. His portraits in the Germanisches Nationalmuseum in Nuremberg, lost during World War II, and in the Wilanów Palace in Warsaw represent him in a rich, chiselled, partially gilt and polychromed blue armor in the type of mezza armatura (half armor), probably made in Milan. Portrait of a man in a suit of armour etched with gold by Domenico Tintoretto of unknown provenance (sold in 2016 at Christie's, lot 163), has almost identical dimensions as effigy of Sigismund III's sister Anna Vasa by Domenico Tintoretto in the Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum (115.3 x 96.1 cm / 115.5 x 96.7 cm). It is possible that they were created at the same time. The man bears a great resemblance to the effigies of Sigismund III Vasa from the early 17th century, especially his portrait painted in Prague in about 1605 by court painter of Emperor Rudolph II, Joseph Heintz the Elder (Alte Pinakothek in Munich). The king was depicted in similar etched armour in the Habiti Antichi Et Moderni di tutto il Mondo ... by Cesare Vecellio (Rè di Polonia / Poloniæ Rex, p. 346), published in Venice in 1598 (Czartoryski Library in Kraków).
Portrait of Sigismund III Vasa in a suit of armour etched with gold by Domenico Tintoretto, ca. 1592-1600, Private collection.
Allegory of suppression of heresy by Domenico Tintoretto, 1600-1619, Alte Pinakothek in Munich.
Portrait of Sigismund III Vasa as Saint Sigismund by workshop of Domenico Tintoretto
Around 1600, most likely an Italian painter Ottavio Zanuoli (d. 1607), created a painting depicting the Communion of the Virgin, today in the Royal Convent of Las Descalzas Reales in Madrid. Zanuoli was a court painter of Archduke Charles of Styria (son of Anna Jagellonica) and his wife Archduchess Maria Anna of Bavaria (granddaughter of Anna Jagellonica). According to handwritten list of all the effigies fixed on the back of the canvas, the painting represent the family of Archduke Charles, depicted as Saint John the Apostle, giving communion to the Virgin. His son Charles of Austria (1590-1624), Prince-Bishop of Wrocław from 1608, is holding a jug as a deacon of the mass. Behind Archduchess Maria Anna, represented as the Virgin Mary, are her daughters including Anna (1573-1598) and Constance (1588-1631), two wives of Sigismund III Vasa. The painting was undoubtedly a gift to Margaret of Austria (1584-1611), a daughter of Charles and Maria, who on 18 April 1599 married King Philip III of Spain, her first-cousin. Margaret became a very influential figure at her husband's court and a great patron of the arts.
The royal convent in Madrid is full of such disguised effigies of the Habsburgs. One of the oldest is a fresco in the Chapel of Mary Magdalene (Capilla de la Magdalena, inventory number PN 00610451). In this composition by an unknown painter and inspired by the Madonna with the Fish (Virgen del pez) by Raphael (Prado Museum), the Madonna presents features of the Infanta Juana de Austria (Joan of Austria, 1535-1573), founder of the convent. Next are the portraits of Emperor Maximilian II (1527-1576) as Saint Valerius of Treves (PN 00615942) and of Archduke Rudolf of Austria (1552-1612), future emperor, as Saint Victor (PN 00615941) and portraits of four daughters of Archduke Charles of Styria in the Hall of Kings (Salón de Reyes) - Anna (1573-1598) as Saint Dorothy, Maria Christina (1574-1621) as Saint Lucy, Catherine Renata (1576-1599) as Saint Catherine and Elizabeth (1577-1586) as Saint Agnes. All were probably painted in 1582 by Giacomo de Monte (Jakob de Monte) - for example the portrait of Archduchess Catherine Renata depicted with the attributes of Saint Catherine of Alexandria (breaking wheel and sword) bears the following inscription in German: "1582, Catherine Renata, Archduchess of Austria, at the age of 6 and 8 months" (1582 / KATERINA RENNEA / ERTZHERTZOGIN ZV / OSTEREICH . IRHES ALTER VI / IAR . VIII MONNET). Archduchess Anna, future Queen of Poland and first wife of Sigismund III, has the attributes of Saint Dorothy of Caesarea (crown and basket of roses, PN 00612064) (compare "Linaje regio y monacal ..." by Ana García Sainz and Leticia Ruiz, p. 146, 148, 150-151 and "Joyas del siglo XVI en seis retratos infantiles ..." by Natalia Horcajo Palomero, pp. 398-399). In 1603 the Queen of Spain commissioned paintings to her private oratory in the Valladolid palace, painted by Juan Pantoja de La Cruz, today in the Prado Museum in Madrid. One, the Birth of the Virgin shows three of her sisters, together with their mother, Archduchess Maria Anna of Bavaria, the other, the Nativity of Jesus, shows three of her brothers and three of her sisters, the Queen as the Virgin Mary and her husband as a shepherd. Around 1620, the youngest of Charles and Maria's daughters, Maria Magdalena, who on 19 October 1608 married Cosimo II de' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany was represented as Saint Mary Magdalene in a painting by Justus Sustermans, preserved in the Palazzo Pitti in Florence, and in a workshop copy in private collection. Such effigies, in guise of Saints and biblical figures were also popular at the Polish-Lithuanian royal court at that time. The Communion of the Jagiellons at Jasna Góra in 1477 (Casimir IV Jagiellon with his sons admitted to Jasna Góra Confraternity), created by workshop of Venetian painter Tommaso Dolabella in the second quarter of the 17th century (Jasna Góra Monastery), shows King Sigismund III and his sons as their predecessors from the Jagiellon Dynasty kneeling before the Black Madonna of Częstochowa. In the Jasna Góra Monastery, there are also two other paintings created by workshop of Tommaso Dolabella depicting Saints Stephen and Ladislaus, Kings of Hungary, both bearing features of King Sigismund III Vasa and a costume known from other portraits of the king. A painting by workshop of Domenico Tintoretto, also attributed to his brother Marco, whom the father's will names as a painter in Domenico's workshop, from a private collection in Southern Germany (oil on canvas, 113 x 89 cm, sold at Lempertz, Cologne on May 2003, lot 1133), basing on some details of the painting is identified as depicting Saint Louis IX, king of France, kneeling before the Crucifix. The traditional symbols of this Saint are indeed visible in the painting, fleur-de-lis on his coat, pendant, crown and sceptre, however there is also a crown embroidered on his coat and the attire is not blue like in the French royal coat of arms, golden fleur-de-lis on a blue field, used continuously for nearly six centuries (1211-1792). Italian painters since the beginning of the 16th century were well aware how the French king should look like and paintings by Ambrogio Bergognone, active in and near Milan, created between 1500-1520 (Accademia Carrara in Bergamo), by Berto di Giovanni, active in Perugia, created in about 1517 (Galleria Nazionale dell'Umbria), by Francesco Curradi, active in Florence, created in about 1600 (Private collection) and Matteo Rosselli, active in Florence, painted between 1613-1614 (Chiesa della Madonna in Livorno), depict the Saint in a mantle of French monarchs with golden fleur-de-lis on a blue field. The Saint from the Tintoretto's painting is therefore not Saint Louis IX. Another saint monarch connected with France is Saint Sigismund (Latin Sigismundus, died 524 AD), King of the Burgundians, patron saint of monarchs and of the Kingdom of Bohemia (in 1366, Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor, transferred Sigismund's relics to Prague and gave the saint's name to one of his sons, the later King Sigismund of Hungary). Arm reliquary of Saint Sigismund from the Guelph treasure, created in the late 11th century (Museum of Decorative Arts in Berlin), was in the late 13th or early 14th century supplemented with an orb surmounted by a fleur-de-lis, a shortened representation of a lily-crowned scepter. Altar painting with Saint Sigismund in the Parish church in Słomczyn near Warsaw (Konstancin-Jeziorna), created in about 1895 after a lost original, is very similar to the painting by workshop of Domenico Tintoretto. The Saint is kneeling before the Crucifix, his crown and sceptre are on a table covered with crimson fabric, his golden mantle and pendant are also very much alike. Another painting in the same church from the 19th century feretory depict Saint Sigismund in similar golden tunic and kneeling before the altar. The church in Słomczyn was founded at the beginning of the 15th century by Mrościsław Cieciszewski and the main patron of the parish from the very beginning was Saint Sigismund. During the Deluge (1655-1660) the church was plundered and invaders destroyed the altars. In 1165 Werner, bishop of Płock (north of Warsaw), brought the relics of Saint Sigismund from Aachen. In 1370 King Casimir III the Great, commissioned a silver reliquary for the Saint, today in the Diocesan Museum in Płock, and in 1601 King Sigismund III Vasa ordered the 13th century diadem to be placed on the reliquary of his patron saint. Sigismund III was frequenlty depicted in a similar żupan-like attire to that visible in Tintoretto's painting, for example in the mentioned Communion of the Jagiellons, in another painting by circle of Tommaso Dolabella representing Tsar of Muscovy Vasili Shuisky swearing an oath of allegiance at the Parliament of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1611 (Lviv Historical Museum) and in the plaque from his sarcophagus with King's military campaigns, created in 1632 (Wawel Cathedral). The man from the Tintoretto's painting bear a resemblance to the portrait of Sigismund III Vasa in a suit of armour etched with gold by the same painter, created between 1592-1600 (Private collection), his effigy in the Battle of Smolensk by Antonio Tempesta or Tommaso Dolabella, painted after 1611 (Private collection) and his profile on gold 10 ducats coin (portuguez), minted by Rudolf Lehman in Poznań in 1600 (National Museum in Kraków). The overall composition resembles the portrait of Piotr Skarga (1536-1612), court preacher of Sigismund III, created in 1588 by Karel van Mallery (National Library of Spain in Madrid). The painting by workshop of Domenico Tintoretto was in the collection in Southern Germany, exaclty as Allegory of suppression of heresy by this painter from the collection of Sigismund III's daughter (Alte Pinakothek in Munich). The king often sent gifts to William V, Duke of Bavaria, like the reliquary of Saints John the Baptist and Dionysius the Areopagite, offered in 1614 (Treasury of the Munich Residence) or silver statue of St. Benno of Meissen offered to the altar of St. Benno in the Munich Cathedral, created by Jeremias Sibenbürger in 1625 in Augsburg (Diocesan Museum in Freising). Together with the statue of St. Benno, the king also donated two silver reliquaries in the shape of a hand (not preserved) and 10,000 guilders for celebrating the daily mass, the so-called Polish mass, in the Cathedral.
Portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa as Saint Sigismund kneeling before the Crucifix by workshop of Domenico Tintoretto, 1592-1600, Private collection.
Portraits of Duke Joachim Frederick by Flemish painters
During the tenure of Andreas Jerin (1585-1596) as the Bishop of Wrocław the counter-reformation began in Silesia. The pressure of militant Catholicism made itself felt also in the Duchy of Brzeg, when, among others, the commander of the Joannites in Oleśnica Mała near Oława removed Lutheran pastors from his estates (1589), while Joachim Frederick's attempt to intervene become futile (after "Brzeg: dzieje, gospodarka, kultura" by Władysław Dziewulski, p. 59).
Joachim Frederick of Brzeg modeled himself on his father George II (1523-1586), but he was a better administrator than him. He confirmed former city privileges and supported the crafts. The castle in Oława was rebuilt and enlarged for Joachim Frederick in the years 1587-1600 by the Italian architect Bernard Niuron from Lugano. Thanks to his family connections and his good relations with the imperial court in Prague and the court in Berlin, he obtained a number of honorary positions. Since 1585 he was Lutheran provost of the chapter of Magdeburg, and in 1588 he was appointed general commander of the regular army of Silesia. After the death of his brother John George, who died without issue in 1592, Joachim Frederick inherited Wołów and after death of his mother and his cousin Frederick IV of Legnica (1552-1596), he become the sole Duke of Legnica-Brzeg-Oława-Wołów (Liegnitz-Brieg-Ohlau-Wohlau in German). Joachim Frederick gained great popularity for his gentleness and diligence. He liked science and he tried to improve the administration of justice in 1599. Since he ranked first among the Silesian princes, from 1592 until his death he had to deal with the matter of helping the emperor, who was at war with the Turks. In 1599, the Duke and his brother-in-law, Charles II of Ziębice-Oleśnica, refused to participate in the election of Bishop Paul Albert because he was not a Silesian and he acquired from Peter Wok von Rosenberg the towns of Złoty Stok (Reichenstein) and Srebrna Góra (Silberberg), rich in gold and silver mines. Joachim Frederick died on March 25, 1602 in Brzeg. The man from the portrait in the National Museum in Poznań (oil on panel, 47 x 38 cm, inventory number Mo 855) resemble the man from the portrait in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna (inventory number GG 808). Many splendid paintings that once adorned the walls of the Silesian Wawel - the Piast Castle in Brzeg and survived the bombing in 1741, when the castle was destroyed by the Prussian forces in the First Silesian War, were moved to Berlin. Possibly also this picture. The image in Poznań was acquired in 1930 from private collection Karl von Wesendonk in Berlin. Both paintings, in Poznań and in Vienna, are attributed to Adriaen Thomasz. Key, however the man from Poznań version is much older. If he was around 25 when the Vienna painting was created in about 1575, then the Poznań version should be dated around 1600, which rules out Key's authorship, as he died in 1589 or after. The most important arts and crafts center in this part of Europe at that time was the imperial court of Emperor Rudolf II in Prague. Many Flemish artists worked for the Emperor and two of them, created very similar portraits of Rudolf. One with light blue eyes, bust-length, wearing a breastplate (sold at Christie's, 27 Jan 2010, lot 344), is attributed to circle of Frans Pourbus the Younger (1569-1622), a Flemish painter from Antwerp, who at the end of the 16th century worked for Archduke Albert and Infanta Isabella in Brussels. The other with dark eyes, attributed to Lucas van Valckenborch (d. 1597) from Leuven, is today in the Liechtenstein collection in Vienna (inventory number GE 2484). The style of the image in Poznań resemble that of Pourbus, especially the portrait of a man in the Museum of Fine Arts in Budapest (inventory number 5862). The same man was depicted in another painting created in about 1600, in which however his face resemble more the Warsaw portrait from 1574 (inventory number M.Ob.819 MNW). His servant gives him a cup of wine. This painting titled sometimes "Two Fools", because of the old man's extravagant outfit, or "Emperor Rudolf II taking the cure", is today in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna (oil on canvas, 175.5 x 109 cm, inventory number GG 2773, verifiable in the gallery depot in 1868). It was attributed to Pieter Isaacsz (d. 1625), circle of Cornelis Ketel (1548-1616) or to Lucas van Valckenborch. The comparison with the painting in the Silesian Museum in Opava (inventory number In 2036 A), which was created by Valckenborch, most probably together with his assistant or only by him - Georg Flegel (1566-1638) is the most accurate. In his only known so far painted effigy from a fresco by Balthasar Latomus, the court painter of George II, in the ducal study of the Brzeg Castle, painted in 1583-1584, Joachim Frederick was depicted in colouful red-brown striped doublet, while his father is wearing a black attire. The Duke of Brzeg is also wearing a ruff and heavy gold chains with a medallion, like in the described painting by Valckenborch or Flegel in Vienna. The man from a large gold medal, most likely minted from the Złoty Stok gold, resemble the most George the Pious (1484-1543), Margrave of Brandenburg-Ansbach. George, son of Sophia Jagiellon, was an early adherent of Protestantism. He maintained correspondence with Martin Luther and introduced the Reformation in his Silesian possessions - Krnov, Bytom, Racibórz and Opole, one of the largest centers of Silesian cloth weaving. His son George Frederick (1539-1603), who from 1577 was also Administrator of the Duchy of Prussia, maintained good relations with Poland-Lithuania. He minted coins with the official motto of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth: "If God be with us, who shall be against us?" (Guldentaler, 1586, Königsberg), his tomb monument in the Heilsbronn monastery, attributed to Endres Dietrich Seidensticker, is adorned with coat of arms of Poland (White Eagle), repeated three times (after "Kloster Heilsbronn ..." by Graf Rudolph Stillfried-Alcántara, p. 163) and his portrait in the National Museum in Wrocław was created by Silesian painter Andreas Riehl the Younger from Wrocław. The portrait of George Frederick was created in 1601 and he is wearing a medal of King Stephen Bathory with the inscription in Latin STEFANVS. REX. POLONIA. 1581 (after "Portret na Śląsku ..." by Ewa Houszka, p. 12). In 1571, the Regent of Prussia also commissioned a series of portraits of his father George the Pious in the workshop of Lucas Cranach the Younger (two are in the Grunewald hunting lodge in Berlin, GKI1192 and GKI1048) and for his wife Elizabeth of Brandenburg-Küstrin (1540-1578), who died while she was staying at the Warsaw court, where George Frederick was to be awarded the dukedom by the Polish king, he commissioned the Dutch sculptor Willem van den Blocke to construct the monument in Königsberg Cathedral, which was completed in 1582. His Silesian lands were close to Brzeg and Legnica, so the Margrave, who stayed mostly in Ansbach, entrusted George II od Brzeg with the implementation of the new laws in his Krnov domain. The bust of a bearded man in mentioned gold medal in the Vienna portrait resemble the portraits of George the Pious by Cranach the Younger and 1534 medal with his bust in the Germanisches Nationalmuseum, Nuremberg. Joachim Frederick, a Lutheran and the most important among the Silesian princes, minted coins in Złoty Stok, like the gold ducat from 1602 (National Museum in Warsaw, NPO 350 MNW). It was therefore him who most probably ordered both the medal and the portrait in the workshop of Flemish painter. In 1582 41 representations of Dutch wars painted on canvas were purchased by the Brzeg city council (after "Op Nederlandse manier ..." by Mateusz Kapustka, p. 35), indicating that Netherlandish art was strongly represented in his domains.
Portrait of Joachim Frederick (1550-1602), Duke of Legnica-Brzeg-Oława-Wołów by circle of Frans Pourbus the Younger, 1597-1602, National Museum in Poznań.
Portrait of Joachim Frederick (1550-1602), Duke of Legnica-Brzeg-Oława-Wołów with gold medal with bust of Margrave George the Pious by Lucas van Valckenborch or Georg Flegel, 1597-1602, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Portrait of Janusz I Radziwill by Leandro Bassano
"The Polish Lord, at whose court Michelagnolo was already employed, has recently written, that he must go there as soon as possible, offering him a most honorable position, that is, a place at his table, dressed like the first gentlemen of his court, two servants, who will serve him, and a carriage with four horses, and more than 200 Hungarian ducats a year's allowance, that is about 300 scudi, except donations, which will be a lot; so that he is resolved to leave as soon as possible, nor expects anything other than the opportunity of good company, and I believe that he will depart in fifteen days, so I must arrange him with money for the journey, and in addition it is necessary for him to bring with him at the request of his Lord some things, for which among the provision for a journey and the said things I cannot fail to accommodate at least 200 scudi" (Signor Pollacco, a presso di chi è stato Michelagnolo, ha ultimamente scritto, che ei deva quanto prima andare là da lui, offerendoli partito honoratissimo, cioè la sua tavola, vestito al pari dei primi gentil' homini di sua corte, due servitori, che lo servino, et una carrozza da quattro cavalli, et di più 200 ducati ungari di provvisione l'anno, che sono circa 300 scudi, oltre ai donativi, che saranno assai; tal che lui è risoluto di andar via quanto prima, nè aspetta altro che l'occasione di buona compagnia, et credo che tra quindici giorni partirà, onde a me bisogna di accomodarlo di danari per il viaggio, et in oltre bisogna che porti seco ad instanza del suo Signore alcune robe, che tra 'l viatico et le dette robe non posso far di manco di non l'accomodare almeno di 200 scudi), informed his mother in a letter from Padua in the Venetian Republic of August 7, 1600 (Mss. Palatini, Parte I, Vol. IV, pag. 11.), Galileo Galilei, famous Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer.
Already in 1593 Michelagnolo Galilei (1575-1631), an Italian composer and lutenist, son of another composer and lutenist, Vincenzo Galilei, and the younger brother of Galileo went to the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, where foreign musicians were in great demand. Most likely invited by the influential Radziwill family, he stayed there till 1599 and returned to his previous employer in Poland-Lithuania in 1600 after a short stay in Italy. The "Polish Lord", Michelagnolo's parton, is somerimes identified as Christopher Nicolaus Radziwill (1547-1603) nicknamed "the Thunderbolt", voivode of Vilnius, Grand Hetman of Lithuania and a representative of the Birzai branch of the Lithuanian magnate family (after "Galileo Galilei e il mondo polacco" by Bronisław Biliński, p. 69), who employed several musicians at his court. Christopher Nicolaus was a son of Nicolaus "the Red" Radziwill (brother of Queen Barbara), a Calvinist and protector of the Calvinists in Poland-Lithuania. By his second wife Katarzyna Ostrogska (1560-1579), daughter of Zofia Tarnowska (1534-1570), he had a son Janusz I (1579-1620), educated in Strasbourg and Basel. Janusz also traveled to Germany, Bohemia, Austria, Hungary, and France. From 1599 he was a cupbearer of Lithuania and on 1 October 1600 he married the Orthodox Princess Sophia Olelkovich-Slutska (1585-1612), the heiress of Slutsk and Kopyl (in present-day Belarus) and the richest bride in Lithuania. Sophia, canonized by the Orthodox Church in 1983, died in childbirth on March 19, 1612, leaving all of her property to her husband, and just few months later, on March 27, 1613 in Berlin, Janusz married Elizabeth Sophie of Brandenburg (1589-1629), a daughter of the Brandenburg Elector John George (1525-1598) and a great-granddaughter of Barbara Jagiellon (1478-1534), Duchess of Saxony. It is possible that Michelagnolo was invited to the Commonwealth for the wedding feast of Janusz and Sophia. According to a Galileo's letter from Padua of November 20, 1601 to his brother in Vilnius, he also traveled to Kraków and Lublin. In April 1606 he returned to Italy to live with his brother in Padua. On May 11, 1606 Galileo wrote to him from Venice about negotiating with a German Lord (Signore tedesco) and he secured him a place at court of the Bavarian Elector in Munich. In 1608 Michelagnolo was married to Chiara Anna Bandinelli in Bavaria, whom he most likely met in Lithuania and who was the sister or daughter of Roberto Bandinelli, nephew of the famous Florentine sculptor Bartolommeo called Baccio, who settled with his family in Lithuania (after "Archivio storico italiano", Volume 17, p. 31). According to the catalogue of exhibition of portraits in the Hague in 1903 (Meisterwerke der Porträtmalerei auf der Ausstellung im Haag, p. 2, item 2a), in the collection of Princess Cecylia Lubomirska née Zamoyska (1831-1904) in Kraków there was a portrait of a lute player by Leandro Bassano. It was later owned by Cecylia's son Kazimierz Lubomirski (1869-1930), most probably lost during World War II. A young man with several rings on his left hand is playing a serenade on a lute to his beloved. He is listened to by his dog, conventional symbol for fidelity, especially marital fidelity, wearing an expensive collar, possibly bearing his coat of arms. The window in the background shows his house, an Italian-style villa similar to the pavillons of the Radziwill Palace in Vilnius, the larger palace of the Calvinist branch of the family. The Radziwill Palace, initially a renaissance manor house built in the 16th century, was reconstructed and extended between 1635 and 1653 for Janusz II Radziwill (1612-1655), nephew of Janusz I (1579-1620). The lavish edifice was constructed by Jan Ullrich and Wilhelm Pohl to design by Italian architect, most probably Constantino Tencalla, and was depicted in 1653 medal by Sebastian Dadler, minted on the occasion of the inauguration of Janusz II as the Voivode of Vilnius. The lute player from the Lubomirski collection was signed and dated by the artist. The inscription in Latin stated that the depicted man was 21 years old in 1600 (Anno aetatis suae XXI, MDC), exaclty as Janusz I Radziwill (born in July 1579 in Vilnius), when he married Sophia Olelkovich-Slutska. The sitter bear a great resemblance to other effigies of the Prince, especially a print by Jan van der Heyden after Jacob van der Heyden, created in 1609 (Herzog Anton Ulrich-Museum), a portrait by unknown artist (State Historical Museum in Moscow) and a medal with his bust, published in Berlin in "Medals of the princely house of Radziwill" (Denkmünzen des Radziwillschen Fürstenhauses, 1846). It is generally belived that Bassano's lute player is tantamount to a painting acquired in Venice by Count Stanisław Kostka Potocki (1755-1821), who recalled in a letter to his wife of September 22, 1785 from Venice: "I end my article on Venice by telling you that I have acquired one of the freshest paintings of Paolo Veronese that I have ever seen, it is a Holy Family of the size of your Rubens, I hope that you will be happy with it, adding here a portrait of Bassen playing the lute painted by himself which is really a masterpiece of this master, and you will be happy with this acquisition (je finis mon article de Venise, par te dire que j'ai fait l'aquisition d'un des plus frais tablaux de Paule Véronèse que la aie jamais vue, c'est une St. Famille de la grandeur à peu près de ton Rubens, j'espère que la en sera contente, ajoute ici un portrait du Bassen jouant du luth peint par lui meme qui est vraiment un chef d'œuvre de ce maître, et tu sera contente de moi, Central Archives of Historical Records in Warsaw, 262 t. 1, page 60). Veronese's Holy Family is today most probably in the Wilanów Palace (inventory number Wil.1000, also considered to be the painting purchased in Paris in 1808) and it is currently attributed to his brother Benedetto Caliari. Even if the lute player from the Lubomirski collection was acquired by Potocki in Venice, it does not exclude that it represents a person from the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, as paintings commissioned abroad were frequently created in series, as gifts to relatives and friends. In this case the possibility that it was a gift to the tutor's brother, Galileo Galilei, or his family is probable. If Michelagnolo was a court musician of Christopher Nicolaus "the Thunderbolt", he could teach music to his son Janusz I. "It was customary that the orders of Polish clients abroad were paid through the bankers' offices that organized the transport. Thus, the intermediary between Sigismund III and Chancellor Zamoyski, on the one hand, and Italian painters, on the other, was the Montelupi company from Kraków, whose post office brought finished and paid works to Poland. Gdańsk bankers mediated between our country and the Netherlands, and thanks to their efforts, paintings and fabrics ordered by Ladislaus IV in Antwerp were transported by sea through the Danish straits" (after "Obrazy z kolegiaty łowickiej i ich przypuszczalny twórca" by Władysław Tomkiewicz, p. 119). In the 1620s, most probably after death of Leandro Bassano, who died on April 15, 1622, a painter from the circle of Bassano brothers settled in Pułtusk, a significant economic centre of Masovia. Between 1624-1627 he created three paintings showing scenes from the life of Mary for the Łowicz Cathedral, commissioned by Henryk Firlej (1574-1626), Archbishop of Gniezno and Primate of Poland, son of Jan Firlej (1521-1574), and a self-portrait, today in the Dominican Monastery in Kraków.
Portrait of Janusz I Radziwill (1579-1620), aged 21 playing a lute by Leandro Bassano, 1600, Lubomirski collection in Kraków, lost.
Portrait of Sebastian Petrycy by Venetian painter
Sebastian Petrycy or Sebastianus Petricius Pilsnanus, was born in 1554 in Pilzno near Tarnów in south-eastern Poland as a son of Stanisław (died after 1590), a wine merchant. In 1583 he graduated with the degree in philosophy at the Kraków Academy and he began lecturing there. A year later, in 1584, Sebastian became a member of the Collegium Minus (College Minor) and took the chair of poetics and in 1588 he became a professor of rhetoric.
In February 1589, Petrycy was granted a leave to travel to Italy and study at a selected foreign university. He decided to study in Padua, where he received the degree of doctor of medical sciences at the beginning of March 1590. When he returned to Kraków, he applied for the recognition of his diploma at the Faculty of Medicine, but was refused admission and left for Lviv, where he got married with already pregnant eighteen-year-old Anna (he was almost forty), the daughter of a wealthy merchant Franz Wenig, and opened his own medical practice. The death of his wife (February 28, 1596) and of his only daughter, Zuzanna, as well as the lost trial for the inheritance of his father-in-law, prompted him to return to Krakow (around 1600). He became the personal physician of the bishop of Kraków Bernard Maciejowski, who in 1603 was made cardinal by Pope Clement VIII. Between 1603-1604 he went with the cardinal to France and Lorraine and in 1606, as a physician of Jerzy Mniszek and his daughter Marina, he left for Moscow, which cost him almost a year and a half in captivity. During his court career, he worked on translations of Aristotle into Polish. He then returned to the medical profession and successfully practiced for the last 10 years of his life. Petrycy died in 1626 in Kraków, and shortly before his death he founded a marble epitaph for himself depicting him in prayer, created by a royal court sculptor. Portrait of a bearded man holding glasses, comes from the collection of John Rushout, 2nd Baron Northwick (1770-1859) at Northwick Park. It was previously attributed to Titian and Lotto Lorenzo, however stylistically is also close to Jacopo Tintoretto (1518-1594) and his son Domenico (1560-1635). The man's costume of crimson silk is very similar to Polish żupan, his coat is lined with fur. This effigy is very similar to portraits of Sebastian Petrycy and his son Jan Innocenty Petrycy (1592-1641), who like father was a physician, professor at the Academy and studied in Bologna. Mentioned portraits are today in the Collegium Maius of the Jagiellonian University and were created in the 1620s by workshop of Tommaso Dolabella (1570-1650), a Venetian artist settled in Kraków and a court painter of king Sigismund III Vasa. It is possible that Dolabella's workshop copied some family owned portraits, created in Venice. Consequently the effigy can be dated to beginning of the 17th century when Petrycy was a court physician in Kraków.
Portrait of Sebastian Petrycy (1554-1626) holding glasses by Venetian painter, possibly Domenico Tintoretto, 1600-1606, Private collection.
Portrait of Uriel Górka, Bishop of Poznań by Odoardo Fialetti
The full-length portrait of Uriel Górka (ca. 1435-1498), Bishop of Poznań in Kórnik Castle near Poznań is one of the oldest effigies of church hierarchs in Poland. This large painting on canvas (219 x 111.5 cm, inventory number MK 3360) bears an inscription in Latin on a band above the figure: VRIÆL / COMES DE GORCA DEI GRATIA EPISCOPVS POSNANI / ENSIS. The band, typical of Gothic paintings, as well as the general style of the work suggest that it is a copy of the original portrait of the bishop, as the painting itself is variably dated to the second half of the 16th century or the middle of the 17th century.
The original may be by Stanisław of Kórnik, who was the bishop's court painter for six years in the 1490s, but also commissioned from abroad. Uriel, the founder of the family's power, distinguished himself in the field of artistic patronage and he was in close contact with the artistic circles of Nuremberg. He ordered silverware from Albrecht Dürer the Elder, father of the painter (according to the bill of August 26, 1486 - Item mein her Uriel her bischoff von Poln hat Albrechtn Durer dem goltschmyd silber gebn), he commissioned various works from the sculptor Simon Leinberger, like the excellent composition of Christ in the Garden of Olives sculpted in 1490 for the Poznań Cathedral, and bronze tombstones for himself and his father Łukasz (died in 1475), the voivode, at the famous Vischer workshop (after "Kultura, naród, trwanie ..." by Maria Bogucka, p. 164). The full-length effigy of Uriel on his tomb slab by the Vischer workshop in Poznań Cathedral is comparable to this portrait. So maybe the original effigy of the bishop was also created in Nuremberg or it was a likeness from the gallery of portraits of Poznań bishops modo chronicae depicta made after 1508, commissioned by Bishop Jan Lubrański from the Kraków painter Stanisław Skórka. The style of the painting is obviously Venetian, close to the Bassanos and influenced by Tintoretto, but no Venetian artist is confirmed in Poznań and the surrounding area at that time, therefore the painting must be an import, ordered from Venice, such as the portraits of the daughters of Łukasz Górka (1482-1542). Stylistically closest is the portrait of Doge Antonio Priuli (1548-1623), reigning from 1618 until his death, in the Kensington Palace (inventory number RCIN 407153). The way the face, hands and gold patterned fabrics were painted is very similar. The portrait of Priuli was one of four portraits of Doges acquired by Sir Henry Wotton during his tenure as ambassador in Venice (1612-1616 and 1619-1621) "done after the life by Eduardo Fialetto", according Wotton's will. The other three portraits are also stylistically close, notably the effigy of Doge Giovanni Bembo (RCIN 407152). Odoardo Fialetti, born in Bologna in 1573 and initiated to painting with the Bolognese Giovanni Battista Cremonini, moved to Padua and then to Venice, where he entered Tintoretto's workshop. It is possible that he also spent some time in Rome, completing his training. From 1604 to 1612, Fialetti was a member of the Venetian Brotherhood of Painters (Fraglia dei Pittori). The most possible founder of the painting is therefore Jan Czarnkowski (d. 1618/19), royal courtier, one of the heirs of the Górka family after childless death of Lutheran magnate Stanisław Górka (1538-1592). Czarnkowski completed the Górka mausoleum in Kórnik in 1603 and handed over the church to the Catholics. The effigy of the Catholic bishop of Poznań, educated in Italy, owner of the Kórnik estate from 1475 who brought a gardener from Italy to Kórnik (after "Zamek w Kórniku" by Róża Kąsinowska, p. 17), fits perfectly into Czarnkowski's Counter-Reformation activity. It was commissioned in Italy possibly in opposition to the predominantly Protestant northern school of painting.
Portrait of Uriel Górka (ca. 1435-1498), Bishop of Poznań by Odoardo Fialetti, ca. 1604, Kórnik Castle.
Portraits of Constance of Austria by Gortzius Geldorp
"Although the king was young, he was more inclined to peace than to war, and he did not even want to find employment in anything in the domain of the god Mars. I heard that one time, when the archbishop and chancellor informed him about the war, he wrote something down in a pugilares. They thought that he was anxious about the fate of the war until the king, who was a good painter, goldsmith and turner, showed them a painted little owl", recalled in his diary Albert Stanislaus Radziwill, Grand Chancellor of Lithuania about the beginnings of the reign of Sigismund III Vasa.
The King, so much inimical to idleness (tanto inimico dell'ozio), in his spare time he occupied himself with a certain artistic work, making his effigies, paintings and other items, which he offered as a gift, like "the one of which he painted with his own hand was the portrait of Saint Catherine of Siena last year" (una delle quali che fece di sua mano, fu il ritratto di S. Catherina di Siena l'anno passato), says of Sigismund III another contemporary witness, the papal nuncio Erminio Valenti (1564-1618), in a handwritten description of Poland and the royal court in 1603 (Relazione del Regno di Polonia). In 1605 the king married his distant relative (as a granddaughter of Anna Jagellonica), the sister of his first wife and sister of Queen of Spain, Constance of Austria (1588-1631). Many eminent guests arrived to Kraków for Sigismund's wedding, the bride with her mother Archduchess Maria Anna, and her sister - Maria Christina, Princess of Transylvania, Radu Șerban, Voivode of Wallachia or his envoy, Mechti Kuli Beg, Ambassador of Persia, Afanasy Ivanovich Vlasiev, Ambassador of Russia, among others. The city was beautifully decorated on the entry of the wedding procession (mechanical Polish eagle, most probably from ephemeral decorations, preserved in the St. Mary's Church in Kraków). Also many artists came to Kraków at that time. The so-called "Stockholm Scroll", a unique, fifteen-metre long painting depicting the 1605 wedding procession, acquired during the Deluge and returned to Poland in 1974 (donated to the Royal Castle in Warsaw), is attributed to Balthasar Gebhardt, court painter of Archduke Ferdinand (1578-1637), Constance's brother. Among the most distinguished works attributed to the king there is a gouache painting on parchment with Allegory of Faith in the Nationalmuseum in Stockholm. It bears the king's coat of arms, his monogram S under the crown, the date 1616 and monogram M.N.D.F.C. Below there is also a signature of king's wife Constantia Regina. Since the effigy of a woman bears resemblance to other effigies of the Queen, it was she who lend her features to the figure. Another painting traditionally linked with Sigismund is Mater Dolorosa in the Alte Pinakothek in Munich (inventory number 5082), painted on copper. It comes from the Castle Haag in Geldern in the district of Kleve, North Rhine-Westphalia and was most probably part of Anna Catherine Constance's dowry. Sigismund's painting is a copy of a work by Gortzius Geldorp depicting a female saint in adoration signed with monogram 'GG F', painted on wood. Crispijn van de Passe the Elder created a print, published in Utrecht in 1612, with similar composition, showing the penitent Mary Magdalene (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, inventory number RP-P-1906-2063), which is however more close to the Sigismund's painting then to the version by Geldorp. The woman in Geldorp's painting has more Habsburg facial features. The same woman with protruding lower lip was depicted in two other paintings by Geldorp one signed with monogram and dated 'AN ° 1605.GG.F.' (sold in 2015 at Christie's, Amsterdam, lot 52, the other sold in 2011 at Christie's, New York, lot 140). Both paintings represent a lady as Berenice, wife of pharaoh Ptolemy III Euergetes. Berenice pledged to sacrifice her hair to the goddess Venus if her husband was safely brought home from battle during the Third Syrian War. Her hair became the constellation called Coma Berenices (Berenice's hair) and the symbol of power of marital love. Very little is known about Gortzius Geldorp. He was born in Leuven (Louvain) in 1553 in what was then the Spanish Netherlands and learned to paint from Frans Francken I and later from Frans Pourbus the Elder. Around 1576 became court painter to the Duke of Terra Nova, Carlo d'Aragona Tagliavia (1530-1599), a Sicilian-Spanish nobleman, who in 1582 was appointed Governor of Milan and whom he accompanied on his trips. The Duke died in Madrid on September 23, 1599, and Geldorp died after 1619. It is very possible that he or his student came to Kraków in 1605. In 1599 Geldorp created a portrait of a young woman in Venetian costume (sold at Christie's New York, 12 January 1994, lot 134, signed and dated top left: Anº.1599./GG.F), similar to costumes of Venetian ladies published in 1590 in De gli habiti antichi, e moderni di diverse parti del mondo libri due by Cesare Vecellio, cousin of the painter Titian (p. 97-112). The same year he also created a portrait of Hortensia del Prado (Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam, inventory number SK-A-2081, signed and dated top left: Anº 1599./GG.F.). Either the painter went for a short time to Venice or Poland-Lithuania, or the lady in Venetian costume visited his studio or most likely sent a miniature, drawing or other portrait to be copied. The same woman as in the painting sold in New York, wearing a similar lace-trimmed Venetian dress, is depicted in another painting, possibly a copy or variant of Geldorp's painting. This painting is also in a private collection (sold at Bonhams London, 6 July, 2005, lot 113). It is attributed to the painter active in Bologna Lavinia Fontana (1552-1614).
Portrait of Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631) as Berenice by Gortzius Geldorp, 1605, Private collection.
Portrait of Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631) as Berenice by Gortzius Geldorp, ca. 1605, Private collection.
Portrait of Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631) as a Saint in adoration (Saint Constance?) by Gortzius Geldorp, ca. 1616, Private collection.
Portrait of a lady in Venetian costume by Gortzius Geldorp, 1599, Private collection.
Portrait of a lady in Venetian costume by Lavinia Fontana, ca. 1599, Private collection.
Portrait of Queen Constance of Austria as Venus by Gortzius Geldorp
"At that time, King Sigismund III of Poland commissioned from him the fable of Diana with Calisto bathing & other Poems. They pleased the King, who ordered him to be invited to his court with a worthy reward. However, the painter accustomed to the comforts of his home, refused such a good opportunity, sending there Tomaso Dolobella, his disciple […] He also painted for the same King part of the fable of Psyche, shared with Palma, and Antonio's work having pleased him, he then ordered from him a canvas with the martyrdom of Saint Ursula, which he executed with great diligence, and on the covers he painted the saints Vladislaus, Demetrius and other saints, whom the King surrounded with a cult, and for that worthy work he was commended with royal letters and presented with some gifts", comments on the works of the Greco-Venetian painter Antonio Vassilacchi (1556-1629) called L'Aliense, Carlo Ridolfi in a book published in 1648 presenting the history of Venetian painting (Le Maraviglie dell'arte). Saint Ursula was probably intended for King's mistress, influential Urszula Meyerin, who was most probably depicted as the saint martyr.
As it was said Palma il Giovane (1549-1628) worked with Vassilacchi on part of the fable of Psyche, and for the Cathedral in Warsaw he created two paintings - one with Baptism of Christ (tavola di Christo al Giordano), according to Ridolfi, and the Virgin and Child with St. John the Baptist and St. Stanislaus (destroyed in 1944). According to Palma's letter from January 1602 Aliense was to begin designs while in Salò, but he would then need to return to Venice to "finish certain works that he is doing for the king of Poland". Two drawings by Palma, one showing Venus and Psyche (British Museum, inventory number 1862,0809.74) and the other Cupid and Psyche (sold at Christie's, July 6, 2021, lot 3), could be preparatory drawing for the Psyche cycle. A letter from the Treasurer of the Crown, Jan Firlej (d. 1614), addressed to King Sigismund III Vasa (dated April 29, 1599) says that in one of the Italian rooms ("in the new buildings") at the Wawel Castle in Kraków, described as "the happiest", "paintings were made in Venice". The themes of these paintings decorating the interior, were most probably taken from erotic and mythological themes. They covered the walls and filled the gilded coffered ceilings in Venetian style. According to inventory description of Wawel from 1665 "Italian paintings with golden frames" were in the antechamber at the Hen's Foot tower, Italian "pictures" decorating "the ceiling carved with gold work" in the main room there and "around eleven Italian paintings with golden frames". In the room "under the birds", according to the inventory from 1692, there were "four pictures above the door, between which there are nine pictures above the panelling, only two with golden frames ... In this room there are nine pictures in the ceiling" (after "Weneckie zamówienia Zygmunta III" by Jan Białostocki). The king had undoubtedly other erotic and Italian rooms and studiolo in other royal residences in Kraków (Łobzów), Warsaw (Royal Castle, Ujazdów), Vilnius, Grodno and Lviv. Cardinal Ferdinando I de' Medici (1549-1609), who became Grand Duke of Tuscany in 1587, most likely owned such a studiolo or camerino in his Villa Medici in Rome, as suggested by the author of the Instagram profile ARTidbits (post published July 27, 2023). There is a pavilion there with two rooms, considered the most intimate in the entire complex. It was decorated by Jacopo Zucchi with frescoes representing a pergola, birds, plants and small animals. Zucchi is the author of numerous portraits of cardinal's mistress Clelia Farnese (1556-1613), Marchioness of Civitanova. She was depicted as Amphitrite, the goddess of the sea, and Ferdinando as her husband Poseidon, as well as various Roman ladies, in the painting entitled The Kingdom of Amphitrite (The Coral Fishers), which is now in the Lviv National Art Gallery (Ж-272, signed and dated lower right: Jacobus Zuchi fior fecci 159[0]). The painting comes from the Lubomirski collection, so provenance from the royal collection of Poland-Lithuania, as a gift for Sigismund III or his aunt Anna Jagiellon, cannot be excluded. Many copies of this painting exist, all however without the disguised portrait of the cardinal. The Grand Duke corresponded with the King of Poland and in a letter dated September 10, 1595, he even recommended two of his musicians Luca Marenzio and Francesco Rasi to Sigismund. According to Le vite de' pittori ... by Giovanni Baglione, published in 1642, a version adorned Ferdinando's studiolo in his Roman residence, the Palazzo Firenze (after "Jacopo Zucchi's The Kingdom of Amphitrite ..." by Federico Giannini, Ilaria Baratta). Clelia, as suggested by ARTidbits, was also depicted as one of the Three Graces, goddesses of charm, beauty, nature, human creativity and fertility in a painting from a private collection in Rome (Casa d'Aste Babuino in Rome, June 27, 2023, lot 280). The latter effigy closely resembles her portrait attributed to Scipione Pulzone from the Palazzo Farnese in Rome (Dorotheum in Vienna, October 22, 2019, lot 15). The huge popularity of erotic images and nudes caused concern to some preachers of the Counter-Reformation. In his poem "Roman and Christian Lucretia", published in Kraków in about 1570, Bishop Jan Dymitr Solikowski (1539-1603), secretary of King Sigismund II Augustus from 1564, demanded that paintings depicting "shameless arts and all Jupiter Vanities, Mars with Venus" to be burned and painters with them, it should be noted however, that the title page of his work shows a beautiful woodcut with half-naked Lucretia by Mateusz Siebeneicher or his circle (University of Warsaw Library). Over a half a century later, in 1629 the court preacher of Sigismund III and Ladislaus IV Dominican Fabian Birkowski (1566-1636) warned against "these painted fornications", which were very popular in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth before the Deluge (1655-1660): "and yet this eye poison can be seen everywhere, full of these filthy images in bedchambers, halls, dining rooms, gardens and fountains, above the doors, on the glasses and cups". He also added "and our heretics have so corrupted their eyes that they throw the image of the crucified Christ out of bedchambers and rooms, and in its place they hang Fauns and painted Cupids, Venus and Fortuna above the table, so that they may dine and sup with them. [...] And there is no image of the Blessed Virgin anywhere; and the image of filthy Venus has a place, and even better at home" (after "Kazania" by Fabian Birkowski, 1858, Vol. 1-2, p. 81-82). Somber and death-filled aura of the late 1620s provoked reflection. At that time the Commonwealth was struggling with Swedish invasion of Polish Prussia, military defeats and outbreaks of plague associated with troop movements. Only in Gdańsk 9,324 people died during epidemic of 1629-1630 (after "Przeszłość demograficzna Polski", Vol. 17-18, p. 66). In 1630 Mikołaj Wolski (1553-1630), Grand Crown Marshal, favorite and friend of Sigismund III Vasa, but above all an excellent collector, who invited to Poland the Italian painter Venanzio di Subiaco (1579-1659), ordered erotic paintings to be burned before his death except those in Venetian style coffered ceilings. He wrote in a letter of March 6 to Jan Witkowski "that images ad libidinem [to lust] and inciting to sin, which can be found in Krzepice castle, should all be burned; and those which are painted naked on the wall in my room where I slept and in my chamber, I beg you, let a painter who is able to paint any dresses and let him cover inhonestates [deceptiveness]. Ceiling paintings, let them remain as they are" (after "Zakon Kamedułów ..." by Ludwik Zarewicz, p. 197). Nevertheless, "a wall full of paintings with naked people" is mentioned in some manor houses still in 1650 (after "Miłość staropolska" by Zbigniew Kuchowicz, p. 165). Two paintings from the Poznań Society of Friends of Learning, lost during World War II, show how wonderful the interiors of the residences of the First Polish Republic were. According to tradition, they represented the interior of the Leszczyński Palace, most probably the Palace of Bogusław Leszczyński, Grand Treasurer of the Crown in Warsaw, built between 1650-1654 to a design by Giovanni Battista Gisleni. "Portrait of an elegant woman in the guise of Venus" by Gortzius Geldorp (oil on panel, 56.6 x 44.1 cm, sold at Sotheby's, New York, January 29, 2016, lot 454) is a version of portrait of Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631) as Berenice, created in 1605. The face is identical, while the composition resembles portraits of Venetian courtesans by Domenico Tintoretto, especially the Lady revealing her breast in Prado (inventory number P000382) and the Portrait of a woman as Flora in the Wiesbaden Museum (inventory number M 296), also attributed to Domenico's half-sister Marietta Robusti. Also the style of the painting with bold brushstrokes is more Venetian and tintoresque, it seems that Geldorp copied a work by Tintoretto and inspired by his style. His Penitent Mary Magdalene in the Mauritshuis in The Hague (inventory number 319), was evidently inspired by Domenico's Magdalene in the Capitoline Museums in Rome (PC 32), painted between 1598 and 1602. He also copied Violante or "La Bella Gatta" by Titan (monogrammed upper left: GG. F., sold at Dorotheum in Vienna, April 19, 2016, lot 122).
Portrait of Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631) as Venus by Gortzius Geldorp, after 1605, Private collection.
Venus and Psyche by Palma il Giovane, first quarter of the 17th century, British Museum.
Cupid and Psyche by Palma il Giovane, first quarter of the 17th century, Private collection.
Entombment of Christ with the portrait of Nicolaus Christopher Radziwill "the Orphan" by Leandro Bassano or workshop
On September 16, 1582 Prince Nicolaus Christopher Radziwill "the Orphan" (1549-1616), Grand Marshal of Lithuania, accompanied by a dozen or so people (friends and servants), set off from his family castle in Nesvizh towards Venice from where in 1583 he went to the Holy Land. Through Dalmatia, the Greek islands, Tripoli, Damascus, he reached Jerusalem in the middle of the year, where in the Basilica of the Holy Sepulcher he was awarded the title of Knight of the Holy Sepulcher. Then through Egypt, where he had the opportunity to see the famous Great Sphinx, the eastern coast of Italy and again Venice he returned to his homeland on July 7, 1584.
Nicolaus Christopher was the son of Nicolaus Radziwill the Black and Elżbieta Szydłowiecka, daughter of Chancellor Krzysztof Szydłowiecki. After his father's death, as a result of his stay in Rome (he also visited Milan, Padua and Mantua), he converted in 1567 from Calvinism to Catholicism. Suffering from syphilis, in February 1580 he again went to Italy for treatment, near Padua and Lucca, and spent the turn of 1580-1581 in Venice, with an attempt to make an expedition to the Holy Land. He vowed that if his health would improve, he would go on a pilgrimage. Just few months after return from the Holy Land, on November 24, 1584, he married Princess Elżbieta Eufemia Wiśniowiecka (1569-1596), who was only 15 at the time and was 20 years younger than himself, and he had 6 sons and 3 daughters with her. In 1593, he and his wife left for the last time in his life the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, for treatment in a health resort in Abano Terme near Padua. Nicolaus Christopher died on February 28, 1616 in Niasvizh. During his lifetime Radziwill founded himself a tombstone in the Jesuit Church in Nesvizh - mentioned in the inscription on the pedestal, as well as in the sermon given by the Jesuit Marcin Widziewicz during his funeral. The co-founder was the wife of Nicolaus Christopher, therefore it should be dated to 1588-1596. The general conception of the tomb was probably modelled after the tomb of Pope Sixtus V in Rome, executed between 1585-1591 by Domenico Fontana and the tomb of Queen Bona Sforza in Bari, created between 1589-1593. Nicolaus Christopher saw the coffin with the body of the Queen in Bari in March 1584 and not without significance were his contacts with Queen Anna Jagiellon, the founder of the tombstone in Bari. The center of his tombstone is filled with a plate with a relief image of the prince in profile kneeling in prayer, with his head raised and in pilgrim's attire. It is crowned with a triangular pediment with the Order of the Knight of the Holy Sepulcher. The tomb was designed by a Jesuit architect Giovanni Maria Bernardoni (d. 1605) and created by an anonymous Italian sculptor active in Lesser Poland, possibly from the royal court. Szymon Starowolski (Starovolscius) in the book "A description of Poland or the state of the Kingdom of Poland" (Polonia sive status Regni Poloniae descriptio) issued in 1632, describing the investments made in his ancestral seat and its immediate vicinity by Nicolaus Christopher "the Orphan" (founding numerous monasteries, hospitals, the Jesuit college in Nesvizh, the palace and the town hall, as well as the reconstruction of the castle in nearby Mir, the arrangement of gardens, orchards and fish ponds, as well as the marking of roads along which there were moats and rows of fruit trees), ended with the statement that the voivode "arranged Italy for us in the middle of Sarmatia" (after "W podróży po Europie" by Wojciech Tygielski, Anna Kalinowska, p. 471). The painting by Leandro Bassano or workshop from the late 16th century in the Lithuanian National Art Museum in Vilnius (oil on canvas, 110 x 177 cm, inventory number LNDM T 3996), shows the scene of Entombment of Christ with a kneeling donor in the right corner, whose pose is identical with the pose of Nicolaus Christopher in his tombstone. Before 1941, the painting was owned by the Society of Friends of Science in Vilnius, to which it was given by count Władysław Tyszkiewicz (1865-1936), the owner of the Lentvaris estate, in 1907. Similar scene of the Entombment was published on page 61 of Stanisław Grochowski's "The Jerusalem procession in the church of the glorious tomb of the Lord Jesus [...] taken from the books of the Jerusalem Peregrination or the Pilgrimage [...] of Nicolaus Christopher Radziwll, prince on Olyka and Nesvizh [...]" (Hierozolimska processia w kosciele chwalebne[g]o grobu Pana Iezusowego [...] wzięta z ksiąg Hierozolymskiey Peregrynatiiey albo Pielgrzymowania [...] Mikołaia Chrzysstopha Radziwiła na Ołyce y Nieświeżu książęcia [...]), released in Kraków in 1607. A similar style painting depicting the Entombment of Christ was photographed around 1880 by Ignacy Krieger in the Prelate's House (Prałatówka) of Saint Mary's Basilica in Kraków (National Museum in Warsaw, DI 29611 MNW). In the basilica's collections are paintings by painters working for the royal court and magnates of Poland-Lithuania, such as the German Hans Suess von Kulmbach (ca. 1480-1522) and the Flemish Jacob Mertens (d. 1609). The man bears a great resemblance to effigies of Nicolaus Christopher "the Orphan", especially to his earliest known portrait, a drawing by David Kandel in the Louvre Museum, created between 1563 and 1564 during his studies in Strasbourg. In the Chapel of Our Lady of Peace (Cappella della Madonna della Pace) at the Santi Giovanni e Paolo in Venice, there is also a horizontal composition by Leandro Bassano. The church is considered the pantheon of Venice due to the large number of Venetian doges and other important figures buried there since its founding. The chapel was built between 1498 and 1503 to house the Byzantine icon of the Madonna, brought to Venice in 1349. The ceiling stuccoes are the work of Ottaviano Ridolfi and the majority of the paintings were done by artists working for King Sigismund III Vasa - Palma il Giovane painted four medallions on the ceiling representing the virtues of Saint Hyacinth of Poland (San Giacinto Odrovaz), Antonio Vassilacchi, known as Aliense, created a large Flagellation of Christ, on the right and Leandro the large canvas with Saint Hyacinth walking on the water of the Dnieper River (oil on canvas, 230 x 462 cm), on the left. This painting is dated around 1606-1610 and depicts the scene "Saint Hyacinth at the coming of the Tartars walks on the water of the River Dnieper bearing to safety the Holy Sacrament and the image of Our Lady". Leandro created other paintings for this temple, such as "Pope Honorius III approving the rule of Saint Dominic in 1216" in which the 13th century scene is transported to early 17th century Rome with many contemporary portraits, the pope in pontifical robes, the cardinals, the pope's Swiss Guards in typical robes with ruffs. The scene of 13th century Ruthenia is also brought back to the 17th century and the majority of the characters wear Italian costumes. Interestingly, in 1606 Tatar raids began in January. The steppe warlord Khan Temir (d. 1637) led 10,000 men to attack Podolia and was defeated by field hetman Stanisław Żółkiewski at the Battle of Udycz (January 28, 1606). "Christopher, Knight of Christ at the Sepulchre" (Christophorus Eques Christi dni Sepulchro) (257) is mentioned among the paintings from the collection of Princess Louise Charlotte Radziwill (1667-1695), inventoried in 1671 (after "Inwentarz galerii obrazów Radziwiłłów z XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska).
Entombment of Christ with the portrait of Prince Nicolaus Christopher Radziwill "the Orphan" (1549-1616) as donor by Leandro Bassano or workshop, before 1616, Lithuanian National Museum of Art in Vilnius.
Portraits of Infanta Anna Vasa by Lavinia Fontana
Sigismund III's sister, Anna Vasa (1568-1625), was passionate about botany. In 1604 she received from her brother the office of starost of Brodnica, and in 1611 of Golub in Pomerania and settled in her estates. She created a real cultural center in Brodnica and Golub and gathered around her people of different backgrounds. Anna financed the printing of Szymon Syreniusz's Herbarium (Zielnik Herbarzem z ięzyka Łacinskiego zowią), published in Kraków in 1613, and she founded a large botanical garden in Golub, where she cultivated medicinal plants and rare herbs, including tobacco.
In Brodnica, the Lutheran princess expanded and reconstructed the interiors of the so-called Palace of Anna Vasa. She also laid out a garden around the palace. Plan of Brodnica in the Military Archives of Sweden (Krigsarkivet) in Stockholm, made for military needs by the Swedes in 1628, just after the death of the princess, shows two gardens in the castle area. The Renaissance palace was built before 1564 by Rafał Działyński, starost of Brodnica, after the fire of the Teutonic castle in 1550 and rebuilt after 1604. The architect was most likely an Italian active at the royal court in Warsaw, possibly Paolo del Corte or Giacomo Rodondo, who were working at the time on the reconstruction of the Royal Castle. For all needs the Princess referred to Warsaw, as she considered herself abandoned in Polish Prussia. From the capital, she brought appropriate dresses, fabrics, beer, wine, mulberry juice, and even paper (after "Listy Anny Wazy (1568–1625)" by Karol Łopatecki, Janusz Dąbrowski, Wojciech Krawczuk, Wojciech Walczak, p. 20, 26, 38, 59, 157-158). From around 1615, Anna also owned a manor in Warsaw, not far from the Royal Castle. It is probably the old house in the garden mentioned in the document from 1622 near the summer residence of Queen Constance. She also resided in a Teutonic castle in Osiek by Lake Kałębie, between Grudziądź and Pelplin, which was transformed into a fine Renaissance residence by starost Adam Walewski in 1565 (demolished in 1772 by the Prussian administration). The princess had a particular fondness for music, dance and ballet. The letter of Nuncio Claudio Rangoni to Cardinal Pietro Aldobrandini (Kraków, July 18, 1604), describes the performance of the wife of Count Cristoforo Sessi signore di Riolo, a lady "excellent in singing and playing the viola", "in the room of the princess [Anna Vasa], also heard by the king [Sigismund III], remaining in a place where he could not be seen" (quel conte Christofaro di Ruolo è partito di ritorno a Praga dopo l'esser stato alcuni giorni qui, ove la moglie sua ha cantato una volta in camera della principessa, sentita anco dal re, ch'era in luogo onde non poteva esser veduto). In 1619 she helped the daughter of a court musician Wincenty Lilius (Vincenzo Gigli) to enter a convent in Braniewo (letter from Warsaw of November 17) and in 1624 she interceded with Urszula Meyerin to ask the king for an annual salary or the post of mayor for another Italian musician Zygmunt Petart (Sigismondo Patard) (letter from Brodnica of October 1). She enjoyed arranging weddings for her court ladies. In 1605, during the celebrations related to the wedding of Sigismund III in Kraków she organized an expensive "Masked Ball of the Ladies". Anna and her court ladies asked first the king, then the archduke, the prince, "and other gentlemen and courtiers, who also had to jump like them". They were especially amused by the gentlemen who weren't good dancers "even though they had been to Italy". A few days earlier, on December 13, 1605, a ballet had taken place in the presence of the whole court in a special dance hall in honor of the new Queen Constance. The masked dancers wore male and female Spanish costumes, there was also an Italian Commedia dell'arte (Pantaleonów włoskich, którzy długo po włosku z sobą się swarzyli), as well as Spanish, Italian and Polish dances. Masked aristocrats played both male and female roles (after "Balety na królewskich godach 1605 roku" by Jacek Żukowski). The masks were probably imported from Venice, because for example in 1609 in Kraków, Wincenty Zygante (Vincenzo Ziganti) together with the second elder of the painters' guild estimated the possessions of Adam Niestachowski (or Romanowski), namely several dozen Venetian masks, with beards, mustaches, trimmed beards, of Black people, old women, young girls, married women, etc. The ballet prepared for the birth of Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa on August 7, 1619 was equally splendid. Anna led "dances with a stomp" performed by noble women, and her nephew, Prince Ladislaus Sigismund, led young men dressed as Turks. The collection of the Museum of Warsaw includes a perfectly preserved outfit of Adam Parzniewski (1565-1614), burgrave of Kraków Castle and court marshal of Princess Anna Vasa, found before 1952 in the crypt of Warsaw Cathedral. It is an outfit made of materials of Italian origin, probably sewn in Warsaw and consists of a cloak, short puffy trousers and an Italian velvet caftan (velluto ceselato), originally purple, called pavonazzo in Italian (after "Marmur dziejowy ...", edited by Ewa Chojecka, p. 232), inspired by Spanish fashion. According to Gabriel Joannica, the publisher and author of the introduction to the herbarium by Szymon Syreniusz, Anna had "the ability to speak languages, first our Polish, as if native, then others, foreign: German, Italian, French, and partly learned Latin". She also spoke her native Swedish well. Her closest confidant at the court in Warsaw was the "minister in a skirt" and "Jesuit's bigotry" Urszula Meyerin (Ursula Meierin), king's mistress and a devout Catholic. She corresponded frequently with Jung frau Ursull, calling her Mein Liebt Vrsul (My Dear Ursul) in German or mosci Pano Vrsolo (Lady Ursola, close to Italian Orsola) in Polish in her letters. The majority of her letters are now kept in Stockholm (Svenska Riksarkivet), taken during the Deluge (1655-1660). In the oldest known letter from the princess to Urszula, dated in Warsaw on August 16, 1599, she asks her to buy hats for the princess and her ladies. To emphasize her hereditary rights to the Swedish crown, the princess, like her aunt Anna Jagiellon before the royal elections in Poland-Lithuania in the 1570s, used the Spanish title of Infanta (Serenissima Infant. Sueciae Annae, Infanti Sueciae Anna, Serenissimae Infantis Sueciae Anne). The inscription on the tin sarcophagus funded by Sigismund III Vasa, published in Monumenta Sarmatarum ... by Szymon Starowolski in 1655, calls her "The Most Serene Princess, D. [Domina/Donna/Doña] Anna Infanta of Sweden" (Serenissima Princeps, D. Anna Infans Sueciæ). Her letters in Polish were usually signed "Anna, Princess of Sweden" (Anna królewna szwedzka) or simply Anna, in letters in German to Urszula Meyerin. The king's favorite Urszula, close to the two wives of Sigismund III, corresponded with their mother Maria Anna of Bavaria (1551-1608), Archduchess of Austria, and she was probably an intermediary in certain artistic commissions from Anna Vasa. The Queen's official physician was the Venetian Giovanni Battista Gemma, who died in Kraków in 1608, sent by her mother to the court in Warsaw. As at the court of the Archduchess (her portraits by the Flemish painter Cornelis Vermeyen, the Italian Giovanni Pietro de Pomis or the Spanish painters) and at the royal court in Warsaw, in Brodnica also Spanish fashion and Flemish and Italian art must have been very popular. Very little is known about the artistic patronage of the Princess-Infanta. Nothing has been preserved in Brodnica or Golub (at least confirmed). The invaders, mainly Swedes, probably looted or destroyed everything. In a letter dated October 21, 1605 from Kraków (Polish Library in Paris, rkps 56/36, in Polish) to Hetman Jan Karol Chodkiewicz (died 1621), she expresses her great joy at the news of the victory of the Commonwealth's army led by Chodkiewicz in the Battle of Kircholm in 1605, during which he inflicted a major defeat on a Swedish army three times larger than his own. The Swedes invaded the Commonwealth in mid-1605, shortly before the marriage of Anna's brother to Constance of Austria (December 11, 1605). Poland-Lithuania was at that time one of the richest countries in Europe, and the Commonwealth could afford a much more powerful and larger army than that of Sweden. However, military spending was limited by Parliament (Sejm) because magnates in the Senate and nobles were afraid that such a powerful army will be used against them to strengthen the power of the king and turn the country into absolute monarchy (compare "Mecenat kulturalny i dwór Stanisława Lubomirskiego ..." by Józef Długosz, p. 33). "Anna, by the grace of God, [hereditary] princess of the Swedes, Goths, and Vandals, heiress of the Grand Duchy of Finland. Lord, dear to us. May God be eternally praised for such a great and significant victory, which he deigned to give against such a main and fierce enemy of the King His Highness and the nation here. [...] And since we have a special and great pleasure from this victory, so that we may have a more perfect one, we therefore urgently ask you in remembrance of this, Your Lordship, that you order an expert and conscious person, taking a painter, to paint the battle scene, formations and all actions how that battle was fought there, having learned the names, places and people, you will do a great and very grateful thing to us", writes the Infanta in the mentioned letter. The oldest and best painting depicting the battle is today in the Château de Sassenage, near Grenoble in France. It is attributed to Peter Snayers, active in Antwerp between 1612 and 1621 and later in Brussels, and probably comes from the collection of the son of Sigismund III, John II Casimir Vasa, who settled in France after his abdication in 1668. Sigismund most likely commissioned it, through his agent at the court of Archduke Albert VII in Brussels in the 1620s, and the original, possibly also by a Flemish or Italian painter, was most likely the painting commissioned by the princess in 1605. Anna died on February 6, 1625 in Brodnica, and the last moments of the Lutheran Princess-Infanta, were vividly commented on in Rome and Florence - letters of Nuncio Giovanni Battista Lancellotti to the Holy See from Warsaw, February 9 and February 18, 1625 and letter of Giovanni Battista Siri, envoy of the Medici family, February 21, 1625 from Kraków (Alii 7 stante passo ad'altra vita la Ser[enissi]ma infante ...). The first Polish monographer of Anna, Marian Dubiecki, wrote in Przegląd Powszechny in 1896 about the efforts of Sigismund III Vasa to obtain papal permission to bury his sister at the Wawel Cathedral. It is possible that through rumors of an alleged deathbed conversion of the Infanta, a devout Lutheran, the Polish court wanted to convince Rome that she should be buried with other members of the family and close to the Jagiellons. It was not until 1636 that her nephew, King Ladislaus IV Vasa, decided to bury Anna in nearby Toruń, in a Baroque mausoleum built especially for this purpose in 1626 at the Church of the Blessed Virgin Mary, then a Protestant temple. The surviving sources confirm that Anna Vasa's body dressed in an expensive dress and decorated with jewels was waiting in Brodnica, in the "vaulted room", unburied. In May 1626 King Gustavus Adolphus launched his invasion of Polish Prussia. On October 4, 1628 Brodnica capitulated, surrendered by the commander of the Polish garrison, the Frenchman La Montagne, and fell into the hands of the Sweds for over a year. Only the truce concluded on September 26, 1629 (in Stary Targ) obliged them to leave the city on October 6, so the night before, the Swedish soldiers organized a plundering. A few of them broke into the tomb of Anna Vasa, where they profaned the corpse of the Princess-Infanta, tearing off her dress and stealing jewels. The citizens of Brodnica were shocked, so the Judicial Court quickly assembled and the royal court in Warsaw was notified. The Chancellor of the Commonwealth, Jakub Zadzik, sent a sharp letter to the king of Sweden, in which, based on a written statement of the Brodnica Court, he presented shameful acts. It was answered by the Chancellor of the Kingdom of Sweden, Axel Oxenstierna, who only partially admitted that the fault lies with his compatriots, while trying to shift the responsibility onto Poles (after "Skarb Anny Wazówny ..." by Piotr Grążawski). The sarcophagus was probably put back in order because the copy of receipt for the take over of Brodnica from the Swedish army issued by Mikołaj Hannibal Stroci (a descendant of the Florentine Strozzi family), a month later (October 26/November 6, 1629), does not mention the desecration of the corpse. Anna Vasa's crypt in Toruń was opened on April 7, 1994 and the exploration confirmed all known information about robberies. No funeral equipment were found. The skeleton was fairly well preserved, however, it turned out that the right forearm was missing, perhaps as the result of the brutal behavior of the burglars during the robbery of the jewels. No trace of the Infanta's jewelry was known until a document was found in Stockholm in the 1980s describing a find in the Uppsala Cathedral in 1777. A gold bracelet was found on the floor with an engraved monogram of Anna - APS (Anna Princeps Sveciae) and the symbols of the Vasa family, now kept at the Royal Armory (Livrustkammaren) in Stockholm (after "Śmierć i problemy pochówku Anny Wazówny ..." by Alicja Saar-Kozłowska, p. 76-77). The bracelet was probably made in Gdańsk or Toruń, since very similar are depicted in portraits of patrician ladies by Anton Möller from the 1590s (National Museum in Gdańsk and National Museum of Finland), in a portrait of a lady, probably a noblewoman from the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, in the National Museum in Stockholm (Gripsholm Castle, NMGrh 426) and a similar gold bracelet was found among the jewelry of Zofia Magdalena Loka (Skrwilno Treasure in Toruń), hidden during the Deluge. The collection of jewelry of Anna Vasa was famous and estimated at 200,000 thalers. Some of these jewels she inherited from her mother Catherine Jagellon. In 1606, to repay various debts intended to modernize the starosty and her residence, she decided to sell some of her jewelry to Tsar False Dmitry I. In 2022, a portrait of a lady in a rich costume adorned with jewels and a garden in the background was sold in New York (oil on canvas, 121 x 95.5 cm, Sotheby's, May 26, 2022, lot 223). The painting comes from a private collection in Connecticut and was previously believed to represent Queen Elizabeth I of England. The face resembles some effigies of the Queen, such as the "Darnley Portrait" or the "Rainbow Portrait", but the model is dressed in Spanish costume from the late 16th or early 17th century. The Queen of England wearing a dress of her greatest enemy, it is very unlikely, so the identification has been changed to Infanta Isabella Clara Eugenia (1566-1633). The portrait is very similar to the portrait of the Spanish Infanta by Juan Pantoja de la Cruz, painted between 1598-1599 (Prado Museum in Madrid, P000717). The costume, the pose, even the landscape are very much alike. In her portrait, Isabella Clara Eugenia holds a miniature of her father Philip II of Spain, while in the described portrait the main jewel is a large gold eagle pendant set with diamonds. Although the Spanish Infanta was not a close member of the Imperial family, she could inherit such a pendant from her grandfather, Emperor Charles V, or receive it from the Austrian branch of the Habsburg family. In 1543, Charles V offered such a "diamond eagle with rubies" (orzeł dyamentowy z rubinami) to his niece Elizabeth of Austria (1526-1545) on the occasion of her marriage with Sigismund II Augustus (today in the Treasury of the Munich Residence, Sch 49). In the majority of her portraits, Isabella Clara Eugenia wears a large diamond cross and no other portrait with an eagle is known. Two important elements are missing to consider the portrait in New York as her effigy - an eagle's head, as the imperial symbol is a bicephalous bird - a gold pendant with a double-headed imperial eagle from the 1600s, most likely belonging to Constance d Austria, is in the Monastery of Jasna Góra in Częstochowa, and the protruding lip of the Habsburgs, clearly visible in her portrait by Pantoja de la Cruz. Therefore, the model is not a member of the imperial family or a Habsburg. A similar eagle pendant can be seen on several portraits of Queen Constance of Austria - by Jakob Troschel from about 1610 (Germanisches Nationalmuseum in Nuremberg, Gm 699, 7009/7277), by unknown painter from the 1610s (Museum of Zamość, 62) or by Pieter Soutman from about 1624 (Staatsgalerie Neuburg, 985). In her portrait in Nuremberg, the queen also wears a gold diadem with a heraldic Polish eagle and a Spanish dress - saya, probably a gift from Spain or sewn alla moda from a Spanish model. The Queen of Poland was also depicted in a typical Spanish dress in her portrait by an Italian painter, now in the Philadelphia Museum of Art (oil on canvas, 186.1 x 107.3 cm, 1883-137), a companion to the portrait of her younger sister Maria Maddalena of Austria, Grand Duchess of Tuscany, in the same collection (1883-136). Spanish, Italian (Venetian and Florentine), Flemish, French and Turkish fashion was at that time very popular in the Commonwealth, as confirmed by Piotr Zbylitowski in his "Reprimand of Women's Extravagant Attire" (Przygana wymyślnym strojom białogłowskim), published in Kraków in 1600. The country became very wealthy from the grain trade and such "extravagant" and rich costumes were not expensive. The next queen of Poland, Cecilia Renata of Austria, was also depicted with an eagle jewel - portrait with a tulip (Alte Pinakothek in Munich, 6781) and an engraving by Eberhard Wassenberg, and a gold brooch with a Polish eagle in the Louvre Museum (MR 418) was probably made for her. Anna Vasa was depicted with an eagle pendant in a miniature by Sofonisba Anguissola from around 1592 (Rohrau Castle). The garden behind the woman in the New York painting was made for her and a villa in the center is her residence. The layout of this garden corresponds almost perfectly to the palace of Anna Vasa in Brodnica, as depicted in the mentioned drawing in Stockholm from 1628. Assuming that the two depictions are very accurate, the differences arise from the fact that the residence has been modified over time (Anna extended the building and built a kitchen) and there is about 20 years difference between them. The painting is attributed to a Flemish painter, however, the style of this work is very characteristic and typical of a great painter Lavinia Fontana (1552-1614) and her studio/workshop. It is comparable to her self-portraits - at the spinet with a maidservant (Accademia Nazionale di San Luca in Rome and private collection), in her studio (Uffizi Gallery in Florence and private collection) from the 1570s, signed portrait of the Gozzadini family from 1584 (Pinacoteca Nazionale in Bologna) and portraits of Margherita Gonzaga (1564-1618) and her ladies and Alfonso II d'Este (1533-1597), Duke of Ferrara in the scene of the visit of the Queen of Sheba to King Solomon from 1599 (National Gallery of Ireland). Lavinia was born in Bologna in the Papal States and she and her family moved to Rome in 1604 at the invitation of Pope Clement VIII. Her father was another prominent painter in the service of the popes - Prospero Fontana (1512-1597). A miniature portrait of a couple from a private collection (oil on copper, 19 cm), attributed to the circle of Prospero, is an effigy of William V, Duke of Bavaria and his wife, Renata of Lorraine. If he or his workshop were authors, he therefore accepted orders from abroad based on study drawings or effigies by other painters, his stay in Bavaria not being confirmed in the sources. The royal court and Polish-Lithuanian magnates frequently commissioned paintings from Rome at the turn of the 16th and 17th centuries. They were delivered to the king by foreigners who stayed in Rome, such as the Jesuit Antonio Possevino (1533-1611), his envoys and courtiers, such as Cardinal Andrew Bathory (1563-1599), Stanisław Reszka (1544-1600) and Tomasz Treter (1547-1610) and others, as well as passers-by, such as Marshals Mikołaj Wolski (1553-1630) and Zygmunt Gonzaga Myszkowski (ca. 1562-1615). Paintings, whose subjects are not known, sent from Rome by Reszka in 1588 must have pleased the king, since Bernard Gołyński reported that they were far superior to the paintings sent to the king by Possevino (after "Z dziejów polskiego mecenatu ..." by Władysław Tomkiewicz, p. 23). Eustachy Wołłowicz (1572-1630), provost (praepositus) of Trakai and a referendary at the court of Sigismund III Vasa possibly owned a painting by Michelangelo (Pietà), reproduced in a 1604 print by Lucas Kilian with his coat of arms and inscription MICHAEL: ANG. / B. pinxit Romae. They also had many portraits, especially of famous Italians. In the second edition of his autobiography, published in 1608, Bologna's best known poet, Giulio Cesare Croce (1550-1609), writes poetically on his portrait made by Lavinia, which was sent to Poland: "And a short time ago I had my portrait made by Lavinia Fontana and my portrait has been taken to live in Poland" (E' poco tempo ch'io mi fei ritrare, / A Lavinia Fontana, e'l mio ritratto, / Fù portato in Polonia ad habitare, "Descrittione della vita del Croce", p. 20). Stylistically the landscape behind the woman in the New York painting resembles the works of Domenico Tintoretto, in particular the portrait of Princess Anna Vasa in the Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum (P24e2). It is possible that Lavinia received a painting by Domenico or his workshop to copy and inspired by his style. The facial features of a woman greatly resemble the Polish-Lithuanian-Swedish Infanta from the mentioned portrait by Tintoretto and the oval portrait by Sofonisba Anguissola, as well as the effigies of her brother Sigismund III by Joseph Heintz the Elder (Alte Pinakothek in Munich, 11885) and by Jakob Troschel (Royal Castle in Warsaw, ZKW 1176). In her 1584 portrait of the Gozzadini family, Lavinia "resurrected" two family members – Ginevra (d. 1581) and her father, Senator Ulisse Gozzadini (d. 1561). If she could paint the deceased as a living person, she could also paint the people living far from her studio, like Anna Vasa. The woman was also depicted in a full-length portrait currently housed in the Lázaro Galdiano Museum in Madrid (oil on canvas, 198 x 114 cm, 08470). This painting was probably acquired between 1936 and 1939 and was part of the collection assembled by José Lázaro in Paris. The model's identity has not been established, although "she must have been a person of high courtly status, judging by her attire" (Se ignora todo de la retratada, que hubo de ser persona de elevada situación cortesana, a juzgar por su traje), according to the museum's description. Due to the woman's rich costume from the early 1600s which is obviously Spanish, the painting has been attributed to the Spanish painter whose style was comparable - Rodrigo de Villandrando (1588-1622). However, not only the face and costume are similar to the New York painting, but also the style of this work. The Madrid portrait resembles the style of the mentioned portrait of the Gozzadini family, but most similar is the way in which the portrait of Raffaele Riario (d. 1592), attributed to Lavinia, was painted (sold at Dorotheum in Vienna, April 24, 2018, lot 52). Also very comparable is the portrait of a lady with a fan and a dog from the beginning of the 17th century, now kept at Lysice Castle in Czechia (oil on canvas, 85 x 65 cm, LS00081a). The details of the costume and the way the hands and face were painted are very close to Fontana's style. The face from the portrait with eagle pendant, as a template, was copied in another painting from the same period sold in 2017, also in New York (oil on canvas, 66.7 x 53.7 cm, Christie's, auction 14963, October 18, 2017, lot 572). It comes from the collection of the Hispanic Society of America in New York. This "Portrait of a lady, bust-length" is also attributed to the Flemish school, but the closest in style is again a painting by Lavinia Fontana, which is now in the National Museum in Kraków (oil on canvas, 77 x 62.3 cm, MNK XII-A-664). The portrait of Bianca Lucia Aliprandi, née Crivelli (sold at Christie's London, auction 20055, December 7, 2021, lot 29) and the mentioned painting by Fontana in the National Gallery of Ireland are also very similar. Another portrait of the same woman by the same painter is in the National Art Gallery in Lviv, Ukraine (54.5 x 42, inventory number Ж-1945). It comes from the Lubomirski collection and was donated to the Ossolineum in Lviv by Prince Henryk Ludwik Lubomirski (recorded in 1826). It was allegedly purchased in 1826 in Vienna from P. della Rovere ("Exhibition catalogue: Peter Paul Rubens - Anthony van Dyck" by Svetlana Stets, pp. 576-577), thus possibly sent to the Habsburgs or coming from the older Lubomirski collections. The painting is attributed to follower of Anthony van Dyck. The style of her dress indicates that the painting was made in the late 1580s as it resembles the Spanish-Italian dress of Margherita Gonzaga (1564-1618), Duchess of Ferrara from her portrait by Jean Bahuet (private collection) or her effigy by Jacopo Ligozzi in Lisbon (National Museum of Ancient Art, 453 Pint), painted around 1593. The mentioned painting by Lavinia Fontana in the National Museum in Kraków may have come from the royal collection, probably mentioned in the collection of King John III Sobieski in the inventory of the Wilanów Palace from 1696 (No. 77). Before 1924 it was in the collection of Antoni Strzałecki in Warsaw. The painting was made at the beginning of the 17th century because her costume and hairstyle are similar to those seen in the effigies of the so-called Bellezze di Artimino in Palazzo Pitti or in the portrait of Margherita Gonzaga (1591-1632), Duchess of Lorraine from about 1605 (Metropolitan Museum of Art, 25.110.21). According to the museum's catalog entry by Dorota Dec and other publications, this is the artist's self-portrait and she depicted herself as the biblical heroine Judith (compare "Judith" by Lawrence M. Wills, p. 140), being basically a woman who overcomes a man's violence with her cunning intelligence. What better gift for patrons from the Realm of Venus?
Portrait of Princess Anna Vasa (1568-1625) by Lavinia Fontana, ca. 1588, National Art Gallery in Lviv.
Portrait of Infanta Anna Vasa (1568-1625), starost of Brodnica, in Spanish dress with eagle pendant by Lavinia Fontana and studio, ca. 1605-1610, Private collection.
Portrait of Infanta Anna Vasa (1568-1625), starost of Brodnica, in Spanish dress by Lavinia Fontana and studio, ca. 1605-1610, Lázaro Galdiano Museum in Madrid.
Portrait of Infanta Anna Vasa (1568-1625), starost of Brodnica, bust-length by Lavinia Fontana, ca. 1605, Private collection.
Self-portrait as Judith with the head of Holophernes by Lavinia Fontana, 1600s, National Museum in Kraków.
Battle of Kircholm in 1605 by Pieter Snayers, 1620s, Château de Sassenage.
Portrait of Queen Constance of Austria by Domenico Tintoretto
At the beginning of the 17th century, as in the previous era, Polish-Lithuanian monarchs and magnates collected portraits of rulers and famous people. In 1612 Jan Ostroróg (1565-1622), voivode of Poznań requested a portrait of the Elector of Brandenburg (letter from Salomon Leuper to John Sigismund, Elector of Brandenburg, February 3, 1612) and in the same year William V, Duke of Bavaria sent a portrait of his son Albert (1584-1666) to Queen Constance of Austria, on the occasion of Albert's marriage (letter of January 4, 1612). The queen exchanged portraits with Albert in 1624. In a letter dated October 15, 1613, Alessandro Cilli reported to the Duke of Urbino that Queen Constance "keeps in her room the portraits of the most serene princes and princesses sent to her from Florence by their Highnesses" (tiene in camera sua i ritratti dei s-mi principi et principesse mandatigli da Fiorenza dalle loro Altezze s-m) (after "Das Leben am Hof ..." by Walter Leitsch, p. 370-371, 911, 2377, 2378, 2381).
Almost two years later, in 1615, through the ambassador Krzysztof Koryciński, Queen Constance also requested and received from Spain portraits of the children and husband of her sister Margaret of Austria "as natural as possible" (los mas naturales que sea possible), according to the Consejo report of January 15, 1615 (El gran desseo que la serenisima reyna su señora tenia de los retratos de VM y de su felicissima prole. Y suplica agora a VM sea servido de mandar se hagan assi el de VM como los de la reyna de Francia, del serenisimo principe nuestro señor, infantes y infantas los mas naturales que sea possible y a proporcion de sus estaturas, porque no podra llevar a la reyna su señora cosa mas cara y que tanto recreasse su vista, como la effigie y semejança de VM y de sus serenisimos hijos y a que nuestro señor le ha quitado la comodidad de ver los originales. Al consejo parece que es muy justo que se le den al dicho embaxador los retratos que pide en nombre de al reyna de Polonia). This was followed by the decision of the Royal Council, probably from April 1615, to grant "portraits of their majesties" (y los retratos de sus majestades y altezas afin que la serenisima reyna su señora reciva el gusto y consuelo que dessea tal vista). In 1620, the new portraits of the Spanish monarchs were delivered to the Polish-Lithuanian royal court, including that of Elisabeth of France (1602-1644), wife of Prince Philip of Spain, future Philip IV (1605-1665), sent through a Polish Dominican Father, according to a letter from Francesco Diotallevi (1579-1622), apostolic nuncio in Poland (1614-1621), to Cardinal Scipione Borghese (1577-1633) (E giunto qua un padre dominicano Polacco, che per molti anni si è tratenuto in Spagna al quale è stato consignato dalla majestà cattolica per presentarlo in suo nome a questa majestà il ritratto della principessa venuta di Francia, moglie del principe figliolo di SM cattolica havendo gli gia per prima mandati i ritratti di tutti gl'altri principi della casa reale, January 10, 1620). Few yers later, in 1624, Queen Constance launched a major campaign to have a proper gallery of family portraits. However, it took time because the painter working in Vienna was very busy. He probably had to make similar or identical portraits for the courts in Madrid, Brussels and Florence. Nikolaus Nusser, Chamberlain of Ferdinand II, wrote at the end of November that completion could only be expected in three months and that Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa will be able to take the pictures with him on the return journey from Italy. Through Prince Radziwill (presumably Sigismund Charles), Empress Eleonora Gonzaga (1598-1655) sent portraits of herself and the Archdukes Maximilian Ernest (1583-1616) and John Charles (1605-1619), both of whom had already died and whose portraits had to be copied in Graz. Nusser, thought that the portraits of the Emperor and Empress should be sent in the same size. "But the empress discovered that she had sent busts to the Polish court" (So hat aber die kaiserin vermelt, das sy bei dem polnischen gesandten brustbilder geschickt), wrote Nusser in June 1625, because the Polish-Lithuanian court did not want to be supplied with too many pictures. Some painters were active at the royal court, but apart from Jakob Troschel, Jan Szwankowski, Jakob Mertens, Tommaso Dolabella, Wojciech Borzymowski, who was supposedly commissioned by Sigismund III to decorate the chambers of the Warsaw castle, and in 1630 for Primate Łubieński he painted a portrait of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund in Gdańsk, and perhaps Philipp Holbein II (goldsmith, jeweller and painter), they were temporary workers or agents of foreign workshops. We only know that Archduchess Maria Anna brought the court painter Balthasar Gebhard with her to Constance's wedding in December 1605, because he had broken a rib during his stay in Kraków. Urszula Meyerin received 100 florins for the care of the patient. In the accounts from 1627 there is also a note: "200 florins given to the Polish painter at the Jasthof [Jazdów?]" (Dem polnischen mahler auf den Jasthof gegeben fl 200, Spetember 12, 1627). At that time, many objects were purchased in Italy, notably in Venice, including books. Gian Battista Gemma, a physician from Veneto, gave the king books to read, some of which were "heretical". This is why the very pious Queen Constance considered Gemma a heretic and even threatened to "throw him out of the room" (per heretico et minacciarli che lo cacciarà di camera), according to Claudio Rangoni's letter to Cardinal Scipione Borghese of November 11, 1606. When in 1606 the pope had a dispute with Venice and imposed prohibitions on the entire state (Venetian Interdict), the king did not want to speak openly against Venice and skillfully avoided making a decision. Crystal tankard with the coat of arms and monogram of Sigismund III Vasa and Constance of Austria (SCA - Sigmundus et Constantia Austriacae), floral motives and a handle in the form of a nude woman, attributed to Miseroni workshop in Milan (Bavarian National Museum, R 2157), is one of the few preserved objects commissioned by the king and his wife in Italy in the early 17th century. At the Prado Museum in Madrid, deposited at the Spanish Embassy in Bern, there is a portrait described as "Queen Eleanor of Austria" (La reina Leonor de Austria) from the early 17th century (oil on canvas, 108 x 88 cm, inventory number P001265). It is said to depict Eleanor of Austria (1498-1558), who subsequently became queen of Portugal (1518-1521) and France (1530-1547). Her Spanish dress and her large ruff indicate that this is rather a person living in the first quarter of the 17th century and not the 16th century. According to an article by Gloria Martínez Leiva ("El incendio de la Embajada española en Lisboa de 1975", January 16, 2018), it is an effigy of Anna of Austria (1573-1598), Queen of Poland from from a series created by Bartolomé González (Retrato de Ana de Habsburgo), but the woman has no resemblance to the effigies of the queen. The attribution of the painting to Juan Bautista Martínez del Mazo (inventory of Buen Retiro, 1794, no. 897) and Bartolomé González is now rejected and the painting is qualified as an anonymous work. The woman wears a tira similar to that visible on several effigies of Margaret of Austria, Queen of Spain (e.g. portrait in the Hungarian National Gallery in Budapest with inscription MARGARETA. AVS/TRIA. HISP. REGINA.) or Magdalene of Bavaria (1587-1628), Countess Palatine of Neuburg and Duchess of Jülich-Berg by Peter Candid (Bavarian State Painting Collections, 2471, 3217), so she is a reigning queen consort or duchess. The model therefore could not have been Margaret's younger sister, Archduchess Eleanor of Austria (1582-1620), who, after unsuccessful attempts at marriage on October 3, 1607, took the veil and became a nun in Hall in Tirol. A similar lace ruff and high hairstyle are seen in a portrait described as depicting a lady-in-waiting of Queen Constance of Austria, purchased in 1935 by the National Museum in Warsaw from Z. Iłowicki (deposited at the Wilanów Palace in Warsaw, oil on canvas, 82 x 65 cm, 120735), generally dated after 1605 (after "Portrety osobistości polskich" by Stefan Kozakiewicz, Andrzej Ryszkiewicz, p. 251). Comparison with several portraits from a series entitled "Beauties of Artimino" (Bellezze di Artimino), indicates that the two women are dressed according to southern Italian fashion, as the closest are the portraits of Roman and Neapolitan ladies - Countess of Castro (Uffizi, Inv. 1890, 2265), Emilia Spinelli (Palazzo Davanzati, Inv. 1890, 2262), Belluccia Carafa, Duchess of Cerce (Uffizi, Inv. 1890, 2263) and Porzia de' Rossi (Uffizi, Inv. 1890, 2266). The series included portraits of Florentine, Roman and Neapolitan ladies linked to the court of Ferdinand I de' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany. In the 1609 inventory of the Villa Medici "La Ferdinanda" in Artimino, drawn up on Ferdinand's death, there were sixty-five effigies of this type, forty-two Florentine, seventeen Roman and six Neapolitan. The effigies of Roman and Neapolitan ladies stand out from the series, not only by their hairstyle, but also by the style of the paintings which were probably painted in Rome between 1602 and 1608 and are attributed to the workshop of Jacopo Ligozzi, perhaps painted by Achille Gianré. The model bears a great resemblance to the effigies of Constance of Austria, notably the portrait by Frans Pourbus the Younger (Kunsthistorisches Museum, GG 3306), Joseph Heintz the Elder (Kunsthistorisches Museum, GG 9452), and by an unknown painter (Wawel Castle, 1783). A portrait painted in a very similar style and from the same period is also in the Prado Museum (oil on canvas, 112 x 92 cm, P002405). According to the museum catalog, it is an effigy of Eleanor de Medici (1567-1611), Duchess of Mantua, however, the model closely resembles the effigies of Margherita Gonzaga (1564-1618), Duchess of Ferrara, Modena and Reggio in mourning, as reproduced by Maike Vogt-Lüerssen (kleio.org, Die Gonzaga). The painting is considered a copy of Rubens, but in the late 18th century it was described as a work by Jacopo Tintoretto (Otra de Tintoreto, retrato de una madama Veneciana, inventory of Buen Retiro, 1794, no. 40). Margherita's portrait as a widow at the Palazzo Franchini in Verona (identified as the portrait of Eleonora Gonzaga by circle of Frans Pourbus the Younger), being a copy of the portrait attributed to circle of Jacopo Ligozzi (Castelvecchio Museum in Verona), is very Venetian in style and could be the work of Alessandro Maganza. The style of both descibed paintngs in Prado, resembles closely the paintings attributed to Jacopo's son Domenico Tintoretto - portrait of a man with a letter and a crucifix (Museo Soumaya in Mexico City) and portrait of a lady (Museum Wiesbaden). The style in which the hands were painted is particularly similar. The details of costume of Constance's Spanish satin saya can also be compared to early 17th century doublet of "a man wearing an elaborately embroidered costume" (Private collection). Although the Queen of Poland was most often depicted in Spanish saya, in two paintings created by her husband, she wears a more comfortable outfit - Allegory of Faith of 1616 (Nationalmuseum Stockholm, NMH 436/1891) and a miniature from the Royal Casket (Czartoryski Museum, DMK Cz 196/I), offered by the king to the court preacher Piotr Skarga (Hanc imaginem, Sigismvndvs Rex. Pol. manv propia pin/xit eamq. donavit Cancionatori svo R. Petro Scargae), according to the inscription on the reverse. Constance also wore an eastern-style jeweled headdress and similar to the Russian kokoshnik, which carried the idea of fertility and was popular in different Slavic countries. She was represented with such a headdress in her portrait from the collection of the Marquis of Leganés in Madrid (oil on canvas, 219 x 140 cm, inscription: La Reina de Polonia, Archivo Moreno, 19513 B), sold in May 2009 with attribution to the Flemish or Genoese school. The possible author could be Sofonisba Anguissola, who lived in Genoa until 1620.
Portrait of Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631) in Spanish/Italian costume by Domenico Tintoretto, ca. 1605-1610, Prado Museum in Madrid.
Portrait of Margherita Gonzaga (1564-1618), Duchess of Ferrara, Modena and Reggio in mourning by Domenico Tintoretto, ca. 1605-1610, Prado Museum in Madrid.
Portrait of Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631) in Spanish dress by Flemish or Genoese school, possibly Sofonisba Anguissola, 1610s, Private collection.
Portraits of Constance of Austria and Hortensia del Prado by Gortzius Geldorp
"Long live King Sigismund the Third, under his auspices Everything that happened, the Lord restored from the foundations" (Vivat Sigismundus Rex Tertius, auspicio ejus Omne quod accepit restituit Dominus a fundamentis), is a fragment of a Latin inscription from 1610 on a non-preserved stone slab, which was before World War II on the façade of the Giza House in Warsaw (Old Town Market Square, number 6). It commemorates the reconstruction of the house after great fire of Warsaw in 1607, during which "many expensive Persian and Turkish goods were burned, 22 houses in the Market Square alone", according to Father Franciszek Kurowski. The Gothic house built between 1448-1455 was reconstructed for a merchant Jan Giza, who also added the following inscription "Bravery and human reason can do a lot, But money will always be the shortest way" (Multa vi et ingenio, sed citius pecunia Comparantur omnia). From 1655, this house was owned by Marcin Martens, a carpenter, possibly a relative of a Dutchman Willem Martens (Mertens, Mertensone, Martinson), who purchased stone and marbles for Sigismund III Vasa between 1618-1619.
Huge profits from grain trade, which was exported from Gdańsk the king and nobles spend on luxury goods commissioned or purchased in different parts of Europe (the Royal Granary in Gdańsk, designed by Abraham van den Blocke, was built by Jan Strakowski in about 1621). Descriptions in the registers of movable property belonging to the nobility often provide information about the place of origin of works of art. They show that they came mostly from abroad (for example, silverware mainly from Augsburg, textiles from France, Italy or the East, furniture and clocks from France) (after "Kolekcjonerstwo w Polsce ..." by Andrzej Rottermund, p. 40). Sigismund III conducted extensive diplomatic correspondence with the rulers of the Southern Netherlands on artistic matters, e.g. concerning stone elements forged on the Meuse River on the basis of patterns delivered directly from Poland. "Archives in Brussels, The Hague and Gdańsk reveal the names of Dutch stonemasons and commercial agents working for Sigismund III. In this context, one can even talk about a well-organized and efficiently functioning trade network between both regions of Europe" (after "Dostawy mozańskiego kamienia budowlanego ..." by Ryszard Szmydki). The king's second wife, Constance, with due care for financial matters, managed the royal court and the lands of her dowry. In 1623 she visited Gdańsk for the first time and a year later for 600,000 zlotys, she acquired Żywiec and made this possession the private property of the House of Vasa, because the monarchs in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth were generally prohibited from acquiring land. She diligently engaged in charity, patronized poets and painters and composer Asprilio Pacelli taught her to sing. Constance was also notoriously famous for her great Catholic piety, intolerance towards other religions and favor towards German speakers, she also attached great importance to strict etiquette, following the Spanish-Habsburg model (after "Dynastia Wazów w Polsce" by Stefania Ochmann-Staniszewska, p. 128). As an example, in Jastrowie, which was part of her dower, the queen asked her husband to confiscate the temple from heretics and in Żywiec, she issued a privilage (on March 5, 1626 in Warsaw), forbidding Jews to trade and live in her city. The queen also arranged marriages of her German ladies-in-waiting with Catholic nobles, thus, representatives of the nobility who professed Protestantism and Orthodoxy and wanting to make a career at court had to convert to Catholicism. She showed great care in her effigies and refused to give her portrait to Marshal Zygmunt Myszkowski, citing the lack of such a custom. Nor did she want to present a similar artifact to an excommunicated Franciscan who begged for such a substitute for an audience (after "Prawna ochrona królewskich wizerunków" by Jacek Żukowski). All this contributed to her great unpopularity in multireligious and multicultural country. Among her artistic agents was Augsburg goldsmith and merchant Simon Peyerle, who took care of sending items inherited by Urszula Meyerin from her mother from Munich to Warsaw as well as large painting inherited by Queen Constance, after the death of her uncle, the Duke of Bavaria (after "Świat ze srebra ..." by Agnieszka Fryz-Więcek, p. 32). Through him, she acquired large amounts of jewelry. It is worth noting that at that time paintings were almost at the very end of the hierarchy, listed among household tools and kitchen utensils and after jewels, parade weapons, silver vessels, decorative fabrics, which were considered the most valuable (after "Kolekcjonerstwo w Polsce ..." by Andrzej Rottermund, p. 40). A small cabinet painting with the Allegory of merchant justice from the first quarter of the 17th century in the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on panel, 37.7 x 28, M.Ob.181 MNW), comes from the collection of Piotr Fiorentini (1791-1858) in Warsaw. The female figure with scales and a sword, a commonly accepted personification of Justice, sits among objects related to trade (weights, barrels, packaged goods, a large scale in the background). The woman has a little crown on her head and her face features with protruding lower lip (Habsburg jaw) resemble other effigies of Constance of Austria. The style of the painting refers strongly to that of Gortzius Geldorp. Another painting very much in the style of Geldorp from the Fiorentini collection in the same museum is the portrait of a young lady, aged 21, dated '1590' (oil on panel, 45.2 x 34.4 cm, M.Ob.196 MNW). Her face and costume resemble greatly that of Hortensia del Prado (d. 1627) from her two portraits by Geldorp in the Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, one dated '1596' (SK-A-2072) and the other '1599' (SK-A-2081). Hortensia, a noblewoman of Spanish descent as her surname indicates, was first married to the merchant Jean Fourmenois and after his death she married Peter Courten in Cologne. The couple settled in Middelburg in the south-western Netherlands, where they lived in Het Grote Huis in Lange Noordstraat, which Courten had commissioned and Hortensia had a beautiful garden with fruit trees "from all foreign lands", plants "from every foreign shore", described by poet Jacob Cats. Portrait of a man by Gortzius Geldorp from the collection of Jan Popławski, identified as depicting a noble Jacques du Mont, shows him in a large ruff from the first quarter of the 17th century (National Museum in Warsaw, inventory number M.Ob.2415 MNW, earlier 35817). It is possible that both portraits found their way to the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth shortly after being painted as gifts for contractors or friends.
Portrait of Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631) as personification of Justice by Gortzius Geldorp or follower, 1605-1625, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Hortensia del Prado (1569-1627), aged 21 by Gortzius Geldorp or workshop, 1590, National Museum in Warsaw.
Miniature portrait of Rafał Leszczyński by workshop of Frans Pourbus the Younger
Rafał Leszczyński, great-grandfather of King Stanisław Leszczyński (Stanislas Leczinski), was born in October 1579 as the only son of Andrzej Leszczyński (d. 1606), voivode of Brześć Kujawski and Anna Firlej, a daughter of Andrzej Firlej (d. 1585), castellan of Lublin. He had three half-brothers: Jan, Grand Chancellor of the Crown, Wacław, the Primate of Poland, and Przecław, voivode of Tartu.
He studied at the school of the Czech Brethren in Koźminek, then he was educated in Silesia (Głogów), Heidelberg (1594), Basel (1595), Strasbourg (1596-1598) and Geneva (1599). He visited England, Scotland, the Netherlands and Italy, where in Padua in 1601 he was a student of the famous Italian physicist, astronomer and mathematician Galileo Galilei. He began his public activity as an envoy to the Sejm from the Sandomierz Voivodeship in 1605. In 1609, he became the marshal of the Central Tribunal, in 1612 - castellan of Wiślica and in 1618 - castellan of Kalisz. As one of the leaders of the Polish Protestants, he was in opposition to the pro-Habsburg policy of King Sigismund III Vasa. He was also called the "Pope of the Polish Calvinists". After return to Poland (1603), he maintained contacts with foreign scientists. He was interested in military and cartography. He commissioned a map of the south-eastern borderlands of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, unfortunately, despite the help of the geodesist and cartographer Maciej Głoskowski, the work was not completed. In addition to Latin, he spoke French, German, and Italian fluently. He wrote poems, like a paraphrase of Guillaume du Bartas's poem "Judith", published by Andrzej Piotrkowczyk in Baranów in 1620. In his beautiful Renaissance castle in Baranów, built by Santi Gucci, he kept a large library, which, according to an inventory from 1627, had about 1,700 volumes. A miniature portrait from Leon Piniński's collection, today in the Lviv National Art Gallery (inventory number Ж-50), shows a man in a fashionable Italian/French costume. It was painted on copper and according to inscription in Latin the man was 28 years old in 1607 ([...] SVAE 28. ANNO DOMINI 1607.), exacly as Rafał Leszczyński. The style of this miniature resemble greatly a miniature portrait of an unknown man from about 1600 in the Victoria and Albert Museum, also painted on copper, and attributed to a Flemish painter (inventory number P.28-1942) and miniature portrait of an unknown man in the Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, created in 1614 (Aº 1614), painted on copper and attributed to a Dutch painter (inventory number SK-A-2104). Portrait of the sculptor Pierre de Francqueville (Pietro Francavilla, 1548-1615) by workshop of Frans Pourbus the Younger in private collection, created between 1609-1615 (after original in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence, inventory number 746 / 1890), represent similar style of painting and costume. Such collar is also visible in a portrait of an unknown man in the Wilanów Palace in Warsaw, created in about 1600 and attributed to Agostino Carracci (inventory number Wil.1627). Major Flemish portrait and miniature painter working in northeast Italy at the beginning of the 17th century was Frans Pourbus the Younger (1569-1622), who from October 1600 was a court painter of Duke Vincenzo Gonzaga in Mantua. He also travelled to Innsbruck (1603 and 1608), Turin (1605 and 1608), Paris (1606) and Naples (1607), and in 1609 Queen Marie de' Medici called him to Paris as court painter. Frans and his workshop also took orders from abroad, not seeing the actual model. Several portraits of Philip III, King of Spain and his wife Margaret of Austria are attributed to him or his workshop (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, The Phoebus Foundation). His visits to Prague and Graz are not confirmed, however a portrait of Emperor Rudolf II (bust-length, wearing a breastplate, private collection) and a portrait of Archduchess Constance of Austria (1588-1631), future Queen of Poland, and her sisters (Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna) are all attributed to him. Around 1604 Hans von Aachen and the second court painter in Prague, Joseph Heintz, also painted their portraits in direct rivalry with Pourbus. Most likely on the occasion of his marriage to Margaret of Savoy in Turin in 1608, Pourbus or his workshop created a miniature portrait of Francesco Gonzaga, the eldest son of Duke Vincenzo I (sold as a "Portrait of a mustachioed young man" by Italian school at Gallery Bassenge in Berlin, Auction 113, lot 6003). In 1609 a painter from the circle of Hans von Aachen created a portrait of a gentleman, aged 40 (inscribed and dated A 1609 A 40., upper right), painting a miniature (private collection). The man was the same age as Pourbus when he moved to Paris in 1609. In 1607 the second son of Rafał Leszczyński was born, named Rafał after his father. On this occasion, Leszczyński, who just inherited the Baranów estate from his father, could commission a series of effigies of himself and his family in Italy. It is also possible that a painter from the workshop of Frans Pourbus in Mantua was at that time in Poland. The man from the described miniature resemble the effigies of Rafał Leszczyński's stepbrothers Jan (1603-1678) and Wacław Leszczyński (1605-1666).
Miniature portrait of Rafał Leszczyński (1579-1636) aged 28 by workshop of Frans Pourbus the Younger, 1607, Lviv National Art Gallery.
Miniature portrait of Francesco Gonzaga (1586-1612) by workshop of Frans Pourbus the Younger, ca. 1608, Private collection.
Portrait of Frans Pourbus the Younger (1569-1622) aged 40, painting a miniature by circle of Hans von Aachen, 1609, Private collection.
Portrait of Adam Wenceslaus, Duke of Cieszyn by Bartholomeus Strobel or circle
Another painting created by Prague school of painting of Joseph Heintz the Elder and Hans von Aachen is a small oval portrait of a man in a gorget. The man also wears a white silk doublet, a military tunic embroidered with gold and a wired reticella lace collar. The painting comes from a private collection in Warsaw and was sold in 2005 (Agra-Art SA, 11 December, Nr 7831). The style of the painting is close to Bartholomeus Strobel, a Mannerist-Baroque painter from Silesia, born in Wrocław, who worked in Prague and in Vienna from about 1608. In 1611 he returns to Wrocław to help his father with work in the Augustinian church and in 1619, thanks to the support of King Sigismund III Vasa, he obtained the status of a court painter (servitor) of Emperor Matthias.
This portrait can be compared with signed works by Strobel, portrait of Władysław Dominik Zasławski-Ostrogski from 1635 in the Wilanów Palace in Warsaw (signed and dated: B. Strobell 1635) and the Crucifixion in the Church of St. James in Toruń (signed and dated: B. Strobel 1634). According to inscription in Latin (AETATIS SVAE 37 / ANNO 1611), the man was 37 years old in 1611, exaclty as Adam Wenceslaus (1574-1617), Duke of Cieszyn when he was appointed supreme commander of the Silesian troops by the new King of Bohemia Matthias, Emperor from 1612. Counting on imperial favors Adam Wenceslaus, raised in Protestantism, converted to Catholicism and expelled the pastor Tymoteusz Lowczany from Cieszyn on February 23, 1611. He accompanied King Matthias at the ceremonial entry to Wrocław with a retinue of almost three hundred horses. The portrait is similar to the effigy of Duke Adam Wenceslaus in the Museum of Cieszyn Silesia, attributed to Piotr Brygierski (ca. 1630-1718). The costume (gorget, silk doublet, military tunic and collar) and facial features are very much alike.
Portrait of Adam Wenceslaus (1574-1617), Duke of Cieszyn, aged 37 by Bartholomeus Strobel or circle, 1611, Private collection.
Portrait of Sigismund Charles Radziwill by Gortzius Geldorp
In 1616, Sigismund Charles Radziwill (1591-1642), son of Nicolaus Christopher Radziwill "the Orphan" (1549-1616) and Elżbieta Eufemia Wiśniowiecka (1569-1596) arrived at the royal court in Warsaw and obtained, in 1617, the titular dignity of Carver of the court of Queen Constance of Austria.
He studied at the Jesuit College in Nesvizh, and then in Bologna. In 1612, he joined the Order of the Knights of Malta (Knights Hospitaller) and fought with the Turks in the Mediterranean. After returning to Poland in 1614, his father founded him a Maltese commandery in Lithuania. At the beginning of 1618, summoned by the Grand Master, he went to Malta. In January 1619, he was in Vienna where a great congregation of Knights Hospitaller was held. He was appointed by the Grand Master general commissioner, together with Charles II Gonzaga (1609-1631), Duke of Nevers. "Having received a license from His Highness the Emperor ... tomorrow, God willing, I am leaving", he wrote in a letter dated January 15, 1619 from Vienna to his brother John George Radziwill (1588-1625). In February 1619 he was in Venice, and he reported again to his brother: "I found his lordship Alexander, our brother, in good health in Venice and I hope that Our Lord will brought him quickly back and your Majesty will see him in our country". After return to the Commonwealth in 1621 he participated in the battle of Khotyn and in 1622 he commanded the unit of the Polish-Lithuanian light cavalry (Lisowczyks) in the Imperial army. He died on November 5, 1642 in Assisi in Italy. Before the discovery of a portrait of a man in black costume dated 1619 and signed by Gortzius Geldorp with his monogram 'GG.F.', it was generally believed that he died in 1616 in Cologne. A copy of Titian's Violante by his hand, sold in 2016 in Vienna (Dorotheum, lot 122, monogrammed upper left: 'GG.F.'), indicate that he was in Venice and in Vienna. According to inscription in Latin in upper right corner of mentioned portrait of a man in black costume the sitter was aged 28 in 1619 (AETATIS. SVAE. 28. / .1619.) exactly as Sigismund Charles Radziwill when he was in Venice and in Vienna. The costume of a man and his facial features bear a startling resemblance to effigy of Sigismund Charles Radziwill in the State Hermitage Museum (ОР-45868), created after original from about 1616. His Spanish style costume, typical for the Imperial court in Vienna, is almost identical to that visible in the portrait of Antonio Barberini, Grand Prior of Rome of the Order of Malta, created in 1625 by Ottavio Leoni. Similar outfits are also visible in portraits by Bernardo Strozzi, like in the likeness of Giovanni Battista Mora the Elder, nobleman of Vicenza near Venice, in the Walters Art Museum and in the portrait of Mikołaj Wolski (1553-1630) by Venanzio di Subiaco in the Camaldolese Monastery in Bielany, created in about 1624.
Portrait of Sigismund Charles Radziwill (1591-1642) aged 28 by Gortzius Geldorp, 1619, Private collection.
Portrait of Łukasz Żółkiewski by Johann Philipp Kreuzfelder
At the end of the 16th century, Flemish/Dutch art was the dominant model for Nuremberg portrait painters. Under the influence of Nicolas Neufchatel and Nicolas Juvenel, two prominent Flemish/Dutch artists settled in the imperial city, the highly developed Antwerp portraiture found its way into local portraiture (after catalogue entry by Judith Hentschel for 1626 portrait of a woman). The pupils of Juvenel were among the most successful and sought-after portrait painters in the city and outside.
Jakob Troschel (1583-1624) from Nuremberg, a court painter of King Sigismund III Vasa, was trained in Juvenel's close circle - according to Johann Gabriel Doppelmayr's "Historische Nachricht ..." he learned from Johann Juvenel and Alex Lindner, and Johann Philipp Kreuzfelder (1577-1636), son of a Nuremberg goldsmith, completed his apprenticeship at Juvenel's workshop between 1593 to 1597. In 1612 and 1617 Kreuzfelder portrayed the Nuremberg councillors and in 1614 Bartolomeo Viatis (1538-1624), a merchant from Venice (City of Nuremberg's Art Collections), then he worked as a portrait painter for the Counts of Oettingen and Hohenlohe-Langenburg. He is believed to have stayed in Rome with the artist Adam Elsheimer (1578-1610) and influences from both Flemish and Italian portraiture may be found in his work. Kreuzfelder has been assigned the monogram 'JC' (for Johannes Creutzfelder) by researchers. In 1626 the painter probably also travelled to Munich, as signed portrait by his hand depicting a lady in rich black dress (sold at Koller Auctions, October 01, 2021, Lot 3013) bears a coat of arms similar to that of Sentlinger family, a wealthy Munich patrician family, and to Constance in the south of Germany in 1628, as effigy of Nikolaus Tritt von Wilderen, a member of the city council of Constance, is attributed to him. A small portrait of a young nobleman (34 x 25.5 cm, oil on copper) from private collection in the south of Germany (sold at Lempertz KG, November 19, 2022, Lot 1516) was painted in the style symilar to the portrait of a woman from the Sentlinger family. He wears elaborately painted, silk, black doublet and loose breeches. The finely painted white lace trimmings of the lavish collar and cuffs, is characteristic of Kreuzfelder. Also the artist's signature in upper right is very similar. The painting was attributed to German School early 17th century and the monogram was deciphered as TB f. (?) (overlapping), however, it could be also JPC f. for Johannes Philippus Creutzfelder fecit in Latin. According to the rest of inscription, also in Latin, the depicted man was 25 years old in 1619 (Aetatis. 25 / 1619), exactly as Łukasz Żółkiewski (1594-1636), the younger son of the Chamberlain of Lviv Mikołaj Żółkiewski (d. 1596). He studied abroad, possibly at the Jesuit College of Ingolstadt, a city between Nuremberg and Munich in the Duchy and Electorate of Bavaria, very popular among Polish-Lithuanian nobility at that time. King Sigismund III ordered works of art in Bavaria and sent them to William V, Duke of Bavaria, while king's mistress, influential "minister in a skirt" or "Jesuit's bigotry" Urszula Meyerin (1570-1635), was most likely born near Munich in Bavaria. Nephew of the famous hetman Stanisław Żółkiewski (1547-1620), Łukasz took part in the Turkish campaign of 1620 and was captured at the battle of Cecora, in which his uncle lost his life. Four years later, in 1624, he accompanied Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (future Ladislaus IV) on a foreign trip at the behest of King Sigismund III. Żółkiewski, who become the voivode of Bratslav, died childless in a battle with the Cossacks in November or December 1636 and was buried in the Jesuit church in Pereiaslav, which he founded a year earlier (1635) along with the Jesuit College. Later, the Cossacks destroyed Pereiaslav including the church, and they threw out the body of the founder from the coffin (after "Ilustrowany przewodnik po zabytkach kultury na Ukrainie" by Jacek Tokarski, Zbigniew Hauser, Volume 4, p. 180). The family resemblance of the 25-year-old man to effigies of hetman Stanisław Żółkiewski, Łukasz's uncle, is striking. The shape of the face, lower jaw and lower lip, hair color and hairstyle are very much alike. The style of the portrait resemble greatly two miniatures from the National Museum in Warsaw (inventory number Min.1014 and Min.1015), identified as effigies of Gotthard Kettler (1517-1587), Duke of Courland, which was part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, and his wife Anna of Mecklenburg (1533-1602). It cannot be excluded that Kreuzfelder arrived at some point of his career to the Commonwealth or Żółkiewski commissioned a series of his effigies during his potential sojourn in Nuremberg, because the painter was known among Polish-Lithuanian clients.
Portrait of Łukasz Żółkiewski (1594-1636), aged 25 by Johann Philipp Kreuzfelder, 1619, Private collection.
Miniature portrait of Gotthard Kettler (1517-1587), Duke of Courland by Johann Philipp Kreuzfelder, first quarter of the 17th century, National Museum in Warsaw.
Miniature portrait of Anna of Mecklenburg (1533-1602), Duchess of Courland by Johann Philipp Kreuzfelder, first quarter of the 17th century, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portraits of Tomasz Zamoyski and Katarzyna Ostrogska by Domenico Tintoretto
In the years 1615-1617, "fulfilling the last will of his father", Tomasz Zamoyski (1594-1638), son of Jan Zamoyski, Grand Chancellor of the Crown (1542-1605) and Barbara Tarnowska (1566-1610), daughter of Stanisław Tarnowski (d. 1618), castellan of Sandomierz, undertook foreign peregrinations. Almost all young magnates made such educational journeys at that time.
Through Kraków in the south of Poland, he reached Gdańsk in the north, where he stayed "about six Sundays" - from around December 12, 1614 to the last days of January 1615, also visiting Malbork and Elbląg. In the last days of January 1615, after receiving letters of recommendation from king Sigismund III Vasa, young Zamoyski set off from Gdańsk accompanied by a small court with Father Wojciech Bodzęcki, professor at the Zamość Academy, and Piotr Oleśnicki, Tomasz's cousin, who studied in Paris and Padua at the expense of Jan Zamoyski. From Lübeck he went to Amsterdam, and from there to England. He arrived in London in mid-July 1615 and spent about 5 months there. James I, captured by Tomasz's wit and kindness, often invited him to hunting and banquets. At the request of Zamoyski the king released several English Catholics from prison - including Father Fludd who was held at Gatehouse Prison. "He was held in high esteem by the King, who often had audiences with him. He often went hunting with his son Charles. The royal horses were always at the disposal of the Lord himself and his servants for fun. King James was given an expensive hat decoration with heron feathers", wrote Tomasz's servant Stanisław Żurkowski in a biography. Wanting to get to know the country better, he went on a trip around the island, which lasted about two months. Then he travelled to France. Zamoyski probably arrived to Tours, where King Louis XIII was staying at that time, in the first days of March 1616. From Tours the he went to Orléans then to Paris. His stay in the capital of France was very busy: he learned the French language, "listened to the courts in the parliament", he was "in academies on various acts and disputes", he improved his skills in fencing and horse riding, and he learned to play the lute. He attended the audiences of King Louis XIII, held receptions for officials and officers of the French court and visited them. He befriended the princes de Guise, de Rohan, de Nevers and de Montmorency. From France young Zamoyski came to Italy in January 1617. From an early age, he had contact with the culture of Italy as his father was educated there. He visited Naples and Rome, where he had audiences with Pope Paul V. Then he went to Loreto, Padua and Venice. Also in Italy he maintained the splendor of his retinue. He visited the studios of masters of engraving, painting and goldsmiths, he acquired luxury goods, he organized parties and gave gifts to people from the ruling class. The cost of Zamoyski's journey was amounted to enormous sum of over 20,000 zlotys, while the income from 1 village at that time fluctuated between 140 and 240 zlotys annually. In the first days of November 1617, through Switzerland, Bavaria, Bohemia and Silesia, Zamoyski returned to Poland, where in Kościan, he was welcomed by servants from Zamość and soldiers from his private units. A few days later, he arrived in Poznań, where "he put away his foreign clothes, cut his hair and returned to Polish attire", as recalled Żurkowski in his biography. From Poznań he went to Łowicz, to pay a visit to the Archbishop of Gniezno, Wawrzyniec Gembicki in his magnificent palace, and then to Warsaw, where he stayed for about two weeks. It was not until December 20 that he arrived in Zamość, where he was solemnly welcomed. Soon after his return his political career advanced, in 1618 he became the voivode of Podolia and in 1619 the voivode of Kiev (after "Peregrynacje zagraniczne Tomasza Zamoyskiego w latach 1615-1617" by Adam Andrzej Witusik). He also decided to marry Katarzyna Ostrogska (1602-1642), granddaughter of Zofia Tarnowska (1534-1570), Princess of Ostroh on paternal side, and great-granddaughter of Duchess Anna of Masovia (1498-1557) on maternal side. 18-year-old Katarzyna and 25-year-old Tomasz were married in the Corpus Christi Church in Jarosław on March 1, 1620. As a dowry, Katarzyna received 53,333 zlotys, 6 castles, 13 cities, about 300 villages and folwarks. She was born in 1602 in the family of Alexander Prince of Ostroh, voivode of Volhynia, and his wife Anna Kostka (1575-1635), as the youngest of eight children. The family lived in the city of Jarosław. Her father died suddenly the year after her birth, leaving a rich inheritance to his three daughters who reached adulthood: Zofia, Anna Alojza and Katarzyna. The portrait of a young man in a black coat lined with fur, attributed to Domenico Tintoretto, today in the National Gallery in London (inventory number NG173), was presented in 1839 by Henry Gally Knight (1786-1846), a British politician and writer. His right hand rests on a table placed before an open window, and on which is a silver vase containing a sprig of myrtle, consecrated to Venus, goddess of love and used in bridal wreaths. In his left hand he holds a black cap. An open window looks out over a landscape of farmland with two rustic buildings, possibly barns, with what look like thatched roofs supported on wooden trunks or poles, typical for Poland, Ukraine and large estates of the Zamoyskis near Zamość. Merchants from such distant countries as Spain, England, Finland, Armenia and Persia arrived for the annual three-week-long big fair, one of the largest in Europe, in nearby Jarosław - according to Łukasz Opaliński (1612-1662), 30,000 cattle were sold at one Jarosław fair (Polonia Defensa Contra Joan. Barclaium, 1648). The same man was also depicted in a full-length portrait, also by Domenico Tintoretto, which before World War II was in the Łańcut Castle close to Jarosław (catalogue "For Peace and Freedom. Old masters: a collection of Polish-owned works of art ...", pic. 37). He wears a fashionable French/English black costume, very similar to the one shown in the portrait of a young man, attributed to Salomon Mesdach, dated on the table: Aº 1617 (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, inventory number SK-A-913). A view of a canal in Venice is visible through the window behind him, suggesting that the portrait is a souvenir of his visit to the city. The man in both portraits bear great resemblance to effigies of Tomasz Zamoyski in Polish costume, as a child aged 12, created by Peter Querradt in 1606 (Österreichische Nationalbibliothek) and aged 44, created by Jan Kasiński in 1637 (Diocesan Museum in Sandomierz). Portrait of a lady, known as Donna delle Rose, in Villa Gyllenberg in Helsinki was painted in the same style as the portrait of a man with myrtle in the National Gallery in London. This work is also attributed to Domenico Tintoretto, it has similar composition and similar dimensions (116.5 x 85.5 cm / 119.5 × 98 cm), therefore can be considered as a pendant or a portrait from a series created at the same time. The modish attire worn by this young woman bespeaks great affluence. Her costume is very similar to Venetian court dresses visible in a print published in 1609 in Giacomo Franco's "Costumes of Venetian Men and Women" (Habiti d'hvomeni et donne venetiane). The northern ruff, however, was replaced with a reticella collar from the late 1610s, like an open peacock's tail behind the head, propped up with sticks, similar to Italian and French collars of courtiers of King Sigismund III Vasa. The Procession with St. Anianus by workshop Tommaso Dolabella (Corpus Christi Church in Kraków) and Banner with Adoration of St. Francis by Jan Troschel (Leżajsk Monastery), testifies to the diversity of the court fashion in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in the 1620s with Polish, Spanish, Italian, French and German styles represented. White rose in her hair symbolizes purity and innocence of a bride. The woman's face bear great resemblance to preserved portraits of Katarzyna Ostrogska, all created when she was a widow and offered to different monasteries (Museum of Zamość), or to the portrait of her daughter Gryzelda Wiśniowiecka (Kozłówka Palace). Lady Zamoyska in a Venetian costume painted by Domenico Tintoretto? This was not surprising for the inhabitants of the Zamoyski estates. There were many Italians in Zamość, at the Academy, in the service of the Chancellor Jan Zamoyski, starting with the court architect, Venetian Bernardo Morando. In 1596 Boniface Vanozzi, secretary of Cardinal Enrico Gaetani in Poland, described Zamość, Renaissance ideal city build for the Chancellor, "a lover of the Italian nation" (amatore della natione italiana), from scratch: "He began to build this town in 1581 and already today it has up to 400 houses, mostly built in Italian style". Before 1604 he commissioned to the main altar of the Collegiate Church in Zamość, several paintings in the workshop of Domenico Tintoretto. Negotiations with the artist were conducted on behalf of Zamoyski by representatives of the Italian Capponi and Montelupi families and completed paintings were delivered to Poland in 1604. The largest painting depicted the Risen Christ with St. Thomas the Apostle - the patron of the temple, paintings in the side parts: St. John the Baptist and St. John the Evangelist - the patrons of the founder, and the painting in the top of the altar - God the Father. This altar was transported to the church in Tarnogród in 1781 and only the side paintings preserved. Tomasz, his father and his wife in Venetian costume were also depicted in two paintings in the Church of the Assumption in Kraśnik (Thanksgiving mass and Rosary procession). Both were created by Tommaso Dolabella in 1626. From 1604 Kraśnik was part of the Zamość estate and the protector of the church was Tomasz Zamoyski, voivode of Kiev. The voivode and his wife founded stalls for the church with their coat of arms and in one of the side altars there is painting of Salvator Mundi by Paris Bordone or his workshop.
Portrait of Tomasz Zamoyski (1594-1638) in French/English costume from the Łańcut Castle by Domenico Tintoretto, ca. 1617, present whereabouts unknown.
Portrait of Tomasz Zamoyski (1594-1638) by Domenico Tintoretto, ca. 1620, National Gallery in London.
Portrait of Katarzyna Ostrogska (1602-1642) in Venetian costume by Domenico Tintoretto, ca. 1620, Villa Gyllenberg in Helsinki.
St. John the Baptist and St. John the Evangelist from the Zamość Collegiate by Domenico Tintoretto, ca. 1604, Church of the Transfiguration in Tarnogród.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa in a ruff by Peter Paul Rubens or workshop
"This prince who was the delight of the Poles alone has now become, o Belgians, the object of your affection and that of the world" (Quod sibi delicium soli tenuere Poloni, / Nunc est, o Belgæ, vester, et orbis amor) is the inscription in Latin, paraphrasing Titus, under an engraving with the portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648), eldest son of King Sigismund III Vasa (after French translation by Alain van Dievoet in "Les Lignages de Bruxelles", No. 75-76, 1978, p. 59). This print was made in Antwerp by Pieter de Jode the Elder (P. de Iode sculp.) and Joannes Meyssens (Ioann. Meyssens exc.), most likely between 1625-1632, and shows the prince in profile in armor, with an order of the Golden Fleece and holding military baton (National Museum in Kraków, MNK III-ryc.-40877).
Although the monarchs of Poland-Lithuania commissioned many works of art from Antwerp and Brussels from at least the early 16th century (mainly tapestries and paintings), after the prince's stay in these cities in 1624 these commissions increased considerably. The prince was painted for the Infanta Isabella Clara Eugenia of Spain by Peter Paul Rubens, ordered ten tapestries depicting the story of Ulysses (Odysseus) from the Brussels weaver Jacob Geubels the Younger and purchased many valuable objects. It should be noted, however, that already a decade earlier, around 1615 or even earlier, the Flemish engraver Pieter Serwouters (1586-1657), who was born and worked in Antwerp before moving to Amsterdam in 1622, created an engraving with another effigy of the prince in national costume (inscription: Vladislaus Sigismundus Dei Gratia Polonia Sueciæq Princeps, signed: P. Serwouters fecit, Veste Coburg, VII,347,1). Regarding costume, Ladislaus was depicted in different outfits and in the first known portraits, mainly in foreign costume - Italian, French or Spanish. The principal tailor of the royal court at that time was Nicolas Dugietto or Nicolas Dugudt (Nicolò Dughetto da Parigi, Dziugiet), serving at least until 1616, most likely a Frenchman from Paris, who was paid 612 florins per year. In June 1617 the prince's servant, actor and musician Jerzy Wincenty, purchased in England for his master, his father and stepmother 36 pairs of silk stockings (black and color), 15 pairs of gloves, perfumes, 2 beaver hats, vest (wastcot) and 6 expensive gloves, 6 other vests and as much nightcaps (night capps) and a dozen equestrian gloves. In 1617 the prince used the services of his father's tailor Sebastian (active at least from 1601), and in April 1624 he was served by a certain Pallioni (after "Pompa vestimentis" by Jacek Żukowski, p. 54-55, 58). Although during his journey he frequently ordered clothes from the best local tailors, the Spanish-style outfit depicted in his portrait by Rubens was most likely made before his departure from Warsaw, as the black satin doublet, perhaps from a fabric ordered in Venice, was decorated with the monogram S, referring to his father Sigismund III. Around September 13, 1624, the French ambassador Nicolas de Bar, lord of Baugy, reported from Brussels to the Secretary of State that: "The painter Rubens is in this town. The Infanta ordered him to take the likeness of the prince of Poland" (Le peintre Rubens est en cest ville. L'Infante luy a commandé de tirer le pourtraict du Prince de Pologne). The original painting by Rubens, mentioned in the inventory of the Coudenberg Palace in Brussels from 1659 (No. 122/84), was probably lost when the palace burned down in 1731, but the prince ordered several copies of this effigy for himself and his friends and some of them have been preserved. The most famous and perhaps the most faithful copy made by Rubens and his workshop is that kept at Wawel Castle in Kraków (oil on canvas, 125.1 x 101 cm, purchased by Metropolitan Museum of Art in 1929, earlier in England, offered by the Met in 2020). Another copy, of which nothing is known, is most likely in a private collection. The oval copy kept at the Durazzo-Pallavicini Palace in Genoa (oil on canvas, 77 x 66 cm, 1890 A), was perhaps a gift for Agostino Balbi, whose palace the prince saw in November 1624. There is also a good 17th century copy in the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 76 x 58 cm, M.Ob.2434, earlier 34348), which, however, more closely resembles the works of Gaspar de Crayer and his workshop, such as the portrait of Ladislaus' cousin Philip IV of Spain (1605-1665) in parade armor at the Met (45.128.14). The copy lost during the Warsaw Uprising of 1944 when the city was destroyed by German forces was comparable in style. This painting was donated by Henryk Bukowski in 1886 to the Polish Museum in Rapperswil (received from the King of Sweden, oil on canvas, 72 x 57 cm, inventory number 501). Willem van Haecht included the same effigy of the prince in his painting of the gallery of Cornelis van der Geest, painted in 1628 (Rubenshuis, oil on panel, 102.5 x 137.5 cm, RH.S.171). Rubens posibly also painted full-length portrait of the prince during the siege of Breda - "he made his portrait from nature" (lo ritrasse al naturale), according to Le vite de' pittori ... by Giovanni Pietro Bellori, published in Rome in 1672, which is sometimes interpreted as life-size. There are several indications that significant contacts between the Polish-Lithuanian monarchs and Rubens' workshop began before 1624. At the turn of 1619 and 1620, Piotr Żeromski vel Żeroński (Petro Jeronsquy), envoy of Sigismund III Vasa, who appeared in Antwerp, bought paintings from Rubens for which the loan amounted to 1,125 Polish ducats (after "Rubens w Polsce" by Juliusz A. Chrościcki, p. 135, 139, 161, 164, 166, 207, 214). Żeromski presented the Cathedral of Saint Nicholas in Kalisz with a large painting by Rubens or workshop, representing the Descent from the Cross (destroyed or stolen in 1973). In 1619 Jan Brueghel the Elder, who frequently cooperated with Rubens, was released from customs by Albert of Austria for paintings made for King of Poland including 9 portraits and in 1621, he painted three portraits of Polish kings for which he was paid 300 florins by the secretariat of Archduke Albert and Infanta Isabella Clara Eugenia on December 16 (En Brusselas, a 11 de deciembre se libraron 300 fl. a Juan Brueghle, pintor, vecino de Amberes, por tres retratos que ha hecho de los reyes de Polonia en el tercio postrero deste anno 1621). Many of Rubens' paintings were in the royal and magnate collections of the Commonwealth before the Deluge (1655-1660). Roger de Piles in his Dissertation sur les ouvrages ..., published in Paris in 1681, states that "The Lion Hunt, for example, and the fall of Saint Paul [The Conversion of Saint Paul] were made for the king of Poland, and four others hunts for the Duke of Bavaria" (La chasse aux Lions, par exemple, & la chûte de S. Paul ont esté faites pour le Roy de Pologne, & quatre autres chasses pour le Duc de Bavières, p. 25). Rubens most likely created a series of effigies of historical kings of Poland and Wespazjan Kochowski in his panegyric written in 1669 on the occasion of the coronation of King King Michael Korybut Wiśniowiecki refers to a painting by the master depicting King Casimir the Great (Na cóż tu Rubens Kazimierzu tobie / Wielki, te mury przydał ku ozdobie?). Another series was probably commissioned in Vienna from Frans Luycx, a student of Rubens, because the large painting depicting Casimir the Great's father - Ladislaus the Short was in the Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden before the Second World War (oil on canvas, 145 x 115 cm, Gal-Nr. 514/Gal.-Nr. 2674 L). Unfortunately, today we can only imagine these paintings, because nothing is preserved in Poland from the original collections. The invaders during the Deluge and other invasions had no respect whatsoever for the country and its people, not to mention its artistic collections. Pierre des Noyers, secretary to Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga, describes the numerous atrocities and barbarities of the invaders between 1655 and 1660, the pillaging of everything including marble floors, windows, the destruction of gilded panels just to obtain a few grams of gold and that "they had even taken the old skirts of the queen's maids of honor and sent them to Sweden" (Ils avaient pris jusqu'aux vieilles jupes des filles de la reine et les avaient envoyées en Suède). In the letter of July 27, 1656 from Warsaw, he added that "the Swedes have done so much damage to Warsaw Castle that it is uninhabitable; they put their horses up to the rooms on the third floor which are full of manure and the dead bodies of their soldiers (Les Suédois ont fait tant de saletés dans le château de Varsovie, qu'il est inhabitable; ils ont mis leurs chevaux jusque dans les chambres du troisième étage qui sont pleines de fumier et de corps morts de leurs soldats). Other towns in the Commonwealth were also pillaged and ruined. In Vilnius, the Russian army destroyed the rich chapel of Saint Casimir and transformed the cathedral into a stable for their horses (after "Lettres de Pierre Des Noyers ...", published in 1859, p. 40, 212). A painting by Peter Paul Rubens, which could possibly come from Lithuanian historical collections, perhaps acquired before the Deluge and which survived the invasions, is now in the National Museum of Art in Kaunas. This is the Crucifixion (oil on panel, 107 x 76 cm, ČDM Mt 1335), which in the second half of the 19th century was in the palace of Counts Tyszkiewicz (Tiškevičius) in Astravas, near Birzai, where the Radziwill family's rich artistic collections were kept. It is interesting to note that this painting is generally dated to the earliest period of Rubens' activity, between 1600-1615, when he was in Italy (1600-1608), Spain (1603) and the Netherlands (1612). In the Neuburg Castle near Munich, where many items from the dowry of sister of Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa were stored before 1804, there is a "Portrait of a young man" by Peter Paul Rubens or his workshop (Neuburg State Gallery, oil on panel, 57.7 x 43.1 cm, 342). The painting comes from the Electoral Gallery in Munich and the Polish-Lithuanian monarchs and the electors of Bavaria frequently exchanged gifts. Already in 1612, Queen Constance praised the artistic interests of her stepson in a letter to Duke William V, Duke of Bavaria, who in February 1623 sent several paintings to Poland-Lithuania and the painting in front of which the duke celebrated services was sent to Warsaw after his death - the transport (via Vienna) lasted from June 1626 to February the following year (after "Świat polskich Wazów: eseje", p. 298-299, 311). The effigy of Polish Saint Stanislaus Kostka in prayer by circle of Rubens, from the collection of the Electors of Bavaria in the Munich Residence (Alte Pinakothek, 7520), could be a gift from Poland, but created in Flanders. The resemblance of the young man to the effigies of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa, depicted in the mentioned engravings by Serwouters and de Jode, as well as in the medals with the profile of the prince by Alessandro Abondio (Kunsthistorisches Museum, Landesmuseum Württemberg or Bode Museum in Berlin), is striking. Also noteworthy is the resemblance to the likeness in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence (Inv. 1890, 2350) as well as the prince's face in the mentioned painting from Rubens' workshop at Wawel Castle. In his early portraits, such as the paintings from the Wittelsbach collections (Royal Castle in Warsaw, ZKW 66, donated by the government of West Germany in 1973) and Neuburg Castle (Bavarian State Painting Collections, 6817), the prince wears a ruff. A very similar ruff is visible on a portrait of Ladislaus Sigismund's uncle, King Philip III of Spain (1578-1621), attributed to Andrés López Polanco and dated around 1617. The portrait of Philip III can now be found at Skokloster Castle (LSH DIG3535) and was probably plundered in Poland-Lithuania by Carl Gustaf Wrangel (1613-1676), close friend and trusted advisor to the "Brigand of Europe" King Charles X Gustav of Sweden. In this portrait the prince does not wear the Order of the Golden Fleece, which he received in 1615, so the portrait could be dated shortly before he received the order, however, in many later effigies, Ladislaus was depicted without the Golden Fleece. For example, in the series of portraits of Polish monarchs commissioned by the Toruń City Council for the Royal Chamber of the City Hall, Sigismund III Vasa wears the order, while his son and successor is depicted without this distinction. In 2019, a miniature copy of this effigy, attributed to Abraham van Diepenbeeck, a student of Rubens who worked for the clients from the Commonwealth and moved to Antwerp in 1621, was sold in the United States (oil on vellum, 13.34 x 9.53 cm, Concept Art Gallery in Pittsburgh, PA, June 8, 2019, lot 1239). In this version of the effigy, the young prince particularly resembles the effigies of his father Sigismund III, notably the profile portrait at Wawel Castle (9009), purchased in Munich in 2008 (Hermann Historica, Auction 54, April 10, 2008, lot 3223).
Crucifixion by Peter Paul Rubens, ca. 1600-1615, National Museum of Art in Kaunas.
Portrait of King Philip III of Spain (1578-1621) by Andrés López Polanco, ca. 1617, Skokloster Castle.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) in a ruff by Peter Paul Rubens or workshop, ca. 1615-1621, Neuburg State Gallery.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) in a ruff by Abraham van Diepenbeeck, after 1621, Private collection.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) in a hat by workshop of Peter Paul Rubens, ca. 1624, Wawel Royal Castle.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) in a hat by workshop of Peter Paul Rubens, ca. 1624, present whereabouts unknown.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) in a hat by workshop of Peter Paul Rubens, ca. 1624, Durazzo-Pallavicini Palace in Genoa.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) in a hat by workshop of Gaspar de Crayer, ca. 1624, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) in a hat by workshop of Gaspar de Crayer, ca. 1624, Polish Museum in Rapperswil, lost.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) in a hat, detail of the Gallery of Cornelis van der Geest by Willem van Haecht, 1628, Rubenshuis in Antwerp.
The palace was built between 1639-1642 by Lorenzo de Sent for the Grand Crown Chancellor Jerzy Ossoliński in Mannerist style. It was constructed on the plan of an elongated rectangle with two hexagonal towers at garden side of the building. The palace was crowned with a terrace with a balustrade, above which stood the upper part of the great representative hall, covered with a spherical roof. A possible inspiration for the palace's upper pavilion and its characteristic roof was Bonifaz Wohlmut's reconstruction of Queen Anne's Summer Palace in Prague, 1557-1563.
Adam Jarzębski, styling himself as Musician of His Highness Ladislaus IV and manager of the construction of the royal palace at Ujazdów, in his "Short Description of Warsaw" (The Main Road, or a Short Description of Warsaw) from 1643, described the residence of Jerzy Ossoliński: Facade with statues of four kings, below inscriptions and a brass statue of Poland holding a sickle, with a plow and a sheaf and marble portal (2427-2435), in the middle of a building a hall covered with roof tiles with gilded brass statues in the corners (2445-2450), Elongated outbuilding with servant lodgings and a kitchen (2711-2713), stables building opposit with a gate (2720-2725), Vestibule with marble portals and iron doors of master craftsmanship (2505-2508), and a staircase with a grille and a large, solid lock (2520-2525), Large dining room (2465) with niches with statues of white marble and a brass statue of a Cupid holding a bow above the door, chandelier and tapestries (2475-2485), with a door to a wine cellar (2491) and a room with silver and gold tableware (2495-2496), Hall with upper windows and a fireplace of black highly polished marble with equestrian portrait of king Ladislaus IV Vasa on white horse against a battle scene (2527-2538), a row of family portraits by painter Hans (?) Amman, and paintings reproducing the epic tales of the ancestors, including a story of a knight wounded during a jousting tournament who was healed by Saint Anne, other stories and battle scenes, above busts of Roman Emperors of white marble (2553-2570), stucco trees in corners, most probably by Giovanni Battista Falconi, ceiling decorated with figures, animals and floral motifs and a painting depicting coronation of Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria in presence of chancellor Ossoliński, door portals of black marble with portiere tapestries with Topór (the Axe) coat of arms (2575-2600), polished marble floor (2605-2607), Lord's chambers with tapestries, French-style parade bed, tables with gold trinkets and silverware and decorative clocks beside the bed, coffers, fireplace adorned with a mosaic (2611-2632), Cabinet of curiosities in a right side tower with bronze statues of different horses, birds and people (2635-2644), silver plated cupboard-cabinet with gold inscriptions describing the contents of each drawer (2649-2652), marble table with rarities on it (2659-2662), Chapel in the left side tower with an altar with an exquisite painting, relics in glass vessels, offered by the Pope, silver coffer reliquary with bones bound by gold chains, wax miniatures, a table with a casket and a door to a staircase (2667-2692). In 1633 Ossoliński was sent with a diplomatic mission to the Pope in Rome by newly elected monarch of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Ladislaus IV Vasa. The King offered him the starostwo of Bydgoszcz, 60,000 zlotys, six horses, a saber (scimitar) worth 10,000 zlotys, five Brussels' tapestries making up the series of the Story of Moses commissioned by King Sigismund Augustus in the 1550s, three of which were given to the Pope, and a construction site in Warsaw. An event from 1633 is also worth mentioning when Ossoliński, traveling to Rome via Veneto, fascinated by the beauty of one of the villas near Padua, ordered to immediately take its dimensions. He made his entry to Eternal City wearing a żupan, richly embroidered with gold, buttoned up with 20 large buttons with diamonds, gold sabre set with jewels valued at 20,000 Polish zlotys and mounting a Turkish stallion having golden horseshoes and a horse tack set with precious stones. In 1638 a life-size statue was cast in brass by Gerdt Benning in Gdańsk according to the design by Georg Münch for then the vice-chancellor Jerzy Ossoliński, most probably to his Castle in Ossolin. It is possible that the same workshop created statues to his Warsaw's palace. Contrary to the Crown Court Marshall Adam Kazanowski, who had a transgender man at his court, the Chancellor Ossoliński kept a transgender woman in his palace: "a boy who thinks he is a girl, and who also wears a dress: He imitates a girl quite well; especially in that, he is very eager of being cuddled", as recounted Jean Le Laboureur in his "Account of the voyage of the Queen of Poland", published in Paris in 1647 (p. 212). An engraved effigy of the Chancellor by Willem Hondius from 1648 was created after a portrait by Bartholomäus Strobel. It is possible then that Strobel created more painting for Ossoliński, including for his Warsaw's residence. In 1645 the chancellor commissioned the silver-ebony altar for the Chapel of Black Madonna of Częstochowa adorned with his coat of arms. The design was most probably by a Royal court artist Giovanni Battista Gisleni, while silver elements were created by the Royal goldsmith Johann Christian Bierpfaff in Warsaw in 1650. The "Inventory of belongings spared from Swedes and escapes made on December 1, 1661 in Wiśnicz" in the Central Archives of Historical Records in Warsaw, lists some of the preserved paintings from Chancellor's rich collection inherited by his daughter Helena Tekla Ossolińska, wife of Aleksander Michał Lubomirski, owner of the Wiśnicz Castle. 30 paintings from Chancellor's collection in the inventory include the paintings by Raphael, Titian, Guido Reni, Guercino, Domenichino, Veronese, Ribera, Albrecht Dürer and Daniel Seghers. There were also there a painting of the Leda and a swan, a gift from the Emperor, a Cupid sharpening his bow, possibly a copy of the famous work by Parmigianino, acquired in Rome, a "large Blessed Virgin Mary, a wreath around her made of fruits, which the angels holds", most probably by duo of Rubens and Jan Brueghel, and a large canvas showing Chancellor's Entry into Rome in 1633. Ossoliński died in his palace in Warsaw on August 9, 1650, at the age of 55. He was buried in the church of St. Joseph in Klimontów, which he built. His opulent palace in Warsaw was destroyed during the invasion of the Commonwealth by neighbouring countries, known as the Deluge (1655-1660).
Adam Jarzębski, styling himself as Musician of His Highness Ladislaus IV and manager of the construction of the royal palace at Ujazdów, in his "Short Description of Warsaw" (The Main Road, or a Short Description of Warsaw) from 1643, dedicated to his benefactor Crown Court Marshall Adam Kazanowski, thoroughly described the residence of this baroque celebrity.
Kazanowski gained prominence as a close friend and companion of crown prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa, who was elected monarch of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth from 1632 as Ladislaus IV. Together with his brother, Stanisław Kazanowski, Adam was raised with crown prince and accompanied him during his attempt to become a Russian Tsar, in the Khotyn war of 1621 and the 1624 to 1625 European voyage. A breakthrough event for Adam was when his elder brother Stanisław, favourite of crown prince, attacked with syphilis was expelled from the court for promiscuity in 1620. Zygmunt Kazanowski, father of both, had great hopes for the relationship of his older son and young Vasa. Faced with the threat of his imminent death, he persuaded the sick to recommend his younger brother to the prince. Both brothers were accused by Jerzy Ossoliński in his Memoirs of organizing "suspicious" amusements for young prince. When the crown prince became king, Adam was showered with gifts and new official titles. In 1628, at the age of about 29, Kazanowski decided to get married. He chose Elżbieta Słuszczanka, a daughter of wealthy Castellan of Minsk, Aleksander Słuszko, for the future bride. The marriage meant for him not only a substantial dowry, but also valuable connections in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. Aleksander Słuszko dismissed the suitor, justifying the refusal with his daughter's young age, as Elżbieta was then only 9 years old. However, thanks to the intervention of the crown prince, Aleksander Słuszko changed his mind. The wedding took place in the spring of 1633, when Elżbieta has reached the legal age of 14. Adam, who also became the Grand Pantler of the Crown that year, gained 50,000 zlotys of dowry. In addition, the young couple received 20,000 zlotys from the king and the value of the gifts was estimated at 40,000 zlotys. When crown prince Ladislaus Sigismund became an adolescent, his father Sigismund III Vasa bought him a wooden mansion of Andrzej Bobola at the Cracow Suburb Street in Warsaw. In 1628, shortly after his return from a journey to Western Europe, the prince ordered Constantino Tencalla a court architect to build him a new palace in the Italian style. Four yers later, in 1632, Ladislaus gave the palace to Kazanowski, which caused serious misunderstanding with his father, and a special Parliament committee was appointed to determine the circumstances behind this gesture. In 1637, Kazanowski enlarged the building, holding to Tencalla's original designs. The new structure was a large four-storied palace with a garden, enormous terrace, central courtyard, copper roofs and tower tops decorated with gilded crowns. 629 verses (1025-1654) of Jarzębski's work portray the lavish mannerist and early baroque palace constructed between 1628 and 1643 in the center of informal capital of the Commonwealth: Large arsenal filled with cannons, muskets, excellent armors, tents and turkish garments, lances and spears arranged on the walls, field guns, matchlocks and a skin of a lioness (1057-1066), Long gallery filled with paintings on both sides with nudes above the table, portraits of the King Ladislaus IV Vasa and his wife Cecilia Renata of Austria, painted Ad vivium and noble ladies, stone statue of Atlas supporting the armillary sphere on the table in the middle (1095-1108), Small arbor room adjacent to gallery with a French window, columns, stone floor and a view of the river Vistula (1121-1127), Dining room with windows on two storeys, a large chandelier with a clock showing hours, a balcony for musicians and Flemish tapestries woven with golden thread (1131-1153), chairs covered with gilded cordovan, plaques with coat of arms of the Lords and Marshals between windows in upper part and landscape paintings and cordovan in lower part, tile stove (1177-1187), window with a wine lift from basement, a large silver wine vessel of 150 litres on wheels in the shape of Bacchus wearing a wreath, sitting on a barrel and holding a goblet, several other barrels half the size of the main and a silver wine fountain in the middle of the room, silver ewers, pitchers and trays (1188-1214), the King and the Queen, envoys from Muscovy, the emperor, the king of Spain, Turkey, France and Persia were received there (1162-1171), Vaulted steam baths near the coach house with two chambers, hot stone, heating house, cold and hot water, copper bathtubs and white benches (1255-1272), Room on upper floor covered with cordovan, with a fireplace, marble portals with gold inscriptions, statues in overdoor (1305-1318) and muskets on the walls (1323), Rooms with paintings and tapestries: animalistic paintings and still-lifes with vegetables by master painters in the first, next room with staircase, seascapes and paintings of ships, casket regals, a harpsichord, a lute, a violin, cymbals, a viol and a harp and doors hung with portieres (1325-1343), next room with live animals, monkey on a chain, white parrot, singing birds in cages, still life paintings with fruits and wines, tapestries, a fireplace and a marble table (1349-1364), Lord's bedroom with a table, a painting of Adam and Eve, a bed against tapestries, good paintings, a fireplace and marble floor, a folding bench with wheels (1381-1392), trellis giving to the chapel, altar with gilded grille and a window to the ladies' room (1365-1376), Lord's study with a mirror, angels' statues holding candles, paintings, tapestries and polished marble floor (1407-1418), Library with foreign books in different languages, khanjar daggers on the table, daggers set with turquoises, gold bowls and rock crystal vessels (1425-1431), Lady's rooms, in one of them tortoiseshell caskets, pendant paintings, one with an old man with a sore eye, tapestries and looms (1437-1449), bedroom covered with goldcloth, a draped bed made of a rich fabric, mirror in silver frame above the table, the other in gold plated frame, automaton clock with a man, paintings in ebony frames, marble floor and marble table (1457-1469), a bedroom with a bed of green goldcloth with fringe and a portrait of mother of Her Majesty, Zofia Konstancja Zenowicz, in the next room in the corner of the palace a portrait of father of Her Majesty, Aleksander Słuszka, in his old age above the door, in both rooms marble fireplaces, tables covered with kilims and marble floors (1473-1495), Treasury on the groundfloor, the first room filled with guns: bird shotguns, Turkish trench guns, carabins, muskets and Italian pistols, laid with gold and silver, tables covered with Persian kilims (1508-1520), treasury room with gilded stuff set with turquoises, eastern backswords, gold sabres, gold and gilded saddles and horse tacks, sable coats, large trays and ewers in boxes and antique treasures, snake skin and a turtle from India (1530-1561), Belvedere room with grille with a view of a garden (1579-1582), wine basement with barrels of wine, mild, sweet and spicy (1590-1596), and a beer basement (1601), in the room above a workshop of Dutch painters (1603-1608), next a room with silverware (1612), and a room with hunting falcons (1613), marble pantry with venison, partridges (1641-1645) and a room of captive Muslim Tatar servants (1649-1651). Three years later, in 1646, Jean Le Laboureur, a companion of the French Ambassador Extraordinaire to Poland, Renée du Bec-Crespin, comtesse de Guébriant, visited the palace and described it in his "Account of the voyage of the Queen of Poland", published in Paris in 1647. He devoted five pages of his book to the building: Five or six large chambers and several smaller rooms, filled with silk and gold oriental fabrics, beds of gold fabric, cabinets of uncommon workmanship, tables with different items of gold, silver, amber and stones (p. 211). Large room with marble floor, as the rest of the lodgings, with a large wine fountain, made of silver in the middle, large platform above the door for the musicians, table with 80 silver-gilt Italian style tazzas (four rows of twenty each) with dried fruit, large pears in sugar, oranges, lemons, melons (p. 213), buffet with extraordinary gold and silver vessels, including Bacchus "of a natural height" sitting on a silver barrel with gold wheels, rock crystal glasses with silver-gilt mountings, Elżbieta Słuszczanka was dancing here with her brother Bogusław Jerzy Słuszka, Court Treasurer of Lithuania and marquis Gonzaga Myszkowski with his wife (p. 214). Kazanowski, struck by the sudden invasion of gout, welcomed the guests at the staircase of his palace carried in a litter (p. 210), accompanied by 300 armed guards, more than 50 pages dressed in yellow satin and short jackets of blue satin, his wife and her ladies (p. 211). In one of the chambers Le Laboureur noted "two extraordinarily small female dwarfs who were standing up like a sentry, to guard two small dogs, who were not less dwarf in their species, for they are the size of a mice, and both were resting in a white basket little larger than the hand, on a pillow of perfumed satin", while the ladies of Elżbieta Słuszczanka had a transgender man, a woman who behaved like a man, "for their entertainment" (p. 212). In 1643 Kazanowski also arranged a marriage of dwarfs, "an unheard wedding, full of laughter", according to Albrycht Stanisław Radziwiłł. Following her visit, Kazanowski and his wife, sent to Madame de Guébriant some small amber cabinets and clocks set with diamonds (p. 212). Little is known about artistic patronage of the Crown Court Marshall. Among confirmed artists at his court was certain Ezechiel Sykora, born in Litomysl in Czechia in 1622, who latinized his family name to Paritius. After Kazanowski's death in 1649 he left Warsaw and went to Silesia. As a żupnik (manager) of the Royal Salt Mines, he commissioned from Gdańsk engraver Willem Hondius in 1645 a series of views of the Wieliczka salt mine. Kazanowski had also a book of friendship (album amicorum/Stammbuch), wich was in collection of Edward Rastawiecki in Warsaw in 1853. Small oblong book bind in crimson velvet had 125 parchment leaves and majority of contributions from the years of between 1624 and 1625 of his European journey and a few from 1627 to 1644, mainly of ambassadors of the Spanish Empire. During his stay in Brussels in 1624 with the crown prince he received from infanta Isabella Clara Eugenia a gold medallion set with precious stones on a gold chain. It is possible that he intentionally tried to emulate great validos of his time, Duke of Lerma or Count-Duke of Olivares. Kazanowski died childless in 1649, leaving all his property to his wife Elżbieta. His opulent palace in Warsaw was destroyed during the invasion of the Commonwealth by neighbouring countries, known as the Deluge (1655-1660). Mannerist and early baroque royal treasures of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth - reconstruction8/19/2020
Before the invasion by neighbouring countries, known as the Deluge (1655-1660), Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth ranked among the wealthiest countries in Europe and its monarchs successfully competed with rulers of other nations as patron of arts.
"Oriental" and "Muscovy" crown of Sigismund III Vasa
King Sigismund III Vasa, elected monarch of the multicultural Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, was known for his refined artistic taste inherited from the Jagiellons and his grandmother Queen Bona Sforza. He commissioned the most exquisite works of art not only in Europe, but also in Persia. In 1601, the king sent Sefer Muratowicz an Armenian merchant from Warsaw to Persia, where he ordered carpets woven with silk and gold, a tent and swords from Damascus steel and other luxury items. Safavid kilims with coat of arms of Sigismund III Vasa (Polish Eagle with Vasa sheaf) preserved in many collections.
The king was so pleased with the results of Muratowicz's expedition that after his return on October 26, 1602, he gave him the title of servitoris ac negotiatoris and obliged him in the future to present all goods brought to Poland from Turkey and Persia, before they were put up for sale, at the royal court, so that he could choose those he liked the most (after "Sztuka islamu w Polsce w XVII i XVIII wieku" by Tadeusz Mańkowski, p. 25). Sigismund III had a particularly rich collection of oriental arms and Persian or Turkish kalkan shield from the Lubomirski collection in Kruszyna was, according to tradition, the property of the king (Wawel Royal Castle). Mechti Kuli Beg, Ambassador of Shah Abbas of Persia, participated in the king's wedding in Kraków in 1605 and Robert Shirley (d. 1628), sent by the shah on a diplomatic mission to European princes, was received solemnly by Sigismund at the Sejm in Warsaw on February 25, 1609. Most probably in Italy the king ordered partially gilded shishak, an oriental-style steel helmet with Hercules killing the Lernean hydra on one side and Hercules fighting Antaeus on the other as well as coat of arms of Muscovy, as a gift to Tsar Feodor I of Russia, handed over by Ambassador Paweł Sapieha in 1591 (Kremlin Museum). In Milan in Italy or in Prague he commissioned the crystal lavabo with his coat of arms and monogram (Treasury of the Munich Residence) and in Augsburg in Germany a silver service for 20,000 florins for the ceremony of receiving the Order of the Golden Fleece (used for the first time during a banquet at the Castle in Warsaw on February 25, 1601) and many other precious items. In Flanders and the Netherlands he purchased tapestries, like 6 pieces with the Story of Diana by workshop of François Spierincx in Delft, in about 1611-1615, paintings in Venice, like the Virgin and Child with St. John the Baptist and St. Stanislaus by Palma il Giovane for the St. John's Cathedral in Warsaw, before 1618, amber items in Gdańsk and Königsberg, like amber games board of Queen Anne of Denmark and other amber gifts, sent to England in 1607 through English envoy in Poland William Bruce. The orders for works of art were related to important dates in king's life. In 1605 he spent large sums for his wedding including costly dresses emboidered with pearls. The bride was a younger sister of his first wife Anna, Constance of Austria (1588-1631), on paternal and maternal side a descendant of Anna Jagellonica (1503-1547). In July 1604, Sigismund sent letters to senators, in which he informed that Emperor Rudolf II did not give his consent for his marriage to Anna of Tyrol (1585-1618), and at the same time informed the lords of the Commonwealth of his intention to marry Constance (after "Najsłynniejsze miłości królów polskich" by Jerzy Besala, p. 169). That same year Joseph Heintz (or Heinz) the Elder, court painter of the emperor, who lived and worked in Rome, Venice, Prague and Augsburg (from 1604), created two portraits of the bride with her favourite monkey. One, less favorable, was originally probably in her family's castle in Graz (Kunsthistorisches Museum Vienna, inventory number 9452), the other in green dress, a color being symbolic of fertility, was sold in London in 1969 and later acquired by The Sterling and Francine Clark Art Institute in Williamstown (inventory number 1982.127). Many objects from the collection of King John II Casimir Vasa, Constance's son, sold in Paris, found its place in England, including most probably this portrait of his mother. Around that time Heintz created also a copy of portrait of Queen Bona Sforza (1494-1557), Sigismund III's grandmother, as Salome by Lucas Cranach the Elder (Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, 862), identified by me, and a portrait of Sigismund III himself (Alte Pinakothek in Munich, 11885), signed: J. Heintzen F. / SIGISMVNDVS .../REX POLONIAE/ & SVECIAE ... on a letter on the table. The portrait of the king was before 1929 in the Schleissheim Palace near Munich, therefore it was was most probably a gift from Sigismund to William V (1548-1626), Duke of Bavaria, like the silver reliquary of Saints John the Baptist and Dionysius the Areopagite, created in 1602 for Tsar Boris Godunov and his son and given to William V in 1614 by the Polish king (Treasury of the Munich Residence, 63). The portrait shows the king with a crown, which was most probably also created around that time, possibly for the coronation of the new queen. Like the portrait, it was made either in Prague or in Augsburg, as Heintz's presence in Poland-Lithuania is not confirmed in sources. However, it cannot be ruled out that the painter or one of his students traveled to Kraków, Warsaw or Vilnius at that time to bring to Poland the portrait of the bride and the crown. Just two years earlier, in 1602, the crown of Emperor Rudolf II, a major work of European goldsmithery was made in Prague by Jan Vermeyen from Brussels (d. 1606), as a private crown for the emperor. Sigismund's crown resemble slightly the crown of Rudolf II (side view), therefore it was most probably created by the same author, nevertheless, it is in many respects atypical of Polish-Lithuanian and European monarchs in general. Unlike the crown seen in the portraits of Queen Anne of Austria (1573-1598) by Martin Kober (1595), only one rim is visible instead of two and the globe and a cross on their intersection is replaced with a pearl or a sharply cut diamond in the form evoking a pyramid, so-called diamatus punctatus. Rudolf II was depicted with his new crown in some effigies (portrait by Hans von Aachen in Apsley House, WM.1509-1948 and engraving in the State Graphic Collection in Munich, 241589D), as well as his successor Matthias (engraving by Aegidius Sadeler in the Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, RP-P-OB-5021) in which some differences with the original are visible, however, despite the fact that no other image of Sigismund's crown is known we cannot attribute it to the fantasy of a painter. Also, the overall shape of described crown is unusual and resemble more the crowns visible in Persian and Indian miniatures. Similar diadems with bent petals can be found in the investiture scene of Malik-Shah I, sultan of the Great Seljuk Empire, from the 14th-century book "Jami' al-tawarikh" (Edinburgh University Library), an illustrated leaf from a manuscript of Nizami's "Khamsa": Bahram Gur entertained in the red pavilion, created in Isfahan, Persia in the mid-17th century (private collection) or a miniature painted between 1610-1618 by Bichitr, an Indian painter during the Mughal period, and showing Moinuddin Chishti, a Persian preacher holding a globe (Chester Beatty Library in Dublin). The oriental style crown visible in king's portrait, as a private possession of the House of Vasa, was most probably melted down during the turbulent reign of his son John II Casimir Vasa, melted and material reused by Sigismund himself who was a talented goldsmith or offered as a gift to someone before 1623, as it was not mentioned in the king's last will from May 5. On May 11, 1606 the gifts from the king were presented to Tsaritsa Marina Mniszech in Moscow - 30 very valuable vessels, while the king's envoy Mikołaj Oleśnicki (1558-1629), castellan of Małogoszcz offered many pieces of jewellery "from himself and from his Wife", including "a crown with pearls, diamonds and rubies" (after "Dzieje panowania Zygmunta III, króla polskiego" by Julian Ursyn Niemcewicz, Volume 2, 1819, p. 569). The crown visible in the portrait by Heintz was also set with pearls, diamonds and rubies. It is therefore highly possible that Oleśnicki and his wife purchased the oriental crown from Sigismund as a gift for Marina. Another "oriental" insignia that entered the collection of Sigismund III Vasa around that time was the so-called Muscovy crown. This crown was supposedly sent to the king by False Dmitry after his coronation as Tsar of Russia in 1605 or it was made in Poland around 1610, after the election of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund (later Ladislaus IV), Sigismund III's son, as tsar (after "Klejnoty w Polsce: czasy ostatnich Jagiellonów i Wazów" by Ewa Letkiewicz, p. 139). Ladislaus bequeathed the crown to the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth's State Treasury, but after the king's death in 1648 his brother and successor John II Casimir ordered the insignia to be melted down into coins. One of the gems from the original crown became the property of Jan Kazimierz Krasiński (1607-1669), Grand Treasurer of the Crown. In the 19th century it was given to Tsar Nicholas I of Russia with a piece of parchment with the inscription in Latin EX CORONA MOSCOVIAE and found its place in the collections of the Kremlin Armoury in Moscow (inventory number ДК-752). The jewel is a double-faced sapphire icon-cameo with Christ Enthroned and Golgotha's Cross, attributed to a Byzantine artist from the 15th century. Sigismund III was depicted with the "crown taken in Moscow" on his head (after "Dzieje panowania Zygmunta III, króla polskiego" by Julian Ursyn Niemcewicz, Volume 2, 1819, p. 557) in a painting attributed to Christian Melich (Wawel Royal Castle). The painting represent the king on his death-bed displayed in the Guard Chamber at the Royal Castle in Warsaw in 1632. It was also depicted in a portrait of Sigismund's successor Ladislaus IV Vasa, attributed to Pieter Soutman and painted in about 1634, therefore created in Haarlem where the painter returned in 1628. The king was portrayed in a pourpoint lavishly adorned with laces and a high crown with a cross at the top on a table beside him (National Museum in Warsaw, 186555). Although Ladislaus was not crowned, he was officially elected and recognized as the Tsar of Muscovy in 1610 and used the title of Grand Duke of Muscovy until 1634. The crown was mentioned in Sigismund III's last will and testament made on May 5, 1623 in Warsaw as part of his successor's inheritance. The will also include "a golden basin with ewer with the Muscovy coats of arms, bought from the soldiers" left to king's wife Constance of Austria. The number of West European-style works of art and portraits connected with Tsar False Dmitry I, suggest that he purchased and ordered directly such items. His beautiful armour created between 1605-1606 in Milan by Pompeo della Cesa is in the Military History Museum in Saint Petersburg and a silver pocket watch with an eagle, possibly owned by Dmitriy, made by German or Polish workshop is in the Moscow Kremlin. At the beginning of January 1606 arrived to Kraków Jan Buczynski, secretary of the tsar, with the mission to acquire jewels for his patron. Several merchants from Kraków and Lviv, as well as jewellers Mikołaj Siedmiradzki and Giovanni Ambrogio Cellari from Milan, encouraged by the prospect of a large gain, embarked on a journey to Moscow. It was probably one of them who created the scepter (Moscow Kremlin, R-18) and orb (R-15), later owned by Tsar Michael I (1596-1645). The style of the orb resemble the mentioned crown of Sigismund III depicted in a portrait of his first wife Anna by Martin Kober. In 1606 Philip II Holbein "a court servant and agent in Augsburg" of Sigismund III, who as S.R.M. jubilerus was present in Kraków in 1605, delivered a considerable number of valuables to the court of False Dmitry I (after "Philip II Holbein – złotnik i agent artystyczny Zygmunta III ..." by Jacek Żukowski, p. 23). Holbein also worked for Emperor Rudolf II, and then - Emperor Matthias. It is possible that Dmitry's emissaries arrived also to Augsburg and Hamburg in Germany. A drawing from Album Amicorum of merchant and banker from Augsburg Philipp Hainhofer (1578-1647), who created the famous so-called Pomeranian Curiosity Cabinet (Pommerscher Kunstschrank) for Duke Philip II of Pomerania, is a copy of a painting by Szymon Boguszowicz depicting the reception of the Polish envoys by Tsar False Dmitriy I in 1606 (Herzog August Library and Hungarian National Museum). Among the designs for the crowns by Hamburg goldsmith Jakob Mores (Mörs) the Elder, who was born around 1540 and lived until around 1612 (after "Archiv Fur Geschichte Des Buchwesens", Volume 65, p. 158) in his "Jewelry book" (Kleinodienbuch, Hamburg State and University Library) there are two crowns which resemble the crown depicted in mentioned portrait of Ladislaus IV by Pieter Soutman, as well as the crowns visible in Coronation of Marina Mniszech in Moscow on May 8, 1606 by Szymon Boguszowicz or follower, created in about 1613 (State Historical Museum in Moscow). It is generally belived that these are designs for the crown of Rudolf II, however the overall shape resemble more the crowns usually associated with Russia (e.g. great imperial crown from 1762) - the "mitre" is more open then in the Rudolf's crown and there is a globe and a cross (globus cruciger) on the intersection of the rims and not a large stone like in the crown created by Vermeyen. A few years earlier, between 1593-1595 Mores created two drawings for the open crown of King Christian IV of Denmark-Norway, which were also included in his "Jewelry book". It was, however, Dirich Fyring and Corvinianus Saur, who between 1595-1596 made the crown for the coronation of Christian IV (Rosenborg Castle), nevertheless the designs by Mores resemble the shape of the final crown. Some pieces of jewellery in Poland are also attributed to Mores or his circle, like hat decorations of Francis of Pomerania (1577-1620), created in about 1600 (National Museum in Szczecin) or a chain of Constance of Austria from the 1600s (Wawel Royal Castle, ZKnW-PZS 1323), while double-headed imperial eagle from the Diamond Robe of the Black Madonna of Częstochowa also created around that time, may have been created by one of the named court goldsmiths for Constance of Austria or Marina Mniszech. The shape of the mentioned imperial insignia with a smaller crown at the top is also similar to the Cap from the Grand Set of Tsar Michael I, created by Moscow Kremlin workshops in 1627. It is also possible that the smaller crown in the "Jewelry book" is not a variant, but the insignia intended for the coronation of Marina Mniszech.
Portrait of Sigismund III Vasa with the "oriental" crown by Joseph Heintz the Elder, ca. 1604, Alte Pinakothek in Munich.
Visualization of the "oriental" crown of Sigismund III Vasa by Jan Vermeyen (attributed to), ca. 1604, © Marcin Latka.
Portrait of Ladislaus IV Vasa with the so-called "Muscovy" crown by Pieter Soutman, ca. 1634, National Museum in Warsaw.
Design for the so-called "Muscovy" crown by Jakob Mores the Elder, ca. 1605-1610, Hamburg State and University Library.
Design for the so-called "Muscovy" crown or the crown of Marina Mniszech by Jakob Mores the Elder, ca. 1605-1610, Hamburg State and University Library.
Bronze busts of Sigismund III Vasa and Constance of Austria
Although the existence of royal busts is purely hypothetical and not confirmed by sources, the fashion for such antique sculptures, stemming from Italy and Imperial court in Prague and Vienna, udoubtedly found its reflection in the cosmopolitan court of the Vasas in Kraków and Warsaw. Bronze cartouche with coat of arms of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth from the Wawel Castle, a full plastic bronze cast that preserved to our days and commissioned by Sigismund III in about 1604 to adorn overdoor in the northern wing of the castle leading to the Senators' Staircase, confirms that the Vasa residences were filled with such items.
In 1624, the Bishop of Kraków, Marcin Szyszkowski, who titled himself "the most faithful servant of the House of Austria" and who together with Zygmunt Myszkowski brought the Queen Constance from Graz to Poland, sponsored a new architectural dome canopy over the reliquary of Saint Stanislaus in the Wawel Cathedral in the style of Roman baroque. It is the work of the royal architect Giovanni Battista Trevano, the same who rebuilt the Royal Castle in Warsaw, made of black and rose marble, gilt-bronze and wood, created in the years 1626-1629. Gilt bronze figures of the Evangelists and Patrons Saints of Poland, flanking the cupola over the canopy, were cast by Antonio Lagostini, active in Kraków from around 1624. In the year of completion of this work, the bishop also ordered a tomb monument for himself in the cathedral near the canopy. According to the letter from Marcin Szyszkowski to Andrzej Łukomski, a Canon of the Cracow Cathedral Chapter, of 20 January 1629, this was also commissioned from Trevano and Lagostini. The model for the cast bronze bust should be attributed to the sculptors related to Trevano, Andrea and Antonio Castelli, sculptors from Lugano, active in Kraków from about 1623. If existed, the royal busts were undoubtedly made in gilded bronze, just as majority of the similar works preserved in many European countries and Bishop Szyszkowski's bust. The material and its frequent military reuse, would also explain why the works have not preserved, as in case of bronze garden statues of Ladislaus IV's garden of the Villa Regia Palace in Warsaw, which are confirmed in sources. The preserved bronze statue of King Sigismund III at the column, so-called Sigismund Column in Warsaw, was also initially gilded. The reconstruction is based on royal portrait paintings with Spanish composition from the 1610s created by workshop of court painter Jakob Troschel, which were in the collection of the Germanisches Nationalmuseum in Nuremberg before World War II. Both effigies, possibly from dowry of Polish-Lithuanian Princess Anna Catherina Constance Vasa, are highly schematical and idealized, hence facial features are based on more realistic effigies of the royal pair created by other court painters.
Gilded bronze bust of King Sigismund III Vasa, mid-1610s to 1631. Hypothetical reconstruction by Marcin Latka ©. All rights reserved.
Gilded bronze bust of Queen Constance of Austria, mid-1610s to 1631. Hypothetical reconstruction by Marcin Latka ©. All rights reserved.
See more pictures of Bronze busts of Sigismund III Vasa and Constance of Austria on Pinterest - Artinpl and Artinplhub
Heraldic pendant of Anna Catherine Constance Vasa
Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa was born in Warsaw on August 7th, 1619. She was the only daughter of Sigismund III Vasa and his second wife Constance of Austria that survied the childhood and the youngest of royal pair's children.
Large Spanish style pendants, like the one described here, become less fashionable with the introduction of the French style in the mid-1630s, that prompted frontal brooches. The creation of the pendant could be then closed in the time span between mid-1620s and 1638 when Anna Catherine Constance came of age and came into possession of counties bestowed to her by the parliament. It was also probably in 1638 that Princess' portrait in red Spanish dress with two gold pendants was created (today in the Imperial castle in Nuremberg). King Sigismund III, himself a talented goldsmith, possibly stood behind the compex emblematic program of this jewel, although it is also possible that it was created long after his death in 1632. Since 1637, a marriage was suggested between Anne Catherine Constance and Ferdinand Charles, Archduke of Austria, heir of Tyrol and nephew of Ferdinand II, Holy Roman Emperor. Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg, and Gaston, Duke of Orléans (brother of King Louis XIII of France), were also candidates for her hand. A jewel stressing splendid dynastic connections and emphasizing vastness of territories ruled by the family would perfectly fit into the Princess' situation at that time. Several heraldic jewels were featured in the official portraits of Anna Catherine Constance's mother Constance of Austria. Anna Catherine Constance's father Sigismund III Vasa was elected monarch of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, bi-federation of Poland and Lithuania ruled by a common monarch in real union, who was both King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania. Since Sigismund's crowning in 1592, Polish Vasas claimed themselves rightful hereditary rulers of Sweden, consequently ignoring Sigismund's dethronement of 1598 by the Swedish parliament. Anna Catherine Constance finally married Philip William of Neuburg (1615-1690), in Warsaw on 8 June 1642. She brought a considerable dowry in jewels and cash, calculated at a total of 2 million thalers. The inventory of Princess' jewels preserved in the Czartoryski Library in Kraków summarizes their value to 443,289 1/3 hard thalers. The heraldic pendant is listed 18th in the section Pendants: A diamond pendant with Figures of the late King Sigmunt and Constantia with crowns on their heads, in the middle ruby grain, and beneath white Eagle, at the bottom coat of arms of the Duchy of Lithuania, on the right hand Swedish and on the left hand Austrian; above this ruby grain a yellow Lion with open jaw, in the front two fangs holds Zygmunt and Constantia together, on the sides and on the bottom five carved round hanging diamonds, valued at 2,000 thalers. It is hard to determine the degree of accuracy of the inventory both in terms of description of items as well as valuation. One "large diamond" in a ring was valued at 30,000 thalers and a ring with "coat of arms of Austria" was valued at only 40 thalers. Also traditionally the Queen was depited to the right and the King to the left, and not like in the description of the pendant, which finds confirmation in Sigismund and Constance's portraiture, as well as location of the royal stalls in the Cathedral of Saint John in Warsaw. The inventory also includes: A necklace of 22 parts, among which 11 with a diamond in a middle, 3 square cut, 3 triangle cut, and set with two pearls. Another 11 parts in which a Lion's head in the center having a pearl in its mouth, four diamonds and four pearls set around it. All with a pendant with sixty two cut diamonds, and on top of a Lion's head and six hanging pearls, a gift from the Queen to the Princess, valued at 80,000 thalers; A pendant in which a Lion with three crowns in the shape of the Swedish coat of arms with twenty-six different diamonds, and three hanging pearls, valued at 150 thalers and A pendant in which a white Eagle with a large ruby on the chest, three small ruby parts, and three large pearls, valued at 700 thalers. The inventory also lists A white Eagle, having a coat of arms on his cheast at which two rubies, all set with diamonds, with three hanging pearls, valued at 1,200 thalers, which is most probably identical with "diamond eagle with rubies" of the House of Austria received in 1543 by Elizabeth of Austria (1526-1545) from Emperor Charles V on the occasion of her marriage with Sigismund II Augustus of Poland, and preserved in the treasury of the Munich Residence. Among renowned jewellers of the Vasas in the first half of the 17th century, that could create the work, were Mikołaj Siedmiradzki (ca. 1550-1630) from Lviv in today's Ukraine, who was in service of Sigismund III since 1604, and who in turn employed in his workshop Mikołaj Pasternakowicz and Zygmunt Frączkiewicz. There were also Jean Barbier from Lorraine, active in Kraków from about 1605, who moved to Gdańsk in 1625 and Beniamin Lanier (d. 1630) from Vitry-le-François in north-eastern France, who was active in Kraków from 1606, both court jewellers of Sigismund III. Jakub Burnett from Edinburgh who settled in Lviv in the first half of the 17th century was employed by Ladislaus IV. Members of the family also commissioned jewels abroad, like Prince John Casimir Vasa who in 1643 paid 9000 florins for jewels to Samuel von Sorgen from Vienna and 189 florins "For diamond heart to Mr Jakub jeweller". Anna Catherine Constance died childless in Cologne on 8 October 1651 and was buried in the church of the Jesuits in Düsseldorf. It is due to purely heraldic character of the jewel, high value of the material and new fashion for more simple jewels that the pendant was most probably melted down, possibly still in the 17th century.
Excerpt from Inventory of Jewels of Her Highness Duchess of Neuburg, Crown Princess of Poland (Spisanie Kleynotów Xiężney Iey Mości Neyburskiey, Królewney Polskiey) by Royal Chancery in Warsaw, 1645, Czartoryski Library in Kraków. Fragment describing Heraldic pendant of Anna Catherine Constance Vasa.
Heraldic pendant of Anna Catherine Constance Vasa, mid-1620s to 1638. Hypothetical reconstruction by Marcin Latka ©. All rights reserved.
See more pictures of Jewels of the Polish Vasas on Pinterest - Artinpl and Artinplhub
Tapestries with Story of Odysseus
During his stay in Antwerp in 1624, the Crown Prince of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa visited Peter Paul Rubens' workshop, admired Jan Brueghel the Elder's paintings and visited the famous art collection of Cornelis van der Geest. He also went to see the tapissierspand (Tapestry house), on the site of the current Bourla Theater, on September 24, 1624. We visited a house, writes Stefan Pac, in his diary where they sell beautiful and precious tapestries that are sent all over the world. A few days later, on October 5, 1624 Gaspard Nagodt, treasurer of the Prince of Poland, signed a contract with a Brussels' weaver Jacob Geubels the Younger for delivery of ten tapestries representing the Story of Odysseus (Ulysses) of six ells height each (Flemish ell was equal to about 70 cm or 27 inches), interwoven with gold and silver thread. The complete set comprised 594 ells and cost 19,008 florins. On October 12, 1624 another contract was signed for a series called "with greenery" i.e. verdure tapestries or "Landscapes and Bocages in fresco", for 9207 florins.
An Antwerp merchant, Jan Bierens, "agent and domestic of His Highness the Serene Prince Wladislaus Sigismundus, Prince of Poland and Sweden", oversaw the weaving of the tapestries of the Story of Odysseus and verdures that Geubels the Younger made in Brussels. A lawsuit brought by Geubels against Jan Bierens in December 1626 for payment, confirms that at least a part of the commissioned tapestries was ready by this date. Notations in the archives reveal the existence of the prince's agents, such as mentioned Jan Bierens and Georges Deschamps or the Frenchman Mathieu Rouault. They had to satisfy Ladislaus Sigismund's creditors and ensure that everything was executed and sent to Poland. Probably due to Prince's financial difficulties the whole set not executed till Geubels' death in 1629 and the commission was accomplished by an unknown workshop. It is uncertain when the Story of Odysseus and verdure tapestries were dispatched from Antwerp and when they arrived in Poland. Ladislaus Sigismund, the newly elected monarch of the Commonwealth as Ladislaus IV, wanted to have them before his coronation on February 6, 1633 in Kraków. By a notarial deed of January 12, 1632 we learn that Jan Bierens had received three chests containing approximately two hundred and fifty - three silver marcs from the hands of Francesco Gissa and Joannes Curius, one butler and the other secretary of Abbot Mikołaj Wojciech Gniewosz (d. 1654), Ambassador of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. The Antwerp merchant had given them two thousand three hundred and ten rixdales as a pledge and had promised to send the precious delivery to Gdańsk to the address of Abraham Pels. In the letter from September 15, 1632 Ladislaus IV asked Christian IV of Denmark to release his tapestries from customs (Rkps Riqsarkivet, Polen A. I, 3). According to François Mols, a number of tapestry cartoons by Jacob Jordaens with the date 1620 were sold at Antwerp in 1774. It is belived that these tapestries were inspired by knowledge of Primaticcio's lost frescoes of the same subject at Fontainebleau. A document from May 15, 1656 in the archives of Antwerp in which Jacob Geubels, son of Jacob Geubels the Younger, had undertaken to weave, tapestries representing the Story of Ulysses after cartoons by Jordaens, confirms that the series were made to his design. Lavish tapestries "hang up in foreign style" among "golden Netherlandish arts" are mentioned in Adam Jarzębski's "Short Description of Warsaw" (The Main Road, or a Short Description of Warsaw) from 1643, as adorning Ladislaus IV's Palace Villa Regia in Warsaw (1950-1956). The series was inherited by Ladislaus' brother John II Casimir, who took them to France after his abdication in 1668 and was sold on auction in Paris in 1673 to the agent of the Charles I Louis, Elector Palatine for 12,000 French pounds (position 728 of the inventory).
Tapestry with Odysseus threatening Circe by workshop of Jacob Geubels II after cartoon by Jacob Jordaens, 1624-1632, with coat of arms of the Crown Prince of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa, the mark of the city of Brussels B B, weaver's monogram and signature IACO GEVBELS. Hypothetical reconstruction by Marcin Latka ©. All rights reserved.
See more pictures of the Villa Regia Palace in Warsaw on Pinterest - Artinpl and Artinplhub
|
Artinpl is individual, educational project to share knowledge about works of art nowadays and in the past in Poland.
If you like this project, please support it with any amount so it could develop. © Marcin Latka Categories
All
Archives
April 2023
|