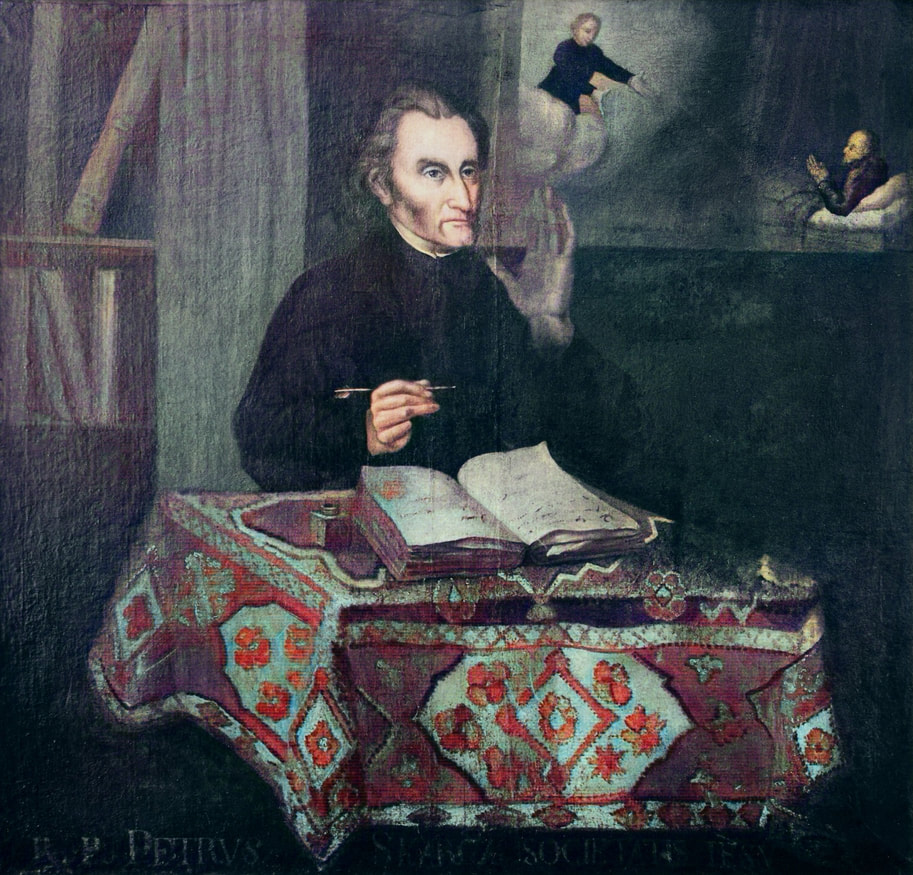
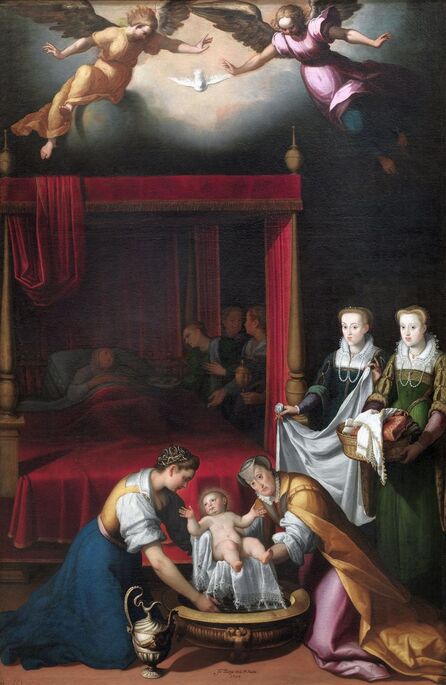
|
The successors of the Jagiellons, the Vasas, shifted the focus of artistic patronage north, supporting Flemish and Dutch painters and acquiring luxury goods and art in the Netherlands, but Italian influences were still strong. "The Italian nation, from which we received the religion, literature, good arts, and the equipment of the more elegant life of the Sarmatians, is the most deserved" (Natio Jtalica optime de nobis merita est, a qua religionem, literas, bonas artes, ac elegatioris vitae apparatum Sarmatae accepimus), wrote in a letter of 1601 the Grand Chancellor Jan Sariusz Zamoyski (1542-1605) to Pope Clement VIII.
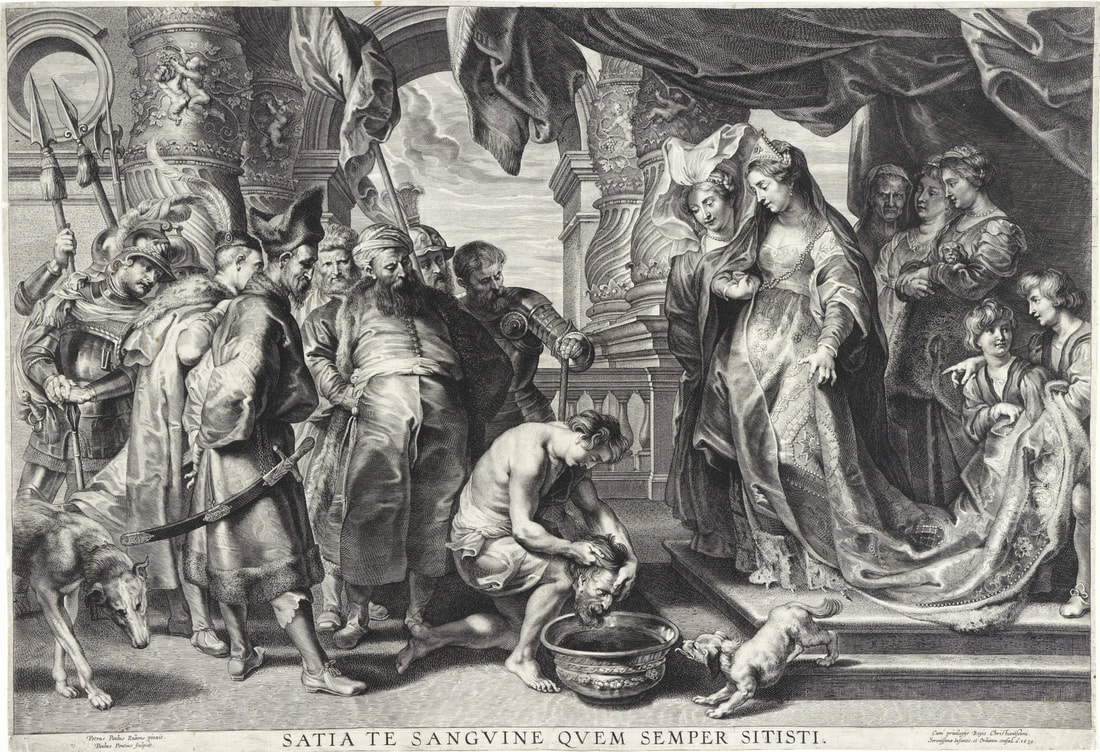
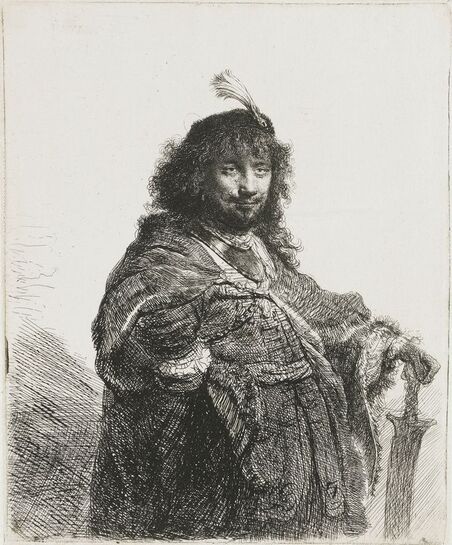
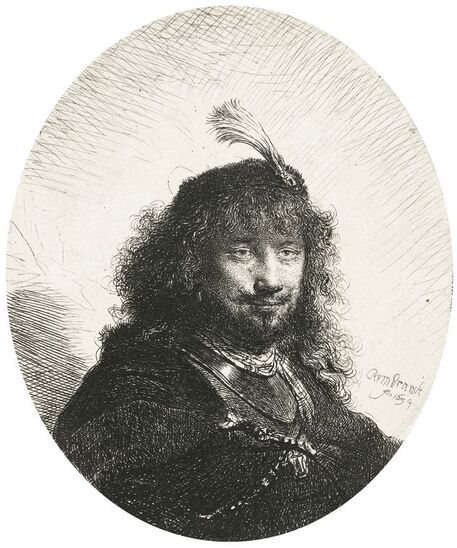
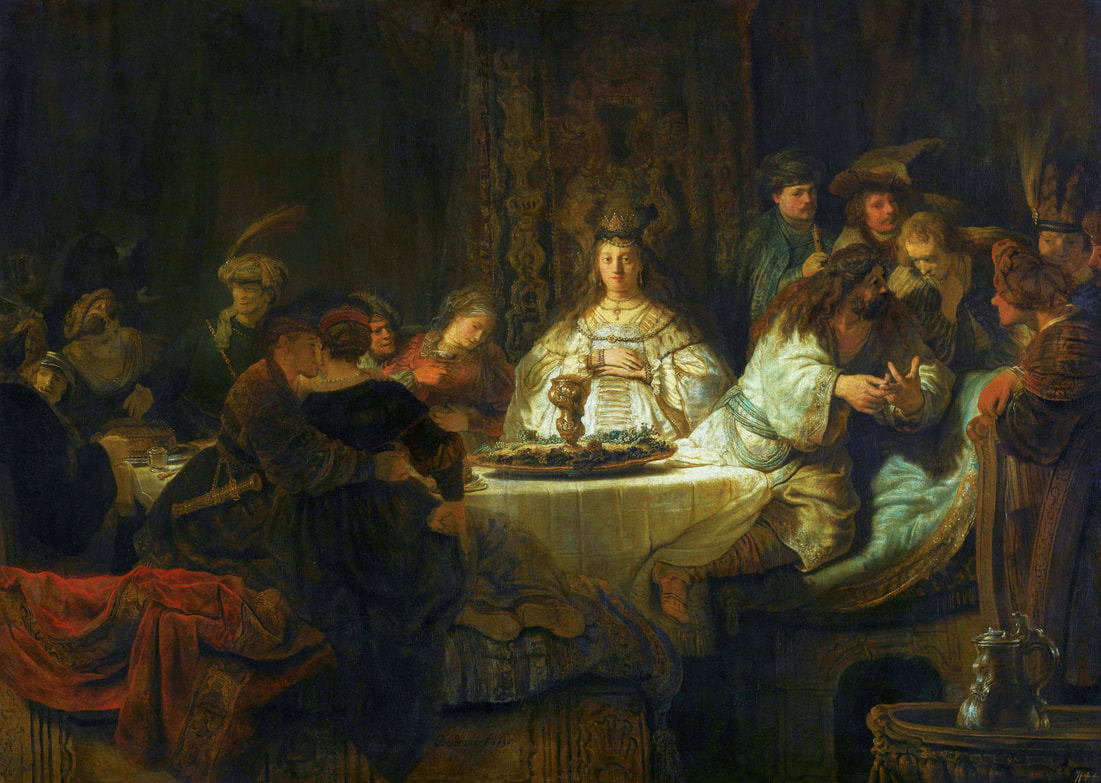
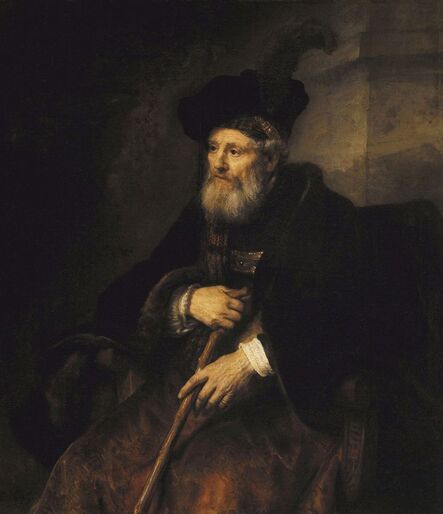
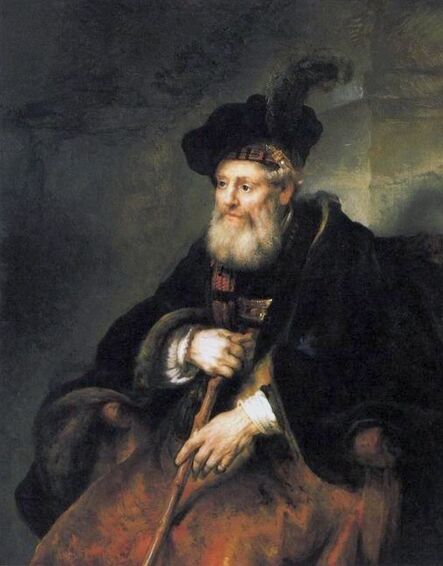
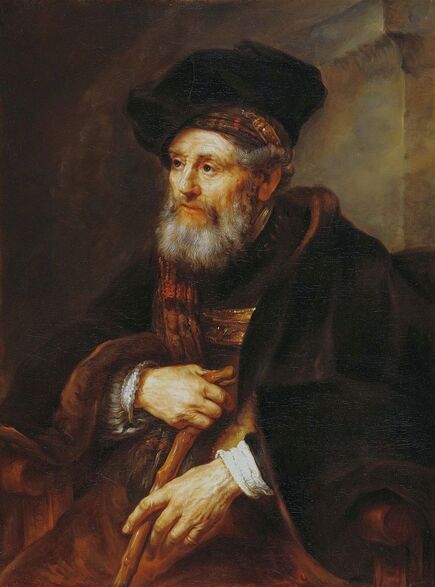
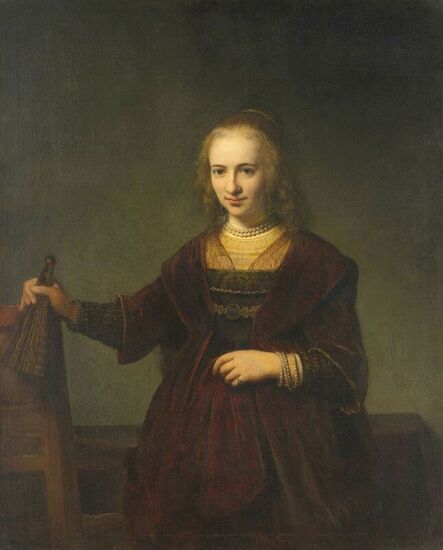
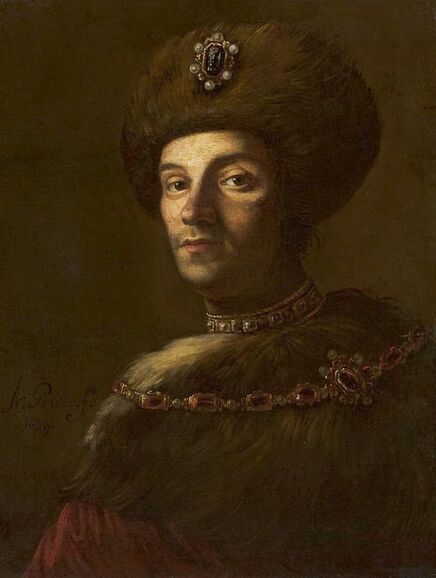
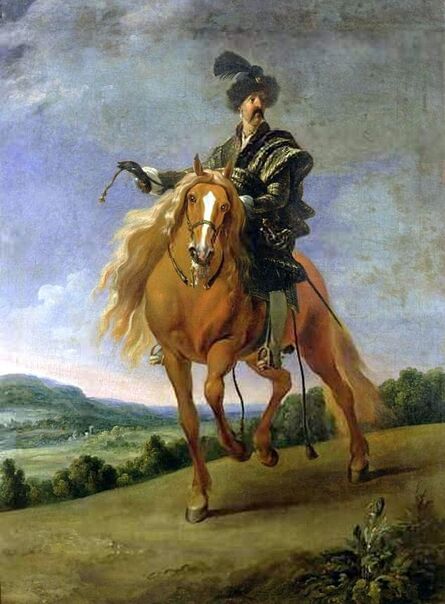
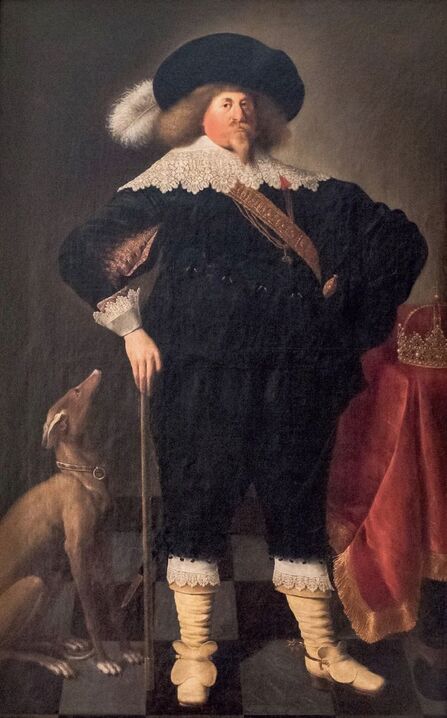
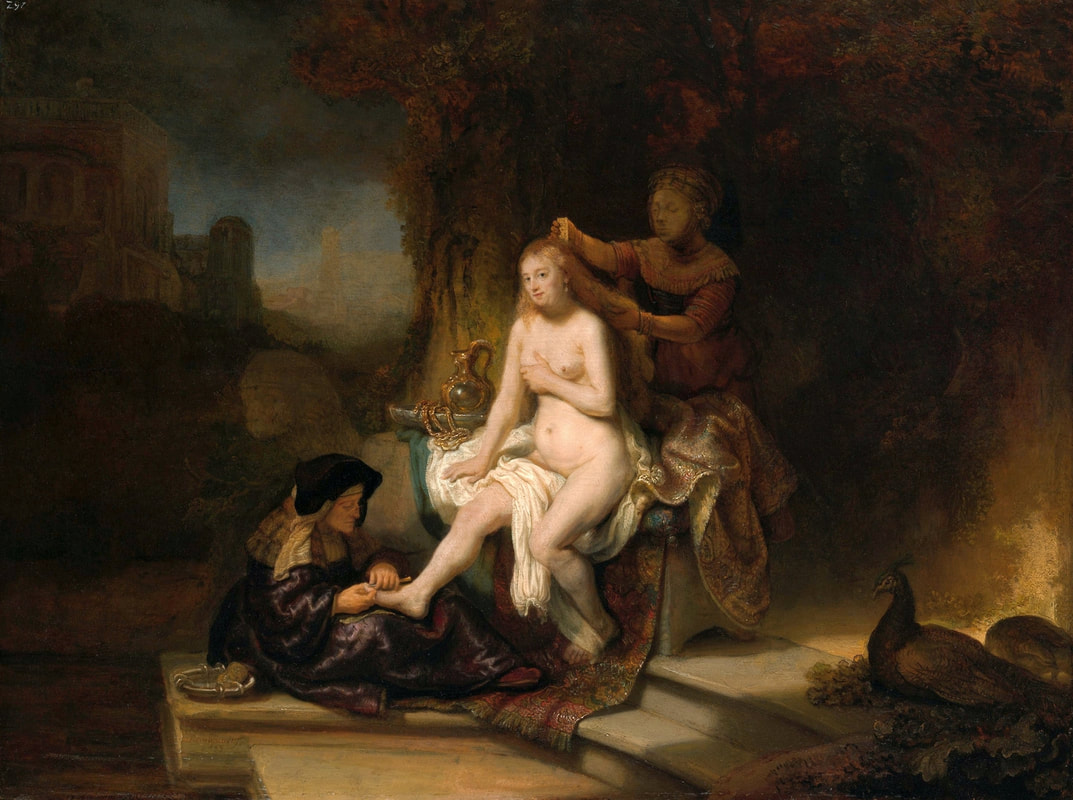
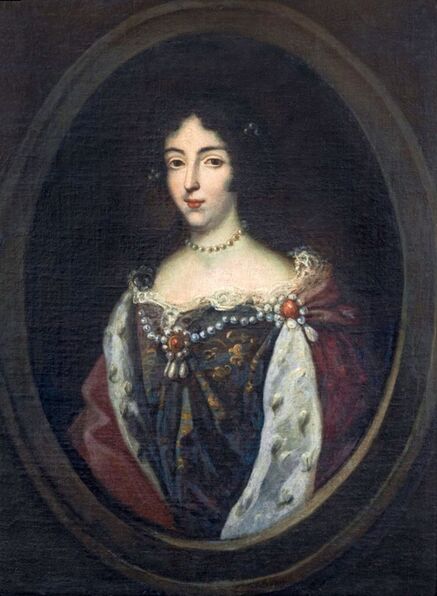
The great influences of Italians and Italian culture in Poland-Lithuania have led to increased interest in the Polish-Lithuanian royal elections on the Italian peninsula, which is now largely forgotten. In 1573, Alfonso II d'Este, Duke of Ferrara dispatched the celebrated poet Giovanni Battista Guarini to Poland-Lithuania, to perorate his cause before the Diet (Sejm). Guarini failed in his mission and on his return to Ferrara was criticized for diplomatic ineptitude (after "Politics and Diplomacy in Early Modern Italy ..." by Daniela Frigo, p. 167). Other important Italian candidates in the first free election of 1573 also included Alessandro Farnese, Duke of Parma and Piacenza and Francesco I de' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany. The latter was also considered in the third free election of 1587, when son of Catherine Jagiellon Sigismund Vasa was elected, and he had strong support. Simone Gengi of Urbino, an architect and military engineer in the service of the late King Stephen Bathory, believed that among the many candidates put forward, he had a good chance of success (...et quanto ella per parere de più principali potessi più d'ogn'altro aspirare a questa corona), as he states in a letter dated January 7, 1587 from Riga (dal nuovo forte di fiume Dvina), addressed to the Grand Duke and his ambassador to the imperial court in Prague Orazio Urbani. He asked to the director of the royal post of Poland-Lithuania Sebastiano Montelupi to spare no effort and money so that the courier with letters to the Grand Duke would reach Vienna as soon as possible. It was Montelupi, who in a letter of December 18, 1586 informed the court in Ferrara about the death of Bathory. He recommended hiring a special messenger dressed in German clothes and fluent in German. From Vienna, through the Tuscan ambassador, the letters were to be sent to Florence. The candidature of the Florentine ruler was supported, among others, by Stanisław Karnkowski, Archbishop of Gniezno, Olbracht Łaski, voivode of Sieradz and by Chancellor Jan Zamoyski. At the beginning of February 1587, they sent an embassy to Florence, which included, among others, the brother-in-law of the voivode of Sieradz, Wincenty de Seve, provost of Łask, who was ordered to invite the Grand Duke to take part in the upcoming election. His candidature was supposedly presented in the Sandomierz voivodship by Chancellor Zamoyski himself, who, according to Urbani, sincerely favored Francesco. According to the Tuscan diplomat, the Dukes of Ferrara and Parma had little chance in the upcoming election as petty and insignificant rulers. The fact that the Florentine milieu in Kraków was also keenly interested in the upcoming election is evidenced by a letter of January 7, 1587, from Filippo Talducci, addressed to Marco Argimoni in Florence, in which, listing the candidates for the Polish Crown, he mentioned the Grand Duke of Tuscany, who, if he wanted to mobilize appropriate financial resources, would have a chance to be elected (il figliuolo del Re di Svetia, il Cardinale Batori, il Duca di Ferrara et il nostro Serenissimo Gran Duca, il quale se volessi attendere con li mezzi sapete, sarebbe cosa riuscibile. Dio lasci seguire il meglio). The aspirations to the Polish crown of the Dukes of Ferrara, Parma and even Savoy are mentioned in the correspondence of the Tuscan ambassadors in Madrid, Bongianni Gianfighacci and Vincenzo Alamanni (letters of February 21, March 27 and April 4, 1587) (after "Dwór medycejski i Habsburgowie ..." by Danuta Quirini-Popławska, pp. 123-126). The portrait of the Grand Duke, today kept in Wilanów Palace (Wil.1494), could refer to this candidacy. It most likely comes from a series of similar small portraits from Ros near Grodno in Belarus, attributed to the 18th century Italian school. This "portrait of a man" is considered a copy of Angelo Bronzino, but it closely resembles the portraits of Francesco made by his court painter Alessandro Allori (1535-1607). Triumphal arches for King Sigismund III Vasa's entry ceremonies into Kraków in 1587 were to be dressed in images of the Jagiellons as the ancestors of the new king. As their faces were almost totally unknown because of their antiquity (Effigies enim eorum, cum plerisque fere vetustate ignotae essent), the aforementioned Chancellor Zamoyski had them extracted from the oldest monuments (ex antiquissimis quibuscumque monumentis eruerat) and provided with them appropriate inscriptions. These inscriptions were printed separately and some are quoted by David Chytraeus in his Chronicon Saxoniae ..., published in Leipzig in 1593 (after "Listy Annibala z Kapui ..." by Aleksander Przezdziecki, p. 107). It is thanks to the efforts of later generations that the identity of many important personalities has been preserved. They added inscriptions to the paintings, created copies or published them as engravings. In the former territories of the Commonwealth, this continuity has been dramatically interrupted by wars and invasions. Italian costumes, food, gardens, music, language and books, paintings, crafts and dances were most popular in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, even the hours were still counted in Italian style under the reign of the elected monarch Sigismund III Vasa - 24 hours from sunset one day to sunset the next day. In two letters, probably from 1614 and 1615, Sigismund III expressed his gratitude to the nuncio Claudio Rangoni for the paintings he sent from Italy. Two years later, in 1617 and the following year, Rangoni again sent two paintings and "some [other] paintings" (alcuni quadri) to the king, then to the queen. According to the nuncio, the king loved paintings and willingly purchased the works of the best masters and demonstrated a passion for expensive jewelry and tapestries. The king was not only an art lover, but also an amateur artist. What is very meaningful is that during the Zebrzydowski rebellion in 1606, he was mocked by his opponents as a "Venecist/Venetian" (wenecysta), who prefers to "ride with the Italians in a gondola, paying richly for their folly, instead of mounting a horse in armor" (after "Odrodzenie w Polsce ...", Volume 5, ed. Bogusław Leśnodorski, p. 358). In his "Sejm Sermons" (Kazania sejmowe), published in 1597 in Kraków, Piotr Skarga, the court preacher of Sigismund III, metaphorically appealed to parliament not to further restrict the king's power in favor of a more Habsburg absolutism: "Good Lords! Do not make the kingdom of Poland a [free] city of the German Reich, do not make a painted king as in Venice. Because you don't have Venetian mindset and you don't live in one city" (Sermon 6). He also scolded the great wealth and luxurious life of the nobility, their expensive clothes of velvet and silk, cellars full of wine, gilded carriages: "See what abundance and riches and joyful life this mother has brought you, and how she has gilded you and granted so much that you have enough money, plenty of food, clothes so expensive, such crowds of servants, horses, carts; so much money and income multiplied everywhere" (Sermon 2), and neglecting the defence of the Commonwealth: "No one living in abundance like this watches the castles and city walls" (Sermon 8). As in the previous epoch, in the 17th century, foreign costumes were still very popular among the nobility. Franciszek Siarczyński in his "Image of the reign of Sigismund III ...", published in Poznań in 1843, claims that he "saw paintings in Kraków in which Zebrzydowski looked like a Sultan, Zborowski like a Roman knight, in Krosno Stanisław Oświęcim, has all the clothes of a Swede, Tarnowski of an armed Greek, etc. Niesiecki described the portrait in Topolno of Krzysztof Konarski, from 1589, in guise of a German knight". A nobleman in Spanish parade outfit, who took part in Prince Ladislaus Vasa's expedition to Moscow in 1612, was ridiculed by other soldiers: "[go back] to Salamanca, to Compostela, Mr. Spaniard" (after "Obraz wieku panowania Zygmunta III ...", p. 73-74). Members of different ethnic groups of Sarmatia traveled to different Western European countries, primarily for doing business, as the country was a major supplier of many important goods, but also to pursue their studies, for a better climate or for health, to make a pilgrimage or simply to visit other countries. After completing studies at the Kraków or Vilnius Academy or other important schools of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, it was customary to continue studies abroad, in Padua, Bologna, Leuven, Leiden or Ingolstadt, among others. Abroad, Sarmatians frequently adopted local costumes, which is confirmed by numerous sources, but some, decided to travel in their traditional costumes - usually a crimson żupan, delia coat and kolpak hat. These costumes were frequently captured by different artists from Italy, Flanders, the Netherlands and France in their works. Some foreigners were also depicted in Sarmatian costumes, such as the painter Martin Ryckaert in his magnificent portrait painted around 1631 by Anthony van Dyck (Prado Museum in Madrid). Nicolas Lagneau (National Library of France), Stefano della Bella, Guercino (Nationalmuseum in Stockholm) and Rembrandt left numerous drawings and engravings representing characters dressed in typical Sarmatian costumes. Such costumes can also be seen in the paintings by Mattia Preti (Capitoline Museums in Rome), Giuseppe Maria Galeppini (private collection in Sweden) and David Teniers the Younger (Louvre and Neuburg State Gallery). Johann Heinrich Schönfeld painted around 1653 his "Sarmatians at the tomb of Ovid" (Museum of Fine Arts in Budapest and Royal Collection), which could be an illustration of one of the many Renaissance accounts of tomb-finding expeditions, such as that described by Stanisław Sarnicki in 1587 (Annales, sive de origine et rebus gestis Polonorum et Lituanorum, p. 73), and Philips Wouwerman produced between 1656 and 1668 a painting representing the Polish-Lithuanian cavalry fighting the army of the "Brigand of Europe" during the Deluge (National Gallery, London). The preserved poetry, created before the Deluge, confirms the image of a wealthy Commonwealth, concerned with various social problems, and not a country ravaged by constant wars and invasions of neighbors, fighting for its independence. The collection of manuscripts by Polish poets, mainly members of the community of Polish Brethren, compiled in 1675 by Jakub Teodor Trembecki (1643-1719/1720), published in 1910-1911 by Aleksander Brückner ("Jakuba Teodora Trembeckiego wirydarz poetycki", volume I), includes the following poems by unknown poets: 27. On an Italian feast, 28. Polish prosperity, 29. Polish playfulness, 165. On foreign costumes in Poland ("Nowadays, you can barely recognize Poles, there are Italians, French, in great number at the courts"); by Jan Gawiński of Wielomowic (ca. 1622 - ca. 1684): 215. On Venus ("Displeased Venus makes no one rich; She has a naked son; pleased, when you pay her"), 262. A girl without shame ("And your beautiful nature and wonderful senses, my Lady, have been spoiled by these oddities of your costumes"), 263. Today's wives ("Among the pagans, wives died for their husbands, and today they would dance on his grave"), 325. The concept of a Ruthenian painter under the painting of Judith beheading Holofernes; by Hieronim Morsztyn (ca. 1581 - ca. 1622): 368. Court disease ("Syphilis, ulcers, buboes, were brought from France and they were accommodated in a brothel"), by Jan Andrzej Morsztyn (1621-1693): 471. To the Italian ("You, Italian, sell Venetian products and you profit greatly from it") and by Daniel Naborowski (1573-1640): 617. To one hermaphrodite ("You have a female form but you have a prick, so you are both [woman and man]"), 643. On nude images in the bathhouse ("It's decent to wash naked in the bathhouse"). For his obscene epigram about female breasts, Hieronim Morsztyn most likely took inspiration from an Italian model: "Cazzo [an Italian vulgarism for phallus], stuck in the crotch, couldn't do its job" (Cazzo w kroku pojmane nie mogło się sprawić) (after "Poeta i piersi" by Radosław Grześkowiak, p. 18). The French-born queen Marie Louise Gonzaga is generally considered to have introduced more daring, not to say inappropriate, female costumes to Poland, mainly due to the marked contrast between effigies of the queen and portraits of her predecessors from the Habsburg dynasty - Cecilia Renata of Austria, Constance of Austria and Anna of Austria. However, many authors seem to forget that these queens preferred the fashion of the imperial or Spanish court which did not allow bare breasts described by Wacław Potocki (1621-1696). The popularity of daring French, Venetian and Florentine costumes was confirmed much earlier by Piotr Zbylitowski in his "Reprimand of Women's Extravagant Attire" (Przygana wymyślnym strojom białogłowskim), published in Kraków in 1600, and Italian fashion dominated at the court of the Jagiellons. Although in fact the fashion introduced by Marie Louise "revealed" more to the public gaze. In a letter from Gdańsk dated February 15, 1646 addressed to Cardinal Jules Mazarin (1602-1661), the queen wrote that "the Polish ladies are dressed how people dressed in France fifteen years ago: hastily sewn dresses, with very short waists and very wide sleeves. They all rush as fast as they can to imitate our clothes. Their materials are extremely expensive and covered with precious stones. The daughter-in-law of Great Crown Chancellor [Katarzyna Ossolińska née Działyńska] changes her outfit every day". The French courtier Jean Le Laboureur (1621-1675) also reports that many members of the nobility dressed in French style for the queen's reception. Szymon Starowolski (1588-1656) in his "Reform of Polish Habits" (Reformacya Obyczaiow Polskich), published before 1653, laments that "almost all of Poland became French, and probably all stricken with the French disease [syphilis]" (wszytka już prawie Polska sfrancuziała, a podobno sfrancowaciała) and Krzysztof Opaliński (1609-1655) could not refrain from ridiculing exaggerated costumes and excessive use of cosmetics by the ladies in his Liryki (donkey milk to brighten the complexion, roasted almonds to darken the eyebrows, crushed corals with sea foam-sepiolite as a powder for the cheeks). "The rich ladies here are very fond of sumptuous clothes, so they order various delicate works from the nuns and pay them well", wrote one of the French nuns of the Visitation of the Virgin Mary, who visited Poland in 1654. She also adds that she saw in several monasteries wonderful silver, gold and silk embroideries, most perfectly finished, decorated with jewels with great splendor, sometimes even luxury. Queen Marie Louise, who had just left Paris, wrote in the mentioned letter to Cardinal Mazarin that: "The splendor is extraordinary [...] In short, I had no idea, despite the best thoughts that I had created to take courage during the journey. Everything exceeded my expectations, so you will have no doubt that I am very satisfied" (after "Studya historyczne" by Wiktor Czermak, p. 75-76, 98-99, 101-102, 123-125, 127). Sometimes foreign ladies also adopted something from Polish fashion. A Frenchwoman and lady-in-waiting to the queen, Marie Casimire de La Grange d'Arquien, confided in one of her letters to Jan Sobieski that she used Polish caps instead of French hairstyles and that she was already tired of the bra she had been wearing so far, and she ordered a new one to be made: "it is more Crimean style, fastened to the side" (il est un peu z krymska zapięty na bakier) with Polish words in a French letter. Although her new garment was not purely Polish, because the word "Crimean style" also indicates the original Tatar pattern. Ladislaus IV purchased and ordered many luxury fabrics from Italian merchants for himself and the queen. In 1637, the sum of 11,281 zlotys was paid to the Kraków merchant Wincenty Barsotti for silk and bed linen intended for the king's wedding and a year later, in September 1638, Ladislaus purchased, through Hieronim Pinocci in Italy, "five pieces of gold cloth" for an amount of 7,265 zlotys, and a few years later, in November 1645, he again owed 4,000 thalers to Pinocci for fabrics brought from Venice and Vienna. According to the king's letter to his treasurer dated December 7, 1634, when the envoy of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth went to Moscow, there was in his entourage a courtier with a royal commission to purchase "various and fine furs" for 20,000 zlotys. According to the registers of 1652-1653, John Casimir purchased satin, velvet, fine silk, gold lace, ribbons, etc., as well as lynx, ermine, sable and dormouse fur, mainly from Jews. In 1667, Miss Ruffini, apparently Italian or of Italian descent as her surname indicates, was paid between 2,318 and 2,528 zlotys per month for the needs of the queen's kitchen. While according to the list of debts of Ladislaus IV, he owed 39,412 zlotys for Italian, French and Hungarian wines imported from Vienna in the years 1636-1639, and 90,000 zlotys to a jeweler and John Casimir paid to the watchmaker approximately 17,500 zlotys between 1652-1653, approximately 13,000 zlotys for his clothes and 74,726 zlotys in total for the beautiful clothes for his servants, the purchase and the execution of several paintings (to Salomon Schindler for the paintings, to Father Karwat for the paintings painted in Rome, to a painter from Elbląg) resulted in an expenditure of only 2,026 zlotys between 1652 and 1653. This lower value does not mean that they were not splendid paintings. We should remember that "Old Masters" became such much later and eminent painters for whose works some are today willing to pay a fortune, sometimes found it difficult to sell their works during their lifetime or their paintings were undervalued, as in the case of El Greco, an eminent Greek-Spanish painter trained in Venice. El Greco received only 350 ducats for the Disrobing of Christ (El Expolio), completed in the spring of 1579 for the high altar of the sacristy of the cathedral of Toledo, although his own expert had valued it at 950 and the Martyrdom of Saint Maurice, painted for El Escorial in 1580 did not satisfy King Philip II. El Greco's only masterpiece in Poland, probably from the Lubomirski collection, was discovered by chance in 1964 in the parish church of Kosów Lacki, east of Warsaw, and was therefore forgotten for several centuries. It cannot be excluded that its "Venetian" style was recognized by the young Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski (1616-1667) and that it was purchased during his visit to Spain in 1634. Nuncio Mario Filonardi (1594-1644) in a letter dated July 11, 1637 to Cardinal Bartolini mentions that to decorate his palace in Ujazdów, Ladislaus IV imported from Florence a large number of bronze statues, marble tables and statuettes. These sculptures were to cost 7,000 thalers, and their installation was carried out by the architect Agostino Locci, trained in Rome. The name of the author is not mentioned, but the main sculptor active at that time in Florence was Pietro Tacca (1577-1640), who worked for Ladislaus' cousins from the Medici family and created equestrian bronze statues of king's uncle King Philip III of Spain and his son of Philip IV, both in Madrid. In 1625, during his visit to Florence or Livorno, from where the prince was to embark for Genoa, Ladislaus also had the opportunity to personally meet the sculptor. There is no trace of these statues anywhere, indicating that they were probably melted down by the invaders to make cannons. Although the land connection with Italy had been used frequently since the Middle Ages, since the end of the 16th century maritime trade relations also intensified and ships from Gdańsk transported grain and other goods to Italy and brought back luxury objects and works of art. Charles Ogier (1595-1654), secretary of the French envoy Claude de Mesmes, Count of Avaux, who visited Poland between 1635 and 1636, wrote in his diary that in the house of a Gdańsk patrician, Karl Schwartzwald, he admired a silver horse, the work of an eminent Florentine sculptor, whom he claimed to be the creator of the equestrian statue located in Paris, on the Pont Neuf. The bronze equestrian statue of Henri IV (1553-1610) on the Pont Neuf was erected in 1614 (demolished in 1792 during the French Revolution), commissioned by Queen Marie de Medici in her native Florence in 1604. The originally commissioned artist, Giambologna, died before its completion, and Pietro Tacca took over the commission. They must have relied on drawings or paintings, sent from France, depicting the king to recreate his features. Schwartzwald also owned a statue of a swimming boy, sculpted in silver after a wax original by Michelangelo and paintings brought from Italy, such as Saint Mary Magdalene "completely naked" and Judith and her servant with the head of Holofernes. In the house of Elisabeth Giese, the widow of mayor Arnold von Holten, in April 1636, the Frenchman saw portraits of Luther and Melanchthon by Lucas Cranach and portraits of the Italian poets Pietro Bembo (1470-1547) and Jacopo Sannazaro (1458-1530), both most likely by Titan, as well as smaller portrait of Erasmus of Rotterdam. He also admired a picture "painted in England" (compare "Życie codzienne w Gdańsku ..." by Maria Bogucka, p. 108). In the house of Johann Ernst Schröer he saw an excellent painting by Albrecht Dürer of a man holding paper in his hand and four paintings by Cranach - portraits of Erasmus, Luther and Melanchthon, and a fourth, slightly larger, depicting Venus with Cupid stealing honey. "This Venus represents a certain mistress of the Saxon Elector Frederick, whom he placed in a rather deserted place among the rocks and forests, and after whose loss he never found peace. These rocks and the castle are represented in this painting signed: Kein Lieb ohn Leid [We have no love without suffering]" (Tres alias habet Lucae Kranic, qui fuit præconsul Wittenbergensis: Erasmi, Lutheri et Melanchtonis; sunt illæ ad vivum expressæ. Habet et quartam maioris paulo voluminis, nam aliæ pedem non excedunt. Venus est nuda, quæ sinistra manu elatoque brachio ramum arboris prehendit auditque Cupidinem suum, qui flens de apibus conqueritur, quæ illum pupugerunt [...] Exprimit illa Venus amasiam quandam Frederici electoris Saxoniæ, quam in loco satis solitario inter rupes ac silvas collocaverat, quam cum deperiret, animus illi conquiescebat nunquam: rupes illæ et castellum in tabula expressæ sunt cum hac inscriptione: Kein Lieb ohn Leid, after "Biblioteka gdańska: Seria źródeł historycznych", Volume 1, 1953, p. 124-125). Besides the well-known large brick residences of Warsaw, Kraków, Vilnius and other major cities, the Polish-Lithuanian Vasas owned several large wooden palaces of which nothing survives today. The most important was Nieporęt, near Warsaw. The palace was built by Sigismund III and later belonged to John Casimir. It had a large courtyard, a beautiful garden and a magnificent chapel. Le Laboureur praises the splendid carpentry work of the building and writes that it had a large number of comfortable rooms, all very beautiful and that it leaves nothing to be desired except that it was made of a more durable material. There were also several wooden mansions built in Warsaw and other cities for different family members and several hunting palaces, such as the one in Białowieża Forest, built before 1639 to the design by Giovanni Battista Gisleni. The palaces and manors of numerous nobles of the Republic of nobles were filles with portraits. Adam Jarzębski noticed in the Kazanowski (Radziejowski) Palace in Warsaw: "Likenesses of different men, / Both monarchs and hetmans", Wespazjan Kochowski wrote about nobles: "He decorated the walls with pictures of his ancestors" and Wacław Potocki concluded: "Darkened images of the ancients mean / Your ancestors ... / Weak proof of nobility a painting" (after "Życie codzienne w Warszawie za Wazów" by Jerzy Lileyko, p. 186). The portraits of the monarchs in the richly decorated royal rooms of the Jasna Góra Monastery burned during the great fire on July 16, 1690 (after "Wiadomość historyczna o starożytnym obrazie Boga-rodzicy ...", p. 71). Baroque poetry also referred to the position of women in society and the value of paintings. "If there were more such [women] in Poland, much more would be achieved!" (O gdyby takich w Polszcze było siła, Daleko by się więcej dokazało!), comments Wacław Potocki in his poem "Judith" (Judyta) after the defeat of the Commonwealth forces at the Battle of Pyliavtsi in September 1648, praising the wisdom, strength and courage of women and criticizing the ineptitude of male leaders. "Why do you refuse such a trivial thing?" (Czemuż mi rzeczy tak lichej żałujesz?), asks the poet, most likely Jan Andrzej Morsztyn (1621-1693) in his "On the Refused Image" (Na obraz odmowiony), commenting on his beloved's refusal to offer him her portrait. This passage confirms that painted effigies were popular and inexpensive. An anecdote from the beginning of the 17th century from an inn in Gdańsk refers to painted effigies commissioned by nobles - a certain nobleman sent a painter to his friend's house to make a portrait of his wife, famous for her beauty, but the husband chased away the painter saying that if the noble liked the portrait, he would also want to see the original every day (after "Mówią wieki", Volume 19, 1976, p. 13). Before 1623, Krystyna Lubomirska (d. 1645), whose famous full-length portrait is in the Wilanów Palace, sent to her husband, hetman Stanisław Koniecpolski (1591-1646), held prisoner in the Yedikule Fortress in Istanbul, a portrait of his son Alexander (1620-1659), born when his father was held captive by Ottoman forces (after "Historyczne pamiątki ..." by Tomasz Święcki, Volume 1, p. 111). The inventories of the royal collections of the Jagiellons and the Vasas of Poland-Lithuania have not been preserved in their entirety, but information preserved in the townspeople's wills, as well as in the inventories of their property, and the patronage of their successors gives an impression of quality of their collections, when the country was one of the leading countries of Europe during the Renaissance and the beginning of the Baroque. Poland-Lithuania was also one of the richest on the continent. Even the lower strata of the Commonwealth's nobility owned the finest items produced in the best local and foreign workshops - such as the silver lavabo with the Rogala coat of arms of Jan Loka, starost of Borzechowo, created in Augsburg by Balthasar Grill, hidden in the ground during the Deluge (1655-1660). The attitude towards art in Brandenburg, which was one of the invaders during the Deluge, and at the royal court of Poland-Lithuania is best illustrated by the report of Andrzej Köhne-Jaski, a Calvinist amber merchant from Gdańsk, also active in diplomacy as envoy of Sigismund III and the electors of Brandenburg. Around 1616, Jaski commented on the destruction of paintings in Brandenburg: "I didn't pay much attention to it this summer, but I remember the magnificent paintings by Albrecht Dürer and Lucas [Cranach] hanging in churches. I wish HM [His Majesty] had such [paintings]" (Ich habe dießen sommer so genaue achtung nicht darauf gegeben, aber erinnere mich, das noch schöne bilder von Albrecht Dührer und Lucas vorhanden und in der kirchen hengen. Wolte wünschen, das EM solche hätten) (after "Das Leben am Hof ..." by Walter Leitsch, p. 2358). At that time, Italian and Flemish art, not German, dominated the royal court. Patricians of the royal city of Kraków, many of whom were of Italian descent as their names suggest, owned many paintings, sometimes by excellent foreign masters, as evidenced by the extract from the will of Jan Paviola (Joannes Benedictus Savioly, d. 1653), councilor of Kraków. The list and estimate of paintings, appraised by the elders of the painters guild Marcin Klossowski and Marcin Blechowski, painters from Kraków, include many portraits and paintings which could be from Italian, Venetian, Flemish, Dutch and German schools, but the author and the origin was not indicated. The word landscape - lanczaft in Old Polish, was used in a very similar form to Landschaft in German and landschap in Netherlandish, which could indicate that these paintings were Dutch/Flemish or German. "Picture of late King Ladislaus IV; Queen Her Highness Louise Marie; Image of the imperial son; his sister; the late Lord of Kraków Koniecpolski; [Picture] in which a crowned woman gives a mug to a soldier; Four pictures, representing the four parts of the world with people; four, depicting day and night, one damaged; three representing a part of the world; Landscape with fishing; Image of Bethsheba: bathing; [Picture] depicting the destruction of the city, with the army below fighting; Four pictures of Joseph's story, very demaged, among them one is whole; Landscape with highwaymen; Judith's painting, broken; female cook with venison; 12 images of Roman Emperors; two on which fish are painted, without frames; Image of King Ladislaus IV in elk skin; Judicium Parisis [Judgement of Paris] with three goddesses; Four images representing the parts of the year with maidens; Portrait of His Majesty King Ladislaus IV in a red coat; Queen Her Highness Cecilia [Renata]; King His Highness Sigismund III; Frederick Henry, Prince of Auraniae [Orange]; King Christian of Denmark; Duke of Saxony; Emperor His Highness Ferdinand III; His wife the empress; Leopold; the old empress; An image of a man with a mug and a scull; cavaliers playing cards with a lady; Orpheus with animals; Landscape with people eating in summer; robbers, on copper, in frame; on copper, without figures, with a column or pillar; Painting on copper, three Kings [Adoration of the Magi]; washing the feet of the apostles; Picture of a garden, on copper; Judith, on copper; Esther, on copper; on copper, Melchisedech offering bread and wine to Daniel; Saint Peter leaving the prison with the angel; the Samaritan on copper; Saint Francis; Five pictures with sea foam on gumi, made with paints on parchment; Picture on panel, a scull". This long and rich list of paintings was made on February 15, 1655. A few months later, in July 1655, two Swedish armies entered Greater Poland, one of the wealthiest and most developed provinces of the Commonwealth, which for centuries had been unaffected by any military conflict. They were soon followed by other countries and the invaders were not as sensitive to art as the patricians of the Commonwealth, precious materials, copper, silver and especially gold were the most important. Paul Würtz (1612-1676), governor of Kraków during Swedish-Transilvanian occupation of the city between 1655-1657 ordered wrought iron bars, marbles, precious wainscoting and floors to be ripped out, and silver sarcophagus of Saint Stanislaus, created in Augsburg in 1630 (founded by Sigismund III), silver altar of Saint Stanislaus, created in Nuremberg in 1512 (founded by Sigismund I), as well as statues and candlesticks from the Wawel Cathedral to be melted (after "Elity polityczne Rzeczypospolitej ..." by Marceli Kosman, p. 323). The true origin of looted items was often concealed or erased like coat of arms on the marble lions in front of Drottningholm Palace near Stockholm. "The day before yesterday, news came to us that they had sacked all the churches of Kraków, and that only one chalice had been saved from which some monks were saying mass in secret", reported in a letter of December 4, 1655 from Głogów Pierre des Noyers, secretary of Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga (after "Lettres de Pierre Des Noyers secrétaire de la reine de Pologne ...", published in 1859, p. 22). The situation was similar in other cities of the Commonwealth, particularly in Vilnius and Warsaw, where during the second occupation the royal residences were subjected to systematic looting by Swedish and Brandenburgian forces. "The Warsaw townspeople had to help in transporting the looted items to the Vistula bank, under pain of confiscation of their own goods. [...] On August 11, the commandant of the capital, General von Bülow [Barthold Hartwig von Bülow (1611-1667)], received an order to transport all valuables and works of art from the Castle. At that time, over 200 paintings were taken away, including plafonds from five castle rooms, royal silverware, furniture and 33 tapestries. The Swedes had already committed truly barbaric acts, scraping gold from the gilded paneling and ceilings, "of which they made at most three or four ducats, and the damage they caused exceeded 30,000 francs" [according to mentioned letter by des Noyers]. Everything of any value was transported by water towards Toruń and Königsberg, e.g. jasper columns from the royal garden" (after "Warszawa 1656" by Mirosław Nagielski, p. 262). "They generally killed everyone in Vilna [Vilnius], both men and women, except young people and children, whom they sent to Muscovy, and put Muscovites to live there. [...] In Vilna, the Muscovites have ruined the beautiful and sumptuous chapel of Saint Casimir, which cost more than three millions; and in the big church they put their horses; it serves them as a stable", adds des Noyers in letters of November 8 and December 28, 1655 (after "Lettres ...", p. 10, 40). The next significant inventory of paintings of a councilor of Kraków, Gerhard Priami, made on July 21, 1671, so few years after the destructive Deluge (1655-1660), is not that impressive: "Portraits of King Sigismund III with the Queen [...]; Image of flagellation [of Christ] [...]; Solomon, upwards [...]; St. Joseph on panel, old-fashioned [...]; Four landscapes [...]; Landscape with a fair [...]; Image of Lot [and his daughters] [...]; Two landscapes at elbow height; Picture of Judith [...]; Three pictures of the story of Tobias; Image of the Blessed Virgin in roses; Saint John the Baptist; Jesus falling [under the cross]; Image of the Blessed Virgin majoris; Two portraits of His Lordship Ossoliński, the second of His Lordship Lubomirski; coats of arms, imperial and royal; Two courtesans, one bigger the other smaller; Portrait of the late Priami, which stays with Mr. Jerzy Priami". According to testament of Jan Pernus, councilor of Kraków, from 1672 he had a large painting of Præsentationis (Presentation), allegedly by Rubens. He collaborated with the Swedes during the invasion in the years 1655-1657 and took part in the shameful looting of the royal palace in Łobzów and the Wawel Cathedral by the occupants. Pernus looted valuable marbles from the Łobzów palace, and it is possible that he took the paintings decorating the royal residence (after "Galeria rajcy Pernusa" by Michał Rożek). "Two paintings of Roman work on copper, which are in my room, one of the Nativity of Christ, the other of the Assumption of the Virgin Mary of equal size; I want my nephew (Franciszek Pernus, heir) to offer them to His Majesty the King, the merciful Lord, from me, the lowest subject [...] To Mr. Reyneker, councilor of Kraków, my son-in-law, [...] I mark him a picture of Saint John Cantius, painted on a metal plate, from the worthy Master Strobel [Bartholomeus Strobel], asking him to accept this tiny gift as a sign of my love and as a souvenir. [...] Living in great friendship with Priest Adam Sarnowski, Canon of Warsaw and Łowicz, private scribe of His Highness, as a souvenir, I give him a painting of the Virgin Mary, of a prominent Roman craftsman. This picture is in the room in the garden, with Saint Joseph and Saint John, plus four paintings on canvas, with flowers on them, about three quarters of a cubit large, with golden frames". Four paintings with flowers of Roman work he donated to the Bielany Monastery and portraits of himself and his wife to the Pernus Chapel at the St. Mary's Basilica in Kraków (after "Skarbniczka naszej archeologji ..." by Ambroży Grabowski, pp. 61-68). Mentioned Adam Sarnowski made provisions for his possessions and paintings in his will signed in Frombork on April 15, 1693, four months before his death. One painting he left to Queen Marie Casimire Sobieska (de La Grange d'Arquien): "To the Queen Her Majesty, My Lady, the original of Three Kings [Adoration of the Magi] by Rembrandt, in black frames, which is upstairs in the hall, and another beautiful that Mr. Locci will choose" (after "Testament Adama Sarnowskiego ..." by Irena Makarczyk, p. 167). Several paintings by Rembrandt, most likely from former royal or magnate collections that survived the Deluge, are mentioned in the 1696 inventory of the Wilanów Palace in Warsaw. Perhaps the earliest known confirmation of the popularity of Rembrandt's works in the Commonwealth is the 1643 letter from Krzysztof Opaliński (1609-1655), voivode of Poznań, to his brother Łukasz (1612-1662), in which he informs him that "Your Lordship will have Rymbrandt's copperplates from Sieraków". Krzysztof also collected prints after the works of Rubens, commissioned paintings based on these prints and acquired numerous paintings in the Netherlands. His correspondence indicates that he was a connoisseur of Flemish and Dutch painting of the period. Nevertheless, sometimes such distant acquisitions were not good. "Thesaurus cineres fuere [The treasure becomes ashes]. Such childish antics were bought, so that in Poznań you get all this and better. The paintings should not be hung on the wall, and these are only two of them, which would have been better painted by a painter from Sieraków", commented disappointed Krzysztof in a letter to his brother about paintings that arrived in Poznań from the Netherlands in 1641 (after "Krzysztofa Opalińskiego stosunek do sztuki ..." by Stanisław Wiliński, p. 195-196). Jadwiga Martini Kacki, later Popiołkowa, in her will of 1696 says: "To Fathers Carmelites na Piasku, please give two paintings painted in Greek style on canvas, and the third one by Salwator". The 1696 property list of Kazimierz Bonifacy Kantelli (Bonifacius Casimirus Cantelli) from Carpineti in Campania, apothecary and royal secretary, who came to Kraków from Krosno, and obtained the city rights in 1625, includes a large number of paintings, mostly religious; but there are also portraits of notable people, such as king John III Sobieski, Ladislaus IV Vasa, Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga, Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria, King John Casimir, King Michael Korybut, Chancellor Ossoliński and many others. Occasionally there are also other objects of art in inventories, like "Amber effigy of King Sigismund III", mentioned in the will of Wolfowicowa, wife of the Kraków councilor in 1679. In 1647 a widow Anna Zajdlicowa née Pernus, in her last will stated: "To Mr Filip Huttini, secretary and decree scribe of the King His Majesty, Kraków councilor, I give and bequest my golden leather upholstery [cordovan], with pictures of Polish kings". There were also many paintings with mythological themes. In the register of property of councilor Kasper Gutteter (1616) there were paintings depicting Venus, Hercules and the mythical Labyrinth. The image of Mercury with Venus was in the house of Wojciech Borowski (1652). Rozalia Sorgierowa (1663) had a painting of Andromeda and the list of movables of Oktawian Bestici from 1665 contained: "Satyr on canvas", "Venus lying naked" and "Three Dianas". In the collection of Andrzej Kortyn (Andrea Cortini) there were six mythological paintings, including Venus and Cupid (after "Mecenat artystyczny mieszczaństwa krakowskiego ..." by Michał Rożek, p. 177). According to the rich inventory of May 10, 1635, the municipal scribe of Poznań Wojciech Rochowicz owned a painting of Pallas Athena, Venus and Juno, as well as 5 small paintings in frames painted on oak boards depicting "Roman people". Several erotic paintings were mentioned in the very rich gallery of Poznań burgher Piotr Chudzic, who died in 1626, like a "naked picture for appetite", "3 paintings of courtesans" and "a very small round Venetian picture on tin of a courtesan" (after "Odzież i wne̜trza domów ..." by Magdalena Bartkiewicz, p. 68 and "Inwentarze mieszczańskie Poznania", p. 407). Rochowicz in Poznań had one image of a courtesan and one of a wenetka (Venetian courtesan), Krzysztof Głuszkiewicz in Lviv had six paintings of courtesans and in Kraków paintings of courtesans were owned by: Franciszek Delpacy (1630), Anna Telani (1647), Oktawian Bestici (1655), Andrzej Cieski (1659), Gerard Priami (1671) and Stanisław Kłosowicz (1673), who had four paintings of courtesans (after "Sztuka a erotyka", ed. Teresa Hrankowska, p. 197). Hieronim Morsztyn (1581-1623), author of the "Worldly Pleasure" (1606) and many erotic poems, in his work "Actaeon. (To Polish Courtesans)" wrote that they would gladly "run naked". Nude and erotic paintings, such as "A round painting in a gilded frame, which represents the 3 Graces with the portrait of His Highness the King" (62), "A painting in a gilded and sculpted frame, representing the 3 Graces, giving the Books of Eternity with the portrait of His Majesty the King" (63) and "A painting that depicts a naked woman with a man, embracing" (65), are mentioned in the inventory of the bathing pavilion of King John III Sobieski in Zhovkva in 1690 (Regestr opisania łaźni w zamku żółkiewskim po odjeździe Króla Jmci na sejm do Warszawy in anno 1690 die 5 Januarii). The Polish Vasas, descendants of the Jagiellons on the maternal side (through Catherine Jagiellon), were renowned patrons who commissioned many beautiful paintings and other objects locally and abroad in the best workshops, such as for example a series of 6 tapestries with the story of Diana, purchased around 1611-1615 by Sigismond III Vasa in the workshop of François Spierincx in Delft. In 1624, Peter Paul Rubens painted Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (future Ladislaus IV) during his visit to Brussels. According to available sources, Rubens and Ladislaus Sigismund's father, king Sigismund III, never met in person, but the beautiful portrait of the king is undoubtedly by his hand (attribution to Rubens by Ludwig Burchard, Heinz Collection Kisters in Kreuzlingen). Although not confirmed in surviving letters or inventories, this effigy of the king was beyond doubt created from some study drawings or miniatures sent from Warsaw. Elected king John III Sobieski (from 1674) consciously organized European opinion, commissioning appropriate works, paintings and engravings in Poland and abroad, in the Netherlands, Flanders, Paris and Italy (works by Romeyn de Hooghe, Reinier de la Haye, Caspar Netscher, Prosper Henricus Lankrink, Ferdinand van Kessel, Adam Frans van der Meulen, Jan Frans van Douven, workshops of Pierre Mignard and Henri Gascar, Jacques Blondeau, Simon Thomassin, Giovanni Giacomo de Rossi, Domenico Martinelli). Exquisite sculptures were also ordered abroad, like statues by Flemish sculptors Artus Quellinus II and his son Thomas II and Bartholomeus Eggers (Wilanów Palace and Summer Garden in Saint Petersburg, taken from Warsaw in 1707), jewellery in Paris (Sobieski diamond) and silverware in Augsburg (works by Abraham II Drentwett, Albrecht Biller, Lorenz Biller II and Christoph Schmidt). The construction of his suburban residence, inspired by the Villa Doria Pamphili in Rome, Sobieski entrusted to Augustyn Wincenty Locci, son of the Italian architect Agostino Locci. The best local and foreign artists, architects and scientists participated in the decoration of the residence and the glorification of the monarch, his wife and the Commonwealth. The 1713 inventory of the splendid Krasiński Palace in Warsaw - built in 1677-1683 for the voivode of Płock, Jan Dobrogost Krasiński, according to design by Tylman Gamerski (Tielman van Gameren), lists "Rembrandt's portrait, original, in a white frame" (Konterfekt Rembrandta orginał w ramie białej, Wtóra skrzynia w której obrazy N° 2, item 3), along some Dutch landscapes (Lanczawt), "A painting of a Dutchman with a Dutch woman in a black frame" (item 13), "A landscape with Venus and Cupid in a golden frame" (item 16), "A painting of a wanton naked woman, after a painting by Correggio" (item 35), Italian religious paintings, "Dürer's painting representing the Pharisees reprimanding a woman [most likely Christ and the adulterous woman with historié portrait of Laura Dianti - compare with the painting in the Alte Pinakothek in Munich, inv. 1411] in a frame black in its box", two small paintings of Galatea by Annibale Carracci (Item obrazy różne stojące i na ścianach, items 1-2), "Painting of kings Ladislaus and [John] Casimir with [Marie] Louise, copy" (item 3), perhaps a copy of a historié portrait in the guise of Roman gods, painted by Justus van Egmont for Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga in Paris in 1650, "Portrait in profile of King Casimir" (item 9), "Painting of Venus, aka some naked woman" (item 10), "Painting of Herodias with the head of Saint John" (item 11), "A large portrait of King Casimir" (item 12), "A large and beautiful painting, original by Rubens, the story of a fish caught in which money was found to pay the tax [Saint Peter Finding the Tribute Money]" (item 34), possibly another version of the painting now in the National Gallery of Ireland (NGI.38) and "The painting of the three kings [Adoration of the Magi], Netherlandish original, beautiful" (item 36, compare "Inwentarze pałacu Krasińskich później Rzeczypospolitej" by Ignacy Tadeusz Baranowski, p. 5-8, 13-14). None of the paintings appear to have survived Warsaw's turbulent history. It is therefore difficult today to determine the reliability of this inventory, however, the inclusion of names indicates that many of these paintings were true originals or signed works. The character of paintings, comparable to those known from previous inventories, indicates that Krasiński acquired them in Poland-Lithuania. The inventory of the Picture Gallery of the Radziwill Palace in Biała Podlaska, called Radziwiłłowska (Alba Radziviliana), from November 18, 1760, provides an interesting insight into the quality and diversity of painting collections in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. The palace was built by Alexander Louis Radziwill (1594-1654), Grand Marshal of Lithuania after 1622 on the site of old wooden mansions. The inventory lists 609 positions of mainly religious and mythological paintings of which nothing preserved in Biała: (52) Painting of Diana, painted on tin with two arrows without frames, (53) Picture of Adonis sleeping with the Goddess Hera [Venus and Adonis], painted on glass in gilded frames, (84) Painting of Diana's hunt, painted on a panel in a gilded frame, (113) Sleeping Venus lying on a bed, without frames, (117) Face of Pallas [Athena], painted on canvas without frame, (128) Venus standing in water [Birth of Venus], painted on copper in gilded frames, (157) Portrait of King Sigismund Jagiello and Grand Duke of Lithuania [Sigismund I] on tin without a frame, (158) Portrait of King Sigismund of Poland and Sweden [Sigismund III Vasa], [...], painted on tin, without frame, (165) Portrait of Henry Helesius [Henry of Valois], King of Gallia and Poland, Grand Duke of Lithuania, painted on copper in frames, (166) Portrait of King Stephen Bathory, painted on tin in black frames, (181) Diana holding a trumpet, painted on canvas in old gilded frames, (192) Story of Vulcan and Venus, painted on canvas, without frames, (193) Second story, also of Venus, also with Venus and Vulcan, large painting on canvas, without frames, (206) Male portrait, painting by Rubens, on canvas in black frames, (210) Picture of Baceba [Bathsheba] at her bath, painted on canvas without frame, (213) Painting of Lucretia, expressive, with a dagger, a fine painting painted on canvas, no frame, (217) Picture of Herodianna [Herodias] with the head of Saint John, painted on canvas without frames, (224) Picture of Hercules, painted on canvas without frame, (233) Painting of Venus descending from the clouds, a large painting on canvas, without frames, (234) Picture of Lucretia pierced with a dagger, painted on canvas, without frames, (235) Painting of nude Venus reclining with Cupid, painted on canvas, no frame, (258) Story of Venus with Adonis, large painting on canvas, without frame, (259) Portrait of a knight, full-length, Rabefso [Rubens?], on canvas without frame, (283) Painting of Bacchus, painted on canvas without frame, (284) Painting of Judith, painted on canvas, without frame, (296) Picture of Lucretia, painted on panel, without frame, (302) Half-naked person, painted on canvas, without frame, (303) Meditating Lucretia, painted on canvas, without frame, (335) Landscape with dwarfs and fruits, painted on canvas, (336) Landscape with dying Diana and the nymphs, on canvas, (348) Painting of Venus sleeping naked, painted on canvas, without frame, (349) Painting of Adonis with Venus enjoying, painted on canvas, without frame, (376) Painting of Venus with Cupid and Zefiriusz with Hetka [most likely homoerotic Zephyrus and Hyacinth], two pieces of similar measure and N°, painted on canvas, without frames, (390) Story of Dyanna on which golden rain falls [Danaë and the shower of gold, possibly by Titian or workshop], painted on canvas without frames, (391) Sleeping Venus, painted on canvas, without frames, (535) Portraits of various Lords ... thirty-six of different sizes, painted on canvas, without frames, (536) Portraits of various Lords and Kings of unequal size, painted on canvas, (544) Different portraits under one No., nineteen pieces, painted on canvas, (577) Portrait of Stephen Bathory, King of Poland, painted on canvas in black frames, (596) Story of Judith with Holofernes, painted on canvas in black frames, (597) Venus asleep on the hunt, painted on canvas, (604) Story of Saint Susanna with two Elders, painted on panel in black gilded frames, (607) Kings of Poland, fifty and one on parchment and (608) A lady with a dog, painted on panel, without frame (after "Zamek w Białej Podlaskiej ..." by Euzebiusz Łopaciński, pp. 37-47). With such a large collection, it was difficult to fully describe the identity of each effigy. The chaos of war also contributed to the forgetting of the names of models and painters. Many valuable works of art in Poland-Lithuania were looted or destroyed during the invasions of the country in the 17th, 18th, 19th and 20th centuries. The country became significantly impoverished due to the wars, so valuable and movable works of art, especially those whose history was lost, were sold. By the end of the 18th century, like the country itself, Poland-Lithuania had almost completely disappeared from the history of European art. Art collections were confiscated during the Partitions of Poland - after collapse of the Kościuszko Uprising in 1794 (especilly Polish crown jewels), November Uprising in 1830-1831 and January Uprising in 1863-1864. To secure their belongings, many aristocrats move their collections abroad, especially to France. When the Second World War broke out in 1939, the Jagiellonian tapestries commissioned in Flanders by king Sigismund II Augustus and recovered from the Soviet Union between 1922-1924, were transported through Romania, France and England to Canada and returned to Poland in 1961. The elective system of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth also favored the outflow of works of art from the country. Paintings and other valuables from the royal collection that survived the Deluge (1655-1660) were transported to France by king John II Casimir Vasa (1609-1672), who abdicated in 1668 and moved to Paris. Many valuables were inherited by Anna Gonzaga (1616-1684), Princess Palatine, who died in Paris. Queen Bona Sforza (1494-1557) moved her belongings to Bari in Italy, Queen Catherine of Austria (1533-1572) to Linz in Austria and Queen Eleonora Wiśniowiecka (1653-1697) to Vienna. French Queen Marie Casimire Sobieska and her sons transported their collections to Rome and France and elective monarchs from the Saxon dynasty in the 18th century moved many items to Dresden. The last monarch of the Commonwealth, Stanislaus II Augustus, abdicated in November 1795 and moved part of his collection to Saint Petersburg. It should also be noted that when the treasures of the Most Serene Republic (Serenissima Respublica Coronae Regni Poloniae Magnique Ducatus Lithuaniae) were plundered by different invaders, in 1683, the army of the Republic under the leadership of the elected monarch John III Sobieski saved the opulent imperial treasures from a similar fate at the gates of Vienna (Relief of Vienna or Battle of Vienna). A century later, between 1772 and 1795, Austria was one of the countries that divided the Republic (Partitions of Poland) and Poland disappeared from the maps of Europe for 123 years.
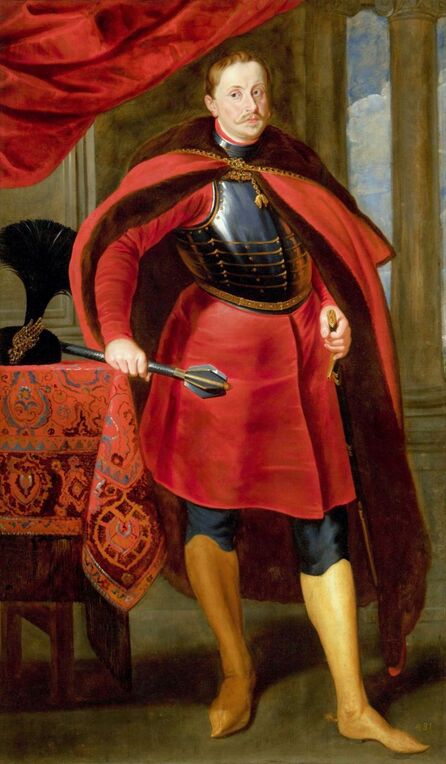
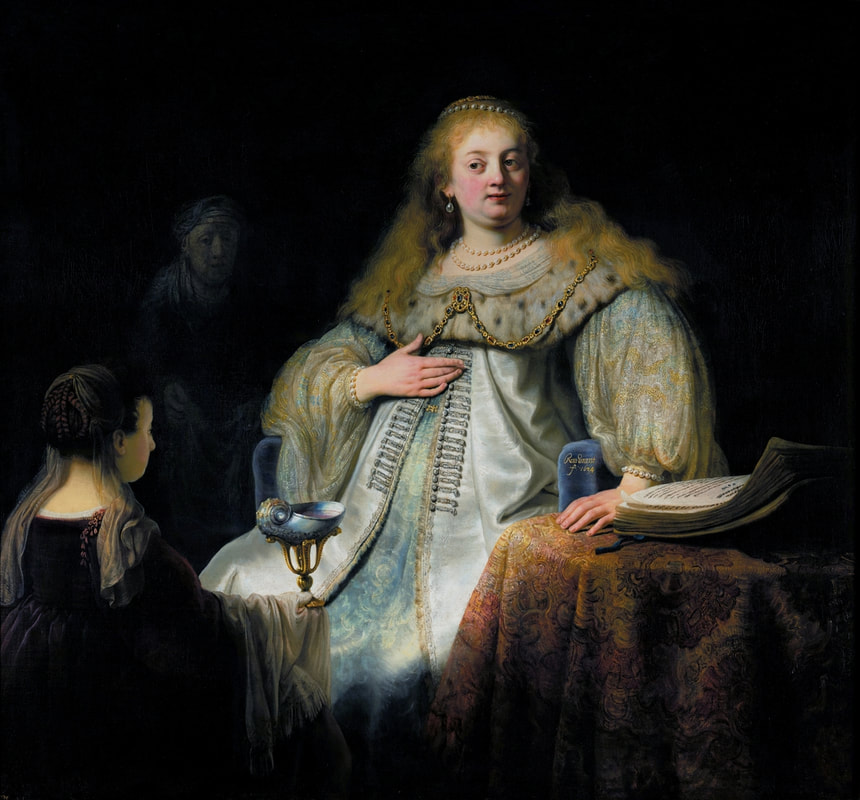
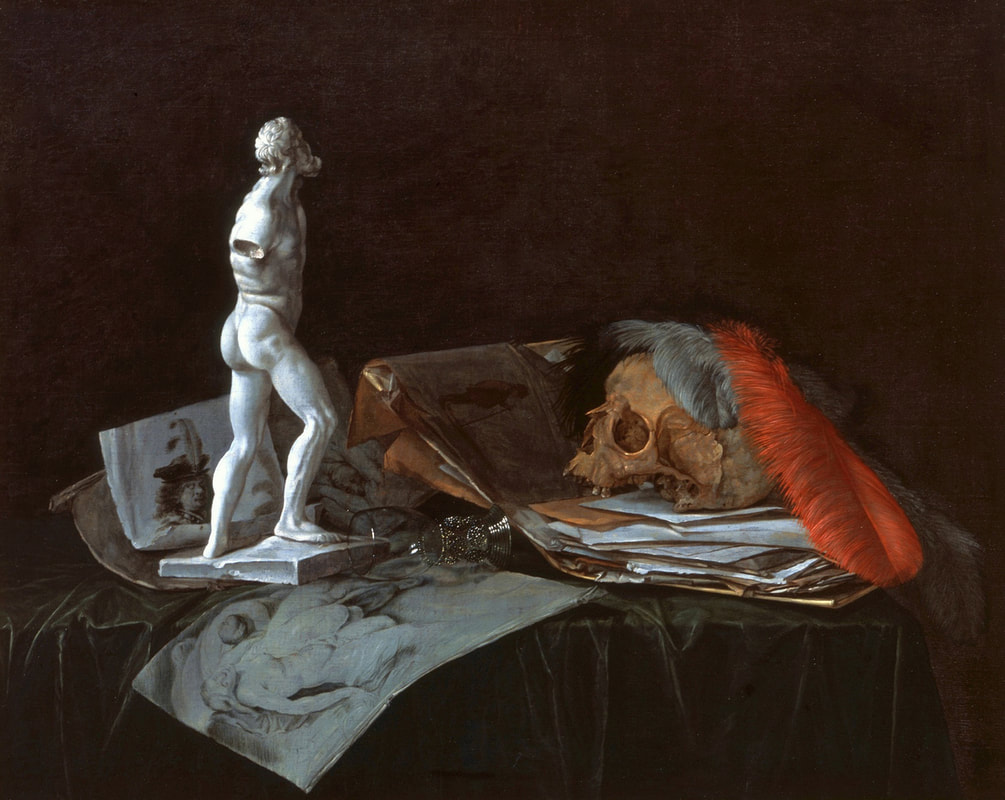
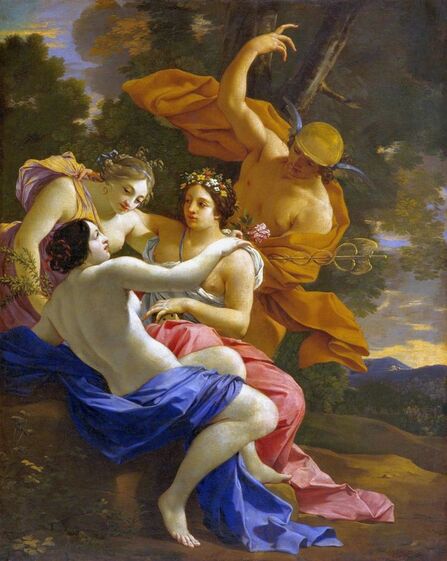
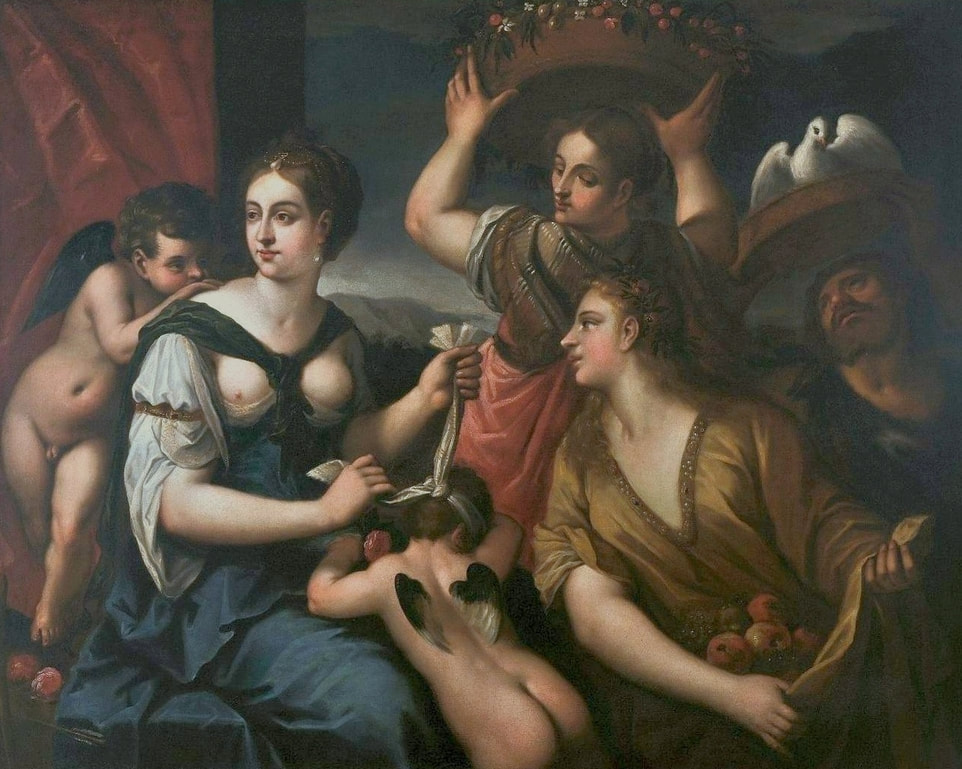
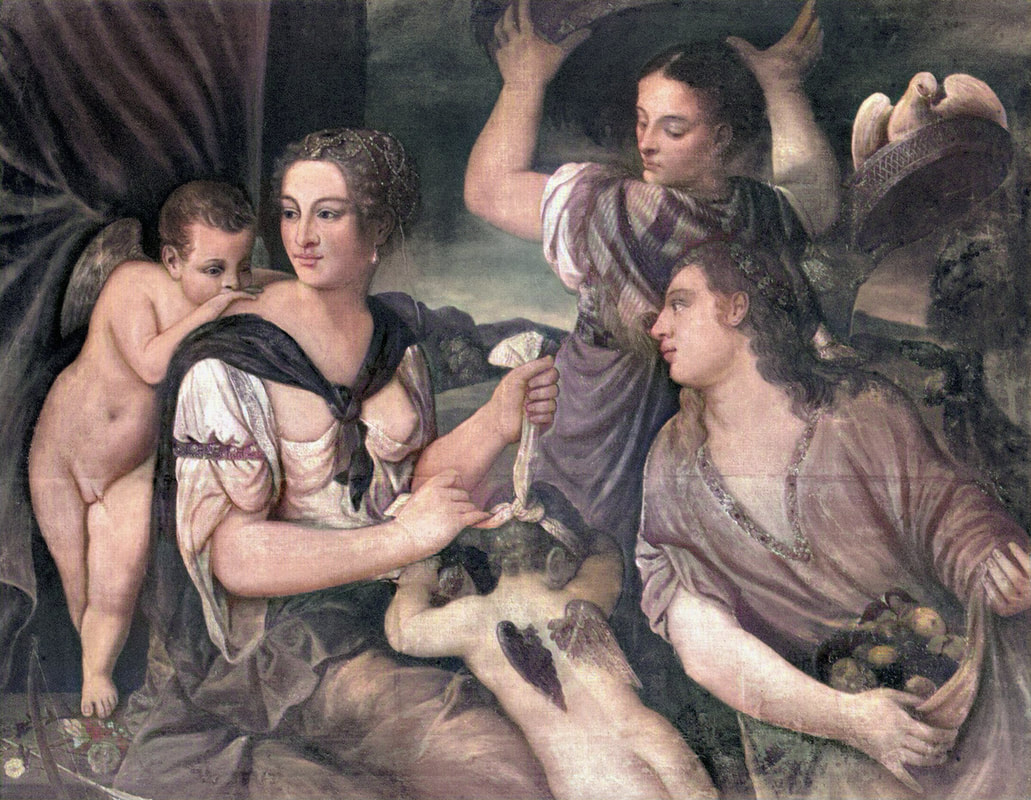
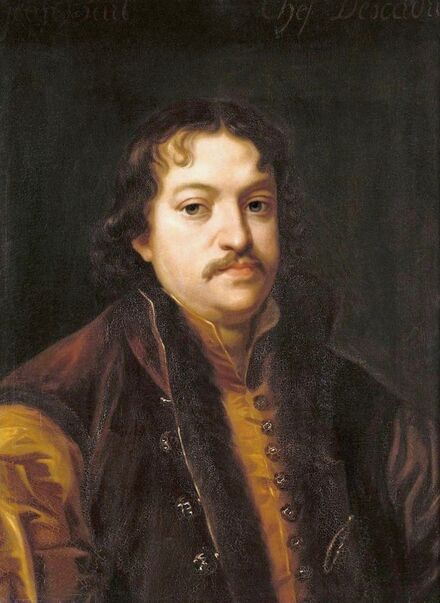
Art collection of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa, attributed to Étienne de La Hire, 1626, Royal Castle in Warsaw.
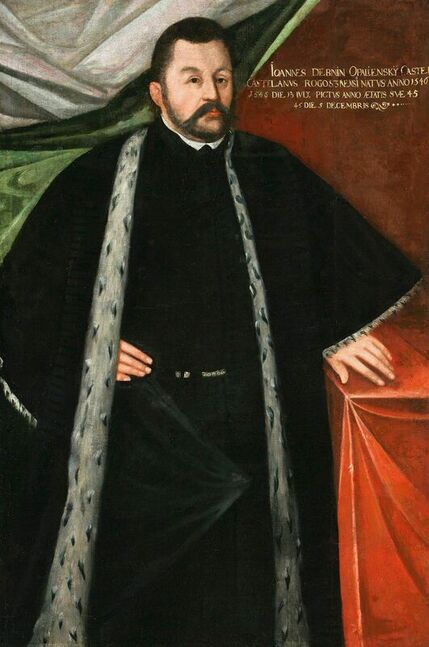
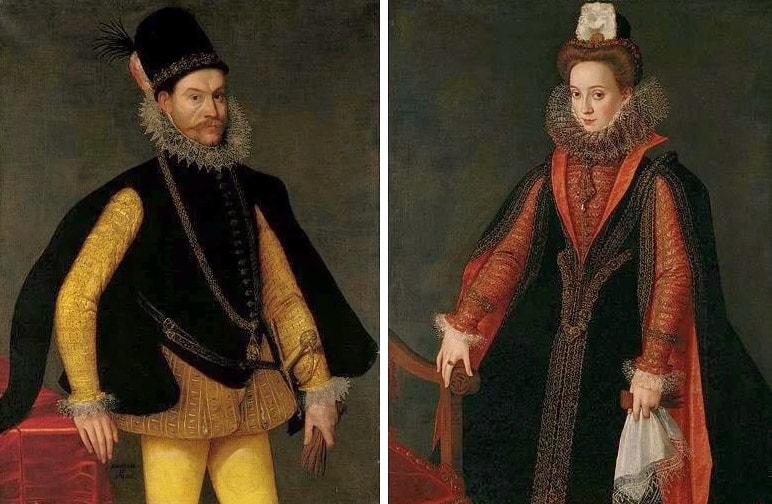
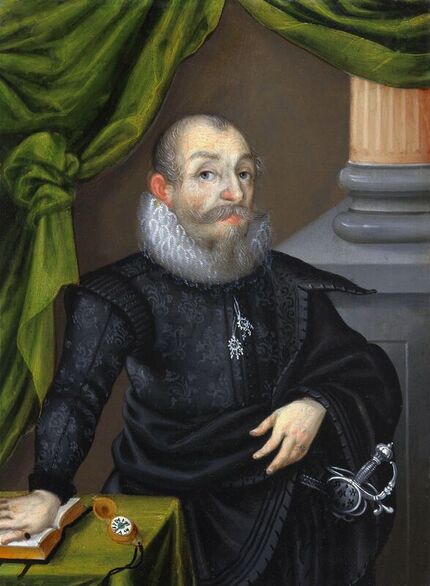
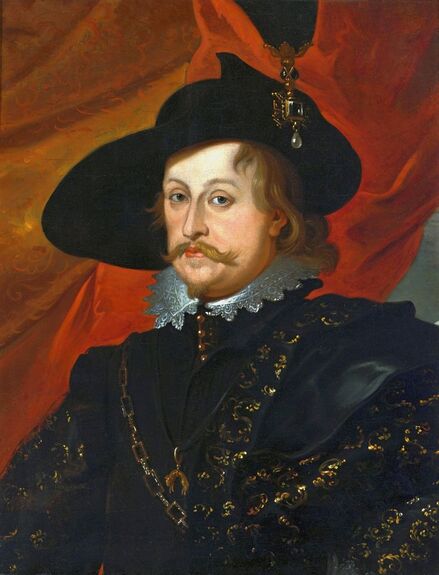
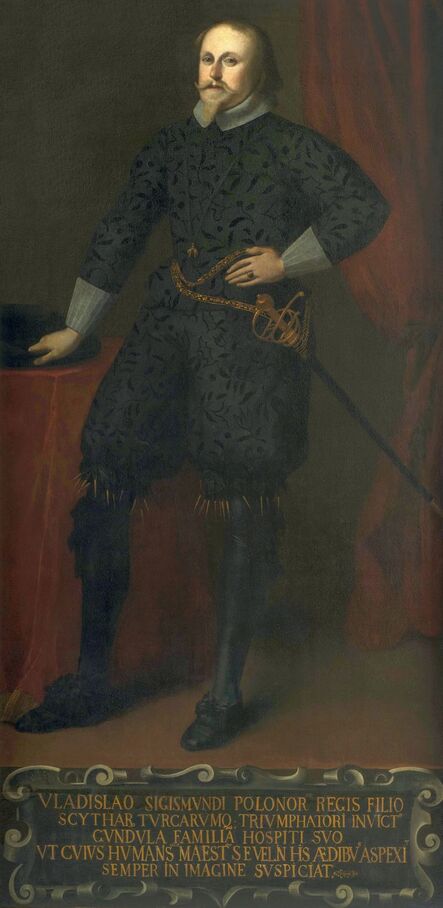
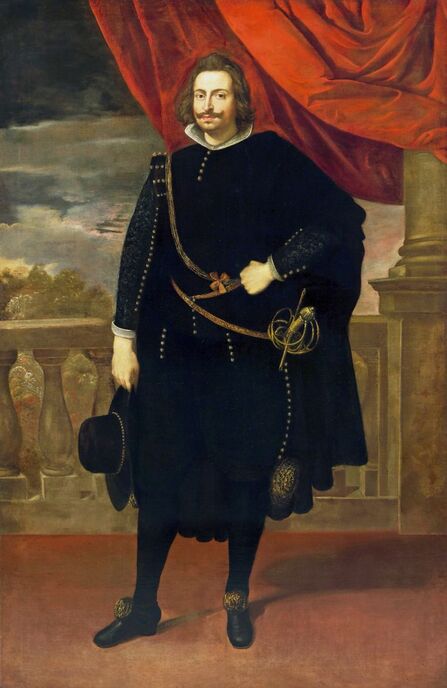
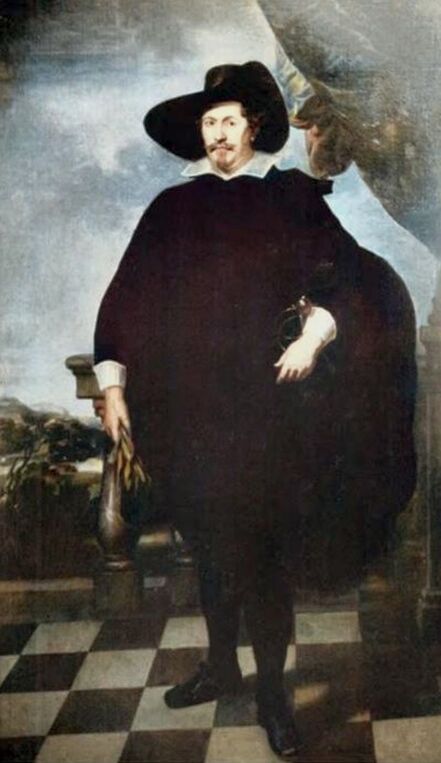
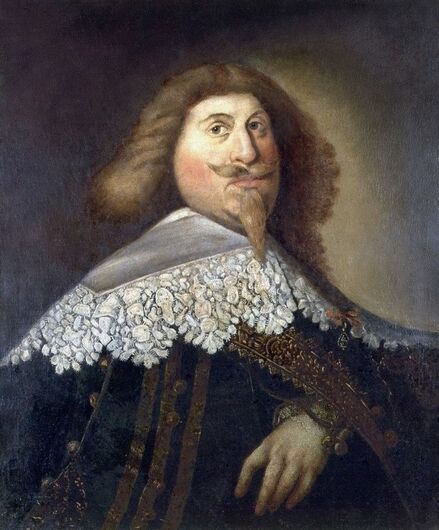
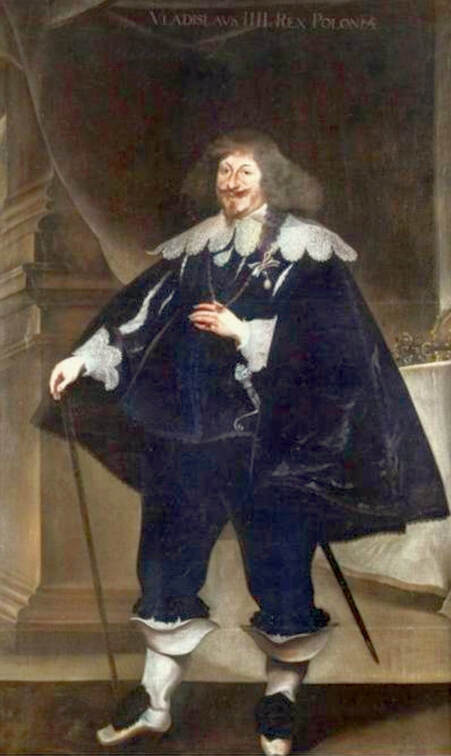
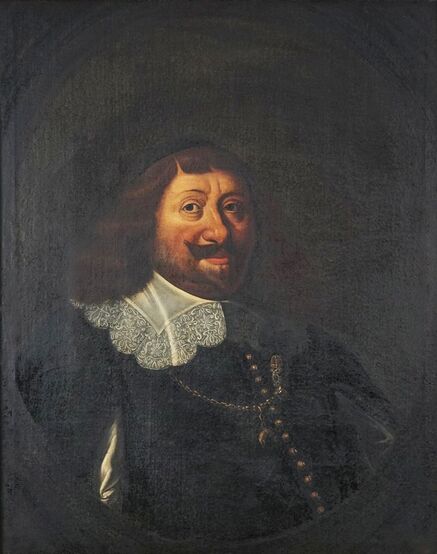
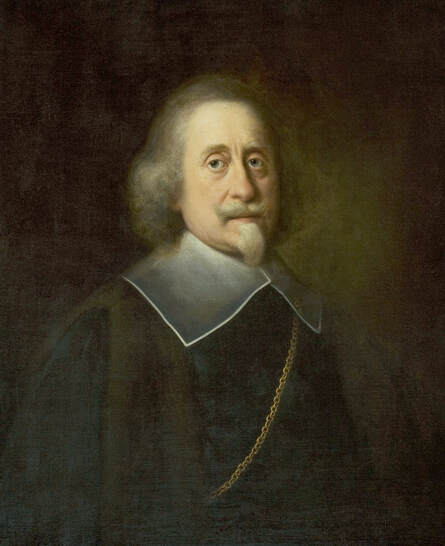
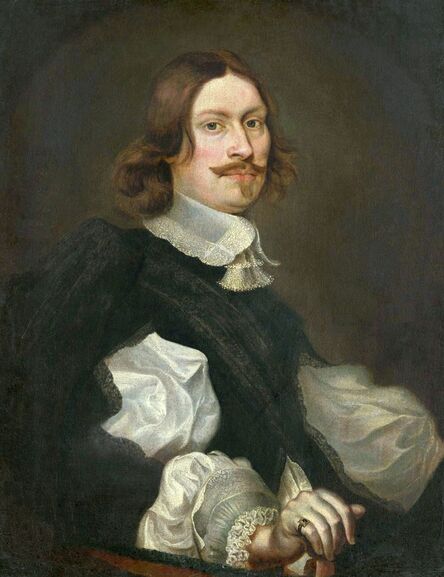
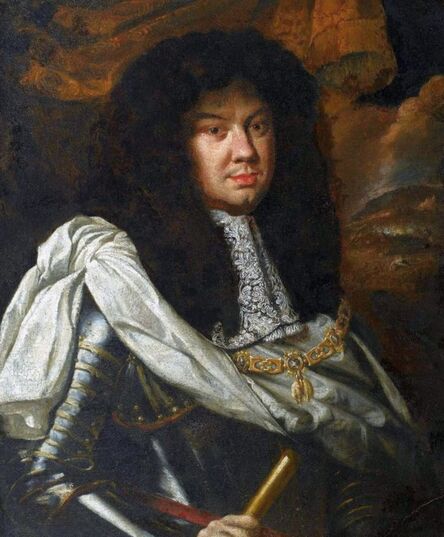
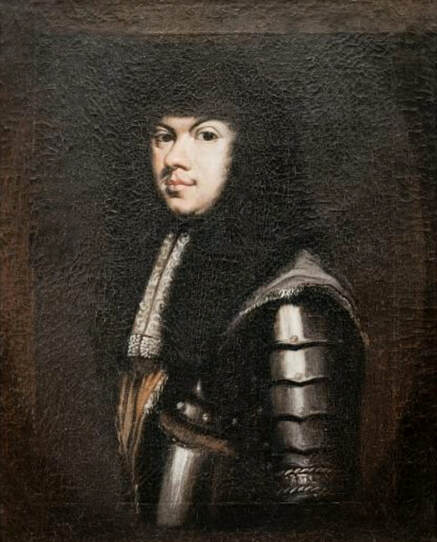
Portraits of Sigismund III Vasa and Stanisław Radziejowski by Daniël van den Queborn or follower of Frans Pourbus the Younger
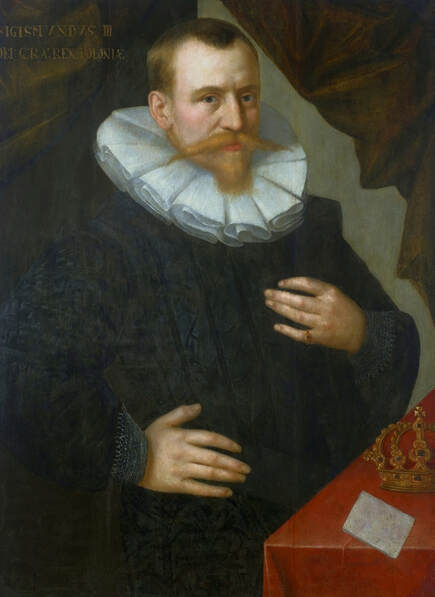
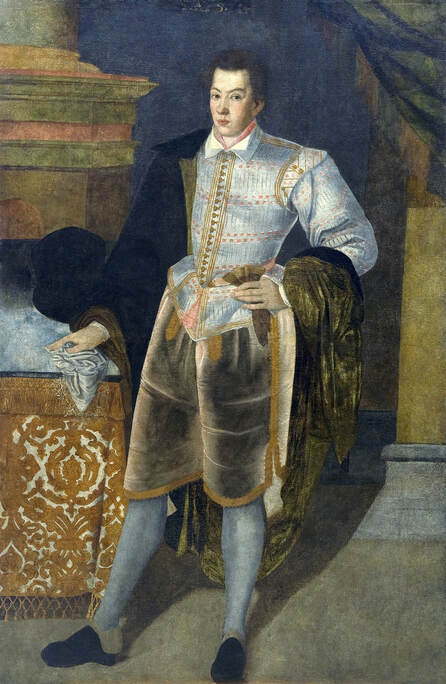
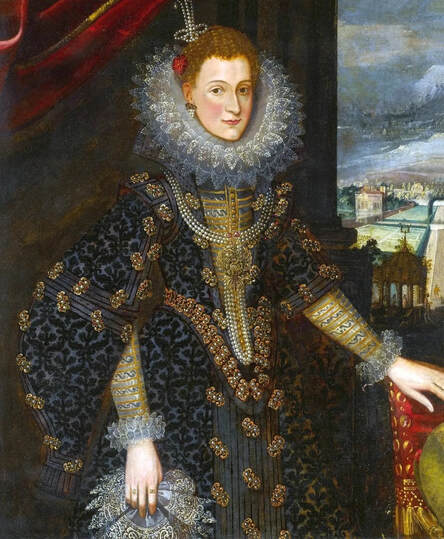
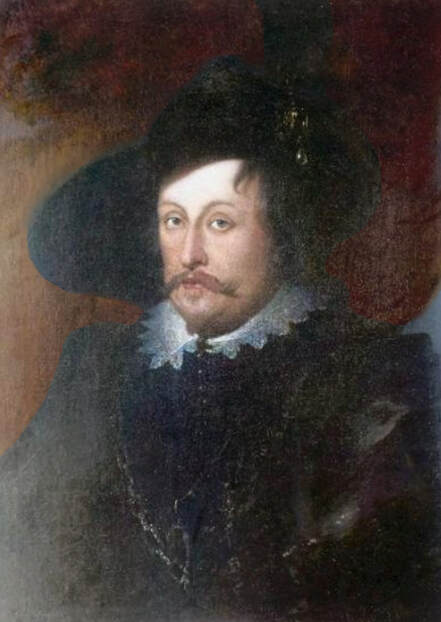
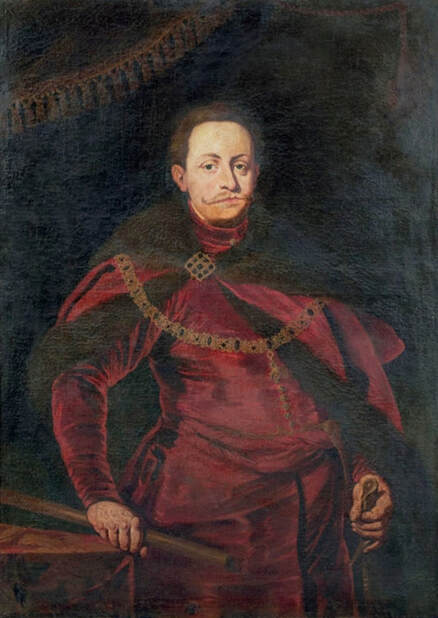
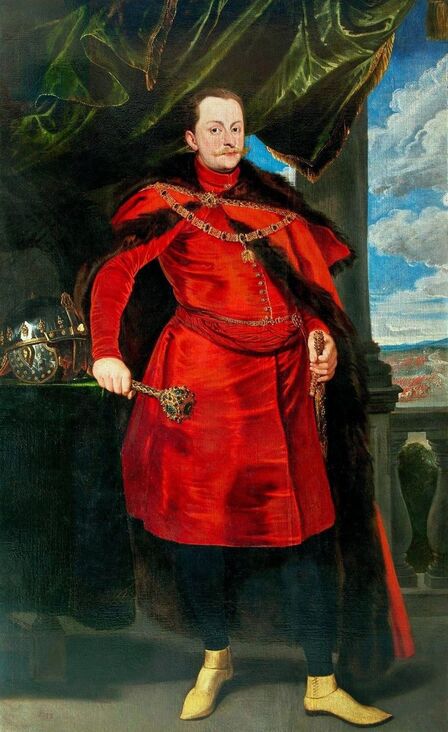
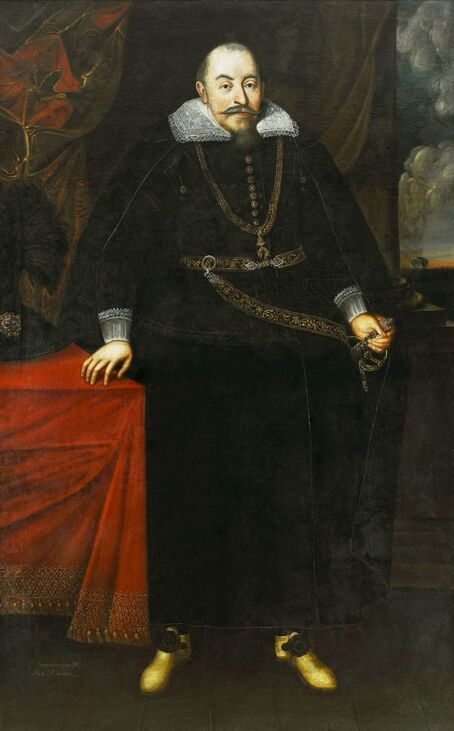
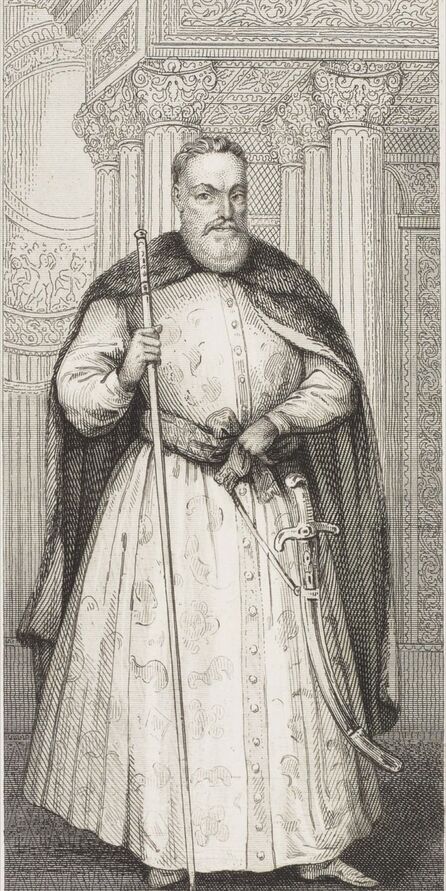
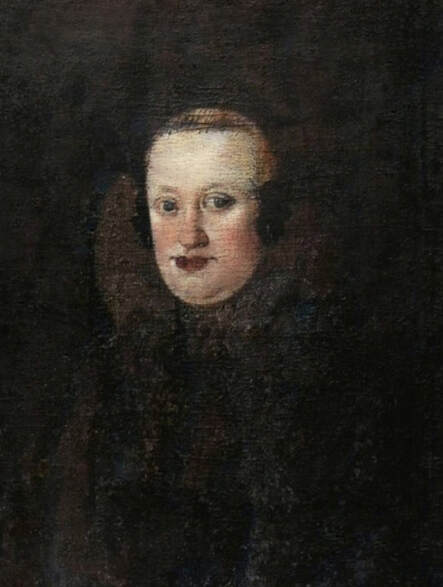
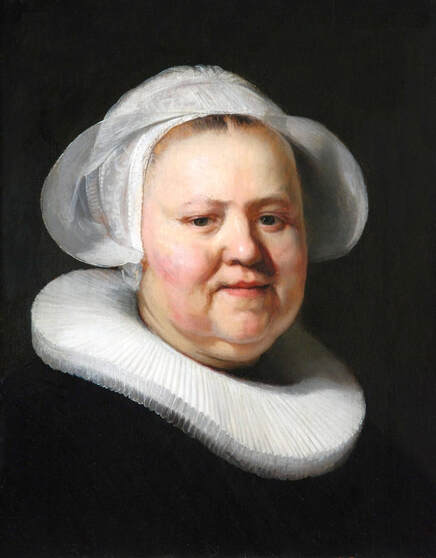
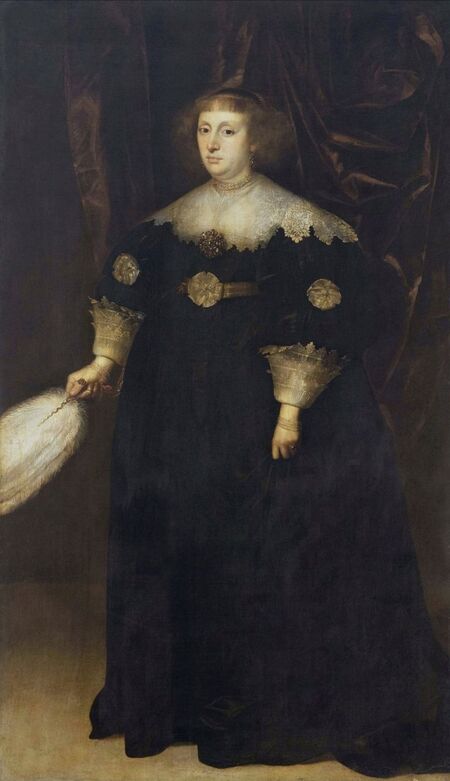
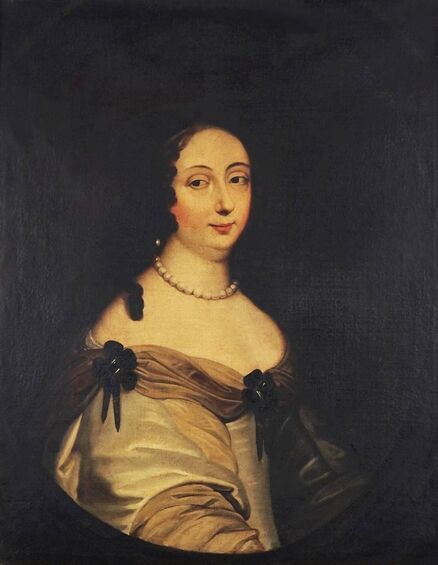
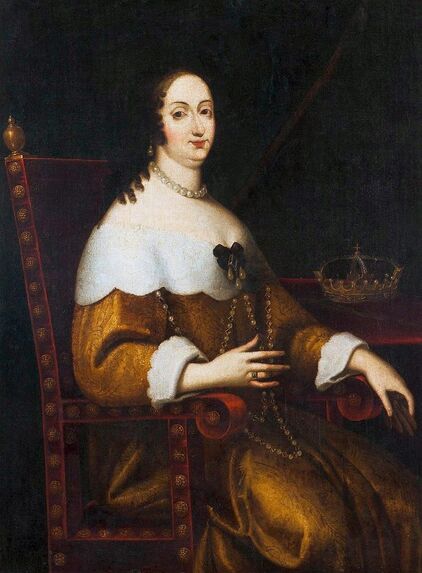
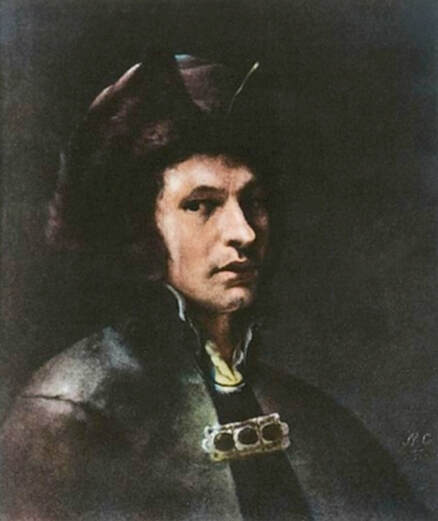
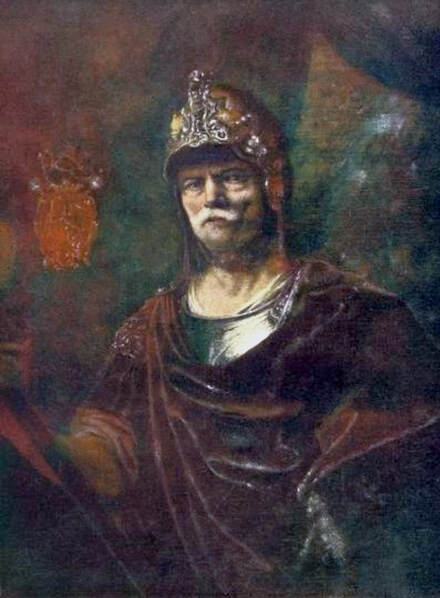
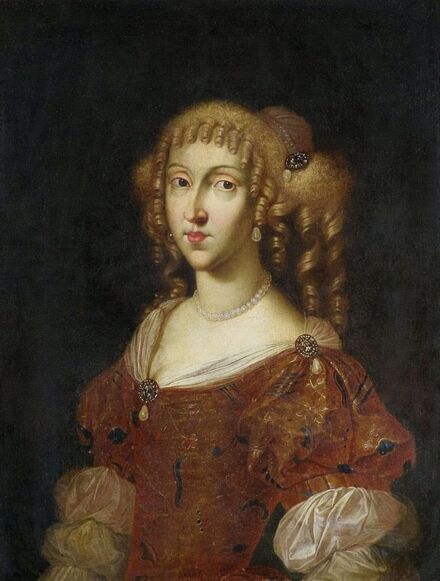
In the Czartoryski Museum in Kraków there is a portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa attributed to Dutch school (oil on panel, 93 x 68 cm, inventory number MNK XII-352). The painting was purchased in 1875, together with other portraits and miniatures, from Mikołaj Wisłocki from Pogorzela. It was initially attributed to Bartholomeus van der Helst (1613-1670) and according to the printed sticker on the back of the painting it was purchased in Podbela in Belarus, near the Białowieża Forest and hung for a long time in the old larch chapel in Białowieża (Zygmunt 3o Król - na drzewie ma być roboty fan der Helsta malarza Holenderskiego - nabyty w Podbiałey, pod puszczą Białowieską - wisiał bardzo długo w Starey Modrzewiowej Kaplicy w Białowieży (gub. Grodzieńska:)).
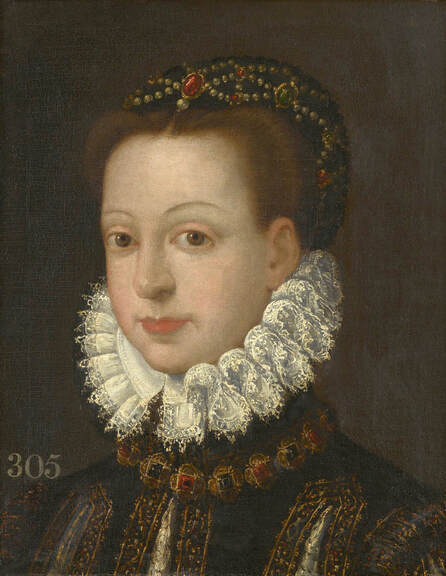
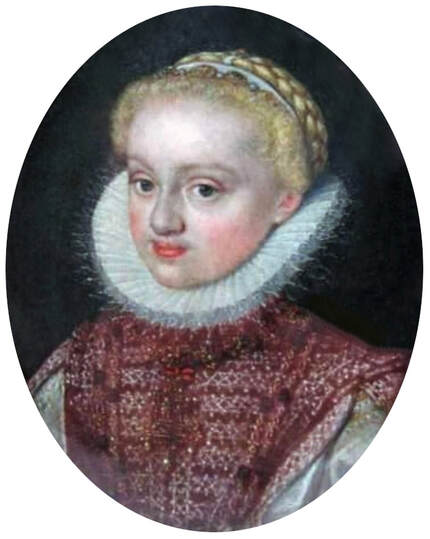
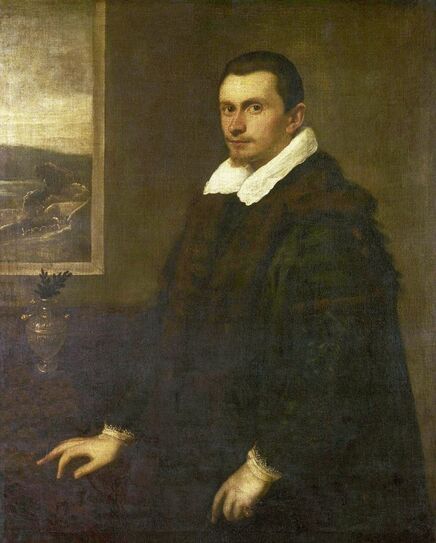
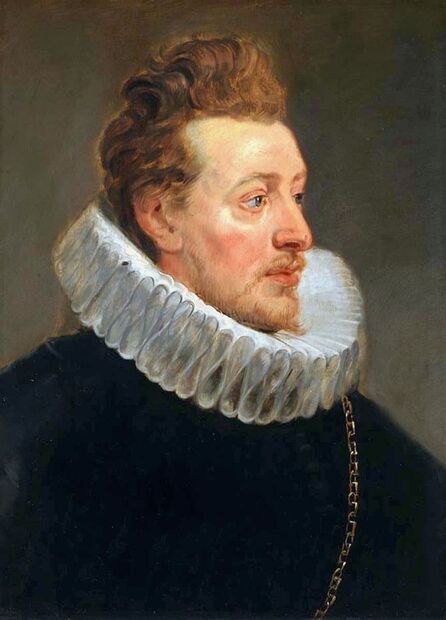
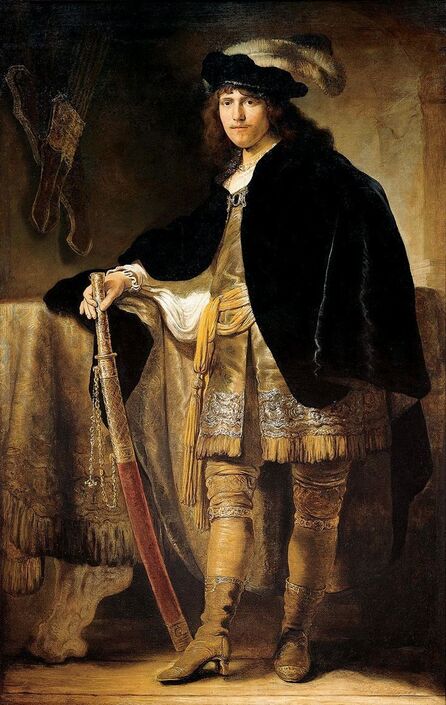
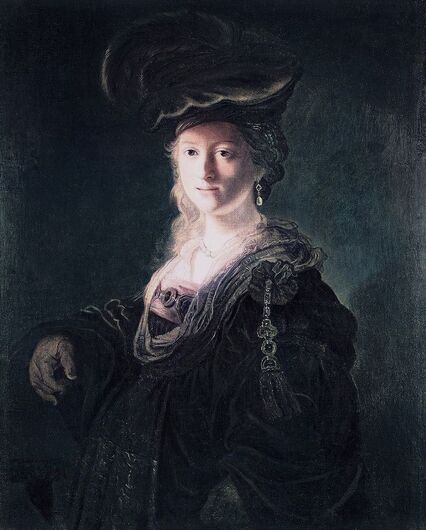
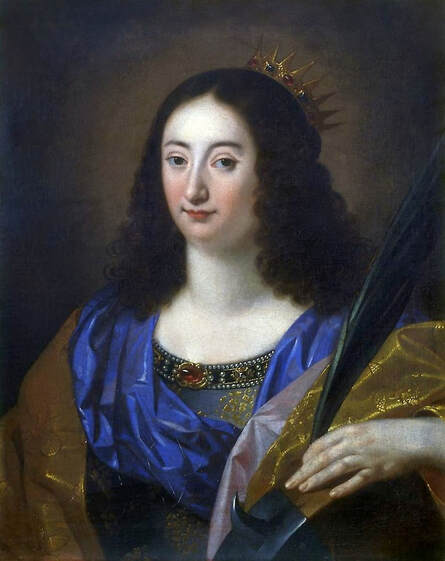
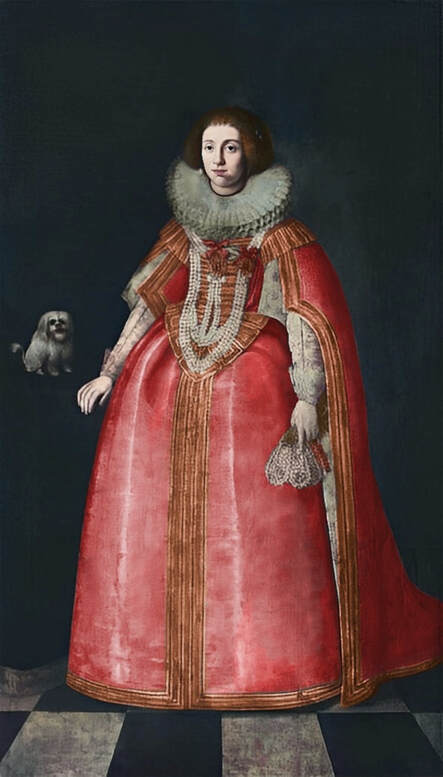
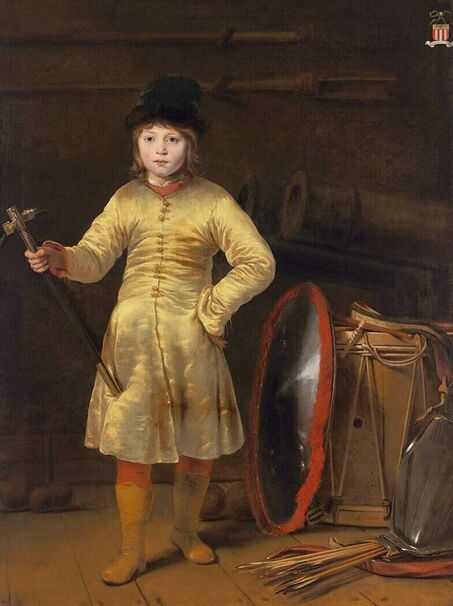
Jagiellonian hunting mansion located in Stara Białowieża was probably used as early as 1409, and around 1594, during the reign of Sigismund III Vasa, it was moved to the center of modern Białowieża, where a mill was also built. Less than a year after his election, in 1588, in the face of the plague in Kraków, the young king left the capital and hunted in the Białowieża Forest. "The manor house in Białowieża built for His Royal Highness for passage and hunting" is mentioned in 1639 and it was destroyed during the Deluge (1655-1660) or soon after and was last mentioned in 1663. In 1597 Sigismund III orders the Court Treasurer of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Dymitr Chalecki (d. 1598), to cancel the charges against the serfs employed in digging "Our Białowieża Pond" and to "relax the heavy burdens in the works" (after "Dwór łowiecki Wazów w Białowieży ..." by Tomasz Samojlik and others, pp. 74, 76-77, 80, 84). In 1651 Sigismund's son John II Casimir empoyed a Dutch architect and engineer Peeter Willer (or Willert) for similar works in Nieporęt near Warsaw and Henry IV of France (1553-1610) brought the best Dutch engineers to dry out, drain, build polders with their canals, locks, meadows, and low farms all round the coast of France (after "The French Peasantry ..." by Pierre Goubert, p. 2). It is quite possible that Sigismund also employed specialists from the Netherlands, also those already active in Polish Prussia, to create ponds and supply plants and fish. The painter probably never saw the king in person, so the resemblance is not striking, especially to portraits by Martin Kober, which has led some authors to suggest that it was originally a portrait of somone else transformed into the king's effigy. Probably in the 17th century, as the style suggest, a Latin inscription (SIGISMVNDVS III / DEI GRA: REX POLONIÆ) and a crown were added, however taking into consideration the provenance from the royal Białowieża, tradition, general resemblance and inscriptions there is no reason to claim that this is not an original portrait of the king commissioned in the Netherlands. A similar effigy of Sigismund with a long mustache and blond hair was included in hand colored map of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth (Poloniae Amplissimi Regni Typvs Geographicvs) from Speculum Orbis Terrarum by Gerard de Jode, published in Antwerp in 1593. The likeness of the king is one of the few effigies in this publication, which could indicate that the Polish court influenced it on this particular map or that it was inspired by the increase in orders for effigies in the Netherlands at that time. The style of the painting from Białowieża is reminiscent of the two portraits unanimously attributed to Frans Pourbus the Younger (1569-1622), a Flemish painter from Antwerp (from about 1592 active in Brussels), in the Galleria nazionale di Parma, identified as Luigi Carafa and his wife Isabella Gonzaga (inventory number 297, 303), however, it is even more similar to two paintings atributed to another painter from Antwerp - Daniël van den Queborn, both in the Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam. One depict a child 18 months old in 1604, possibly Louis of Nassau, the illegitimate son of Prince Maurice of Orange (SK-A-956) and the other, dated '1601', Francisco de Mendoza, Admiral of Aragon and Marquis of Guadalest, who was mayordomo mayor (lord high steward) in the household of Albert VII, Archduke of Austria and took part in different diplomatic missions to Poland, Hungary, Styria and the Holy Roman Empire (SK-A-3912). In 1579 Daniël joined the guild of Middelburg and in 1594 he became court painter to Prince Maurice in The Hague. The style of the king's costume and ruff is very similar to that seen in Gortzius Geldorp's portraits of the 1590s - portrait of Jean Fourmenois, dated '1590' (Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam, SK-A-912) and portrait of Gottfried Houtappel, dated '1597' (The State Hermitage Museum, ГЭ-2438). Portrait of Joachim Ernst (1583-1625), Margrave of Brandenburg-Ansbach (sold at Christie's, 27 October 2004, lot 46) from the 1610s, as his costume indicate, is attributed to follower of Frans Pourbus the Younger. In 1609, Pourbus moved to Paris and Joachim Ernst's stay in France at that time is not confirmed in sources. On August 14, 1593 Sigismund III arrived in Gdańsk with his wife Anna of Austria, sister Anna Vasa and the entire court. The city was a major port of the Commonwealth where Netherlandish influences became predominant at that time in almost all aspects of life (trade, art, architecture and fashion). The river cruise from Warsaw to Gdańsk lasted 12 days and the ceremonial welcome took place at the Green Gate. On 15 August 1593 the court took part in the procession at the Dominican Church. The ceremony was presided over by the Bishop of Kuyavia, Hieronim Rozdrażewski, who purportedly commissioned a drawing illustrating the event (possibly a study for a painting), attributed to Anton Möller the Elder (Wawel Royal Castle). The king then went with the court to Wisłoujście, from where on September 16, on 56 or 57 ships, he sailed with the people accompanying him and a detachment of the Polish-Lithuanian army to Sweden. The king embarked on a ship provided by the city of Amsterdam (after "Polacy na szlakach morskich świata" by Jerzy Pertek, p. 56). It is possible that among the courtiers accompanying the king was also the young nobleman Stanisław Radziejowski (1575-1637). He was a courtier at the court of the widowed Queen Anna Jagiellon in Warsaw, where he received the title of court steward and after her death in 1596 he passed to the court of Sigismund Vasa, where he again served mainly Queen Anna of Austria and her son Ladislaus Sigismund. He later did not hold any functions at the court, but he took part in confidential missions abroad and in the Commonwealth (after "Radziejowice: fakty i zagadki" by Maria Barbasiewicz, p. 41). Stanisław studied abroad, in Würzburg in 1590. In 1598 he was sent as a peace delegate to Moscow, he become the starost of Sochaczew in 1599 and he accompanied the king during his travels (e.g. in 1634 to Gdańsk). Radziejowski often had the opportunity to host the entire royal court under his roof in his estate in Radziejowice near Warsaw. There was no foreign envoy, no apostolic nuncio who did not experience his hospitality and Queen Constance of Austria, Sigismund's second wife, willingly took a bath in Radziejowice. No effigy of Stanisław preserved in Poland, but as a courtier so close to the queen who traveled abroad, he undoubtedly dressed primarily in Western European fashion. The painting in the National Museum in Kraków (inventory number MNK I-20) depicting the Adoration of the Crucifix with King Sigismund III Vasa and his male courtiers, painted by Wojciech Maliskiewic in 1622, clearly shows the disposition of fashion at the royal court. Only a quarter of the courtiers are dressed in national costume, the others wear ruffs and fashionable hose. In 1583 Balthasar Bathory de Somlyo, nephew of King Stephen Bathory raised at his court in Kraków, was portraited by Hendrick Goltzius in French costume during his visit to the Netherlands with his friend Stanisław Sobocki. Treasurer (Jan Firlej, Grand Treasurer of the Crown) from Stanisław Sarnicki's "Statutes and records of crown privileges", published in Kraków in 1594, also wears western attire, as well as Stanisław's infamous son Hieronim (1612-1667), who was depicted dressed according to Western European fashion in a print by Jeremias Falck Polonus, created in 1652. In 2022 a portrait of a young man painted in similar style to the Białowieża portrait was sold at Dorotheum in Vienna (oil on canvas, 65.5 x 55 cm, 11.05.2022, lot 25). This painting is attributed to Frans Pourbus the Younger and comes from private collection in Uruguay (since the 1920s). The exact provenance is unknown, so it is possible that it was associated with Polish immigration to Uruguay where the first Poles arrived in the 19th century as political refugees who fled after the January Uprising (the first Polish organization in Montevideo was established in 1921). The young man is wearing a fashionable embroidered doublet and a lace ruff. According to Latin inscription in upper part of the painting it was created in Antwerp and the sitter was 18 in 1593 (ANTVE'[rpiae] ANo SAL.. / 1593 / ÆTA' SVÆ.18..), exacly as Radziejowski, when he may have finished his studies and could board a ship in Antwerp for Gdańsk or just order it from Gdańsk in Antwerp, like his grandson Cardinal Michał Stefan Radziejowski, who ordered his portrait in Paris (attributed to painter from Antwerp Jacob Ferdinand Voet, Czartoryski Museum, MNK XII-377). The family resemblance is striking with the portrait of Michał Stefan in the Museum of Warsaw (MHW 15948), and mentioned effigy of Stanisław's son, the shape of the nose, the puffiness under the eyes and a dimple in the chin being particularly similar in these family members. A painting attributed to Frans Pourbus the Younger, which may come from the collection of Sigismund III and possibly linked to Radziejowski's diplomatic activity, is in the Lithuanian National Museum of Art in Vilnius (oil on canvas, 56 x 44 cm, LNDM T 4019). This "Portrait of a woman with a red ribbon" is dated at the top right '1604' and belonged to the same gallery as "Portrait of a woman with a diadem", dated '1614' (LNDM T 4018), which is an effigy of Marie de' Medici (1575-1642), Queen of France by Alessandro Maganza, identified and attributed by me. The woman's costume is also similar to that visible in another effigy of the Queen of France, created by Thomas de Leu or circle around 1605 (Austrian National Library), while her facial features resemble those of Christina of Lorraine (1565-1637), Grand Duchess of Tuscany (wife of Marie's uncle), after a print by Thomas de Leu, produced between 1587-1590 (The Royal Collection, RCIN 615750). Her features also resemble those in Christine's other portraits, such as that by the French painter, perhaps François Quesnel, from 1588 (Uffizi Gallery in Florence, Inv. 1890, n. 4338) or a copy by the Italian painter, painted after 1589 (sold at Sotheby's New York, May 26, 2023, lot 314). Around 1604, Frans Pourbus painted Christine's future daughter-in-law - Archduchess Maria Magdalena of Austria (1587-1631) in a yellow dress (Kunsthistorisches Museum, GG 3385) and her older sister Constance (GG 3306). Several portraits of the Polish-Lithunian Vasas preserved in Florence, such as the full-length portrait of Sigismund III (Inv. 1890, n. 2270) dating from around 1610. The monarchs of the Commonwealth undoubtedly also owned numerous effigies of the sovereigns of Tuscany. Some of them may also have been brought by Radziejowski, who was in Florence in 1616 and who in 1615 gave Grand Duchess Maria Magdalena a mirror in an amber frame.
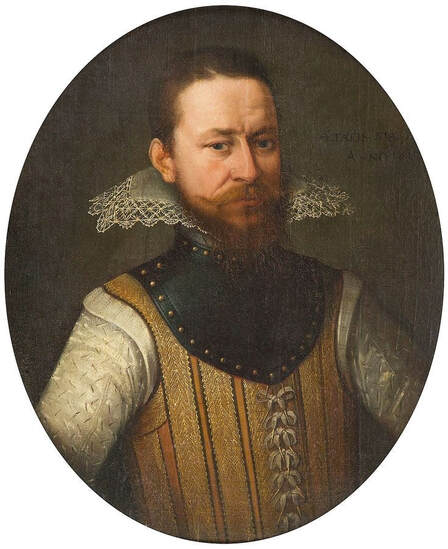
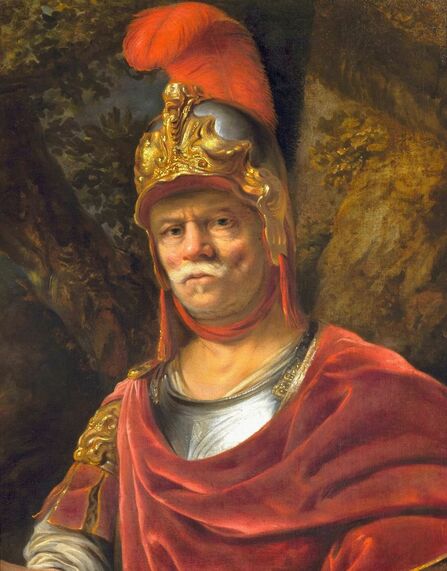
Portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa (1566-1632) by Daniël van den Queborn or follower of Frans Pourbus the Younger, 1590s, Czartoryski Museum in Kraków.
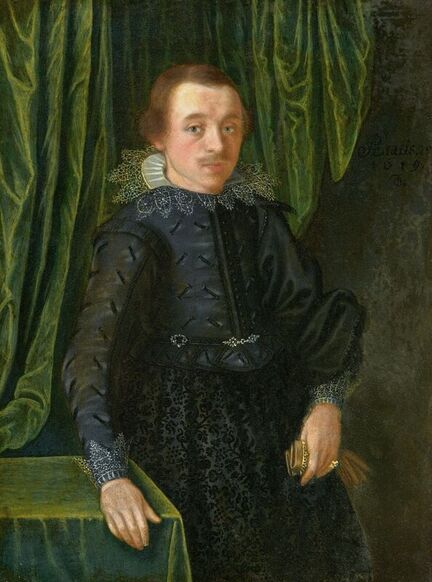
Portrait of courtier Stanisław Radziejowski (1575-1637), aged 18 by Daniël van den Queborn or follower of Frans Pourbus the Younger, 1593, Private collection.
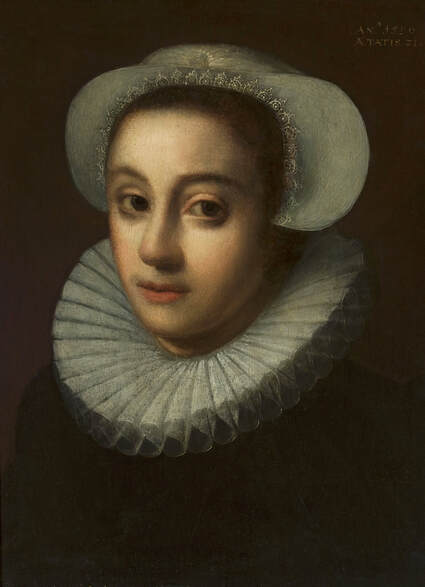
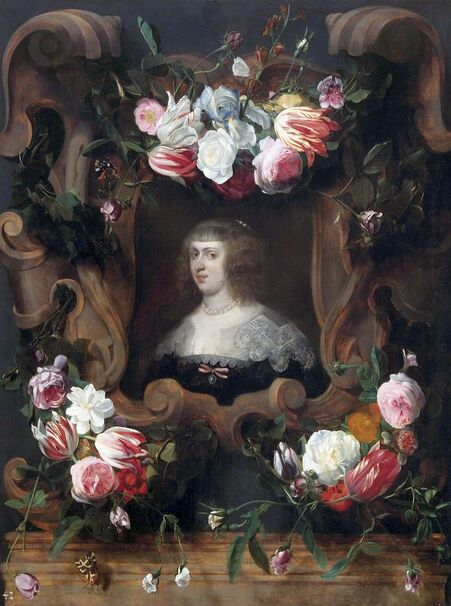
Portrait of Christina of Lorraine (1565-1637), Grand Duchess of Tuscany in French costume by workshop of Frans Pourbus the Younger, 1604, Lithuanian National Museum of Art in Vilnius.
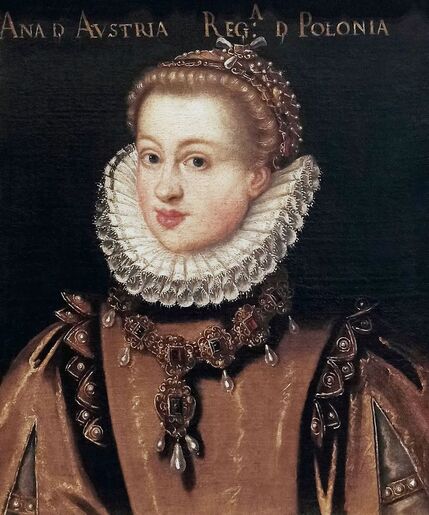
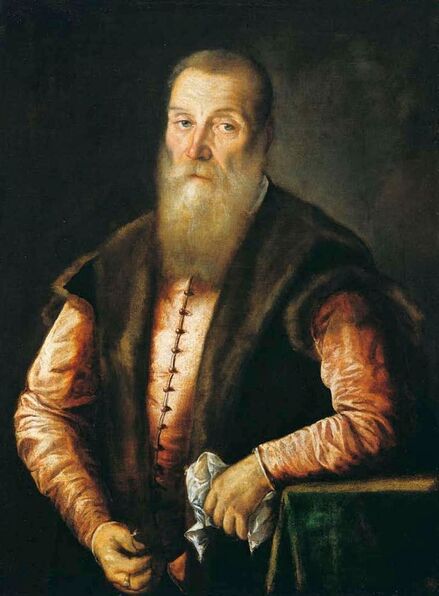
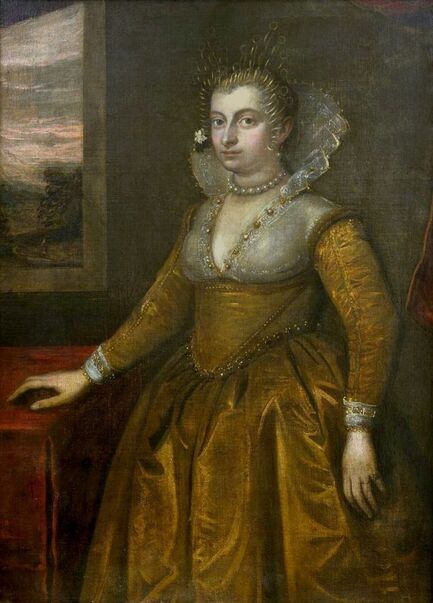
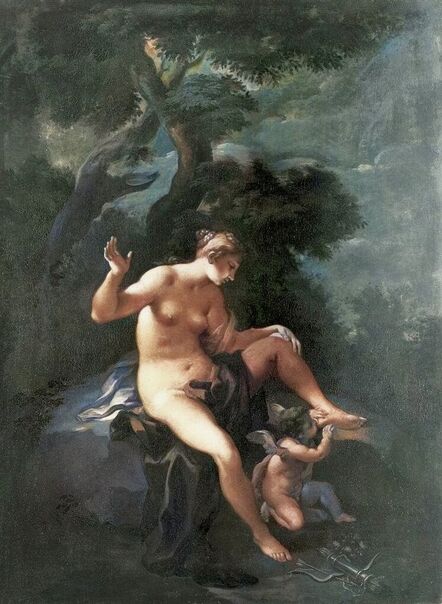
Portrait of Queen Anna of Austria by Jacopo Tintoretto
Italian painters, faithful to ancient Roman tradition, frequently idealized their models. On the other hand, painters of the Nordic, Netherlandish and German schools, preferred a sometimes grotesque naturalism. This is best seen in the portraits of Emperor Charles V. In the paintings by Marco Cardisco, Parmigianino, Titian, Giorgio Vasari and Francesco Terzi, he is a quite handsome man with harmonious features and large eyes, while in the paintings by Lucas Cranach, Jakob Seisenegger, Jan Cornelisz Vermeyen and Flemish painters, he sometimes looks more like a court jester than a ruler of one of the greatest empires in history.
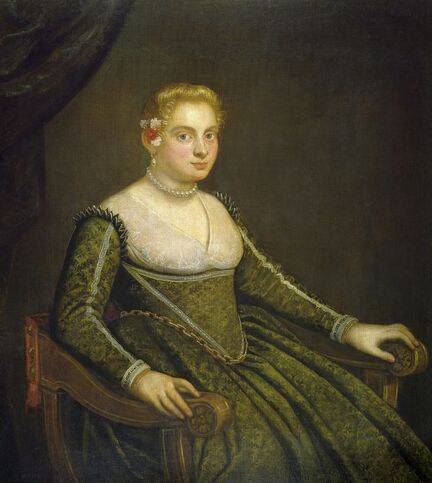
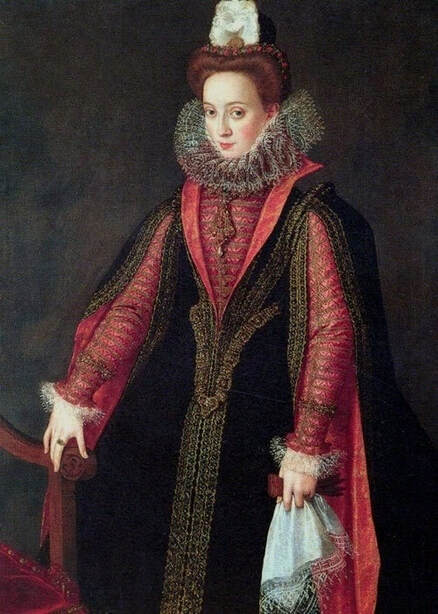
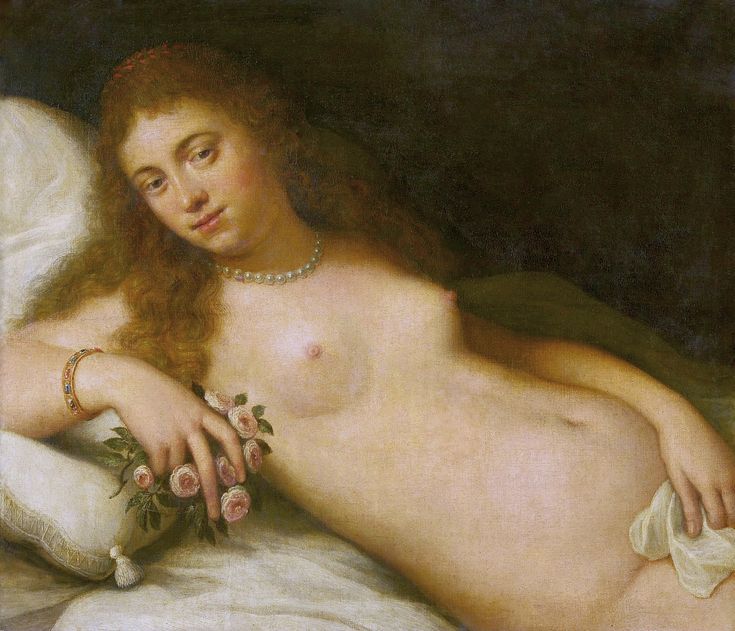
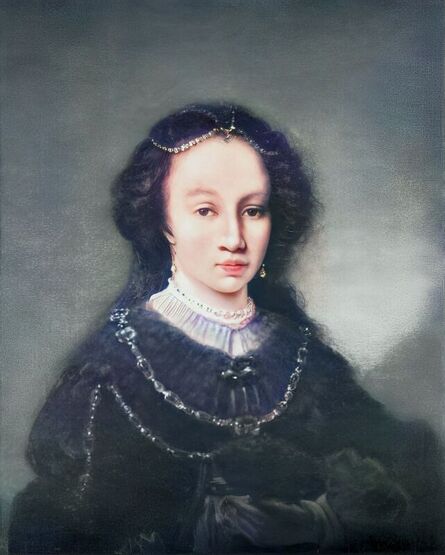
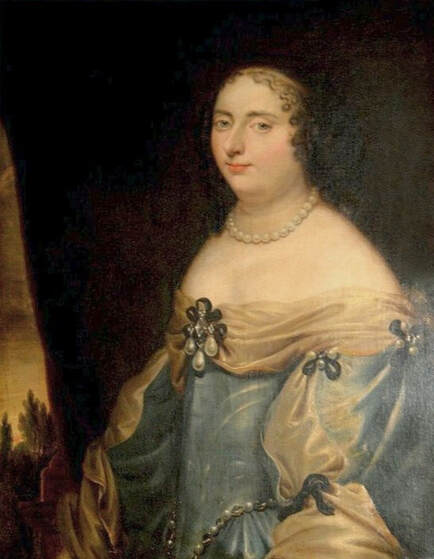
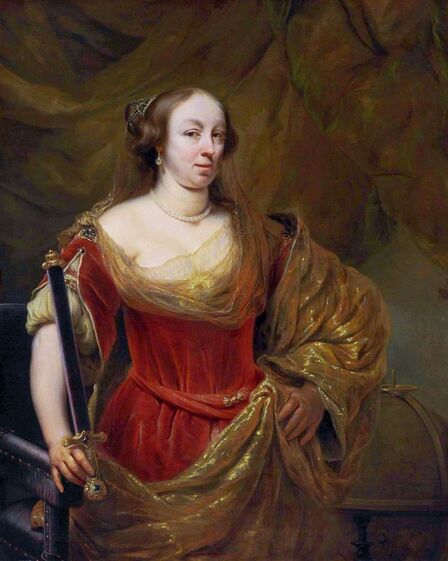
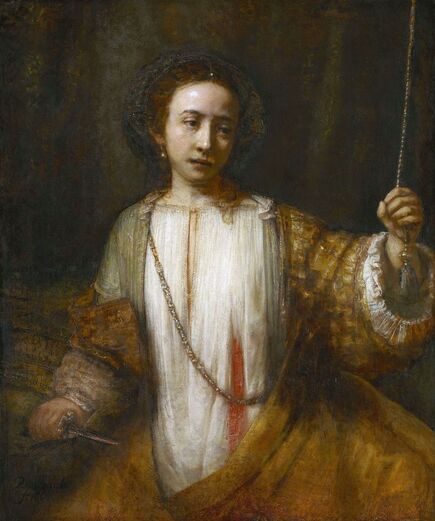
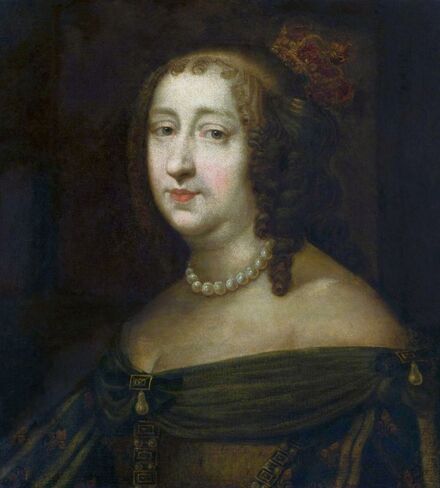
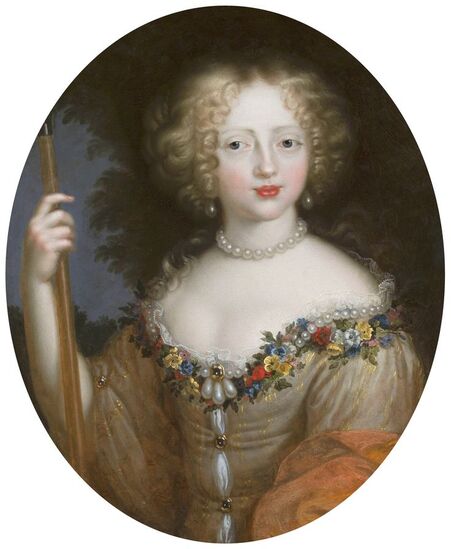
It was also a strong Habsburg tradition to collect effigies of different rulers of Europe, especially members of their own family. The effigies of Habsburg women who became queens of Bohemia, Hungary, Portugal, France, Denmark, duchesses of Tuscany, Mantua, Savoy, Parma, Bavaria or princesses of Transylvania are richly represented in their collections in Madrid and Vienna. It is therefore quite unusual that the Polish queens from the House of Austria are almost not represented in the collections known today. Some preserved inventories prove that the effigies of Polish monarchs were in the Habsburg collections in Madrid and Vienna. For example, the inventory of certain belongings of Queen Margaret of Austria, sister-in-law of King Sigismund III Vasa, subject to her guardian of the jewels (guardajoyas) Hernando Rojas, from October 1611, lists a miniature portrait (naipe) of the son of the king of Poland (Un retrato del hijo del rey de Polonia en un naipe, item 146) and thirteen "miniature portraits of members of the queen's household, our lady" (Trece retratos de naipe de personajes de la cassa de la reyna, nuestra señora, item 151) (after "Inventare aus dem Archivo del Palacio zu Madrid" by Rudolf Beer, p. CLXXV). For Sigismund's first wife, Anna of Austria (1573-1598), the portraits of her family left in Graz and lost during the Wawel fire in 1595 were obviously of great importance. After the fire, new portraits of the family in Graz had to be painted. The mother, Archduchess Maria Anna of Bavaria, soon sent a portrait of herself, but Anna said the picture bore no resemblance to her mother. "I'm sorry that YH [Your Highness] doesn't have a painter yet. My husband gave me permission for his painter to send him out to paint everyone when he has time, so he will have plenty of work to do" (Es ist mir ye gar laid, das ED [Eure Durchlaucht] jez kain maler hat. Mein gemahel hat mir sein maler bewilligt, wan es wider ED nit wer, denselben hinauszuschigken und alle abzemalen, wann er ainmal zeit hat, dann er hat jez gar vil ze arbaiten), she wrote to her mother in a letter dated April 6, 1595 most likely about the court painter Martin Kober (after "Das Leben am Hof ..." by Walter Leitsch, p. 371, 1267-1269, 1280, 1284, 2376, 2378-2379, 2562). Some information preserved in Austria on the portraits exchanged in preparation for the king's first marriage. The beginnings of the negotiation date back to a time when both were still children, the bride was not yet eight years old and the groom was fourteen and a half years old. It is possible that a portrait of an eight-year-old girl was sent by the Habsburgs. When the affair came to light nine years later, a portrait had to be sent again. "I would like to affirm that the king, as soon as he received the Archduchess Anna's effigy, fell deeply in love with it, opened it in his chamber and, having stood in front of it for a long time, also sent a retrato [Spanish for portrait] of her to his father, the king in Sweden, who was also happy to accept such things" (wol affirmiren, das der könig, alsbald er dero erzherzogin Anna contrafee bekomben, sich stark darein verliebt, dasselbe in seiner camer aufgemacht und villmallen ein guette lange weil darvor gestanden seye, auch seinem herrn vattern, dem könig in Schweden, ein retrato darvon geschickt habe, der im solches gleichsfalls gar wol gefallen lassen), wrote Sebastian Westernacher to Archduchess Maria Anna of Bavaria on May 19, 1591. The effigy of sixteen-year-old Anna hung in the king's bedroom and she was depicted wearing "a white-silver embroidered dress" (in einem weiß silbernen gewirkten rock abconterfeyet), according to a Kraków newspaper about the wedding in May/June 1592. Contemporaries certainly knew that these portraits were often largely beautified, so that the groom had only two options if he wanted to avoid exposing himself to the unknown: send beauty spies or trust the pictures. Before his first marriage, Sigismund sent such spies, but he probably also trusted the effigies. An emissary of the king delivered his portrait to the court master (Hofmeister) of Anna's mother, representing him wearing a jewel with the monogram SA, most probably of his uncle Sigismund Augustus or the groom and bride (Sigismund and Anna), recounted Archduchess Maria Anna to Emperor Rudolf II, in a letter from Graz, dated July 8, 1591 (seines künigs contrafet in ainem tafelein von ebano, darbey auch ain gemaldes glainot an einer klainen gulden kettl an des künigs hals hangend, und darinnen dise zwen puechstaben SA zu sehen). According to some sources, Sigismund's first wife did not care much for luxury. Her confessor, Fabian Quadrantinus (1549-1605) from Starogard Gdański, educated in Rome, affirmed that: "No gold, no jewels, no precious stones were seen on her. She was dressed mostly in black". Other documents prove she did it. According to one inventory, the queen owned more than a hundred items of clothing, and according to a second inventory, more than two hundred. She ordered goods from Florence and purchased luxury goods from Gdańsk. She always ate with a gold spoon and wore jewelry, regularly a ruby and emerald ring, as well as a necklace with a sapphire. Urszula Meyerin, in a letter dated April 3, 1598, claimed that even when she was young, Anna "never respected the voluptuousness, splendor, joys or lusts of the world, but despised and rejected them" (nimmermehr der welt üppigkeit, pracht, freuden oder wollusten geachtet, sondern vielmehr verachtet und verworfen). Jan Bojanowski, however, wrote shortly after her arrival that she was far from being melancholy (krolowa pani nasza is iest pani od melancholiei daleka) and that she was always joyful, but with a gracious dignity (letter of June 22, 1592). When the king wanted to go into battle against the Tatars, the queen expressed the wish to stay close to him, "if necessary, she also wanted to become a mercenary and wear armor" (wan's sein müeste, wolt sie auch ein landsknechtin weren und das fäleisen nachtragen, letter from Ernhofer to Archduchess Maria Anna, April 5, 1595). When she was sent a new portrait of her brother who had become fat, she wrote to her mother: "That's why it seems to me that he was in his 10th month [of pregnancy]" (Darum es dunkt mich auch, ehr sei ihn 10. monat gwesen, letter of February 1, 1597). In another letter to her mother, she commented "that the good old King of Spain is really funny and that you can really enjoy him" (das der guett alt kinig von Hispania erlich paufellig ist und das man sein auch schier gnueg hatt, letter of May 3, 1597). The queen was also adventurous and repeatedly went out incognito to see something, such as the procession on January 27, 1595. Together with Anna Radziwiłłowa née Kettler (1567-1617), she went out in a sleigh "dressed like a patrician lady" (wie burgerin geklaidet). They were not recognized by Polish women and when one of them tried to force her way before the queen, Radziwiłłowa began to argue with her (letter from Ernhofer to Archduchess Maria Anna, March 6, 1595). Similar to other Polish-Lithuanian ladies who experimented with fashion, the young queen undoubtedly also wore Venetian, French, Florentine or Flemish dresses, as described by Piotr Zbylitowski in his "Reprimand of Women's Extravagant Attire" (Przygana wymyślnym strojom białogłowskim), published in Kraków in 1600. Although the queen was very pious, she was not stubbornly zealous like her mother. From August 1592 to August 1593, the young queen lived near the Italianate court of the elderly Queen Anna Jagiellon, sending letters from residences in Ujazdów and Łobzów. Relations between the two queens were probably a bit difficult for many reasons. Above all, they had no common language, as the young queen only spoke German and Spanish and understood Latin and Polish - according to Giovanni Paolo Mucante (Intende, come dicono, la lingua latina, la spagnola, la todesca et anco la polacca, ma non parla se non todesca et spagnola, letter of September 25, 1596). Anna Jagiellon spoke Latin, Polish and Italian. At the beginning there were also some difficulties with priority. During the last six months of her life, the old queen once again lived under the same roof as the young queen. Anna of Austria one day sent her mother the gifts she had received from Anna Jagiellon (letter of November 22, 1593). Young Anna also cared for the old, sick queen herself. The relationship between the two was so good that Archduchess Maria Anna became truly jealous (letter from Salome von Thurn to Archduchess Maria Anna, May 5, 1594). In the Prado Museum in Madrid there is a portrait of a young woman in a green dress sitting on a chair (oil on canvas, 114 x 100 cm, inventory number P000484). The painting comes from the Spanish Royal Collection (no. 597) and was initially attributed to Paolo Veronese (1528-1588) and now to Jacopo Tintoretto (1518-1594). The woman has flowers in her hair and her costume indicate that the painting was made in the 1590s. A similar dress can be seen in a portrait of a woman from the Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden (inventory number Gal.-Nr. 249), dated around 1590 and previously thought to represent Marie de' Medici, Queen of France. Comparison with two woodcuts from Habiti Antichi Et Moderni di tutto il Mondo ... by Cesare Vecellio (Czartoryski Library, 2434 I Cim), book published in Venice in 1598 and assembling contemporary fashion from across the world - Gentildonne ne'Regiment (p. 104) and Donne per casa (p. 108), indicates that she wears the costume of a Venetian noblewoman at home. In this book, the effigy of King Sigismund III (Rè di Polonia / Poloniæ Rex, p. 346) was published with some typical costumes of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. Her protruding lower lip and provenance of the painting indicate that she is a Habsburg. The painter beautified the effigy by making the nose and lips smaller, however, the resemblance to other effigies of the Queen of Poland is notable, in particular the portrait from the Royal Castle in Warsaw (FC ZKW 1370), her effigy in the scene of the Birth of the Virgin by Juan Pantoja de la Cruz in the Prado Museum (P001038) and her portrait by Martin Kober in the Uffizi Gallery (2392 / 1890). Idealization was common at that time. The portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa in a large hat by workshop of Philipp Holbein II, which was before 1939 in the collection of Jan Perłowski in Warsaw (lost during the World War II), is the best example of this practice, perhaps initiated by the painter, who wanted the model to conform more to his standards of beauty. The woman in this portrait also closely resembles the queen's younger sister, Constance, who a decade later would become the second wife of Sigismund III, in her idealized portrait at Wawel Royal Castle (inventory number 1783). According to inventories of Queen Anna's clothing held at the National Archives of Sweden in Stockholm (Riksarkivet, Extranea 85), probably made around 1595, the queen also owned a dress similar to the one depicted in the painting: "A green damask skirt with gold edges" (Ain grien damasten rock mit golt gebrämbt, 92).
Portrait of Queen Anna of Austria (1573-1598) in a Venetian damask dress by Jacopo Tintoretto, ca. 1592-1594, Prado Museum in Madrid.
Portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa in a large hat by workshop of Philipp Holbein II, 1610s, lost during World War II.
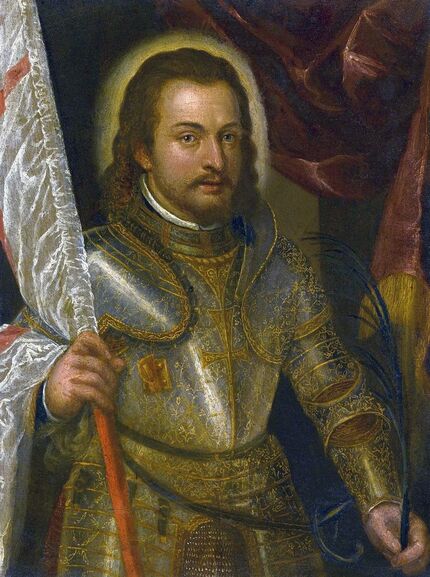
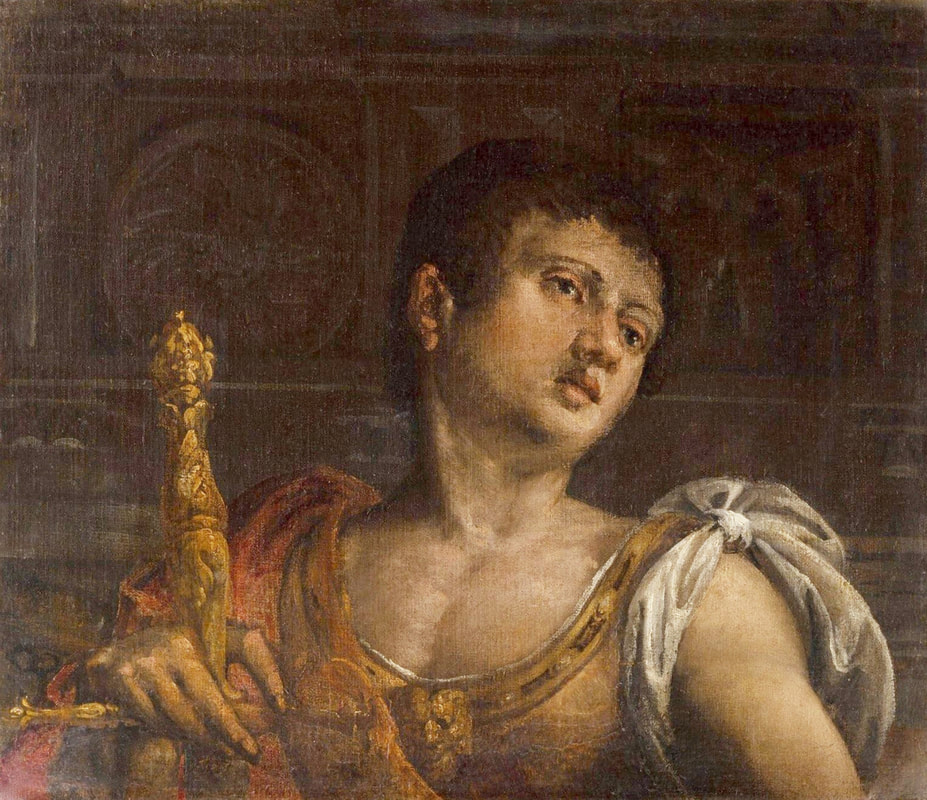
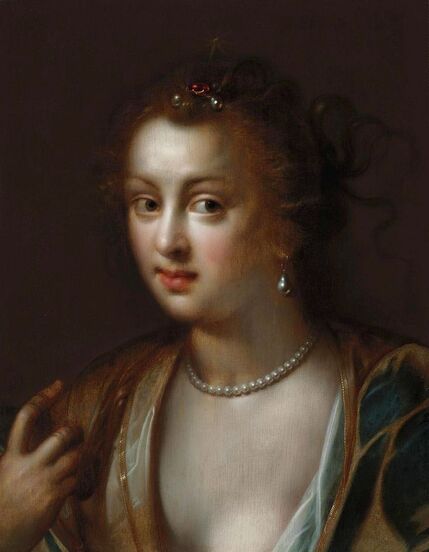
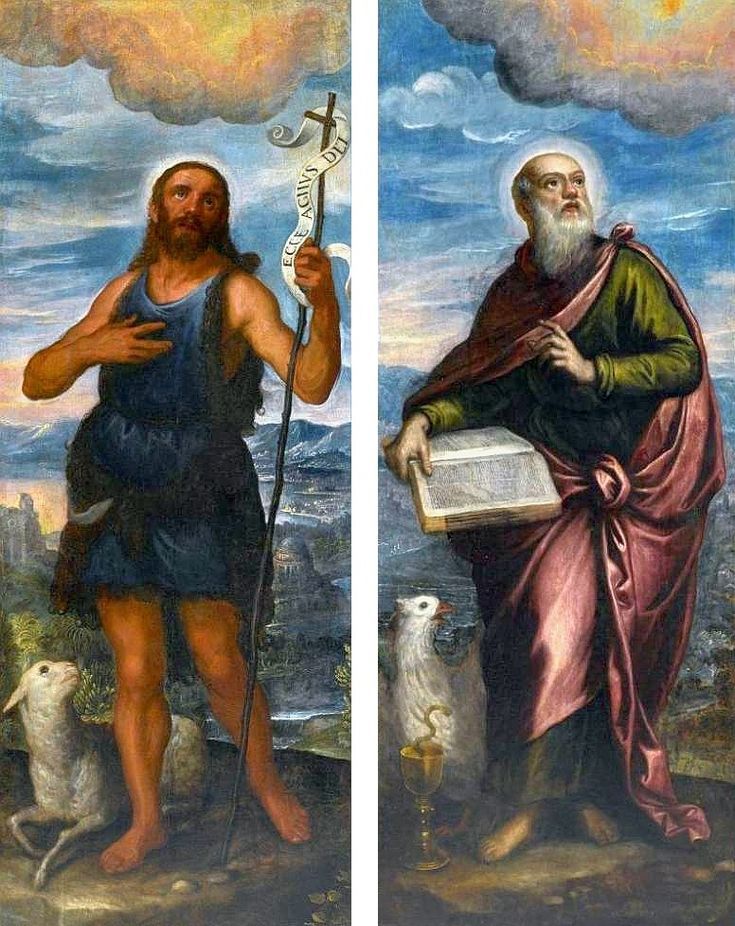
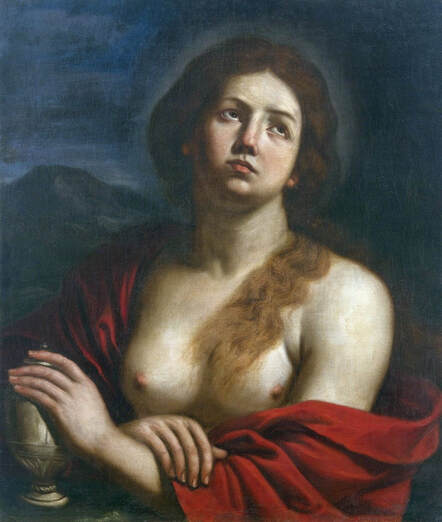
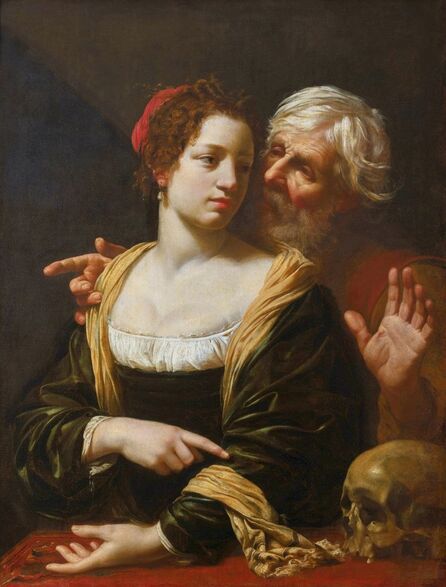
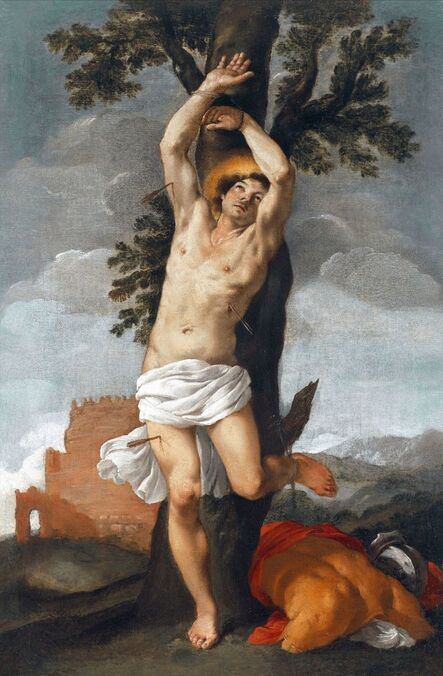
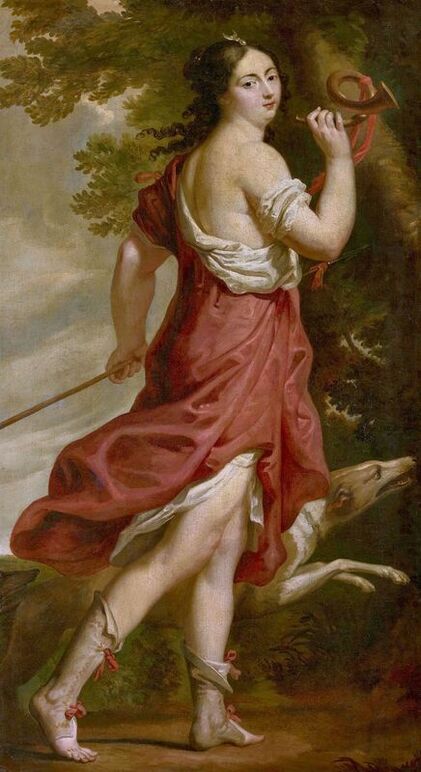
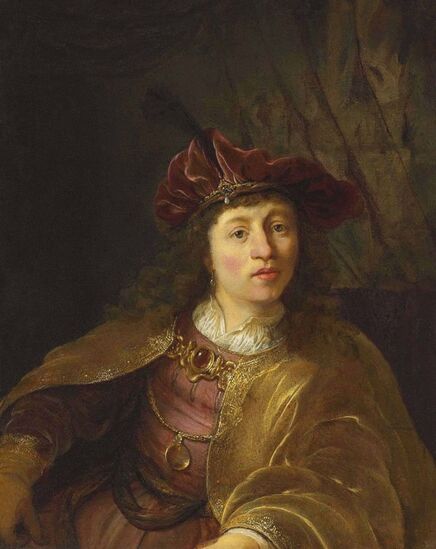
Portrait of Prince Jerzy Zbaraski as Saint George by Paolo Fiammingo
In 1591, after initial studies in the country, the young Zbaraski brothers Jerzy (George) or Yuriy (1574-1631) and Krzysztof (Christopher) or Kryshtof (1579-1627), descendants of Ruthenian Prince Fyodor Nesvitsky (died before 1442), went on a long trip abroad. They visited Germany, Italy and France. They studied in Padua (1592-1593) and visited Venice, Rome and Naples. In France, they went to Lyon, Bordeaux and Paris. While studying abroad, the brothers converted from Calvinism to Catholicism, however, they were supporters of religious tolerance and opponents of the enormous influence of the Jesuit Order.
They returned to the country at the turn of 1594 and 1595. In the following year (1596) they participated in the expedition to Hungary, in the Moldavian expedition and in the siege of Suceava. In 1598 Jerzy was in the retinue accompanying King Sigismund III Vasa in Sweden. Probably at the turn of 1600 and 1601, both Zbaraski brothers went to the Netherlands, where Jerzy studied Greek and history under Justus Lipsius in Louvain. Between 1602-1605, Krzysztof stayed in Italy again, where he mastered mathematical science under the supervision of Galileo. In 1616 also Jerzy returned to Padua where he enrolled at the university. In 1620, after the death of Janusz Ostrogski, Jerzy Zbaraski was appointed Castellan of Kraków. Like his yonger brother Krzysztof, he was not married and had no children. The Zbaraski brothers were the heirs of their father's enormous fortune, in addition to the estates of their mother, Duchess Anna Chetvertynska (Czetwertyńska), a member of the Ruthenian princely family, who according to Józef Wolff were descendants of Yaroslav the Wise, Grand Prince of Kiev. In the 16th century Chetvertynski family owned large estates in Ukraine and Belarus and like Zbaraski family, they had Ruthenian Pogonia, displaying Saint George defeating the dragon, in their coat of arms. Already in June 1589, in the retinue of bishop Radziwill and voivode Mikołaj Firlej, Jerzy visited the imperial court in Prague, where he had the opportunity to admire exquisite art collections of Emperor Rudolf II. From Venice, Jerzy, a great connoisseur and lover of art, brought the painting of Our Lady of Myślenice, later famous for miracles. According to "The History of the Miraculous painting of Our Lady in Myślenice", published in 1642 in Kraków, the original painting belonged to Pope Sixtus V, who left it in his will to the granddaughter of his sister, who became the abbess of a convent in Venice. When Prince Jerzy Zbaraski saw it in the convent, he wanted to have it, but the abbess did not want to give him the original, but agreed to make a copy. During the plague in Kraków in 1624, the painting was supposed to be burnt as "infected", but was spared from destruction. In 1633, the painting was transferred to the parish church in Myślenice. The image of the Virgin Mary is painted on a wood panel (50.3 x 67.8 cm) and because of some style similarities it is attributed to the Prague school from the beginning of the 17th century. The face and pose of the Virgin is however almost identical as in the painting showing Bathsheba at her bath (sold at Cambi Casa d'Aste in Genoa on 30 June 2020, lot 100), created by Paolo Fiammingo (Paul the Fleming, ca. 1540-1596). Fiammingo, born Pauwels Franck, was a Flemish painter, who, after training in Antwerp, was active in Venice for most of his life. He also possibly worked in Florence. Around 1573 he settled permanently in Venice, where he became a student of Jacopo Tintoretto. He opened a successful studio, which received commissions from all over Europe. One of his most important clients was Emperor Rudolf II and Hans Fugger, the heir of a German banking dynasty, who commissioned him in 1580 to produce several paintings to decorate the Swabian Escorial - Kirchheim Castle near Augsburg. The style of the hand of Mary in Myślenice painting is similar to that visible in the Lady revealing her breast (An honest courtesan) by Domenico Tintoretto, dated to the 1580s (Prado Museum in Madrid, inventory number P000382). The portrait of a man as Saint George in private collection, attributed to Italian or Venetian school, is also similar to Tintoretto's style. This small painting (28.7 x 21.7 cm) was painted on copper and the style of painting resemble more precisely the image entitled Profession of arms from the Munich Residence, attributed Fiammingo and created in the 1590s (Alte Pinakothek in Munich). Prince Jerzy Zbaraski was a founder of at least two churches dedicated to his patron saint, Saint George. One in the main seat of the Prince and his brother, Zbarazh in Volhynia, was the burial place of part of the Zbaraski family. The wooden church and fortified Bernardine monastery was founded in 1606, and from 1627 the new brick church was built, most probably to design by Venetian architect and engineer of His Highness King Sigismund III Vasa, Andrea or Andrzej dell'Aqua, driving nearly 1,600 piles into the marshy area. This church was destroyed in 1648. In 1630 Zbaraski also founded Saint George's church in Pilica. Between 1611-1612, Krzysztof commissioned to Vincenzo Scamozzi in Venice, a project for a fortified palace intendend for Zbarazh. In a commentary to his design, published in 1615 in his "L'Idea Della Architettura Universale", Scamozzi recalled numerous meetings and discusions on military architecture with the learned Ruthenian aristocrat. It was however a design of the Flemish military engineer Hendrik van Peene and Venetian Andrea dell'Aqua that was used to built the new Zbarazh fortress between 1626-1631. His treatise on artillery "Praxis ręczna działa" from 1630 (manuscript in the Kórnik Library), dell'Aqua dedicated to Prince Jerzy Zbaraski. In 1627 Jerzy founded the Zbaraski Chapel at the Gothic Dominican Church in Kraków, as a mausoleum for himself and his brother. It was built by the masons and sculptors Andrea and Antonio Castelli, probably according to the design of the royal architect Constantino Tencalla. In the baroque chapel there are monuments to two brothers carved in black Dębnik marble and white alabaster. Jerzy is depicted sleeping in armour and in a pose almost identical to that in the tomb monument of King Sigismund I the Old in the Sigismund's Chapel (1529-1531). His hairstyle is typical of a Polish-Lithuanian magnate from this period and he is holding his mace like if he was holding his manhood, a less subtle allusion to his virility or promiscuity. It is possible that some of the highly erotic works by Fiammingo were commissioned by Prince Zbaraski. The man depicted as Saint George resemble Jerzy Zbaraski from his tomb sculpture, his portrait painted in the 1780s after original from the 1620s (Wilanów Palace in Warsaw) and effigies of his brother Krzysztof (National Museum of the History of Ukraine and Lviv National Art Gallery). Jerzy was accused of a dissolute lifestyle and when he decided to put an end to coin counterfeiters with whom he was about to cooperate, they "persuaded one lady who visited the prince to give him a poison" (after "Niepokorni książęta" by Arkadiusz Bednarczyk, Andrzej Włusek). Despite having no children, the memory of the last Prince Zbaraski preserved in the exquisite works of art that he commissioned.
Portrait of Prince Jerzy Zbaraski (1574-1631) as Saint George by Paolo Fiammingo, 1592-1594, Private collection.
Our Lady of Myślenice by Paolo Fiammingo, 1592-1594, Saint Mary's church in Myślenice.
Portrait of royal courtier Sebastian Sobieski by Leandro Bassano
Around October 16, 1593, king Sigismund III Vasa departed from Gdańsk for his coronation as the hereditary king of Sweden. He was accompanied by his courtiers, including Sebastian Sobieski (ca. 1552-1614), third son of captain Jan Sobieski (ca. 1518-1564) and Katarzyna Gdeszyńska. Earlier that year, in February, Sebastian was sent by the King as his envoy to the Lublin Sejmik (regional assemby). It is the first confirmed important function of this royal courtier. "Instructions for the Lublin Sejmik given from His Majesty to Sebastian Sobieski, a royal courtier in Warsaw on February 16, 1593", is in the Czartoryski Library in Kraków (BCz 390).
Sobieski most probably studied at the Calvinist school in Bychawa near Lublin. On December 17, 1576, probably thanks to the intercession of the Crown Vice-Chancellor Jan Zamoyski, he was admitted, as a page, to the court of king Stephen Bathory. Then, like his brothers, due to growing influence of the Counter-Reformation movement at the royal court, he converted to Roman Catholicism. On May 1, 1584, he was transferred to the group of salatariati saeculares (lay beneficiaries) in which he was until the death of the king. He became a supporter of Zamoyski, supported the election of king Sigismund III and, apparently, he participated in the defense of Kraków against the attack of the troops of Archduke Maximilian II in 1587 and the Battle of Byczyna in 1588. From May 1596, he held the position of Standard-Bearer of the Crown and as such he was depicted in the "Entry of the wedding procession of Sigismund III Vasa into Kraków in 1605" (Royal Castle in Warsaw). Portrait of a bearded man in oriental costume from private collection in France, due some similarity to the style and, possibly, dates of his life is attributed to Hans von Aachen (1552-1615), a German painter trained in Italy. In 1592, while he was still working in Munich, von Aachen was appointed a court painter of Rudolph II, Holy Roman Emperor and moved to Prague in 1596. According to inscription in Latin in upper right corner the man was 41 years old in 1593 (ANNO 1593 / ÆTATIS 41), exacly as Hans von Aachen, but also Sebastian Sobieski, born in about 1552. The portrait is evidently not a self-portrait of imperial court painter and this wealthy nobleman was depicted in a crimson silk żupan buttoned up to with gold buttons, very similar to żupan buttons of Stanisław Piwo, deputy cup-bearer of Płock, from the second quarter of the 17th century (Skrwilno Treasure, Toruń Regional Museum). His black coat trimmed with lynx fur it is almost identical to the one shown in the portrait of Jan Opaliński (1546-1598), created in 1591 (National Museum in Poznań), or in Twelve Polish and Hungarian types by Abraham de Bruyn, created in about 1581 (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam). His lace collar is very similar to the one in the effigy of The Marshal (Stanisław Przyjemski with a marshal staff) from Stanisław Sarnicki's "Statutes and records of crown privileges" by Jörg Brückner in Kraków, created in 1594 (Czartoryski Library). Letters on the table are very important documents, most probably envoy instructions given by the king. The style of painting is identical with portrait of Doge Marino Grimani (1532-1605), created in about 1595 by Leandro Bassano, signed: LEANDER A PONTE BASS [ANO] EQVES F. (Princeton University Art Museum). The man bear a resemblance to effigies of Sebastian Sobieski's brother Marek Sobieski (ca. 1550-1605), voivode of Lublin (1862 woodcut after lost portrait from the Zamoyski collection) and his brother's descendant (Marek's grandson), king John III Sobieski (portrait painting from the 1670s in the Kórnik Castle). Mentioned portrait of Jan Opaliński in Poznań, a copy of a painting destroyed during World War I (from the burnt manor house in Rogów near Opatowiec), is considered by Michał Walicki as a very definite manifestation of the Venetian tradition "referring to the portraits of the Bassanos" (after "Malarstwo polskie: Gotyk, renesans, wczesny manieryzm", p. 33). Stilistically very similar was the painting which was before World War II in the Saint Lazarus hospital in Warsaw bearing the inscription in Latin: R. P. PETRVS SKARGA SOCIETATIS IESV. It represented the court preacher of King Sigismund III Vasa, Piotr Skarga (1536-1612), who became the first priest to hold it. The hospital was established in 1591 on his initiative for the poor and lepers and the founder was depicted sitting in his study before a table covered with an oriental carpet.
Portrait of royal courtier Sebastian Sobieski (ca. 1552-1614) aged 41 by Leandro Bassano, 1593, Private collection.
Portrait of Jan Opaliński (1546-1598) aged 45 by follower of the Bassanos, 1591, National Museum in Poznań.
Portrait of preacher Piotr Skarga (1536-1612) by follower of the Bassanos, after 1591, Saint Lazarus hospital in Warsaw, lost.
Portraits of Queen Anna of Austria and her sisters by Martin Kober and Spanish painters
The inventories of Queen Anna's clothing held at the National Archives of Sweden in Stockholm (Riksarkivet, Extranea 85) were probably made around 1595 because include many items created when she was already queen, such as pillows embroidered with the coats of arms of Poland and Lithuania. The young queen dressed primarily in black Spanish saya in the Central European version as shown in her official portraiture by Martin Kober. She also had specifically "Polish clothing" (Volgen IM polnische klaider, items 205-212) and shorter Spanish dresses (Spänische kurze jänger). In private, she wear many colorful clothes - brown, purple, leibfarb (skin color), yellow, red, white, tyrkroth (Turkish red), aschenfarb (gray), blue and others. She also had at least three green dresses: "A green gold cloth robe" (Ain grien gulden stuck, 72), "A green satin skirt with gold edges" (Ain grien atleser rock mit gulden porten, 87) and "A green damask skirt with gold edges" (Ain grien damasten rock mit golt gebrämbt, 92) (after "Das Leben am Hof ..." by Walter Leitsch, p. 1282, 2381, 2555-2562, 2569, 2571).
The green satin "skirt" (87), a symbolic color of fertility, mentioned in the inventory could be the same dress that was depicted in a portrait of Archduchess Anna at the age of 18, dated 1592 (ANNA ARCHIDVCISSA AVSTRIÆ. / ANNO ÆTATIS / XVIII. / MD / LXXXXII.) from the Bavarian State Painting Collections (on permanent loan to the Germanisches Nationalmuseum in Nuremberg, oil on canvas, 60.5 x 50.9 cm, Gm661 / 6846). This portrait, as well as other similar portraits of her mother and siblings, come from Neuburg Castle. It was therefore most likely originally part of the dowry of Constance of Austria (because her portrait is missing from this series) and later the dowry of her daughter Anna Catherine Constance Vasa. Her large golden pendant shows Jupiter and Danae. The young archduchess was therefore painted shortly before her marriage to Sigismund and the style of this painting is close to Martin Kober, who also worked for the Habsburgs - notably similar to the portrait of Anna's daughter Anna Maria Vasa (1593-1600) at the convent of Las Descalzas Reales in Madrid and portrait of Stanisław Lubomirski (1583-1649) and his sister Katarzyna (d. 1612) at the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna. All of Anna's sisters were depicted in similar dresses. Because of this and the strong family resemblance of all the sisters, it is sometimes difficult to determine the model in other series, such as that from the dowry of Archduchess Maria Magdalena of Austria, today at the Villa del Poggio Imperiale in Florence. This series is attributed to Giacomo de Monte (Jakob de Monte), although the style is also close to Kober. In the series in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, probably from Graz Castle, the portrait of Maria Christina of Austria (1574-1621), is identifed to depict Anna (inventory number GG 3238). This effigy is attributed to de Monte, who used the same set of study drawings as Kober to create the portrait from the Neuburg Castle painted in 1595, when the Archduchess was 21 years old (MARIA CRISTIERNA ARCHIDVCISSA AVSTRIÆ. / ANNO ÆTATIS XXI. / M.D. / XCV., Alte Pinakothek in Munich, oil on canvas, 60.5 x 52 cm, 6845). In the series from the Convent of the Descalzas Reales in Madrid, also attributed to Giacomo de Monte, the four sisters were transformed into Christian saints - Anna was depicted as Saint Dorothy, Maria Christina as Saint Lucy, Catherine Renata as Saint Catherine and Elizabeth as Saint Agnes. Among the portraits of the family members of Margaret of Austria, Queen of Spain, which were in the Queen's Gallery of the Royal Alcazar in Madrid in 1636, there was undoubtedly also a portrait of the Queen of Poland. These portraits were described as: "Parents and brothers of Queen Doña Margarita. Thirteen half-length portraits of the parents and brothers of Queen Doña Margarita, without frames (?), and made by Bartholome Gonçalez for El Pardo" (Padres y hermanos de la Señora Reina Doña Margarita. Treçe retratos de medio cuerpo arriba de los Padres y hermanos de la Señora Reina Doña Margarita, sin molduras, y los hiço Bartholome Gonçalez para el Pardo, Inventory of the Alcázar of 1636, pp. 185-188). Seven portraits from the series, created by the court painter Bartolomé González y Serrano (1564-1627) before 1627, were deposited in 1918 at the Spanish embassy in Lisbon and were destroyed during the fire of 1975. One of them was reproduced in 1968 in the Antemurale XII (Institutum Historicum Polonicum Romae) as a portrait of Anna of Austria (Anna Regina Poloniae, Museo del Prado). In this likeness, she wears a typical Spanish saya from the end of the 16th century. According to an article by Gloria Martínez Leiva ("El incendio de la Embajada española en Lisboa de 1975", January 16, 2018), it is not an effigy of Anna, but of her sister Archduchess Catherine Renata of Austria (1576-1599). The young girl actually resemble more the effigy of Catherine Renata in 1595, when the Archduchess was 18 years old (CATERINA RENEA ARCHIDVCISSA / AVSTRIÆ. ANNO ÆTATIS XVIII. / M.D. / XCV., Germanisches Nationalmuseum, oil on canvas, 60.6 x 50.9 cm, Gm665 / 6847) by Kober then the portrait of her elder sister from the same series. Posthumous effigies of Archduchess Maria Anna and her husband Charles II of Austria (1540-1590) by González, painted after 1608 (Prado Museum, P002434, P002433), were most likely part of the Lisbon series. Regarding the series by Kober, in which some effigies bear different dates (1590, 1592 and 1595), the painter probably created them at the same time but they show the models at different ages and dates. He most likely copied several effigies of Constance's family while working on paintings for her (or one of her sisters') dowry in 1595 in Graz. The eldest daughter of Archduchess Maria Anna was also depicted with her sisters and mother in the scene of the Birth of the Virgin by Juan Pantoja de la Cruz in the Prado Museum (oil on canvas, 260 x 172 cm, P001038). This painting, commissioned by Queen Margaret of Austria for her private oratory in the palace of Valladolid, was created in 1603 (signed and dated: Juº Pantoja Dela .+. Faciebat. / 1603). It probably commemorates the birth and death of the Infanta Maria of Spain, who died in infancy in her first month (March 1, 1603). Her grandmother, Archduchess Maria Anna, is depicted as a divine midwife accompanied by her already deceased daughters - Anna, Queen of Poland and Archduchess Catherine Renata of Austria, who died at the age of twenty-three before her marriage to Ranuccio I Farnese, Duke of Parma. That is why both of them wear more Italian dresses, because in Poland-Lithuania, Italian fashion was popular. All three look at the viewer. The young girl near Saint Anne's bed also looks at the viewer. Her Habsburg features allow her to be identified as Constance of Austria, who in 1602, with her younger sister Maria Magdalena, was considered at the court of Madrid as a candidate to marry Ferdinand I, Grand Duke of Tuscany, but ultimately married Sigismund III in 1605. Although Pantoja accompanied the royal family on journeys to Valladolid, Burgos, Lerma and El Escorial, he probably never left Spain. Archduchess Maria Anna visited Spain for her daughter Margaret's wedding, but that was in 1599. So all the effigies were created by the Spanish painter based on other portraits of family members of the queen or on study drawings, like the mentioned paintings by Bartolomé González. Archduchess Maria Anna's great attachment to her eldest daughter is demonstrated by the fact that when the Archduchess fell into panic because of the Ottoman advance, she wanted to flee to Poland to be with her daughter, and not to Munich, Prague, Brussels or Madrid. In a letter dated September 18, 1594 from Poznań, the queen assured her mother that she could come to Kraków (solang mein gmahel und ich waß haben, so sol ED auch allezeit unverlassen sein).
Portrait of Archduchess Anna of Austria (1573-1598), aged 18 in 1592, by Martin Kober, ca. 1595, Germanisches Nationalmuseum.
Portrait of Archduchess Maria Christina of Austria (1574-1621), aged 21, by Martin Kober, 1595, Alte Pinakothek in Munich.
Portrait of Archduchess Catherine Renata of Austria (1576-1599), aged 18, by Martin Kober, 1595, Germanisches Nationalmuseum.
Birth of the Virgin with portraits of Archduchess Maria Anna and her daughters by Juan Pantoja de la Cruz, 1603, Prado Museum in Madrid.
Portrait of Queen Anna of Austria (1573-1598) and her sister Archduchess Catherine Renata of Austria (1576-1599) in the scene of the Birth of the Virgin by Juan Pantoja de la Cruz, 1603, Prado Museum in Madrid.
Portrait of Archduchess Catherine Renata of Austria (1576-1599) in Spanish dress by Bartolomé González y Serrano, after 1608, Prado Museum in Madrid, destroyed.
Portraits of Queen Anna of Austria nude (Sleeping Venus) by Dirck de Quade van Ravesteyn
Queen Anna of Austria, first wife of Sigismund III, frequently exchanged effigies with members of her family in Austria. Her portraits (conterfet, conterfeit), usually small miniatures (Meiner klein conterfet schick ich ED), are frequently mentioned in her letters to her mother. In January 1595, Anna's brother, Ferdinand of Austria (1578-1637), was about to send two paintings, one for his mother, "the other for your sister, the queen" (das ander für dein schwester die kinigin), according to a letter from Archduchess Maria Anna to him dated January 3, 1595 from Graz (after "Das Leben am Hof ..." by Walter Leitsch, p. 1278, 2380, 2569).
"The reigning queen is 19 years old, slim, but of nice face, pleasant and polite" wrote the Venetian envoy, Pietro Duodo, in his 1592 report to the Venetian Senate (after "Zbiór pamiętników ..." by Julian Ursyn Niemcewicz, p. 76). Judging by the official portraits of the queen by Kober, nothing can be said about her figure, because she is completely covered by her Spanish dress and only her face is clearly visible. So was Duodo allowed to see the queen naked or admire her naked effigy? In a letter of May 19, 1591 to Archduchess Maria Anna, regarding the portrait of Anna received by Sigismund, Sebastian Westernacher reports that the king "opened it in his room" (in seiner camer aufgemacht). The fact that the king admired it in his private chamber indicates that the portrait was nude or erotic as such effigies were frequently covered. For example, the inventory of paintings from the collection of Princess Louise Charlotte Radziwill (1667-1695), drawn up in 1671, mentions "A closed filthy picture" (Obraz plugawy zamykany, item 685 / 56) (after "Inwentarz galerii obrazów Radziwiłłów z XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska, p. 279). Regarding one of her portraits, sent from Kraków to Vienna, the Queen declared in a letter that she preferred it to be destroyed rather than fall into the wrong hands (after "Sztuka i polityka ..." by Juliusz Chrościcki, p. 33-34). Such a statement clearly indicates that the effigy must have been very intimate in nature. The same statement concerns the effigies of her family which were lost in the fire of Wawel Castle in 1595. Some of the Queen's personal belongings, including jewelry, were thrown out of windows into the garden and then not all the items were found, some were stolen, including the chest with "portraits of Her Ducal Highness and all the young princes and princesses" (comterfett von ir f[irstlich] d[urchlaucht] und der ganzen jungen herschaft), according to a letter from Urszula Mayerin dated April 7, 1595. "I would prefer them to burn, instead of being stolen" (Es wer mir lieber, sie weren verbrunnen, ais das mans gestolen hat), the queen said, which also indicates that some of them could be erotic in nature. In many ways, the young queen tried to imitate or compete with the old queen Anna Jagiellon. After the fire, she regretted losing all her tiaras: "I lost all my diadems, including one of 53 very large pearls, almost as large as those on the old queen's string of pearls, and various small things" (Ich hab alle meine krenl verloren, darunder ainẞ [mit] 53 gar grosse perl, schier so groẞ alẞ der alten kinigin grosse sch[n]uer und allerlay kleine sachen) (after "Der Brand im Wawel ..." by Walter Leitsch, p. 248, 251). The marriage of all of Anna Jagiellonica's granddaughters was a highly political affair, so their cousin, Emperor Rudolf II, controlled many aspects of the marriage arrangements. Entire galleries of bridal portraits were made for the emperor during these years and Anna of Tyrol (1585-1618) and Constance of Stiria (1588-1631), the sister of Queen Anna of Austria, were also painted for Sigismund after the death of his first wife. At the end of 1603, the emperor sent the painter Hans von Aachen to Innsbruck. The painter then left for Bavaria, Savoy and Modena, when Rudolf changed his mind and thwarted the negotiations with Sigismund III regarding the marriage with Anna of Tyrol. It was even suspected that the painter would "not paint well" (nichz guttz mallen) to prevent the marriage. The effigy of Anna of Tyrol's older sister, Archduchess Maria of Austria (1584-1649) by Hans von Aachen, now kept at the National Art Gallery in Lviv (inventory number 3857), was most likely created for Sigismund in 1604 (dated upper left). The naturalism of this effigy as well as that of Constance (Kunsthistorisches Museum, GG 9452) is almost grotesque, closer to the paintings from the imperial cabinet of curiosities (Wunderkammer) than to the effigies of relatives of the emperor. The effigies of the young queen Anna of Austria sent to the Medicis preserved in Florence (a three-quarter-length portrait and a miniature - Uffizi Gallery, 2392 / 1890, Inventario Palatina, n. 624) and in Munich, offered to the Wittelsbach family (full-length portrait - Alte Pinakothek in Munich, 6992 and a miniature - Bavarian National Museum, R. 1459). As was customary at the time, the emperor had to receive images of his cousin, the Queen of Poland, but no portrait of Anna sent to her family in Vienna, Graz or Innsbruck is known. In the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna there is a painting of a reclining nude woman ("Sleeping Venus" or "Venus in repose") (oil on panel, 80 x 152 cm, GG 1104). The painting probably comes from the collection of Rudolf II, but it is clearly evidenced in the gallery in 1783 (after "Joseph Heintz ..." by Jürgen Zimmer, p. 101). The painting was thought to be identical to the painting mentioned in the inventory of the Vienna collection between 1610-1619: "Item a nude lady, painted by Joseph Hainzen" (Item ein nackhets weib von Joseph Hainzen untermahlt, No. 83) and to depict a courtesan at the court of Rudolf II in Prague or his mistress, such as Kateřina Stradová also known as Catherina Strada (ca. 1568-1629), the daughter of the painter Ottavio Strada the Elder, with whom he had six children. However, no clear evidence has ever been established. Such private and intimate effigies were not intended for the general public, as today when they can be easily seen in museums and different exhibitions, but for a narrow circle of spectators, so we would probably never find clear written confirmation of who was represented. The painting is now attributed to Dirck de Quade van Ravesteyn, a Dutch painter who, between 1589 and 1608, was painter at the court of Rudolf II in Prague, where several painters from Holland and Flanders were working at the time. He was admitted in June 1589 as a portraitist. In 1598, there is evidence that he owned a house in Prague's Malá Strana and even lent large sums of money to other people, including artists. He was inspired by the works of other painters, including two "wandering" Flemish painters Hans Vredeman de Vries and his son Paul, who came from Gdańsk to Prague in 1596. At the Museum of Fine Arts in Dijon, there is a pendant (companion piece) to this painting (oil on panel, 90 x 164 cm, CA 134). It also most likely came from the imperial collection in Vienna and, before 1809, it was in the gallery of the Belvedere Palace from where it was taken by Napoleon. There are some differences between the two paintings, such as the color of the pillow, however, both paintings depict the same woman, seen from a different angle. A recent restoration revealed the presence of gold coins at the top of the painting, so originally the composition was intended to represent the model in the mythological scene of Danae, seduced by Jupiter transformed into golden rain. A large gold pendant with the scene of Jupiter and Danae can be seen in the portrait of Archduchess Anna at the age of 18 (Germanisches Nationalmuseum, Gm661). The Vienna version was cut on the left and also indicated the presence, at the top of the composition, of gold coins. The two paintings were exhibited together at the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna during the temporary exhibition "Baselitz - Naked Masters" from March 7 to June 25, 2023. Embroidered pillows as elaborate as those depicted in the paintings were mentioned in the inventory of the queen's possessions (Riksarkivet in Stockholm, Extranea 85) - "a pillow with the Lithuanian coat of arms embroidered in silver, gold and silk" (Ain kyß mit dem litauischen wapen mit silber, golt und seyden gestickt, 213), "a pillow embroidered with silver, gold and silk with the Polish coat of arms" (Mer ain gewirkts kyß von silber, golt und seyden mit dem polnischen wapen, 214) or "a pillow embroidered with silver, gold and silk with the coat of arms of the Tęczyński family" (Mer ain gewirkt kiß von silber, golt und seyden mit dem tentschinischen wapen, 215). A work from de Quade van Ravesteyn's early period of work, dating from around 1590, showing the mystical marriage of Saint Catherine, is in the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on panel, 29.5 x 21.5 cm, M.Ob.108, earlier 235). It comes from the collection of Piotr Fiorentini in Warsaw, bequeathed to the School of Fine Arts in 1858. It is possible that it was part of the royal collection which survived the Deluge (1655-1660) and that the painter visited the Polish-Lithuanian royal court in the 1590s. Two portraits of Sigismund III are also close to the style of de Quade van Ravesteyn - a miniature in the Czartoryski Museum in Kraków showing the king at the age of 30, thus created in 1596 (inscription: SIGISMVND[US] POLONIÆ ET / SVECIÆ REX M[AGNUS] DVX LITH[UANIÆ] / ET FINLANDIÆ ANNO ÆTA / TIS XXX, oil on copper, 17.2 x 14.2 cm, MNK XII-144) and a portrait in the National Museum in Warsaw (inscription: SIGISMVNDT. D.G. REX POLONIÆ, oil on panel, 27 x 20 cm, MP 188 MNW). At the turn of the 16th and 17th centuries, numerous paintings were commissioned and purchased in Prague by the Polish-Lithuanian royal court from the artists of the imperial court of Rudolf II. Some of them or their agents also arrived in the Commonwealth. The best example of such a work, produced in Prague, Augsburg or Kraków, is the signed portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa by Joseph Heintz the Elder (J. Heintzen F. / SIGISMVNDVS ... / REX POLONIAE / & SVECIAE ...) in the Alte Pinakothek in Munich (inventory number 11885). Another example is a composition inspired by Pomarancio's fresco at Santo Stefano Rotondo in Rome - Stoning of Saint Stephen, attributed to Hans von Aachen. It was created or acquired for Saint Stephen's Church in Kraków (demolished in 1801, now in the new Saint Stephen's Church). In 1601, Andrzej Opaliński (1575-1623) acquired in Prague a portrait of Michael the Brave (1558-1601), prince of Wallachia, for the king, perhaps by Bartholomeus Spranger and a work signed by Spranger (B. SPRANGERS. ANT .F.) from the same period, depicting Vanitas (Putto with a skull), is in the Wawel Royal Castle (inventory number 935, from the Miączyński-Dzieduszycki collection). One such early import to the Commonwealth could also be Spranger's Saint Ursula with female martyrs in the Lithuanian National Museum of Art (LNDM T 3995), donated to the Vilnius Society of Friends of Science before 1937. At the National Museum in Warsaw there is also the Allegory of Fortune from the circle of Spranger (M.Ob.763 MNW) and his signed drawing depicting Original Sin (B(?) Spranger in., Rys.Ob.d.701, from the Society for the Encouragement of Fine Arts in Warsaw), as well as the portrait of Alfonso II d'Este, Duke of Ferrara close to the style of Hans von Aachen (M.Ob.1913, from the collection of Jan Popławski) and Martyrdom of Saint Sebastian, after the print by Jan Harmensz. Muller, painted by von Aachen or circle (M.Ob.812, from the post-WWII Art Repository in Kraków). Both paintings clearly reference Titian's Jagiellonian nudes, particularly the portrait of Princess Isabella Jagiellon (Venus of Urbino) and the portrait of Anna Jagiellon as Venus with an organist and a dog, copies of which undoubtedly also appeared in the royal collection before the Deluge. The woman greatly resemble Anna of Austria from her portraits by Sofonisba Anguissola (private collection) and Tintoretto (Prado Museum, P000484), identified by me. It must therefore be concluded that through these paintings, the young Queen of Poland wanted to show her cousin the Emperor, that she is not a specimen from his cabinet of curiosities, but a beautiful sovereign of the Realm of Venus.
Mystical marriage of Saint Catherine by Dirck de Quade van Ravesteyn, ca. 1590, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Queen Anna of Austria (1573-1598) nude (Sleeping Venus) by Dirck de Quade van Ravesteyn, ca. 1595, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Portrait of Queen Anna of Austria (1573-1598) nude (Sleeping Venus) by Dirck de Quade van Ravesteyn, ca. 1595, Museum of Fine Arts in Dijon.
Miniature portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa, aged 30 by workshop of Dirck de Quade van Ravesteyn, ca. 1596, Czartoryski Museum.
Portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa by workshop of Dirck de Quade van Ravesteyn, after 1596, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Archduchess Maria of Austria (1584-1649) by Hans von Aachen, 1604, Lviv National Art Gallery.
Portraits of Stanisław Lubomirski and Bianca Cappello by Alessandro Maganza
On New Year's Day 1595, at the age of about 11, Stanisław Lubomirski (1583-1649), the eldest son of count Sebastian Lubomirski (d. 1613), together with his brother Joachim (1588-1610), left Wola Justowska near Kraków for further education at the Jesuit college in Munich. He was looked after by the trusted servants of his father, Piotr Szczepanowski, and Jan Gębczyński, a graduate of the Kraków University, who kept records of all expenses incurred at that time. Lubomirski stayed in Munich until May 1597. This stay was interrupted by financial difficulties and the wedding of the eldest sister Katarzyna who was marrying Prince Janusz Ostrogski. The costs of studying at the college and the expenses incurred during the over two-year stay in Munich were quite significant, amounting to 4,921 thalers. After returning to Poland, on July 21, 1597, his father ceded to him - with the king's consent - the starosty of Nowy Sącz (after "Stanisław Lubomirski (1583-1649) ..." by priest Andrzej Bruździński, p. 93).
At the end of 1598 or at the beginning of the following year, accompanied by the poet Piotr Kochanowski (1566-1620) and the aforementioned Jan Gębczyński, he went abroad again, this time to the south – to Italy. In 1599 he enrolled at the University of Padua and he also went to France and the Netherlands. He returned in 1601 and the following year he was admitted to the royal court. King Stephen Bathory was Stanisław's godfather. As the Kraków Żupnik between 1581-1592 his father built his fortune primarily from "salt" as well as usurious loans, which was assessed negatively in the Commonwealth. In 1597 even the crown jewels were pawned with Lubomirski and in 1595 Sebastian became the count of Wiśnicz from the imperial nomination. Around that time the "travelling belongings" of magnates and nobles were carried on "treasure carts" and in "room chariots" covered with leather in chests and boxes, often of French manufacture, very sophisticated and waterproof, intended for a specific type of objects, like "a tin case for pictures", according to inventory of the Radziwill family (after "Mieszkańcy Rzeczypospolitej w podróży ... " by Urszula Augustyniak, p. 375). Stanisław, who would later become the patron of a prominent Italian architect, Matteo Trapola, also acquired and commissioned works of art abroad. One such ambiguous expense for a meeting with a painter was recorded by Gębczyński during his stay in Munich - "For the copy of Stach and with the painter" (Za kopią Stach i z malarzem), 5 zlotys 21 grosz. "Everything cannot be entrusted to paper", wrote in a letter of July 8, 1588 from Venice, diplomat Stanisław Reszka and matters which could not be discussed directly were conveyed orally by a trusted and additionally authenticated messenger, who sometimes substituted a letter, simply for lack of time to write it (after "W podróży po Europie" by Wojciech Tygielski, Anna Kalinowska, p. 14). In the Wilanów Palace in Warsaw there is a portrait of an elegant 14-year-old young man against the background of a column and a curtain by Venetian school (oil on canvas, 176 x 115 cm, inventory number Wil.1150). It comes comes from the Wiśnicz Castle and it was moved to Warsaw before 1821. The castle in Wiśnicz was purchased by Sebastian Lubomirski in 1593 and between 1615 and 1621 Trapola enlarged and rebuilt it for his son Stanisław. The original inscription in Latin: Aetatis 14, above his head confirms the model's age, while the later inscription identifying the model as Sebastian Lubomirski (Sobestian Lubomirski Wielkorządca Kr.: W: Woryniecki zmarły R. 1613) was transferred to the back of the doubled canvas. Basing on this information the painting is dated to about 1560 (Sebastian was born in about 1546) and attributed to Giovanni del Monte or de Monte, painter active at that time at the royal court of Poland-Lithuania (he left for Venice in 1557). However, as noted by Wanda Drecka ("Portrety Sebastiana Lubomirskiego ...", p. 92), the cut of his hose or trousers can only be compared with the costumes of the guards in the Entry of the wedding procession of Sigismund III Vasa into Kraków in 1605 (Royal Castle in Warsaw), so-called "Stockholm roll" because it was taken to Sweden during the Deluge (1655-1660) and returned to Poland in 1974. The boy's shoes are very similar to those depicted in the portrait of Swedish statesman Mauritz Stensson Leijonhufvud, dated '1596' (ANNO DOMINO 1596, Skokloster Castle) and the pose and costume can be compared to the portrait of Sir Walter Raleigh and his son, dated '1602' (National Portrait Gallery in London). Similar trousers and shoes can also be seen in a double portrait of two children in matching green costumes, now in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna (oil on canvas, 116 x 91 cm, GG 3299). The portrait is identified to possibly represent members of the Polish royal family and attributed to the German or Polish school. This is mainly because the girl's costume and pose are very similar to those of Stanisław's sister, most likely Krystyna in her portrait in the National Museum in Warsaw (128871). A ruff similar to that of the boy's effigy was depicted in the portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa, also in the Kunsthistorisches Museum (GG 3302) and the portraits of his children Princess Anna Maria Vasa at the age of 3 (ÆTATIS SVÆ Ao. III.) and Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa at the age of 1 (ÆTATIS SVÆ I. Ao.) in the Monastery of Las Descalzas Reales in Madrid, painted in 1596. The portraits of King Sigismund and his children were created by his court painter Martin Kober of Wrocław, who died before 1598 in Kraków or Warsaw. All were sent to king's relatives in Vienna and Spain. A copy of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund's effigy was also sent to Bavaria (Alte Pinakothek in Munich). Moreover, the mentioned portrait of two children in Vienna also resembles in style the aforementioned portraits of Kober, who in 1595 went to Graz to paint the family of Sigismund's wife, Anna of Austria (1573-1598). In the same year, on July 14, when Stanisław stayed in Munich, his father Sebastian received confirmation and recognition from Emperor Rudolf II of the hereditary title of Imperial Count of Wiśnicz, granted by Emperor Charles V on February 15, 1523 to his ancestors (after "Genealogie rodów utytułowanych ..." by Tomasz Lenczewski, p. 41). On this occasion or even earlier, the emperor most likely received the portraits of the count and his family members, including his eldest son and his sister Katarzyna. The girl in the described portrait is apparently older than the boy, exactly like Katarzyna born around 1581, who was depicted in a similar rich costume in her portrait in the National Museum in Warsaw (157500). The boy in the painting could be 7 years old, so the painting must be dated to around 1590, when Kober returned from the imperial court in Prague to Poland. The painting can be verified at the Imperial Gallery in Vienna in 1772. His satin doublet of silver color, collar and hairstyle are almost identical as in the portraits of James I(VI) Stuart, king of England and Scotland by Adrian Vanson, dated '1595' (Scottish National Gallery and private collection) and portrait of a gentleman, formerly suggested to be William Shakespeare, dated '1602' (private collection). The portrait should consequently be dated to around 1597, when 14-year-old Stanisław Lubomirski become the starost of Nowy Sącz and soon left for Italy. The boy's facial features closely resemble other effigies of Stanisław Lubomirski in the Wilanów Palace (Wil.1565, Wil.1258). The same boy was depicted in another portrait from Lubomirski collection painted in the same style, today in the Lviv National Art Gallery (oil on canvas, 67 x 78 cm, Ж-1377). It is presumably a fragment of a larger composition showing him in guise of biblical David with a sword. The style of both paintings, in Wilanów and Lviv, is very close to that of Alessandro Maganza (1556-1630), a painter born and active in Vicenza, as well as in Venice, influenced by Tintoretto, Palma the Younger and Veronese. His distinctive technique is particularly well visible in a painting dated '1590' (M.D.LXXXX), today in the Nationalmuseum in Stockholm (NM 32), representing the Virgin and Child with Saints, as well as in the portrait of a woman with pearls (sold at Capitolium Art in Brescia on October 17, 2018, oil on canvas, 40 x 53 cm). The latter effigy is a version of a portrait of Bianca Cappello (1548-1587), Venetian noblewoman who become the Grand Duchess of Tuscany, painted by Scipione Pulzone in 1584 (Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, GG 1138). The painter most likely received a drawing or miniature of the Grand Duchess to copy, as his stay in Florence is unconfirmed. It was probably the same with the effigies of the young starost of Nowy Sącz ahead of his visit to Italy. Another interesting "Portrait of a woman", painted in the same style, is in the Lithuanian National Museum of Art in Vilnius (oil on canvas, 56 x 44 cm, inventory number LNDM T 4018). It is attributed to Frans Pourbus the Younger because of a certain resemblance to his works and the woman represented is obviously Marie de' Medici (1575-1642), Queen of France. It is dated '1614' in upper right corner. Presumably in 1613 Nicolaus Christopher Radziwill of Olyka (1589-1614), went to France, from where he returned via northern Italy and in May 1614, because of his illness, he stayed in Verona, from where, on May 9, 1614, he sent a letter to his friend Ferdinand I Gonzaga (1587-1626), Duke of Mantua (after "Zagraniczna edukacja Radziwiłłów ..." by Marian Chachaj, p. 69). It could be he who commissioned this painting in the Republic of Venice, or it was commissioned by the Vasas. In 1614 the so-called "Treter Eagle" (Ordo et series regum Poloniae) with effigies of monarchs of Poland was published in Paris by Jean le Clerc, and a year later, in 1615, a niece of the Queen of Poland, the Infanta Anne of Austria (1601-1666) married Louis XIII of France, son of Marie de' Medici.
Portrait of Stanisław Lubomirski (1583-1649) and his sister Katarzyna (d. 1612) by Martin Kober, ca. 1590, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Portrait of Stanisław Lubomirski (1583-1649), starost of Nowy Sącz, aged 14 by Alessandro Maganza, ca. 1597, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
Portrait of Stanisław Lubomirski (1583-1649) holding a sword by Alessandro Maganza, ca. 1597, Lviv National Art Gallery.
Portrait of Bianca Cappello (1548-1587), Grand Duchess of Tuscany by Alessandro Maganza, ca. 1584, private collection.
Portrait of Marie de' Medici (1575-1642), Queen of France by Alessandro Maganza, 1614, Lithuanian National Museum of Art.
Portraits of Dukes of Savoy by Sofonisba Anguissola
The diplomatic contacts of Poland-Lithuania with the Duchy of Savoy in the 16th century date back with certainty to the year 1535, when Queen Bona planned to marry her eldest daughter Isabella Jagiellon with Louis (Ludovico) of Savoy (1523-1536), Prince of Piedmont, son of Charles III and Beatrice of Portugal. She wrote about this to the ambassador of King Ferdinand I, Sigismund von Herberstein, from Vilnius on December 14, 1535 and the matter was discussed earlier by her envoy Ludovico Alifio (after "Królowa Bona ..." by Władysław Pociecha, p. 206). As was customary, the portrait of the Jagiellonian princess was certainly sent to Savoy, while she received the portrait of Louis. Sadly the prince died in Madrid on November 25, 1536. Some informal contacts were much earlier, for example in February 1416 in Chambéry Janusz of Tuliszków, a knight of the Dryja coat of arms from Greater Poland and a diplomat, received the Order of the Collar (later Order of the Most Holy Annunciation) from Amadeus VIII (considered the last historical antipope). They undoubtedly increased around 1587 when the candidature of the Duke of Savoy in the third free election was discussed in Madrid (after "Dwór medycejski i Habsburgowie ..." by Danuta Quirini-Popławska, p. 123).
In the 16th and 17th centuries portraiture was part of diplomacy and monarchs of different countries in Europe frequently exchanged their effigies. Portraits were also sent to friends and family members. In 1558, Georgius Sabinus (1508-1560), a German poet and diplomat, was sent to Poland-Lithuania to win the support of Polish-Lithuanian lords, including Stanisław Ostroróg, Jan Janusz Kościelecki, Łukasz Górka, Jan Tarnowski and Jan Zborowski, to the candidacy of Sigismund of Brandenburg (1538-1566), son of Joachim II Hector, elector of Brandenburg from his second marriage with Hedwig Jagiellon (1513-1572), for the throne after his uncle Sigismund Augustus. In the name of young Prince Sigismund, he gave each of them a gold chain, from which hung the portrait of the prince. As he was only known to a few of them, he wanted to present his effigy to them "as a symbol of friendship" (als ein Symbol der Freundschaft). The Polish-Lithuanian lords reciprocated so that "hardly any other envoy sent to Poland has ever returned home with as much wealth and gifts as he does" (mit so vielem Reichtum und Gaben wie er, sei wohl kaum je ein zweiter nach Polen beordneter Gesandter heimgekehrt, after "Forschungen zur brandenburgischen und preussischen Geschichte ...", Volume 11, p. 156). The miniatures probably came from Cranach's workshop, like the portraits of Sigismund's father, although it cannot be ruled out that they were commissioned in Italy by the prince's mother Hedwig. Diplomatic missions were frequently accompanied by the exchange of valuable gifts and they generally represented the country's most valuable exports, so the Italians offered paintings, rich fabrics and luxury cosmetics and the Poles offered clocks, sables, horses and amber. Cardinal Enrico Gaetani, papal legate in Poland from April 1596 to June 1597, offered King Sigismund III Vasa some paintings by famous masters, the queen richly embroidered veils and a conch with musk set in a rich setting, all worth at least 800 scudi. The king gave the cardinal a beautiful temple-shaped clock with moving figurines showing the procession and blessing of the Holy Father worth over 3,000 scudi, and 40 sables worth 500 scudi. The Bishop of Kuyavia in Wolbórz gave the legate two horses with rich Turkish-style shabracks, and the cardinal distributed gold medals with his image to the courtiers. Boniface Vanozzi, sent from the same Cardinal Gaetani to Chancellor Jan Zamoyski, distributed beads, rosaries, medals, agnus dei, pictures on metal sheet in ebony frames and he received a horse with velvet Turkish-style shabrack, a large gold medal depicting King Stephen Bathory, an elk hoof, lots of game, vinegar, oil and sweets. To the king and queen Vanozzi presented paintings, tapestries woven in Spain (or more likely in the Spanish Netherlands), colorful gloves with scent, and musk. The king gave him very expensive sables and a clock worth 1,000 thalers and the queen, various utensils made of white amber for the chapel, a crucifix, a tray for altar cruets, a pax and a monstrance, all beautifully carved in Gdańsk. In 1597, the ambassador of the Spanish king, Don Francisco de Mendoza (1547-1623), Admiral of Aragon and Marquis of Guadalest, received from Sigismund III sables worth 2,000 scudi and his courtiers were offered golden cups (after "Domy i dwory ..." by Łukasz Gołębiowski, pp. 258-259). At that time, the elected monarch of the Commonwealth also sent his brother-in-law, the King of Spain, portraits of his children by Martin Kober, both dated '1596' (Monastery of las Descalzas Reales in Madrid) and in 1621, the Polish ambassador in London, Jerzy Ossoliński, was given portraits "att length" of the King and Prince Charles. The royal collections of the Commonwealth before 1655 were therefore comparable to those of the Spanish monarchs (Prado Museum in Madrid and El Escorial), Holy Roman Emperors (Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna and Hofburg), Dukes of Tuscany (Uffizi Gallery in Florence and Pitti Palace) or Dukes of Savoy (Galleria Sabauda in Turin and Palazzo Madama). Unfortunately very little preserved today in the former territories of the Commonwealth, including inventories and other documents. In the National Museum in Warsaw there is a portrait of two boys, attributed to circle of Dutch painter Anthonis Mor, who worked for Spanish and Portuguese monarchs (oil on canvas, 56.5 x 46 cm, inventory number M.Ob.941 MNW, earlier 231117). It was purchased in 1962 from Romuald Malangiewicz. Its earlier history is unknown, so we cannot exclude the provenance from the royal or magnate collection in Poland-Lithuania. The painting was cut from a larger group portrait painting, as a fragment of a woman's dress, most likely the mother of the two boys, is visible to the right. Such portraits were particularly popular in Italy at the turn of the 16th and 17th centuries - portrait of Maria di Cosimo Tornabuoni, a Florentine noblewoman, and her two little sons, one dressed in dominican habit, by Tiberio di Tito (Tiberio Titi) or a portrait of Bianca degli Utili Maselli surrounded by six of her children, painted by Lavinia Fontana in Rome. If the painting comes from the royal or magnate collection then the main part depicting the woman was destroyed when Commonwealth residences were ransacked and burned during the Deluge (1655-1660) or later, or it was cut into pieces to sell the picture more profitably when the country became impoverished due to wars and invasions. A portrait painted in a similar style and with a woman resembling the two boys in the Warsaw painting is now in Kensington Palace in England (oil on canvas, 42.3 x 33 cm, RCIN 402954, inscription: 305). It comes from the Royal Collection, possibly recorded in the King's Dressing Room next Paradise at Hampton Court in 1666 (number 60), and was previously thought to represent Elisabeth of Valois (1545-1568), Queen of Spain. Consequently, it was attributed to Spanish court portraitist Anthonis Mor and later to his pupil and successor under Phillip II, Alonso Sánchez Coello. It is now identifed to possibly depict Elisabeth's eldest daughter, Infanta Isabella Clara Eugenia. A companion portrait is therefore thought to possibly represent her sister Infanta Catalina Micaela of Spain (oil on canvas, 42.2 x 32.6 cm, RCIN 402957, 306). These effigies indeed resemble other effigies of the infantas, however comparing with portraits of Isabella Clara Eugenia by Coello in the Prado Museum in Madrid, painted in 1579 (P01137) and by Juan Pantoja de la Cruz from about 1599 (P000717) and signed portraits of her sister Catalina Micaela from the Castle of Racconigi (0100399544) and attributed to Sofonisba Anguissola (sold at Christie's New York, October 14, 2021, lot 101), indicate that it should be the other way around - 305 is the portrait of Catalina Micaela and 306 of Isabella Clara Eugenia. In 1585, Catalina Micaela became Duchess of Savoy by marrying Charles Emmanuel I, Duke of Savoy in Zaragoza. A similar small portrait (oil on canvas, 55.9 x 45.7 cm) bearing the inscription: DVQUESA / DE.SAVOI, was sold at Period Oak Antiques. The style of the portrait of Catalina Micaela in the Royal Collection resembles the portrait of her mother in the Prado, attributed to Sofonisba Anguissola (P001031) and Sofonisba's self-portrait at the easel (Łańcut Castle). The composition and style of the portrait of two boys in Warsaw is in turn similar to the portrait of Infanta Juana de Austria (Joan of Austria) with female dwarf Ana de Polonia by Sofonisba (Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum in Boston, P26w15). The two boys should therefore be identified as the eldest sons of Catalina Micaela - Philip Emmanuel (1586-1605) and Victor Amadeus (1587-1637) and their known iconography matches perfectly. Both princes were frequently depicted in their youth and in many of their effigies, mostly created by the Dutch painter Jan Kraeck, known as Giovanni Caracca, they wear a similar smaller ruff (e.g. double portrait from private collection in Naples, sold at Blindarte, November 30, 2019, lot 153). Some of them were created in several versions, such as the triple portrait from 1589 (sold at Aste Bolaffi, September 25, 2013 and in Quirinale Palace in Rome). From around 1584 to 1615, Sofonisba resided in Genoa. Although in 1585 she met the Infanta Catalina Micaela on her arrival in Genoa and probably accompanied her on the way to Turin, all the portraits mentioned were probably made from sketches, study drawings or paintings by other painters, such as Kraeck. It was she who, around 1590, produced a miniature portrait of Charles Emmanuel I (sold in 2005, Christie's in London, lot 1009, as the effigy of Victor Amadeus I) and the portrait of the duke with his wife Catalina Micaela and their children (Palazzo Madama in Turin, 0611/D), as indicate the style of the two paintings. The portrait of two princes in Warsaw was therefore a gift to Sigismund III Vasa or his aunt Anna Jagiellon and was probably brought by the Spanish ambassador Mendoza or another envoy.
Portrait of Infanta Catalina Micaela (1567-1597), Duchess of Savoy by Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1590, Kensington Palace.
Portait of Victor Amadeus (1587-1637) and Philip Emmanuel (1586-1605), sons of Infanta Catalina Micaela (1567-1597), Duchess of Savoy by Sofonisba Anguissola or workshop, ca. 1596-1597, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Infanta Catalina Micaela (1567-1597), Duchess of Savoy with her sons by Sofonisba Anguissola or workshop, ca. 1596-1597. Possible layout of original painting. © Marcin Latka
Miniature portraits of the Vasas by Sofonisba Anguissola and workshop
Rich gifts accompanied all diplomatic missions. On June 14, 1592, "after the mass sung at dinner", Sigismund III, in his private room in the presence of some senators, gave audience to Pietro Duodo, orator of the Republic of Venice (Petro Dodo oratori S. Reipublicae Venetiarum), accompanied by eight Venetian nobles and seated on a bench decorated with green velvet (scamno ornato velluto viridi). He arrived to congratulate the king on his marriage to Anna. The king knighted Duodo and "presented him with a necklace worth a thousand in gold, and granted him the insignia [effigies?] of the royal family" (et donavit ei torquem millium aureorum, et concessit insignia familiae regiae). He then went to visit the queen, to whom he also gave a letter, and in the name of the Republic of Venice he presented various vessels of engraved silver, for the price of four thousand in gold (donavit S. Reginae vasa diversa argenti caelati pro pretio quatuor millium aureorum).
At that time, portraits were exchanged with Florence. In 1596, the king paid a large sum of 120 florins to the merchant Lawrence (Laurentio mercatori) "for images of Charles V, Emperor of the Romans" (pro imaginibus Caroli Quinti Caesaris Romanorum). Giovanni Paolo Mucante (d. 1617), master of ceremonies of the delegation of the papal legate, Cardinal Gaetano, wrote in a letter dated September 21, 1596 that the portrait of the late Queen Anna Jagiellon in the room was "very natural" (il suo ritratto, come dicevano, naturalissimo) and in 1601 Andrzej Opaliński (1575-1623) acquired in Prague a portrait of Michael the Brave (1558-1601), prince of Wallachia, for the king, according to a letter from nuncio Claudio Rangoni to Cardinal Pietro Aldobrandini (June 3) (after "Das Leben am Hof ..." by Walter Leitsch, p. 370, 953, 2277, 2381). Painters are sometimes mentioned, but names are missing. In 1592, before the wedding, the tailor Claudio Aubert went to Italy to get everything he needed. Among other things, he paid 96 guilders "to the painters sent to Poland to serve His Majesty" (alli pittori mandati in Polonia al servitio di SM). Much information about the wedding has been preserved, but there is no mention of Italian painters nowhere. In the accounts of 1601, there is only the following note: "Vilnius for the payment to the painters and for the repair of the tents, on August 28" (Vilnae in solutionem pictoribus et in reparationem tentoriorum, die 28 augusti, fl 110). This indicates that different workshops in Italy worked on royal commissions and sent their agents to Poland-Lithuania only to prepare the initial drawings. Besides the Venetian Redutti, who helped the king in goldsmithing work, there is evidence that Ruggiero Salomoni worked with Sigismund. He came to Poland as chaplain to the king's first wife. He was well known for his talent, because as early as 1595 he created the Easter tomb decoration for Cardinal Radziwill in Kraków Cathedral, according to a letter from Sigismundus Ernhofer to Archduchess Maria Anna dated April 5, 1595. Salomoni then acted as the king's agent in Naples around 1619, sending Italian paintings, tapestries and curiosities for the royal collection (after "The Grove Encyclopedia ...", ed. Gordon Campbell, p. 455). Luxury items were purchased in Italy, but also given to friends there. Sigismund's mother owned a silver mirror, perhaps made in Italy, and the royal courtier Stanisław Radziejowski gave Maria Maddalena of Austria, Grand Duchess of Tuscany and sister-in-law of the king an "amber mirror" (spechio di ambra), according to his letter to the Grand Duchess (June 12, 1615). The king ordered a large mirror (speculum grande cocavum) from Italy, mentioned in his letter to Salomoni (January 20, 1614). Royal envoys went to Italy, not only to acquire or order luxury goods, but also to bring renowned artists and musicians, as in December 1594, when Krzysztof Kochanowski (nephew of the poet Jan) came to Rome to recruit Italian musicians for Sigismund III or mentioned Aubert, before 1592. Around 1598, the Polish-Lithunian royal court sent numerous effigies of members of the royal family to foreign courts. The Vasas, like their ancestors the Jagiellons, and other important monarchs of Europe, commissioned their effigies from the best artists. This is why their miniature reliefs in colored wax were made by the famous workshop of Alessandro Abondio - busts of Sigismund III and his wife Anna of Austria at the Bode Museum in Berlin (inventory number 881, 882) and at the Nationalmuseum in Stockholm (NMGrh 1994, NMGrh 1995). Abondio was probably recommended to Sigismund III by his mother-in-law, Archduchess Maria Anna of Bavaria and her husband Charles II, grandson of Anna Jagiellonica (1503-1547), whose wax miniatures by Alessandro's father, Antonio, are located at Abegg-Stiftung (9.7.63). However, if we consider the enormous destruction of art in Poland-Lithuania during the Deluge (1655-1660) and other invasions, nothing can be said with certainty about this and we could also say the opposite that the Jagiellons or the Vasas recommended Abondios to the Habsburgs. At that time, the most renowned miniaturist working for the Habsburgs in Spain and Austria was Sofonisba Anguissola, who produced several of her self-portraits in miniature or small format - at the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston (60.155), Fondation Custodia in Paris (6607) or the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna (GG 285), the latter was most likely a gift for the Austrian Habsburgs. In her portrait in the Prado Museum in Madrid (P001031), recently attributed to Sofonisba, Queen Elisabeth of Valois holds in her hands a miniature of her husband King Philip II, probably also painted by Anguissola. This portrait is a sign of special recognition for the artist. Around 1575 she created a miniature of Emperor Maximilian II (1527-1576), son of Anna Jagiellonica (1503-1547), sold in Paris in 2016 (Sotheby's, June 16, 2016, lot 12, inscribed verso in Italian: Di mano / da Sofonisba / Anguisciola Cre / Monese / Dama Della Regina Isabella / di spagna moglie … / di filippo …). Sofonisba is also the author of several portrait miniatures from the collection of the Dukes of the Infantado in Madrid, which probably originally belonged to the Spanish royal collection. Among the effigies of Archduchess Maria Anna (Archivo de Arte Español - Archivo Moreno, 01616 B), Emperor Rudolf II (01696 B) and King Sigismund III in Polish costume (01784 B), there was also her self-portrait in Spanish costume (01616 B). A miniature of one of Maria Anna's daughters was also sold in Paris with attribution to the circle of Peter Paul Rubens, around 1610 (oil on panel, 8 x 6 cm, sold at the Hôtel Drouot, November 21, 2014, lot 29). This miniature probably comes from a private French collection, so the provenance from the collection of John II Casimir Vasa, who settled in France after his abdication in 1668, or from another Polish collection transferred to France in the 19th century cannot be excluded. Given this and the resemblance to the portrait in the Germanisches Nationalmuseum (Gm661), the model is most likely Anna of Austria (1573-1598), future Queen of Poland. The style of this painting also resembles greatly mentioned works by Sofonisba. Several miniatures of the Polish-Lithuanian Vasas created around 1598 are now in the Bavarian National Museum in Munich. All were probably gifts to the Wittelsbachs or came from the dowry of the Polish-Lithuanian princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa. This cycle of small paintings on brass and tin (all approximately 4.5 x 3.5 cm) includes effigies of Sigismund III (R. 1462), his first wife Anna of Austria (R. 1459, R. 1465) and their children Anna Maria Vasa (R. 1497) and Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (R. 1446). Another miniature of Queen Anna in the same style, most likely a gift to the Medicis, is in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence (oil on brass, 4.1 x 3.5, Inventario Palatina, n. 624). The miniature of Sigismund III from this cycle is particularly similar to the mentioned miniature of Emperor Maximilian II. Another miniature of Ladislaus Sigismund in the same collection (R. 1455), created around 1601, was also created in Anguissola's style. So, all miniatures were painted by the same artist and her studio. It was also Sofonisba's workshop that produced the portrait of Queen Anna at the Royal Castle in Warsaw (inscription: ANA D' AVSTRIA REG:A D' POLONIA, oil on canvas, 61 x 48 cm, FC ZKW 1370). The style of her jewelry as well as the inscription is similar to that in the portrait of Catalina Micaela of Spain (1567-1597), Duchess of Savoy, attributed to Anguissola (sold at Christie's New York, live auction 19994, October 14, 2021, lot 101). Therefore, like all mentioned Habsburg effigies, the Vasa liknesses were commissioned in the painter's workshop on the basis of other effigies or study drawings.
Miniature portrait of a daughter of Maria Anna of Bavaria (1551-1608), most probably Archduchess Anna of Austria (1573-1598), by Sofonisba Anguissola or studio, ca. 1592, Private collection.
Miniature portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa (1566-1632) by Sofonisba Anguissola or studio, ca. 1598, Bavarian National Museum in Munich.
Miniature portrait of Queen Anna of Austria (1573-1598) by Sofonisba Anguissola or studio, ca. 1598, Bavarian National Museum in Munich.
Miniature portrait of Queen Anna of Austria (1573-1598) by Sofonisba Anguissola or studio, ca. 1598, Bavarian National Museum in Munich.
Miniature portrait of Queen Anna of Austria (1573-1598) by Sofonisba Anguissola or studio, ca. 1598, Uffizi Gallery in Florence.
Miniature portrait of Princess Anna Maria Vasa (1593-1600) by workshop of Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1598, Bavarian National Museum in Munich.
Miniature portrait of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) by workshop of Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1598, Bavarian National Museum in Munich.
Portrait of Queen Anna of Austria (1573-1598) by workshop of Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1592-1598, Royal Castle in Warsaw.
Portraits of Anna Vasa and Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa by Sofonisba Anguissola
In 1594 a marriage project appeared during Anna Vasa's stay in Sweden. The candidate was John George of Brandenburg (1577-1624), the administrator of Strasbourg from 1592 and a grandson of the Brandenburg elector, who was to become the governor of Prussia, a feudal fief of the Crown of Poland. In the spring of 1596, an envoy, Paweł Arciszewski, secretary of King Sigismund III, traveled to Sweden with a portrait of John George to Anna Vasa in order to strengthen the princess's sympathy for her bridegroom (after "Das Leben am Hof ..." by Walter Leitsch, p. 2378). The painter was most likely a court painter of Sigismund III or an overseas workshop working for the Polish-Lithuanian monarchs.
Negotiations on this marriage were conducted on the Brandenburg side by the Magdeburg chancellor Wilhelm Rudolf von Meckbach and Johann von Löben who both travelled to Kraków, and on the Polish side by royal secretary Jan Skrzetuski, who travelled to Berlin, and Samuel Łaski. The date of the wedding was set for April 10, 1598 in Stockholm and Anna even received a dowry of 100,000 thalers from her brother Sigismund III Vasa, as well as jewelery, horses, furniture and 10,000 guilders as a wedding gift. Anna and her descendants were to be granted the inheritance rights to Sweden. Death of John George, Elector of Brandenburg on 8 January 1598, death of Sigismund's wife Anna of Austria (1573-1598) on 10 February and the outbreak of the uprising in Sweden made it impossible to conclude the wedding at the planned place and date. When Sigismund's uncle depose him in Sweden, these plans did not materialize. The portrait of a noblewoman and her husband in costumes from the late 1590s by Sofonisba Anguissola (oil on canvas, 123.3 x 93 cm, sold at Sotheby's London, July 11, 2002, lot 177) is very similar to other effigies of Anna Vasa. Her costume in Spanish style and pose resemble closely portrait of queen Anna of Austria by Martin Kober, created in 1595 (Bavarian State Painting Collections and Uffizi Gallery in Florence) and portrait of Archduchess Maria Anna of Bavaria (1574-1616) by Joseph Heintz the Elder, created in 1604 (Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna). The man's costume is typical for France and Protestant countries in the late 16th century. After return to Poland Sigismund made Anna starost of Brodnica on October 2, 1604, after death of Zofia Działyńska née Zamoyska and in December 1605 she attended Sigismund's wedding in Kraków, sitting in the bride's carriage. The negotiations with John George of Brandenburg were finally discontinued in 1609 and on June 3, 1610 he married Eva Christine von Württemberg (1590-1657), while Anna remained unmarried. Like her mother, Queen Catherine Jagiellon, the princess maintained a splendid and diverse court with different people as evidenced by her letter to Halszka Sapieżyna née Radziwill from Kraków, dated January 28, 1605: "We thank YL [Your Ladyship] for the female dwarf that YL brought us, and we urgently ask YL to send her with someone trusted" (Za karlice, WMci dziękujem, którąś WMć dla nas przywiozła, pilnie prosiem, abyś ją WMć przy kim pewnym sam posłała) (after "Archiwum domu Sapiehów ..." by Antoni Prochaska, p. 449). Although court dwarves of the 16th and 17th centuries are now mainly associated with Spain and their magnificent portraits by Anthonis Mor, Juan van der Hamen and especially Diego Velázquez, many paintings of this type were undoubtedly also found in Poland-Lithuania before the Deluge (1655-1660). In 1551, the painter Andreas Rul from Wrocław (Andreae Rul pictori Vratislaviensi) painted the portraits of 7 royal female dwarves, for which on March 3 he received 42 thalers, plus reimbursement of accommodation costs, and the portrait of king Sigismund Augustus, Anna's uncle, for which on March 17 he received 10 Hungarian ducats (after "Słownik artystów polskich i obcych ..." by Jolanta Maurin Białostocka, p. 355). The oval portrait in private collection in Massachusetts (oil on canvas, 65 x 52.5 cm, sold at Bonhams Skinner, November 11, 2021, lot 1036, as by school of Frans Pourbus the Younger), very similar to Anna's miniature in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence, is also stylistically close to Sofonisba as well as a miniature of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa in the Bavarian State Painting Collections (oil on tin plate, 4.4 x 3.7 cm, R. 1455).
Portrait of Princess Anna Vasa (1568-1625) in Spanish costume by Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1598, Private collection.
Portraits of Princess Anna Vasa (1568-1625) and John George of Brandenburg (1577-1624) by Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1598, Private collection.
Portrait of Princess Anna Vasa (1568-1625), starost of Brodnica by Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1605, Private collection.
Miniature of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa by Sofonisba Anguissola, ca. 1605, Bavarian State Painting Collections.
Portrait of Sigismund III Vasa in armour by Domenico Tintoretto
"The imago will be gratiosissima to the King. The King His Highness waits for paintings with great joy: a strange thing how he loves when he has something wonderful" (Imago będzie Królowi gratiosissima. Obrazów król Jmć czeka z wielką radością: dziwna rzecz jako się w nich kocha kiedy co cudnego ma), reveals in a letter dated July 12, 1588, written to Stanisław Reszka (1544-1600), who was in Rome, a Jesuit Bernard Gołyński (1546-1599) about the paintings commissioned by Sigismund III Vasa in Italy.
Sigismund was also a talented painter and goldsmith. According to historian Franciszek Siarczyński (1758-1829) in his "Picture of the Era of Sigismund III" (Obraz wieku panowania Zygmunta III), the king with the help of his court goldsmith, a Venetian Redutti (Reduta, Redura) made many church utensils, such as monstrances, chalices, lamps and candlesticks, which he gave to several churches. In the collection of the Alte Pinakothek in Munich there is a painting which according to Edward Rastawiecki in his "Dictionary of Polish painters" (Słownik malarzów polskich, pp. 96-97) is "another work of this kind" and it was given to king's daughter Anna Catherine Constance Vasa, "on the back, the preserved inscriptions and seals confirm the origin and authenticity of this interesting souvenir". This work is however listed in Johann Nepomuck Edler von Weizenfeld's "Description of the electoral picture gallery in Schleissheim" of 1775 as the work of Tintoretto (Jacopo Robusti, 1518-1594). Stylistically the painting is very close to this Venetian painter and his son Domenico (1560-1635). The monarch with the chain of the Order of the Golden Fleece is very similar to that visible in the study for a portrait of a king, most probably Sigismund III Vasa, in the collection of Francis Springell, attributed to Peter Paul Rubens, and to Sigismund's effigy in the Procession with St. Anianus by circle of Tommaso Dolabella in the Corpus Christi Church in Kraków. In the background, among the colonnades, there is a statue of the Madonna and Child, and in the clouds the figure which is interpreted as Saint Sigismund, patron saint of the monarchs. Heresy, depicted as an old woman, lies chained on the steps of the church. On the right are two Jesuits. Saint Sigismund has also a chain of the Order of the Golden Fleece and he bears a strong resemblance to Sigismund III's father-in-law Archduke Charles II of Austria (1540-1590), son of Anna Jagellonica. His crown is bordered with ermine like the Archducal hat (coronet). Curiously also the crown of the main monarch is bordered with ermine. It might be the painter's mistake or that Sigismund III commissioned an effigy of his brother-in-law Ferdinand II (1578-1637) who was raised by the Jesuits and dealt with heresy in his country before becoming emperor in 1619. Sigismund III received the Order of the Golden Fleece from his brother-in-law king Philip III of Spain in 1600. On this occasion he commissioned silver table service in Augsburg for 20,000 florins. The service, created by Hermann Plixen, was used for the first time during a banquet at the Castle in Warsaw on February 25, 1601. The king also commissioned other exquisite items in Augsburg, like the silver sarcophagus of Saint Stanislaus for the Wawel Cathedral in Kraków, and in other locations. Through his agent in Persia, Sefer Muratowicz, he commissioned a series of kilims with his coat of arms in 1601 and in about 1611-1615 he purchased a series of 6 tapestries in François Spierincx's workshop in Delft with the Story of Diana. On October 29, 1621 Jan Brueghel the Elder wrote to E. Bianchi about sending a lot of paintings to the King (molti pitture al Re) and the "Battle of Kircholm in 1605" by Pieter Snayers, also created for Sigismund, is today in the Château de Sassenage. In Milan, in about 1600, he commissioned a crystal lavabo (ewer and basin) with his coat of arms and monogram (Treasury of the Munich Residence) and most probably the shishak helmet offered to Feodor I of Russia (Kremlin Museum), created before 1591. His portraits in the Germanisches Nationalmuseum in Nuremberg, lost during World War II, and in the Wilanów Palace in Warsaw represent him in a rich, chiselled, partially gilt and polychromed blue armor in the type of mezza armatura (half armor), probably made in Milan. Portrait of a man in a suit of armour etched with gold by Domenico Tintoretto of unknown provenance (sold in 2016 at Christie's, lot 163), has almost identical dimensions as effigy of Sigismund III's sister Anna Vasa by Domenico Tintoretto in the Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum (115.3 x 96.1 cm / 115.5 x 96.7 cm). It is possible that they were created at the same time. The man bears a great resemblance to the effigies of Sigismund III Vasa from the early 17th century, especially his portrait painted in Prague in about 1605 by court painter of Emperor Rudolph II, Joseph Heintz the Elder (Alte Pinakothek in Munich). The king was depicted in similar etched armour in the Habiti Antichi Et Moderni di tutto il Mondo ... by Cesare Vecellio (Rè di Polonia / Poloniæ Rex, p. 346), published in Venice in 1598 (Czartoryski Library in Kraków).
Portrait of Sigismund III Vasa in a suit of armour etched with gold by Domenico Tintoretto, ca. 1592-1600, Private collection.
Allegory of suppression of heresy by Domenico Tintoretto, 1600-1619, Alte Pinakothek in Munich.
Portrait of Sigismund III Vasa as Saint Sigismund by workshop of Domenico Tintoretto
Around 1600, most likely an Italian painter Ottavio Zanuoli (d. 1607), created a painting depicting the Communion of the Virgin, today in the Royal Convent of Las Descalzas Reales in Madrid. Zanuoli was a court painter of Archduke Charles of Styria (son of Anna Jagellonica) and his wife Archduchess Maria Anna of Bavaria (granddaughter of Anna Jagellonica). According to handwritten list of all the effigies fixed on the back of the canvas, the painting represent the family of Archduke Charles, depicted as Saint John the Apostle, giving communion to the Virgin. His son Charles of Austria (1590-1624), Prince-Bishop of Wrocław from 1608, is holding a jug as a deacon of the mass. Behind Archduchess Maria Anna, represented as the Virgin Mary, are her daughters including Anna (1573-1598) and Constance (1588-1631), two wives of Sigismund III Vasa. The painting was undoubtedly a gift to Margaret of Austria (1584-1611), a daughter of Charles and Maria, who on 18 April 1599 married King Philip III of Spain, her first-cousin. Margaret became a very influential figure at her husband's court and a great patron of the arts.
The royal convent in Madrid is full of such disguised effigies of the Habsburgs. One of the oldest is a fresco in the Chapel of Mary Magdalene (Capilla de la Magdalena, inventory number PN 00610451). In this composition by an unknown painter and inspired by the Madonna with the Fish (Virgen del pez) by Raphael (Prado Museum), the Madonna presents features of the Infanta Juana de Austria (Joan of Austria, 1535-1573), founder of the convent. Next are the portraits of Emperor Maximilian II (1527-1576) as Saint Valerius of Treves (PN 00615942) and of Archduke Rudolf of Austria (1552-1612), future emperor, as Saint Victor (PN 00615941) and portraits of four daughters of Archduke Charles of Styria in the Hall of Kings (Salón de Reyes) - Anna (1573-1598) as Saint Dorothy, Maria Christina (1574-1621) as Saint Lucy, Catherine Renata (1576-1599) as Saint Catherine and Elizabeth (1577-1586) as Saint Agnes. All were probably painted in 1582 by Giacomo de Monte (Jakob de Monte) - for example the portrait of Archduchess Catherine Renata depicted with the attributes of Saint Catherine of Alexandria (breaking wheel and sword) bears the following inscription in German: "1582, Catherine Renata, Archduchess of Austria, at the age of 6 and 8 months" (1582 / KATERINA RENNEA / ERTZHERTZOGIN ZV / OSTEREICH . IRHES ALTER VI / IAR . VIII MONNET). Archduchess Anna, future Queen of Poland and first wife of Sigismund III, has the attributes of Saint Dorothy of Caesarea (crown and basket of roses, PN 00612064) (compare "Linaje regio y monacal ..." by Ana García Sainz and Leticia Ruiz, p. 146, 148, 150-151 and "Joyas del siglo XVI en seis retratos infantiles ..." by Natalia Horcajo Palomero, pp. 398-399). In 1603 the Queen of Spain commissioned paintings to her private oratory in the Valladolid palace, painted by Juan Pantoja de La Cruz, today in the Prado Museum in Madrid. One, the Birth of the Virgin shows three of her sisters, together with their mother, Archduchess Maria Anna of Bavaria, the other, the Nativity of Jesus, shows three of her brothers and three of her sisters, the Queen as the Virgin Mary and her husband as a shepherd. Around 1620, the youngest of Charles and Maria's daughters, Maria Magdalena, who on 19 October 1608 married Cosimo II de' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany was represented as Saint Mary Magdalene in a painting by Justus Sustermans, preserved in the Palazzo Pitti in Florence, and in a workshop copy in private collection. Such effigies, in guise of Saints and biblical figures were also popular at the Polish-Lithuanian royal court at that time. The Communion of the Jagiellons at Jasna Góra in 1477 (Casimir IV Jagiellon with his sons admitted to Jasna Góra Confraternity), created by workshop of Venetian painter Tommaso Dolabella in the second quarter of the 17th century (Jasna Góra Monastery), shows King Sigismund III and his sons as their predecessors from the Jagiellon Dynasty kneeling before the Black Madonna of Częstochowa. In the Jasna Góra Monastery, there are also two other paintings created by workshop of Tommaso Dolabella depicting Saints Stephen and Ladislaus, Kings of Hungary, both bearing features of King Sigismund III Vasa and a costume known from other portraits of the king. A painting by workshop of Domenico Tintoretto, also attributed to his brother Marco, whom the father's will names as a painter in Domenico's workshop, from a private collection in Southern Germany (oil on canvas, 113 x 89 cm, sold at Lempertz, Cologne on May 2003, lot 1133), basing on some details of the painting is identified as depicting Saint Louis IX, king of France, kneeling before the Crucifix. The traditional symbols of this Saint are indeed visible in the painting, fleur-de-lis on his coat, pendant, crown and sceptre, however there is also a crown embroidered on his coat and the attire is not blue like in the French royal coat of arms, golden fleur-de-lis on a blue field, used continuously for nearly six centuries (1211-1792). Italian painters since the beginning of the 16th century were well aware how the French king should look like and paintings by Ambrogio Bergognone, active in and near Milan, created between 1500-1520 (Accademia Carrara in Bergamo), by Berto di Giovanni, active in Perugia, created in about 1517 (Galleria Nazionale dell'Umbria), by Francesco Curradi, active in Florence, created in about 1600 (Private collection) and Matteo Rosselli, active in Florence, painted between 1613-1614 (Chiesa della Madonna in Livorno), depict the Saint in a mantle of French monarchs with golden fleur-de-lis on a blue field. The Saint from the Tintoretto's painting is therefore not Saint Louis IX. Another saint monarch connected with France is Saint Sigismund (Latin Sigismundus, died 524 AD), King of the Burgundians, patron saint of monarchs and of the Kingdom of Bohemia (in 1366, Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor, transferred Sigismund's relics to Prague and gave the saint's name to one of his sons, the later King Sigismund of Hungary). Arm reliquary of Saint Sigismund from the Guelph treasure, created in the late 11th century (Museum of Decorative Arts in Berlin), was in the late 13th or early 14th century supplemented with an orb surmounted by a fleur-de-lis, a shortened representation of a lily-crowned scepter. Altar painting with Saint Sigismund in the Parish church in Słomczyn near Warsaw (Konstancin-Jeziorna), created in about 1895 after a lost original, is very similar to the painting by workshop of Domenico Tintoretto. The Saint is kneeling before the Crucifix, his crown and sceptre are on a table covered with crimson fabric, his golden mantle and pendant are also very much alike. Another painting in the same church from the 19th century feretory depict Saint Sigismund in similar golden tunic and kneeling before the altar. The church in Słomczyn was founded at the beginning of the 15th century by Mrościsław Cieciszewski and the main patron of the parish from the very beginning was Saint Sigismund. During the Deluge (1655-1660) the church was plundered and invaders destroyed the altars. In 1165 Werner, bishop of Płock (north of Warsaw), brought the relics of Saint Sigismund from Aachen. In 1370 King Casimir III the Great, commissioned a silver reliquary for the Saint, today in the Diocesan Museum in Płock, and in 1601 King Sigismund III Vasa ordered the 13th century diadem to be placed on the reliquary of his patron saint. Sigismund III was frequenlty depicted in a similar żupan-like attire to that visible in Tintoretto's painting, for example in the mentioned Communion of the Jagiellons, in another painting by circle of Tommaso Dolabella representing Tsar of Muscovy Vasili Shuisky swearing an oath of allegiance at the Parliament of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1611 (Lviv Historical Museum) and in the plaque from his sarcophagus with King's military campaigns, created in 1632 (Wawel Cathedral). The man from the Tintoretto's painting bear a resemblance to the portrait of Sigismund III Vasa in a suit of armour etched with gold by the same painter, created between 1592-1600 (Private collection), his effigy in the Battle of Smolensk by Antonio Tempesta or Tommaso Dolabella, painted after 1611 (Private collection) and his profile on gold 10 ducats coin (portuguez), minted by Rudolf Lehman in Poznań in 1600 (National Museum in Kraków). The overall composition resembles the portrait of Piotr Skarga (1536-1612), court preacher of Sigismund III, created in 1588 by Karel van Mallery (National Library of Spain in Madrid). The painting by workshop of Domenico Tintoretto was in the collection in Southern Germany, exaclty as Allegory of suppression of heresy by this painter from the collection of Sigismund III's daughter (Alte Pinakothek in Munich). The king often sent gifts to William V, Duke of Bavaria, like the reliquary of Saints John the Baptist and Dionysius the Areopagite, offered in 1614 (Treasury of the Munich Residence) or silver statue of St. Benno of Meissen offered to the altar of St. Benno in the Munich Cathedral, created by Jeremias Sibenbürger in 1625 in Augsburg (Diocesan Museum in Freising). Together with the statue of St. Benno, the king also donated two silver reliquaries in the shape of a hand (not preserved) and 10,000 guilders for celebrating the daily mass, the so-called Polish mass, in the Cathedral.
Portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa as Saint Sigismund kneeling before the Crucifix by workshop of Domenico Tintoretto, 1592-1600, Private collection.
Portraits of Duke Joachim Frederick by Flemish painters
During the tenure of Andreas Jerin (1585-1596) as the Bishop of Wrocław the counter-reformation began in Silesia. The pressure of militant Catholicism made itself felt also in the Duchy of Brzeg, when, among others, the commander of the Joannites in Oleśnica Mała near Oława removed Lutheran pastors from his estates (1589), while Joachim Frederick's attempt to intervene become futile (after "Brzeg: dzieje, gospodarka, kultura" by Władysław Dziewulski, p. 59).
Joachim Frederick of Brzeg modeled himself on his father George II (1523-1586), but he was a better administrator than him. He confirmed former city privileges and supported the crafts. The castle in Oława was rebuilt and enlarged for Joachim Frederick in the years 1587-1600 by the Italian architect Bernard Niuron from Lugano. Thanks to his family connections and his good relations with the imperial court in Prague and the court in Berlin, he obtained a number of honorary positions. Since 1585 he was Lutheran provost of the chapter of Magdeburg, and in 1588 he was appointed general commander of the regular army of Silesia. After the death of his brother John George, who died without issue in 1592, Joachim Frederick inherited Wołów and after death of his mother and his cousin Frederick IV of Legnica (1552-1596), he become the sole Duke of Legnica-Brzeg-Oława-Wołów (Liegnitz-Brieg-Ohlau-Wohlau in German). Joachim Frederick gained great popularity for his gentleness and diligence. He liked science and he tried to improve the administration of justice in 1599. Since he ranked first among the Silesian princes, from 1592 until his death he had to deal with the matter of helping the emperor, who was at war with the Turks. In 1599, the Duke and his brother-in-law, Charles II of Ziębice-Oleśnica, refused to participate in the election of Bishop Paul Albert because he was not a Silesian and he acquired from Peter Wok von Rosenberg the towns of Złoty Stok (Reichenstein) and Srebrna Góra (Silberberg), rich in gold and silver mines. Joachim Frederick died on March 25, 1602 in Brzeg. The man from the portrait in the National Museum in Poznań (oil on panel, 47 x 38 cm, inventory number Mo 855) resemble the man from the portrait in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna (inventory number GG 808). Many splendid paintings that once adorned the walls of the Silesian Wawel - the Piast Castle in Brzeg and survived the bombing in 1741, when the castle was destroyed by the Prussian forces in the First Silesian War, were moved to Berlin. Possibly also this picture. The image in Poznań was acquired in 1930 from private collection Karl von Wesendonk in Berlin. Both paintings, in Poznań and in Vienna, are attributed to Adriaen Thomasz. Key, however the man from Poznań version is much older. If he was around 25 when the Vienna painting was created in about 1575, then the Poznań version should be dated around 1600, which rules out Key's authorship, as he died in 1589 or after. The most important arts and crafts center in this part of Europe at that time was the imperial court of Emperor Rudolf II in Prague. Many Flemish artists worked for the Emperor and two of them, created very similar portraits of Rudolf. One with light blue eyes, bust-length, wearing a breastplate (sold at Christie's, 27 Jan 2010, lot 344), is attributed to circle of Frans Pourbus the Younger (1569-1622), a Flemish painter from Antwerp, who at the end of the 16th century worked for Archduke Albert and Infanta Isabella in Brussels. The other with dark eyes, attributed to Lucas van Valckenborch (d. 1597) from Leuven, is today in the Liechtenstein collection in Vienna (inventory number GE 2484). The style of the image in Poznań resemble that of Pourbus, especially the portrait of a man in the Museum of Fine Arts in Budapest (inventory number 5862). The same man was depicted in another painting created in about 1600, in which however his face resemble more the Warsaw portrait from 1574 (inventory number M.Ob.819 MNW). His servant gives him a cup of wine. This painting titled sometimes "Two Fools", because of the old man's extravagant outfit, or "Emperor Rudolf II taking the cure", is today in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna (oil on canvas, 175.5 x 109 cm, inventory number GG 2773, verifiable in the gallery depot in 1868). It was attributed to Pieter Isaacsz (d. 1625), circle of Cornelis Ketel (1548-1616) or to Lucas van Valckenborch. The comparison with the painting in the Silesian Museum in Opava (inventory number In 2036 A), which was created by Valckenborch, most probably together with his assistant or only by him - Georg Flegel (1566-1638) is the most accurate. In his only known so far painted effigy from a fresco by Balthasar Latomus, the court painter of George II, in the ducal study of the Brzeg Castle, painted in 1583-1584, Joachim Frederick was depicted in colouful red-brown striped doublet, while his father is wearing a black attire. The Duke of Brzeg is also wearing a ruff and heavy gold chains with a medallion, like in the described painting by Valckenborch or Flegel in Vienna. The man from a large gold medal, most likely minted from the Złoty Stok gold, resemble the most George the Pious (1484-1543), Margrave of Brandenburg-Ansbach. George, son of Sophia Jagiellon, was an early adherent of Protestantism. He maintained correspondence with Martin Luther and introduced the Reformation in his Silesian possessions - Krnov, Bytom, Racibórz and Opole, one of the largest centers of Silesian cloth weaving. His son George Frederick (1539-1603), who from 1577 was also Administrator of the Duchy of Prussia, maintained good relations with Poland-Lithuania. He minted coins with the official motto of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth: "If God be with us, who shall be against us?" (Guldentaler, 1586, Königsberg), his tomb monument in the Heilsbronn monastery, attributed to Endres Dietrich Seidensticker, is adorned with coat of arms of Poland (White Eagle), repeated three times (after "Kloster Heilsbronn ..." by Graf Rudolph Stillfried-Alcántara, p. 163) and his portrait in the National Museum in Wrocław (inv. VIII-1514), was created by Silesian painter Andreas Riehl the Younger from Wrocław. The portrait of George Frederick was created in 1601 and he is wearing a medal of King Stephen Bathory with the inscription in Latin STEFANVS. REX. POLONIA. 1581 (after "Portret na Śląsku ..." by Ewa Houszka, p. 12). An earlier version of this portrait, painted in 1599 as a pendant to the likeness of George Frederick's wife, both from a private collection in Moscow, was sold in London in 2024 (Sotheby's, April 10, 2024, lot 7). Riehl is also the author of the portrait of King Stephen Bathory (National Museum in Wrocław, VIIl-2711). In 1571, the Regent of Prussia also commissioned a series of portraits of his father George the Pious in the workshop of Lucas Cranach the Younger (two are in the Grunewald hunting lodge in Berlin, GKI1192 and GKI1048) and for his wife Elizabeth of Brandenburg-Küstrin (1540-1578), who died while she was staying at the Warsaw court, where George Frederick was to be awarded the dukedom by the Polish king, he commissioned the Dutch sculptor Willem van den Blocke to construct the monument in Königsberg Cathedral, which was completed in 1582. His Silesian lands were close to Brzeg and Legnica, so the Margrave, who stayed mostly in Ansbach, entrusted George II od Brzeg with the implementation of the new laws in his Krnov domain. The bust of a bearded man in mentioned gold medal in the Vienna portrait resemble the portraits of George the Pious by Cranach the Younger and 1534 medal with his bust in the Germanisches Nationalmuseum, Nuremberg. Joachim Frederick, a Lutheran and the most important among the Silesian princes, minted coins in Złoty Stok, like the gold ducat from 1602 (National Museum in Warsaw, NPO 350 MNW). It was therefore him who most probably ordered both the medal and the portrait in the workshop of Flemish painter. In 1582 41 representations of Dutch wars painted on canvas were purchased by the Brzeg city council (after "Op Nederlandse manier ..." by Mateusz Kapustka, p. 35), indicating that Netherlandish art was strongly represented in his domains.
Portrait of Joachim Frederick (1550-1602), Duke of Legnica-Brzeg-Oława-Wołów by circle of Frans Pourbus the Younger, 1597-1602, National Museum in Poznań.
Portrait of Joachim Frederick (1550-1602), Duke of Legnica-Brzeg-Oława-Wołów with gold medal with bust of Margrave George the Pious by Lucas van Valckenborch or Georg Flegel, 1597-1602, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Portrait of Janusz I Radziwill by Leandro Bassano
"The Polish Lord, at whose court Michelagnolo was already employed, has recently written, that he must go there as soon as possible, offering him a most honorable position, that is, a place at his table, dressed like the first gentlemen of his court, two servants, who will serve him, and a carriage with four horses, and more than 200 Hungarian ducats a year's allowance, that is about 300 scudi, except donations, which will be a lot; so that he is resolved to leave as soon as possible, nor expects anything other than the opportunity of good company, and I believe that he will depart in fifteen days, so I must arrange him with money for the journey, and in addition it is necessary for him to bring with him at the request of his Lord some things, for which among the provision for a journey and the said things I cannot fail to accommodate at least 200 scudi" (Signor Pollacco, a presso di chi è stato Michelagnolo, ha ultimamente scritto, che ei deva quanto prima andare là da lui, offerendoli partito honoratissimo, cioè la sua tavola, vestito al pari dei primi gentil' homini di sua corte, due servitori, che lo servino, et una carrozza da quattro cavalli, et di più 200 ducati ungari di provvisione l'anno, che sono circa 300 scudi, oltre ai donativi, che saranno assai; tal che lui è risoluto di andar via quanto prima, nè aspetta altro che l'occasione di buona compagnia, et credo che tra quindici giorni partirà, onde a me bisogna di accomodarlo di danari per il viaggio, et in oltre bisogna che porti seco ad instanza del suo Signore alcune robe, che tra 'l viatico et le dette robe non posso far di manco di non l'accomodare almeno di 200 scudi), informed his mother in a letter from Padua in the Venetian Republic of August 7, 1600 (Mss. Palatini, Parte I, Vol. IV, pag. 11.), Galileo Galilei, famous Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer.
Already in 1593 Michelagnolo Galilei (1575-1631), an Italian composer and lutenist, son of another composer and lutenist, Vincenzo Galilei, and the younger brother of Galileo went to the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, where foreign musicians were in great demand. Most likely invited by the influential Radziwill family, he stayed there till 1599 and returned to his previous employer in Poland-Lithuania in 1600 after a short stay in Italy. The "Polish Lord", Michelagnolo's parton, is somerimes identified as Christopher Nicolaus Radziwill (1547-1603) nicknamed "the Thunderbolt", voivode of Vilnius, Grand Hetman of Lithuania and a representative of the Birzai branch of the Lithuanian magnate family (after "Galileo Galilei e il mondo polacco" by Bronisław Biliński, p. 69), who employed several musicians at his court. Christopher Nicolaus was a son of Nicolaus "the Red" Radziwill (brother of Queen Barbara), a Calvinist and protector of the Calvinists in Poland-Lithuania. By his second wife Katarzyna Ostrogska (1560-1579), daughter of Zofia Tarnowska (1534-1570), he had a son Janusz I (1579-1620), educated in Strasbourg and Basel. Janusz also traveled to Germany, Bohemia, Austria, Hungary, and France. From 1599 he was a cupbearer of Lithuania and on 1 October 1600 he married the Orthodox Princess Sophia Olelkovich-Slutska (1585-1612), the heiress of Slutsk and Kopyl (in present-day Belarus) and the richest bride in Lithuania. Sophia, canonized by the Orthodox Church in 1983, died in childbirth on March 19, 1612, leaving all of her property to her husband, and just few months later, on March 27, 1613 in Berlin, Janusz married Elizabeth Sophie of Brandenburg (1589-1629), a daughter of the Brandenburg Elector John George (1525-1598) and a great-granddaughter of Barbara Jagiellon (1478-1534), Duchess of Saxony. It is possible that Michelagnolo was invited to the Commonwealth for the wedding feast of Janusz and Sophia. According to a Galileo's letter from Padua of November 20, 1601 to his brother in Vilnius, he also traveled to Kraków and Lublin. In April 1606 he returned to Italy to live with his brother in Padua. On May 11, 1606 Galileo wrote to him from Venice about negotiating with a German Lord (Signore tedesco) and he secured him a place at court of the Bavarian Elector in Munich. In 1608 Michelagnolo was married to Chiara Anna Bandinelli in Bavaria, whom he most likely met in Lithuania and who was the sister or daughter of Roberto Bandinelli, nephew of the famous Florentine sculptor Bartolommeo called Baccio, who settled with his family in Lithuania (after "Archivio storico italiano", Volume 17, p. 31). According to the catalogue of exhibition of portraits in the Hague in 1903 (Meisterwerke der Porträtmalerei auf der Ausstellung im Haag, p. 2, item 2a), in the collection of Princess Cecylia Lubomirska née Zamoyska (1831-1904) in Kraków there was a portrait of a lute player by Leandro Bassano. It was later owned by Cecylia's son Kazimierz Lubomirski (1869-1930), most probably lost during World War II. A young man with several rings on his left hand is playing a serenade on a lute to his beloved. He is listened to by his dog, conventional symbol for fidelity, especially marital fidelity, wearing an expensive collar, possibly bearing his coat of arms. The window in the background shows his house, an Italian-style villa similar to the pavillons of the Radziwill Palace in Vilnius, the larger palace of the Calvinist branch of the family. The Radziwill Palace, initially a renaissance manor house built in the 16th century, was reconstructed and extended between 1635 and 1653 for Janusz II Radziwill (1612-1655), nephew of Janusz I (1579-1620). The lavish edifice was constructed by Jan Ullrich and Wilhelm Pohl to design by Italian architect, most probably Constantino Tencalla, and was depicted in 1653 medal by Sebastian Dadler, minted on the occasion of the inauguration of Janusz II as the Voivode of Vilnius. The lute player from the Lubomirski collection was signed and dated by the artist. The inscription in Latin stated that the depicted man was 21 years old in 1600 (Anno aetatis suae XXI, MDC), exaclty as Janusz I Radziwill (born in July 1579 in Vilnius), when he married Sophia Olelkovich-Slutska. The sitter bear a great resemblance to other effigies of the Prince, especially a print by Jan van der Heyden after Jacob van der Heyden, created in 1609 (Herzog Anton Ulrich-Museum), a portrait by unknown artist (State Historical Museum in Moscow) and a medal with his bust, published in Berlin in "Medals of the princely house of Radziwill" (Denkmünzen des Radziwillschen Fürstenhauses, 1846). It is generally belived that Bassano's lute player is tantamount to a painting acquired in Venice by Count Stanisław Kostka Potocki (1755-1821), who recalled in a letter to his wife of September 22, 1785 from Venice: "I end my article on Venice by telling you that I have acquired one of the freshest paintings of Paolo Veronese that I have ever seen, it is a Holy Family of the size of your Rubens, I hope that you will be happy with it, adding here a portrait of Bassen playing the lute painted by himself which is really a masterpiece of this master, and you will be happy with this acquisition" (je finis mon article de Venise, par te dire que j'ai fait l'aquisition d'un des plus frais tablaux de Paule Véronèse que la aie jamais vue, c'est une St. Famille de la grandeur à peu près de ton Rubens, j'espère que la en sera contente, ajoute ici un portrait du Bassen jouant du luth peint par lui meme qui est vraiment un chef d'œuvre de ce maître, et tu sera contente de moi, Central Archives of Historical Records in Warsaw, 262 t. 1, Mikrofilm: 19007, page 60). Veronese's Holy Family is today most probably in the Wilanów Palace (inventory number Wil.1000, also considered to be the painting purchased in Paris in 1808) and it is currently attributed to his brother Benedetto Caliari. Even if the lute player from the Lubomirski collection was acquired by Potocki in Venice, it does not exclude that it represents a person from the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, as paintings commissioned abroad were frequently created in series, as gifts to relatives and friends. In this case the possibility that it was a gift to the tutor's brother, Galileo Galilei, or his family is probable. If Michelagnolo was a court musician of Christopher Nicolaus "the Thunderbolt", he could teach music to his son Janusz I. "It was customary that the orders of Polish clients abroad were paid through the bankers' offices that organized the transport. Thus, the intermediary between Sigismund III and Chancellor Zamoyski, on the one hand, and Italian painters, on the other, was the Montelupi company from Kraków, whose post office brought finished and paid works to Poland. Gdańsk bankers mediated between our country and the Netherlands, and thanks to their efforts, paintings and fabrics ordered by Ladislaus IV in Antwerp were transported by sea through the Danish straits" (after "Obrazy z kolegiaty łowickiej i ich przypuszczalny twórca" by Władysław Tomkiewicz, p. 119). In the 1620s, most probably after death of Leandro Bassano, who died on April 15, 1622, a painter from the circle of Bassano brothers settled in Pułtusk, a significant economic centre of Masovia. Between 1624-1627 he created three paintings showing scenes from the life of Mary for the Łowicz Cathedral, commissioned by Henryk Firlej (1574-1626), Archbishop of Gniezno and Primate of Poland, son of Jan Firlej (1521-1574), and a self-portrait, today in the Dominican Monastery in Kraków.
Portrait of Janusz I Radziwill (1579-1620), aged 21 playing a lute by Leandro Bassano, 1600, Lubomirski collection in Kraków, lost.
Portrait of Sebastian Petrycy by Venetian painter
Sebastian Petrycy or Sebastianus Petricius Pilsnanus, was born in 1554 in Pilzno near Tarnów in south-eastern Poland as a son of Stanisław (died after 1590), a wine merchant. In 1583 he graduated with the degree in philosophy at the Kraków Academy and he began lecturing there. A year later, in 1584, Sebastian became a member of the Collegium Minus (College Minor) and took the chair of poetics and in 1588 he became a professor of rhetoric.
In February 1589, Petrycy was granted a leave to travel to Italy and study at a selected foreign university. He decided to study in Padua, where he received the degree of doctor of medical sciences at the beginning of March 1590. When he returned to Kraków, he applied for the recognition of his diploma at the Faculty of Medicine, but was refused admission and left for Lviv, where he got married with already pregnant eighteen-year-old Anna (he was almost forty), the daughter of a wealthy merchant Franz Wenig, and opened his own medical practice. The death of his wife (February 28, 1596) and of his only daughter, Zuzanna, as well as the lost trial for the inheritance of his father-in-law, prompted him to return to Krakow (around 1600). He became the personal physician of the bishop of Kraków Bernard Maciejowski, who in 1603 was made cardinal by Pope Clement VIII. Between 1603-1604 he went with the cardinal to France and Lorraine and in 1606, as a physician of Jerzy Mniszek and his daughter Marina, he left for Moscow, which cost him almost a year and a half in captivity. During his court career, he worked on translations of Aristotle into Polish. He then returned to the medical profession and successfully practiced for the last 10 years of his life. Petrycy died in 1626 in Kraków, and shortly before his death he founded a marble epitaph for himself depicting him in prayer, created by a royal court sculptor. Portrait of a bearded man holding glasses, comes from the collection of John Rushout, 2nd Baron Northwick (1770-1859) at Northwick Park. It was previously attributed to Titian and Lotto Lorenzo, however stylistically is also close to Jacopo Tintoretto (1518-1594) and his son Domenico (1560-1635). The man's costume of crimson silk is very similar to Polish żupan, his coat is lined with fur. This effigy is very similar to portraits of Sebastian Petrycy and his son Jan Innocenty Petrycy (1592-1641), who like father was a physician, professor at the Academy and studied in Bologna. Mentioned portraits are today in the Collegium Maius of the Jagiellonian University and were created in the 1620s by workshop of Tommaso Dolabella (1570-1650), a Venetian artist settled in Kraków and a court painter of king Sigismund III Vasa. It is possible that Dolabella's workshop copied some family owned portraits, created in Venice. Consequently the effigy can be dated to beginning of the 17th century when Petrycy was a court physician in Kraków.
Portrait of Sebastian Petrycy (1554-1626) holding glasses by Venetian painter, possibly Domenico Tintoretto, 1600-1606, Private collection.
Portrait of Uriel Górka, Bishop of Poznań by Odoardo Fialetti
The full-length portrait of Uriel Górka (ca. 1435-1498), Bishop of Poznań in Kórnik Castle near Poznań is one of the oldest effigies of church hierarchs in Poland. This large painting on canvas (219 x 111.5 cm, inventory number MK 3360) bears an inscription in Latin on a band above the figure: VRIÆL / COMES DE GORCA DEI GRATIA EPISCOPVS POSNANI / ENSIS. The band, typical of Gothic paintings, as well as the general style of the work suggest that it is a copy of the original portrait of the bishop, as the painting itself is variably dated to the second half of the 16th century or the middle of the 17th century.
The original may be by Stanisław of Kórnik, who was the bishop's court painter for six years in the 1490s, but also commissioned from abroad. Uriel, the founder of the family's power, distinguished himself in the field of artistic patronage and he was in close contact with the artistic circles of Nuremberg. He ordered silverware from Albrecht Dürer the Elder, father of the painter (according to the bill of August 26, 1486 - Item mein her Uriel her bischoff von Poln hat Albrechtn Durer dem goltschmyd silber gebn), he commissioned various works from the sculptor Simon Leinberger, like the excellent composition of Christ in the Garden of Olives sculpted in 1490 for the Poznań Cathedral, and bronze tombstones for himself and his father Łukasz (died in 1475), the voivode, at the famous Vischer workshop (after "Kultura, naród, trwanie ..." by Maria Bogucka, p. 164). The full-length effigy of Uriel on his tomb slab by the Vischer workshop in Poznań Cathedral is comparable to this portrait. So maybe the original effigy of the bishop was also created in Nuremberg or it was a likeness from the gallery of portraits of Poznań bishops modo chronicae depicta made after 1508, commissioned by Bishop Jan Lubrański from the Kraków painter Stanisław Skórka. The style of the painting is obviously Venetian, close to the Bassanos and influenced by Tintoretto, but no Venetian artist is confirmed in Poznań and the surrounding area at that time, therefore the painting must be an import, ordered from Venice, such as the portraits of the daughters of Łukasz Górka (1482-1542). Stylistically closest is the portrait of Doge Antonio Priuli (1548-1623), reigning from 1618 until his death, in the Kensington Palace (inventory number RCIN 407153). The way the face, hands and gold patterned fabrics were painted is very similar. The portrait of Priuli was one of four portraits of Doges acquired by Sir Henry Wotton during his tenure as ambassador in Venice (1612-1616 and 1619-1621) "done after the life by Eduardo Fialetto", according Wotton's will. The other three portraits are also stylistically close, notably the effigy of Doge Giovanni Bembo (RCIN 407152). Odoardo Fialetti, born in Bologna in 1573 and initiated to painting with the Bolognese Giovanni Battista Cremonini, moved to Padua and then to Venice, where he entered Tintoretto's workshop. It is possible that he also spent some time in Rome, completing his training. From 1604 to 1612, Fialetti was a member of the Venetian Brotherhood of Painters (Fraglia dei Pittori). The most possible founder of the painting is therefore Jan Czarnkowski (d. 1618/19), royal courtier, one of the heirs of the Górka family after childless death of Lutheran magnate Stanisław Górka (1538-1592). Czarnkowski completed the Górka mausoleum in Kórnik in 1603 and handed over the church to the Catholics. The effigy of the Catholic bishop of Poznań, educated in Italy, owner of the Kórnik estate from 1475 who brought a gardener from Italy to Kórnik (after "Zamek w Kórniku" by Róża Kąsinowska, p. 17), fits perfectly into Czarnkowski's Counter-Reformation activity. It was commissioned in Italy possibly in opposition to the predominantly Protestant northern school of painting.
Portrait of Uriel Górka (ca. 1435-1498), Bishop of Poznań by Odoardo Fialetti, ca. 1604, Kórnik Castle.
Portraits of Constance of Austria by Gortzius Geldorp
"Although the king was young, he was more inclined to peace than to war, and he did not even want to find employment in anything in the domain of the god Mars. I heard that one time, when the archbishop and chancellor informed him about the war, he wrote something down in a pugilares. They thought that he was anxious about the fate of the war until the king, who was a good painter, goldsmith and turner, showed them a painted little owl", recalled in his diary Albert Stanislaus Radziwill, Grand Chancellor of Lithuania about the beginnings of the reign of Sigismund III Vasa.
The King, so much inimical to idleness (tanto inimico dell'ozio), in his spare time he occupied himself with a certain artistic work, making his effigies, paintings and other items, which he offered as a gift, like "the one of which he painted with his own hand was the portrait of Saint Catherine of Siena last year" (una delle quali che fece di sua mano, fu il ritratto di S. Catherina di Siena l'anno passato), says of Sigismund III another contemporary witness, the papal nuncio Erminio Valenti (1564-1618), in a handwritten description of Poland and the royal court in 1603 (Relazione del Regno di Polonia). In 1605 the king married his distant relative (as a granddaughter of Anna Jagellonica), the sister of his first wife and sister of Queen of Spain, Constance of Austria (1588-1631). Many eminent guests arrived to Kraków for Sigismund's wedding, the bride with her mother Archduchess Maria Anna, and her sister - Maria Christina, Princess of Transylvania, Radu Șerban, Voivode of Wallachia or his envoy, Mechti Kuli Beg, Ambassador of Persia, Afanasy Ivanovich Vlasiev, Ambassador of Russia, among others. The city was beautifully decorated on the entry of the wedding procession (mechanical Polish eagle, most probably from ephemeral decorations, preserved in the St. Mary's Church in Kraków). Also many artists came to Kraków at that time. The so-called "Stockholm Scroll", a unique, fifteen-metre long painting depicting the 1605 wedding procession, acquired during the Deluge and returned to Poland in 1974 (donated to the Royal Castle in Warsaw), is attributed to Balthasar Gebhardt, court painter of Archduke Ferdinand (1578-1637), Constance's brother. Among the most distinguished works attributed to the king there is a gouache painting on parchment with Allegory of Faith in the Nationalmuseum in Stockholm. It bears the king's coat of arms, his monogram S under the crown, the date 1616 and monogram M.N.D.F.C. Below there is also a signature of king's wife Constantia Regina. Since the effigy of a woman bears resemblance to other effigies of the Queen, it was she who lend her features to the figure. Another painting traditionally linked with Sigismund is Mater Dolorosa in the Alte Pinakothek in Munich (inventory number 5082), painted on copper. It comes from the Castle Haag in Geldern in the district of Kleve, North Rhine-Westphalia and was most probably part of Anna Catherine Constance's dowry. Sigismund's painting is a copy of a work by Gortzius Geldorp depicting a female saint in adoration signed with monogram GG F, painted on wood (oil on panel, 54 x 44.5 cm, Artcurial in Paris, June 3, 2015, lot 238). Crispijn van de Passe the Elder created a print, published in Utrecht in 1612, with similar composition, showing the penitent Mary Magdalene (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, RP-P-1906-2063), which is however more close to the Sigismund's painting then to the version by Geldorp. The woman in Geldorp's painting has more Habsburg facial features. The same woman with protruding lower lip was depicted in two other paintings by Geldorp one signed with monogram and dated AN ° 1605.GG.F. (oil on panel, 49.9 x 37.7 cm, sold in 2015 at Christie's, Amsterdam, lot 52, the other, oil on panel, 47.3 x 36.5 cm, sold in 2011 at Christie's, New York, lot 140). Both paintings represent a lady as Berenice, wife of pharaoh Ptolemy III Euergetes. Berenice pledged to sacrifice her hair to the goddess Venus if her husband was safely brought home from battle during the Third Syrian War. Her hair became the constellation called Coma Berenices (Berenice's hair) and the symbol of power of marital love. Very little is known about Gortzius Geldorp. He was born in Leuven (Louvain) in 1553 in what was then the Spanish Netherlands and learned to paint from Frans Francken I and later from Frans Pourbus the Elder. Around 1576 became court painter to the Duke of Terra Nova, Carlo d'Aragona Tagliavia (1530-1599), a Sicilian-Spanish nobleman, who in 1582 was appointed Governor of Milan and whom he accompanied on his trips. The Duke died in Madrid on September 23, 1599, and Geldorp died after 1619. It is very possible that he or his student came to Kraków in 1605. In 1599 Geldorp created a portrait of a young woman in Venetian costume (oil on panel, 43.8 x 36.2 cm, Christie's New York, 12 January 1994, lot 134, signed and dated top left: Anº.1599./GG.F), similar to costumes of Venetian ladies published in 1590 in De gli habiti antichi, e moderni di diverse parti del mondo libri due by Cesare Vecellio, cousin of the painter Titian (p. 97-112). The same year he also created a portrait of Hortensia del Prado (Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam, inventory number SK-A-2081, signed and dated top left: Anº 1599./GG.F.). Either the painter went for a short time to Venice or Poland-Lithuania, or the lady in Venetian costume visited his studio or most likely sent a miniature, drawing or other portrait to be copied. The same woman as in the painting sold in New York, wearing a similar lace-trimmed Venetian dress, is depicted in another painting, possibly a copy or variant of Geldorp's painting. This painting is also in a private collection (oil on canvas, 47.5 x 38 cm, Bonhams London, 6 July, 2005, lot 113). It is attributed to the painter active in Bologna Lavinia Fontana (1552-1614).
Portrait of Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631) as Berenice by Gortzius Geldorp, 1605, Private collection.
Portrait of Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631) as Berenice by Gortzius Geldorp, ca. 1605, Private collection.
Portrait of Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631) as a Saint in adoration (Saint Constance?) by Gortzius Geldorp, ca. 1616, Private collection.
Portrait of a lady in Venetian costume by Gortzius Geldorp, 1599, Private collection.
Portrait of a lady in Venetian costume by Lavinia Fontana, ca. 1599, Private collection.
Portrait of Queen Constance of Austria as Venus by Gortzius Geldorp
"At that time, King Sigismund III of Poland commissioned from him the fable of Diana with Calisto bathing & other Poems. They pleased the King, who ordered him to be invited to his court with a worthy reward. However, the painter accustomed to the comforts of his home, refused such a good opportunity, sending there Tomaso Dolobella, his disciple […] He also painted for the same King part of the fable of Psyche, shared with Palma, and Antonio's work having pleased him, he then ordered from him a canvas with the martyrdom of Saint Ursula, which he executed with great diligence, and on the covers he painted the saints Vladislaus, Demetrius and other saints, whom the King surrounded with a cult, and for that worthy work he was commended with royal letters and presented with some gifts", comments on the works of the Greco-Venetian painter Antonio Vassilacchi (1556-1629) called L'Aliense, Carlo Ridolfi in a book published in 1648 presenting the history of Venetian painting (Le Maraviglie dell'arte). Saint Ursula was probably intended for King's mistress, influential Urszula Meyerin, who was most probably depicted as the saint martyr.
As it was said Palma il Giovane (1549-1628) worked with Vassilacchi on part of the fable of Psyche, and for the Cathedral in Warsaw he created two paintings - one with Baptism of Christ (tavola di Christo al Giordano), according to Ridolfi, and the Virgin and Child with St. John the Baptist and St. Stanislaus (destroyed in 1944). According to Palma's letter from January 1602 Aliense was to begin designs while in Salò, but he would then need to return to Venice to "finish certain works that he is doing for the king of Poland". Two drawings by Palma, one showing Venus and Psyche (British Museum, inventory number 1862,0809.74) and the other Cupid and Psyche (sold at Christie's, July 6, 2021, lot 3), could be preparatory drawing for the Psyche cycle. A letter from the Treasurer of the Crown, Jan Firlej (d. 1614), addressed to King Sigismund III Vasa (dated April 29, 1599) says that in one of the Italian rooms ("in the new buildings") at the Wawel Castle in Kraków, described as "the happiest", "paintings were made in Venice". The themes of these paintings decorating the interior, were most probably taken from erotic and mythological themes. They covered the walls and filled the gilded coffered ceilings in Venetian style. According to inventory description of Wawel from 1665 "Italian paintings with golden frames" were in the antechamber at the Hen's Foot tower, Italian "pictures" decorating "the ceiling carved with gold work" in the main room there and "around eleven Italian paintings with golden frames". In the room "under the birds", according to the inventory from 1692, there were "four pictures above the door, between which there are nine pictures above the panelling, only two with golden frames ... In this room there are nine pictures in the ceiling" (after "Weneckie zamówienia Zygmunta III" by Jan Białostocki). The king had undoubtedly other erotic and Italian rooms and studiolo in other royal residences in Kraków (Łobzów), Warsaw (Royal Castle, Ujazdów), Vilnius, Grodno and Lviv. Cardinal Ferdinando I de' Medici (1549-1609), who became Grand Duke of Tuscany in 1587, most likely owned such a studiolo or camerino in his Villa Medici in Rome, as suggested by the author of the Instagram profile ARTidbits (post published July 27, 2023). There is a pavilion there with two rooms, considered the most intimate in the entire complex. It was decorated by Jacopo Zucchi with frescoes representing a pergola, birds, plants and small animals. Zucchi is the author of numerous portraits of cardinal's mistress Clelia Farnese (1556-1613), Marchioness of Civitanova. She was depicted as Amphitrite, the goddess of the sea, and Ferdinando as her husband Poseidon, as well as various Roman ladies, in the painting entitled The Kingdom of Amphitrite (The Coral Fishers), which is now in the Lviv National Art Gallery (Ж-272, signed and dated lower right: Jacobus Zuchi fior fecci 159[0]). The painting comes from the Lubomirski collection, so provenance from the royal collection of Poland-Lithuania, as a gift for Sigismund III or his aunt Anna Jagiellon, cannot be excluded. Many copies of this painting exist, all however without the disguised portrait of the cardinal. The Grand Duke corresponded with the King of Poland and in a letter dated September 10, 1595, he even recommended two of his musicians Luca Marenzio and Francesco Rasi to Sigismund. According to Le vite de' pittori ... by Giovanni Baglione, published in 1642, a version adorned Ferdinando's studiolo in his Roman residence, the Palazzo Firenze (after "Jacopo Zucchi's The Kingdom of Amphitrite ..." by Federico Giannini, Ilaria Baratta). Clelia, as suggested by ARTidbits, was also depicted as one of the Three Graces, goddesses of charm, beauty, nature, human creativity and fertility in a painting from a private collection in Rome (Casa d'Aste Babuino in Rome, June 27, 2023, lot 280). The latter effigy closely resembles her portrait attributed to Scipione Pulzone from the Palazzo Farnese in Rome (Dorotheum in Vienna, October 22, 2019, lot 15). The huge popularity of erotic images and nudes caused concern to some preachers of the Counter-Reformation. In his poem "Roman and Christian Lucretia", published in Kraków in about 1570, Bishop Jan Dymitr Solikowski (1539-1603), secretary of King Sigismund II Augustus from 1564, demanded that paintings depicting "shameless arts and all Jupiter Vanities, Mars with Venus" to be burned and painters with them, it should be noted however, that the title page of his work shows a beautiful woodcut with half-naked Lucretia by Mateusz Siebeneicher or his circle (University of Warsaw Library). Over a half a century later, in 1629 the court preacher of Sigismund III and Ladislaus IV Dominican Fabian Birkowski (1566-1636) warned against "these painted fornications", which were very popular in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth before the Deluge (1655-1660): "and yet this eye poison can be seen everywhere, full of these filthy images in bedchambers, halls, dining rooms, gardens and fountains, above the doors, on the glasses and cups". He also added "and our heretics have so corrupted their eyes that they throw the image of the crucified Christ out of bedchambers and rooms, and in its place they hang Fauns and painted Cupids, Venus and Fortuna above the table, so that they may dine and sup with them. [...] And there is no image of the Blessed Virgin anywhere; and the image of filthy Venus has a place, and even better at home" (after "Kazania" by Fabian Birkowski, 1858, Vol. 1-2, p. 81-82). Somber and death-filled aura of the late 1620s provoked reflection. At that time the Commonwealth was struggling with Swedish invasion of Polish Prussia, military defeats and outbreaks of plague associated with troop movements. Only in Gdańsk 9,324 people died during epidemic of 1629-1630 (after "Przeszłość demograficzna Polski", Vol. 17-18, p. 66). In 1630 Mikołaj Wolski (1553-1630), Grand Crown Marshal, favorite and friend of Sigismund III Vasa, but above all an excellent collector, who invited to Poland the Italian painter Venanzio di Subiaco (1579-1659), ordered erotic paintings to be burned before his death except those in Venetian style coffered ceilings. He wrote in a letter of March 6 to Jan Witkowski "that images ad libidinem [to lust] and inciting to sin, which can be found in Krzepice castle, should all be burned; and those which are painted naked on the wall in my room where I slept and in my chamber, I beg you, let a painter who is able to paint any dresses and let him cover inhonestates [deceptiveness]. Ceiling paintings, let them remain as they are" (after "Zakon Kamedułów ..." by Ludwik Zarewicz, p. 197). Nevertheless, "a wall full of paintings with naked people" is mentioned in some manor houses still in 1650 (after "Miłość staropolska" by Zbigniew Kuchowicz, p. 165). Two paintings from the Poznań Society of Friends of Learning, lost during World War II, show how wonderful the interiors of the residences of the First Polish Republic were. According to tradition, they represented the interior of the Leszczyński Palace, most probably the Palace of Bogusław Leszczyński, Grand Treasurer of the Crown in Warsaw, built between 1650-1654 to a design by Giovanni Battista Gisleni. "Portrait of an elegant woman in the guise of Venus" by Gortzius Geldorp (oil on panel, 56.6 x 44.1 cm, sold at Sotheby's, New York, January 29, 2016, lot 454) is a version of portrait of Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631) as Berenice, created in 1605. The face is identical, while the composition resembles portraits of Venetian courtesans by Domenico Tintoretto, especially the Lady revealing her breast in Prado (inventory number P000382) and the Portrait of a woman as Flora in the Wiesbaden Museum (inventory number M 296), also attributed to Domenico's half-sister Marietta Robusti. Also the style of the painting with bold brushstrokes is more Venetian and tintoresque, it seems that Geldorp copied a work by Tintoretto and inspired by his style. His Penitent Mary Magdalene in the Mauritshuis in The Hague (inventory number 319), was evidently inspired by Domenico's Magdalene in the Capitoline Museums in Rome (PC 32), painted between 1598 and 1602. He also copied Violante or "La Bella Gatta" by Titan (monogrammed upper left: GG. F., sold at Dorotheum in Vienna, April 19, 2016, lot 122).
Portrait of Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631) as Venus by Gortzius Geldorp, after 1605, Private collection.
Venus and Psyche by Palma il Giovane, first quarter of the 17th century, British Museum.
Cupid and Psyche by Palma il Giovane, first quarter of the 17th century, Private collection.
Entombment of Christ with the portrait of Nicolaus Christopher Radziwill "the Orphan" by Leandro Bassano or workshop
On September 16, 1582 Prince Nicolaus Christopher Radziwill "the Orphan" (1549-1616), Grand Marshal of Lithuania, accompanied by a dozen or so people (friends and servants), set off from his family castle in Nesvizh towards Venice from where in 1583 he went to the Holy Land. Through Dalmatia, the Greek islands, Tripoli, Damascus, he reached Jerusalem in the middle of the year, where in the Basilica of the Holy Sepulcher he was awarded the title of Knight of the Holy Sepulcher. Then through Egypt, where he had the opportunity to see the famous Great Sphinx, the eastern coast of Italy and again Venice he returned to his homeland on July 7, 1584.
Nicolaus Christopher was the son of Nicolaus Radziwill the Black and Elżbieta Szydłowiecka, daughter of Chancellor Krzysztof Szydłowiecki. After his father's death, as a result of his stay in Rome (he also visited Milan, Padua and Mantua), he converted in 1567 from Calvinism to Catholicism. Suffering from syphilis, in February 1580 he again went to Italy for treatment, near Padua and Lucca, and spent the turn of 1580-1581 in Venice, with an attempt to make an expedition to the Holy Land. He vowed that if his health would improve, he would go on a pilgrimage. Just few months after return from the Holy Land, on November 24, 1584, he married Princess Elżbieta Eufemia Wiśniowiecka (1569-1596), who was only 15 at the time and was 20 years younger than himself, and he had 6 sons and 3 daughters with her. In 1593, he and his wife left for the last time in his life the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, for treatment in a health resort in Abano Terme near Padua. Nicolaus Christopher died on February 28, 1616 in Niasvizh. During his lifetime Radziwill founded himself a tombstone in the Jesuit Church in Nesvizh - mentioned in the inscription on the pedestal, as well as in the sermon given by the Jesuit Marcin Widziewicz during his funeral. The co-founder was the wife of Nicolaus Christopher, therefore it should be dated to 1588-1596. The general conception of the tomb was probably modelled after the tomb of Pope Sixtus V in Rome, executed between 1585-1591 by Domenico Fontana and the tomb of Queen Bona Sforza in Bari, created between 1589-1593. Nicolaus Christopher saw the coffin with the body of the Queen in Bari in March 1584 and not without significance were his contacts with Queen Anna Jagiellon, the founder of the tombstone in Bari. The center of his tombstone is filled with a plate with a relief image of the prince in profile kneeling in prayer, with his head raised and in pilgrim's attire. It is crowned with a triangular pediment with the Order of the Knight of the Holy Sepulcher. The tomb was designed by a Jesuit architect Giovanni Maria Bernardoni (d. 1605) and created by an anonymous Italian sculptor active in Lesser Poland, possibly from the royal court. Szymon Starowolski (Starovolscius) in the book "A description of Poland or the state of the Kingdom of Poland" (Polonia sive status Regni Poloniae descriptio) issued in 1632, describing the investments made in his ancestral seat and its immediate vicinity by Nicolaus Christopher "the Orphan" (founding numerous monasteries, hospitals, the Jesuit college in Nesvizh, the palace and the town hall, as well as the reconstruction of the castle in nearby Mir, the arrangement of gardens, orchards and fish ponds, as well as the marking of roads along which there were moats and rows of fruit trees), ended with the statement that the voivode "arranged Italy for us in the middle of Sarmatia" (after "W podróży po Europie" by Wojciech Tygielski, Anna Kalinowska, p. 471). The painting by Leandro Bassano or workshop from the late 16th century in the Lithuanian National Art Museum in Vilnius (oil on canvas, 110 x 177 cm, inventory number LNDM T 3996), shows the scene of Entombment of Christ with a kneeling donor in the right corner, whose pose is identical with the pose of Nicolaus Christopher in his tombstone. Before 1941, the painting was owned by the Society of Friends of Science in Vilnius, to which it was given by count Władysław Tyszkiewicz (1865-1936), the owner of the Lentvaris estate, in 1907. Similar scene of the Entombment was published on page 61 of Stanisław Grochowski's "The Jerusalem procession in the church of the glorious tomb of the Lord Jesus [...] taken from the books of the Jerusalem Peregrination or the Pilgrimage [...] of Nicolaus Christopher Radziwll, prince on Olyka and Nesvizh [...]" (Hierozolimska processia w kosciele chwalebne[g]o grobu Pana Iezusowego [...] wzięta z ksiąg Hierozolymskiey Peregrynatiiey albo Pielgrzymowania [...] Mikołaia Chrzysstopha Radziwiła na Ołyce y Nieświeżu książęcia [...]), released in Kraków in 1607. A similar style painting depicting the Entombment of Christ was photographed around 1880 by Ignacy Krieger in the Prelate's House (Prałatówka) of Saint Mary's Basilica in Kraków (National Museum in Warsaw, DI 29611 MNW). In the basilica's collections are paintings by painters working for the royal court and magnates of Poland-Lithuania, such as the German Hans Suess von Kulmbach (ca. 1480-1522) and the Flemish Jacob Mertens (d. 1609). The man bears a great resemblance to effigies of Nicolaus Christopher "the Orphan", especially to his earliest known portrait, a drawing by David Kandel in the Louvre Museum, created between 1563 and 1564 during his studies in Strasbourg. In the Chapel of Our Lady of Peace (Cappella della Madonna della Pace) at the Santi Giovanni e Paolo in Venice, there is also a horizontal composition by Leandro Bassano. The church is considered the pantheon of Venice due to the large number of Venetian doges and other important figures buried there since its founding. The chapel was built between 1498 and 1503 to house the Byzantine icon of the Madonna, brought to Venice in 1349. The ceiling stuccoes are the work of Ottaviano Ridolfi and the majority of the paintings were done by artists working for King Sigismund III Vasa - Palma il Giovane painted four medallions on the ceiling representing the virtues of Saint Hyacinth of Poland (San Giacinto Odrovaz), Antonio Vassilacchi, known as Aliense, created a large Flagellation of Christ, on the right and Leandro the large canvas with Saint Hyacinth walking on the water of the Dnieper River (oil on canvas, 230 x 462 cm), on the left. This painting is dated around 1606-1610 and depicts the scene "Saint Hyacinth at the coming of the Tartars walks on the water of the River Dnieper bearing to safety the Holy Sacrament and the image of Our Lady". Leandro created other paintings for this temple, such as "Pope Honorius III approving the rule of Saint Dominic in 1216" in which the 13th century scene is transported to early 17th century Rome with many contemporary portraits, the pope in pontifical robes, the cardinals, the pope's Swiss Guards in typical robes with ruffs. The scene of 13th century Ruthenia is also brought back to the 17th century and the majority of the characters wear Italian costumes. Interestingly, in 1606 Tatar raids began in January. The steppe warlord Khan Temir (d. 1637) led 10,000 men to attack Podolia and was defeated by field hetman Stanisław Żółkiewski at the Battle of Udycz (January 28, 1606). "Christopher, Knight of Christ at the Sepulchre" (Christophorus Eques Christi dni Sepulchro) (257) is mentioned among the paintings from the collection of Princess Louise Charlotte Radziwill (1667-1695), inventoried in 1671 (after "Inwentarz galerii obrazów Radziwiłłów z XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska).
Entombment of Christ with the portrait of Prince Nicolaus Christopher Radziwill "the Orphan" (1549-1616) as donor by Leandro Bassano or workshop, before 1616, Lithuanian National Museum of Art in Vilnius.
Portraits of Infanta Anna Vasa by Lavinia Fontana
Sigismund III's sister, Anna Vasa (1568-1625), was passionate about botany. In 1604 she received from her brother the office of starost of Brodnica, and in 1611 of Golub in Pomerania and settled in her estates. She created a real cultural center in Brodnica and Golub and gathered around her people of different backgrounds. Anna financed the printing of Szymon Syreniusz's Herbarium (Zielnik Herbarzem z ięzyka Łacinskiego zowią), published in Kraków in 1613, and she founded a large botanical garden in Golub, where she cultivated medicinal plants and rare herbs, including tobacco.
In Brodnica, the Lutheran princess expanded and reconstructed the interiors of the so-called Palace of Anna Vasa. She also laid out a garden around the palace. Plan of Brodnica in the Military Archives of Sweden (Krigsarkivet) in Stockholm, made for military needs by the Swedes in 1628, just after the death of the princess, shows two gardens in the castle area. The Renaissance palace was built before 1564 by Rafał Działyński, starost of Brodnica, after the fire of the Teutonic castle in 1550 and rebuilt after 1604. The architect was most likely an Italian active at the royal court in Warsaw, possibly Paolo del Corte or Giacomo Rodondo, who were working at the time on the reconstruction of the Royal Castle. For all needs the Princess referred to Warsaw, as she considered herself abandoned in Polish Prussia. From the capital, she brought appropriate dresses, fabrics, beer, wine, mulberry juice, and even paper (after "Listy Anny Wazy (1568–1625)" by Karol Łopatecki, Janusz Dąbrowski, Wojciech Krawczuk, Wojciech Walczak, p. 20, 26, 38, 59, 157-158). From around 1615, Anna also owned a manor in Warsaw, not far from the Royal Castle. It is probably the old house in the garden mentioned in the document from 1622 near the summer residence of Queen Constance. She also resided in a Teutonic castle in Osiek by Lake Kałębie, between Grudziądź and Pelplin, which was transformed into a fine Renaissance residence by starost Adam Walewski in 1565 (demolished in 1772 by the Prussian administration). The princess had a particular fondness for music, dance and ballet. The letter of Nuncio Claudio Rangoni to Cardinal Pietro Aldobrandini (Kraków, July 18, 1604), describes the performance of the wife of Count Cristoforo Sessi signore di Riolo, a lady "excellent in singing and playing the viola", "in the room of the princess [Anna Vasa], also heard by the king [Sigismund III], remaining in a place where he could not be seen" (quel conte Christofaro di Ruolo è partito di ritorno a Praga dopo l'esser stato alcuni giorni qui, ove la moglie sua ha cantato una volta in camera della principessa, sentita anco dal re, ch'era in luogo onde non poteva esser veduto). In 1619 she helped the daughter of a court musician Wincenty Lilius (Vincenzo Gigli) to enter a convent in Braniewo (letter from Warsaw of November 17) and in 1624 she interceded with Urszula Meyerin to ask the king for an annual salary or the post of mayor for another Italian musician Zygmunt Petart (Sigismondo Patard) (letter from Brodnica of October 1). She enjoyed arranging weddings for her court ladies. In 1605, during the celebrations related to the wedding of Sigismund III in Kraków she organized an expensive "Masked Ball of the Ladies". Anna and her court ladies asked first the king, then the archduke, the prince, "and other gentlemen and courtiers, who also had to jump like them". They were especially amused by the gentlemen who weren't good dancers "even though they had been to Italy". A few days earlier, on December 13, 1605, a ballet had taken place in the presence of the whole court in a special dance hall in honor of the new Queen Constance. The masked dancers wore male and female Spanish costumes, there was also an Italian Commedia dell'arte (Pantaleonów włoskich, którzy długo po włosku z sobą się swarzyli), as well as Spanish, Italian and Polish dances. Masked aristocrats played both male and female roles (after "Balety na królewskich godach 1605 roku" by Jacek Żukowski). The masks were probably imported from Venice, because for example in 1609 in Kraków, Wincenty Zygante (Vincenzo Ziganti) together with the second elder of the painters' guild estimated the possessions of Adam Niestachowski (or Romanowski), namely several dozen Venetian masks, with beards, mustaches, trimmed beards, of Black people, old women, young girls, married women, etc. The ballet prepared for the birth of Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa on August 7, 1619 was equally splendid. Anna led "dances with a stomp" performed by noble women, and her nephew, Prince Ladislaus Sigismund, led young men dressed as Turks. The collection of the Museum of Warsaw includes a perfectly preserved outfit of Adam Parzniewski (1565-1614), burgrave of Kraków Castle and court marshal of Princess Anna Vasa, found before 1952 in the crypt of Warsaw Cathedral. It is an outfit made of materials of Italian origin, probably sewn in Warsaw and consists of a cloak, short puffy trousers and an Italian velvet caftan (velluto ceselato), originally purple, called pavonazzo in Italian (after "Marmur dziejowy ...", edited by Ewa Chojecka, p. 232), inspired by Spanish fashion. According to Gabriel Joannica, the publisher and author of the introduction to the herbarium by Szymon Syreniusz, Anna had "the ability to speak languages, first our Polish, as if native, then others, foreign: German, Italian, French, and partly learned Latin". She also spoke her native Swedish well. Her closest confidant at the court in Warsaw was the "minister in a skirt" and "Jesuit's bigotry" Urszula Meyerin (Ursula Meierin), king's mistress and a devout Catholic. She corresponded frequently with Jung frau Ursull, calling her Mein Liebt Vrsul (My Dear Ursul) in German or mosci Pano Vrsolo (Lady Ursola, close to Italian Orsola) in Polish in her letters. The majority of her letters are now kept in Stockholm (Svenska Riksarkivet), taken during the Deluge (1655-1660). In the oldest known letter from the princess to Urszula, dated in Warsaw on August 16, 1599, she asks her to buy hats for the princess and her ladies. To emphasize her hereditary rights to the Swedish crown, the princess, like her aunt Anna Jagiellon before the royal elections in Poland-Lithuania in the 1570s, used the Spanish title of Infanta (Serenissima Infant. Sueciae Annae, Infanti Sueciae Anna, Serenissimae Infantis Sueciae Anne). The inscription on the tin sarcophagus funded by Sigismund III Vasa, published in Monumenta Sarmatarum ... by Szymon Starowolski in 1655, calls her "The Most Serene Princess, D. [Domina/Donna/Doña] Anna Infanta of Sweden" (Serenissima Princeps, D. Anna Infans Sueciæ). Her letters in Polish were usually signed "Anna, Princess of Sweden" (Anna królewna szwedzka) or simply Anna, in letters in German to Urszula Meyerin. The king's favorite Urszula, close to the two wives of Sigismund III, corresponded with their mother Maria Anna of Bavaria (1551-1608), Archduchess of Austria, and she was probably an intermediary in certain artistic commissions from Anna Vasa. The Queen's official physician was the Venetian Giovanni Battista Gemma, who died in Kraków in 1608, sent by her mother to the court in Warsaw. As at the court of the Archduchess (her portraits by the Flemish painter Cornelis Vermeyen, the Italian Giovanni Pietro de Pomis or the Spanish painters) and at the royal court in Warsaw, in Brodnica also Spanish fashion and Flemish and Italian art must have been very popular. Very little is known about the artistic patronage of the Princess-Infanta. Nothing has been preserved in Brodnica or Golub (at least confirmed). The invaders, mainly Swedes, probably looted or destroyed everything. In a letter dated October 21, 1605 from Kraków (Polish Library in Paris, rkps 56/36, in Polish) to Hetman Jan Karol Chodkiewicz (died 1621), she expresses her great joy at the news of the victory of the Commonwealth's army led by Chodkiewicz in the Battle of Kircholm in 1605, during which he inflicted a major defeat on a Swedish army three times larger than his own. The Swedes invaded the Commonwealth in mid-1605, shortly before the marriage of Anna's brother to Constance of Austria (December 11, 1605). Poland-Lithuania was at that time one of the richest countries in Europe, and the Commonwealth could afford a much more powerful and larger army than that of Sweden. However, military spending was limited by Parliament (Sejm) because magnates in the Senate and nobles were afraid that such a powerful army will be used against them to strengthen the power of the king and turn the country into absolute monarchy (compare "Mecenat kulturalny i dwór Stanisława Lubomirskiego ..." by Józef Długosz, p. 33). "Anna, by the grace of God, [hereditary] princess of the Swedes, Goths, and Vandals, heiress of the Grand Duchy of Finland. Lord, dear to us. May God be eternally praised for such a great and significant victory, which he deigned to give against such a main and fierce enemy of the King His Highness and the nation here. [...] And since we have a special and great pleasure from this victory, so that we may have a more perfect one, we therefore urgently ask you in remembrance of this, Your Lordship, that you order an expert and conscious person, taking a painter, to paint the battle scene, formations and all actions how that battle was fought there, having learned the names, places and people, you will do a great and very grateful thing to us", writes the Infanta in the mentioned letter. The oldest and best painting depicting the battle is today in the Château de Sassenage, near Grenoble in France. It is attributed to Peter Snayers, active in Antwerp between 1612 and 1621 and later in Brussels, and probably comes from the collection of the son of Sigismund III, John II Casimir Vasa, who settled in France after his abdication in 1668. Sigismund most likely commissioned it, through his agent at the court of Archduke Albert VII in Brussels in the 1620s, and the original, possibly also by a Flemish or Italian painter, was most likely the painting commissioned by the princess in 1605. Anna died on February 6, 1625 in Brodnica, and the last moments of the Lutheran Princess-Infanta, were vividly commented on in Rome and Florence - letters of Nuncio Giovanni Battista Lancellotti to the Holy See from Warsaw, February 9 and February 18, 1625 and letter of Giovanni Battista Siri, envoy of the Medici family, February 21, 1625 from Kraków (Alii 7 stante passo ad'altra vita la Ser[enissi]ma infante ...). The first Polish monographer of Anna, Marian Dubiecki, wrote in Przegląd Powszechny in 1896 about the efforts of Sigismund III Vasa to obtain papal permission to bury his sister at the Wawel Cathedral. It is possible that through rumors of an alleged deathbed conversion of the Infanta, a devout Lutheran, the Polish court wanted to convince Rome that she should be buried with other members of the family and close to the Jagiellons. It was not until 1636 that her nephew, King Ladislaus IV Vasa, decided to bury Anna in nearby Toruń, in a Baroque mausoleum built especially for this purpose in 1626 at the Church of the Blessed Virgin Mary, then a Protestant temple. The surviving sources confirm that Anna Vasa's body dressed in an expensive dress and decorated with jewels was waiting in Brodnica, in the "vaulted room", unburied. In May 1626 King Gustavus Adolphus launched his invasion of Polish Prussia. On October 4, 1628 Brodnica capitulated, surrendered by the commander of the Polish garrison, the Frenchman La Montagne, and fell into the hands of the Sweds for over a year. Only the truce concluded on September 26, 1629 (in Stary Targ) obliged them to leave the city on October 6, so the night before, the Swedish soldiers organized a plundering. A few of them broke into the tomb of Anna Vasa, where they profaned the corpse of the Princess-Infanta, tearing off her dress and stealing jewels. The citizens of Brodnica were shocked, so the Judicial Court quickly assembled and the royal court in Warsaw was notified. The Chancellor of the Commonwealth, Jakub Zadzik, sent a sharp letter to the king of Sweden, in which, based on a written statement of the Brodnica Court, he presented shameful acts. It was answered by the Chancellor of the Kingdom of Sweden, Axel Oxenstierna, who only partially admitted that the fault lies with his compatriots, while trying to shift the responsibility onto Poles (after "Skarb Anny Wazówny ..." by Piotr Grążawski). The sarcophagus was probably put back in order because the copy of receipt for the take over of Brodnica from the Swedish army issued by Mikołaj Hannibal Stroci (a descendant of the Florentine Strozzi family), a month later (October 26/November 6, 1629), does not mention the desecration of the corpse. Anna Vasa's crypt in Toruń was opened on April 7, 1994 and the exploration confirmed all known information about robberies. No funeral equipment were found. The skeleton was fairly well preserved, however, it turned out that the right forearm was missing, perhaps as the result of the brutal behavior of the burglars during the robbery of the jewels. No trace of the Infanta's jewelry was known until a document was found in Stockholm in the 1980s describing a find in the Uppsala Cathedral in 1777. A gold bracelet was found on the floor with an engraved monogram of Anna - APS (Anna Princeps Sveciae) and the symbols of the Vasa family, now kept at the Royal Armory (Livrustkammaren) in Stockholm (after "Śmierć i problemy pochówku Anny Wazówny ..." by Alicja Saar-Kozłowska, p. 76-77). The bracelet was probably made in Gdańsk or Toruń, since very similar are depicted in portraits of patrician ladies by Anton Möller from the 1590s (National Museum in Gdańsk and National Museum of Finland), in a portrait of a lady, probably a noblewoman from the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, in the National Museum in Stockholm (Gripsholm Castle, NMGrh 426) and a similar gold bracelet was found among the jewelry of Zofia Magdalena Loka (Skrwilno Treasure in Toruń), hidden during the Deluge. The collection of jewelry of Anna Vasa was famous and estimated at 200,000 thalers. Some of these jewels she inherited from her mother Catherine Jagellon. In 1606, to repay various debts intended to modernize the starosty and her residence, she decided to sell some of her jewelry to Tsar False Dmitry I. In 2022, a portrait of a lady in a rich costume adorned with jewels and a garden in the background was sold in New York (oil on canvas, 121 x 95.5 cm, Sotheby's, May 26, 2022, lot 223). The painting comes from a private collection in Connecticut and was previously believed to represent Queen Elizabeth I of England. The face resembles some effigies of the Queen, such as the "Darnley Portrait" or the "Rainbow Portrait", but the model is dressed in Spanish costume from the late 16th or early 17th century. The Queen of England wearing a dress of her greatest enemy, it is very unlikely, so the identification has been changed to Infanta Isabella Clara Eugenia (1566-1633). The portrait is very similar to the portrait of the Spanish Infanta by Juan Pantoja de la Cruz, painted between 1598-1599 (Prado Museum in Madrid, P000717). The costume, the pose, even the landscape are very much alike. In her portrait, Isabella Clara Eugenia holds a miniature of her father Philip II of Spain, while in the described portrait the main jewel is a large gold eagle pendant set with diamonds. Although the Spanish Infanta was not a close member of the Imperial family, she could inherit such a pendant from her grandfather, Emperor Charles V, or receive it from the Austrian branch of the Habsburg family. In 1543, Charles V offered such a "diamond eagle with rubies" (orzeł dyamentowy z rubinami) to his niece Elizabeth of Austria (1526-1545) on the occasion of her marriage with Sigismund II Augustus (today in the Treasury of the Munich Residence, Sch 49). In the majority of her portraits, Isabella Clara Eugenia wears a large diamond cross and no other portrait with an eagle is known. Two important elements are missing to consider the portrait in New York as her effigy - an eagle's head, as the imperial symbol is a bicephalous bird - a gold pendant with a double-headed imperial eagle from the 1600s, most likely belonging to Constance d Austria, is in the Monastery of Jasna Góra in Częstochowa, and the protruding lip of the Habsburgs, clearly visible in her portrait by Pantoja de la Cruz. Therefore, the model is not a member of the imperial family or a Habsburg. A similar eagle pendant can be seen on several portraits of Queen Constance of Austria - by Jakob Troschel from about 1610 (Germanisches Nationalmuseum in Nuremberg, Gm 699, 7009/7277), by unknown painter from the 1610s (Museum of Zamość, 62) or by Pieter Soutman from about 1624 (Staatsgalerie Neuburg, 985). In her portrait in Nuremberg, the queen also wears a gold diadem with a heraldic Polish eagle and a Spanish dress - saya, probably a gift from Spain or sewn alla moda from a Spanish model. The Queen of Poland was also depicted in a typical Spanish dress in her portrait by an Italian painter, now in the Philadelphia Museum of Art (oil on canvas, 186.1 x 107.3 cm, 1883-137), a companion to the portrait of her younger sister Maria Maddalena of Austria, Grand Duchess of Tuscany, in the same collection (1883-136). Spanish, Italian (Venetian and Florentine), Flemish, French and Turkish fashion was at that time very popular in the Commonwealth, as confirmed by Piotr Zbylitowski in his "Reprimand of Women's Extravagant Attire" (Przygana wymyślnym strojom białogłowskim), published in Kraków in 1600. The country became very wealthy from the grain trade and such "extravagant" and rich costumes were not expensive. The next queen of Poland, Cecilia Renata of Austria, was also depicted with an eagle jewel - portrait with a tulip (Alte Pinakothek in Munich, 6781) and an engraving by Eberhard Wassenberg, and a gold brooch with a Polish eagle in the Louvre Museum (MR 418) was probably made for her. Anna Vasa was depicted with an eagle pendant in a miniature by Sofonisba Anguissola from around 1592 (Rohrau Castle). The garden behind the woman in the New York painting was made for her and a villa in the center is her residence. The layout of this garden corresponds almost perfectly to the palace of Anna Vasa in Brodnica, as depicted in the mentioned drawing in Stockholm from 1628. Assuming that the two depictions are very accurate, the differences arise from the fact that the residence has been modified over time (Anna extended the building and built a kitchen) and there is about 20 years difference between them. The painting is attributed to a Flemish painter, however, the style of this work is very characteristic and typical of a great painter Lavinia Fontana (1552-1614) and her studio/workshop. It is comparable to her self-portraits - at the spinet with a maidservant (Accademia Nazionale di San Luca in Rome and private collection), in her studio (Uffizi Gallery in Florence and private collection) from the 1570s, signed portrait of the Gozzadini family from 1584 (Pinacoteca Nazionale in Bologna) and portraits of Margherita Gonzaga (1564-1618) and her ladies and Alfonso II d'Este (1533-1597), Duke of Ferrara in the scene of the visit of the Queen of Sheba to King Solomon from 1599 (National Gallery of Ireland). Lavinia was born in Bologna in the Papal States and she and her family moved to Rome in 1604 at the invitation of Pope Clement VIII. Her father was another prominent painter in the service of the popes - Prospero Fontana (1512-1597). A miniature portrait of a couple from a private collection (oil on copper, 19 cm), attributed to the circle of Prospero, is an effigy of William V, Duke of Bavaria and his wife, Renata of Lorraine. If he or his workshop were authors, he therefore accepted orders from abroad based on study drawings or effigies by other painters, his stay in Bavaria not being confirmed in the sources. The royal court and Polish-Lithuanian magnates frequently commissioned paintings from Rome at the turn of the 16th and 17th centuries. They were delivered to the king by foreigners who stayed in Rome, such as the Jesuit Antonio Possevino (1533-1611), his envoys and courtiers, such as Cardinal Andrew Bathory (1563-1599), Stanisław Reszka (1544-1600) and Tomasz Treter (1547-1610) and others, as well as passers-by, such as Marshals Mikołaj Wolski (1553-1630) and Zygmunt Gonzaga Myszkowski (ca. 1562-1615). Paintings, whose subjects are not known, sent from Rome by Reszka in 1588 must have pleased the king, since Bernard Gołyński reported that they were far superior to the paintings sent to the king by Possevino (after "Z dziejów polskiego mecenatu ..." by Władysław Tomkiewicz, p. 23). Eustachy Wołłowicz (1572-1630), provost (praepositus) of Trakai and a referendary at the court of Sigismund III Vasa possibly owned a painting by Michelangelo (Pietà), reproduced in a 1604 print by Lucas Kilian with his coat of arms and inscription MICHAEL: ANG. / B. pinxit Romae. They also had many portraits, especially of famous Italians. In the second edition of his autobiography, published in 1608, Bologna's best known poet, Giulio Cesare Croce (1550-1609), writes poetically on his portrait made by Lavinia, which was sent to Poland: "And a short time ago I had my portrait made by Lavinia Fontana and my portrait has been taken to live in Poland" (E' poco tempo ch'io mi fei ritrare, / A Lavinia Fontana, e'l mio ritratto, / Fù portato in Polonia ad habitare, "Descrittione della vita del Croce", p. 20). Stylistically the landscape behind the woman in the New York painting resembles the works of Domenico Tintoretto, in particular the portrait of Princess Anna Vasa in the Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum (P24e2). It is possible that Lavinia received a painting by Domenico or his workshop to copy and inspired by his style. The facial features of a woman greatly resemble the Polish-Lithuanian-Swedish Infanta from the mentioned portrait by Tintoretto and the oval portrait by Sofonisba Anguissola, as well as the effigies of her brother Sigismund III by Joseph Heintz the Elder (Alte Pinakothek in Munich, 11885) and by Jakob Troschel (Royal Castle in Warsaw, ZKW 1176). In her 1584 portrait of the Gozzadini family, Lavinia "resurrected" two family members – Ginevra (d. 1581) and her father, Senator Ulisse Gozzadini (d. 1561). If she could paint the deceased as a living person, she could also paint the people living far from her studio, like Anna Vasa. The woman was also depicted in a full-length portrait currently housed in the Lázaro Galdiano Museum in Madrid (oil on canvas, 198 x 114 cm, 08470). This painting was probably acquired between 1936 and 1939 and was part of the collection assembled by José Lázaro in Paris. The model's identity has not been established, although "she must have been a person of high courtly status, judging by her attire" (Se ignora todo de la retratada, que hubo de ser persona de elevada situación cortesana, a juzgar por su traje), according to the museum's description. Due to the woman's rich costume from the early 1600s which is obviously Spanish, the painting has been attributed to the Spanish painter whose style was comparable - Rodrigo de Villandrando (1588-1622). However, not only the face and costume are similar to the New York painting, but also the style of this work. The Madrid portrait resembles the style of the mentioned portrait of the Gozzadini family, but most similar is the way in which the portrait of Raffaele Riario (d. 1592), attributed to Lavinia, was painted (sold at Dorotheum in Vienna, April 24, 2018, lot 52). Also very comparable is the portrait of a lady with a fan and a dog from the beginning of the 17th century, now kept at Lysice Castle in Czechia (oil on canvas, 85 x 65 cm, LS00081a). The details of the costume and the way the hands and face were painted are very close to Fontana's style. The face from the portrait with eagle pendant, as a template, was copied in another painting from the same period sold in 2017, also in New York (oil on canvas, 66.7 x 53.7 cm, Christie's, auction 14963, October 18, 2017, lot 572). It comes from the collection of the Hispanic Society of America in New York. This "Portrait of a lady, bust-length" is also attributed to the Flemish school, but the closest in style is again a painting by Lavinia Fontana, which is now in the National Museum in Kraków (oil on canvas, 77 x 62.3 cm, MNK XII-A-664). The portrait of Bianca Lucia Aliprandi, née Crivelli (sold at Christie's London, auction 20055, December 7, 2021, lot 29) and the mentioned painting by Fontana in the National Gallery of Ireland are also very similar. Another portrait of the same woman by the same painter is in the National Art Gallery in Lviv, Ukraine (54.5 x 42, inventory number Ж-1945). It comes from the Lubomirski collection and was donated to the Ossolineum in Lviv by Prince Henryk Ludwik Lubomirski (recorded in 1826). It was allegedly purchased in 1826 in Vienna from P. della Rovere ("Exhibition catalogue: Peter Paul Rubens - Anthony van Dyck" by Svetlana Stets, pp. 576-577), thus possibly sent to the Habsburgs or coming from the older Lubomirski collections. The painting is attributed to follower of Anthony van Dyck. The style of her dress indicates that the painting was made in the late 1580s as it resembles the Spanish-Italian dress of Margherita Gonzaga (1564-1618), Duchess of Ferrara from her portrait by Jean Bahuet (private collection) or her effigy by Jacopo Ligozzi in Lisbon (National Museum of Ancient Art, 453 Pint), painted around 1593. The mentioned painting by Lavinia Fontana in the National Museum in Kraków may have come from the royal collection, probably mentioned in the collection of King John III Sobieski in the inventory of the Wilanów Palace from 1696 (No. 77). Before 1924 it was in the collection of Antoni Strzałecki in Warsaw. The painting was made at the beginning of the 17th century because her costume and hairstyle are similar to those seen in the effigies of the so-called Bellezze di Artimino in Palazzo Pitti or in the portrait of Margherita Gonzaga (1591-1632), Duchess of Lorraine from about 1605 (Metropolitan Museum of Art, 25.110.21). According to the museum's catalog entry by Dorota Dec and other publications, this is the artist's self-portrait and she depicted herself as the biblical heroine Judith (compare "Judith" by Lawrence M. Wills, p. 140), being basically a woman who overcomes a man's violence with her cunning intelligence. What better gift for patrons from the Realm of Venus?
Portrait of Princess Anna Vasa (1568-1625) by Lavinia Fontana, ca. 1588, National Art Gallery in Lviv.
Portrait of Infanta Anna Vasa (1568-1625), starost of Brodnica, in Spanish dress with eagle pendant by Lavinia Fontana and studio, ca. 1605-1610, Private collection.
Portrait of Infanta Anna Vasa (1568-1625), starost of Brodnica, in Spanish dress by Lavinia Fontana and studio, ca. 1605-1610, Lázaro Galdiano Museum in Madrid.
Portrait of Infanta Anna Vasa (1568-1625), starost of Brodnica, bust-length by Lavinia Fontana, ca. 1605, Private collection.
Self-portrait as Judith with the head of Holophernes by Lavinia Fontana, 1600s, National Museum in Kraków.
Battle of Kircholm in 1605 by Pieter Snayers, 1620s, Château de Sassenage.
"Portrait of Baroness Ebba Grip" by Lavinia Fontana
In the 17th century Djursholm Castle, just 15 km north of central Stockholm, there is an interesting full-length portrait believed to depict the Swedish baroness Ebba Grip (1583-1666). She was the wife of Svante Gustafsson Banér (1583-1628), who, through his marriage to Ebba (August 28, 1617), became the owner of three large estates. Svante became a councilor and was granted a post of a governor in Riga, which was captured by the Swedish Empire from the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth after the siege. In 1628 her husband died in Riga. As a single mother, she continued to manage the Djursholm estate and other properties for almost 40 years.
The portrait is displayed in the main hall of the castle with a portrait of Ebba's husband painted by another painter. It bears the model's coat of arms and the appropriate inscription in Swedish identifying the model in the upper right corner, probably added later. The painting is attributed to Jacob Heinrich Elbfas (d. 1664), a Baltic German portraitist active in Sweden from 1622. The sitter's costume resembles that from another three-quarter portrait of Ebba, most likely in the same collection, known thanks to a black and white photo. There would be nothing unusual in all this if it were not for the fact that the collar and cuffs and partly the face of the model seem to have been painted by another painter. The mentioned fragments resemble Elbfas' style, but the rest appears to have been painted by a more talented painter. Another very unusual element of this portrait is Ebba's costume and jewelry, much richer than in her three-quarter portrait. She wears a Spanish-style saya, a court dress typical for European countries of the early 17th century in the Habsburg sphere. The Polish queens from the Habsburg dynasty, Anna of Austria and her younger sister Constance, wives of Sigismund III, were depicted in similar dresses in their official portraits. A similar dress can also be seen in a portrait of Sigismund's sister, Infanta Anna Vasa (1568-1625), starost of Brodnica, painted by Lavinia Fontana and her studio (Lázaro Galdiano Museum in Madrid, inv. 08470), identified and attributed by me. What is also interesting is that not only the costume and Spanish-style pose of the model are similar to the Madrid painting, but also the style of the painting itself, as if both were painted by the same painter. The style of the painting is also reminiscent of the portrait of Raffaele Riario (d. 1592), attributed to Fontana (Dorotheum Vienna, April 24, 2018, lot 52) or her signed portrait of the Gozzadini family (Pinacoteca Nazionale in Bologna). The little dog resembles that in the Gozzadini portrait or the portrait of a lady with a fan by Lavinia at Lysice Castle (LS00081a), attributed by me, all with clear Spanish influences. Portrait of a Swedish noblewoman, close to the ruling family of Sweden, depicted in Spanish costume and painted in Rome, seat of the papacy, by a painter patronized by the popes, all this is very unusual and indicates that the painting initially depicted someone else and was repainted with Ebba's likeness at a later date. Perhaps an x-ray of the painting would confirm this theory and the true identity of the sitter. Taking all factors into account, we can assume that originally the painting may have depicted Sigismund III's wife, Constance of Austria (comparable to her portrait in crimson saya at the Royal Castle in Warsaw, ZKW 2049 or another version at Wawel Castle, ZKnW-PZS 1783) or his sister Anna Vasa. A similar small dog is visible in the portrait of Constance in Spanish dress kept in the Germanisches Nationalmuseum (deposited in the Imperial Castle of Nuremberg, inv. Gm 699, 7009/7277). Therefore, the painting was probably looted from the estates of Anna Vasa in Polish Prussia between 1628 and 1629, during the Swedish invasion, or during the Deluge (1655-1660) and probably witnesses horrible crimes committed by the invaders, like the plundering of the Infanta's coffin or massacres of people, after the looting of rich castles in Ćmielów or Tenczyn (compare "Encyklopedia powszechna", Volume 5, p. 755 and "Szwedzi i siedmiogrodzianie w Krakowie od 1655 do 1657 roku" by Ludwik Sikora, p. 44), only to be finally repainted in the portrait of a Swedish aristocrat after its transport to Sweden.
"Portrait of Baroness Ebba Grip" by Lavinia Fontana, ca. 1605-1610, Djursholm Castle.
Portrait of a lady with a fan and a dog by Lavinia Fontana, early 17th century, Lysice Castle.
Portrait of Queen Constance of Austria by Domenico Tintoretto
At the beginning of the 17th century, as in the previous era, Polish-Lithuanian monarchs and magnates collected portraits of rulers and famous people. In 1612 Jan Ostroróg (1565-1622), voivode of Poznań requested a portrait of the Elector of Brandenburg (letter from Salomon Leuper to John Sigismund, Elector of Brandenburg, February 3, 1612) and in the same year William V, Duke of Bavaria sent a portrait of his son Albert (1584-1666) to Queen Constance of Austria, on the occasion of Albert's marriage (letter of January 4, 1612). The queen exchanged portraits with Albert in 1624. In a letter dated October 15, 1613, Alessandro Cilli reported to the Duke of Urbino that Queen Constance "keeps in her room the portraits of the most serene princes and princesses sent to her from Florence by their Highnesses" (tiene in camera sua i ritratti dei s-mi principi et principesse mandatigli da Fiorenza dalle loro Altezze s-m) (after "Das Leben am Hof ..." by Walter Leitsch, p. 370-371, 911, 2377, 2378, 2381).
Almost two years later, in 1615, through the ambassador Krzysztof Koryciński, Queen Constance also requested and received from Spain portraits of the children and husband of her sister Margaret of Austria "as natural as possible" (los mas naturales que sea possible), according to the Consejo report of January 15, 1615 (El gran desseo que la serenisima reyna su señora tenia de los retratos de VM y de su felicissima prole. Y suplica agora a VM sea servido de mandar se hagan assi el de VM como los de la reyna de Francia, del serenisimo principe nuestro señor, infantes y infantas los mas naturales que sea possible y a proporcion de sus estaturas, porque no podra llevar a la reyna su señora cosa mas cara y que tanto recreasse su vista, como la effigie y semejança de VM y de sus serenisimos hijos y a que nuestro señor le ha quitado la comodidad de ver los originales. Al consejo parece que es muy justo que se le den al dicho embaxador los retratos que pide en nombre de al reyna de Polonia). This was followed by the decision of the Royal Council, probably from April 1615, to grant "portraits of their majesties" (y los retratos de sus majestades y altezas afin que la serenisima reyna su señora reciva el gusto y consuelo que dessea tal vista). In 1620, the new portraits of the Spanish monarchs were delivered to the Polish-Lithuanian royal court, including that of Elisabeth of France (1602-1644), wife of Prince Philip of Spain, future Philip IV (1605-1665), sent through a Polish Dominican Father, according to a letter from Francesco Diotallevi (1579-1622), apostolic nuncio in Poland (1614-1621), to Cardinal Scipione Borghese (1577-1633) (E giunto qua un padre dominicano Polacco, che per molti anni si è tratenuto in Spagna al quale è stato consignato dalla majestà cattolica per presentarlo in suo nome a questa majestà il ritratto della principessa venuta di Francia, moglie del principe figliolo di SM cattolica havendo gli gia per prima mandati i ritratti di tutti gl'altri principi della casa reale, January 10, 1620). Few yers later, in 1624, Queen Constance launched a major campaign to have a proper gallery of family portraits. However, it took time because the painter working in Vienna was very busy. He probably had to make similar or identical portraits for the courts in Madrid, Brussels and Florence. Nikolaus Nusser, Chamberlain of Ferdinand II, wrote at the end of November that completion could only be expected in three months and that Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa will be able to take the pictures with him on the return journey from Italy. Through Prince Radziwill (presumably Sigismund Charles), Empress Eleonora Gonzaga (1598-1655) sent portraits of herself and the Archdukes Maximilian Ernest (1583-1616) and John Charles (1605-1619), both of whom had already died and whose portraits had to be copied in Graz. Nusser, thought that the portraits of the Emperor and Empress should be sent in the same size. "But the empress discovered that she had sent busts to the Polish court" (So hat aber die kaiserin vermelt, das sy bei dem polnischen gesandten brustbilder geschickt), wrote Nusser in June 1625, because the Polish-Lithuanian court did not want to be supplied with too many pictures. Some painters were active at the royal court, but apart from Jakob Troschel, Jan Szwankowski, Jakob Mertens, Tommaso Dolabella, Wojciech Borzymowski, who was supposedly commissioned by Sigismund III to decorate the chambers of the Warsaw castle, and in 1630 for Primate Łubieński he painted a portrait of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund in Gdańsk, and perhaps Philipp Holbein II (goldsmith, jeweller and painter), they were temporary workers or agents of foreign workshops. We only know that Archduchess Maria Anna brought the court painter Balthasar Gebhard with her to Constance's wedding in December 1605, because he had broken a rib during his stay in Kraków. Urszula Meyerin received 100 florins for the care of the patient. In the accounts from 1627 there is also a note: "200 florins given to the Polish painter at the Jasthof [Jazdów?]" (Dem polnischen mahler auf den Jasthof gegeben fl 200, Spetember 12, 1627). At that time, many objects were purchased in Italy, notably in Venice, including books. Gian Battista Gemma, a physician from Veneto, gave the king books to read, some of which were "heretical". This is why the very pious Queen Constance considered Gemma a heretic and even threatened to "throw him out of the room" (per heretico et minacciarli che lo cacciarà di camera), according to Claudio Rangoni's letter to Cardinal Scipione Borghese of November 11, 1606. When in 1606 the pope had a dispute with Venice and imposed prohibitions on the entire state (Venetian Interdict), the king did not want to speak openly against Venice and skillfully avoided making a decision. Crystal tankard with the coat of arms and monogram of Sigismund III Vasa and Constance of Austria (SCA - Sigmundus et Constantia Austriacae), floral motives and a handle in the form of a nude woman, attributed to Miseroni workshop in Milan (Bavarian National Museum, R 2157), is one of the few preserved objects commissioned by the king and his wife in Italy in the early 17th century. At the Prado Museum in Madrid, deposited at the Spanish Embassy in Bern, there is a portrait described as "Queen Eleanor of Austria" (La reina Leonor de Austria) from the early 17th century (oil on canvas, 108 x 88 cm, inventory number P001265). It is said to depict Eleanor of Austria (1498-1558), who subsequently became queen of Portugal (1518-1521) and France (1530-1547). Her Spanish dress and her large ruff indicate that this is rather a person living in the first quarter of the 17th century and not the 16th century. According to an article by Gloria Martínez Leiva ("El incendio de la Embajada española en Lisboa de 1975", January 16, 2018), it is an effigy of Anna of Austria (1573-1598), Queen of Poland from from a series created by Bartolomé González (Retrato de Ana de Habsburgo), but the woman has no resemblance to the effigies of the queen. The attribution of the painting to Juan Bautista Martínez del Mazo (inventory of Buen Retiro, 1794, no. 897) and Bartolomé González is now rejected and the painting is qualified as an anonymous work. The woman wears a tira similar to that visible on several effigies of Margaret of Austria, Queen of Spain (e.g. portrait in the Hungarian National Gallery in Budapest with inscription MARGARETA. AVS/TRIA. HISP. REGINA.) or Magdalene of Bavaria (1587-1628), Countess Palatine of Neuburg and Duchess of Jülich-Berg by Peter Candid (Bavarian State Painting Collections, 2471, 3217), so she is a reigning queen consort or duchess. The model therefore could not have been Margaret's younger sister, Archduchess Eleanor of Austria (1582-1620), who, after unsuccessful attempts at marriage on October 3, 1607, took the veil and became a nun in Hall in Tirol. A similar lace ruff and high hairstyle are seen in a portrait described as depicting a lady-in-waiting of Queen Constance of Austria, purchased in 1935 by the National Museum in Warsaw from Z. Iłowicki (deposited at the Wilanów Palace in Warsaw, oil on canvas, 82 x 65 cm, 120735), generally dated after 1605 (after "Portrety osobistości polskich" by Stefan Kozakiewicz, Andrzej Ryszkiewicz, p. 251). Comparison with several portraits from a series entitled "Beauties of Artimino" (Bellezze di Artimino), indicates that the two women are dressed according to southern Italian fashion, as the closest are the portraits of Roman and Neapolitan ladies - Countess of Castro (Uffizi, Inv. 1890, 2265), Emilia Spinelli (Palazzo Davanzati, Inv. 1890, 2262), Belluccia Carafa, Duchess of Cerce (Uffizi, Inv. 1890, 2263) and Porzia de' Rossi (Uffizi, Inv. 1890, 2266). The series included portraits of Florentine, Roman and Neapolitan ladies linked to the court of Ferdinand I de' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany. In the 1609 inventory of the Villa Medici "La Ferdinanda" in Artimino, drawn up on Ferdinand's death, there were sixty-five effigies of this type, forty-two Florentine, seventeen Roman and six Neapolitan. The effigies of Roman and Neapolitan ladies stand out from the series, not only by their hairstyle, but also by the style of the paintings which were probably painted in Rome between 1602 and 1608 and are attributed to the workshop of Jacopo Ligozzi, perhaps painted by Achille Gianré. The model bears a great resemblance to the effigies of Constance of Austria, notably the portrait by Frans Pourbus the Younger (Kunsthistorisches Museum, GG 3306), Joseph Heintz the Elder (Kunsthistorisches Museum, GG 9452), and by an unknown painter (Wawel Castle, 1783). A portrait painted in a very similar style and from the same period is also in the Prado Museum (oil on canvas, 112 x 92 cm, P002405). According to the museum catalog, it is an effigy of Eleanor de Medici (1567-1611), Duchess of Mantua, however, the model closely resembles the effigies of Margherita Gonzaga (1564-1618), Duchess of Ferrara, Modena and Reggio in mourning, as reproduced by Maike Vogt-Lüerssen (kleio.org, Die Gonzaga). The painting is considered a copy of Rubens, but in the late 18th century it was described as a work by Jacopo Tintoretto (Otra de Tintoreto, retrato de una madama Veneciana, inventory of Buen Retiro, 1794, no. 40). Margherita's portrait as a widow at the Palazzo Franchini in Verona (identified as the portrait of Eleonora Gonzaga by circle of Frans Pourbus the Younger), being a copy of the portrait attributed to circle of Jacopo Ligozzi (Castelvecchio Museum in Verona), is very Venetian in style and could be the work of Alessandro Maganza. The style of both descibed paintngs in Prado, resembles closely the paintings attributed to Jacopo's son Domenico Tintoretto - portrait of a man with a letter and a crucifix (Museo Soumaya in Mexico City) and portrait of a lady (Museum Wiesbaden). The style in which the hands were painted is particularly similar. The details of costume of Constance's Spanish satin saya can also be compared to early 17th century doublet of "a man wearing an elaborately embroidered costume" (Private collection). Although the Queen of Poland was most often depicted in Spanish saya, in two paintings created by her husband, she wears a more comfortable outfit - Allegory of Faith of 1616 (Nationalmuseum Stockholm, NMH 436/1891) and a miniature from the Royal Casket (Czartoryski Museum, DMK Cz 196/I), offered by the king to the court preacher Piotr Skarga (Hanc imaginem, Sigismvndvs Rex. Pol. manv propia pin/xit eamq. donavit Cancionatori svo R. Petro Scargae), according to the inscription on the reverse. Constance also wore an eastern-style jeweled headdress and similar to the Russian kokoshnik, which carried the idea of fertility and was popular in different Slavic countries. She was represented with such a headdress in her portrait from the collection of the Marquis of Leganés in Madrid (oil on canvas, 219 x 140 cm, inscription: La Reina de Polonia, Archivo Moreno, 19513 B), sold in May 2009 with attribution to the Flemish or Genoese school. The possible author could be Sofonisba Anguissola, who lived in Genoa until 1620.
Portrait of Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631) in Spanish/Italian costume by Domenico Tintoretto, ca. 1605-1610, Prado Museum in Madrid.
Portrait of Margherita Gonzaga (1564-1618), Duchess of Ferrara, Modena and Reggio in mourning by Domenico Tintoretto, ca. 1605-1610, Prado Museum in Madrid.
Portrait of Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631) in Spanish dress by Flemish or Genoese school, possibly Sofonisba Anguissola, 1610s, Private collection.
Portraits of Constance of Austria and Hortensia del Prado by Gortzius Geldorp
"Long live King Sigismund the Third, under his auspices Everything that happened, the Lord restored from the foundations" (Vivat Sigismundus Rex Tertius, auspicio ejus Omne quod accepit restituit Dominus a fundamentis), is a fragment of a Latin inscription from 1610 on a non-preserved stone slab, which was before World War II on the façade of the Giza House in Warsaw (Old Town Market Square, number 6). It commemorates the reconstruction of the house after great fire of Warsaw in 1607, during which "many expensive Persian and Turkish goods were burned, 22 houses in the Market Square alone", according to Father Franciszek Kurowski. The Gothic house built between 1448-1455 was reconstructed for a merchant Jan Giza, who also added the following inscription "Bravery and human reason can do a lot, But money will always be the shortest way" (Multa vi et ingenio, sed citius pecunia Comparantur omnia). From 1655, this house was owned by Marcin Martens, a carpenter, possibly a relative of a Dutchman Willem Martens (Mertens, Mertensone, Martinson), who purchased stone and marbles for Sigismund III Vasa between 1618-1619.
Huge profits from grain trade, which was exported from Gdańsk the king and nobles spend on luxury goods commissioned or purchased in different parts of Europe (the Royal Granary in Gdańsk, designed by Abraham van den Blocke, was built by Jan Strakowski in about 1621). Descriptions in the registers of movable property belonging to the nobility often provide information about the place of origin of works of art. They show that they came mostly from abroad (for example, silverware mainly from Augsburg, textiles from France, Italy or the East, furniture and clocks from France) (after "Kolekcjonerstwo w Polsce ..." by Andrzej Rottermund, p. 40). Sigismund III conducted extensive diplomatic correspondence with the rulers of the Southern Netherlands on artistic matters, e.g. concerning stone elements forged on the Meuse River on the basis of patterns delivered directly from Poland. "Archives in Brussels, The Hague and Gdańsk reveal the names of Dutch stonemasons and commercial agents working for Sigismund III. In this context, one can even talk about a well-organized and efficiently functioning trade network between both regions of Europe" (after "Dostawy mozańskiego kamienia budowlanego ..." by Ryszard Szmydki). The king's second wife, Constance, with due care for financial matters, managed the royal court and the lands of her dowry. In 1623 she visited Gdańsk for the first time and a year later for 600,000 zlotys, she acquired Żywiec and made this possession the private property of the House of Vasa, because the monarchs in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth were generally prohibited from acquiring land. She diligently engaged in charity, patronized poets and painters and composer Asprilio Pacelli taught her to sing. Constance was also notoriously famous for her great Catholic piety, intolerance towards other religions and favor towards German speakers, she also attached great importance to strict etiquette, following the Spanish-Habsburg model (after "Dynastia Wazów w Polsce" by Stefania Ochmann-Staniszewska, p. 128). As an example, in Jastrowie, which was part of her dower, the queen asked her husband to confiscate the temple from heretics and in Żywiec, she issued a privilage (on March 5, 1626 in Warsaw), forbidding Jews to trade and live in her city. The queen also arranged marriages of her German ladies-in-waiting with Catholic nobles, thus, representatives of the nobility who professed Protestantism and Orthodoxy and wanting to make a career at court had to convert to Catholicism. She showed great care in her effigies and refused to give her portrait to Marshal Zygmunt Myszkowski, citing the lack of such a custom. Nor did she want to present a similar artifact to an excommunicated Franciscan who begged for such a substitute for an audience (after "Prawna ochrona królewskich wizerunków" by Jacek Żukowski). All this contributed to her great unpopularity in multireligious and multicultural country. Among her artistic agents was Augsburg goldsmith and merchant Simon Peyerle, who took care of sending items inherited by Urszula Meyerin from her mother from Munich to Warsaw as well as large painting inherited by Queen Constance, after the death of her uncle, the Duke of Bavaria (after "Świat ze srebra ..." by Agnieszka Fryz-Więcek, p. 32). Through him, she acquired large amounts of jewelry. It is worth noting that at that time paintings were almost at the very end of the hierarchy, listed among household tools and kitchen utensils and after jewels, parade weapons, silver vessels, decorative fabrics, which were considered the most valuable (after "Kolekcjonerstwo w Polsce ..." by Andrzej Rottermund, p. 40). A small cabinet painting with the Allegory of merchant justice from the first quarter of the 17th century in the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on panel, 37.7 x 28, M.Ob.181 MNW), comes from the collection of Piotr Fiorentini (1791-1858) in Warsaw. The female figure with scales and a sword, a commonly accepted personification of Justice, sits among objects related to trade (weights, barrels, packaged goods, a large scale in the background). The woman has a little crown on her head and her face features with protruding lower lip (Habsburg jaw) resemble other effigies of Constance of Austria. The style of the painting refers strongly to that of Gortzius Geldorp. Another painting very much in the style of Geldorp from the Fiorentini collection in the same museum is the portrait of a young lady, aged 21, dated '1590' (oil on panel, 45.2 x 34.4 cm, M.Ob.196 MNW). Her face and costume resemble greatly that of Hortensia del Prado (d. 1627) from her two portraits by Geldorp in the Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, one dated '1596' (SK-A-2072) and the other '1599' (SK-A-2081). Hortensia, a noblewoman of Spanish descent as her surname indicates, was first married to the merchant Jean Fourmenois and after his death she married Peter Courten in Cologne. The couple settled in Middelburg in the south-western Netherlands, where they lived in Het Grote Huis in Lange Noordstraat, which Courten had commissioned and Hortensia had a beautiful garden with fruit trees "from all foreign lands", plants "from every foreign shore", described by poet Jacob Cats. Portrait of a man by Gortzius Geldorp from the collection of Jan Popławski, identified as depicting a noble Jacques du Mont, shows him in a large ruff from the first quarter of the 17th century (National Museum in Warsaw, inventory number M.Ob.2415 MNW, earlier 35817). It is possible that both portraits found their way to the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth shortly after being painted as gifts for contractors or friends.
Portrait of Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631) as personification of Justice by Gortzius Geldorp or follower, 1605-1625, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Hortensia del Prado (1569-1627), aged 21 by Gortzius Geldorp or workshop, 1590, National Museum in Warsaw.
Miniature portrait of Rafał Leszczyński by workshop of Frans Pourbus the Younger
Rafał Leszczyński, great-grandfather of King Stanisław Leszczyński (Stanislas Leczinski), was born in October 1579 as the only son of Andrzej Leszczyński (d. 1606), voivode of Brześć Kujawski and Anna Firlej, a daughter of Andrzej Firlej (d. 1585), castellan of Lublin. He had three half-brothers: Jan, Grand Chancellor of the Crown, Wacław, the Primate of Poland, and Przecław, voivode of Tartu.
He studied at the school of the Czech Brethren in Koźminek, then he was educated in Silesia (Głogów), Heidelberg (1594), Basel (1595), Strasbourg (1596-1598) and Geneva (1599). He visited England, Scotland, the Netherlands and Italy, where in Padua in 1601 he was a student of the famous Italian physicist, astronomer and mathematician Galileo Galilei. He began his public activity as an envoy to the Sejm from the Sandomierz Voivodeship in 1605. In 1609, he became the marshal of the Central Tribunal, in 1612 - castellan of Wiślica and in 1618 - castellan of Kalisz. As one of the leaders of the Polish Protestants, he was in opposition to the pro-Habsburg policy of King Sigismund III Vasa. He was also called the "Pope of the Polish Calvinists". After return to Poland (1603), he maintained contacts with foreign scientists. He was interested in military and cartography. He commissioned a map of the south-eastern borderlands of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, unfortunately, despite the help of the geodesist and cartographer Maciej Głoskowski, the work was not completed. In addition to Latin, he spoke French, German, and Italian fluently. He wrote poems, like a paraphrase of Guillaume du Bartas's poem "Judith", published by Andrzej Piotrkowczyk in Baranów in 1620. In his beautiful Renaissance castle in Baranów, built by Santi Gucci, he kept a large library, which, according to an inventory from 1627, had about 1,700 volumes. A miniature portrait from Leon Piniński's collection, today in the Lviv National Art Gallery (inventory number Ж-50), shows a man in a fashionable Italian/French costume. It was painted on copper and according to inscription in Latin the man was 28 years old in 1607 ([...] SVAE 28. ANNO DOMINI 1607.), exacly as Rafał Leszczyński. The style of this miniature resemble greatly a miniature portrait of an unknown man from about 1600 in the Victoria and Albert Museum, also painted on copper, and attributed to a Flemish painter (inventory number P.28-1942) and miniature portrait of an unknown man in the Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, created in 1614 (Aº 1614), painted on copper and attributed to a Dutch painter (inventory number SK-A-2104). Portrait of the sculptor Pierre de Francqueville (Pietro Francavilla, 1548-1615) by workshop of Frans Pourbus the Younger in private collection, created between 1609-1615 (after original in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence, inventory number 746 / 1890), represent similar style of painting and costume. Such collar is also visible in a portrait of an unknown man in the Wilanów Palace in Warsaw, created in about 1600 and attributed to Agostino Carracci (inventory number Wil.1627). Major Flemish portrait and miniature painter working in northeast Italy at the beginning of the 17th century was Frans Pourbus the Younger (1569-1622), who from October 1600 was a court painter of Duke Vincenzo Gonzaga in Mantua. He also travelled to Innsbruck (1603 and 1608), Turin (1605 and 1608), Paris (1606) and Naples (1607), and in 1609 Queen Marie de' Medici called him to Paris as court painter. Frans and his workshop also took orders from abroad, not seeing the actual model. Several portraits of Philip III, King of Spain and his wife Margaret of Austria are attributed to him or his workshop (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, The Phoebus Foundation). His visits to Prague and Graz are not confirmed, however a portrait of Emperor Rudolf II (bust-length, wearing a breastplate, private collection) and a portrait of Archduchess Constance of Austria (1588-1631), future Queen of Poland, and her sisters (Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna) are all attributed to him. Around 1604 Hans von Aachen and the second court painter in Prague, Joseph Heintz, also painted their portraits in direct rivalry with Pourbus. Most likely on the occasion of his marriage to Margaret of Savoy in Turin in 1608, Pourbus or his workshop created a miniature portrait of Francesco Gonzaga, the eldest son of Duke Vincenzo I (sold as a "Portrait of a mustachioed young man" by Italian school at Gallery Bassenge in Berlin, Auction 113, lot 6003). In 1609 a painter from the circle of Hans von Aachen created a portrait of a gentleman, aged 40 (inscribed and dated A 1609 A 40., upper right), painting a miniature (private collection). The man was the same age as Pourbus when he moved to Paris in 1609. In 1607 the second son of Rafał Leszczyński was born, named Rafał after his father. On this occasion, Leszczyński, who just inherited the Baranów estate from his father, could commission a series of effigies of himself and his family in Italy. It is also possible that a painter from the workshop of Frans Pourbus in Mantua was at that time in Poland. The man from the described miniature resemble the effigies of Rafał Leszczyński's stepbrothers Jan (1603-1678) and Wacław Leszczyński (1605-1666).
Miniature portrait of Rafał Leszczyński (1579-1636) aged 28 by workshop of Frans Pourbus the Younger, 1607, Lviv National Art Gallery.
Miniature portrait of Francesco Gonzaga (1586-1612) by workshop of Frans Pourbus the Younger, ca. 1608, Private collection.
Portrait of Frans Pourbus the Younger (1569-1622) aged 40, painting a miniature by circle of Hans von Aachen, 1609, Private collection.
Portrait of Queen Constance of Austria by workshop of Valore and Domenico Casini
Important commercial and diplomatic relations united Poland-Lithuania with Tuscany already in the 16th century. Ships from Gdańsk bring to the newly built port of Livorno (Porto Mediceo) in Tuscany the greatest treasure of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth - grain (in 1590 several ships loaded with Polish grain sailed from Gdańsk to Livorno). From there, ships brought to the Commonwealth the treasures of Italy - paintings and sculptures.
The Italian-born merchants Sebastiano Montelupi (1516-1600) and his nephew and adopted heir Valerio Tamburini Montelupi (1548-1613), the richest citizens of Kraków, corresponded with Ferdinando I de' Medici (1549-1609), Grand Duke of Tuscany. In one letter they expressed gratitude for a gift from a Florentine mosaic, including for two pietra dura tables for Sigismund III (sent in 1593), or medicines from the Grand Duke's pharmacy (after "Biblioteka warszawska", Volume 1, 1850, p. 549). In another dated June 5, 1593, they commented on the acquisitions made in Florence by the king's wife Anna of Austria, who also acquired numerous goods in Gdańsk (after "Das Leben am Hof ..." by Walter Leitsch, p. 1267). At the beginning of the 17th century, important ruling family connections were added to commercial and diplomatic relations. "I therefore ask Your Royal Highness to recommend me most humbly to His Majesty, and I most cordially entrust myself, together with my son, the Grand Duke [Ferdinando II de' Medici], and all my children. I ask Your Royal Highness to convey my gracious and cordial greetings to all your children. Given at Pisa, March 14, 1625", wrote Maria Maddalena of Austria (1589-1631), Grand Duchess of Tuscany, to her older sister, Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631), second wife of King Sigismund III (letter preserved in the National Archives of Sweden, compare "Listy Władysława IV Wazy ..." by Jacek Żukowski, p. 116). The Polish-Lithuanian Vasas who visited Florence were entertained by their aunt with a splendid feasts and theatrical and opera performances. La precedenza delle dame barriere nell'arena di Sparta by Andrea Salvadori, published in Florence in 1625, dedicated to Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa with a title page decorated with his coat of arms, commemorates the tournament in honor of the prince and is one of many works created on this occasion. Gifts were exchanged. Constance sent the sons of the Grand Duchess of Tuscany rich Polish costumes in which they were painted. Many exquisite amber objects, kept in the Treasury of the Grand Dukes at the Pitti Palace in Florence (Museo degli Argenti), such as the beautiful amber table fountain, created in Königsberg around 1610 (Sala delle Ambre, 78 cm, inv. Bargello (I) n. 95 (1917)), were probaly gifts from the Commonwealth, as well as probably a silver plaque with the Washing of the Feet (upper part) and the Last Supper (lower part), made between 1623-1625 in Augsburg by Matthias Walbaum (Museo del Bargello, 78 x 62 cm, inv. Oreficerie religiose n. 47) - several similar were created for Sigismund III and members of his family (one in Diocesan Museum in Płock, two in Visitandines Monastery in Warsaw and one in Vilnius Cathedral). Several beautiful works of art sent by the family from Tuscany must have adorned the residences of the Polish-Lithuanian Vasas, however nothing preserved in the former territories of the Commonwealth. Many portraits must also have been exchanged, however two portraits of Queen Constance from the Medicean collections turned out to be effigies of Duchess Magdalene of Bavaria (1587-1628) (Uffizi Gallery, inv. 2408/1890 and Villa del Poggio Imperiale, inv. 3239/1870). In 2023, a portrait of the young Prince John Casimir Vasa (1609-1672), eldest son of Constance, in Spanish costume, attributed to the Tuscan painter, was sold in L'Aquila near Rome (Gliubich Casa d'Aste, July 7, 2023, lot 164, inscription: IOANNES CASIMIRVS). Italian painters produced many such paintings depicting distant monarchs and their relatives. An example is the portrait of Maximilian I (1573-1651), Duke of Bavaria holding his hand on a globus cruciger, painted by Jacopo Chimenti da Empoli or workshop around 1635 (Métayer in Paris, October 18, 2018, lot 66), identified and attributed by me. At the Philadelphia Museum of Art, there is a full-length portrait from around 1610, identified as possibly depicting Grand Duchess Maria Maddalena (oil on canvas, 186.1 x 107.3 cm, 1883-136). The grand ducal crown on the table next to the woman indicates that she is indeed the wife of the ruler of Tuscany, while the protruding lower lip, known as the "Hapsburg lip", indicates that she is a member of this dynasty. The effigy resembles another portrait of Maria Maddalena with her husband Cosimo II, in a private collection in Florence (Codice di catalogo nazionale, 0900623102). In both portraits, the Grand Duchess is dressed in a Spanish court dress - saya. The port visible through the window in the Philadelphia portrait is most likely Livorno. This portrait has a complementary piece, depicting a similar woman in similar Spanish dress (oil on canvas, 186.1 x 107.3 cm, 1883-137). The closed crown (corona clausa) on the table indicates that she is a queen, but it cannot be Marie de Medici, queen of France, as indicated on the museum website, because the woman like Maria Maddalena has a protruding lip, so it is her sister. Three sisters of Maria Maddalena become a queen: Anna of Austria, Queen of Poland and Sweden from 1592, Margaret of Austria (1584-1611), Queen of Spain and Portugal from 1599 and Constance, Queen of Poland from 1605. Since Anna died in 1598 and Margaret was never depicted with a royal crown (compare with paintings in the Uffizi, inv. 2392/1890 and 2356/1890), it is undoubtedly Constance who is depicted in this portrait. Her facial features were similarly depicted in a gouache miniature by the Monogrammist I. K., made around 1600 (Bavarian National Museum in Munich, inscription in Spanish: La Archiduquesa Constantina / Reyna de Polonia, i.e. Archduchess Constance, Queen of Poland), in a destroyed portrait with a parrot (Germanisches Nationalmuseum in Nuremberg, Gm 707) or a portrait in a maternity dress (Zamość Museum, inv. 62). The style of the two paintings recalls works attributed to Valore (1590-1660) and Domenico Casini (1588-1660), two brothers, active in Florence, mainly as portraitists, such as the portrait of a young man holding a letter to Mr. Ruberto Bonsi in Florence (Wannenes Art Auctions in Genoa, March 15, 2022, lot 86) or portrait of Catarina de' Medici (1593-1629), governor of Siena, attributed to Domenico (Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, GG 8272). Since the Philadelphia paintings are less elaborately painted than these two, they were most likely created with the help of assistants in their studio, perhaps as part of a series of similar paintings. A painting painted in a similar style is now in the Nationalmuseum in Stockholm (oil on canvas, 64 x 49 cm, NMGrh 1499, inscription: FERDIN II M. DVX ÆTRVR.). It represents the eldest son of Maria Maddalena - Ferdinando II (1610-1670), aged around 15, thus created in 1625, the year of the visit to Florence of his cousin Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa. The painting comes from Gripsholm Castle, housing the Swedish royal collections and spoils of war, so it was probably looted from Poland-Lithuania.
Portrait of Constance of Austria (1588-1631), Queen of Poland and Grand Duchess of Lithuania by workshop of Valore and Domenico Casini, 1610s, Philadelphia Museum of Art.
Portrait of Maria Maddalena of Austria (1589-1631), Grand Duchess of Tuscany by workshop of Valore and Domenico Casini, 1610s, Philadelphia Museum of Art.
Portrait of Ferdinando II de' Medici (1610-1670), Grand Duke of Tuscany by workshop of Valore and Domenico Casini, ca. 1625, Nationalmuseum in Stockholm.
Portrait of Adam Wenceslaus, Duke of Cieszyn by Bartholomeus Strobel or circle
Another painting created by Prague school of painting of Joseph Heintz the Elder and Hans von Aachen is a small oval portrait of a man in a gorget. The man also wears a white silk doublet, a military tunic embroidered with gold and a wired reticella lace collar. The painting comes from a private collection in Warsaw and was sold in 2005 (Agra-Art SA, 11 December, Nr 7831). The style of the painting is close to Bartholomeus Strobel, a Mannerist-Baroque painter from Silesia, born in Wrocław, who worked in Prague and in Vienna from about 1608. In 1611 he returns to Wrocław to help his father with work in the Augustinian church and in 1619, thanks to the support of King Sigismund III Vasa, he obtained the status of a court painter (servitor) of Emperor Matthias.
This portrait can be compared with signed works by Strobel, portrait of Władysław Dominik Zasławski-Ostrogski from 1635 in the Wilanów Palace in Warsaw (signed and dated: B. Strobell 1635) and the Crucifixion in the Church of St. James in Toruń (signed and dated: B. Strobel 1634). According to inscription in Latin (AETATIS SVAE 37 / ANNO 1611), the man was 37 years old in 1611, exaclty as Adam Wenceslaus (1574-1617), Duke of Cieszyn when he was appointed supreme commander of the Silesian troops by the new King of Bohemia Matthias, Emperor from 1612. Counting on imperial favors Adam Wenceslaus, raised in Protestantism, converted to Catholicism and expelled the pastor Tymoteusz Lowczany from Cieszyn on February 23, 1611. He accompanied King Matthias at the ceremonial entry to Wrocław with a retinue of almost three hundred horses. The portrait is similar to the effigy of Duke Adam Wenceslaus in the Museum of Cieszyn Silesia, attributed to Piotr Brygierski (ca. 1630-1718). The costume (gorget, silk doublet, military tunic and collar) and facial features are very much alike.
Portrait of Adam Wenceslaus (1574-1617), Duke of Cieszyn, aged 37 by Bartholomeus Strobel or circle, 1611, Private collection.
Portraits of Queen Constance of Austria as Saint Mary Magdalene and Saint Veronica by Gortzius Geldorp
Everything changes so quickly, we say. Fashion, technology, but also customs. Some natural aspects of our current lives might be funny or strange to future generations. Certain dramatic events like natural disasters or wars also have an impact on the way people live and perceive the world.
More and more researchers today study the effects of foreign invasions on the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, which for many reasons have been forgotten. The Deluge (1655-1660), which some say was more destructive to Poland than the Second World War, was undoubtedly an event that changed many things. For many people, it was a punishment sent from heaven for a sinful life, so reform was much needed. Apart from political instability and other causes, the invasions and pillaging of the country have contributed to its impoverishment, the fall of the economy, education, art and other areas. Men "raised in pillows" by "Italian courtesans" (i.e. Italianized Polish women), according to Szymon Starowolski's "Votum on the improvement of the Commonwealth" (Votvm o naprawie Rzeczypospolitey, p. 18), published in 1625, who did not want to defend the eastern lands against invasions, over a quarter a century later, had to face the incredible brutality of different invaders who broke into the center of the Commonwealth. In the Commonwealth, the prudish invaders were confronted with a more frivolous Latin culture and Italian influences, as well as Renaissance and early Baroque art that often included nudity. In addition to the sometimes lascivious images of Catholic saints, the residences of the Commonwealth were filled with numerous images of Roman gods and disguised or historicised (historié) portraits, which probably increased the aggressiveness and contempt of the conquerors, terrified by the "impious" lifestyle of the Sarmatians. Many sources confirm that the barbaric invaders had no mercy for the conquered country. In the center of Stockholm, visitors can admire a "monument" to the inhuman imperialism of the invaders - the warship Vasa prepared for the invasion of the Commonwealth, which was nevertheless so overloaded with heavy military equipment that it sank shortly after leaving port on August 10, 1628. The people of the Commonwealth were ridiculed with figures of Polish nobles hiding under the table or bench and allegedly barking like a dog, located next to the toilet (compare Vasamuseet website, "The Sculptures of Vasa. Insulting the enemy"). The invaders shaped the image of the population of the conquered land and also had an impact on cultural changes. Moreover, in the post-Deluge Commonwealth, steeped in mourning, there was little room for extravagance and eroticism. In the Czartoryski Museum in Kraków there is a mysterious image of Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631), second wife of King Sigismund III Vasa (oil on copper, 22.3 x 18.8 cm, DMK Cz 196/I). The painting comes from the Royal Casket, a collection of royal memorabilia of the Commonwealth assembled by Princess Izabela Czartoryska (1746-1835). The casket was looted by the Nazi German invaders during World War II, however, this image has survived. On the reverse is an inscription engraved in Latin according to which this effigy was painted by King Sigismund III, who was a talented painter, and offered to his court preacher Piotr Skarga (1536-1612): Hanc imaginem, Sigismvndvs Rex. Pol. manv propia pin/xit eamq. donavit Cancionatori svo R. Petro Scargae ... (after "Sztuka dworu Wazów w Polsce ...", ed. Andrzej Fischinger, item 38, p. 51-52, 150-151). The painting must have been produced between 1605 (year of the marriage to Constance) and 1632 (year of the king's death). The woman's royal regalia and Habsburg features indicate that she is indeed Queen Constance. The most unusual element is the model's costume and hairstyle, more typical of the third quarter of the 17th century. This led to the sitter being identified as Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga (1611-1667). The format and style of the painting indicate that it is a Flemish work, comparable to paintings attributed to Gonzales Coques (died 1684), active in Antwerp. A somewhat similar painting depicting a boy counting his coins, attributed to the circle of Gonzales Coques, comes from a private Swedish collection (ClassicArtworks Stockholm, AnticStore, Ref : 104843). It seems that around 1660, so after the Deluge, someone decided to recreate the painting made by the king, an important souvenir, and to dress the queen in a costume from that year. The original painted by Sigismund was probably destroyed or damaged during the invasion. Also taking into account my findings regarding portraiture in Poland-Lithuania, it is also quite possible that the original painting was "inappropriate" by post-Deluge standards. In the 18th century, a beautiful partly gilded silver riza or oklad (shaty in Ukrainian or sukienka in Polish), i.e. a robe with frame, was added to the portrait (silver, almandine, turquoise, 24.8 x 24 cm, MNK IV-V-1415/2). This repoussé work, pierced to expose elements of the underlying painting, is typical of Orthodox sacred icons (for example silver-gilt riza for the icon of Our Lady, made between 1676 and 1684 in Gdańsk by Peter Rohde II, State Historical Museum of Moscow, ОК 9639 / ГИМ 75940). Poland's most famous riza is the ruby robe of the Black Madonna of Częstochowa, decorated with jewels from private donations and made after the Deluge, in gratitude to the Virgin for saving the country from the total annihilation by the invaders. It should be noted here that, according to Translacio tabule, a source from the first half of the 15th century, the real author of the icon of the Black Madonna is said to be Saint Luke the Evangelist, who painted the first image of the Virgin Mary (Translacio tabule Beate Marie Virginis, quam Sanctus Lucas depinxit propriis manibus, Archive of Jasna Góra, sygn. II 19, fols 216v-220r). The rococo riza of the queen's potrait is dated to the second half of the 18th century, but we cannot exclude that the portrait originally had another riza created at the same time as the painting, which however did not survive to another disastrous invasion - the Great Northern War (1700-1721). It is quite unusual that the riza, typical of sacred images, was added to this portrait of the queen. Was it originally a portrait in guise of a Christian saint or a tradition has survived that portraits of Queen Constance should be "venerated" in this way? Or maybe people believed that Queen Constance needed appropriate dress? It is difficult to determine this due to the lack of sources and comparable works. In the Prado Museum in Madrid, there is a painting of Saint Mary Magdalene holding a crucifix, considered to be a work of unknown 16th century painter (La Magdalena, oil on panel, 70 x 58 cm, P003657). The painting was offered in 1889 by María Dionisia Vives y Zires, Duchess of Pastrana, and it was considered to be the work of Flemish painter Frans Floris de Vriendt (1519-1570). The Dukes of Pastrana were important landowners in Spain and the III Duke of Pastrana Ruy III Gómez de Silva Mendoza y de la Cerda (1585-1626) was State Councilor and Ambassador to Rome between 1623-1626. The effigy of a woman represented as Mary Magdalene resembles the disguised portraits of Queen Constance, painted by Gortzius Geldorp, notably the effigy as Venus (Sotheby's in New York, January 29, 2016, lot 454). The style of the painting is also similar. Facial features were depicted in the same way as in the portrait of Constance with a parrot (Germanisches Nationalmuseum, Gm 707, lost) or in the portrait with a crown (Philadelphia Museum of Art, 1883-137). A similar costume is visible in the portrait of the queen in the Allegory of Faith of 1616 (Nationalmuseum Stockholm, NMH 436/1891) and in the scene of the feasting courtiers, detail of the painting "Before the Deluge" by Isaac van den Blocke, painted after 1608 for the Main Town Hall of Gdańsk. Among the aristocrats and "courtesans" in rich costumes, some in Roman style, one can see the mayor of Gdańsk - Johann von (van) der Linde (1542-1619), a pious Protestant close to the Radziwill family to whom he rented a house in Gdańsk. Another painting from the series titled "Division of Nations" depicts figures dressed in other costumes typical of Gdańsk and the Commonwealth. A comparison with the portraits of Queen Anne of Denmark (1574-1619), wife of King James VI, is very appropriate here. They differ not only in costumes, but also in hair color (blonde, red and dark) and facial features. Around 1606, a marriage between James VI's daughter, Elizabeth (1596-1662), and Sigismund III's son, Ladislaus Sigismund, was seriously considered. In 1607, Sigismund sent Queen Anne a portrait of himself with his son and some amber through the English envoy to Poland William Bruce (after "Anglia a Polska w pierwszej połowie XVII w." by Edward Alfred Mierzwa, p. 34), while according to Jakub Sobieski's 1609 account, the princess Elizabeth had a portrait of the Prince of Poland above her bed. Effigies of the English monarchs must also have been sent to Poland-Lithuania, and it should be noted that the big décolletage dominated English women's fashion in the first quarter of the 17th century, as evidenced by portraits of Queen Anne, the portrait of Elizabeth Gray (1582-1651), Countess of Kent (Tate Britain, T00398) or portrait of Amalia of Solms-Braunfels (1602-1675), Princess of Orange, in English costume (Museum of Warmia and Masuria, MNO 100 OMO). Another similar portrait of Constance in the guise of another Christian saint - Saint Veronica, attributed to Geldorp, was sold in Germany in 2023 (oil on panel, 71 x 55 cm, Auktionshaus Plückbaum in Bonn, June 3, 2023, lot 1475). It comes from a private collection (owned for two generations). On the reverse there is an old adhesive label with attribution and note of restoration carried out in 1933 by Gerhard Fischer (City Archives of Cologne). In 1617, Pope Paul V presented Queen Constance with a copy of an important relic - the Volto Santo or Vera Icon (Veil of Veronica), today kept in the Diocesan Museum in Łowicz. It was made by Pietro Strozzi in Rome. Jacopo Grimaldi, notary at St. Peter's Basilica, recounted how those responsible for guarding the relic prepared a copy of the Volto Santo for the Queen of Poland. The silver-gilt frame of the picture was founded by Primate Jan Wężyk around 1631. The "Saint Veronica" is less finely painted than the other mentioned works by Geldorp, which indicate the work of the workshop. Among the gifts given to the Black Madonna of Częstochowa by King Sigismund III are a so-called Vasa chain from the so-called diamond dress of Our Lady, possibly the work of the king, and a disguised likeness of his second wife, Queen Constance depicted as the Virgin and Child, painted by his own hand around 1617. This small painting was formerly mounted in a mannerist metal frame, originally a mirror frame made in Lüneburg, gilded and decorated with precious stones, which probably came from the queen's dowry (after "Jasnogórska Bogurodzica: 1382-1982" by Jan Majdecki, p. 115). The frame was previously believed to be a gift from King Augustus III and currently, a much later image of Our Lady of Częstochowa is placed there. The portrait of the queen in this frame was photographed around 1896 by Stanisław Trzciński (National Museum in Warsaw, DI 16540 MNW) and shows Constance in a crown and holding the Child. The mirror, a symbol of vanity in Renaissance painting, was replaced by a divine (virtuous) effigy (reflection) of the queen. The portrait of Queen Constance's approximately 10-year-old nephew - Cardinal-Infante Ferdinand of Austria (Don Fernando de Austria, 1609-1641), Archbishop of Toledo, depicted as Salvator Mundi in a painting by the Spanish school of circa 1620 (Setdart Auction House in Barcelona, December 29, 2022, lot 30), as well as Adoration of the Magi with King Sigismund III Vasa as Saint Melchior, his son Prince Ladislaus Sigismund as Saint Caspar and their courtiers, painted by Jakub Charzyński (or Harzyński) in 1629 (Church St. Hedwig in Nieszawa, Chapel of St. John the Baptist, founded by Bishop Andrzej Lipski for the Włocławek Cathedral, NID/WLX 114 000533, compare "W asystencji, w przebraniu ..." by Jacek Żukowski, p. 21-24), proves that such depictions were popular in the first quarter of the 17th century. In a small painting, also attributed to King Sigismund III, according to Marian Sokołowski (1839-1911), Saint Peter leads the king's son, the young prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (the painting is now attributed to an 18th century painter and interpreted as representing Saint Joseph and the Infant Jesus, Czartoryski Museum, MNK XII-550). In the funeral oration on the occasion of the royal couple's funeral in 1633, published by the Kraków canon Jan Lipski (1589-1641), who was secretary to Sigismund III from 1616 and then chancellor to the queen, he praised the king as the Constantine the Great (venerated as a saint in Eastern Christianity) and compared his wife to the emperor's mother, Saint Helena: "Oh, also the new Helena and the new mother of Constantine, Constance! Not a finder, indeed, but a pious worshiper and cross-bearer who, during her life, worshiped with the utmost piety the wonderful image in this basilica [the crucifix of Queen Jadwiga in the Wawel Cathedral], which spoke to the Holy Relative, and before her death decorated it with a net veil woven with her own hands" (O nouam etiam Helenam, & nouorum Constantinorum Matrem Constantiam! non inuentricem quidem Crucis, sed piam cultricem, ac gestatricem: cuius & in hac Basilica admirandam effigiem, Cognatae Diuae olim locutam, summa pietate viuens coluit, & prope moriens, reticulato velamine propria manu intexto, ornauit, after "Konstancja Austriaczka w kręgu świętych niewiast i władczyń ..." by Krzysztof J. Czyżewski, p. 10). Constance of Austria was the queen of a large and wealthy country in central Europe and the mother of King John II Casimir. She corresponded and exchanged gifts and portraits with her older sister Margaret of Austria (1584-1611), Queen of Spain (depicted as the Virgin Mary in the paintings by Juan Pantoja de la Cruz), and with her younger sister Maria Maddalena of Austria (1589-1631), Grand Duchess of Tuscany (depicted as Saint Mary Magdalene in the paintings by Justus Sustermans). The portraits of Queen Constance must have been as numerous as her sisters. Besides enormous destruction, the oblivion of the person after the fall of the Commonwealth as a European power after 1655, among other factors which contributed to the fact that so few of her portraits (before this article) were known are a great diversity of representations, costumes and painters, idealization and copying which distorted facial features, disguised portraits and finally nudity, considered inappropriate in some countries.
Portrait of Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631) as Saint Mary Magdalene holding a crucifix by Gortzius Geldorp, 1610s, Prado Museum.
Portrait of Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631) as Saint Veronica holding her veil by workshop of Gortzius Geldorp, ca. 1617, Private collection.
Mannerist frame of a mirror of Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631) with her portrait as Madonna and Child by the Lüneburg workshop (frame) and King Sigismund III Vasa (painting), before 1617, Treasury of the Jasna Góra Monastery. Virtual reconstruction, © Marcin Latka
Portrait of Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631) by circle of Gonzales Coques, ca. 1660, Czartoryski Museum.
Portrait of Sigismund Charles Radziwill by Gortzius Geldorp
In 1616, Sigismund Charles Radziwill (1591-1642), son of Nicolaus Christopher Radziwill "the Orphan" (1549-1616) and Elżbieta Eufemia Wiśniowiecka (1569-1596) arrived at the royal court in Warsaw and obtained, in 1617, the titular dignity of Carver of the court of Queen Constance of Austria.
He studied at the Jesuit College in Nesvizh, and then in Bologna. In 1612, he joined the Order of the Knights of Malta (Knights Hospitaller) and fought with the Turks in the Mediterranean. After returning to Poland in 1614, his father founded him a Maltese commandery in Lithuania. At the beginning of 1618, summoned by the Grand Master, he went to Malta. In January 1619, he was in Vienna where a great congregation of Knights Hospitaller was held. He was appointed by the Grand Master general commissioner, together with Charles II Gonzaga (1609-1631), Duke of Nevers. "Having received a license from His Highness the Emperor ... tomorrow, God willing, I am leaving", he wrote in a letter dated January 15, 1619 from Vienna to his brother John George Radziwill (1588-1625). In February 1619 he was in Venice, and he reported again to his brother: "I found his lordship Alexander, our brother, in good health in Venice and I hope that Our Lord will brought him quickly back and your Majesty will see him in our country". After return to the Commonwealth in 1621 he participated in the battle of Khotyn and in 1622 he commanded the unit of the Polish-Lithuanian light cavalry (Lisowczyks) in the Imperial army. He died on November 5, 1642 in Assisi in Italy. Before the discovery of a portrait of a man in black costume dated 1619 and signed by Gortzius Geldorp with his monogram GG.F. (oil on panel, 58 x 39 cm), it was generally believed that he died in 1616 in Cologne. A copy of Titian's Violante by his hand, sold in 2016 in Vienna (Dorotheum, lot 122, monogrammed upper left: GG.F.), indicate that he was in Venice and in Vienna. According to inscription in Latin in upper right corner of mentioned portrait of a man in black costume the sitter was aged 28 in 1619 (AETATIS. SVAE. 28. / .1619.) exactly as Sigismund Charles Radziwill when he was in Venice and in Vienna. The costume of a man and his facial features bear a startling resemblance to effigy of Sigismund Charles Radziwill in the State Hermitage Museum (ОР-45868), created after original from about 1616. His Spanish style costume, typical for the Imperial court in Vienna, is almost identical to that visible in the portrait of Antonio Barberini, Grand Prior of Rome of the Order of Malta, created in 1625 by Ottavio Leoni. Similar outfits are also visible in portraits by Bernardo Strozzi, like in the likeness of Giovanni Battista Mora the Elder, nobleman of Vicenza near Venice, in the Walters Art Museum and in the portrait of Mikołaj Wolski (1553-1630) by Venanzio di Subiaco in the Camaldolese Monastery in Bielany, created in about 1624.
Portrait of Sigismund Charles Radziwill (1591-1642) aged 28 by Gortzius Geldorp, 1619, Private collection.
Portrait of Łukasz Żółkiewski by Johann Philipp Kreuzfelder
At the end of the 16th century, Flemish/Dutch art was the dominant model for Nuremberg portrait painters. Under the influence of Nicolas Neufchatel and Nicolas Juvenel, two prominent Flemish/Dutch artists settled in the imperial city, the highly developed Antwerp portraiture found its way into local portraiture (after catalogue entry by Judith Hentschel for 1626 portrait of a woman). The pupils of Juvenel were among the most successful and sought-after portrait painters in the city and outside.
Jakob Troschel (1583-1624) from Nuremberg, a court painter of King Sigismund III Vasa, was trained in Juvenel's close circle - according to Johann Gabriel Doppelmayr's "Historische Nachricht ..." he learned from Johann Juvenel and Alex Lindner, and Johann Philipp Kreuzfelder (1577-1636), son of a Nuremberg goldsmith, completed his apprenticeship at Juvenel's workshop between 1593 to 1597. In 1612 and 1617 Kreuzfelder portrayed the Nuremberg councillors and in 1614 Bartolomeo Viatis (1538-1624), a merchant from Venice (City of Nuremberg's Art Collections), then he worked as a portrait painter for the Counts of Oettingen and Hohenlohe-Langenburg. He is believed to have stayed in Rome with the artist Adam Elsheimer (1578-1610) and influences from both Flemish and Italian portraiture may be found in his work. Kreuzfelder has been assigned the monogram 'JC' (for Johannes Creutzfelder) by researchers. In 1626 the painter probably also travelled to Munich, as signed portrait by his hand depicting a lady in rich black dress (sold at Koller Auctions, October 01, 2021, Lot 3013) bears a coat of arms similar to that of Sentlinger family, a wealthy Munich patrician family, and to Constance in the south of Germany in 1628, as effigy of Nikolaus Tritt von Wilderen, a member of the city council of Constance, is attributed to him. A small portrait of a young nobleman (34 x 25.5 cm, oil on copper) from private collection in the south of Germany (sold at Lempertz KG, November 19, 2022, Lot 1516) was painted in the style symilar to the portrait of a woman from the Sentlinger family. He wears elaborately painted, silk, black doublet and loose breeches. The finely painted white lace trimmings of the lavish collar and cuffs, is characteristic of Kreuzfelder. Also the artist's signature in upper right is very similar. The painting was attributed to German School early 17th century and the monogram was deciphered as TB f. (?) (overlapping), however, it could be also JPC f. for Johannes Philippus Creutzfelder fecit in Latin. According to the rest of inscription, also in Latin, the depicted man was 25 years old in 1619 (Aetatis. 25 / 1619), exactly as Łukasz Żółkiewski (1594-1636), the younger son of the Chamberlain of Lviv Mikołaj Żółkiewski (d. 1596). He studied abroad, possibly at the Jesuit College of Ingolstadt, a city between Nuremberg and Munich in the Duchy and Electorate of Bavaria, very popular among Polish-Lithuanian nobility at that time. King Sigismund III ordered works of art in Bavaria and sent them to William V, Duke of Bavaria, while king's mistress, influential "minister in a skirt" or "Jesuit's bigotry" Urszula Meyerin (1570-1635), was most likely born near Munich in Bavaria. Nephew of the famous hetman Stanisław Żółkiewski (1547-1620), Łukasz took part in the Turkish campaign of 1620 and was captured at the battle of Cecora, in which his uncle lost his life. Four years later, in 1624, he accompanied Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (future Ladislaus IV) on a foreign trip at the behest of King Sigismund III. Żółkiewski, who become the voivode of Bratslav, died childless in a battle with the Cossacks in November or December 1636 and was buried in the Jesuit church in Pereiaslav, which he founded a year earlier (1635) along with the Jesuit College. Later, the Cossacks destroyed Pereiaslav including the church, and they threw out the body of the founder from the coffin (after "Ilustrowany przewodnik po zabytkach kultury na Ukrainie" by Jacek Tokarski, Zbigniew Hauser, Volume 4, p. 180). The family resemblance of the 25-year-old man to effigies of hetman Stanisław Żółkiewski, Łukasz's uncle, is striking. The shape of the face, lower jaw and lower lip, hair color and hairstyle are very much alike. The style of the portrait resemble greatly two miniatures from the National Museum in Warsaw (inventory number Min.1014 and Min.1015), identified as effigies of Gotthard Kettler (1517-1587), Duke of Courland, which was part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, and his wife Anna of Mecklenburg (1533-1602). It cannot be excluded that Kreuzfelder arrived at some point of his career to the Commonwealth or Żółkiewski commissioned a series of his effigies during his potential sojourn in Nuremberg, because the painter was known among Polish-Lithuanian clients.
Portrait of Łukasz Żółkiewski (1594-1636), aged 25 by Johann Philipp Kreuzfelder, 1619, Private collection.
Miniature portrait of Gotthard Kettler (1517-1587), Duke of Courland by Johann Philipp Kreuzfelder, first quarter of the 17th century, National Museum in Warsaw.
Miniature portrait of Anna of Mecklenburg (1533-1602), Duchess of Courland by Johann Philipp Kreuzfelder, first quarter of the 17th century, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portraits of Tomasz Zamoyski and Katarzyna Ostrogska by Domenico Tintoretto
In the years 1615-1617, "fulfilling the last will of his father", Tomasz Zamoyski (1594-1638), son of Jan Zamoyski, Grand Chancellor of the Crown (1542-1605) and Barbara Tarnowska (1566-1610), daughter of Stanisław Tarnowski (d. 1618), castellan of Sandomierz, undertook foreign peregrinations. Almost all young magnates made such educational journeys at that time.
Through Kraków in the south of Poland, he reached Gdańsk in the north, where he stayed "about six Sundays" - from around December 12, 1614 to the last days of January 1615, also visiting Malbork and Elbląg. In the last days of January 1615, after receiving letters of recommendation from king Sigismund III Vasa, young Zamoyski set off from Gdańsk accompanied by a small court with Father Wojciech Bodzęcki, professor at the Zamość Academy, and Piotr Oleśnicki, Tomasz's cousin, who studied in Paris and Padua at the expense of Jan Zamoyski. From Lübeck he went to Amsterdam, and from there to England. He arrived in London in mid-July 1615 and spent about 5 months there. James I, captured by Tomasz's wit and kindness, often invited him to hunting and banquets. At the request of Zamoyski the king released several English Catholics from prison - including Father Fludd who was held at Gatehouse Prison. "He was held in high esteem by the King, who often had audiences with him. He often went hunting with his son Charles. The royal horses were always at the disposal of the Lord himself and his servants for fun. King James was given an expensive hat decoration with heron feathers", wrote Tomasz's servant Stanisław Żurkowski in a biography. Wanting to get to know the country better, he went on a trip around the island, which lasted about two months. Then he travelled to France. Zamoyski probably arrived to Tours, where King Louis XIII was staying at that time, in the first days of March 1616. From Tours the he went to Orléans then to Paris. His stay in the capital of France was very busy: he learned the French language, "listened to the courts in the parliament", he was "in academies on various acts and disputes", he improved his skills in fencing and horse riding, and he learned to play the lute. He attended the audiences of King Louis XIII, held receptions for officials and officers of the French court and visited them. He befriended the princes de Guise, de Rohan, de Nevers and de Montmorency. From France young Zamoyski came to Italy in January 1617. From an early age, he had contact with the culture of Italy as his father was educated there. He visited Naples and Rome, where he had audiences with Pope Paul V. Then he went to Loreto, Padua and Venice. Also in Italy he maintained the splendor of his retinue. He visited the studios of masters of engraving, painting and goldsmiths, he acquired luxury goods, he organized parties and gave gifts to people from the ruling class. The cost of Zamoyski's journey was amounted to enormous sum of over 20,000 zlotys, while the income from 1 village at that time fluctuated between 140 and 240 zlotys annually. In the first days of November 1617, through Switzerland, Bavaria, Bohemia and Silesia, Zamoyski returned to Poland, where in Kościan, he was welcomed by servants from Zamość and soldiers from his private units. A few days later, he arrived in Poznań, where "he put away his foreign clothes, cut his hair and returned to Polish attire", as recalled Żurkowski in his biography. From Poznań he went to Łowicz, to pay a visit to the Archbishop of Gniezno, Wawrzyniec Gembicki in his magnificent palace, and then to Warsaw, where he stayed for about two weeks. It was not until December 20 that he arrived in Zamość, where he was solemnly welcomed. Soon after his return his political career advanced, in 1618 he became the voivode of Podolia and in 1619 the voivode of Kiev (after "Peregrynacje zagraniczne Tomasza Zamoyskiego w latach 1615-1617" by Adam Andrzej Witusik). He also decided to marry Katarzyna Ostrogska (1602-1642), granddaughter of Zofia Tarnowska (1534-1570), Princess of Ostroh on paternal side, and great-granddaughter of Duchess Anna of Masovia (1498-1557) on maternal side. 18-year-old Katarzyna and 25-year-old Tomasz were married in the Corpus Christi Church in Jarosław on March 1, 1620. As a dowry, Katarzyna received 53,333 zlotys, 6 castles, 13 cities, about 300 villages and folwarks. She was born in 1602 in the family of Alexander Prince of Ostroh, voivode of Volhynia, and his wife Anna Kostka (1575-1635), as the youngest of eight children. The family lived in the city of Jarosław. Her father died suddenly the year after her birth, leaving a rich inheritance to his three daughters who reached adulthood: Zofia, Anna Alojza and Katarzyna. The portrait of a young man in a black coat lined with fur, attributed to Domenico Tintoretto, today in the National Gallery in London (inventory number NG173), was presented in 1839 by Henry Gally Knight (1786-1846), a British politician and writer. His right hand rests on a table placed before an open window, and on which is a silver vase containing a sprig of myrtle, consecrated to Venus, goddess of love and used in bridal wreaths. In his left hand he holds a black cap. An open window looks out over a landscape of farmland with two rustic buildings, possibly barns, with what look like thatched roofs supported on wooden trunks or poles, typical for Poland, Ukraine and large estates of the Zamoyskis near Zamość. Merchants from such distant countries as Spain, England, Finland, Armenia and Persia arrived for the annual three-week-long big fair, one of the largest in Europe, in nearby Jarosław - according to Łukasz Opaliński (1612-1662), 30,000 cattle were sold at one Jarosław fair (Polonia Defensa Contra Joan. Barclaium, 1648). The same man was also depicted in a full-length portrait, also by Domenico Tintoretto, which before World War II was in the Łańcut Castle close to Jarosław (catalogue "For Peace and Freedom. Old masters: a collection of Polish-owned works of art ...", pic. 37). He wears a fashionable French/English black costume, very similar to the one shown in the portrait of a young man, attributed to Salomon Mesdach, dated on the table: Aº 1617 (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, inventory number SK-A-913). A view of a canal in Venice is visible through the window behind him, suggesting that the portrait is a souvenir of his visit to the city. The man in both portraits bear great resemblance to effigies of Tomasz Zamoyski in Polish costume, as a child aged 12, created by Peter Querradt in 1606 (Österreichische Nationalbibliothek) and aged 44, created by Jan Kasiński in 1637 (Diocesan Museum in Sandomierz). Portrait of a lady, known as Donna delle Rose, in Villa Gyllenberg in Helsinki was painted in the same style as the portrait of a man with myrtle in the National Gallery in London. This work is also attributed to Domenico Tintoretto, it has similar composition and similar dimensions (116.5 x 85.5 cm / 119.5 × 98 cm), therefore can be considered as a pendant or a portrait from a series created at the same time. The modish attire worn by this young woman bespeaks great affluence. Her costume is very similar to Venetian court dresses visible in a print published in 1609 in Giacomo Franco's "Costumes of Venetian Men and Women" (Habiti d'hvomeni et donne venetiane). The northern ruff, however, was replaced with a reticella collar from the late 1610s, like an open peacock's tail behind the head, propped up with sticks, similar to Italian and French collars of courtiers of King Sigismund III Vasa. The Procession with St. Anianus by workshop Tommaso Dolabella (Corpus Christi Church in Kraków) and Banner with Adoration of St. Francis by Jan Troschel (Leżajsk Monastery), testifies to the diversity of the court fashion in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in the 1620s with Polish, Spanish, Italian, French and German styles represented. White rose in her hair symbolizes purity and innocence of a bride. The woman's face bear great resemblance to preserved portraits of Katarzyna Ostrogska, all created when she was a widow and offered to different monasteries (Museum of Zamość), or to the portrait of her daughter Gryzelda Wiśniowiecka (Kozłówka Palace). Lady Zamoyska in a Venetian costume painted by Domenico Tintoretto? This was not surprising for the inhabitants of the Zamoyski estates. There were many Italians in Zamość, at the Academy, in the service of the Chancellor Jan Zamoyski, starting with the court architect, Venetian Bernardo Morando. In 1596 Boniface Vanozzi, secretary of Cardinal Enrico Gaetani in Poland, described Zamość, Renaissance ideal city build for the Chancellor, "a lover of the Italian nation" (amatore della natione italiana), from scratch: "He began to build this town in 1581 and already today it has up to 400 houses, mostly built in Italian style". Before 1604 he commissioned to the main altar of the Collegiate Church in Zamość, several paintings in the workshop of Domenico Tintoretto. Negotiations with the artist were conducted on behalf of Zamoyski by representatives of the Italian Capponi and Montelupi families and completed paintings were delivered to Poland in 1604. The largest painting depicted the Risen Christ with St. Thomas the Apostle - the patron of the temple, paintings in the side parts: St. John the Baptist and St. John the Evangelist - the patrons of the founder, and the painting in the top of the altar - God the Father. This altar was transported to the church in Tarnogród in 1781 and only the side paintings preserved. Tomasz, his father and his wife in Venetian costume were also depicted in two paintings in the Church of the Assumption in Kraśnik (Thanksgiving mass and Rosary procession). Both were created by Tommaso Dolabella in 1626. From 1604 Kraśnik was part of the Zamość estate and the protector of the church was Tomasz Zamoyski, voivode of Kiev. The voivode and his wife founded stalls for the church with their coat of arms and in one of the side altars there is painting of Salvator Mundi by Paris Bordone or his workshop.
Portrait of Tomasz Zamoyski (1594-1638) in French/English costume from the Łańcut Castle by Domenico Tintoretto, ca. 1617, present whereabouts unknown.
Portrait of Tomasz Zamoyski (1594-1638) by Domenico Tintoretto, ca. 1620, National Gallery in London.
Portrait of Katarzyna Ostrogska (1602-1642) in Venetian costume by Domenico Tintoretto, ca. 1620, Villa Gyllenberg in Helsinki.
St. John the Baptist and St. John the Evangelist from the Zamość Collegiate by Domenico Tintoretto, ca. 1604, Church of the Transfiguration in Tarnogród.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa in a ruff by Peter Paul Rubens or workshop
"This prince who was the delight of the Poles alone has now become, o Belgians, the object of your affection and that of the world" (Quod sibi delicium soli tenuere Poloni, / Nunc est, o Belgæ, vester, et orbis amor) is the inscription in Latin, paraphrasing Titus, under an engraving with the portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648), eldest son of King Sigismund III Vasa (after French translation by Alain van Dievoet in "Les Lignages de Bruxelles", No. 75-76, 1978, p. 59). This print was made in Antwerp by Pieter de Jode the Elder (P. de Iode sculp.) and Joannes Meyssens (Ioann. Meyssens exc.), most likely between 1625-1632, and shows the prince in profile in armor, with an order of the Golden Fleece and holding military baton (National Museum in Kraków, MNK III-ryc.-40877).
Although the monarchs of Poland-Lithuania commissioned many works of art from Antwerp and Brussels from at least the early 16th century (mainly tapestries and paintings), after the prince's stay in these cities in 1624 these commissions increased considerably. The prince was painted for the Infanta Isabella Clara Eugenia of Spain by Peter Paul Rubens, ordered ten tapestries depicting the story of Ulysses (Odysseus) from the Brussels weaver Jacob Geubels the Younger and purchased many valuable objects. It should be noted, however, that already a decade earlier, around 1615 or even earlier, the Flemish engraver Pieter Serwouters (1586-1657), who was born and worked in Antwerp before moving to Amsterdam in 1622, created an engraving with another effigy of the prince in national costume (inscription: Vladislaus Sigismundus Dei Gratia Polonia Sueciæq Princeps, signed: P. Serwouters fecit, Veste Coburg, VII,347,1). Regarding costume, Ladislaus was depicted in different outfits and in the first known portraits, mainly in foreign costume - Italian, French or Spanish. The principal tailor of the royal court at that time was Nicolas Dugietto or Nicolas Dugudt (Nicolò Dughetto da Parigi, Dziugiet), serving at least until 1616, most likely a Frenchman from Paris, who was paid 612 florins per year. In June 1617 the prince's servant, actor and musician Jerzy Wincenty, purchased in England for his master, his father and stepmother 36 pairs of silk stockings (black and color), 15 pairs of gloves, perfumes, 2 beaver hats, vest (wastcot) and 6 expensive gloves, 6 other vests and as much nightcaps (night capps) and a dozen equestrian gloves. In 1617 the prince used the services of his father's tailor Sebastian (active at least from 1601), and in April 1624 he was served by a certain Pallioni (after "Pompa vestimentis" by Jacek Żukowski, p. 54-55, 58). Although during his journey he frequently ordered clothes from the best local tailors, the Spanish-style outfit depicted in his portrait by Rubens was most likely made before his departure from Warsaw, as the black satin doublet, perhaps from a fabric ordered in Venice, was decorated with the monogram S, referring to his father Sigismund III. Around September 13, 1624, the French ambassador Nicolas de Bar, lord of Baugy, reported from Brussels to the Secretary of State that: "The painter Rubens is in this town. The Infanta ordered him to take the likeness of the prince of Poland" (Le peintre Rubens est en cest ville. L'Infante luy a commandé de tirer le pourtraict du Prince de Pologne). The original painting by Rubens, mentioned in the inventory of the Coudenberg Palace in Brussels from 1659 (No. 122/84), was probably lost when the palace burned down in 1731, but the prince ordered several copies of this effigy for himself and his friends and some of them have been preserved. The most famous and perhaps the most faithful copy made by Rubens and his workshop is that kept at Wawel Castle in Kraków (oil on canvas, 125.1 x 101 cm, purchased by Metropolitan Museum of Art in 1929, earlier in England, offered by the Met in 2020). Another copy, of which nothing is known, is most likely in a private collection. The oval copy kept at the Durazzo-Pallavicini Palace in Genoa (oil on canvas, 77 x 66 cm, 1890 A), was perhaps a gift for Agostino Balbi, whose palace the prince saw in November 1624. There is also a good 17th century copy in the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 76 x 58 cm, M.Ob.2434, earlier 34348), which, however, more closely resembles the works of Gaspar de Crayer and his workshop, such as the portrait of Ladislaus' cousin Philip IV of Spain (1605-1665) in parade armor at the Met (45.128.14). The copy lost during the Warsaw Uprising of 1944 when the city was destroyed by German forces was comparable in style. This painting was donated by Henryk Bukowski in 1886 to the Polish Museum in Rapperswil (received from the King of Sweden, oil on canvas, 72 x 57 cm, inventory number 501). Willem van Haecht included the same effigy of the prince in his painting of the gallery of Cornelis van der Geest, painted in 1628 (Rubenshuis, oil on panel, 102.5 x 137.5 cm, RH.S.171). Rubens posibly also painted full-length portrait of the prince during the siege of Breda - "he made his portrait from nature" (lo ritrasse al naturale), according to Le vite de' pittori ... by Giovanni Pietro Bellori, published in Rome in 1672, which is sometimes interpreted as life-size. There are several indications that significant contacts between the Polish-Lithuanian monarchs and Rubens' workshop began before 1624. At the turn of 1619 and 1620, Piotr Żeromski vel Żeroński (Petro Jeronsquy), envoy of Sigismund III Vasa, who appeared in Antwerp, bought paintings from Rubens for which the loan amounted to 1,125 Polish ducats (after "Rubens w Polsce" by Juliusz A. Chrościcki, p. 135, 139, 161, 164, 166, 207, 214). Żeromski presented the Cathedral of Saint Nicholas in Kalisz with a large painting by Rubens or workshop, representing the Descent from the Cross (destroyed or stolen in 1973). In 1619 Jan Brueghel the Elder, who frequently cooperated with Rubens, was released from customs by Albert of Austria for paintings made for King of Poland including 9 portraits and in 1621, he painted three portraits of Polish kings for which he was paid 300 florins by the secretariat of Archduke Albert and Infanta Isabella Clara Eugenia on December 16 (En Brusselas, a 11 de deciembre se libraron 300 fl. a Juan Brueghle, pintor, vecino de Amberes, por tres retratos que ha hecho de los reyes de Polonia en el tercio postrero deste anno 1621). Many of Rubens' paintings were in the royal and magnate collections of the Commonwealth before the Deluge (1655-1660). Roger de Piles in his Dissertation sur les ouvrages ..., published in Paris in 1681, states that "The Lion Hunt, for example, and the fall of Saint Paul [The Conversion of Saint Paul] were made for the king of Poland, and four others hunts for the Duke of Bavaria" (La chasse aux Lions, par exemple, & la chûte de S. Paul ont esté faites pour le Roy de Pologne, & quatre autres chasses pour le Duc de Bavières, p. 25). Rubens most likely created a series of effigies of historical kings of Poland and Wespazjan Kochowski in his panegyric written in 1669 on the occasion of the coronation of King King Michael Korybut Wiśniowiecki refers to a painting by the master depicting King Casimir the Great (Na cóż tu Rubens Kazimierzu tobie / Wielki, te mury przydał ku ozdobie?). Another series was probably commissioned in Vienna from Frans Luycx, a student of Rubens, because the large painting depicting Casimir the Great's father - Ladislaus the Short was in the Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden before the Second World War (oil on canvas, 145 x 115 cm, Gal-Nr. 514/Gal.-Nr. 2674 L). Unfortunately, today we can only imagine these paintings, because nothing is preserved in Poland from the original collections. The invaders during the Deluge and other invasions had no respect whatsoever for the country and its people, not to mention its artistic collections. Pierre des Noyers, secretary to Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga, describes the numerous atrocities and barbarities of the invaders between 1655 and 1660, the pillaging of everything including marble floors, windows, the destruction of gilded panels just to obtain a few grams of gold and that "they had even taken the old skirts of the queen's maids of honor and sent them to Sweden" (Ils avaient pris jusqu'aux vieilles jupes des filles de la reine et les avaient envoyées en Suède). In the letter of July 27, 1656 from Warsaw, he added that "the Swedes have done so much damage to Warsaw Castle that it is uninhabitable; they put their horses up to the rooms on the third floor which are full of manure and the dead bodies of their soldiers (Les Suédois ont fait tant de saletés dans le château de Varsovie, qu'il est inhabitable; ils ont mis leurs chevaux jusque dans les chambres du troisième étage qui sont pleines de fumier et de corps morts de leurs soldats). Other towns in the Commonwealth were also pillaged and ruined. In Vilnius, the Russian army destroyed the rich chapel of Saint Casimir and transformed the cathedral into a stable for their horses (after "Lettres de Pierre Des Noyers ...", published in 1859, p. 40, 212). A painting by Peter Paul Rubens, which could possibly come from Lithuanian historical collections, perhaps acquired before the Deluge and which survived the invasions, is now in the National Museum of Art in Kaunas. This is the Crucifixion (oil on panel, 107 x 76 cm, ČDM Mt 1335), which in the second half of the 19th century was in the palace of Counts Tyszkiewicz (Tiškevičius) in Astravas, near Birzai, where the Radziwill family's rich artistic collections were kept. It is interesting to note that this painting is generally dated to the earliest period of Rubens' activity, between 1600-1615, when he was in Italy (1600-1608), Spain (1603) and the Netherlands (1612). In the Neuburg Castle near Munich, where many items from the dowry of sister of Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa were stored before 1804, there is a "Portrait of a young man" by Peter Paul Rubens or his workshop (Neuburg State Gallery, oil on panel, 57.7 x 43.1 cm, 342). The painting comes from the Electoral Gallery in Munich and the Polish-Lithuanian monarchs and the electors of Bavaria frequently exchanged gifts. Already in 1612, Queen Constance praised the artistic interests of her stepson in a letter to Duke William V, Duke of Bavaria, who in February 1623 sent several paintings to Poland-Lithuania and the painting in front of which the duke celebrated services was sent to Warsaw after his death - the transport (via Vienna) lasted from June 1626 to February the following year (after "Świat polskich Wazów: eseje", p. 298-299, 311). The effigy of Polish Saint Stanislaus Kostka in prayer by circle of Rubens, from the collection of the Electors of Bavaria in the Munich Residence (Alte Pinakothek, 7520), could be a gift from Poland, but created in Flanders. The resemblance of the young man to the effigies of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa, depicted in the mentioned engravings by Serwouters and de Jode, as well as in the medals with the profile of the prince by Alessandro Abondio (Kunsthistorisches Museum, Landesmuseum Württemberg or Bode Museum in Berlin), is striking. Also noteworthy is the resemblance to the likeness in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence (Inv. 1890, 2350) as well as the prince's face in the mentioned painting from Rubens' workshop at Wawel Castle. In his early portraits, such as the paintings from the Wittelsbach collections (Royal Castle in Warsaw, ZKW 66, donated by the government of West Germany in 1973) and Neuburg Castle (Bavarian State Painting Collections, 6817), the prince wears a ruff. A very similar ruff is visible on a portrait of Ladislaus Sigismund's uncle, King Philip III of Spain (1578-1621), attributed to Andrés López Polanco and dated around 1617. The portrait of Philip III can now be found at Skokloster Castle (LSH DIG3535) and was probably plundered in Poland-Lithuania by Carl Gustaf Wrangel (1613-1676), close friend and trusted advisor to the "Brigand of Europe" King Charles X Gustav of Sweden. In this portrait the prince does not wear the Order of the Golden Fleece, which he received in 1615, so the portrait could be dated shortly before he received the order, however, in many later effigies, Ladislaus was depicted without the Golden Fleece. For example, in the series of portraits of Polish monarchs commissioned by the Toruń City Council for the Royal Chamber of the City Hall, Sigismund III Vasa wears the order, while his son and successor is depicted without this distinction. In 2019, a miniature copy of this effigy, attributed to Abraham van Diepenbeeck, a student of Rubens who worked for the clients from the Commonwealth and moved to Antwerp in 1621, was sold in the United States (oil on vellum, 13.34 x 9.53 cm, Concept Art Gallery in Pittsburgh, PA, June 8, 2019, lot 1239). In this version of the effigy, the young prince particularly resembles the effigies of his father Sigismund III, notably the profile portrait at Wawel Castle (9009), purchased in Munich in 2008 (Hermann Historica, Auction 54, April 10, 2008, lot 3223).
Crucifixion by Peter Paul Rubens, ca. 1600-1615, National Museum of Art in Kaunas.
Portrait of King Philip III of Spain (1578-1621) by Andrés López Polanco, ca. 1617, Skokloster Castle.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) in a ruff by Peter Paul Rubens or workshop, ca. 1615-1621, Neuburg State Gallery.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) in a ruff by Abraham van Diepenbeeck, after 1621, Private collection.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) in a hat by workshop of Peter Paul Rubens, ca. 1624, Wawel Royal Castle.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) in a hat by workshop of Peter Paul Rubens, ca. 1624, present whereabouts unknown.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) in a hat by workshop of Peter Paul Rubens, ca. 1624, Durazzo-Pallavicini Palace in Genoa.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) in a hat by workshop of Gaspar de Crayer, ca. 1624, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) in a hat by workshop of Gaspar de Crayer, ca. 1624, Polish Museum in Rapperswil, lost.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) in a hat, detail of the Gallery of Cornelis van der Geest by Willem van Haecht, 1628, Rubenshuis in Antwerp.
Portrait of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa by Giovanni Antonio Galli
After World War II, which was the culmination of horrific invasions and partitions of Poland by its neighbors, very few effigies of Polish-Lithuanian Vasas were preserved in the former territories of the Commonwealth. What is very meaningful is that many of them were acquired abroad in the 19th century by aristocrats wishing to preserve the memory of the most tolerant country in Renaissance Europe. One of these paintings is a full-length portrait of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa, future King Ladislaus IV, painted by an Italian painter during his peregrination in the Italian peninsula in 1624-1625, now at Kórnik Castle near Poznań (oil on canvas, 234 x 116 cm, inventory number MK 03369).
It was purchased in 1850 in Paris by Count Tytus Działyński (1796-1861). According to the inscription at the bottom, the effigy was commissioned by the Gundulić family (known in Italian as Gondola), patricians from Dubrovnik (Republic of Ragusa), who settled in Ancona in the Papal States. It was intended as a souvenir of the prince's stay at their house on December 13 and 14, 1624. Ivan Gundulič (1589-1638), a relative of the hosts, an outstanding Croatian poet and patrician from Dubrovnik, probably met the Polish-Lithuanian prince there and dedicated the poem "Osman" to him. He was probably also the author of the inscription on the portrait (VLADISLAO SIGISMUNDI POLONORum REGIS FILIO / SCYTHAR, TVRCARVMQ: TIVMPHATORI INVICTo / GVNDVLA FAMILIA HOSPITI SVO / VT CVIVS HVMANSmam MAEST SEVELIN HIS ÆDIBVs ASPEXIt / SEMPER IN IMAGINE SVSPICIAT.). In the 19th century, the image hung in Casa Gunduli in Ancona (after "„Królewska” galeria obrazów ..." by Barbara Dolczewska, p. 250). The balding prince, who later frequently wore wigs, was depicted in a fashionable black Spanish-Italian costume with the Order of the Golden Fleece hanging on his chest and a rapier at his side. During his peregrination, Ladislaus Sigismund was considered a connoisseur, which is confirmed by the fact that Duke William V of Bavaria asked the prince to evaluate the copy of the painting of Saint Veronica, made according to the Roman original. Already in 1612, Queen Constance praised her stepson's artistic interests in a letter to Duke William. Ladislaus Sigismund's letter of September 18, 1624, sent from Brussels to Urszula Meyerin, and indirectly to his father, contains an important mention of his collector's awareness: "I bought several original paintings. There are many real masterpieces [capolavori] here". In Milan he admired the "crystal crafts". He probably visited van Dyck's studio in Genoa and looked at the paintings in the local Neri palace and the frescoes by Agostino Carracci in the summer palace in Parma. He admired the works of Domenico Ghirlandaio in Florence and visited Guido Reni's studio in Bologna (after "Świat polskich Wazów: eseje", p. 311-312). The prince's aunt, Grand Duchess of Tuscany, in a conversation with the Mantua envoy, Ferrante Agnelli Soardo, said that he "likes to be well received, appreciates music, likes paintings" (according to a letter of Soardo to Ferdinand I Gonzaga, Duke of Mantua, Florence, February 4, 1625). In a letter sent on February 26, 1625 from Bologna, Ladislaus Sigismund mentions hiring a "good organist" (possibly Angelo Simonelli) and a "eunuch" (possibly famous castrato Baldassare Ferri) into the royal service, also expressing hope for employing a skilled alto player. In Naples, he could admire the representative attire of the viceroy Antonio Álvarez de Toledo y Beaumont, 5th Duke of Alba, who had "a diamond jewel on him and a cynturyn [belt - cinturón, citrine?] in his hat, which was estimated at several hundred thousand" and that at the age of seventy (septuagenario) he dyed his hair and beard (after "Obraz dworów Europejskich ..." by Stefan Pac, p. 134). In the late afternoon of January 12, 1625, he listened to "Adriana [Basile-Baroni] singing with her son and daughters". In Venice, which in his opinion "is probably the truest wonder of the world" (letter to Urszula Meyerin, March 5, 1625), he visited the house of a merchant selling diamonds. On March 7, he went to Murano "to listen to a nun who was famous here for her wonderful voice". Two days later he appeared incognito "at the Council of Venice" and on March 20, 1625, from Palmanova, the prince sent a letter of thanks to the Republic of Venice for a lavish reception. He brought numerous gifts to the country - sculptures, caskets, jewels and "paintings by old, famous masters", received from the Duke of Mantua, Carlo Magalotti, Cardinal Francesco Barberini and a painting in a precious frame from Pope Urban VIII. He also made numerous purchases and, like in Venice, they were exempt from customs duties and additional fees (after "Listy Władysława Wazy ..." by Jacek Żukowski, p. 63, 66, 71, 73, 76, 78). Italians also received many gifts and effigies of the prince and members of the royal family. In the Durazzo-Pallavicini Palace in Genoa there is a good workshop copy of Ladislaus Sigismund's portrait by Rubens. Cardinal Francesco Maria del Monte (1549-1627), patron of Caravaggio, had in his Roman Palazzo Madama "a portrait of the Prince, son of the King of Poland in a black frame" (un ritratto del Principe figlio del Re di Polonia con cornice nere) and Cardinal Francesco Peretti di Montalto (1597-1655), had in 1655 "a painting with a portrait of the Prince of Bologna [Poland] in Polish dress, holding a jewel [most likely bulava mace] in his hand" (quadro uno con ritratto del Principe di Bologna [Polonia] in habito Polacco, che tiene in mano un gioielo). These were probably copies of portrait of Ladislaus Sigismund in Polish costume by Rubens, as the Flemish painter most likely created two versions of his effigy, one commissioned by the Infanta "with a hat on his head" (con el sombrero en la caveza), and the other - alla polacca, i.e. in Polish costume. Two such copies, identified by me in 2012, were offered to the Medicis (Pitti Palace in Florence, Inv. 1890, 5178 and 5673). They were believed to be images of King Michael Korybut Wiśniowiecki, and one of them even has an inscription in Italian: MICHELE VIESNOVISKI RE DI / POLONIA. While Poles often preferred Italian, French, or Flemish fashion, foreign aristocrats wanted Polish-style clothing. The Grand Duchess of Tuscany received such outfits from her sister Queen Constance of Austria in 1622. In 1631, Archduke Leopold V (1586-1632) also wanted Polish clothes for his three-year-old son Ferdinand Charles (1628-1662), which were made and sent by the queen. Leopold liked the clothes and wanted to pay for them, but Constance said that a portrait of "young dear Pollack" (deß jungen lieben Pollacken conterfet) would be sufficient (according to Urszula Meyerin's letter to the Archduke, April 4, 1631). The portraits of the young Dukes of Tuscany in Polish clothing existed in several versions and copies, some of which were undoubtedly also sent to Poland-Lithuania. This is why the portrait of a prince, made in a style close to Justus Sustermans and resembling the effigies of the sons of Ladislaus Sigismund's aunt, Maria Magdalena of Austria, Grand Duchess of Tuscany, is considered the effigy of one of Ladislaus Sigismond's brothers (Academy of Saint Luke in Rome, inventory number 298). The effigy of the young Vasa in his sumptuous costume was undoubtedly also created in several copies for the prince, his family and his friends. Unfortunately, this is the only version known to date, which also indicates the extent of the destruction of art in Poland. Similar to other exquisite effigies created during his journey, this one is also finely painted. The closest is the Penitent Mary Magdalene from the Walters Art Museum in Baltimore (37.651), dated circa 1625-1635. This canvas is attributed to a painter active in Rome Giovanni Antonio Galli, called lo Spadarino (1585-1652), member of the Caravaggisti (followers of Caravaggio). Another work painted in the same way can be found in Ancona, where the portrait of the prince was initially kept. It is also attributed to Spadarino and shows a full-length effigy of Saint Thomas of Villanova giving alms. The painting, now at the Pinacoteca Civica di Ancona (oil on canvas, 192 x 112 cm, inv. 51), is dated to about 1618-1620 (in 1618 the Spanish saint was beatified by Pope Paul V). It comes from the sacristy of the medieval Sant'Agostino church in Ancona, mentioned by Marcello Oretti, who visited Ancona in 1777. Two pendant effigies of Ladislaus and his second wife Marie Louise Gonzaga, created in the style of Spadarino or his workshop, were sold in Rome in 2022. No signed portraits by Spadarino are known, so perhaps all were destroyed in Poland-Lithuania or are awaiting discovery.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) in Spanish-Italian costume by Giovanni Antonio Galli, called lo Spadarino, ca. 1624-1625, Kórnik Castle.
Portraits of Ladislaus Vasa in national and Spanish costume by Gaspar de Crayer and Pieter Claesz. Soutman
In 1633, the newly elected king Ladislaus IV Vasa decided to amaze the Western European powers with the wealth, diversity and oriental charm of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. The "Lord of the Three Crowns", because in addition to being elected monarch of the Commonwealth, he was also titular hereditary King of Sweden and titular elected Grand Duke of Moscow (Rè di Polonia, e Suetia eletto gran Duca di Moscovia) (apart from the emblem of Sweden), sent his ambassador Jerzy Ossoliński to Pope Urban VIII, with official announcement of the coronation and confirmation of his loyalty to the pope. The ambassador's grand retinue with 20 carriages, 10 camels and a large number of horses, oxen and mules, passing through Vienna, Treviso, Padua and Bologna arrived at the borders of Rome on November 20, 1633. On November 27, 1633, the envoy made a magnificent entry into the Eternal City.
This splendid entry was immortalized in several paintings as well as in engravings by the Florentine draughtsman and printmaker Stefano della Bella (1610-1664), as well as in Relatione della solenne entrata ... by Virginio Parisi, Urban VIII's chamber attendant, published in two editions (in 1633 and 1634), including one with a dedication to the ambassador. According to Parisi's account and the descriptions in della Bella's prints, the suite included richly dressed camels led by Persians and Armenians, twenty pages dressed in satin, horses with rich harnesses including five beautiful Turkish horses led by Tartars and Armenians, with very superb saddles covered with pure gold, diamonds, rubies and turquoises. The majority of the members of the retinue were dressed in national costumes. Mr. Kociszewski (Chociszewski or Cochiszewsky), senior chamblain of the envoy, most likely of Armenian origin, was dressed in a rich Persian costume (alla Persiana) and rode a richly dressed horse with golden horseshoes and Jakub Zieliński, marshal of the court of the envoy, was holding in his hand a mace of silver (mazza d'Argento in mano). Parisi adds that "each of the horses had large bunches of heron's feathers on their heads, and on their legs horseshoes of solid gold, two of which broke into several pieces as they walked, which were for the most part prey of the people [of Rome]" (Haveva ciascuno de' Cavalli grossi mazzi d'Aironi in testa, et alle gambe, e piedi grosse maniglie, e ferri d'oro massiccio, doi de' quali nel camminare si ruppero in diversi pezzi, che per lo più furono preda del popolo). Several Spanish (Diversi Signori Spagnoli), French (altri Cavalieri franzesi) and Italian aristocrats as well as courtiers from the cardinals' courts joined the procession. Since Rome was the capital of the Christian world for Catholics, this propaganda entry was dedicated not only to Italians but also to monarchs of Spain and France. In addition to prestige and the strengthening of alliances against the enemies of the Commonwealth, the aim was probably also to encourage the arrival of specialists because the Republic of nobles constantly needed engineers, architects, craftsmen, artists and even skilled soldiers to protect the borders. Fabulously wealthy aristocrats and dignitaries of the Commonwealth ordered luxury items from the best workshops abroad, not only in Europe, but also in Persia and Turkey. In 1603, Jan Zamoyski (d. 1614), Catholic archbishop of Lviv, ordered twenty large carpets decorated with his coat of arms from Istanbul and donated them to the Lviv Cathedral (after "Sztuka Islamu w Polsce ..." by Tadeusz Mańkowski, p. 20). The country became very rich thanks to trade (grain, wood, cattle, animal pelts, horses, amber, Polish cochineal, mead, honey, wax and luxury items imported from east), salt, lead, sulfur and copper mining. Persian rugs, killims and saddles, Turkish horse tacks, harnesses, fabrics and weapons are frequently mentioned in inventories before 1655, as well as Venetian glass, Italian, Dutch and Flemish paintings and tapestries, Augsburg silver and Ruthenian and Russian icons. Thanks to this activity, they considerably supported foreign economies, crafts and trade. To meet the demand for oriental-style items, Armenian workshops in the Commonwealth also produced such products. For example, the 1633 inventory of Radziwill Castle in Lubcha in Belarus (Central Archives of Historical Records in Warsaw, 1/354/0/26/45) lists 16 different rich saddles, some in velvet, embroidered with gold, decorated with silver, rubies, turquoises and nacre, mainly made locally (domowey Roboty) and Persian (Adziamskie), as well as 7 Cossack saddles and 2 German, 19 horse tacks, made locally or in Turkey (Rząd srebrny złocisty suty Turecki, five items - 2, 3, 6, 7, 9) and numerous Persian carpets. The diversity of the country is also reflected in various coins. In the first quarter of the 17th century, Pyotr of Ossa Ozhga (Piotr Ożga, d. 1622), crown referendary and starost of Terebovlia, kept in his chest 8,000 ducats, 270 Portuguese (or Portuguese-style) 20 ducat coins, 700 Spanish (or Spanish-style) doubloons, 1,000 Moscow gold coins and 2,000 thalers. One-off commercial transaction (sales of oxen) carried out by the starost of Sniatyn, Piotr Potocki (d. 1648), brought him 55,000 in gold and the dowries of rich noblewomen could range from 25,000 to 400,000 in gold (after "Obieg pieniężny ..." by Andrzej Mikołajczyk, p.129). The wealth of the Republic of nobles brought a huge tragedy - Deluge (1655-1660) during which neighboring countries invaded the Commonwealth (from the north, south, east and west) with superior force and engaged in a looting and destruction that lasted five years. The treasures of Skrwilno (discovered in 1961), Nieszawa (1963), Bydgoszcz (2018), Kiekrz in Poznań (1890) or Nasvytaliai (1926) recall these horrible events. The invasion left the majority of the country in ruins and significantly impoverished, so many structures were never rebuilt and were abandoned. While in many European countries visitors can admire magnificent castles and palaces, in Poland the castle ruins of Tenczyn, Krzyżtopór, Ogrodzieniec, Janowiec, Kazimierz Dolny, Tarnów, Pińczów, Siewierz, Bodzentyn, Kamieniec, Drzewica, Chęciny and other places are just memories of their past glory. Some rich casles and palaces disappeard completly like the Palace in Łowicz, Royal Castles and Palaces in Knyszyn, Radom and Kalisz. The destruction of heritage was so considerable that many significant objects linked to the monarchs of Poland-Lithuania had to be acquired abroad, such as a series of miniatures of the Jagiellon family by the workshop of Lucas Cranach the Younger purchased in London in the mid-19th century by Adolf Cichowski (Czartoryski Museum). In 1648, the Dutch painter Pieter Claesz. Soutman (died 1657) created an interesting painting for the so-called Orange Hall (Dutch: Oranjezaal) of the Huis ten Bosch palace in The Hague (signed: P. Soutman. F. 1648.). It comes from a series of paintings created by different Dutch and Flemish painters glorifying Frederick Henry (1584-1647), Prince of Orange and his wife Amalia of Solms-Braunfels (1602-1675). Soutman's painting depicts a triumphal procession with spoils of war, including prizes in gold and silver. A similar painting by Salomon de Bray, produced two years later (signed: SDBray - 1650) represents a triumphal procession with captured weapons. It is unclear whether the triumph refers to a particular event. In some paintings of the cycle there is a reference to the Spanish Empire - banner in the procession with the standard bearers by Pieter de Grebber (signed: P. DGrebber Ao 1648) and to the Holy Roman Empire - imperial banner in the procession with musicians and captured banners by Salomon de Bray (signed: SD:Bray. - 1649). They could refer to the Battle of Prague, which occurred between July 25 and November 1, 1648, following which part of the fabulous art collection of the relatives of Ladislaus IV, collected at Prague Castle by the emperor Rudolf II (1552-1612), was plundered and shipped to Sweden. In de Bray's painting from 1650, we can see German mercenaries (Landsknecht) carrying spoils consisting of Italian-style armors and helmets, quivers of arrows and leading oriental horses, as in reference to the print by della Bella showing the pages of the Commonwealth's envoy in 1633 (letter I). The original title of Soutman's painting is "Triumphal procession of the conquered weapons, silver bowls, basins and large cup, a wreathed woman with a silver candlestick in front" (Triomftocht van de veroverde wapens, zilveren schalen, bekkens en grote beker, een bekranste vrouw met zilveren kandelaar voorop). It was made in the painter's studio in Haarlem before December 1648 and he was paid 500 guilders. Among the weapons in the painting we can see the sign SPQR - "The Senate and People of Rome" (Senatus Populusque Romanus), although continued to be used under the Roman Empire, this abbreviated expression generally refers to the ancient Roman Republic. The sweaty man on the right could be Hercules and the gold statues the children are holding probably refer to Roman customs of worshiping various gods in the form of small statues (after "Oranjezaal" by Charles Julien, p. 26). The composition could therefore be interpreted as a triumph over ancient paganism or old-fashioned pluralism. The most intriguing element of this painting, however, is the helmet crowning the composition together with a gilded vase. Almost identical helmet was depicted in two portraits painted by Soutman and his workshop a few years earlier. Both depict Ladislaus IV Vasa when he was crown prince and wearing national costume - one in the Wilanów Palace (oil on canvas, 206 x 127.5 cm, Wil.1134) and the other in the Lviv Historical Museum - Korniakt Palace, both probably from the late 1620s or early 1630s. Such portraits were usually produced in series as gifts for different courts in Europe. The inventories of the Coudenberg collections in Brussels from 1643, 1659 and 1692 mention several portraits of the Prince in Polish or Hungarian costume or in armor (compare "Rubens w Polsce" by Juliusz Chrościcki, p. 214-215). In Henry Metcalfe's collection in the mid-19th century there was probably a similar portrait of Ladislaus in red national costume. It is possible that such a painting by Soutman was also in The Hague. The prince's costume probably inspired a painter who created the biblical scene of Ruth in the field of Boaz, now housed in the National Gallery of Denmark (oil on canvas, 124 x 163.5 cm, KMSsp356). This painting is attributed to Adam Camerarius, active in Groningen and Amsterdam in the 1640s (also attributed to Pieter de Grebber and Soutman). The biblical story about King David's grandfather and the barley harvest seems perfectly suited to the scenery of the Commonwealth, the country once called the "Paradise of the Jews" (Paradisus Judæorum) and the "Granary of Europe" (Granarium Europæ) (sometimes narrowed to Gdańsk, which was the country's main port). The helmet, inspired by the Persian kulah khuds, was typical of Polish-Lithuanian winged hussars and was depicted in the Gołuchów table, frontispiece to Florus Polonicus by Joachim Pastorius, published in Leiden in 1641, and in the so-called "Stockholm Roll" dating from around 1605. It was included in the portrait of the prince because it was an important symbol, a symbol of the military strength of the Commonwealth. The inclusion of such an object in the painting in the Huis ten Bosch was also symbolic, as were other elements of the composition. On May 20, 1648, Ladislaus IV died and on November 17 of the same year, his half-brother John Casimir Vasa was elected new king. Among the important paintings in the Orange Hall is a portrait of Frederick Henry's son-in-law, Frederick William (1620-1688), Elector of Brandenburg, painted with his wife by Gerard van Honthorst (signed: GHonthorst 1649). Today, however, we can only assume that the elector, vassal of the Commonwealth, who knew perfectly the weaknesses of the country and who, during the Deluge (in 1656), according to Wawrzyniec Jan Rudawski, "took to Prussia as a spoil, the most valuable paintings and silverware of the royal table", was already in 1648 planning or anticipating the great pillage by the "northern conquerors" after 1655 (including himself) and suggested it to his Dutch allies. Soutman, who "should also be recognized as a royal painter in Poland" (Petrus Soutman co nomine celebrandus quoque, quod regius Pictor in Polonia fuerit), according to Theodori Schreveli Harlemum, sive vrbis Harlemensis incunabula, published in Leiden in 1647 (p. 290) is generally considered to be the court painter of Sigismund III Vasa between 1624 and 1628. Perhaps the painter Peter, mentioned in accounts of the court of Sigismund III, who was paid 315 florins apparently for preparing the paintings (made from November 1, 1626 to November 30, 1627), was Soutman. Returning to his hometown of Haarlem on October 20, 1628, he asked the administrative authorities in the Spanish Netherlands for permission to bring a box containing paintings from Poland for the Infanta Isabella. These were most likely portraits of the family of Sigismund III, mentioned in the Coudenberg inventories, which were hung in the most important rooms of the Brussels residence, mainly in the Grand Gallery built by the regent of the Netherlands, Mary of Hungary (after "Świat polskich Wazów: eseje", p. 48, 287). Although the majority of paintings from the Vasa period made in Flanders or in the Flemish style are attributed to Soutman and Rubens or their workshops, because their contacts with the monarchs of Poland-Lithuania are confirmed in the sources, the portrait of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund in national costume, preserved in the Czartoryski Museum (oil on canvas, 198 x 118 cm, MNK XII-353), recalls the works of another eminent painter of the Spanish Netherlands - Gaspar de Crayer. Its style is particularly reminiscent of several effigies of Ladislaus' cousin, King Philip IV of Spain, such as the portrait in parade armor from the Metropolitan Museum of Art (45.128.14), portrait with a dwarf from the Palacio de Viana in Madrid or the equestrian portrait in the Alte Pinakothek in Munich (2529), perhaps from the dowry of Ladislaus' half-sister. Effigies of family members were frequently exchanged with Spain and commissioned from the same painters. For the baptism of Anna Catherine Constance in 1619, her mother, Queen Constance of Austria, managed to obtain portraits of children from the court of Madrid and in 1624, in order to update the family gallery, the queen launched another major campaign and ordered the paintings in Vienna. Two other portraits of Ladislaus Sigismond in national costume, also close to de Crayer and his workshop, are today in the Pitti Palace in Florence (oil on canvas, 135 x 98, Inv. 1890, 5178 and oil on canvas, 131.5 x 90, Inv. 1890, 5673). Both are considered effigies of King Michael I Korybut Wiśniowiecki (1640-1673) and were correctly identified by me in 2012. The paintings were probably gifts to Prince's aunt Maria Magdalena of Austria (1589-1631), Grand Duchess of Tuscany or other Italian dukes. Another similar portrait from the collection of Izydor Czosnowski (1857-1934) was before 1961 at the Embassy of the Republic of Poland to the Holy See (reproduced in "Elementa ad Fontium Editiones", Volume III, Tab. I-III), with two other paintings from the same collection - portrait of Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga (1611-1667) dating from around 1650 and portrait of a prince in profile (a copy of the painting now in the Academy of San Luca in Rome, 298), identified as portrait of John Casimir Vasa, but most likely representing the cousin of Ladislaus IV and John Casimir - Giancarlo de' Medici (1611-1663), frequently depicted in Polish-Lithuanian costumes in childhood. In 1976, Izydor's son Leon donated several paintings from his father's collection to the Polish Hospice in Rome, including the portrait of the prince (oil on canvas, 133 x 95 cm, after "Kościół polski w Rzymie ..." by Józef Skrabski, p. 294, 296). The greater contrast of shades and colors in the portrait of the prince from the Czosnowski collection and the greater resemblance to Soutman's painting in Wilanów, indicate that he or more likely his workshop were the authors. Numerous magnates of the Commonwealth also owned royal effigies, arguably created by the finest painters. The inventory of paintings from the collection of Princess Louise Charlotte Radziwill (1667-1695), drawn up in 1671, lists two portraits of young Ladislaus, which could be paintings by Soutman or de Crayer, however the names of the painters are not not mentioned - "King Ladislaus in Polish style, when young" (157/8) and "Prince Ladislaus in Polish style with a mace" (191/17) (after "Inwentarz galerii obrazów Radziwiłłów z XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska). The relatively small number of preserved paintings also illustrates the extent of the destruction of the Commonwealth's heritage. In the Wilanów Palace there is also another intriguing portrait of Ladislaus, attributed to the Dutch School of the 19th century (oil on canvas, 65.6 x 54 cm, Wil.1394). It is also very close to the style of Soutman (especially how the hair of his mustache was painted and the contrast of colors and shades), comparable to the paintings signed by this painter, such as the mentioned triumphal procession in The Hague or A young man holding a staff in the National Gallery of Art in Washington (2010.19.1, signed: P. Soutman / F.A. 1640) and attributed works, such as Portrait of a woman holding a glove in the Mauritshuis in The Hague (inventory number 755). Ladislaus is older in this portrait than in the other effigies mentioned. He wears a Spanish costume and this image closely resembles the portraits of Ladislaus' cousin, King Philip IV of Spain, painted by the workshop of Diego Velázquez around 1656 (Hermitage Museum, ГЭ-297 and Royal Academy of Fine Arts of San Fernando in Madrid, 0634) or an earlier portrait, painted around 1632 (Kunsthistorisches Museum, GG 314). The likeness of the Polish king should be dated to around 1634, when he intensified his contacts with Spain and sent Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski (1616-1667) as ambassador. The inventory of the property of Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga, drawn up three months after her death, on September 27, 1667, lists a "portrait of the King of Poland on horseback in the Spanish style" (le portraict du Roy de Pologne à cheval à l'Espagnole). It was probably an effigy of her first (Ladislaus IV) or her second husband (John Casimir) in Spanish costume.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) in national costume by Gaspar de Crayer, 1624-1632, Czartoryski Museum.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) in national costume by Gaspar de Crayer or workshop, 1624-1632, Pitti Palace in Florence.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) in national costume by workshop of Gaspar de Crayer, 1624-1632, Pitti Palace in Florence.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) in national costume by workshop of Pieter Claesz. Soutman, 1624-1632, Polish Hospice in Rome.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) in national costume by Pieter Claesz. Soutman, 1624-1632, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
Portrait of King Ladislaus IV Vasa (1595-1648) in Spanish costume by Pieter Claesz. Soutman, ca. 1634, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
Ruth in the field of Boaz by Adam Camerarius or Pieter Claesz. Soutman, 1640s, National Gallery of Denmark.
Triumphal procession with spoils of war by Pieter Claesz. Soutman, 1648, Huis ten Bosch Palace in The Hague.
Portraits of Sigismund Guldenstern (The Laughing Cavalier) by Frans Hals and Bartholomeus Milwitz
In 1623, Sigismund Guldenstern (1598-1666), also known as Zygmunt Guldensztern or Sigismund Güldenstern, traveled with his older brother Johan (1597-1658) to Leiden in the Netherlands, where they enrolled in the famous university on February 27 that year. It is not known how long they stayed there, but in 1626 Johan became chamberlain to Maria Eleonora of Brandenburg (1599-1655), Queen of Sweden, and Sigismund returned to Poland-Lithuania.
Sigismund Guldenstern was born as the son of the Swedish admiral Johan Nilsson Gyllenstierna (1569-1617) from the Lundholm branch of the Danish-Swedish noble family and his wife Countess Sigrid Brahe (1568-1608). His father sided with Sigismund III Vasa and after king's deposition in Sweden he emigrated to the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth with his entire family. He probably also named his son after the king. They settled in the royal city of Toruń, which was one of the largest and most influential towns in Polish Prussia (Chełmno Voivodeship) and enjoyed the right to vote in free royal elections. Since the German-speaking community dominated the region, they began to use their surname in the German form - Guldenstern, which derives from their coat of arms, seven-pointed gold star. Before going abroad, young Guldenstern attended the Academic Gymnasium in Toruń (Schola Thoruniensis) and, in February 1615, enrolled with his brother to study at the University of Rostock. Later, before arriving in Leiden, he also attended the University of Strasbourg. During his studies, he learned several foreign languages. After returning to the Commonwealth in the mid-1620s, he served as a courtier at the court of King Sigismund III and was appointed the royal bed-keeper - łożniczy (responsible for the royal bedroom). In 1633, during the coronation Sejm, he received from the new king Ladislaus IV an indigenat (naturalization), that is to say a recognition of foreign nobility in the Commonwealth, after which he acquired all the rights and freedoms of the local nobles. Throughout his life he maintained cordial relations with the ruling house of Poland-Lithuania and the letter of Princess-Infanta Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651), written in Polish from Vilnius on July 14, 1636, is a good example. In 1636, together with Christopher Radziwill (1585-1640), voivode of Vilnius and Andrzej Rej (d. 1641), starost of Libusza, he presided over the funeral of Princess-Infanta Anna Vasa (1568-1625), the aunt of King Ladislaus IV, in Toruń at the Lutheran church. It was the last such large-scale political manifestation of dissenters in the Commonwealth. Due to religious differences, the king himself did not take part in the funeral (after "Listy Anny Wazy (1568-1625)", p. 47). Religion, which in previous epoch was not an obstacle in a country where Orthodox Christians and Jews dominated in many regions, the Protestants were senators, envoys and important officials, Catholics married Orthodox, Lutherans or Calvinists, due to Counter-Reformation and Habsburg influences at the royal court, often became an obstacle during the Vasas. Most likely in 1627, in Warsaw, Sigismund married the daughter of Fabian Czema (d. 1636), castellan of Chełmno and starost of Sztum, Anna Czemówna (1599-1673). She was heiress to large estates in Kashubia, transformed by her father and mother Katarzyna Leszczyńska into centers of Calvinism. By marrying his only daughter to a Lutheran, Fabian obliged him by a marriage contract to maintain Calvinist preachers in Anna's estates (after "Bracia czescy w Wielkopolsce ..." by Jolanta Dworzaczkowa, p. 105). The inventory of Czemówna's trousseau - "Register of things that His Lordship the Lord of Chełmno, some for himself, some for his daughter, Mrs. Anna Cemianska, took from Toruń in 1627, on May 20, some with her (including jewelry) when going to Poland [the Crown] from Toruń [Polish Prussia] a year ago" (Spisanie rzeczy, ktore Jego Mość Pan chełminski częścią dla siebie, częścią dla Corki swey Jej Mci Panny Anny Cemianskey Roku 1627 d 20. Maja z Torunia wiosł, częścią tej z sobą (jako niektore kleinoty) przed rokiem z Torunia jadąc do Polski wzięła) in the State Archives in Toruń (69/833/0/16.4/498, p. 157-162), lists a large number of jewels and other valuable objects, such as gold medals with effigies of Rafał Leszczyński (1579-1636), voivode of Belz and that of the Lady of Vilnius, most probably Elizabeth Radziwill (1583-1611), wife of Lew Sapieha (1557-1633), gold spoons and forks, 9 "Flemish collars" and "two red Persian carpets for Her Ladyship on her way to Warsaw" (Odlewka twarzy na złocie duże Jedna Jego Mci Pana Wojewody Bełskiego, Druga Xięzney Pani Wilenskey [...] Złota łyszka, Złote widelice, [...] Flamskich kołnierzów No. 9, [...] Dwa Kobierce Adziamskie czerwone dla Jej Mci w drogę do Warszawy). Paintings and other household utensils, such as pots and linens, were probably inventoried separately or not listed because they were considered of lesser value. Today, nothing has preserved in Poland of this great wealth, nor any effigy. During the Deluge (1655-1660), the Swedes plundered and burned the Guldenstern estates, including the Lutheran church in Jasna near Dzierzgoń (after "Protestanci w dobrach prywatnych ..." by Aleksander Klemp, p. 119). Taking into account his education abroad as well as his important position at court, the effigies of Sigismund must have been numerous and splendid. The best known of the family's movable possessions is the so-called Kretkowski-Guldenstern carpet kept in the Bavarian National Museum in Munich (inv. 1612). It was most likely made in Armenian workshops in the Commonwealth or in Turkey on the occasion of the marriage of Jan Kazimierz Kretkowski and Katarzyna Lukrecja Guldensztern, daughter of Sigismund and Anna Czemówna, perhaps as part of her trousseau and adorned with their coat of arms (she married Kretkowski in January 1670). In 1624, while Sigismund was probably still studying in Leiden, Frans Hals the Elder (1582/83-1666), a painter active in the nearby town of Haarlem, painted his famous portrait of The Laughing Cavalier also known as The Dutch Knight (De Hollandse ridder), now in the Wallace Collection in London (oil on canvas, 83 x 67.3 cm, P84). The provenance of the painting dates back to the collection of Johan Hendrik van Heemskerk (1689-1730) in The Hague, then it was in Amsterdam, Paris and finally in London. The stadtholders of the Dutch Republic had their residence in The Hague, so the provenance from their collections is possible. A copy of this painting by a different painter and showing differences in costume, dated circa 1630, was sold in 2010 in London (oil on panel, 69.7 x 59.8 cm, Bonhams, July 7, 2010, lot 34). For over a century, when the painting became famous under its current title, the identity of the sitter has not been established with certainty, indicating that he was not Dutch as many believe. Art historian Pieter Biesboer has suggested that the painting may depict the Dutch linen and silk merchant Tieleman Roosterman (1598-1673), who was the same age as the sitter and who is also the subject of another portrait by Hals, painted in 1634, now in the Cleveland Museum of Art (1999.173). However, the differences in his facial physiognomy are evident: Roosterman has a larger nose, more hair, and a different eye color. Such differences would be possible if the portraits had been painted by different painters, who moreover would not have seen the real model and copied other effigies, but Roosterman was one of the richest citizens of Haarlem, at the time where Hals lived there. While in the portrait of Roosterman painted in 1634 his costume is rather typical for a merchant, the richly embroidered doublet of "The Laughing Cavalier" indicates that he is rather a wealthy aristocrat (or posing as such), like Janusz Radziwill (1612-1655), whose portrait in rich French costume was painted in Leiden by David Bailly around 1632 (National Museum in Wrocław, VIII-578). A rich nobleman wearing a similar costume walks through the forest with his wife dressed in a typical Gdańsk costume in a drawing from the book of friendship (album amicorum/Stammbuch) of Heinrich Böhm of Namysłów, made between 1627 and 1633 (Kórnik Library, BK01508). The Catholic Gabriel Kilian Ligęza of Bobrek was depicted in a similar costume in the engraving from his thesis, made by Schelte Adamsz. Bolswert in 1628 (British Museum, 1858,0417.1259), as well as Christopher Michael Sapieha/Sapega (1607-1631) in his portrait painted in 1709 after the original from around 1631 (Wawel Royal Castle, 9150). It has also been proposed that the portrait could be a betrothal portrait, as suggested by the emblems associated with fortune, strength, love and virtue (arrows, flaming cornucopias and lovers' knots), embroidered on his costume. Such a good portrait would help the man to make a career at court and obtain the hand of a rich heiress. According to the Latin inscription in the upper right corner, the man in Hals' portrait was 26 years old in 1624 (Æ'TA. SVÆ 26 / A° 1624), exactly like Sigismund Guldenstern, when he probably visited Haarlem before his marriage with Czemówna. Despite the fact that the painter wanted to see his models, and for his large painting known as "The meagre company" in March 1636 he promised to complete the painting quickly, provided that the sixteen guardsmen of the XIth District of Amsterdam come to Haarlem (Rijksmuseum, SK-C-374), he and his studio also painted figures the painter probably never met in person, such as the French philosopher René Descartes (1596-1650), who lived in the Netherlands between 1628 and 1649. Although there is no record of their meeting, the portraits of Descartes in the Louvre (INV 1317; MR 738) and at the Statens Museum for Kunst in Copenhagen (DEP7) are attributed to the workshop of Hals or to a follower and the original painted by Hals, considered lost, was engraved by Jonas Suyderhoef around 1650 (Rijksmuseum, RP-P-OB-60.717, signed: F. Hals pinxit). Because the original of "The Laughing Cavalier" was painted in Haarlem, the later copy sold in 2010 was attributed to the School of Haarlem, however, the style of this painting closely resembles paintings attributed to Bartholomeus Milwitz (ca. 1590-1656), a painter most likely from West Pomerania, active in Gdańsk from 1615. On 18 November 1606 he married Geertruyd Arnouts from 's-Hertogenbosch and between 1626 and 1629, during the Polish-Swedish War, he lived in Amsterdam. Around 1633, he painted the splendid portrait of Ladislaus IV Vasa in coronation robe, now kept in the Royal Castle in Warsaw as a deposit of the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 150 x 116 cm, MP 4982). The portrait of the king comes from the collection of the last elected monarch of the Commonwealth Stanislaus Augustus Poniatowski (no. 181) and was purchased from Roman Potocki in 1950. The portrait of the Gdańsk councilor Salomon Giese (1590-1651) in the Museum of Gdańsk (MHMG/S/17), is also attributed to Milwitz and is very similar in style to that sold in London. Besides portraits, Milwitz also painted large landscapes and batalistic scenes, such as the 1627 Battle of Oliwa from the main town hall of Gdańsk, painted in 1649 and most likely destroyed during World War II. Magnificent paintings depicting the entry of Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga into Gdańsk on February 11, 1646, now at Wawel Castle (ZKnW-PZS 5520 and ZKnW-PZS 6934), are also attributed to Bartholomeus. As with the portraits of Descartes, Hals and his workshop most likely created several versions and copies of the 1624 portrait, one of which was later copied by Milwitz.
Portrait of Sigismund Guldenstern (1598-1666), aged 26 by Frans Hals, 1624, Wallace Collection in London.
Portrait of Sigismund Guldenstern (1598-1666) by Bartholomeus Milwitz, ca. 1630, Private collection.
Portrait of King Ladislaus IV Vasa (1595-1648) in coronation robe by Bartholomeus Milwitz, ca. 1633, Royal Castle in Warsaw.
Portraits of Sigismund III Vasa and Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa by Gaspar de Crayer
In 2009 a portrait of Mechteld Lintermans (d. 1641) and her two children was put on an auction in New York (oil on canvas, 231.1 x 130.8 cm, Sotheby's, June 4, 2009, lot 15). This painting is considered to be a counterpart to one of the two known full-length portraits of Mechteld's husband Jan Bierens (1591-1641), artistic agent of Ladislaus IV Vasa (1595-1648), elected monarch of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth.
One of these portraits of Bierens, in a breastplate, appeared with the portrait of his wife in the Sulley collection in London, until they were sold as separate lots in 1934. The other, now kept at the Arnot Art Museum in New York (oil on canvas, 235 x 135 cm), comes from the collection of Baron Maximilian van Erp in Rome. The effigies of Bierens and his wife have a very similar composition and dimensions. Mechteld's portrait has been attributed to various Flemish painters, such as Anthony van Dyck, circle of Pieter Claesz. Soutman and Cornelis de Vos. The companion piece, representing Bierens, is not as fine in quality as that of his wife, and has been attributed to another artist of lesser importance than de Vos. Erick Duverger, in his 1995 article on Bierens, suggests that Abraham van Diepenbeeck (1596-1675), the godfather of Maria Bierens, could be the likely author of Mechteld's portrait. "However, while Diepenbeeck was known to paint miniatures of the family, he was never known to have painted large format compositions such as the present canvas". The portrait of Bierens in New York is also attributed to Diepenbeeck, while the effigy of his wife was offered for sale with attribution to Gaspar de Crayer (1584-1669), due to his "ties to the Court, his patronage by the upper-class, and the predominance of formal full length portraits in his oeuvre" (after Catalogue Note by Amy Walsh). De Crayer was a prolific artist drawing inspiration from his various counterparts, including Rubens, van Dyck and Cornelis de Vos, as well as 16th-century Venetian masters, particularly Titian and Paolo Veronese. Like Rubens he also cooperated with painters specialized in certain fields, such as Peter Snayers, a painter known for his panoramic battle scenes (the landscape in portrait of Count-Duke of Olivares by de Crayer is attributed to Snayers). Although born in Antwerp, de Crayer lived and worked in Brussels for most of his life. From 1612 he was in the service of Archduke Albrecht VII of Austria and Infanta Isabella Clara Eugenia of Spain and their successors - Cardinal-Infante Ferdinand of Austria (1609-1641) and Archduke Leopold Wilhelm of Austria (1614-1662), relatives of Ladislaus IV. In 1641 he was appointed court painter to Ladislaus's cousin, King Philip IV of Spain. Furthermore, de Crayer created a large number of altarpieces for churches, monasteries and abbeys throughout his career. Similar to Jan Brueghel the Elder, de Crayer also engaged in activities of an artistic agent for his Habsburg patrons. In 1619 Brueghel, a painter of flower still lifes and cabinet pictures, was released from customs by Albert of Austria for paintings made for Sigismund III, including 9 portraits of European monarchs, which could be by de Crayer or Rubens. Between 1640 and 1645 Gaspar purchased works of art from the Rubens estate for Philip IV. He received many commissions and had a large studio, where he trained a large number of pupils, who retouched and partially completed de Crayer's works, including presumably Anselm van Hulle, Jan Boeckhorst, Nicolas de Liemaeckere, Antoon van den Heuvel, François Duchatel, Jacques d'Artois, Lodewijk de Vadder, Pieter Boel, Jan van Cleve (III), and François Monnaville. Although, according to known sources, he probably never left the Spanish Netherlands, a considerable number of effigies of people he probably never met in person are attributed to him. These include the portrait of Empress Anna of Tyrol (1585-1618), who was a candidate to marry King Sigismund III in 1603, painted around 1612 (Nationalmuseum in Stockholm, NM 408), King Philip IV with a dwarf, from about 1627-1632 (Palacio de Viana in Madrid) and in parade armor, from about 1628 (Metropolitan Museum of Art, 45.128.14) and mentioned portrait of Don Gaspar de Guzmán (1587-1645), Count-Duke of Olivares on horseback, painted between 1627-1628 (The Weiss Gallery in 2018). Olivares was a royal favourite (valido) of Philip IV. Equestrian portraits are frequent in his oeuvre and he and his studio produced numerous versions and copies of these effigies. Around 1635-1640, he produced several versions of the equestrian portrait of Cardinal-Infante Ferdinand. The portrait of King Philip IV on horseback from Neuburg Castle, painted around 1628, could come from the dowry of Ladislaus' sister, Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (Alte Pinakothek in Munich, 2529). At this time he also painted the equestrian portrait of Don Diego Felipez de Guzmán (1580-1655), 1st Marquess of Leganés (Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, GG 9112), while Cornelis de Vos made a portrait of Sigismund III on horseback (Nationalmuseum in Stockholm, NMGrh 2012), both inspired by Rubens's portrait of the Duke of Lerma, painted in 1603 and the portrait of Don Rodrigo Calderón, Count of Oliva from around 1612-1615. Very similar in style and composition to Olivares' equestrian portrait is the portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (later Ladisalus IV) on horseback, which can be found today at Wawel Castle (oil on canvas, 262 x 188.5 cm, 6320). It was purchased in London by Julian Godlewski, residing in Lugano, and offered to the Wawel collections in 1977. From September 6 to October 14, 1624, the Prince, traveling incognito and accompanied by around forty people, stayed in Brussels, Antwerp, at the Breda camp and again in Brussels where he met Rubens. The preparatory drawings could be made during this visit, but they could also be borrowed from Rubens or sent from Poland-Lithuania. What is interesting about this portrait and the effigy of Prince's father by de Vos is that the painter also used the same set of study drawings as in the portrait of Archduke Albert VII of Austria with a view of Ostend. The original version, believed to be lost, is most likely the painting that Jan Brueghel the Elder documented in 1617 in an Allegory of Sight (Prado, P001394). While the original in Brueghel's painting appears rather proportionate, in the copies, probably made by the workshop of Gaspar de Crayer, the Archduke's head and hand have not been skillfully added and he has a grotesque appearance (sold at Dorotheum in Vienna, October 10, 2016, lot 87 and Collections of the Prince of Liechtenstein, GE 402). If all these paintings were originally created for the Coudenberg in Brussels, as some authors believe, the governors of the Spanish Netherlands had a rather peculiar collection of effigies of different monarchs where only a few details differed. Considering the enormous destruction of art in Poland during numerous wars and invasions, we cannot also exclude that an effigy of Sigismund III is the original and not that of Albert VII. The portrait of Bierens kept at the Arnot Art Museum is comparable in style to all the mentioned works of de Crayer. Its composition recalls another painting by him - portrait of the Cardinal-Infante Ferdinand kept in the Prado Museum in Madrid, dated '1639' (P001472). A painting similar in style and composition (baroque twisted column, landscape, fabric) to the effigies of Bierens and his wife is the portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa from Neuburg Castle, now in the Alte Pinakothek in Munich (oil on canvas, 220.5 x 138.2 cm, 4576). It probably also comes from the dowry of Anna Catherine Constance, the king's daughter. Sigismund was depicted with Spanish-style ruff, armor and hose. Similar to the portrait of Sigismund, both in terms of technique and composition, is the portrait of Duke John II of Braganza (1604-1656), future John IV of Portugal, at the Royal Castle in Warsaw, deposited by the Ciechanowiecki Foundation (oil on canvas, 224 x 147 cm, ZKW-dep.FC/25). The portrait of the duke in turn closely resembles the style of Saint Benedict receiving Totila, King of the Ostrogoths in the church of Our Lady of St. Peter's in Ghent by Gaspar de Crayer. Ties between the Commonwealth and Spain at this time were strong, which was reflected in literature (e.g. La vida es sueño by Pedro Calderón de la Barca, premiered in 1635) and fashion. Poles in the royal court frequently wore Spanish clothing, while one of the popular types of hose in Spain during this era were the Polish-style hose (calzas a la polaca de rayas transversales) (after "Glosario de voces de armería" by Enrique de Leguina, p. 194). Even the "fashion" of court favorites (validos) was emulated, intentionally or not, in Poland-Lithuania. Philip III of Spain, brother-in-law of Sigismund III, had as valido the Duke of Lerma, who was succeeded by the Count-Duke of Olivares, under the reign of Philip IV. In the Commonwealth there was the "minister in skirt", influential mistress of Sigismund III, Urszula Mayerin, and later Adam Kazanowski under Ladislaus IV. It was the same for portraiture: if Rubens and de Crayer painted Spanish monarchs, they also worked for their relatives in Poland-Lithuania. A fact which may partly document de Crayer's contacts with the Commonwealth is that he included several figures in eastern costumes in some of his compositions. Among the canvases which could represent the nobles of Poland-Lithuania who visited his workshop, we can mention Saint Benedict receiving Totila, painted in 1633 (Art Gallery of Ontario, 95/140), with the central figure wearing a white-crimson cloak, the Beheading of John the Baptist, painted in 1658 (Saint Bavo Cathedral in Ghent), with the central figure wearing a crimson żupan kaftan and kolpak fur hat and the Martyrdom of Saint Dorothea (sold at Christie's London, auction 6708, April 9, 2003, lot 7), in which the figure of the pagan lawyer Theophilus on the right was most likely inspired by effigies of Emperor Matthias (1557-1619) in Hungarian-Bohemian costume or King Sigismund III Vasa in Polish-Lithuanian national costume. In all the Vasas' contacts with de Crayer and other painters, Bierens, "agent and servant of his Highness the Serene Prince Ladislaus Sigismund, Prince of Poland and Sweden" (agent et domesticque de son Alteze le Sérénissime Prince Wladislaus Sigismundus, Prince de Poloigne et de Suède), also called "agent of the Lord Prince of Poland" (agente del Signor Principe di Polonia), was undoubtedly an intermediary. This merchant-jeweller was the son of Lucas Bierens, a merchant from Eindhoven. He was probably born in 1591 because in 1637 he claimed to be 46 years old and died on July 25, 1641. Bierens owned a house in Antwerp in the Kerkhofstraat, and from the mid-1630s he occupied a spacious residence on the corner of Zwanestraat, made up of two previously separate houses (after "Annotations concernant ..." by Erik Duverger, p. 119-157). Between 1624 and 1627, he supervised the weaving of tapestries with the Story of Ulysses and verdure tapestries made in Brussels by Jacob Geubels the Younger for Ladislaus. In his collection he had "a large painting on canvas with the portrait of prince Ladislaus of Poland" (een groote schilderye op doeck wesende het conterfeytsel van prince Vladislaus van Polen), as well as two gold medals bearing the image of Ladislaus, when he was a prince and after his election as king of Poland.
Equestrian portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa (1566-1632) by Cornelis de Vos, ca. 1625-1630, Nationalmuseum in Stockholm.
Equestrian portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) by Gaspar de Crayer, ca. 1625-1630, Wawel Royal Castle.
Portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa (1566-1632) by Gaspar de Crayer, ca. 1625-1630, Alte Pinakothek in Munich.
Portrait of Duke John II of Braganza (1604-1656) by Gaspar de Crayer, ca. 1630, Royal Castle in Warsaw.
Portrait of Jan Bierens (1591-1641), artistic agent of Ladislaus IV Vasa by Gaspar de Crayer, ca. 1625-1630, Arnot Art Museum.
Portraits of King Sigismund III Vasa by Peter Paul Rubens and workshop of Tommaso Dolabella
The portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa (1566-1632) from the Heinz Kisters collection in Kreuzlingen in Switzerland (oil on canvas, 121 x 91 cm) is considered by experts to be the work of Peter Paul Rubens himself (attributed by Ludwig Burchard), but they also agree that the painter never visited the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth (compare "Rubens w Polsce" by Juliusz A. Chrościcki, p. 135, 176). Any attempt to determine how the painter and the king met would be futile, as Sigismund did not leave the borders of the Commonwealth after his deposition in Sweden (1599).
The portrait must therefore have been made from another effigy of the king or from study drawings sent from Poland. The old age of the king makes it possible to date the work towards the end of his life, it is therefore possible that the author of the initial study was Pieter Claesz. Soutman who stayed in Poland-Lithuania between 1624 and 1628 and who in numerous letters sent from Haarlem between 1629 and 1645 calls himself in Italian: "Painter of His Majesty of Poland" (Pittore di Sua Maesta de Polonia) - for example letters dated December 19, 1644 and February 8, 1645 to Matthijs Musson (1593-1678) (in "Na Peter Pauwel Rubens" by Jean Denucé, p. 26-28). The painting of the Crucifixion with the similar signature of this painter at the foot of the cross (P. P. Soutman Pittore de sua de Polonia f.) is in the Franciscan convent in Seville (Convento de los Terceros Franciscanos) (after "Archivo hispalense ...", Volume 3, p. 385-386). What is also interesting about this painting is that it has long been considered the effigy of the doctor Théodore Turquet de Mayerne (1573-1655), who treated the kings of France and England, due to a certain resemblance to his portraits by Rubens. It was in 1953 that the portrait was reproduced by Horace Shipp in "The Flemish Masters" as an effigy of Sigismund III (after "Un Portrait de Sigismond III ..." by Karolina Lanckorońska, p. 175). If Rubens took drawings or a painting by Soutman as a model, they were sent to him from Brussels or Haarlem. It is also possible that they were made by other painters of the king's court, because a very similar full-length portrait of Sigismund at Wilanów Palace (oil on canvas, 207 x 127 cm, Wil.1164, earlier 572) is definitely not a work of Soutman, nor of Rubens or their workshops. This painting is first mentioned in the Wilanów collection in a catalog of paintings from the mid-19th century. Although the portrait of the king at Wilanów is not as well painted, the most comparable in style seems to be the famous portrait of Stanisław Tęczyński, a masterpiece attributed to the Venetian painter Tommaso Dolabella, active in the Commonwealth, created between 1633 and 1634 (National Museum in Warsaw, 128850, deposited at Wawel Castle). Works painted in the same way include Hetman Stanisław Żółkiewski's presentation of the Shuysky brothers at the Warsaw Diet in 1611 at the Lviv Historical Museum and the Judgment of the Arians in 1638 from the Venetian-style ceiling in the Palace of the Kraków Bishops in Kielce, attributed to the workshop of Tommaso Dolabella. As we can see from the preserved photograph, the portrait of hetman Stanisław Żółkiewski from the Zamoyski Palace in Warsaw (lost during World War II), painted around 1606, was similar in style. When it comes to composition (pose, fabric, table), the most similar is the full-length portrait of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa in the Lviv Historical Museum, most likely created by the workshop of Pieter Claesz. Soutman. Artists from the Dutch Republic and the Spanish Netherlands were considered among the best in Europe in the first half of the 17th century. Painting and printing workshops developed there significantly and provided high quality, so that when in the 16th century customers from Poland-Lithuania preferred Venice, in the following century many books were published in the Netherlands and Flanders. As an example, we can cite Respublica Siue Status Regni Poloniæ, Lituaniæ, Prussiæ, Livoniæ, etc. diuersorum Autorum, published in Leiden in 1627 with a title page showing the coat of arms of Sigismund III Vasa, created by Pieter Serwouters, who had previously created the engraved effigy of the king's son. In 1632, Peter Paul Rubens designed the frontispiece of Maciej Kazimierz Sarbiewski's Lyricorvm libri IV (Plantin-Moretus Museum in Antwerp, MPM.V.IV.058), engraved by Cornelis Galle the Elder and published in Antwerp in 1632 (Pet. Paul. Rubens pinxit, Corn. Galle sculpsit., National Library of Poland, SD W.2.1241). An artist close to Peter Paul Rubens probably made the portrait of Sarbiewski, court preacher of King Ladislaus IV Vasa, considered the most eminent Latin poet of the 17th century (a drawing in the Plantin-Moretus Museum). So, despite the distance, regarding the works of Rubens, the artistic collections of Poland-Lithuania were undoubtedly comparable to those of Madrid or Munich, but today almost nothing is preserved in the former territories of the Commonwealth. In addition to the portrait of Sigismund III in Switzerland, among the works of the master himself (and not of the workshop or the followers) which were probably commissioned by the Polish-Lithuanian Vasas, we can cite the Madonna in a wreath of flowers by Rubens and Jan Brueghel the Elder (Alte Pinakothek in Munich, 331). This painting comes from the Düsseldorf gallery, like the portraits of Sigismund III and his wife in coronation robes (Neuburg State Gallery, 984 and 985). The letter from Juan de Arrazola Oñate, secretary of the Infanta Isabella of September 18, 1619, in which he addressed the general treasurer Monsieur Monfort to release from customs the paintings sent by Jan Brueghel the Elder to Poland, confirms the first known order of Sigismund III (6 landscapes, 9 portraits including portraits of Archduke Albert and the Infanta Isabella and other European monarchs, 3 large battalistic paintings). On October 29, 1621 Jan Brueghel the Elder wrote to his agent, the Milanese nobleman Ercole Bianchi, about sending a lot of paintings to the King Sigismund III Vasa (molti pitture al Re) and in a letter to cardinal Federico Borromeo, dated August 22, 1625 his son refers to a large garland with the image of Mary by Brueghel the Elder sold for 400 escudi to the prince of Poland, "who bought almost all of his works" (... la Madonna, ma è ordinato tutto in un altra maniera che quello delli fiori che tiene v. s. Ill.mo in la biblioteca, e larga tre palmi et alto qualro e medso incirca. El paro di questo fu venduto al sig. Prencipe di Pollonia, il quale compraua quasi tutti li sue opre, lo fu pagato 400 escudi, in "Giovanni Brueghel pittor fiammingo ..." by Giovanni Crivelli, p. 340). This painting could be a gift for the Electors of Bavaria, like the portrait of young Ladislaus Sigismund in a ruff by Rubens or workshop (Neuburg State Gallery, 342), identified by me, or the image of the Polish saint Stanislaus Kostka by circle of Rubens (Alte Pinakothek, 7520). In a letter dated June 8, 1632 from Antwerp to the art dealer Crisostomo van Immerseel, Jan Brueghel the Younger (1632, Amberes 8 Junio Juan Bruegel) refers to Garland of fruits with figures by Rubens, the most important work made by his father, which was sold to Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa for 1,600 florins (te weten den grooten Girlande van vruchten, de beelden van Rubens, het fraijste ent meeste werc dat vader syn leven gedaen heeft gelyc UI can considereren aen den prys twelc het verkocht is, te weten voor 1600 gul. aen den prins van Polen). This painting is sometimes considered as Nature and her followers in the Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum in Glasgow, dating from around 1615 (oil on panel, 106.7 x 72.4 cm, inv. 609, compare "Rubens & Brueghel", edited by Anne T. Woollett, Ariane van Suchtelen, p. 157, 164-165). The March of Silenus depicted in the Art collection of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund, painted in Warsaw in 1626 (Royal Castle in Warsaw, ZKW 2123), was undoubtedly the work of Rubens. Some paintings mentioned in the inventory of the collection of the last Vasa on Polish throne - John II Casimir, sold in Paris in 1673, could be the works of Rubens, such as no. 107, Miracles of Saint Ignatius of Loyola, which might resemble the painting in the Dulwich Picture Gallery (inv. 148) or no. 439, Education of the Virgin, which might be similar to the painting in the Royal Museum of Fine Arts Antwerp (inv. 306). In the room of Count de Buy, king's chamberlain at Nevers, there was "a horizontal painting on canvas, representing nude Cupid arching his bow with two little children between his legs" (un tableau en hauteur, peint sur toile, représentant en nudité un Cupidon, qui bande son arc, avec deux petits enfants entre ses jambes), a copy of Cupid carving his bow by Parmigianino, now in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna (after "Z dziejów polskiego mecenatu ..." by Władysław Tomkiewicz, p. 234). There is a painting by Rubens in Munich dated 1614, which is a copy of the painting by Parmigianino from Vienna whose oldest mention in the electoral gallery dates from 1748 (oil on canvas, 142.5 x 107 cm, 1304), so it is possible that it was acquired in Paris after the death by John Casimir, who managed to evacuate certain paintings from the royal collections to Silesia in 1655 during the Deluge. In Vienna, there is in turn a copy of the portrait of the mother of Sigismund III in white, based on the original by Titian (GG 531), identified by me. The painting which could come from the royal collections of Poland-Lithuania is very well painted portrait of Elisabeth of France (1602-1644), queen of Spain, painted after 1628 and attributed to the workshop of Rubens, now at Wawel Castle (oil on canvas, 58.5 x 46 cm, 6378). The painting comes from the private collection in Kraków (donated in 1978 to the State Collections) and there is no proven link with the royal collections, but this is very likely since many portraits were exchanged with Spain at the beginning of the 17th century. Another painting that could possibly originate from the royal or magnate collections of Poland-Lithuania is the Three Graces Holding a Basket of Flowers from the workshop of Rubens and Jan Brueghel the Younger, painted between 1620 and 1625, today in Nationalmuseum in Stockholm (NM 601). Nothing is known of its early history, except that it had already arrived in Sweden in the 17th century and was part of the collection of Count Magnus Gabriel De la Gardie (1622-1686), who, during the Deluge, plundered with his army a large part of the country. Important contacts contacts of clients from the Commonwealth with Rubens and Flemish painters are reflected in two other paintings from the early 1620s. They depict Tomyris, Queen of the Massagetae (also known as Queen of the Scythians), who led her armies to defend against an attack by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid Empire, and defeated and killed him in 530 BC. One of these paintings is in the Museum of Fine Arts in Boston (oil on canvas, 205.1 x 361 cm, 41.40) and most likely comes from the collection of Infanta Isabella Clara Eugenia of Spain (1566-1633), later, before 1662, in the collection of Queen Christina of Sweden in Rome. The other is in the Louvre in Paris (oil on canvas, 263 x 199 cm, INV 1768 ; MR 991) and comes from the collection of Everhard Jabach (1618-1695), who sold it to King Louis XIV in 1671. A drawing for an engraving (not made), attributed to Pieter Claesz. Soutman, similar to the painting in Paris, is today kept at the Plantin-Moretus Museum (PK.OT.00117). Although the two paintings mentioned, in Boston and Paris, are attributed to Rubens or his school, their style is closer to the works of Gaspar de Crayer, painter to the court of the Infanta, notably portraits of Sigismund III and Constance of Austria, attributed by me. Queen Tomyris ordered Cyrus' body brought to her, then decapitated him and dipped his head in a vessel of blood in a symbolic gesture of revenge for his bloodlust and the death of her son. The original painting by Rubens, engraved by Paulus Pontius in 1630 (Rijksmuseum, RP-P-OB-70.057), inscribed: "Satiate thyself with that blood which thou hast always thirsted for" (SATIA TE SANGVINE QVEM SEMPER SITISTI) and signed: Petrus Paulus Rubens pinxit. / Paulus Pontius sculpsit., differs in many details from the Boston painting. The original must therefore be considered lost. A reduced copy of Rubens' painting dating most likely from the 17th century was in the Kielce Cathedral, whose portal was founded by Cardinal John Albert Vasa in 1635. This painting is now in the Diocesan Museum in Kielce. It should be also noted that the queen in both paintings bears a close resemblance to the effigies of the Infanta Isabella Clara Eugenia, notably the portrait in the style of Gaspar de Crayer at the National Gallery in London (NG3819) and by Rubens and Jan Brueghel the Elder at the Prado Museum in Madrid (P001684). In both compositions, the Queen's soldiers wear traditional costumes of the nobles of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, another perfect illustration of the destroyed and forgotten Realm of Venus at the height of its wealth and power before the Deluge, and a powerful warning to all tyrants. Already around 1522, Andrzej Krzycki (1482-1537), secretary of Queen Bona Sforza, in an epitaph dedicated to Anna Radziwill (1476-1522), compared the Duchess of Masovia to Queen Tomyris (Qualis erat Tomyrisque suae Cleopatraque genti, / Qualis Amazonio Penthesilea solo, / Talis erat fecunda tibi, Masovia tellus, / Anna Radiviliae gloria magna domus).
Cupid carving his bow by Peter Paul Rubens after Parmigianino, 1614, Alte Pinakothek in Munich.
Nature and her followers by Peter Paul Rubens and Jan Brueghel the Elder, ca. 1615, Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum.
Portrait of Hetman Stanisław Żółkiewski (1547-1620) by workshop of Tommaso Dolabella, ca. 1606, Zamoyski Palace in Warsaw, lost during World War II.
Portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa (1566-1632) by workshop of Tommaso Dolabella, ca. 1625-1632, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
Portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa (1566-1632) by Peter Paul Rubens, ca. 1625-1632, Heinz Kisters collection in Kreuzlingen.
Portrait of Elisabeth of France (1602-1644), Queen of Spain by workshop of Peter Paul Rubens, after 1628, Wawel Royal Castle.
Queen Tomyris orders that Cyrus' head be lowered into a vessel of blood, with figures in traditional costumes of the nobles of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth by Gaspar de Crayer, 1620s, Louvre Museum.
Queen Tomyris orders that Cyrus' head be lowered into a vessel of blood, with figures in traditional costumes of the nobles of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth by Pieter Claesz. Soutman, 1620s, Plantin-Moretus Museum in Antwerp.
Queen Tomyris orders that Cyrus' head be lowered into a vessel of blood, with figures in traditional costumes of the nobles of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth by Gaspar de Crayer, 1620s, Museum of Fine Arts in Boston.
Queen Tomyris orders that Cyrus' head be lowered into a vessel of blood, with figures in traditional costumes of the nobles of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth by Paulus Pontius after Peter Paul Rubens, 1630, Rijksmuseum Amsterdam.
Portrait of Zygmunt Kazanowski by Gaspar de Crayer
From September 6 to October 14, 1624, the young nobleman of the Grzymała coat of arms, Adam Kazanowski (ca. 1599-1649), friend and valet of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa, stayed in Brussels and Antwerp with the prince and about forty people of his entourage.
The two-week stay in Brussels was a series of grand entertainments and parties in honor of the prince, organized by Infanta Isabella Clara Eugenia of Spain (1566-1633). In Antwerp, they visited the studios of various painters, including Peter Paul Rubens and Jan Brueghel the Elder, as well as the the gallery of Cornelis van der Geest. During this trip, Kazanowski kept an album Liber Amicorum in which the entries of the Habsburgs, such as Archduke Leopold V of Tyrol (no. 11), Archduke Leopold William (13) and her sister Cecilia Renata, future Queen of Poland (16), made in Vienna, and many Spanish diplomats appear. In Munich, we find the inscriptions of Maximilian I, elector of Bavaria and his wife (45-46), in Augsburg members of the Fugger family (48-51), in Brussels of the Infanta (54), Geneviève d'Urfé, Duchess de Croy (65) and the Spanish nobles. After a stay in Italy, they returned to Warsaw in May 1625. The following year, 1626, Kazanowski's album contains entries from Spanish diplomats in Poland-Lithuania - Jean de Croÿ, Count de Solre and Charles de Bonnières, Baron d'Auchy (no. 145-146), as well as Louis de Custine, seigneur de Villers-le-Rond, maître de camp of the Infanta (June 26, 1626, no. 147, all three came from the Spanish Netherlands), and other Spanish and French envoys (after "Biblioteka Warszawska", 1853, Volume 2). They show how important contacts with Spain and the Spanish Netherlands were for the young Kazanowski. Between 1627 and 1628 Adam studied in Padua. In the following years, and especially after the election of Ladislaus as new king, his wealth and influence increased considerably. As the new king's favourite, he replaced the influential "minister in a skirt" Urszula Meyerin (1570-1635), and his position can be compared, in some respects, even to that of Gaspar de Guzmán, Count-Duke of Olivares, favourite (valido) of Philip IV of Spain, cousin of Ladislaus. In 1639-1642, Kazanowski attempted to force an anti-French military alliance with Spain and in the spring of 1639 he negotiated with Philip IV's envoy, D. Fernando de Monroy (d. 1656). From 1642 he was the Court Marshal of the Crown (mareschalus curiæ) whose usual powers included supervision of the royal court and being deputy to the Grand Marshal of the Crown. When he received a palace from Ladislaus in 1632, he enlarged and embellished it. This magnificent building was second only to the Royal Castle in size, but was larger than the palace of Chancellor Jerzy Ossoliński, the palace of the Grand Hetman of the Crown Stanisław Koniecpolski, and perhaps even larger than the Villa Regia (Royal Villa), as visible in a print by Nicolas Pérelle from 1696 representing Warsaw around 1655. This print was made after a drawing by a Swedish military engineer, Count Erik Dahlbergh. It is interesting to note that in comparison with a print made by Adam Pérelle after another drawing by Dahlbergh, showing the capital of the empire which wanted to destroy the Commonwealth (Treaty of Radnot) - Stockholm in 1669, we see a clear difference. Dahlbergh, who knew how to glorify the Swedish Empire, sometimes enlarged the buildings in his drawings and made them more grandiose. However, while in the panorama of Warsaw the structures are of comparable size, in the panorama of Stockholm the Royal Castle (Arx Regia, Tre Kronor) dominates the center of the composition and the entire urban landscape. In the Ossoliński Palace, between the portraits of the chancellor's ancestors, Roman emperors and historical paintings, there was a portrait of Ladislaus IV with the inscription "First among equals" (Primus inter pares) (after "Piękno ocalone ..." by Maria Lewicka, Barbara Szymanowska, p. 44). In republican Poland-Lithuania, magnates boldly competed with the king in many areas, including patronage. Like the king, Kazanowski most likely also acquired and commissioned works of art in the Netherlands and Italy, including his effigies, however nothing has been preserved in Poland. He also received from the king many valuable objects, such as a painting of the Lamentation of Christ by Rubens, painted on wood, which in 1840 belonged to Mr. Piotr Romanowicz, a lawyer in Lviv (after "Rzecz o obrazach ..." by Ludwik Zieliński, z. 3, Lwowianin, p. 63). He may also have received such objects from his Spanish and Belgian friends and, like them, commissioned the paintings from the same painters. In the "Polish Varieties" (Rozmaitości Polskie / Variétés polonaises) from around 1833, a collection of engravings by Antoni Oleszczyński (1794-1879), there is an interesting full-length effigy of Kazanowski. While in the effigies of Jan Karol Chodkiewicz (d. 1621) and Lew Sapieha (1557-1633), he created a neo-Gothic or a background with panoplies, in the image of Kazanowski he used a background similar to that visible in a portrait of Ladislaus IV's cousin - Anne of Austria (1601-1666), Queen of France, made by Rubens' workshop between 1620-1625 (Louvre Museum, INV 1794 ; MR 984). It was also used in a portrait of a woman seated in an interior by Gonzales Coques (private collection). However, if in the portrait of the queen and the woman the background is almost identical, in the engraving by Oleszczyński the niche behind Kazanowski is different and shows a scene with a dancing naked woman and a bear. Adam Jarzębski in his "The main road or a brief description of Warsaw" (Gościniec abo krótkie opisanie Warszawy) from 1643 mentions in the Marshal's Palace many paintings, including "Naked people above the table" (Nad stołem nagie osoby, verse 1097). If Oleszczyński copied the background of the original painting, the painting was probably created by Rubens' studio or by another Flemish painter. On August 13, 1634, Adam's father Zygmunt Kazanowski died in Warsaw. Together with his brother Stanisław Kazanowski (1601-1648), starost of Krasno, who was removed from the court by Sigismund III for promiscuity, Adam founded a magnificent marble tomb for his father. In 1843, the monument was transferred to Warsaw Cathedral from the demolished church of the Bernardine nuns, located near the royal castle. It was destroyed during a German bombing of the cathedral in 1944. The monument was made of multicolored marble, similar in shape to the altar. The base was carved from brown stone, on which were two pillars with white Corinthian capitals. In the middle, on a black slab, a white marble bas-relief depicted Kazanowski kneeling before the Virgin Mary (after "Katedra św. Jana w Warszawie ..." by Wiktor Czajewski, p. 99-100). Zygmunt was represented in national costume, as was the custom for funerary monuments, because at court the majority of people preferred foreign costume, so that an unknown poet before the Deluge exclaimed: "Nowadays, you can barely recognize Poles, there are Italians, French, in great number at the courts" (after "Jakuba Teodora Trembeckiego ..." by Aleksander Brückner, Volume I, poem 165). Although in everyday life or at court the people preferred foreign costume, in the official portraiture they always wanted to underline their attachment to the Commonwalth and its traditions with an appropriate costume. This monument is attributed to the sculptor Conrad Walther from Gdańsk and his workshop and, according to specialists, it was made mainly from imported limestone, mainly from Belgium - "Belgian black" from the province of Namur (Noir Belge, Noir de Namur) and very expensive English alabaster (after "Lapidarium warszawskie" by Michał Wardzyński, Hubert Kowalski, Piotr Jamski, p. 288). Zygmunt was chamberlain during the reign of kings Stephen Bathory and Sigismund III Vasa, then tutor and court marshal of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund. During the military expedition of 1617-1618, as advisor to the prince, he intrigued against Chodkiewicz, the supreme commander. Zygmunt's two sons, Adam and Stanisław, were raised at the royal court and were friends of Ladislaus Sigismund, exerting influence over the young prince. At the funerals of King Sigismund and Queen Constance, Zygmunt carried the royal insignia. In 1627 he handed over the villages of Grzymałów, Kazanów and Ciepielów to his sons. In 1607, Seweryn Bączalski dedicated a panegyric to Kazanowski: "The Polish crown, very sad, makes heartfelt requests ..." (Korona polska barzo smutna prośby serdeczne czyni), praising Zygmunt as a model of honesty, masculinity, chivalry, piety, courtly customs and reason, so that the king found him worthy and entrusted him with guardianship of his son. Others have compared Kazanowski to Aristotle, the teacher of Alexander the Great. Kazanowski's employment as the prince's tutor was a turning point in his life, and probably that of the entire family. He was considered a friend both by Catholics, such as Albert Stanislaus Radziwill, and by Protestants, such as Christopher Radziwill, Duke of Birzai. He owned several boats located on the Vistula, near Solec in Warsaw (after "Kariera rodu Kazanowskich ..." by Krzysztof Zemeła, p. 45, 47-48), and thus participated in river transport and Gdańsk's trade. In the National Gallery in London is a "Portrait of a Man" by the Flemish painter, previously attributed to Rubens and Jordaens (oil on canvas, 116.2 x 85.8 cm, NG1895). It was purchased from T. Humphrey Ward, Clarke Fund, in 1902. The pose of the model and the composition are directly inspired by the portrait of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund, produced by Rubens in 1624 and engraved by Paulus Pontius (Ex Archetypo Petri Pauli Rubenij Paulus Pontius fecit anno MDCXXIIII, National Library of Poland, G.10661/II). Similar to Ladislaus, the old man wears a Spanish-Flemish costume. The fact that the man in this portrait wanted to be depicted in a similar way to the Crown Prince of Poland-Lithuania indicates that he was someone close to him, which has led to interpretation that it is a portrait of Prince's father Sigismund III (compare "Rubens w Polsce" by Juliusz A. Chrościcki, p. 178). This was a common practice at that time, for example the equestrian portrait of Don Diego Felipez de Guzmán (1580-1655), 1st Marquis of Leganés, cousin of the powerful valido Count-Duke of Olivares, painted by Gaspar de Crayer between 1627-1628 (Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, GG 9112), is very similar in many respects to the portrait of Olivares on horseback, painted by de Crayer and Peter Snayers (landscape) at the same period (The Weiss Gallery in 2018). The man cannot be Sigismund III, because according to the original Latin inscription he was 63 years old in 1626 (ÆTATIS SVE / 63 1626), while the king at that time was 60 years old (born 1566) and the man does not wear the Order of the Golden Fleece, which should be included in the Spanish-Flemish style portrait. The London portrait also bears a coat of arms, which, however, was painted in a different style and was added later, because the inscription indicating the age, which should normally be skillfully placed under the emblem, is in this case moved to the right. The position of the inscription, close to the edge and almost cut off, indicates that the painting was probably cut when the coat of arms was added. The emblem is identified as belonging to the De Waha family, whose estates were close to Namur, from where the marbles for Kazanowski's tomb were acquired. In previous publications the model is called Baron Waha de Linter of Namur, but no connection with a concrete member of this family has ever been established. It is possible that they owned the portrait and when the sitter's identity was lost he was considered a member of the family, and perhaps around 1816, when they were given the title of baron, the coat of arms was added. The man in the portrait bears a great resemblance to Adam Kazanowski's father as shown in his funerary sculpture (ear shape, mustache, eyebrows) and is comparable to effigies of Adam - after a painting by Peter Danckerts de Rij and an engraving by Jeremias Falck Polonus. His age also matches perfectly with Zygmunt, the marshal of the princely court, who was 63 years old in 1626 when several Spanish-Flemish envoys arrived in Warsaw - he was 71 years old at the time of his death in 1634 according to the inscription on his tomb, therefore born in 1563 (placide vitam cum morte commutavit Varsaviæ die XIII Augusti anno Christi MDCXXXIV ætatis suæ 71 patri desideratissimo Adamus tituli paterni successor). The style of this painting is closest to the mentioned equestrian portraits of the Marquis of Leganés and the Count-Duke of Olivares, painted by Gaspar de Crayer, court painter to the Infanta Isabella Clara Eugenia, and to the portrait of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund kept in the National Museum in Warsaw (M.Ob.2434 MNW), considered to be the 17th century copy after Rubens' original.
Portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (1595-1648) by Paulus Pontius after Peter Paul Rubens, 1624, National Library of Poland.
Portrait of Zygmunt Kazanowski (1563-1634), marshal of the court of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa, aged 63, by Gaspar de Crayer, 1626, National Gallery in London.
Portrait of Adam Kazanowski (ca. 1599-1649), Court Marshal of the Crown by Antoni Oleszczyński after lost original by Gaspar de Crayer from about 1642 (?), ca. 1833, National Library of Poland.
Portrait of Archduchess Cecilia Renata of Austria by Justus Sustermans
"It was reported here that the Polish prince had left the kingdom to marry the daughter of the emperor [Ferdinand II] or the king of Spain [Philip III], which caused great suspicions in the [Turkish] empire", wrote the English ambassador in Istanbul in a letter to London about the journey of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa between 1624-1625. He also added that Queen Constance of Austria, his stepmother, tried to create a faction supporting her oldest son of John Casimir Vasa in his bid for the throne. English ambassador in distant Istanbul had good informants, because at the meeting of the Consejo de Estado in Madrid on November 1624, the letter of Infanta Isabella Clara Eugenia, written in Brussels, was discussed. The Infanta asked King Philip IV for permission to marry the Polish prince with infanta Maria Anna of Spain (1606-1646), the king's sister and cousin of Ladislaus Sigismund as the daughter of his mother's sister. One of the participants of this council commented as follows: "Marriage with a Polish prince is very good, but with a German prince it is more advantageous". Concerning the marriage with the emperor's daughters, there was the lack of consent of Pope Urban VIII to a possible dispensation for the marriage of the prince with a close relative Archduchess Maria Anna (1610-1665) or Cecilia Renata (1611-1644), who eventually became his first wife (after "Świat polskich Wazów: eseje", p. 48, 280-281, 311).
In order to prove to his son that the daughters of his uncle Emperor Ferdinand II were not affected by disabilities, unlike their mother Maria Anna of Bavaria (1574-1616), Sigismund III Vasa had them specially portrayed, as reported Bishop Giovanni Battista Lancellotti, papal nuncio in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, in a letter dated March 17, 1627 to Cardinal Francesco Barberini (Scuoprì meco di nuovo SM l'intento suo desiderio d'accasarlo con una delle figliuole dell'imperadore per altro aborrite da SA asserendo ella questa esser derivata in quelle da certa natural indispositione della loro madre e mi disse SM d'haverne fatto venir qua i ritratti per certezza del contrario) (after "Das Leben am Hof ..." by Walter Leitsch, p. 2378). It is not known whether these effigies were good or faithful, perhaps as in the case of the portraits of Sigismund's aunt Anna Jagiellon or his two wives they were nude paintings, however, later in a letter written in Warsaw on October 31, 1644, Ladislaus requested from Cardinal Mazarini reliable portraits of candidates for his second wife. During his stay in Vienna on June 23, 1624, the prince had the opportunity to meet the emperor's two daughters. He also admired the emperor's artistic collections, including "a set of portraits of many emperors and other notable figures of the House of Austria". In Salzburg he saw "various paintings", in Munich the Antiquarium and in Augsburg the paintings of the Fugger family. Philipp Hainhofer, connoisseur and art agent from Augsburg, recounts in his diary that the prince gave him "unusual trinket made of yellow amber". In Nuremberg, Ladislaus Sigismund admired "the famous paintings by Dürer" and the ceiling paintings by Rubens. In the 1620s, two daughters of Emperor Ferdinand II were frequently depicted and their effigies were sent to various friendly courts in Europe, including that of Poland-Lithuania (all probably destroyed or lost during the wars). Most of them are close in style to the works of the Flemish painter Justus Sustermans, court painter of the Medici family, who between 1623 and 1624 worked in Vienna on commission from the emperor. In a painting from the Esterházy collection at Forchtenstein Castle, probably made by the Sustermans workshop, Maria Anna and Cecilia Renata are depicted together. The two sisters kneel together behind their mother Maria Anna of Bavaria and their stepmother Eleonora Gonzaga (1598-1655) in a votive painting of Emperor Ferdinand II by Matthias Mayer, painted in 1631 for St. Vitus Cathedral in Prague. A few years later, around 1640, a painter close to Frans Luycx created similar effigies of the imperial family kneeling before Virgin in the Dominican church in Vienna, when Cecilia Renata, was already queen of Poland and her sister Maria Anna, electress of Bavaria (their likenesses were inspired by other portraits sent to Vienna). Among the portraits of Maria Anna made by Sustermans and his studio is a painting from Neuburg Castle (Alte Pinakothek in Munich, inventory number 2792). This is a copy of a painting from the Medici collection, now kept at the Medici Villa of Cerreto Guidi (inv. 1890 / 4275), which is considered to represent Princess Eleonora de' Medici (1591-1617), daughter of Ferdinando I de' Medici, as well as another similar portrait of Maria Anna's sister Cecilia Renata in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence (inv. 1890/2297), however, both are "clearly identified as Emperor Ferdinand's daughters in the 1624 inventory of the Villa del Poggio Imperiale and as Emperor Ferdinand's sisters in the 1654-1655 inventory" (after "The Grand Duke's Portraitist ..." by Lisa Goldenberg Stoppato, p. 35). A copy of the mentioned effigy of Cecilia Renata from the Uffizi (inv. 1890 / 2297), is also in Munich (inv. 6958), but the model's face is damaged. It is believed to represent Archduchess Margaret of Austria and also comes from Neuburg Castle. The two archduchesses were also depicted in two similar portraits from the Wallenstein gallery, today at Hrádek u Nechanic Castle (after "The Wallenstein portrait gallery in the Cheb Museum", p. 71). In these effigies, Maria Anna (inv. 3318 / 3802) and Cecilia Renata (inv. 3320 / 3804) look very similar and wear identical Spanish costumes. One of them was also represented in a painting at the Royal Castle of Racconigi, which was the official residence of the Carignano line of the House of Savoy, attributed to the Flemish painter (oil on canvas, 64 x 49 cm, R 5576). The woman was formerly identified as Princess of the House of Savoy and now as Margaret of Austria (1584-1611), Queen of Spain and Portugal. Her face more closely resembles the effigy of Cecilia Renata from the Uffizi (inv. 1890 / 2297) and Hrádek u Nechanic (inv. 3320 / 3804). A very similar effigy of the Queen of Poland was reproduced in an anonymous etching made before 1700 (Leipzig University Library, 8/61) with an inscription in German: Cecilia Renata ErtzHerzogin zu Osterreich / Uladislas Königs in Pohlen Gemahlin. Comparison with later effigies of the two sisters - portraits of Maria Anna, Electress of Bavaria by the circle of Joachim von Sandrart, created around 1643, from Dachau Castle (Alte Pinakothek in Munich, 3093) and from the Medici collection, identified by me (Pitti Palace in Florence, inv. 1890 / 5261) and Cecilia Renata by Peter Danckerts de Rij also painted in 1643, at Gripsholm Castle, most likely looted during the Deluge (signed: Peter. Danckers fecit A:o 1643, Nationalmuseum in Stockholm, NMGrh 299) and reduced version from the Marble Room at the Royal Castle in Warsaw (State Historical Museum in Moscow, И I 5922 / 74493), indicates that it is a portrait of the future Queen of Poland because the electress has a pointed nose. The style of this painting is particularly close to the portraits of Cecilia Renata's relatives at the Pitti Palace in Florence - her father Emperor Ferdinand II (Palatina 209), her stepmother Eleonora Gonzaga (Palatina 203) and her uncle Archduke Charles of Austria (1590-1624), prince-bishop of Wrocław as Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights (Palatina 293). All these paintings were made by Justus Sustermans around 1623. Since this effigy is a version of a portrait at Hrádek u Nechanic, showing her around 1626-1627, it could be made on the occasion of the preparation of the likenesses for Sigismund III. The color of the dresses of the two archduchesses (white and red, used as the national colors of Poland-Lithuania in the so-called "Stockholm Roll" from about 1605, Royal Castle in Warsaw, ZKW/1528/1-39) in paintings in Hrádek u Nechanic and in a portrait in Racconigi could also indicate that one of them was considered a future queen of Poland in 1627.
Portrait of Archduchess Cecilia Renata of Austria (1611-1644), future Queen of Poland by Justus Sustermans, ca. 1626-1627, Royal Castle of Racconigi.
Portrait of Archduke Charles of Austria (1590-1624), Prince-Bishop of Wrocław by Justus Sustermans, ca. 1623, Pitti Palace in Florence.
Portraits of Sigismund III Vasa and Constance of Austria in coronation robes by Gaspar de Crayer
"A life-size portrait that shows the emperor in pontifical attire, with a crown on his head, with a scepter in his right hand and a royal orb in his left, this is the king of Poland" (No. 26/22) and "Portrait of the empress, dressed in silver cloth, with a scepter in her right hand and an orb in her left hand, his wife" (No. 27/23), this is how the inventory of the Coudenberg Palace in Brussels from 1659 describes the portraits of King Sigismund III Vasa and his second wife Constance of Austria in coronation dresses, known from the copies, today in the Neuburg State Gallery.
The Brussels paintings could be the paintings that Pieter Claesz. Soutman brought from Poland-Lithuania in 1628 for Infanta Isabella Clara Eugenia of Spain (1566-1633), governess of the Spanish Netherlands, but nothing is known of their author and the paintings were probably destroyed in an accidental fire which declared itself on the night of February 3, 1731. Three other portraits of Sigismund's son and successor Ladislaus IV were also included in the collection of the governors of the Spanish Netherlands - in full length when the prince in national costume with a hand on his sword (No. 40/36), in a hat by Peter Paul Rubens (No. 122/84) and in crimson costume, called Hungarian (No. 123/85) and another portrait of Sigismund with a hat and a fur-lined coat (No. 124/86) (compare "Rubens w Polsce" by Juliusz A. Chrościcki, p. 158, 162, 214). The Neuburg portraits have a similar composition (so-called pendants) and dimensions (oil on canvas, 220.5 x 131.8 cm, 984 and oil on canvas, 219 x 132.7 cm, 985). The two are believed to come from the dowry of the Infanta Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651), the daughter of Sigismund and Constance, and would therefore have been made shortly before her marriage in Warsaw in 1642. Both have also been attributed to Soutman (after "Portrety tzw. koronacyjne ..." by Jerzy Lileyko, p. 377). Portraits of monarchs were frequently produced in series and sometimes copied by different painters. It is possible that the originals were actually created by Soutman before 1628. However, although the attribution to this painter is now rejected, the portraits in Neuburg are clearly made by a painter trained in Flanders, as their style indicates. The king and his son organized the orders and transport of works of art through their agents including Jan Bierens (1591-1641), as well as another Antwerp merchant and financier Joris Descamps. He acted as an intermediary in transferring 1,000 and then 800 florins from a bank in Amsterdam to Rubens as an outstanding payment for paintings for Sigismund III. At the same time, Descamps agreed to transfer another 1,000 florins from an Amsterdam bank for the previously delivered paintings for Ladislaus Sigismund's collection. The letter of July 16, 1626 mentions two further creditors of the prince, namely the already mentioned Bierens (290 florins) and a certain Jacob Wijz or Weez (20 thalers). Among the prince's agents was also the Frenchman Mathieu Rouault, who was commissioned in September 1625 to deliver the objects purchased in Antwerp to Gdańsk. On one occasion, Spanish border guards at Dunkirk found and confiscated from his traveling trunks portraits of the French royal family, namely Henry IV and his wife Marie de Medici, Louis XIII and his wife Anne of Austria, Gaston, Duke of Orléans and Cardinal Richelieu, as well as effigies of King James I of England, Infanta Isabella Clara Eugenia and her husband Archduke Albert of Austria, Archduke Ernest of Austria, Emperor Ferdinand II and Elisabeth of Lorraine, Electress of Bavaria (after "Świat polskich Wazów: eseje", p. 290-291). In many ways, including fashion and patronage, the elected monarchs of the Commonwealth emulated the rulers of the greatest empire of the time, Spain. Although there were many prominent painters in Spain, artists from other regions of the empire frequently worked for the Madrid-based court, the Spanish Habsburgs, their relatives and allies. This is how the painting collections of Florence (Uffizi, Pitti Palace), Vienna (Kunsthistorisches Museum, Hofburg), Munich (Alte Pinakothek, the Residence) are in many aspects comparable to those of Madrid (Prado, historical Alcazar), especially when it comes to the portraits exchanged between countries. Therefore the royal collections of the Commonwealth before 1655 should be comparable, unfortunately almost all perished in deliberate destruction by invaders, burning and looting. Several important portraits of Queen Constance's nephew, King Philip IV of Spain, were made by Gaspar de Crayer, court portraitist of his aunt the Infanta Isabella Clara Eugenia (like the equestrian portrait in the Prado Museum in Madrid, P001553), who probably never met the king in person. It is known that between 1621-1622 de Crayer painted the king and his wife Elisabeth of France for the Chamber of Accounts of Brabant, but these works have been lost. The portraits of Juan de Velasco and his brother José de Velasco, probably painted around 1620 during their stay in Brussels, are attributed to Gaspar, who even in his later works did not apply the loose brushwork of Rubens's painting, but continued to work in the traditional style with which he perhaps responded to a preference of his customers (after "Gaspar de Crayer ..." by Hans Vlieghe, Volume I, pp. 43, 213, 251-252). In his later works we can see more of the influences of Anthony van Dyck and Paolo Veronese, best seen in the signed painting depicting Saint Ambrose, created around 1655 (Prado, P005198, signed lower right: GAS. DE CRAYER FE.), as part of a series of the Holy Founders from the convent of Saint Francis in Burgos. As for the composition, the portrait of the King and Queen of Poland in Neuburg follows the same convention with a full-length representation and an open loggia in the background. In terms of style, the paintings more closely resemble the portrait of Mechteld Lintermans (d. 1641), wife of Jan Bierens (Sotheby's New York, June 4, 2009, lot 15), which is dated 1625-1630 and portrait of Juan de Velasco (1574-1621), secretary to King Philip III of Spain, brother-in-law of Queen Constance (private collection in Cantabria). Thus created before van Dyck's influences became more visible in his work from 1631 onwards. In the Alte Pinakothek in Munich, another similar effigy of Queen Constance from Neuburg Castle is preserved, therefore probably also from her daughter's dowry. This "portrait of a lady", attributed to the German School, is in a poor state of conservation (oil on canvas, 77 x 59 cm, 6807), however the style of de Crayer is noticeable as well as a similarity with the portrait of brother of Juan de Velasco - José (1571-1623) (private collection in Madrid). Regarding the Brussels paintings, around 30 years after their creation, the notion of who was represented was very vague. If it was not clearly stated that this is an effigy of the Polish king in the inventory, the entries could be considered to concern effigies of members of the Habsburg family - the emperor and his wife. The main document confirming de Crayer's contacts with clients from the Commonwealth is his letter to Matthijs Musson (1593-1678) in Antwerp, dated December 2, 1645 from Brussels, concerning the arrival of Krzysztof Opaliński (1609-1655), voivode of Poznań, envoy of King Ladislaus IV Vasa, and his entourage: "We were informed that the Poles would be here on Friday or perhaps Thursday. They have seen an Assumption of Our Lady at Lier that I made for the Jesuit Fathers and they desire a copy" (Wy hebben hier avies dat de Polacken zullen hier wesen vrydagh oft mogelyck donderdach. Zy hebben gesien een Hemelvaert van Onse live Vrouwe tot Lier die ick hebbe gemackt voor de paters van Jesuiten en hebben begeert eene copye) (after "Na Peter Pauwel Rubens ..." by Jean Denucé, p. 36). Opaliński visited the painter's workshop and ordered a copy of his Assumption. 19th-century copies of portraits of the king and queen in coronation robes can be found at Wawel Royal Castle (8555, 8556). The copies from the Przeździecki collection in Warsaw and the collection of Leopold Méyet, also in Warsaw, were most likely destroyed during the Second World War.
Portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa (1566-1632) in coronation robes by Gaspar de Crayer, ca. 1630, Neuburg State Gallery.
Portrait of Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631) in coronation robes by Gaspar de Crayer, ca. 1630, Neuburg State Gallery.
Portrait of Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631) by Gaspar de Crayer or workshop, ca. 1630, Alte Pinakothek in Munich.
Portraits of Prince John Casimir Vasa by Rembrandt
Polish-Lithuanian kings and aristocrats owned many works by Rembrandt, his workshop or followers, he frequently painted people in costumes very similar to these known from effigies of the Polish-Lithuanian nobility, he began his career in the workshop of supplier of the King of Poland and married his relative, he lived in Amsterdam, where tons of Polish grain, large quantities of fur and other products were shipped every year in the 17th century, yet he allegedly painted no Pole known by name (concerning preserved effigies).
Due to the lack of written sources explicitly confirming it even the "Polish rider" or the "Polish nobleman" by Rembrandt or his school are questioned as possibly not representing Polish-Lithuanian people, the same with the "Queen of Poland" by Rembrandt's pupil Ferdinand Bol. This vast, multicultural country with incomprehensible languages, an elective monarchy, religious tolerance and the growing influence of papists and Habsburgs, represented all the evil of this planet for pious Protestants. They must have welcomed the fact that Calvinist Prince of Transylvania George II Rakoczi (1621-1660) joined other contries and invaded the Polish-Lithuanian Commonweath from the south during the Deluge (1655-1660). Joost Cortwiert published in 1657 in The Hague an eight-page Dutch-language pamphlet entitled "A manifesto by George Rakoczi, prince of Transylvania, containing the reasons why he is attacking the kingdom of Poland with his army" (Manifest van Georgius Ragotsky, prins van Transilvanien. Vervattende de redenen waer om hy metsyn chrijchs-macht int koninck-rijck Polen valt). Also around that time a portrait of this important ally was published, though due to the lack of a proper effigy, possibly by mistake, an earlier print by Jan van Vliet after a painting by Rembrandt was used. It was created in 1631 and represents an eastern prince, who however bear no resemblance to other effigies of George II Rakoczi (1621-1660) or his father George I (1593-1648) (compare "323 The Rákóczy identity" by Gary Schwartz). This likeness was also published as a portrait of Skanderbeg (1405-1468), Lord of Albania. The march of Rakoczi army towards Warsaw was marked by atrocities, destruction, and looting. Simultaneously, Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski's forces organized a revenge invasion of Transylvania. After the defeat and subsequent retreat of his Cossack allies, Rakoczi capitulated to Lubomirski, promising to break his alliance with Sweden and abandon the royal city of Kraków. Not only pople were killed, property looted, buildings destroyed, but foreign invasion triggered epidemic diseases, profound economic crisis and ethnic cleansing. People who survived the invasion were struggling to survive in destroyed country, like in Kazimierz Dolny on the Vistula River, the mannerist gem of the Commonwealth, which raised into prominence after 1561 thanks to grain trade as an important river port. The city was ransacked and burned in February 1656 by the troops of the Brigand of Europe (as he was called by Stefan Czarniecki), Charles X Gustav of Sweden, who invaded the country from the north, and again by Transilvanian troops in 1657. Before 1661 the troops of Stefan Czarniecki destroyed the local synagogue and killed many Jews, who were accused by the Catholics of supporting invaders. From one of the wealthies nations in Europe, Poland-Lithuania has become one of the poorest. The opulent magnate and royal residences were ransacked and burned. One preserved document - inventory of goods transported to Stockholm from Warsaw by March 9, 1657 lists "188 large and small paintings and portraits painted on panel and canvas" (188 St. stoora och små Skillerij och Conterfey på trää och lerfft måhlat), "One painting from the altar, painted on wood" (1 måhlat alltaretafla af trää duger intet) and "Oil paintings which were in coffered ceilings in Warsaw, from five rooms" (Schillerij som hafwer suttit under taket i Warschow till 5 Cambrer af Wattnferger) from the inventory of items taken from the Warsaw Castle in 1656 (after "Inwentarz przedmiotów wywiezionych z Warszawy ..." by Katarzyna Wagner). Venetian-style gilded frame ceilings in royal residences were filled with oil paintings, similar to these preserved in the Palace of the Kraków Bishops in Kielce, created by workshop of Tommaso Dolabella (1570-1650) in about 1642, or in the Koniecpolski Castle in Pidhirtsi (Podhorce) near Lviv in western Ukraine, also by workshop of Tommaso Dolabella and Dutch painter Jan de Baen (1633-1702), a pupil of Jacob Adriaensz Backer in Amsterdam (1640s and 1660s). Polish shipments of grain and other products to Amsterdam virtually ceased during the invasion, but Johann Köstner, a Gdańsk merchant, pointed out in 1660 that Holland had managed with grain from elsewhere. Curiously, however, the decline in Rembrandt's career coincided with the invasion of the Commonweath. On 24 November 1655 the 14-year-old Titus, the fourth and only surviving child of Rembrandt, made his last will and testament and named his father as his sole heir, including what he had inherited from his mother. The painter, who lived beyond his means, failed to pay off the loans. In 1656 he filed for bankruptcy and his property was sold. The monarch of the Commonweath at that time was John II Casimir Vasa, the eldest son of Sigismund III and his second wife Constance of Austria, elected by the Polish-Lithuanian Parliament to succeed his half-brother Ladislaus IV in 1648. During the Deluge he fled to Silesia taking some of the most valuable items from the royal collection. Already in 1626, during the Toruń Sejm, he was proposed by his mother's supporters and on her initiative as a candidate for the heir to the throne. Simultaneously, at the end of the 1620s, contacts between the Polish-Lithuanian royal court and the Dutch Republic intensified. Abraham van Booth secretary of the Dutch delegation that visited Poland between 1627-1628 with a mediation mission in the dispute that arose between Sigismund III Vasa and Gustavus Adolphus, King of Sweden, created some drawings, including of the Royal Castle in Warsaw and audience before Sigismund III in the Old Senate Chamber. The ultra-Catholic camp in the Commonwealth, by which Prince John Casimir was considered the leader, lost its importance after the sudden death of the queen in 1631. Between 1632 and 1635, Ladislaus IV sought to enhance his influence by negotiating John Casimir's marriage to Queen Christina of Sweden, his distant relative. John Casimir, a great patron of the arts like his father and brother, was probaly one of the first royal connoisseurs of Rembrandt's art. The king had in his collection a painting of "Diana bathing and Actaeon" by Rembrandt (Un tableau en hauteur, peint sur toile, qui est un bain de Diane avec Acteon) sold in 1673 in Paris to François Andrault de Buy de Langeron (item 88 of the inventory). His residence in Nieporęt near Warsaw, "a masterpiece of carpentry" according to Jean Le Laboureur who visited the palace on March 3, 1646, was richly decorated mainly with Flemish tapestries. Before 1643 Samuel von Sorgen paid to an unknown painter in Vienna, most probably Frans Luycx, "ad rationem altars to Nieporęt" and in 1651 a Dutch architect and a Mennonite Peeter Willer (or Willert) built a lock in Nieporęt on the Narew river, a "Dutch house" (a hunting manor) and a brewery, and in Warsaw a pavilion called "pleasure house" (lusthauz) for Queen's ladies at the Villa Regia Palace and a mill. Possibly after his accession to the throne around 1649 John Casimir's court painter, Daniel Schultz, created his portrait to the Marble Room at the Royal Castle in Warsaw. Schultz was trained in the Netherlands and he studied in Leiden in 1643 (most likely he is mentioned as "Daniel Schultz Borussus"). The mentioned portrait from the Marble Room, very in Rembrandt's style, shows the king in a tall fur hat, a shirt and a chain very similar to the portrait of a man in profile with feathered cap and long wavy hair in private collection in Germany, monogrammed lower left 'RHL', exactly as a print by Jan van Vliet, signed in the plate 'RHL. v Rijn. jn. / 1631. / JG v. vliet fecit' (compare "323 The Rákóczy identity" by Gary Schwartz). This portrait, most probably one of a series, was undoubtedly a model to van Vliet's print. The same profile was also included in a study drawing or preliminary sketch by Rembrandt in the Barber Institute of Fine Arts in Birmingham. The young man with protruding lower lip resemble greatly other effigies of John Casimir (especially his marble bust by Giovanni Francesco Rossi), who was 22 years old in 1631 when the portraits were created and inherited the Habsburg (Masovian) jaw from his mother Constance of Austria. The same year Rembrandt moved from Leiden into the house of an art agent to King Sigismund III Vasa, Hendrick van Uylenburgh, in Amsterdam. Rembrandt became chief painter of the studio and in 1634 married Van Uylenburgh's relative Saskia. Also in 1631, two important Polish-Lithuanian magnates arrived to the Netherlands, Janusz Radziwill (1612-1655) to Leiden and Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski (1616-1667) to Louvain in the Spanish Netherlands (possibly also to Leiden that year).
A sheet of figure studies with a portrait of Prince John Casimir Vasa (1609-1672) by Rembrandt, 1630s, The Barber Institute of Fine Arts.
Portrait of Prince John Casimir Vasa (1609-1672) in a fur hat by Rembrandt or follower, ca. 1631, Private collection.
Portrait of Prince John Casimir Vasa (1609-1672) in a fur hat by Jan van Vliet after Rembrandt, 1631, Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam.
Portraits of Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski by Rembrandt and Ferdinand Bol
In 1629, Jerzy Sebastian (1616-1667) and his older brother Aleksander Michał (1614-1677), sons of fabulously rich voivode of Ruthenia Prince Stanisław Lubomirski (1583-1649), set out to study abroad. Aleksander was 15, and Jerzy 13 years old. Jakub Piotrowicki, Catholic priest and professor of the Kraków Academy, became their guardian, they were also accompanied by steward Sebastian Kokwiński. The first destination was the Jesuit university in Ingolstadt (September 17, 1629). From there they went to Leuven/Louvain in the Spanish Netherlands in 1630, where there was also a Catholic university, very popular with the Polish nobility and magnates, and to Cologne in 1632. Then in April 1633 Jerzy Sebastian was in the Protestant Leiden to study military engineering and there he probably met Janusz Radziwill (1612-1655), a Calvinist, who was also studying there. Later he visited England, France, Spain and Italy. During these journeys, he learned the art of fortification, rhetoric, grammar, mathematics, languages, and he had the opportunity to meet foreign nobles and monarchs. He returned to Poland in 1636.
Between 1639-1641, a Flemish painter Mattheus Ingermann (Ingenraen) from Antwerp, who studied painting in Rome, worked as a court painter of Stanisław Lubomirski (Jerzy Sebastian's father), portraying his son Aleksander, which is confirmed by the preserved inventory of the Wiśnicz gallery. His "Annunciation" fom the chapel of the Wiśnicz Castle is today in the Saint Anne's Church in Warsaw-Wilanów. He also made large-format paintings for the Carmelite Church in Nowy Wiśnicz. After Stanisław's death in 1649 his three sons Jerzy Sebastian, Aleksander Michał and the youngest Konstanty Jacek (1620-1663) managed the estates including the opulent Wiśnicz Castle. During the Deluge (1655-1660) Aleksander Michał secured some rich furnishings of the Wiśnicz estate (Castle and Monastery), taking them to Spiš. Leaving Wiśnicz on September 19, 1656, the army of the Brigand of Europe, as he was called by Stefan Czarniecki, king Charles X Gustav of Sweden, plundered the most valuable things and reportedly took away as many as 150 wagons of precious loot and 35 cannons. The "Inventory of belongings spared from Swedes and escapes made on December 1, 1661 in Wiśnicz" in the Central Archives of Historical Records in Warsaw, lists some of the preserved paintings, mainly by Italian masters like Raphael, Titian, Veronese, Guido Reni, Guercino, Domenichino, from the Flemish names are only Paul Bril and Daniel Seghers, but next to them the inventory lists plenty of Flemish and Dutch paintings, "in general, much more than Italian paintings", according to Jerzy Mycielski (1856-1928) - meeting of the Commission for the Study of Art History in Poland on February 26, 1903, moreover, the portraits of the Lubomirski family, painted in Venice by Nicolas Régnier (Niccolò Renieri) and in Gdańsk by Daniel Schulz. In 1660 Jerzy Sebastian invited to Poland Tylman Gamerski (Tielman van Gameren, born in Utrecht), a Dutch architect and engineer, who was at that time working in Venice, reportedly as a painter of battle scenes. From 1674 Gamerski worked in the Royal Ujazdów Castle in Warsaw, devastated during the Deluge and sold to Jerzy Sebastian's son Stanisław Herakliusz Lubomirski (1642-1702). One of the earliest works of possibly most gifted pupil of Rembrandt, Carel Fabritius (1622-1654), the Raising of Lazarus in the National Museum in Warsaw painted in about 1643 (signed CAR.FABR.), comes from the Lubomirski estate in Ujazdów (before 1702 most probably in the St. Anne's Church in Ujazdów together with a a statue of dead Christ by Flemish sculptor Giusto Le Court). Some members of the Lubomirski family also owned paintings by Rembrandt or his circle. Before 1790 in the collection of Count Lubomirski in Lviv there was a Portrait of a young man (oil on canvas 71 x 59.7 cm), attributed to Barent Fabritius and later to Samuel van Hoogstraten (after "Rembrandt After Three Hundred Years ..." by Jay Richard Judson, Egbert Haverkamp Begemann, p. 74). The catalog of paintings from the collection of Countess Eleonora Teresa Jadwiga Lubomirska née Husarzewska (1866-1940), exhibited in Lviv in 1909 ("Katalog ilustrowany wystawy mistrzów dawnych ..." by Mieczysław Treter, item 52, p. 18), is the oldest surely documented provenance of the painting by Rembrandt or follower, today kept at the Indianapolis Museum of Art (2023.4). According to the catalog, the painting was signed and dated lower left: f. R. H. 1628 (year not visible today). It is considered one of the earliest of his self-portraits. The painting was probably evacuated from Poland during World War II (1939-1945) by its owners. The Countess also owned "Hagar's exile in the wilderness" by School of Rembrandt (oil on canvas, 75 x 52 cm, item 56, p. 19). Majority of preserved effigies of Jerzy Sebastian come from his later years and were created by Flemish artists, including a portrait by Jan de Herdt (Royal Castle in Warsaw), created in about 1664. Portrait of a young man with a sword by Ferdinand Bol in Dayton Art Institute (oil on canvas, 205.7 x 130.8 cm, 1962.18), depict a man in rich princely costume. His heavily embroidered velvet tunic, pose and oriental sabre are very similar to effigy of King Ladislaus IV Vasa from "Het Groot Balet" (Caricature of the peace negotiations after Battle of Lützen) in the Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam, anonymous print created after 1632. Very similar leather shoes in Polish style, together with velvet arrow case and quiver were offered by John II Casimir Vasa, elected monarch of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, to five year old king of Sweden Charles XI in about 1660. They are also visible in famous Polish Rider (Lisowczyk) by Rembrandt or his circle, which most probably depict Marcjan Aleksander Ogiński (1632-1690), colonel of the Polish-Lithuanian light cavalry. The latter painting, today in the Frick Collection in New York City, comes from the Polish royal collection (acquired in 1791 by king Stanislaus Augustus Poniatowski). Ogiński was portraited by Bol at the time of his studies in the Netherlands. This effigy bearing the inscription MO / STR (bottom right), identified as "Marcjan Ogiński / Starost of Trakai", and showing him in a fur hat is in a private collection (after "O amerykańskich polonikach Rembrandta ..." by Zdzisław Żygulski, p. 49). Bol, who was the same age as Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski, both born in 1616, was brought as a child to Amsterdam. He must have entered Rembrandt's studio at an early age, probably when he was about sixteen (after Emile Michel "Rembrandt, His Life, His Work and His Time", Volume 1, p. 244). Described portrait is dated to about 1635-1640, therefore most probably when Lubomirski was no longer in the Netherlands, however, this does not exclude the possibility that it was made on the basis of drawings created earlier in the artist's atelier or sent from Poland. Jerzy Sebastian's oriental style sabre and horse tack are today in the Czartoryski Museum in Kraków. The same man was depicted in two paintings by Rembrandt or his circle. One entitled Young man with a plumed hat, today in the Toledo Museum of Art (oil on panel, 81.3 x 66 cm, 1926.64), was created in 1631 when Rembrandt moved to Amsterdam from his native Leiden (monogrammed and dated lower left: RHL. 1631), to live in the house of the artistic agent of the King of Poland. The second, in the North Carolina Museum of Art (oil on canvas, 118.1 x 96.5 cm, GL.60.17.68), signed and dated '1633' in upper right corner, shows the man holding a heavy ancient sword, similar to Bronze Age swords found in Nowy Żmigród, south-eastern Poland, not far from Lubomirski estates in Łańcut and Nowy Wiśnicz, today in the Subcarpathian Museum in Krosno. He is not a simple soldier, he is a tremendously rich connoisseur, a descendant of the ancient belligerent Sarmatians (legendary ancestors of Polish nobility), trained in Leiden as a military engineer.
Portrait of Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski (1616-1667) with a pumed hat by Rembrandt or circle, 1631, Toledo Museum of Art.
Portrait of Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski (1616-1667) with an ancient sword by Rembrandt or circle, 1633, North Carolina Museum of Art.
Portrait of Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski (1616-1667) with an oriental sabre by Ferdinand Bol, 1634-1640, Dayton Art Institute.
The Raising of Lazarus by Carel Fabritius, ca. 1643, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Daniel Mikołajewski by Frans Hals
In 1632, the so-called Gdańsk Bible, a translation of the Holy Scriptures into Polish, one of the most popular Polish Protestant translations, made jointly by the Czech Brethren and the Calvinists, was published in the main port of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. The main role in the creation of this translation was played by Daniel Mikołajewski (1560-1633), superintendant of Greater Poland congregations. For his translation he used earlier Polish, Latin, French, German and Czech texts.
This new edition was published in the printing house of Andreas Hünefeld (Andrzej Hunefeld, 1581-1666), more than half a century after the Brest Bible, published in 1563 in Brest (Belarus) on the initiative of Nicolaus "the Black" Radziwill (1515-1565). Although it bears the date 1632 (MDCXXXII), printing was probably completed early the following year (1633) because the letter from the translation's main patron Prince Christopher Radziwill (1585-1640) to King Ladislaus IV, published as a preface (before the dedication to the prince), is dated December 4, 1632 (Z Orla 4. Decembris Roku Pańskiego M DC XXXII). Mikołajewski completed his work in 1623, for which he was thanked by the provincial synod of Oksza (1625), but the issue of printing the Bible dragged on for several years, because of the Lithuanians, who insisted on reprinting the Brest Bible with only a few really necessary corrections. For this reason, the decision to print the Bible was not approved until 1629. The translator himself zealously supervised its progress. Also Hünefeldt put a lot of effort and financial resources into the work. He took care of the proofreading, which was done seven times for each sheet. Following the example of Dutch publishing houses, he wanted to produce cheap Bibles in a small, handy format (after "Pismo Święte w języku polskim ..." by Ks. Rajmund Pietkiewicz, p. 311, 315). Hünefeld, born in Halberstadt in Saxony, came from a Dutch family (after "Rocznik gdański", Volume 50, p. 141). He was a Calvinist and worked as a factor, that is, technical manager of the printing house of Wilhelm (Guillaume) Guillemot (Guilemonthanus, died in 1606) in Gdańsk. Guillemot and his wife arrived in Gdańsk from the Netherlands in September 1603. Two years after Wilhelm's death, in 1608, Hünefeld married his widow and thus became the owner of the printing house. He grew the business by importing fonts, initials, and other typographical and decorative resources, probably mostly from Antwerp. The title page of the Bible was most likely commissioned in Amsterdam, as it was made by the Dutch engraver Cornelis Claesz. Duysend, whose stay in Poland-Lithuania is not confirmed (signed: Cornelis Claeßen Duysend Sculpsit., National Library of Poland, SD XVII.3.4795). In many cases, despite the distance, customers from the Commonwealth turned to specialists in the Netherlands. In 1633, Hünefeld published another work by Mikołajewski, the funeral sermon on the death of Mikolaj Latalski, Count of Łabiszyn (Sermon pogrzebny nad szlachetnym ciałem [...] Mikolaia Latalskiego ...). In January of the same year, Daniel convened the synod in Ostroróg in Greater Poland, but he fell ill while visiting his sick friend Jakub Gembicki (1569-1633) in Dębnica near Gniezno, and died there on April 8, in the 73rd year of his life. Daniel was a nobleman of the Habdank (Abdank) coat of arms. He was born in 1560 in the royal town of Radziejów as the son of Jan Mikołajewski. After beginning his studies in his hometown, he attended several universities in Germany. He returned to the Commonwealth in 1586 (after "O kościołach Braci Czeskich ..." by Józef Łukaszewicz, p. 371-372). In 1591, he was ordained a minister in Radziejów and in 1597, he became the senior of the Reformed congregations in Kuyavia. In 1601 he went to Basel and Geneva, where he met Theodore Beza. At the Tokyo Fuji Art Museum in Tokyo, Japan, there is a portrait of an older blond man, attributed to Frans Hals (oil on canvas, 102.9 x 88.9 cm, inv. 1235). Before 1833, the painting was owned by William Danby (1752-1833), an English writer, in Swinton Park, England. The man, in a black costume with a white ruff, holds his left hand over a small sized book, most likely a Bible, in a gesture of a preacher referring to the Holy Scripture. On the book there is an inscription in Dutch: Gerustheyt des gemoets, which means "Peace of mind". This may be a quote from the book or another phrase important to the sitter, possibly referring to peace among Christians, such as the fragment from "Vlaardingen's mount rhetoric" (Vlaerdings Redenrijck-bergh, met middelen beplant ...), containing the contributions to the Vlaardingen contest of 1616, published in Amsterdam in 1617 (Gerustheyt des gemoets, daer by der Kercken vrede). This inscription, however, does not mean that the man was Dutch or even that he knew the Dutch language, like people today who make tattoos with inscriptions in Hebrew or Chinese and referring only to a culture or a specific concept. Moreover, as an important preacher and superintendent of Calvinist congregations in a country with a considerable Dutch community, Mikołajewski was undoubtedly an important person to them, as well as for the notable Calvinists of the Commonwealth, who undoubtedly had his effigies. Items 270/1 to 291/22 of the 1671 inventory of paintings from the collection of Princess Louise Charlotte Radziwill (1667-1695), granddaughter of Prince Christopher Radziwill, list portraits of priests and notable foreigners (including Dutch), such as "The unfinished painting of Father Rejnold", i.e. portrait of Reinhold Adami, rector of Slutsk schools, who accompanied Janusz Radziwill on a trip abroad in 1628 (272/3), "Two paintings of priests" (273-4/4-5), "Another priest" (275/6), Duc d'Ora[n]gie (281/12) and "Admiral Dump [Maarten Tromp, admiral of the Dutch navy]" (284/15), but also "A person in black costume in German style, black hair" (270/1) and "A person in black costume in German style, yellow hair" (271/2, compare "Inwentarz galerii obrazów Radziwiłłów z XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska), which could be a copy of the painting by Hals. The man's millstone ruff, known as such because of its resemblance to millstones for grinding grain, is still worn today by Lutheran pastors in northern German cities such as Hamburg, Lübeck, Wismar, Rostock, Stralsund and Augsburg in southern Germany as well as in Denmark, the Faroe Islands and Greenland. A very similar ruff was depicted in the portrait of a member of the Sanguszko family in the District Museum in Tarnów (MT-A-M/196). According to the Latin inscription on the right, the man was 73 years old in 1633 (ÆTAT SVÆ 73 / AN° 1633) exactly like Mikołajewski, when his most important work - the Gdańsk Bible was finally completed and he convened the synod in Ostroróg.
Portrait of Daniel Mikołajewski (1560-1633), superintendant of Greater Poland congregations, aged 73, by Frans Hals, 1633, Tokyo Fuji Art Museum.
Portrait of a member of the Sanguszko family by Anthonie Palamedesz.
Around 1880, Edward Trzemeski photographed the Eastern Antechamber of the Koniecpolski Palace in Pidhirtsi, near Lviv. It is one of the rare preserved representations of this splendid interior filled with numerous paintings. Above the door hung several portraits, including a portrait of a woman in millstone ruff, placed between the portrait of Anna Kiszczanka (1593-1644), Princess Radziwill and the portrait of Christina Kiszczyna née Drutska-Sokolinska (d. 1640), identified by me.
A very similar portrait, known as the "Portrait of a young Dutch woman", is now kept in the District Museum in Tarnów (Museum of Tarnów Land, Dębno Castle, oil on panel, 64.5 x 48.5 cm, MT-A-M/196). It comes from a collection of 26 portraits from the Sanguszko (Sangushko) collection at the Gumniska Palace in Tarnów. 17 images are signed with the inscription: Sławuta, related to the Volhynian seat of the Sanguszko family in Slavuta (Ukraine), including the "Portrait of a young Dutch woman" and portraits of members of the Sanguszko family from the 17th to the 19th century (after "Pamiątki wołyńskie ..." by Jacek Feduszka, p. 410). The rich Slavuta Palace, which housed many Dutch, Flemish and Italian works of art, was looted and burned in 1917, during World War I, by the Russian army and demolished in 1922. The family managed to evacuate some works of art before the war, such as the mentioned portraits and verdure tapestries, decorated with the Sanguszko coat of arms, made in the Netherlands or Flanders or by Dutch/Flemish weavers in Poland-Lithuania, one today in the São Paulo Museum of Art (MASP.00793, gift of Prince Roman Sanguszko) and seven others at the Wawel Royal Castle, probably made in the 17th century. In the Sanguszko collection, the "Portrait of a young Dutch woman" was considered to depict the family member - Zofia Sanguszkowa née Hołowczyńska (d. 1605), member of the Ruthenian Golovchinsky family, daughter of Jarosław and Halszka née Chodkiewicz, wife of Hryhoriy Sangushko of the Kashyrskyi line, castellan of Lubaczów. In the 19th century, a piece of paper was affixed to the back of the painting, confirming this traditional identification of the model, questioned in recent publications in which the painting is considered to represent a Dutch patrician. The model's costume indicates that indeed it was probably not Zofia Sanguszkowa who was depicted, as similar effigies are generally dated to the 1630s, so almost three decades after her death. A somewhat similar portrait of a woman with a book by Willem van der Vliet from the collection of Jan Feliks Tarnowski, now in the National Museum in Kraków, is dated 1636 (ÆTATIS 56 / Ao 1636, MNK XII-A-881). Another alleged portrait of Zofia, with a coat of arms and an inscription from the 18th century, is in the Lviv Historical Museum. It depicts a woman in a costume from the 1630s, similar to that in Anthony van Dyck's portrait of Amalia de Solms-Braunfels (1602-1675), Princess of Orange (Prado Museum, P001483). The style of this painting is comparable to the works of Tomasz Muszyński, active in Lublin. It is also worth noting that not only written sources confirm the popularity of Dutch and Flemish costumes in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, but also some survived effigies, such as the portrait of a noble family as donors in the National Museum in Kraków, most likely painted in the 1620s or 1630s, in which a woman's ruff, bonnet and dress closely resemble those in portrait from the Sanguszko collection. The style of the painting resembles works signed by Anthonie Palamedesz. (1602-1673), Dutch painter active in Delft, such as portrait of a lady, sold in Bonn in 2022 (Plückbaum Auction House, October 29, 2022, lot 1272). The city of Delft was at this time also an important center of tapestry weaving – many tapestries produced for Commonwealth's clients are attributed to the workshop of Maximilian van der Gucht (1603-1689) in Delft. Since the Sanguszkos probably ordered their tapestries in the Netherlands, they could also order their effigies there. Zofia Sanguszkowa had two daughters - Aleksandra (1594-1625), who entered the Bernardine monastery in Lviv in 1613 under the name Magdalena, and Anna, wife of Jerzy Krasicki (d. 1645), starost of Dolina and standard-bearer of Halych, and a son Adam Aleksander (d. 1653), who married Katarzyna de Służewo Uchańska (d. 1650). Who knows, maybe Anna or Katarzyna were models for this portrait.
Portrait of a young woman in a ruff, probably member of the Sanguszko family, by Anthonie Palamedesz. or circle, second quarter of the 17th century, District Museum in Tarnów.
Portrait of Prince Vladislav Dominik Zaslavsky-Ostrogsky by follower of Frans Hals
On June 12, 1633, a wealthy heir to the Zaslavsky and Ostrogsky fortunes, Prince Vladislav Dominik (d. 1656) married Zofia Pudencjana Ligęzianka (d. 1649), who was set to receive a dowry of 60,000 florins in cash and 10,000 in jewelry. At the age of about 15, the groom was the owner of huge estates in southern Poland and Ruthenia - 23 towns and about 400 villages and allodial estates consisting of 19 towns and about 160 villages. Shortly after the marriage, the young magnate was sent with the nobles Florian Zamoyski and Piotr Minocki on an educational trip, first to Padua and then to Bologna. He also visited Leiden, Paris, Lyon, Florence, Loreto, Rome, Naples and Pozzuoli. In November 1635 he returned to the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth by sea via Gdańsk, probably from the Netherlands, and the journey cost 26,053 zlotys (compare "Akademickie niestatki ..." by Jarosław Pietrzak, p. 17-18).
Most likely in Gdańsk, in 1635, Bartholomeus Strobel painted the magnificent portrait of the prince, depicted in a rich French costume, today in the Wilanów Palace (Wil. 1654) and soon after he or his entourage also painted a full-length version, now kept in the National Art Museum of Belarus (ЗЖ-106). Vladislav Dominik was born before June 22, 1618 because he is mentioned in a document of this date issued by his maternal grandfather Prince Janusz Ostrogski (1554-1620) regarding the inheritance of the Ostroh estates. From the earliest years, the prince's entire education was managed by a council of tutors headed by his mother, Euphrosyne Zaslavska née Ostrogska (d. 1628), as well as Bogusław Radoszewski, bishop of Lutsk and Marcin Szyszkowski, bishop of Kraków. Before going on an educational trip abroad, the prince studied at the Kraków Academy. The studies in Protestant Leiden were probably important to the tutors or to the prince himself, as his two younger brothers Constantine Alexander (1620-1642) and Janusz Isidore (1622-1649) also studied there. After studying in Padua (from October 1638), the Zaslavsky brothers and their tutor Jan Hieronim Rychłowski moved to the Netherlands in 1641, where they received 12,000 guilders from the the guardians to continue their studies. Janusz Isidore died suddenly at the age of 22 and his funeral took place in Leiden on July 15, 1642. The ceremony, postponed for several months, brought together many Poles from all over the Netherlands in Leiden. It was honored by a speech by the Dutch scholar Marcus Zuerius van Boxhorn (1612-1653), linguist and professor at the University of Leiden, published in 1642 - Oratio in excessum illustrissimi et splendidissimi principis Constantini Alexandri, principis Ostrogiae, ducis Zasłaviae etc. Prince Zaslavsky-Ostrogsky was known for his lavish lifestyle. He spent enormous sums on his constant travels around the country, to organize entertainments, such as concerts by royal artists, performances by actors, hunting, and to maintain his own music orchestra. Fixed sums were spent on paintings, drawings and books. The inventory of his property from 1657 contains 415 paintings, mainly portraits, 887 books and a small number of drawings and graphics. The gallery of mainly Netherlandish paintings, founded by prince's father Alexander (d. 1629), was supplemented by other works brought from abroad and purchased later (after "Bartłomiej Strobel ..." by Jacek Tylicki, p. 185). In addition to portraits by Strobel, another painted portrait of Vladislav Dominik, full-length, in national costume is known, today kept in the Wilanów Palace (Wil.1167). It was previously believed to be the effigy of his great-grandfather Constantine Vasily (1526-1608), Prince of Ostroh, and it was correctly identified by me in 2014 by comparison with a lost drawing with Vladislav Dominik's portrait from the mid-17th century (National Museum in Warsaw, Rys.Pol.2500). His father, educated at the universities of Ingolstadt, Padua and Bologna, who according to Kasper Niesiecki (1682-1744), "did not spend much on his clothes", had warned him before leaving to study abroad "not to change the Polish costume" (after "Tłuścioch wilanowski ..." by Jacek Żukowski). The registers of the magnate's movable property from 1649 and 1656 list French-style costumes, purple doublets including one embroidered with silver, an alomont of green cloth, numerous sleeves, a pair of silk and cotton stockings, belts studded with precious stones and numerous jewels. Thus, not only during his journey and shortly afterwards, as evidenced by the portrait by Strobel, the prince wore foreign costumes. Later, an anonymous pamphlet ridiculed the education of Vladislav Dominik abroad: "He was not like his father and mother / raised carelessly and licentiously by his guardians [Catholic bishops] / Introduced to all kinds of pleasures in Kraków / Under the name of liberal arts. / A lazy, inactive, stupid heir and a luxury-loving young man / Who, rushing contemptuously abroad / learned nothing in Padua, indulging in pleasures". In the Anhalt Picture Gallery-Georgium in Dessau there is a portrait of a boy in a ruff-like collar, previously attributed to Frans Hals and now to a follower (oil on panel, 66 x 50 cm, inv. 62). It comes from the collection of Princess Henriette Amalie of Anhalt-Dessau (1720-1793), who purchased the majority of the paintings privately and at auction, notably during the auction of the estate of Caroline Louise of Waldeck and Pyrmont (1748-1782), Duchess of Courland in Frankfurt in January 1783 (after "Catalog der Gemälde-Sammlung der Fürstlichen Amalienstiftung zu Dessau", p. 3, 27). Courland was then part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. The boy looks very similar to Prince Zaslavsky-Ostrogsky from his mentioned portraits. According to the inscription at the top left, the portrait was created in 1634, when the prince was traveling and studying abroad, and the sitter's age is read as 15, but the last digit is indistinct (AETATIS SUAE. 1[5?] / FH A 1634) (compare "Die holländischen Gemälde ...", ed. Alexandra Nina Bauer, p. 63). The number could also be 16 or 18, which generally corresponds to Vladislav Dominik's age in 1634, considered to have been born between 1616 and 1618. Despite that no paintings by Hals are found today in public collections in Poland, several come from Polish historical collections, such as two portraits from the collection of the last elected monarch of the Commonwealth Stanislaus Augustus Poniatowski (1732-1798), now in private collection (compare "Frans Hals" by Henricus Petrus Baard, p. 71-72) or two portraits from the collection of Count Maurycy Zamoyski (1871-1939) in Warsaw (Saint Louis Art Museum, 272:1955 and The Nelson-Atkins Museum of Art, 31-90). The man in the portrait, which comes from the collection of Counts Branicki in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 79.5 x 58.5 cm, Sotheby's London, December 4, 2013, lot 35), could be, like Vladislav Dominik, a visitor to the Netherlands from the Commonwealth.
Portrait of Prince Vladislav Dominik Zaslavsky-Ostrogsky (d. 1656) by follower of Frans Hals, 1634, Anhalt Picture Gallery-Georgium in Dessau.
Portrait of a man in black with lace collar from the Branicki collection in Warsaw by Frans Hals, 1635-1640, Private collection.
Portraits of Anna Kiszczanka by Rembrandt and Giacinto Campana
"May I have, honorable lady, according to your dignity, / A golden gift for your name day / And foreign countries subtle works" (Żebym miał, zacna pani, według twej godności / Na twoje imieniny upominek złoty / I krajów cudzoziemskich subtelne roboty), expressed his wishes on St. Anne's Day in 1633 in a poem dedicated to Anna Kiszczanka (1593-1644), Princess Radziwill, court poet Daniel Naborowski (after "Anna Kiszczanka Radziwiłłowa ..." by Mariola Jarczykowa, p. 95-97, 102-103).
It was written in a gloomy atmosphere of war with Moscow, when during the royal election after the death of Sigismund III Vasa, the Russian army, supported by Sweden, attacked the eastern border and besieged Smolensk. Naborowski praised Princess Anna's piety, which was confirmed in a letter from the Calvinist minister Baltazar Krośniewicz from Birzai (August 29, 1617). In 1631, with her husband Christopher Radziwill (1585-1640), she founded "a large brick church in the square of Kedainiai" and a Calvinist school. Moreover, they founded "a second brick church and a cemetery for evangelical funerals on the mountain near our manor house, on the square they call Januszów. There, in Januszów, we are building a hospital for the poor, the elderly, the infirm, the disabled and the sick" (after "Upamiętnienie Radziwiłłów ..." by Aliaksandr Prudnikau, p. 92-93). Kiszczanka's strong anti-Catholic sentiment best illustrates the document of June 8, 1644. This is an extract from the tribunal files containing the protest of Mikołaj Karol Białozor, the parish priest of Kedainiai, against Anna, for not allowing the Corpus Christi procession in Kedainiai. She arrived in town on the eve of the celebration, i.e. on May 25, 1644, and imposed penalties on all those who would go in the procession the next day. On the holiday itself, she ordered the bridge to be blocked, which prevented the procession from passing (after "Katolikom nabożeństwa zabroniła ...", Habemus Documentum, AGAD 1/354/0/10/707). Anna was the daughter of Stanislaus Kiszka and Elizabeth Sapieha and the heiress to huge estates, including Kedainiai. She married Christopher in 1606, when she was only 13 years old. Of their six children, two survived to adulthood, Janusz (1612-1655) and Catherine (1614-1674). Her son, Janusz, graduated from the Calvinist gymnasium in Slutsk and went to study abroad at the age of 16. He continued his studies in Leipzig, Altdorf and Leiden. In 1632, as Commonwealth ambassador, he visited France and England. A year later, in 1633, after having hired 1,000 infantrymen and 200 dragoons in the Netherlands, he returned to Poland-Lithuania and participated in the Smolensk war. In the summer of 1628, Boguslaus Radziwill (1620-1669), who lived in Germany with his mother, after her second marriage was entrusted to the care of his uncle and aunt and moved to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. Boguslaus was educated, like earlier Janusz, by Protestant pastor Paweł Demitrowicz, who had previously been the rector of Calvinist schools in Vilnius and Slutsk. Shortly after becoming a courtier of King Ladislaus IV Vasa, he also went to study in the Netherlands in 1637, like his cousin Janusz. Among the best painted effigies of the two cousins are portraits created by Dutch painters - the portrait of Janusz by David Bailly (1584-1657), painted around 1632 in Leiden (National Museum in Wrocław, VIII-578) and the portrait of Boguslaus, attributed to Willem van Honthorst (1594-1666), painted around 1665 as his costume indicates (private collection), perhaps on the occasion of his marriage to his Catholic relative Anna Maria Radziwill (1640-1667). Due to connections of the Protestant branch of the Radziwill family in Europe, in 1633, during the Smolensk war, the bedridden Prince John Casimir Vasa proposed to marry Anna's daughter Catherine. Her father, however, undoubtedly involved in the two Protestant unions desired by the king - John Casimir was to marry Queen Christina of Sweden and Ladislaus wanted to marry her mother Maria Eleonora of Brandenburg, politely refused. Catherine Radziwill lived with her sick mother - Princess Anna wrote to her husband from Birzai on October 9, 1628 that she had ulcers on her left ear. She drank thermal water and finally went to recover in 1632 in Cieplice Śląskie-Zdrój, according to a letter from Dolatycze near Novogrudok to Janusz, dated July 9. In Kapyl, on the advice of doctors, the princess "took steam in the bathtub" (after "Zdrowie Władysława IV" by Rumbold z Połocka, p. 171-172). To commemorate their son and his cousin Anna and Christopher founded two towns named after them - Januszpol near Kedainiai and Bogusławpol near Minsk, which were to become important craft and trade centers. Due to the decline of the Protestant lineage of the Radziwill family after the Deluge, Januszpol and Bogusławpol lost their names. On August 17, 1643, the widow Anna Kiszczanka issued the privilege for Januszpol, also known as Januszów and Janopol, confirming that the majority of its inhabitants were foreigners, invited to settle in the new town by her husband. According to the document, "I was greeted by the famous inhabitants of my town, Januszów, people of foreign nations, recruited by various letters of his majesty the prince, voivode of Vilnius, grand hetman of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, my husband". Responding to the request of the people of Januszpol, Anna ordered her governor of Kedainiai, Andrzej Przystanowski, sword-bearer of Samogitia, to measure the squares and distribute them to people "coming from foreign nations". The new residents were freed for 10 years from all monetary and customs charges to the princely treasury. The settlers of Januszpol and Kedainiai were mostly evangelical refugees from Scotland, England, the Netherlands and Germany. In a letter dated January 12, 1612 from Hamburg, Daniel Naborowski informed his patron Christopher Radziwill about the recruitment of Englishmen in the Netherlands (after "Korespondencja i literatura okolicznościowa ..." by Mariola Jarczykowa, p. 114). The architecture of Kedainiai before 1655, as shown in virtual reconstructions created for the Kedainiai Museum, resembles towns in the Netherlands, England and Germany more than towns founded by Catholic patrons, such as Zamość settled with Italians, Armenians, Jews and Greeks. The register of Anna Kiszczanka's expenses from 1641 for her estate in Zabłudów near Białystok indicates that most of her expenses went for personal purposes, food, renovation of manor rooms and the purchase of luxury goods, most of which were imported goods purchased in Gdańsk and Toruń. Expenses related to charitable or educational activities constituted a margin of income from Zabłudów estates (after "Rozchody i wydatki księżnej Anny Kiszczanki" by Antoni Mironowicz, p. 274). No painted effigy of Princess Anna is known, but there must have been many, probably by Dutch painters or by a royal court painter. Inventory of paintings from the collection of Anna's great-granddaughter (Boguslaus' daughter and Janusz's granddaughter) Louise Charlotte Radziwill (1667-1695), drawn up in 1671, lists two effigies of Anna Kiszczanka - item 78/8 and 106/5 (after "Inwentarz galerii obrazów Radziwiłłów z XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska). The painters are not mentioned, but this collection undoubtedly included the paintings of the best European Old Masters. Some titles indicate that some of the paintings were created in the Netherlands, such as "A young Dutch woman" (314/23), "A Dutchman with a glass and a pipe" (337/13), "A Dutchman plays an instrument and laughs" (343/19), "A Dutchman plays the viol and sings" (345/21), "A Dutchman plays the pipe" (346/22), "Dutch art, drinking peasants" (429/17), "A Dutch painting" (446/6), "A Dutchman courtes a lady and she takes money from his pouch" (492/12), "A Dutch lady with a watering can" (696/9), "A Dutch lady is reading a book and a watering can is next to her" (730/43) and trompe-l'œil painting "A Dutchman painted on panel but on canvas" (797/13). Alongside portraits of Polish-Lithuanian monarchs, monarchs of France, electors of Brandenburg and Saxony, foreign and Polish-Lithuanian nobles like Leszczyński or Lubomirski, the inventory includes numerous effigies of members of the Radziwill family from both branches Catholic (Nesvizh-Olyka) and Calvinist (Birzai-Dubingiai). An effigy created around the time of Anna Kiszczanka's lifetime is confirmed. This is a drawing kept in the Hermitage Museum (ОР-45863), a study for an engraving from a series of effigies of family members (possibly created between 1646 and 1653). It is inscribed in Polish: Anna Kiszczanka Żona and shows her in a rich 1620s Spanish-style saya and a typical Polish-Lithuanian fur hat and coat. The series was probably not printed because of the Deluge, which also significantly affected and impoverished the Radziwill family. We can assume that the studies were created to be sent to a renowned engraver in Gdańsk, such as the Dutch Willem Hondius, or the Netherlands. This effigy (or very similar) was published more than a century later, in 1758, in the cycle Icones familiæ ducalis Radivilianæ, where Anna's face was slightly modified. The same goes for the image of Anna's son Janusz, which may have been modeled on his portrait by Daniel Schultz, now housed in the National Art Museum of Belarus. During the Deluge (1655-1660), invaders plundered almost everything that the inhabitants could not evacuate or protect in some way. Over the following centuries, the Radziwills had to evacuate their collections several times. Such activities as well as post-war chaos contributed to incorrect identifications of models in preserved effigies, which is why there are obvious errors in Icones familiæ ducalis Radivilianæ, such as the portrait of Anna Kiszczyna née Radziwill (1525-1600) in which the model resembles effigies from the end of the 17th century or early 18th century and not from the 16th century or another Anna Kiszczanka, who according to the inscription lived in the first quarter of the 16th century (born in 1513 and died in 1533) and the effigy depicts a lady in costume similar to the mentioned effigy of a wife of Christopher Radziwill, thus created in the first quarter of the 17th century. At the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York there is a portrait of a woman by Rembrandt, which comes from the Radziwill collection in their Nesvizh Castle (oil on wood, 67.9 x 50.2 cm, inventory number 14.40.625). Later in the collection of Cyprian Lachnicki (1824-1906) in Warsaw, the painting was sold in Paris on June 15, 1867 ("Catalogue de la collection de tableaux de M. Lachnicki", Hôtel Drouot, no. 24). In the Paris sale, it appeared after the portrait of Rembrandt, now at the National Museum in Warsaw (M.Ob.296, earlier 734). The work was signed and dated by the painter (lower left): Rembrandt f· / 1633·, although it is also considered the work of Rembrandt (face) and his collaborators (costume). The sitter's costume is typical of Dutch fashion of this era and can be seen in many portraits by different painters. Rembrandt's portrait of Aechje Claesdr. in the National Gallery in London (NG775) is very similar, both in terms of composition and the sitter's attire. Aechje was the widow of Rotterdam brewer Jan Pesser and one of the leading figures in the Remonstrant community of Rotterdam. The Remonstrants were Protestant, but their beliefs were slightly different from the Calvinist orthodoxy that dominated religion in Holland at the time. This painting was also signed and dated (Rembrandt.ft / 1634) and also indicates her age (Æ. SVE. 83). An effigy similar to that in New York was also reproduced in the Icones familiæ ducalis Radivilianæ. The woman's ruff indicates that it was painted around the same time as Rembrandt's painting, but according to the inscription it shows Anna Fiedkonis née Radziwill (d. 1492). What is very interesting is that in Lithuania a copy of Nesvizh's painting has been preserved, today at the National Museum of Art in Vilnius (oil on canvas, 72 x 51 cm, LNDM T 4153). It was obviously painted by another painter, so it is not associated with Rembrandt but, mainly because of the woman's costume, with the 17th century Dutch school. Although the woman wears the attire of a Protestant woman from the Netherlands, the style of this painting is more Italian than Dutch and can be compared to Giacinto Campana's Saint Mary Magdalene at the Wilanów Palace in Warsaw (Wil.1732), attributed by me. Campana arrived in Warsaw in 1637 and in 1639 he worked in Vilnius so that he could copy a picture by Rembrandt or another painter from the Radziwill collection. The woman in both paintings resembles Anna Kiszczanka, Princess Radziwill from all the mentioned effigies, as well as the portraits of her son Janusz by Bailly, by Bartholomeus Strobel (National Art Museum of Belarus) and engraving by Hondius (Czartoryski Museum). The Nesvizh (New York) portrait or a series was therefore ordered from Rembrandt's workshop in 1633 on the occasion of Anna's name day. The Vilnius portrait has a pendant depicting another woman of similar age and costume (oil on canvas, 71.5 x 50 cm, LNDM T 3990). The two were depicted together because they were sisters or otherwise related. Assuming the first woman is Anna Kiszczanka, the other should be identified as her sister-in-law Christina Kiszczyna née Drutska-Sokolinska (d. 1640). Like her father, Michael Drutsky-Sokolinsky (d. 1621), voivode of Polotsk and Smolensk, she was most likely also a Calvinist. Christina's husband, Janusz Kiszka (ca. 1586-1654), Field Hetman of Lithuania and voivode of Polotsk, raised in Calvinism, converted to Catholicism around 1606. In 1624-1626 he studied in Padua, where on March 4, 1625 he met the Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa and accompanied him to Venice. Papal nuncio Honorato Visconti gave the following description of the voivode of Polotsk and Field Hetman of Lithuania (report to Cardinal Francesco Barberini, July 15, 1636 from Warsaw): "he is also a better soldier than senator. Catholic but only in name, impulsive, not very pious, he still has many heretical superstitions, in which his father remained" (after "Relacye nuncyuszów apostolskich" by Erazm Rykaczewski, Volume 2, p. 252). Janusz Kiszka married Christina, the widow of Sebastian Gnoiński, in 1608 or 1609. She enjoyed the great trust of her husband, as evidenced by the fact that during his stay abroad for several years, on April 20, 1624, he entrusted her with the management of all estates. Returning to the country in 1627, preoccupied with military service, he left his property under her full management until May 16, 1633. In 1629, Kiszczyna concluded a contract with Abraham Jonaszewicz, a burgher from Gdańsk, for the sale of the Czaśniki estate with the Smolany farm. Gdańsk merchants wanted to organize the export of forestry and agricultural products on a large scale, bypassing the Vitebsk chamber customs (after "Próba utworzenia gdańskiej faktorii handlowej ..." by Jarosław Zawadzki, p. 43, 46). Christina died in 1640 and in connection with her funeral, a mourning booklet entitled "Mourning Shadows After Bright Rays" (Cienie żałobne po jasnych promieniach) by Melchior Stanislav Savitsky was published in Vilnius. Another version or original of this portrait is now in the Kremer collection in Amsterdam (oil on panel, 45 x 35.5 cm). It comes from the collection of the Kielmansegg family in Vienna and was cut, perhaps from an oval shape. This painting is attributed to Rembrandt's follower Jacob Adriaensz Backer and dates from around 1634. Stanisław Koniecpolski (1591-1646), Grand Hetman of the Crown, may have received copies of the portraits of the two women, because two of such paintings are visible in a photograph by Edward Trzemeski taken around 1880 and showing the Eastern Antechamber of his palace in Pidhirtsi near Lviv in Ukraine. In a portrait of a family as donors by a Kraków painter, painted around 1620 (National Museum in Kraków), the sitters wear Italian (the man and boy next to him) and Dutch costumes (the other members of the family). The painting style is inspired by the Italian school, while the family kneeling before the resurrected Christ looks more like Dutch, Silesian or Gdańsk paintings. Although the nobility of Poland-Lithuania had favored different fashions since at least the second quarter of the 16th century, specific garments had important connotations and were expressions of political opinions and sympathies. In a painting created in 1665, in the Corpus Christi Church in Poznań, Queen Jadwiga (Hedwig of Anjou, 1373-1399) was depicted in a typical Spanish costume from the 1620s. This effigy was probably inspired by the portrait of Queen Constance of Austria (1588-1631) or other unpreserved effigies of Jadwiga commissioned by Catholics sympathetic to the Spanish Empire and the Habsburgs. It was natural that when the Catholics and Habsburgs asserted their position at the royal court in Warsaw and their supporters manifested it through Spanish, Italian or Flemish fashion, the Calvinist aristocrats were represented in the Dutch costumes. The portrait of Queen Bona Sforza d'Aragona (1494-1557) kept at the National Museum in Lublin (oil on canvas, 60.5 x 51 cm, S/Mal/609/ML), painted in a style comparable to the two paintings in Vilnius, shows the queen in the convention of bourgeois portraits of the 17th century, emphasized by all authors. Its style is more Italian, however, the costume is clearly Nordic and the painting is attributed to the Dutch school. Similar ones can be seen in numerous portraits made around 1640 and attributed to the Dutch school (such as portrait of Dorothea Berck, private collection), Willem van Honthorst (Museum of Fine Arts in Lille), circle of Bartholomeus van der Helst (private collection), several portraits attributed to the Flemish school (dated 1641 and 1646, private collection) or a portrait of a French lady, perhaps Huguenot, signed by the unknown painter Panuier and painted in 1641 (private collection). Unlike the royal court, her dress is modest and her hair is not dyed Venetian blonde. The inscription with a crown - REGINA BONA, appears to be original, therefore the painting was most likely created to remind some people that the Commonwealth was from the beginning a tolerant country with different people, customs and religions.
Portrait of Anna Kiszczanka (1593-1644), Princess Radziwill by Rembrandt, 1633, Metropolitan Museum of Art.
Portrait of Christina Kiszczyna née Drutska-Sokolinska (d. 1640) by Jacob Adriaensz Backer, ca. 1634, Kremer collection in Amsterdam.
Portrait of Anna Kiszczanka (1593-1644), Princess Radziwill by Giacinto Campana, ca. 1639, National Museum of Art in Vilnius.
Portrait of Christina Kiszczyna née Drutska-Sokolinska (d. 1640) by Giacinto Campana, ca. 1639, National Museum of Art in Vilnius.
Portrait of Queen Bona Sforza d'Aragona (1494-1557) by Giacinto Campana or circle, ca. 1640, National Museum in Lublin.
Saint Mary Magdalene by Giacinto Campana, 1640s, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
Portraits of Princess Catherine Radziwill by Rembrandt and workshop
The famous 17th century Dutch painter Rembrandt was probably so busy with this small number of paintings that experts agree to directly attribute to him, that he didn't even know what color his famous wife's eyes were. Likewise for the members of his workshop, who probably saw Rembrandt's wife every day. Saskia van Uylenburgh (1612-1642), the relative of the Polish king's artistic agent Hendrick van Uylenburgh (d. 1661), the muse and one of the greatest celebrities of 17th century Europe (although in fact very few people probably heard of her during her lifetime), has different eye color in similar pictures (from blue, blue-brown to brown).
Despite her average beauty, apparently many people wanted to have her likeness and paid a lot to obtain it, so many portraits had to be created. The painter, his workshop and many followers copied the effigy of Saskia. They depicted the wife of a painter of Dutch merchants as an oriental princess, wearing clothes of expensive fabrics and jewelry. The sarcasm is justified because it doesn't make sense. Although there is no reliable evidence from the epoch, many people still want to believe in this invention probably dating back to the 19th century, when Poland did not exist on the maps of Europe, that Rembrandt mainly painted himself, his wife and his family. Many Poles also believed in this concept, which is why portraits of unknown women from Rembrandt's cycle from old Polish collections are traditionally known as Saskia. The earliest known mention of Saskia by an independent biographer is a note by Arnold Houbraken, who wrote about Rembrandt in 1718: "he had as wife a little farm woman from Raarep, or Ransdorp in Waterland, rather small of person, but well made in appearance and a plump body" (Hy had ten Huisvrouw een Boerinnetje van Raarep, of Ransdorp in Waterlant, wat klein van persoon maar welgemaakt van wezen, en poezel van lichaam). Around 1633, when many alleged portraits of Rembrandt's wife were created, one of the richest brides in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth was Princess Catherine Radziwill (1614-1674). In 1633, Rembrandt painted a portrait of the princess's mother - Anna Kiszczanka (1593-1644) (Metropolitan Museum of Art, 14.40.625), in 1635 the painter and his workshop created a portrait of her father Christopher Radziwill (1585-1640), Grand Hetman of Lithuania, wearing a feathered cap (Buckland Abbey, NT 810136) and around 1640 Govert Flinck, one of Rembrandt's best pupils, created his full-length portrait holding a cane (National Museum in Warsaw, M.Ob.2584 MNW), all identified by me. Catherine was born in Jasiunai near Vilnius in December 1614. Raised in the Evangelical faith, she received a home education at her mother's court appropriate to her social position. As can be seen from her own correspondence, she knew the Bible well, was interested in theological issues, and personally supervised her property affairs. Her father planned a marriage for her abroad (after "Testamenty ewangelików ..." by Urszula Augustyniak, p. 215). So potential candidates must have received her portraits. During the interregnum after the death of Sigismund III Vasa in 1632, rumors circulated of the intention to marry Catherine by the king's eldest son, Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa, elected as Ladislaus IV (compare "Dynastia Wazów ..." by Stefania Ochmann-Staniszewska, p. 184). According to the papal nuncio Honorato Visconti (report to Cardinal Francesco Barberini, July 15, 1636 from Warsaw), Ladislaus "had a penchant for the daughter of Prince Christopher Radziwill - voivode of Vilnius, hetman of Lithuania, leader of the Calvinists" (after "Relacye nuncyuszów ..." by Jan Chrzciciel Albertrandy, p. 206). The princess could therefore have become the first Protestant queen of Poland, but the king married Cecilia Renata of Austria in 1637. On February 25, 1640, Catherine married the Catholic George Charles Hlyabovich (d. 1669), Hlebowicz in Polish, steward of Lithuania, who guaranteed her free exercise of her religion and allowed to raise their two daughters as Calvinists. The wedding was officiated by a Calvinist minister and was magnificently feasted with races and fireworks. The king sent the newlyweds a gift of 20,000 zlotys and a bed woven with gold. After her marriage, she continued to hold the title of princess. Catherine was involved in the affairs of the Evangelical Church of Lithuania. She was deeply affected by the trial over the Protestant church in Vilnius in 1640, as evidenced by her letters to her father. Her firstborn daughter Marcybella Anna (1641-1681) married Marcjan Aleksander Ogiński (1632-1690), whose portrait on horseback by Rembrandt is in the Frick Collection in New York (1910.1.98). She died on December 2, 1674. In her will, written on August 16 of the same year in Ros near Grodno (Belarus), she asked to be buried next to her parents, in the crypt of the Kedainiai church. No reliable portrait of the princess is known. The effigy from Icones familiae ducalis Radivilianae - CATHARINA PRINCEPS RADIVILIA / CHRISTOPHORI II Defuncti 1640 ..., shows a woman in early 17th century costume, so it cannot represent her as she was born in 1614. In the painted copy of this effigy made between 1733-1737 (National Museum in Warsaw, MP 4453 MNW), she has gray hair which was fashionable at the time this painting was made, but indicates that the author copied a simplified drawing representing a member of the Radziwill family. Although in general the effigies in this series are reliable, there are also many errors, as in the case of an effigy of the second wife of Catherine's brother - Maria Lupu of Moldavia (1625-1660). An engraving of her portrait with Janusz's first wife by Johann Schröter in the National Art Museum of Belarus (ЗЖ-125), or another version of it, has been wrongly described as Katarzyna Tomicka (ca. 1517-1551). The register of paintings belonging to Catherine's cousin Boguslaus Radziwill (1620-1669) from 1657 (AGAD 1/354/0/26/84), lists three portraits of her husband (P. Hlebowicz Sta Zmudzki, P. Hlebowicz młody, Chlebowicz Sta Zmudzki) and "The Entry of Mr. Hlyabovich into Smolensk" (Wiazd P. Hlebo do Smolenska), as well as two portraits of her mother (Anna Kiszczanka Wdzina Wilenska, Kiszczanka Radziwiłowa Wdzina Wilen) and a single one which probably depicted Mrs. Hlyabovich (Katarzyna Radziwiłowna) after which "A Dutch painting" (Obraz Holenderski) is mentioned. This small number of her effigies in this inventory is probably due to the fact that the voivodess Hlebowiczowa had property disputes with her cousin and then with the guardians of his daughter Louise Charlotte, and even attacked some of his estates with her private army. Rembrandt's oval "Portrait of Saskia", also known in the catalog of the Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam as "Young woman in fantasy costume" (oil on panel, 65 x 48 cm, SK-A-4057) is known from several contemporary copies by workshop or circle of the painter. This painting was produced in 1633 (signed and dated: Rembrandt ft. 1633). The earliest confirmed provenance of this painting is the private collection of Thomas Bruce (1766-1841), 7th Earl of Elgin and 11th Earl of Kincardine. Her "fantasy costume" closely resembles that of Teodora Krystyna Sapieżyna née Tarnowska (1625-1652) from her 18th century portrait, a copy of original from the 1640s (Wawel Royal Castle, 8690) and the woman has a strong family resemblance with Anna Kiszczanka from her mentioned portrait by Rembrandt in the Met. A good copy of this painting in the style of Salomon Koninck (1609-1656), painter from Rembrandt's circle and the academy of Hendrick van Uylenburgh, was sold in 2014 in London with attribution to the 18th century copyist (oil on canvas, 65.2 x 53.6 cm, Bonhams, October 29, 2014, lot 165). It is not an exact copy because Koninck added a baroque brooch to her bust, similar to that visible in portrait of Maria Eleonora Stibichen (d. 1660), possibly by Tomasz Muszyński, in the Lithuanian National Museum of Art in Vilnius (LNDM T 3940). Another good copy made by the painter's workshop in 1634 (signed: Rembrandt f. 1634) is in the Lázaro Galdiano Museum in Madrid (oil on canvas, 91 x 80.4 cm, 08452). It was part of the collection assembled by José Lázaro in Paris, probably acquired at the end of 1939 as an original by Rembrandt. In 1633, Govert Flinck, usually living in the house of Hendrick van Uylenburgh in Amsterdam, created another similar portrait of the same woman dressed as a shepherdess, now in the Metropolitan Museum of Art (oil on canvas, transferred from wood, 66.7 x 50.5 cm, 60.71.15). This painting was most likely in Paris in the 18th century. It was inscribed at the bottom right: Rembrandt f. / 1633. This signature was long considered original and the work as a painting by the master himself, which indicates that Rembrandt, working in 1633 on a large princely commission, signed a work by his student. His wealthy customers from the Commonwealth expected not only good quality, but also that the paintings be made by the master himself. However, in the case of large orders this was probably difficult to achieve. Another similar painting of the same woman by Flinck, also signed by Rembrandt (Rembrandt f / 1633), is in the Fries Museum in Leeuwarden (oil on panel, 72 x 48 cm, S1948-041). The painting probably comes from the collection of Cardinal Joseph Fesch (1763-1839) in Rome, sold in 1845. Who knows, perhaps this splendid princely "portrait of Saskia" was already sent to Rome in 1633. Another version of this portrait was probably in Paris in the 18th century because it was engraved by Antoine de Marcenay de Ghuy in 1768 under the title "The Lady with the Pearls" (La Dame aux Perles) or "The lady with the feather" (La dame a la plume) and inscription: Rembrant pinx. The same woman, in similar costume, also painted in 1633, was depicted in a painting now in the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on panel, 60.4 x 49.6 cm, M.Ob.35, earlier 60). The painting is also attributed to Govert Flinck, although it also bears the same signature: Rembrandt / 1633 (center right). The painting was purchased in 1865 from the collection of Karol Jezierski. "Princess Saskia" wearing a diadem, pearl earrings, a pearl and coral necklace with a pendant, a double gold chain hanging around her body and two bracelets on her left arm, an expensive dress of crimson velvet and holding a pink in her right hand was also depicted in a painting kept in the Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden (oil on panel, 98.5 x 82.5 cm, Gal.-Nr. 1562). This painting signed lower left: [...]brandt. f 1641 was purchased in 1742 by De Brays from Araignon in Paris (price 1500 livres) for the collection of the elected monarch of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth Augustus III (1696-1763) in Dresden. The woman's gesture, holding a carnation, symbol of love, indicates that she is addressing her husband, probably represented on an unknown pendant painting. A good, possibly 17th or 18th century copy of this painting, coming from the Radziwill collection, is in the Nieborów Palace (pastel on paper, 64,5 x 54 cm, NB 791 MNW). The author could be Louis Marteau or Anna Rajecka, pastelists who worked for the Polish-Lithuanian aristocracy. In addition to several paintings by Rembrandt that were in the Nieborów Palace before 1835, the catalog of the Radziwill collection also lists a painting by Govert Flinck: "340. Portrait of a lady in a bonnet, white ruff and black clothes; she holds a white handkerchief in her hand. Painted on wood" (after "Katalog galeryi obrazow sławnych mistrzów ..." by Antoni Blank, p. 102). A very good studio copy of Rembrandt's self-portrait in a ruff, painted in 1632 (signed and dated: RHL van Rhyn / 1632), now in the Burrell Collection in Glasgow (35/600), can be found at the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on panel, 64 x 47.2 cm, M.Ob.296, earlier 734). This unsigned copy comes from the collection of Cyprian Lachnicki (1824-1906), who acquired numerous paintings from historical Polish-Lithuanian collections in former Commonwealth's territories or in Saint Petersburg where many paintings were moved after the partitions of Poland. At least two other old copies of this self-portrait preserved in Poland, one very probably from the 19th century, in the National Museum in Warsaw (211446 MNW) and the other octagonal in shape, very probably from the second half of the 18th century, in Łańcut Castle (S.1419MŁ). It is likely that many effigies of this type found their way to Poland-Lithuania as early as the 17th century, indicating that, through this tronie-like portrait, Rembrandt or Hendrick van Uylenburgh was advertising the painter's workshop in the Commonwealth or that customers from the country wanted to have an effigy of a painter who worked for them. The style of the portrait from the Lachnicki collection resembles the 1633 portrait of Catherine by Flinck in the National Museum in Warsaw, it was therefore very probably painted by this student of Rembrandt.
Portrait of Rembrandt in a ruff by Govert Flinck, after 1633, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Princess Catherine Radziwill (1614-1674) by Rembrandt, 1633, Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam.
Portrait of Princess Catherine Radziwill (1614-1674) by Salomon Koninck, ca. 1633, Private collection.
Portrait of Princess Catherine Radziwill (1614-1674) by workshop of Rembrandt, 1634, Lázaro Galdiano Museum in Madrid.
Portrait of Princess Catherine Radziwill (1614-1674) as a shepherdess by Govert Flinck, 1633, Metropolitan Museum of Art.
Portrait of Princess Catherine Radziwill (1614-1674) by Govert Flinck, 1633, Fries Museum in Leeuwarden.
Portrait of Princess Catherine Radziwill (1614-1674) by Govert Flinck, 1633, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Princess Catherine Radziwill (1614-1674), holding a carnation by Rembrandt, 1641, Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden.
Portrait of Princess Catherine Radziwill (1614-1674) after Rembrandt, after 1641, Nieborów Palace.
Portraits of Prince Boguslaus Radziwill at a young age by studio of Rembrandt
At the beginning of 1631, Prince Christopher Radziwill (1585-1640) took with him to Warsaw his ten-year-old nephew Boguslaus Radziwill (1620-1669), son of his brother Janusz (1579-1620), for the Sejm which began on 29 January. On February 25, the boy delivered a learned speech before the king. According to an anecdote cited by Boguslaus's anonymous biographer, when his uncle ordered him to fall at the king's feet, the latter replied: "After all, the king is a man like me", to which Sigismund III Vasa, delighted with "child's wonderful wit", said smiling: "Leave him alone! He is a rebel". After the Sejm, he returned to his uncle's court in Kedainiai, where we find him on May 13, 1632 (after "Autobiografia" by Bogusław Radziwiłł, Tadeusz Wasilewski, p. 18).
The prince himself confirms the oration before the king in his autobiography, published in 1841 by Edward Raczyński ("Żywot Xięcia Bogusława Radziwiłła", p. 4): "In 1631 I was with the prince, my uncle, at the Warsaw Sejm, where I had a case with the voivode of Vilnius, Sapieha, over Kapyl, which he won. On this occasion, I gave a speech to King Sigismund III. In 1632 I continued my studies at Kedainiai sub [under] Joanne Pruscio et Friderico Starchio. In 1633, my older sister, Elizabeth Eleonora, died on August 5 in Dresden in the presence of her aunt, the Electress of Saxony. I studied in a congregation in Vilnius sub Artico". Born in Gdańsk, in a brick house rented to his father by the mayor of Gdańsk, Johann van der Linde, where he lived the first years of his life, the young prince was educated by Calvinist teachers, such as the priest Paweł Demitrowicz. His godfather was "the Winter King" Frederick V of the Palatinate. When he was six months old, his father died. In his will, Janusz ordered that Boguslaus be raised in the evangelical spirit in local schools, away from Catholic colleges. He forbade his son from traveling to Italy and Spain until he reached the age of majority and also recommended that he remain a Protestant for the rest of his life. He learned the catechism and Latin, from the texts of Cato. In October 1630, little Boguslaus began to learn the "orations" sent to him regarding the dispute over Kapyl. The Radziwills were keen to preserve their effigies from a young age and despite enormous losses, several effigies of young Radziwills have survived. Notable examples include the silver medals with the bust of the young Nicolaus Christopher "the Orphan" Radziwill (1549-1616), made in 1554 and around 1555-1560, a drawing with his portrait, made by David Kandel around 1563/1564 (Louvre, INV 18707, Recto), the monument of his son Nicolaus Radziwill (1587-1588), sculpted by Gaspare Fodiga after 1589 (Corpus Christi church in Nesvizh) or an engraving with portrait of his three sons made in Augsburg in 1604 (National Museum in Kraków, MNK III-ryc.-33956), alabaster relief from the child epitaph of Stanislaus Radziwill (d. 1590) from the Collegiate Church of the Holy Trinity in Olyka (Diocesan Museum in Lutsk) or a 1637 portrait of a boy from the Radziwill family in a green żupan (private collection). Although Boguslaus probably did not manage to move all of his portraits to Königsberg/Królewiec in 1657, the inventory of his paintings (AGAD 1/354/0/26/84) lists a few portraits of children, such as "A Boy with a parrot", "A beautiful little boy", "Little Christopher Radziwill", "Dead child without a name", "Item the second dead child without a name". His portraits at a young age are not mentioned, however, according to custom, several portraits of a 10-year-old orator also had to be made for friends and relatives at home and abroad. Around 1633, when several portraits of members of the Calvinist branch of the Radziwll family, identified by me, were made, Rembrandt and his workshop also produced a series of portraits of a boy. Mainly due to the child's "fancy costume", the portraits are considered as tronies, "the new type of painting evolved by Rembrandt and Lievens in their Leiden studio where unidentified models were depicted in exotic garments" (after "A Boy in Fanciful Costume", Art UK). When similar effigies in more Western costumes are considered "portraits", the oriental aigrette (egreta, szkofia) or the richly embroidered cape of an Eastern prince, determine in this case that the portraits are considered tronies. One of these "tronies" is in the Wallace Collection in London (oil on panel, 21 x 17.7 cm, P201). The painting was signed and dated: Rembrandt ft / 1633, however it is attributed to studio of Rembrandt, possibly Govert Flinck. Before 1803, the painting belonged to François Pauwels, master brewer in Brussels and was sold with a pendant portrait of the same dimensions representing an old man, considered in the catalog as the father (it could also be his uncle) of the boy - Catalogue de tableaux des plus grands maîtres ..., edited by Pierre-Joseph de Marneffe. During his studies in the Netherlands between 1631 and 1632, Boguslaus's cousin Janusz (1612-1655) visited Brussels as an envoy of the Polish-Lithuanian monarch, Boguslaus was there in 1646 and Prince's artistic agent Matthijs Musson (1593-1678) was active mainly in Antwerp and Brussels (compare "Galerie obrazów i "Gabinety Sztuki" Radziwiłłów w XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska, p. 89, 96). A similar portrait of the same boy is in the Hermitage Museum in Saint Petersburg (oil on panel, 67 x 47.5 cm, ГЭ-724). It is also attributed to the workshop of Rembrandt, perhaps Govert Flinck, and dated to the first half of the 1630s (1630-1635). The painting entered the Hermitage between 1785 and 1787, so provenance from the Radziwill collection or another magnate collection in the Commonwealth is possible (the first partition of Poland took place in 1772). The effigy resembles the portrait of a boy wearing a cape and turban, considered to be the likeness of Prince Rupert of the Palatinate (1619-1682) in Oriental costume, painted by Jan Lievens around 1631 (Leiden Collection, JL- 104). His pose indicates that he was a good speaker. Another portrait of this boy was also in Saint Petersburg, where many paintings from the historical collections of Poland-Lithuania were transferred after the partitions. Before 1908 it belonged to Prince Yusupov (oil on panel, 19.7 x 16.7 cm, signed and dated: Rembrandt ft / 1633). Most likely, an 18th century copy of this effigy by an unknown painter is in the Bowes Museum (B.M.663). The boy resembles the older Boguslaus from his portraits painted between 1636-1637 by Govert Flinck, identified by me.
Portrait of Prince Boguslaus Radziwill (1620-1669) at a young age by studio of Rembrandt, 1633, The Wallace Collection in London.
Portrait of Prince Boguslaus Radziwill (1620-1669) at a young age by studio of Rembrandt, ca. 1633, Hermitage Museum in Saint Petersburg.
Portrait of Prince Boguslaus Radziwill (1620-1669) at a young age by studio of Rembrandt, 1633, Private collection.
Portraits of Jan Zawadzki, Ambassador of the King of Poland by Rembrandt
"The next day, in fine weather and the most favorable wind, we came to Amsterdam. Beautiful are edifices of this city, canals crossing it, streets lined with linden trees, forests of ship masts, rich merchant warehouses. [...] The merchant market is beautiful and rich. Reformatory House, magnificent Indian Company buildings, full of the most expensive goods. On the 14th day, having sent the court and things to The Hague, we arrived alone in Leiden, on the day of Pentecost, we listened to mass in a private Catholic chapel. There we met with joy, the sons of Prince Wiśniowiecki, voivode of Ruthenia, who invited us to dinner; then we were visited from our other countrymen, that is from Gentlemen Żółkiewski, Zieliński, Kreitz and Korfa. On that day the envoy, the Council of the Bohemian Queen, informed about his arrival, who immediately invited him on the following day for an audience at three in the afternoon. [...] After 16 days of expensive stay on June 1, we left The Hague. [...] On June 22, near the village of Leith near Edinburgh, we dropped the anchor. He immediately sent an envoy to the Scottish Chancellor to announce his arrival", recalls the author of the manuscript from the collection of Count Józef Sierakowski about Jan Zawadzki (d. 1645), starost of Świecie and Chamberlain of the King, envoy of His Highness Ladislaus IV, king of Poland and Sweden to the German princes, to the Queens of Sweden and Bohemia, to the United Provinces of the Netherlands, and to the King of England in 1633.
On July 19 Zawadzki arrived to London. "We visited the house of the Duke of Buckingham, killed by a murderer four years ago. [...] In this palace, the rooms are beautifully painted by Vandyck. [...] We were also at the merchant market [...] Here, by the old custom, the envoy received gifts from the King, three large basins with ewers, six large cups, four smaller ones, a censer, cups for salt and sugar. The envoy gave to the bearers 50 Jacobs (2000 fl.). From London, we set off for the Netherlands again, [...] on August 10th we came to Amsterdam". The envoy also brought many valuable gifts: "to the Royal Undersecretary, I gave a gift of money so that he would be careful about our affairs. I gave the Master of Ceremonies a chain with diamonds, the Kitchen Master Cupbearer and other officials, expensive rings, or gifts in money". In 1636 he offered to the King of England, after a private audience, the horses, "dressed in tacks with broadswords and maces. Hussar pure breed horse with a horse tack set with turquoises, a leopard skin on it, on a bay, second tack in Arabic style - a bow, a quiver, a very beautiful tack. [...] Two soroks of sable for the Queen, with which they are very surprised, and estimate for a lot of money. He also gave the Prince, five tovaglia tablecloths, whose work is great in admiration" (after "Zbiór pamiętników o dawnej Polszcze" by Julian Ursyn Niemcewicz, Volume 3, p. 105-133). During the solemn audience in 1636 before the King of England Zawadzki's servants were dressed in red velvet żupans, beige or scarlet delias, and having ostrich feathers on their hats. They were followed by fifteen other people dressed in Italian style and by Mr. Poręmbski and Mr. Wilczkowski holding golden maces, both dressed in red velvet żupans lined with lynx and sable. Then the son of Zawadzki in a robe of gold cloth, a hat with crane feathers and a diamond clasp and the envoy himself in a czamara coat lined with sable fur, ruby clasp and a chain. He was followed by servants in red delias and with three crane feathers on their caps, red, white and blue, and wearing azure delias. Ambassador's retinue numbered about 66 people. Zawadzki was a son of Jan of Rogala coat of arms, judge of Ciechanów and Swedish Izabela Guldenstern (de Gyllenstierna). Through his mother he was related to the royal house of the Vasas. He was probably born in 1580 and at the age of 18 he entered the Jesuit college in Braniewo and after graduation he went to Louvain to continue his education. At that time, he entered the service of Count Christopher of East Frisia (1569-1636), son of Edzard II, Count of East Frisia, and the Swedish princess Catherine Vasa (1539-1610). King Sigismund III maintained close contacts with this part of the family, and a special intimacy with Count Christopher is evidenced by the correspondence they exchanged. The Count sent Zawadzki as his envoy to Sigismund III. Zawadzki's cheerful and friendly disposition guaranteed him the king's sympathy and he performed various diplomatic missions for him. Before October 1617 he was also appointed a royal secretary and between 1624 and 1625 he was a member of the retinue accompanying Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (future Ladislaus IV) on his journeys to Western Europe (after "Misja Jana Zawadzkiego na dwory Europy Północnej ..." by Marta Szymańska). Willing to regain the Swedish throne, Ladislaus IV sent eight legations to various European countries between 1633-1634. In addition to the embassy of 1633, Jan Zawadzki was sent on a mission to England, The Hague and to Paris in 1636. Among objectives of these missions was also the King's marriage and possibly other family matters, however, these negotiations were kept secret. "After the hearing with the King of England, our envoy will go to the Queen Her Majesty and will ask her for a secret audience", instructed Zawadzki Bishop Jan Gębicki in 1636. At the beginning of 1634, Zawadzki stayed briefly in Hamburg (8 days, during which he was plagued by fever) to discuss with Hugo Grotius (Hugo de Groot, 1583-1645), a Dutch humanist, diplomat and lawyer, his possible employment by the King of Poland. Aside from his memoirs, Zawadzki is credited with being the author of a memorandum dated 1634, dealing with the campaign in Prussia against the Swedes. An etching by Rembrandt from 1634 depicting a man with a wart under the eye (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, inventory number RP-P-OB-42), despite bearing no resemblance whatsoever, is frequenly identified as his self-portrait. In the same year, the artist actually created his self-portrait in eastern costume holding an oriental sword. Both etchings are signed and dated: Rembrandt f. 1634. Rembrandt also created other version of the first mentioned etching in oval (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, RP-P-1961-990A), also signed and dated: Rembrandt f. 1634. In the larger version of the print the man is holding a heavy ancient sword, similar to Bronze Age swords found in Nowy Żmigród, south-eastern Poland, identical to that visible in a portrait of Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski (1616-1667) in the North Carolina Museum of Art, created by Rembrandt or a follower in 1633. Also his pose is identical, like if the man ordered similar portrait from Rembrandt in the pose of an ancient Sarmatian (legendary ancestors of Polish nobility), after which the artist created the etching. This pose is similar to that visible in a portrait of Zawadzki's friend Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa (future Ladislaus IV), created by workshop of Peter Paul Rubens, as one of the series, during his visit to Brussels and Antwerp in 1624 (Wawel Royal Castle). Pieter Claesz Soutman, court painter of the King of Poland, was also depicted in similar pose in his portrait by Anthony van Dyck (Louvre Museum), while Boaz in his painting in the National Gallery of Denmark (Ruth in Boaz's field, attributed), wears the outfit of a Polish magnate and also has a hand on his hip. Finally, this pose is also visible in the famous Polish rider by Rembrandt (The Frick Collection in New York). The man wears a fur beret with a hat decoration (egreta) with feathers, similar to that visible in a portrait of a man in a fur coat and a feathered hat by Isaac de Joudreville, who worked in Rembrandt's workshop from November 1629 (oil on panel, 62 x 50 cm, sold at Christie's London, auction 15497, December 7, 2018, lot 155), from private collection in Germany. Similar hat was also depicted in an effigy of bearded Polish nobleman created in Rembrandt's style in 1644 (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, RP-P-1882-A-6250) and several paintings of Polish-Lithuanian soldiers and nobles from book of friendship (album amicorum/Stammbuch) of Michael Heidenreich, created in Gdańsk in the 1600s by Anton Möller or Isaak van den Blocke (Kórnik Castle). Similar headdress can be found in many other images of Polish-Lithuanian nobles, like in the Allegory of Gdańsk trade by Isaak van den Blocke in the Red Hall of the Main Town Hall in Gdańsk, created in 1608, View of Gdańsk from the northwest (The Parable of the Rich Man and Lazarus) by Hans Krieg, created in about 1620 (National Museum in Gdańsk), or in a painting entitled Head of Cyrus brought to Queen Tomyris by Peter Paul Rubens, created between 1622-1623 (Museum of Fine Arts in Boston). He also wears a jerkin similar to czamara, a coat lined with fur similar to delia and a gold chain. This proud Sarmatian must therefore be Jan Zawadzki, envoy of His Highness Ladislaus IV. In 2016 a painting attributed to follower of Rembrandt from a private collection in the USA and similar to the oval print was sold at auction (oil on canvas, 70 x 58 cm, Doyle New York, Jan 27, 2016, lot 59). Stilistically this painting is close to Peter Danckers de Rij, especially portrait of Court Chamberlain Adam Kazanowski in the Wawel Royal Castle and even more to the paintings by Adolf Boy. The painting was sold together with a portrait of a lady (oil on canvas, 81.3 x 68.5 cm, lot 60), painted in similar style, however, slightly larger and with not matching composition. It it possible that effigies of these important courtiers of Ladislaus IV were sent to their friends or relatives in England or Scotland. At the beginning of the 17th century Scottish Eva Forbes, was a wet nurse of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund. An old copy, perhaps made for Stanisław Koniecpolski (1591-1646), Grand Hetman of the Crown, is now in the Lviv National Art Gallery. It was previously in the hetman's palace at Pidhirtsi near Lviv in Ukraine, hanging above the portal of the Yellow Chamber, as shown in a photograph by Edward Trzemeski taken around 1880.
Portrait of Jan Zawadzki (d. 1645), Ambassador of the King of Poland with an ancient sword by Rembrandt, 1634, Rijksmuseum Amsterdam.
Portrait of Jan Zawadzki (d. 1645), Ambassador of the King of Poland in oval by Rembrandt, 1634, Rijksmuseum Amsterdam.
Portrait of Jan Zawadzki (d. 1645), Ambassador of the King of Poland by follower of Rembrandt, possibly Adolf Boy, 1634-1645, Private collection.
Portrait of a lady in a fur coat by follower of Rembrandt, possibly Adolf Boy, 1634-1645, Private collection.
Portrait of Polish-Lithuanian noble in a fur coat and a feathered hat by Isaac de Joudreville, 1630s, Private collection.
Portrait of Prince Alexander Charles Vasa by Rembrandt
"He is all according to your customs and the Polish spirit: he is bold, agile and quick-witted - why shouldn't you elect him", noted the words of king Sigismund III Vasa who was appealing to the nobility in 1626 in favor of his youngest son Alexander Charles Vasa (1614-1634), the French diplomat Charles Ogier, who visited Poland between 1635-1636. Unlike his brothers, Alexander was very sociable, because of this he resembled his half-brother Ladislaus. He was considered as a possible successor to Ladislaus and as the most gifted of the royal brothers. Alexander was also artistically talented: like his father, he could draw, he also learned to sing. His singing teacher was the musician and Jesuit Szymon Berent, who accompanied the prince on his trip to Italy (July 1633 - July 1634).
During the 1632 election, he supported his older brother Ladislaus, who was crowned king of Poland on 6 February 1633. Soon after Alexander set off on a trip to Spain. The prince was warmly welcomed in Rome, where Cardinal Antonio Barberini organized a major equestrian event in Piazza Navona in his name. While in Italy he resigned from visiting the royal court in Madrid. Probably one of the reasons was the rejection by king Philip IV of his endeavors to marry beautiful Anna Carafa della Stadera (1607-1644), Princess Stigliano, one of the richest heiresses of the entire Kingdom of Naples at that time. After a month and a half in Rome, the prince went to Florence, where he met his relatives from the house of Medici who had hosted Ladislaus nine years earlier. Lorenzo Medici, brother of Cosimo II, escorted him to Livorno, from where the prince was to sail to Genoa. In Milan, at the end of March 1634, he met his cousin Cardinal-Infante Ferdinand, brother of Philip IV, who was Governor of the Spanish Netherlands from November 1634. The prince also visited Vienna twice, where he spent over three months in total. In May 1634, just before leaving, he stayed with his uncle in Laxenburg for several days (after Ryszard Skowron's "Budowanie prestiżu królewskiego rodu", p. 72). Alexander returned to Poland in July 1634. He went to Lviv in today's Ukraine, where he was preparing for the Turkish expedition and in October 1634 he met with Prince John Casimir. There he probably contracted smallpox from his brother and died on November 19, 1634 on his way to Warsaw. From December 19, 1634 to January 2, 1635 king Ladislaus IV stayed in Gdańsk, where he commissioned a series of his portraits, created by Silesian painter Bartholomeus Strobel from Wrocław, who settled in Gdańsk in 1634. On this occasion the king also commssioned a series of maps commemorating the relief of Smolensk and surrender of Muscovite forces, who besieged the Polish garrison, in February 1634. One large map, created by Willem Hondius, a Dutch engraver from The Hague, who moved to Gdańsk in about 1636, is in the Skokloster Castle in Sweden (SKO 10693) and in the National Museum in Kraków (MNK III-ryc.-33883). Salomon Savery in Amsterdam created a print with king's effigy in Polish costume and Surrender of Mikhail Shein at Smolensk in the base after a painting by Pieter Claesz. Soutman (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, inventory number RP-P-OB-5592) and a print with the Relief of Smolensk (National Museum in Kraków, MNK III-ryc.-150 and The Royal Collection Trust, RCIN 722074.a), after a painting or a drawing by Ladislaus' court painter Adolf Boy, published by Willem Blaeu in Amsterdam in 1635. Additionally around that time a view of Kraków from the northwest by Nicolaes Visscher I after a drawing by Pieter Hendricksz. Schut was published in Amsterdam (MNK III-ryc.-29449). It is very possible that paintings have also been commissioned in Amsterdam in 1634. Some portraits from this period depicting Ladislaus (in the National Museum in Warsaw, 186555 and in the National Museum in Poznań, MNP Mo 2184) are attributed to the court painter of Sigismund III Vasa, Pieter Claesz Soutman, who from 1628 was active in nearby Haarlem, and who created the mentioned painting of Surrender of Mikhail Shein at Smolensk, engraved by Savery. The so-called Self-portrait with shaded eyes by Rembrandt comes from the collection of Christian Gottlob Frege (1715-1781), his son or grandson who bear the same name (according to two wax seals on the reverse). Frege was a Leipzig banker and merchant, who learned the exchange business in 1728 from a grocer in Dresden (then the informal capital of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth as the main residence of the Saxon kings) and had trading partners in Warsaw, Wrocław and other cities. Saxon kings transferred from the royal collection in Warsaw some preserved paintings by Rembrandt or his circle, all in the Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister, like Portrait of a man in the hat decorated with pearls (inventory number 1570), Portrait of a bearded man (1567) or Portrait of a man in a red kolpak (1568). In 1763 Dresden court appointed Frege electoral chamber councilor. In 2008 the work was acquired by the Leiden Collection in New York. The painting was signed and dated by the artist: Rembrandt. f. / 1634 and was overpainted relatively soon after its original execution. The man's oriental costume, removed from the 1950s to the 1980s, was similar to that visible in Rembrandt's Self-portrait with raised sabre dated '1634' (etching in the Print Room of the Warsaw University Library, inventory number Inw.zb.d. 2891) wearing a fur coat, similar to royal mantle and a tall Polish/Ruthenian-style hat, a so-called kolpak or kalpak, adorned with jewels, like in the portrait of unknown nobleman from the collection of Jan Popławski (1860-1935) in the National Museum in Warsaw (inventory number M.Ob.1639 MNW) or portrait of a bearded cleric by Helmich van Tweenhuysen (II) in the National Museum in Wrocław (inventory number VIII–489). The man however is much younger then in Rembrandt's Self-portrait with raised sabre. He has a slimmer nose and a bit protruding lower lip - the Habsburg (Masovian) jaw and resemble greatly Alexander Charles Vasa in his portrait in the Alte Pinakothek in Munich, possibly by Peter Danckers de Rij, or his effigy as a child from about 1619 (1885 copy in the National Museum in Warsaw, Rys Pol.3269) as well as effigies of his brothers John Casimir and Charles Ferdinand Vasa.
Portrait of Prince Alexander Charles Vasa (1614-1634) by Rembrandt, 1634, The Leiden Collection (version with additions in about 1935).
Portrait of Prince Alexander Charles Vasa (1614-1634) by Rembrandt, 1634, The Leiden Collection.
Portraits of Anna Catherine Constance Vasa by Rembrandt
At the beginning of September 1634, young Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski (1616-1667), son of Stanisław, voivode of Ruthenia, who just finished his studies in Leiden, set off to Spain. The year 1634 was the time of intensification of contacts between Ladislaus IV and his cousin Philip IV of Spain. The king, using various methods, skillfully influenced the court in Madrid. In January, he defended the commercial interests of Jerzy Hewel (Höwel, Hövelius), a Gdańsk merchant and a Calvinist, who had his ship and goods seized in the Netherlands. Hewel was a relative of famous astronomer Johannes Hevelius, who in 1630 studied jurisprudence at Leiden. In 1634 on his ship "Fortuna" he delivered weapons to King Philip IV. At that time the king of Poland set up a naval commission and, with the help of Hewel, created a fleet (11 ships, including one galley) equipped with 200 guns and 600-700 crew.
Three months later Ladislaus asked the King of Spain: "We must wage war with the Swedes, enemies of Our Royal House after a six-year truce, we will need all sorts of talented and experienced people, such as can be found especially in the Belgian provinces of Your Ducal Highness. So for this purpose, we send someone there to first of all call the masters skilled in building trenches and bring them to us" (after Mirosław Nagielski's "Z dziejów stosunków Rzeczypospolitej Obojga Narodów ze Szwecją w XVII wieku", pp. 47-49). Apart from politics, Polish-Lithuanian envoys in Spain also talked about personal matters. In 1633 the Scottish Wilhelm (William) Forbes, son of Alexander Forbes of Drumallachie (Drumlasie), sought salaries for the brothers of the Polish king. After the death of both parents, Ladislaus' younger siblings were left at the mercy of their brother, as the elective system of the Commonwealth did not provide for any due income or public functions for them. In June Philip IV promised to grant John Albert and Charles Ferdinand (his cousins) a salary for a period of two years, in 1634 he considered awarding the Order of the Golden Fleece to Prince John Casimir and in April 1636 his envoy proposed to the emperor to marry his daughter Cecilia Renata with Ladislaus IV. The mission of Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski to Madrid must have been successful as in October 1634 he was grated the wealthy Spiš County in today's Slovakia, obtaining the consent of the king to change the Spiš estates from royal to private and hereditary. On March 7, 1632, Balthasar Charles (1629-1646), the only son of King Philip IV and his first wife, Elisabeth of France, was sworn before the nobility and the Cortes of Castile as "His Majesty's Heir". His father soon began diplomatic efforts to seek a bride. Balthasar Charles' cousin Mary, Princess Royal (1631-1660), was proposed as a potential bride, but he was betrothed in 1646 to another cousin Mariana of Austria, daughter of Philip IV's sister Empress Maria Anna of Spain (1606-1646). Mariana of Austria was born on 24 December 1634 and after death of Balthasar Charles, the 14-year-old girl married her widowed 44-year-old uncle Philip IV in October 1649. The increased contacts of the Polish-Lithuanian diplomacy in 1634 left a significant mark in Spanish literature (compare "Clorilene, her son Segismundo and other Polish Princes and Princesses in the Spanish Golden Age Theater at 1634: Pedro Calderón de la Barca, Antonio Coello, Francisco de Rojas Zorrilla with Lope de Vega in the Background" by Beata Baczyńska). It is higly possible that in 1634 Ladislaus IV considered a marriage of his only sister Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) with the heir to the Spanish throne. Later her marriage to 9 years younger Archduke Ferdinand Charles of Austria-Tyrol (1628-1662) was considered. Philip IV undoubtedly must have received a portrait of this important bride, his cousin, whose godmother was Infanta Isabella Clara Eugenia (1566-1633), governor of the Spanish Netherlands, and the godfather Archduke Leopold V of Austria-Tyrol (1586-1632). Rembrandt was an eminent painter and his style infulenced generations of painters. Some 19th-century authors, when Poland did not exist on the maps of Europe, got us used to the idea that majority of the women he painted must be his wife Saskia van Uylenburgh: blonde, brown-haired, fat or slim, rich or poor. But was Saskia so exceptional that so many people were willing to pay for her effigy? On the other hand fabulously rich Princess Anna Catherina Constance Vasa, the only daughter of elected monarch of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and hereditary king of Sweden Sigismund III Vasa, sister of his sucessor Ladislaus IV, cousin of the ruler of half the known world, king Philip IV of Spain, niece of the Holy Roman Emperor Ferdinand II and a cousin of his successor Ferdinand III, descendant of the kings of Poland and Sweden, dukes of Milan and kings of Naples, could be, before my discoveries, identified on a handful of effigies. Rembrandt, supposedly met Saskia at the home of her relative, Hendrick van Uylenburgh, a painter and art dealer of King of Poland. Until she married Rembrandt, she assisted her brother-in-law, the Polish theology professor Jan Makowski (Johannes Maccovius, 1588-1644). Rembrandt and Saskia were married on 2 July 1634. The painting of Judith at the banquet of Holofernes (also known as Artemisia receiving Mausolus' ashes and Sophonisba receiving the poisoned cup) by Rembrandt in the Prado Museum in Madrid (oil on canvas, 143 x 154.7 cm, P002132) was possibly in the collection of Don Jerónimo de la Torre, secretary of state of Philip IV. Jerónimo died in Madrid in 1658, leaving his son Don Diego de la Torre as universal heir, and the work is probably tantamount to description in the appraisal of paintings of Don Diego made on September 3, 1662 by the painter Francisco Pérez Sierra: "The beautiful Judit, valued under the name of a Venetian woman, original, at four thousand reais" (La bella Judit, tasada devajo del nombre de una mujer veneciana, original, en quatro mill rreales) (after "¿Judit o Ester? El Rembrandt del Museo del Prado" by Juan María Cruz Yábar). The title of Venetian woman is most probably a reference to the woman's bleached hair. Blonde hair was valued as an association with youth and divinity and Venetian women of the 16th century created the famous 'Venetian Blondes' by exposing their hair to sunlight and applying bleaching mixtures (after "Being Beautiful: An inspiring anthology of wit and wisdom on what it means to be beautiful" by Helen Gordon, p. 81). In the inventory of the collection of King Charles III from 1772 the subject is also identified as Judith: "A painting showing Judith to whom some maids serve a goblet and on a round table an open book, figures of more than half length, an original by Rembrandt, seven quarters long and one and a half varas high" (Un quadro que representa a Judic, a quien unas doncellas sirven una copa, y en una mesa redonda tiene un libro abierto, figuras de más de medio cuerpo, original de Rembrandt, de siete quartas de largo y vara y media de caída). Biblical heroine Judith, exemplary in virtue and in guarding her chastity, unlike in the paintings showing Anna Catherina Constance's great-grandmother Bona Sforza by Lucas Cranach, is depicted after arriving at Holofernes's camp and before killing him. The artist signed and dated the painting which is clearly visible on the chair below the Judith's hand: Rembrant. /f 1634. In about 1634 Pieter Claesz Soutman and his workshop in nearby Haarlem created two effigies of King Ladislaus IV Vasa. One, in Spanish costume, is in Wilanów Palace in Warsaw, the other was published by Claes Jansz. Visscher in Amsterdam (Österreichische Nationalbibliothek). The same woman was also depicted in other paintings by Rembrandt. The earlierst of them shows her as Bellona, ancient Roman goddess of war. The work is signed and dated: Rembrandt f:/ 1633 and there is also inscription on the shield: BELLOON[A]. The woman is slightly younger than the Madrid version and her hair is not bleached. By 1797 this painting was in the collection of George Nugent Temple Grenville, 1st Marquess of Buckingham in Stowe House, Buckinghamshire in England, today in The Metropolitan Museum of Art (oil on canvas, 127 x 97.5 cm, 32.100.23). In 1633 Jan Zawadzki (ca. 1580-1645), a courtier of king Ladislaus IV was send on a mission to the Netherlands and England to discuss the marriage of the king with Elisabeth of the Palatinate (1618-1680), the eldest daughter of Frederick V, Elector Palatine (who was briefly King of Bohemia), and Elizabeth Stuart. Chancellor Jakub Zadzik, in his letter from Warsaw, dated January 15, 1633, recommended Zawadzki to the care of a councilor from Amsterdam. That same year Zadzik commissioned in nearby Delft a series of heraldic portiere tapestries with his coat of arms in the workshop of Maximiliaan van der Gucht (created between 1633-1636, Cathedral Museum at Wawel Hill and Czartoryski Museum in Kraków). After his stay in The Hague in May 1633, Zawadzki went to Scotland and obtained an audience with Charles I of England on June 26 in Edinburgh. Then he traveled around Scotland and England, during which he met Thomas Roe (after "Misja Jana Zawadzkiego na dwory Europy Północnej w 1633 roku…" by Marta Szymańska, p. 93). Undeniably, he brought some diplomatic gifts with him and portraits of the members of the royal family. She was also depicted in a portrait wearing a pearl necklace, associated with purity, chastity and innocence. The painting, signed: Rembrandt f. 1634 and sold in Lucerne (Fischer, 5-9-1922), is today in the National Museum of Fine Arts in Buenos Aires (oil on canvas, 62.5 x 55.6 cm, 8622). Another painting by Rembrandt, in the National Gallery in London (oil on canvas, 123.5 x 97.5 cm, NG4930), shows her as Flora, the Roman goddess of fertility, flowers and vegetation. It was signed and dated by the artist Rem(b).a... / 1635 and before 1756 it was in the collection of Marie Joseph d'Hostun de La Baume-Tallard, duc d'Hostun, comte de Tallard in Paris. Its earlier history is unknown, therefore we cannot exclude the possibility that it was brought to Paris by John Casimir Vasa, Anna Catherina Constance's brother, after his abdication in 1668 or it was sent as a gift to Anna Catherina Constance's cousin Anne of Austria (1601-1666), Queen of France. Two copies of this painting, probably made by Rembrandt's workshop, are known. One, sold in Paris in 2023 (oil on canvas, 121.1 x 95.4 cm, Bonhams, April 19, 2023, lot 25), was most likely before 1908 in Ms. Ellice's collection in Invergarry, Scotland. The other, full length, was in London before 1908 (oil on canvas, 154 x 127 cm, Thomas Agnew & Sons, compare "Rembrandt: des Meisters Gemälde in 643 Abbildungen" by Wilhelm Valentiner, p. 535, items B 187, B. 188). A drawing in the British Museum (inventory number Oo,10.133), attributed to Ferdinand Bol, who worked as an apprentice in Rembrandt's studio in Amsterdam, could be a preparatory drawing to the painting by Rembrandt in London. The same as in the painting representing the same woman as Minerva, Roman goddess of wisdom, justice and victory, in her study. A drawing signed by Ferdinand Bol (F:bol.ft.) is in the Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam (RP-T-1975-85), while the painting from the collection of James, 13th Lord Somerville in Drum House, Gilmerton, signed by Rembrandt (Rembrandt. f. / 1635), is today in The Leiden Collection in New York (oil on canvas, 138 x 116.5 cm, RR-107). Apparently in 1635 Rembrandt and his pupils worked on some large commission, maybe conneted with another diplomatic mission of Jan Zawadzki, who was sent again to England, The Hague and also to Paris in 1636. The same sitter, with protruding lip of the Habsburgs and Masovian dukes clearly visible and wearing a crown, was depicted in the painting by Rembrandt from 1638 (signed and dated: Rembrandt. f. 1638.) showing the Wedding feast of Samson, today in the Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden (oil on canvas, 125.6 x 174.7 cm, Gal.-Nr. 1560). It was acquired by Augustus II, elected King of Poland and Elector of Saxony, before 1722. On October 18, 1641 the painter Philips Angel commented on the painting in his speech to the painters of Leiden on St. Luke's Day. In 1654, the work was probably in the estate of Cathalijntje Bastiaens (1607-1654), widow of Cornelis Cornelisz. Cras (d. 1652), mentioned as "a wedding by Rembrandt" (een bruyloft van Rembrandt). Most probably in 1777, when he was working for Izabela Czartoryska in Voŭčyn (Wołczyn, Wolssin en Lithuanie), Jean-Pierre Norblin de La Gourdaine created a drawing after this composition, today in the National Museum in Warsaw. It is possible that he saw it in Dresden, however since his drawing is not identical with the painting in Dresden, it is possible that another version was also in the Czartoryski collection. Norblin was a great admirer of Rembrandt's work and frequently created paintings, drawings and etchings in his style. It is also possible that he included in his portfolio a drawing by the master or his workshop. In this painting the biblical hero Samson poses a riddle to the guests at his wedding feast, dressed in oriental and Polish costumes. It is not Samson, however, who is in the center of the composition, but his Philistine bride, another biblical femme fatale who betrayed her husband. Therefore the painting could be a warning of what type of wife the woman should not be and it was most probably commissioned by the man in a turban, holding a flute and gazing at the viewer. It could be also a subtle allusion to politics, exaclty as Daniel and king Cyrus before Bel (Prophet Daniel exposing the fraud of the priests of Idol Baal) by Bartholomeus Strobel in the National Museum in Warsaw (M.Ob.1284), created between 1636 and 1637 and considered to be political allegory of the reign of Ladislaus IV Vasa. She was also represented in a small painting, wearing a large ruby pendant. This picture, painted on oak wood panel, comes most probably from the old collection of the Royal Palace on the Isle in Warsaw (oil on panel, 21.5 x 17 cm, M.Ob.2663 MNW, Dep 473). It is attributed to an 18th century imitator of Rembrandt and could a copy of a lost original from the 1630s. A very similar painting in the Israel Museum in Jerusalem (oil on panel, 11.5 x 9 cm, B86.0906), is attributed to follower of Rembrandt and dated to the first half of the 1630s (1630-1635). It comes from the collection of French banker and art collector Ernest May (1845-1925) in Strasbourg and Paris. Among the paintings belonging to the "Victorious King" John III Sobieski (1629-1696), which could come from earlier royal collections and mentioned in the inventory of the Wilanów Palace from 1696, we find "The image of Pallas" (Obraz na ktorym Pallas, No. 243). The painting was brought to the Royal Marywil Palace in Warsaw from other royal residences after the king's death. This inventory included several paintings by Rembrandt (Rynbranta Malarza, No. 74, 75, 92, 93, 210) and other Dutch painters from the the king's collection. "A painting of Judith, in a carved and gilded frame" (Obraz Judyty, wramach rzniętych złocistych, No. 77), which is sometimes identified as a self-portrait of Lavinia Fontana disguised as Judith with the head of Holofernes (National Museum in Kraków, MNK XII-A-664), hung in the King's Bedroom among tronie-like portraits of artistic agent of the Polish-Lithuanian Vasas Hendrick van Uylenburgh (called the Portuguese rabbi) and his daughter Sara (the Jewish girl in a biret) by Rembrandt (No. 74, 75, now at the Royal Castle in Warsaw). The painting of Judith was valued at 200 thalers, while the mentioned paintings by Rembrandt at 150 and 190. The higher value indicates that this painting must have been comparable to the other two, or even better, and that it was perhaps also by Rembrandt or another Dutch painter. The descriptions contained in this register are generally quite detailed. For example regarding a painting of Herodias, worth 40 thalers, identified with the painting kept at the Wilanów Palace (Wil.1519), being a disguised portrait of Princess Elisabeth of Hesse (1502-1557), it is states "A painting of Herodias with the head of Saint John on a panel in a black frame" (Obraz Herodyady z głową Swiętego Iana na desce wramach czarnych, No. 217). "The head of Holofernes" is therefore missing in the description of Sobieski Judith, as in the Prado painting, was it therefore a copy of this work by Rembrandt or its reduced version? Maybe we'll never know. There is also a large image of Pallas (Athena/Minerva) in the Radziwill collection in the 17th century. The inventory of paintings from the collection of Princess Louise Charlotte Radziwill (1667-1695), drawn up in 1671, lists several portraits of Sigismund III and his successor Ladislaus IV, two portraits of Queen Cecilia Renata (61/1, 110/9), one of Prince Sigismund Casimir Vasa (52/2), one of Prince Alexander Charles Vasa (52/3), and one of Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga (307/16). Several effigies of other members of the Polish-Lithuanian royal family are missing. It is possible that their portraits were "disguised" and their true identity was lost after the Deluge. The inventory mentions "Two large similar paintings on tin plate in black frames, one of Pallas and the other of a battle" (Obrazów dwa wielkich jednakich na blasze w ramach czarnych, na jednym Pallas, a na drugim bitwa jakaś, 740-741) (compare "Inwentarz galerii obrazów Radziwiłłów z XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska). Although no paintings by Rembrandt or his school painted on tin are known, especially in large format, this cannot be ruled out. This painting was certainly destroyed to reuse the material, either by invaders or due to the impoverishment of the family and the country. Princess Anna Catherina Constance, who died childless on October 8, 1651, aged 32, was forgotten shortly after her death. Before her marriage in 1642 the workshop of Maximilian van der Gucht in Delft, not far from Amsterdam, created a tapestry with her coat of arms and monogram A.C.C.P.P.S. (Anna Catharina Constantia Principissa Poloniae Sueciae), most likely one of the series, that she brought to Neuburg an der Donau (today in the Munich Residence). Chancellor Zadzik commissioned his tapestries in van der Gucht worshop as well as Mikołaj Wojciech Gniewosz, Bishop of Włocławek, secretary of Kings Sigismund III and Ladislaus IV (today in the Skokloster Castle in Sweden). The princess brought with her to Neuburg the most exquisite works of art created not only in Europe, but also in Persia (Safavid kilims with coat of arms of her father are in the Munich Residence and Wittelsbacher Ausglechsfonds in Munich) while her portraits were created by Rembrandt.
Portrait of Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) as Bellona by Rembrandt, 1633, The Metropolitan Museum of Art.
Portrait of Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) as Judith at the banquet of Holofernes by Rembrandt, 1634, Prado Museum in Madrid.
Portrait of Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) wearing a pearl necklace by Rembrandt, 1634, National Museum of Fine Arts in Buenos Aires.
Modello or ricordo drawing for a portrait of Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) as Flora by Ferdinand Bol, ca. 1635, British Museum.
Portrait of Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) as Flora by Rembrandt, 1635, National Gallery in London.
Portrait of Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) as Flora by workshop of Rembrandt, ca. 1635, Private collection.
Portrait of Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) as Flora by workshop of Rembrandt, ca. 1635, Private collection.
Modello or ricordo drawing for a portrait of Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) as Minerva in her study by Ferdinand Bol, ca. 1635, Rijksmuseum Amsterdam.
Portrait of Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) as Minerva in her study by Rembrandt, 1635, The Leiden Collection.
The Wedding feast of Samson with portrait of Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) by Rembrandt, 1638, Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden.
The Wedding feast of Samson by Jean-Pierre Norblin de La Gourdaine after Rembrandt or Rembrandt's pupil, 1777 (?), National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) with a ruby pendant by follower of Rembrandt, possibly Maerten van Couwenburgh, 18th century (?) after original from the 1630s, Palace on the Isle in Warsaw.
Portrait of Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) by follower of Rembrandt, 1630s, Israel Museum in Jerusalem.
Portraits of Prince Christopher Radziwill wearing a feathered bonnet by Rembrandt and studio
The signed and dated portrait by Rembrandt kept at the Musée Jacquemart-André in Paris (RHL van Ryn 1632, inventory number 423) was long considered to be the effigy of his wife Saskia van Uylenburgh, relative of Hendrick van Uylenburgh, artistic agent of king Sigismund III Vasa. It was mentioned with this identification in numerous publications, such as "Treasures of Musee Jacquemart-Andre, Institute de France" (Issue 8, p. 2), published in 1956 or the postcards from the Museum by J.E. Bulloz, signed Portrait de Saskia. It was after restoration in 1965 that the painting was identified as being the pendant of the portrait of Frederick Henry (1584-1647), Prince of Orange, signed by Gerard van Honthorst (GHonthorst fe 1631), formerly at the Huis ten Bosch Palace in The Hague. The woman is now identified as Frederick Henry's wife, Amalia of Solms-Braunfels (1602-1675), Princess of Orange and this identification was confirmed in the inventory of the Stadtholders Quarters in The Hague drawn up in 1632, where "A likeness of Her Excellency in profile done by Rembrants" (Een contrefeytsel van Haere Excie in profijl bij Rembrants gedaen) is mentioned.
The woman in the painting resembles many women painted by Rembrandt and she looks more like a patrician lady than the wife of the stadtholder and his political advisor, so probably Rembrandt's portrait was replaced by the portrait painted by Gerard van Honthorst in which she was depicted in more aristocratic attire. She has lighter hair than in the other portraits and the resemblance is also very general. Nineteenth-century authors, when the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth disappeared from the maps of Europe after numerous invasions ultimately divided by insatiable imperialist neighbors, led us to believe that Rembrandt made a living from painting himself and his family, which is obviously absurd. Although many of his works are in fact true self-portraits, at a time when there were no public or other subsidies for artists, Rembrandt created an impressive collection of his own effigies. Some of them could be tronies, so popular in the 17th century in the Commonwealth according to preserved inventories, an advertisement of his talent, as in the case of the self-portraits of Sofonisba Anguissola, sent to different patrons in Europe, or simply created for practice, but who was this mysterious benefactor, thanks to whom he could paint himself so often? Among the artist's major works between 1628 and 1656 are approximately 27 of his self-portraits and over 40 in his lifetime, which is an impressive number for a 17th-century painter. According to known historiography, Rembrandt was not a court painter of an important person. He painted the ambassador of the King of Poland, but he is not considered a painter of European monarchs, like Rubens who worked for Sigismund III and his son Ladislaus IV, painted the monarchs of Spain, France, England, the rulers of Flanders, Lorraine, Mantua and Genoa or Diego Velázquez, court painter to the King of Spain, sovereign of an immense empire. While Rubens and Velázquez only produced a few of their self-portraits, when compared with Rembrandt's works found in many different collections (in Rome, Austria, France, Poland and Sweden), we will have the impression that this painter of the Dutch patricians was a true Prince or even the king of the Baroque portrait painters. In some of Rembrandt's "Self-portraits", as in the case of likeness of Amalia of Solms-Braunfels, the resemblance to the painter is quite general. This is the case of a series of effigies wearing a feathered bonnet, created by Rembrandt and his followers in 1635. The "Prince of painters" was depicted in a truly princely pose and outfit. It is strange that so many experts want to believe that in the highly hierarchical Western Europe of the 17th century, Rembrandt allowed himself to be portrayed in this way in a series that appears to be official portraits. The portrait, now kept at Buckland Abbey in Devon (oil on panel, 91.2 x 71.9 cm, NT 810136), was signed and dated by the painter (bottom right: Rembran(..) / f ... 1635) and comes from the collection of the princes of Liechtenstein, first mentioned in the catalog of the Liechtenstein collection in Vienna in 1767 (Descrizzione completa di tutto ciò che ritrovasi nella galleria di pittura e scultura di sua altezza Giuseppe Wenceslao ... by Vincenzo Fanti). The "Prince of painters" apparently sent his portrait to the princes of Liechtenstein or even to the emperor in Vienna. A good copy of the portrait, probably painted by Rembrandt's circle, is in the Palazzo Corsini in Rome (oil on panel, 82 x 71.5 cm, inventory number 887). This palace was built at the end of the 15th century by the Riario family, nephews of Pope Sixtus IV della Rovere and in the 17th century the palace was inhabited by Queen Christina of Sweden, so the portrait was probably offered to the Pope, the cardinals or the Queen of Sweden. In the same collection there is also the portrait of Prince John Casimir Vasa (1609-1672) in a fur hat by follower of Rembrandt (inventory number 305), identified by me. Another very good workshop copy, restored by Marina Aarts in Amsterdam in 2020, was sold in 2017 in Sweden (oil on panel, 77 x 63 cm, sold at Uppsala Auktions Kammare, June 7 - 10, 2017, lot 1105). The painting comes from Viderup Castle in Scania, which become the Swedish province in 1658. An old copy from the Wiesbaden Museum is mentioned in Iconographia Batavia by Ernst Wilhelm Moes, Volume 2 (item 34, p. 313) and another is in the Museum of Fine Arts in Budapest. Interestingly, along with the Wiesbaden portrait, Moes mentions two portraits by Rembrandt wearing a Polish coat (op en Poolschen mantel aan, items 35 and 36) - self-portrait in the Norton Simon Museum in Pasadena and portrait of a man from Me Lellan collection in Glasgow. In a series of portraits of a man in a fur hat, also identified as Rembrandt's self-portraits, his costume is also very eastern, not to say Polish-Lithuanian or Ruthenian (e.g. from the collection of Michiel Onnes van Nijenrode, Kasteel Nijenrode). In 1914, a copy of Rembrandt's portrait from the collection of the Prince of Liechtenstein in Vienna was in the Cook Collection, Doughty House, Richmond (oil on canvas, 87 x 66 cm). The same collection also included a portrait of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa, future Ladislaus IV, on horseback by the workshop of Peter Paul Rubens (after "A catalogue of the paintings at Doughty House ...", items 321 and 344, p. 79, 91), today at the Wawel Royal Castle (inventory number 6320). In 2017, a miniature attributed to the German miniaturist Joseph Kaltner (born ca. 1758 - died after 1824), probably based on a painting formerly in the Liechtenstein collection, was sold in Vienna (oil on paper, mounted on metal, 18.2 x 14.8 cm, sold at Dorotheum, September 13, 2017, lot 33). In the 17th century, as in previous era, many elements of portraits had important symbolic meaning. The man in the mentioned series by Rembrandt and his followers, created in 1635, wears a parade gorget and the decoration of his hat resembles the eastern szkofia or aigrette, popular in Poland-Lithuania and Hungary. A somewhat similar szkofia can be seen in a portrait of Prince Christopher II Radziwill (1585-1640), husband of Anna Kiszczanka (1593-1644), kept in the National Art Museum of Belarus in Minsk. The feathers on his hat also had a symbolic meaning: one is white and the other orange or brown. However, the Vanitas still life, attributed to Abraham Susenier, indicates that its true color should be red. This painting, now at Agnes Etherington Art Centre in Kingston (oil on canvas, 59.7 x 73.7 cm, 57-001.32), is variably dated between 1635-1668 or 1669/1672. In 1932 it was in the private collection of B. Zimmermann in Switzerland. If this collector was Bernard Zimmermann (1885-1931) - Polish architect of Jewish origin, active in Kraków, this painting could come from a Polish aristocratic collection. In this still life with a statuette, a skull, an overturned roemer and a portfolio of drawings, the two feathers, white and red placed on the skull, most likely symbolize the death of an important person. This man must be identified as the man from paintings created in 1635 by Rembrandt and studio, because a study drawing with the same image lies on the table. The gorget in the portraits indicates that the man is a soldier, his rich outfit and pose that he is a prince, szkofia-like hat decoration that he comes from Eastern Europe and the colors of feathers that he is an important official of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. Although today these colors are mainly associated with Poland and not Lithuania, in the 17th century they were the colors of Sarmatia, that is, the Commonwealth of Poland, Lithuania, Ruthenia, Prussia, etc., as evidenced by the so-called Stockholm Roll at the Royal Castle in Warsaw (ZKW/1528/1-39), showing the entry of the wedding procession of Sigismund III Vasa into Kraków in 1605. Many dignitaries, as well as guards, wear white and red (crimson) clothing. The horses are also painted white and red. The man is therefore Prince Christopher II Radziwill (1585-1640), whose wife's portrait by Rembrandt or studio is in the Metropolitan Museum of Art (14.40.625) and he commissioned this series of his splendid effigies on the occasion of receiving the important and long-awaited position of Grand Hetman of Lithuania, the highest-ranking military officer of the Grand Duchy, in early 1635. King Ladislaus IV Vasa, in the Grand Hetman's Privilege issued on January 1, 1635 in Gdańsk, stated that the Grand Hetman is the commander of the entire army of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. In the later privilege issued in Toruń, he named Christopher's brother-in-law Janusz Kiszka (1586-1654), Field Hetman of Lithuania (after "Rzeczpospolita Wazów II ... " by Henryk Wisner, p. 28). The studies for the portraits were therefore most likely made in Gdańsk. As mentioned above, the resemblance to Rembrandt's features is very general, the man has a smaller nose and flatter cheeks than the artist in his self-portrait in a gorget from around 1629 (Germanisches Nationalmuseum in Nuremberg), mentioned effigy in a Polish coat in Pasadena and self-portrait at the age of 34, painted in 1640 (National Gallery, London). His facial features resemble those in the portrait of the Grand Hetman of Lithuania, such as the portrait in Minsk at the age of 51, painted in 1635 (CHRISTOPHORVS RADZI/WIL DVX [...] ANNO. 1635. / ÆTATIS 51.), engraving by Willem Jacobsz Delff after a painting by Michiel Jansz. van Mierevelt, "Which portrait was painted and modified by Michaele Johan Miereveldio based on the model sent from Poland" (Quam effigiem a Michaele Johan Miereveldio iusta exemplar e Polonia transmissum depictam et reformatam ...), created in 1639 and a drawing preserved in the State Hermitage Museum (ОР-45862), made between 1646 and 1653. The prince, who in Mierevelt's portrait is bald, probably like King Ladislaus IV wore wigs with more courtly attire (Ladislaus in his portrait at Kórnik Castle from around 1625 is almost bald, while in his coronation portrait at the National Museum in Warsaw from around 1633 he has lush hair). After Sigismund III Vasa's second marriage in 1605 to Constance of Austria (1588-1631), the influence of sometimes fanatical Catholics increased significantly at the royal court and difficult times began for people of other religions. Christopher's commitment to Calvinism was the reason Sigismund III blocked his nomination to the Senate for years. He took several thousand armed soldiers with him to the election after his death (1632) and appealed for help from the Elector of Brandenburg to ensure the protection of his co-religionists. He studied at the universities of Leipzig and Heidelberg. On December 20, 1602 in Heidelberg, it was proposed to elect him rector, but this idea was rejected (after "Studia z dziejów epoki Renesansu" by Henryk Zins, p. 44). He traveled to Switzerland, France, England and the Netherlands. In 1603, he stayed at the camp of Maurice of Orange (1567-1625) at 's-Hertogenbosch, learning the art of war and fortification. To increase the profitability of his estates, he brought settlers from the Netherlands and England, imported cattle from the Netherlands, established fish ponds and horse farms. He inherited the leadership of the Lithuanian Calvinists from his father Christopher Nicolaus Radziwill (1547-1603). As a tolerant person, he counted among his friends Eustachy Wollowicz (Eustachijus Valavičius; 1572-1630), Catholic bishop of Vilnius. Christopher had his portraits, mentioned in certain preserved inventories. Wollowicz was a great patron of the arts and had several of his effigies made by Lucas Kilian, a German engraver active in Augsburg, in 1604, 1618, 1621. Kilian also made an engraving (in 1604), perhaps based on a painting by Michelangelo, and representing Pietà with the Wollowicz coat of arms (British Museum, V,2.41). Henryk Wisner, in his monographic work, writes that "the prince was a connoisseur of painting, his assessments being much ahead of his time" (after "Książka i literatura w kręgu Radziwiłłów birżańskich ..." by Mariola Jarczykowa, p. 23). Before 1629, the Hetman purchased paintings in Utrecht from Hendrick ter Brugghen, one of the most prominent representatives of Caravaggionism in the Netherlands. Perhaps the large painting of the Battle of Nieuwpoort painted by Adriaen van de Venne, active in The Hague, for a Polish prince was associated with the hetman (after "Galerie obrazów i "Gabinety Sztuki" Radziwiłłów w XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska, p. 88). The inventory of Radziwill Castle in Lubcha in Belarus (Central Archive of Historical Archives in Warsaw, 1/354/0/26/45) lists many valuable items from the prince's collection. It also mentions several of his garments which could be depicted in the paintings, like hat decorations and feathers (Kity y Piora), including: "Indian broad spotted feather", "Four red parrot feathers, Eight better white crane feathers", "Three wonderful black crane feathers" (Pioro Indyiskie szerokie Pstre, [...] Pior Papuzych Czerwonych Cztery, Pior żorawich Białych Przednieyszych osm [...], Pior Czarnych żorawich Cudnych trzy), 10 magierka caps, incluing 3 black "hairy" (kosmate - velvet?) and 4 "smooth" (gładkie - silk?) or 19 different kurta (a jacket or a short kaftan), like "yellow satin kurta with stitching" or "perfumed leather kurta" (Kurta Atłasowa żótła Przeszywana [...] Kurta skurzana Perfomowana). Christopher strongly supported Ladislaus IV's plans for a Protestant marriage to Princess Elizabeth of Bohemia (1618-1680), the eldest daughter of Frederick V, Elector Palatine (who was briefly King of Bohemia) and Elizabeth Stuart. Effigies of the princess are mentioned in several inventories of the Radziwill collections. However, the king, feeling deceived during the peace negotiations with the Swedes in 1635 by the Protestant magnates, changed his mind and decided to seek the support of the Catholic camp, notably the Habsburgs, to regain the Swedish crown. In the spring of 1636, Holy Roman Emperor Ferdinand II proposed a marriage between Ladislaus and Archduchess Cecilia Renata of Austria. The emperor offered a substantial dowry, financial support to regain the Swedish throne, as well as salaries and titles for the royal brothers (after "Projekt kalwińskiego małżeństwa ..." by Zofia Trawicka, p. 98-99). In 1636, Rembrandt placed the man with two feathers in his famous print Ecce Homo (British Museum, F,4.182). The etching bears the signature: Rembrandt f. 1636 cum privile and it is considered a joint work with a Leiden engraver, Jan Gillisz. van Vliet (died 1668). The painting Ecce Homo in grisaille kept at the National Gallery in London (NG1400), signed and dated: Rembrandt.f./1634, is often considered to be the original composition. The artist modified and added several elements, including the man. "According to the Gospel of John (19:5), Pontius Pilate showed Jesus to the crowds during the trial with the words "Ecce homo" (Behold the man). However, the picture of Rembrandt seems to be dominated by the diagonally displayed knobbly staff. One could obviously think of a judge's staff" (after "The Road to Justice: The Bible and the law ...", p. 109). The notion of divine justice seems to be the most important message of this work of art. The bust on a high pedestal on the left is considered to be the effigy of the Roman emperor Tiberius Caesar. Rembrandt's drawing depicting the bust of Emperor Galba (Berlin Museum of Prints and Drawings) and other similar studies (Albertina in Vienna and Royal Library of Turin) prove that he knew what a Roman emperor should look like. However, his Tiberius Caesar with the bushy mustache looks more like a Polish-Lithuanian nobleman than a Roman emperor and resembles several effigies of King Ladislaus IV - in Roman costume on horseback in Friedrich Getkant's Topografia practica (1638), as a sculpted bust in Paweł Szczerbicz's Speculum Saxonum (1646), with laurel wreath in Triumphal arch by Jeremias Falck Polonus (1646) or, also in the form of a sculpted bust, in Apotheosis of John II Casimir Vasa by Cornelis Bloemaert after Lazzaro Baldi (ca. 1648). A good painting dated 1647 kept in the National Museum in Gdańsk, attributed to the Dutch painter active in Gdańsk Helmich van Tweenhuysen (II) or Johann Aken, is one of the oldest inspirations by Rembrandt's print and proves its popularity in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. The painting was founded by Adrian von der Linde (1610-1682), mayor of Gdańsk and a zealous Lutheran, who, nota bene, opposed the growing Calvinist influence in the city. The German inscription on the panel also refers to the concept of justice – the righteousness of God (2 Corinthians 5:21). An old painted transposition of the print, created between 1640 and 1715, can be found in Kołobrzeg Cathedral. According to inscription in Latin it was painted on April 3, 1640 (IOACHIMUS. KNOCHENHOWERUS. pinxit. ANNO. 1640. / D: 3. APRIL.) and renovated in 1715 by the grandson Aegidius Knochenhauer. The man in the print ostentatiously hold a large mace known as morning star (Morgenstern in German), which was in common use from the 14th to the 17th century, mainly in plebeian and peasant units (especially popular among the Hussites and German peasant insurgents of the 16th century). They were also popular in Poland-Lithuania in the 17th century (called nasiek, nasieka, nasiekaniec, siekaniec, siekanka, kropacz, palica, wekiera or morgensztern), so that "peasants were forbidden to go to the market with nasiek, sticks or clubs" (after "Encyklopedja staropolska ..." by Zygmunt Gloger, Volume 3, p. 255). The morning star is most often used as the name for the planet Venus when it appears in the east before sunrise, while in classical mythology the name of the planet Venus as the morning star is Lucifer ("light-bringer" in Latin). Interpretations could vary, however, the composition can be compared to the masterfully painted Daniel and King Cyrus before the Idol Bel by Bartholomeus Strobel in the National Museum in Warsaw (M.Ob.1284 MNW), painted around the same time (1636 and 1637). The painting by Strobel is frequently interpreted as a political allegory for the reign of Ladislaus IV, when the Protestant party was deeply disappointed by the king's failure to seek the hand of Princess Elizabeth of Bohemia. The direct and explicit link between the paintings and prints and the Radziwills may never be established, but given all the information presented as well as the amount of work by Rembrandt and his students which, despite enormous destruction, looting, confiscations and evacuations, can be linked to Poland-Lithuania, the man can inevitably be identified as a splendid patron Christopher Radziwill.
Portrait of Prince Christopher Radziwill (1585-1640), Grand Hetman of Lithuania, wearing a feathered bonnet by Rembrandt and studio, 1635, Buckland Abbey.
Portrait of Prince Christopher Radziwill (1585-1640), Grand Hetman of Lithuania, wearing a feathered bonnet by follower of Rembrandt, ca. 1635, Palazzo Corsini in Rome.
Portrait of Prince Christopher Radziwill (1585-1640), Grand Hetman of Lithuania, wearing a feathered bonnet by follower of Rembrandt, ca. 1635, Private collection.
Portrait of Prince Christopher Radziwill (1585-1640), Grand Hetman of Lithuania, wearing a feathered bonnet by follower of Rembrandt, ca. 1635, Museum of Fine Arts in Budapest.
Portrait of Prince Christopher Radziwill (1585-1640), Grand Hetman of Lithuania, wearing a feathered bonnet by Joseph Kaltner after Rembrandt, ca. 1806, Private collection.
Ecce Homo with portrait of Prince Christopher Radziwill (1585-1640), Grand Hetman of Lithuania by Rembrandt and Jan Gillisz. van Vliet, 1636, British Museum.
Vanitas still life with art collection of Prince Christopher Radziwill (1585-1640), Grand Hetman of Lithuania by Abraham Susenier, ca. 1640, Agnes Etherington Art Centre in Kingston.
Portraits of Elżbieta Kazanowska by circle of Rembrandt and Adolf Boy
In spring of 1633, Adam Kazanowski, thanks to the support of King Ladislaus IV, married the then 14-year-old Elżbieta (Halszka) Słuszczanka (1619-1671). For Kazanowski, the marriage meant not only a substantial dowry (50,000 zlotys), numerous movable and immovable property, but also valuable connections. On the occasion of the wedding, Halszka received a pure gold mug and 20,000 zlotys from the king, the value of other gifts amounted to 40,000 zlotys.
Earlier that year, on March 2, 1633 Elżbieta's father Aleksander Słuszka or Słuszko (1580-1647) become the voivode of Minsk. He was brought up as a Calvinist, but later, in about 1621, he converted to Catholicism together with his wife Zofia Konstancja Zenowicz. For his favourite, Adam Kazanowski, who already recived a magificent palace in Warsaw, later known as Kazanowski (or Radziejowski) Palace, the king restored the office of the Crown Steward in 1633, and soon after that, he become the Pantler of the Crown and recieved other offices. In 1634 he most probably accompanied the king to Gdańsk and on June 1635, he came with him to Toruń. In 1635, he conducted a successful purchase of a fleet of ships for Ladislaus IV in Gdańsk (12 ships for 379,500 zlotys). Kazanowski also participated in the Vistula grain trade and one of the largest granaries in Warsaw's Skaryszew belonged to him. Słuszczanka and her husband accompanied the king in 1638 on a trip to Baden near Vienna, and in the Imperial capital she won in women's rifle shooting competition, for which she received "a nice jewel". The Lithuanian (Litewka), as Łukasz Opaliński called her, was famous for her frivolous sexual conduct, just like her husband. Years passed and she did not get pregnant. Perhaps she contracted syphilis from Kazanowski, who according to rumors, gained property and offices because he kept a harem of lovers for the ruler (after "Jak romans doprowadził do jednej z największych tragedii w dziejach Polski" by Jerzy Besala). Educated in Braniewo, Würzburg, Leiden and Padua (after Marcin Broniarczyk "Wykształcenie świeckich senatorów w Koronie za Władysława IV", p. 280), Kazanowski was a patron of arts. According to Adam Jarzębski's "Short Description of Warsaw" in his palace there was a workshop of Dutch painters (lines 1605-1608, Olandrowie, Nie Polacy). His portrait at the age of 44 as a Court Chamberlain (Wawel Royal Castle), was created by Dutch painter Peter Danckers de Rij, born in Amsterdam (signed: P Donckers fecit / AETATI[S) SVAE 44). Other preserved effigies of Kazanowski were created by another Dutchman Willem Hondius: engraving with a portrait against the Vistula River and his estates in Praga and Skaryszew, created in 1646, and two other created in 1648 after paintings by Maerten van Couwenburgh, most probably a relative of Christiaen van Couwenbergh from Delft. Other effigy from the 1640s (Royal Castle in Warsaw) is attributed to engraver Jeremias Falck Polonus from Gdańsk. In 1645 Hondius also created a series of views of the Wieliczka salt mine, sponsored by Kazanowski, who was a żupnik (manager of a mining district) from 1642. "Never has Poland seen and will never see so much wealth in the hands of a single man", wrote about the Court Chamberlain Wawrzyniec Jan Rudawski (1617-1674). Kazanowski died childless on December 25, 1649 and his beautiful wife Halszka become heiress to a large fortune. Just few monts later, in May 1650, she married another royal courtier Hieronim Radziejowski (1612-1667). This marriage was reportedly arranged by her lover, the new king John II Casimir Vasa (half brother of Ladislaus IV). Soon, however, disagreements began. The reason was supposed to be the portrait of the deceased Kazanowski, which the lady did not want to remove from her room, others said that it was not the portrait, but the young Jan Tyzenhaus, a handsome royal valet, who had quarreled the couple. Violent Radziejowski became very angry when his wife's affair with the king was revealed in the late spring of 1651. Elżbieta left the military camp near Sokal and took refuge in the convent. She also filed a lawsuit for annulment of the marriage. Despite repeated attempts, Radziejowski did not manage to break into the Kazanowski Palace, defended by Elżbieta's brother Bogusław Słuszka. At the time, John Casimir and pregnant Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga were staying in the nearby Royal Castle. At the Sejm session Radziejowski was accused of offending the majesty and violating the security of the royal residence and sentenced to banishment and infamy. Słuszczanka and her brother Bogusław received much lighter sentences - a fine of 4,000 zlotys and a year and six weeks of hard imprisonment in the tower. Halszka drove to the prison at the Castle in the carriage drawn by six horses. After twelve weeks, she was forgiven and her brother left the prison earlier (after "Życie codzienne w Warszawie za Wazów" by Jerzy Lileyko, p. 270). Portrait of a lady holding a fan from the Jan Popławski collection was offered to the National Museum in Warsaw in 1935 (inventory number 34661), most probably lost during World War II. This small painting (28 x 22 cm) was painted on a wood panel and attributed to a imitator of Dutch painting from the 18th century (after "Katalog wystawy obrazów ze zbiorów dr. Jana Popławskiego" by Jan Żarnowski, number 97, p. 53). The pose of a woman with her right hand on a table and holding a fan in her left hand is very similar to portraits representing the king's sister Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (Ambras Castle, GG 5611) and Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria (Nationalmuseum in Stockholm/Gripsholm Castle, NMGrh 1417), both holding fans and painted by Adolf Boy, court painter of Ladislaus IV, in the late 1630s or early 1640s, as the style indicate. Also the woman's hand is very similar to the hand of Anna Catherine Constance in Ambras painting. If not the material and dimensions, this portrait could be considered as a pendant to mentioned portrait of Kazanowski by Danckers de Rij (oil on canvas, 119.5 x 94.5 cm), as the composition match perfectly. Since the portraits of such notables were created in series, in different dimensions and by different court painters (such as other versions of portrait of Ladislaus IV by Boy from the Royal Castle in Warsaw, ZKW 559 dep.), this cannot be excluded. Maybe a reduced portrait of Kazanowski painted on panel by Boy was also created at that time. The Wawel painting was acquired the as a gift from Julian Godlewski from Switzerland in 1970. Consequently the portrait of a woman from Popławski collection can be dated to about 1643, like the Kazanowski portrait. She wears a strange wide-brimmed hat with a hole cut through the crown with her blonde hair spread over the broad brim. The woman is bleaching her hair like Venetian women in engravings by Cesare Vecellio or Pietro Bertelli from the late 16th century or in the Album Amicorum of Burchard Grossmann, created between 1624-1645, and other albums of foreign travellers in Venice. Venetian women bleached their hair using a solana (a wide brim hat with a hole in the centre) and sitting in the sun. The hair, soaked in a concoction of lemon juice and urine, was thrown out of the crown space and spread over the brim, which shaded the person from the sun (after "Venice: the Queen of the Adriatic" by Clara Erskine Clement Waters, p. 224). Venetians, who settled in great number in Poland-Lithuania from the beginning of the 16th century, undoubtedly introduced this technique there. Her coat, lined with fur, is very similar to the coat visible in an engraving showing a Polish noblewoman (FOEMINA NOBILIS POLONICA), illustration to Hans Weigel's "Habitus Praecipuorum Populorum", published in 1577. The same woman, with identical earring in her left ear, was depicted in a series of paintings by circle of Rembrandt. One signed and dated (upper right: Rembrandt f. 1635 or 1638, oil on canvas, 99.5 x 71 cm) was before 1794 in the collection of Louis-Marie Lebas de Courmont, Marquis de Pomponne in Paris. In 1669 king John II Casimir Vasa brought many paintings from Polish royal collection to Paris after his abdication. A pastel after this version, or other not preserved painting, most probably by an 18th century French pastelist, was sold on 11 June 2020 in Amsterdam. Other version (oil on canvas, 100.5 × 81 cm) was first mentioned in 1854, when hung in the collection of the Earl of Listowel, lost. Another, smaller picture (oil on canvas, 77 x 63 cm) was sold in New York (Doyle, 2016-01-27, lot 56). The style of this painting can be compared with the Lovers by Christiaen van Couwenbergh in the Kunsthalle Bremen, painted in 1632. It is possible that this copy after original by Rembrandt was made by Maerten van Couwenburgh. Other, more simplified versions are in Kunstmuseum Basel (oil on canvas, 33 x 29.5 cm, inventory number 501), acquired in 1859 from the Birmann collection and in private collection (oil on canvas, 56 x 46 cm), sold on November 18, 2020. The "fanciful custume" of a woman is similar to those visible in the Feast of Herod by Bartholomeus Strobel, court painter of Ladislaus IV, created in the 1630s (Prado Museum in Madrid) and to the costume of Queen of Sheba from the copper-silver sarcophagus of Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria (scene of Queen of Sheba before Solomon), created by Johann Christian Bierpfaff before 1648 (Wawel Cathedral). In the portrait of a lady with forget-me-nots in the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 69 x 61 cm, M.Ob.2510), painted in the style of Adolf Boy, the woman resemble closely the woman wearing a solana hat from the Popławski collection. Her black dress, most likely a mourning dress, is evidently Central European of the epoch and similar to that visible in a portrait of a lady aged 26, created in 1645 (National Museum in Kraków, inventory number MNK I-689), in epitaph portrait of Zofia Kochańska née Świerczewska, created in mid-17th century (Saint James church in Sanka), or in a portrait of a lady, said to be a member of the Węsierski family, painted by Danckers de Rij in about 1640 (National Museum in Gdańsk). As a consequence, the portrait depict Kazanowska in mourning after death of her first husband (1649) or imprisonment in the tower (1652) and was most probably adressed to her former lover, king John Casimir Vasa. This painting comes from the collection of the Krosnowski family in Saint Petersburg (formed in the years 1888-1917), donated to the Polish state and transported to Poland under the regulations of the Treaty of Riga (1921). The woman from all mentioned portraits bear a resemblance to a man depicted in a portrait, today in the Lithuanian National Museum of Art in Vilnius, which according to inscription depict Aleksander Słuszka, voivode of Minsk and father of Elżbieta. The portrait of Słuszka in Vilnius is similar to full-length portrait of Józef Bogusław Słuszka (1652-1701), Lithuanian Field Hetman, which was in the collection of the Radziwill family in Niasvizh, lost. The costume is almost identical and more typical of the end of the 17th century, the man is holding a bulava mace (a sort of military baton), typical for Field Hetmans and other effigies of Józef Bogusław, therefore both depict Aleksander Słuszka's descendant (a grandson), however, some family resemblance to described female portraits is still visible. A man with a mustache in an oriental costume, very similar to the woman in the mentioned portraits, was depicted in another painting in the collection of the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on panel, 23.5 x 18.5 cm, inventory number 131229 MNW). It was transferred by the Central Board of Museums and Monuments Preservation in 1949 (after "Early Netherlandish, Dutch, Flemish and Belgian Paintings 1494–1983" by Hanna Benesz and Maria Kluk, Vol. 2, item 923). The style of this small effigy is similar to that of the portraits which could be attributed to Maerten van Couwenburgh. Consequently the man should be identified as Elżbieta's brother Bogusław Jerzy Słuszka, who died after January 9, 1658. Together with his brother Eustachy Adam, who at a very young age became a courtier of Ladislaus IV, he went to study abroad. In 1637 he was matriculated at the University of Ingolstadt, and after return he become the starost of Rechytsa (1639), Lithuanian Pantler (1643) and Lithuanian Court Treasurer (1645). Beautiful marble epithaph of Eustachy Adam Słuszka (1615-1639), the brother of Elżbieta and Bogusław Jerzy, in the Church of Saint Stanislaus of the Poles (Santo Stanislao dei Polacchi) in Rome, is the only preserved and hitherto known example of splendid patronage of the family in the late 1630s and early 1640s. Eustachy Adam was a courtier of King Ladislaus IV and he died in Rome on August 27, 1639 at the age of 24. The monument was founded by Bogusław Jerzy and created after 1639 by Giovanni Francesco de Rossi or workshop of Giuliano Finelli.
Portrait of Elżbieta (Halszka) Kazanowska née Słuszczanka (1619-1671) from the Marquis de Pomponne collection in Paris by circle of Rembrandt, 1635-1638, Private collection.
Pastel portrait of Elżbieta (Halszka) Kazanowska née Słuszczanka (1619-1671) by French pastelist after original by circle of Rembrandt, 18th century, Private collection.
Portrait of Elżbieta (Halszka) Kazanowska née Słuszczanka (1619-1671) from the Earl of Listowel collection by circle of Rembrandt, 1635-1638, Private collection.
Portrait of Elżbieta (Halszka) Kazanowska née Słuszczanka (1619-1671) by Dutch painter, possibly Maerten van Couwenburgh, 1635-1638, Private collection.
Portrait of Elżbieta (Halszka) Kazanowska née Słuszczanka (1619-1671) by Dutch painter, possibly Maerten van Couwenburgh, 1635-1638, Kunstmuseum Basel.
Portrait of Elżbieta (Halszka) Kazanowska née Słuszczanka (1619-1671) by Dutch painter, possibly Maerten van Couwenburgh, 1635-1638, Private collection.
Portrait of Elżbieta (Halszka) Kazanowska née Słuszczanka (1619-1671) in solana hat by Adolf Boy, ca. 1643, National Museum in Warsaw, lost.
Portrait of Elżbieta (Halszka) Kazanowska née Słuszczanka (1619-1671) with forget-me-nots by Adolf Boy, 1649-1652, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Bogusław Jerzy Słuszka by Dutch painter, possibly Maerten van Couwenburgh, 1640s, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Martin Opitz by Harmen Hals
In 1636, thanks to the recommendation of Gerard Denhoff (1589-1648), Martin Opitz von Boberfeld (1597-1639), considered the "Father of German poetry", began his career at the court of the elected monarch of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth - Ladislaus IV Vasa as royal agent and secretarius iuratus. He met the king during his stay in Toruń in January 1636 and Ladislaus ordered Opitz to accompany him to Gdańsk. It was then that Opitz personally handed the king his panegyric in German - "To the Royal Majesty of Poland and Sweden" (An die Königliche Majestät zu Polen und Schweden), published in Frankfurt am Main in Weltliche Poemata in 1644. In this poem he praises the king as a peaceful monarch - "Oh hero! Who values peace more highly than something in the world that perishes with the world" (O Held! Den Frieden höher schätzt, als etwas in der Welt, Das mit der Welt vergeht), while dedication in Latin is designed like that to a Roman emperor: "Most Serene and powerful King of Poland and Sweden Ladislaus IV, tamer of barbarian peoples, initiator of public security ..." (SERENISSIMO POTENTISSIMOQVE / Polonia & Suecorum Regi / VLADISLAO IV. / DOMITORI GENTIVM / BARBARARVM: SEGVRITATIS / PVBLICÆ AVCTORI ...).
In 1636 he also published in Toruń his Panegyricvs serenissimae Suecorum ..., dedicated to king's aunt, Lutheran Princess-Infanta Anna Vasa (1568-1625) and poems dedicated to notable Calvinists of the Commonwealth - Rafał Leszczyński (1579-1636), voivode of Belz - Panegyricvs inscriptus honori et memoriae [...] Domini Raphaelis comitis Lesnensis ..., and Fabian Czema (d. 1636), castellan of Chełmno - Laudatio funebris illustrissimi domini Fabiani Lib. Baronis a Cema ... Opitz was well aware that he would gain powerful patrons with flattery, and he actually achieved this, so that Ladislaus IV appointed him as his historiographer and secretary with an annual salary of 1,000 thalers. On June 24, 1637 he received an official nomination for this position, approved by the Sejm (after "Zasłużeni ludzie Pomorza Nadwiślańskiego XVII wieku: szkice biograficzne", p. 160). It was probably on this occasion that he commissioned his magnificent portrait, now kept in the Gdańsk library of the Polish Academy of Sciences (inv. EM 2). It was painted by Ladislaus IV's court painter and Martin's friend Bartholomeus Strobel. His pose, fashionable French costume and wig resemble those in a masterpiece signed by Strobel, portrait of Prince Vladislav Dominik Zaslavsky-Ostrogsky (d. 1656), also known as Władysław Dominik Zasławski-Ostrogski in Polish, in Wilanów Palace (oil on canvas, 112 x 84 cm, Wil.1654, signed and dated: B. Strobell / 1635), as well as that of the king by the Gdańsk painter Adolf Boy (Royal Castle in Warsaw, ZKW 559 dep.). Interestingly, the identity of the model for Wilanów's portrait was unknown for a long time, and this fabulously wealthy Ruthenian prince was correctly identified by Elena Kamieniecka in her 1971 publication ("W sprawie portretu nieznanego magnata Bartłomieja Strobla") after probably several centuries of oblivion. In 1637 in Gdańsk, the poet published his Variarvm Lectionvm Liber: In quo præcipue Sarmatica, dedicated to Chancellor Tomasz Zamoyski (1594-1638). On the occasion of the marriage of the king and the Archduchess Cecilia Renata of Austria in 1637, he created a Latin poem Felicitati augustae honorique nuptiar ... Like Strobel, Opitz came from Silesia, he was born in Bolesławiec (Bunzlau) as son of a butcher. Although he advocated the use of the German language in poetry, he frequently wrote in Latin and his 1635 drama "Judith" was based on the Italian opera libretto by Andrea Salvadori, while his "Antigone", dedicated to Gerard Denhoff, was based on one of the eight Greek texts by Demetrius Triclinius. He went to the Netherlands in 1620 and in 1622 to Transylvania to teach philosophy in Alba Iulia. After returning to Silesia, in 1624 he was appointed advisor to the Duke of Legnica and Brzeg and in 1630 he went to Paris. He moved to Toruń in 1635 with the duke. As secretary, Opitz was probably responsible for handling foreign correspondence. He was entrusted with numerous state affairs, which had to be settled with the kings of France, England and Denmark. Ladislaus also intended to send Opitz to Stockholm. Due to his ambiguous contacts with the Chancellor of Sweden Axel Oxenstierna (1583-1654), he is suspected of disloyalty towards the King of Poland. He died in 1639 in Gdańsk. The portraits of such an important poet and state official also had to be in the Commonwealth's residences in Warsaw, Kraków and Vilnius. Since the German-speaking community was large in many cities and regions of the country, it was also necessary to underline their importance and to remind its members that they owe their prosperity to the wise reign of Ladislas IV who employs the best. The mentioned portrait by Strobel in Gdańsk is considered to belong to the poet, but it is also possible that it came from the royal collection in the city, where the main representative residence was the Green Gate. It was offered to the Library of the Gdańsk City Council before 1701. This portrait was reproduced in an engraving by Johann Christoph Sysang made around 1739 confirming both the identity of the model and the author of the painting (OPITIVM [...] Hac manus in tabula Se Lips STROBELIANA dedit ...). Other portrait paintings of Opitz are unknown. However, they must have been numerous given the number of different engravings with his image that preserved. In the National Museum in Warsaw, there is a portrait of a man holding his hand on a table (oil on panel, 106 x 80.5 cm, M.Ob.217, earlier 494). On the table next to him are writing utensils, red sealing wax to seal letters, indicating that the man is a secretary or a diplomat. The painting comes from the collection of Wojciech Kolasiński, acquired on November 23, 1881 for 125 rubles by the Museum of Fine Arts in Warsaw, the previous provenance is not known. Due to its style and the artist's monogram in ligature FH, the painting was considered the work of Frans Hals (after "Wojciech Kolasiński (1852-1916)" by Maria Kluk, p. 107-108) and now as a work of his follower. Although the influence of Hals' style with loose brushstrokes and strong illumination is undeniable, it does indeed differ from the artist's other works, which appear softer and more lightly painted and the most similar painting is A Merry Couple, now in the Frans Hals Museum in Haarlem. The painting in Haarlem is signed and dated: H / 1648, therefore considered to be the work of Frans's son, Harmen (1611-1669), who with his brothers, also painters, worked in his father's workshop. The fact that the Warsaw painting was signed with a monogram indicating that his father was the author, indicates in turn that it may have been part of a large painting commission and that they do not want to fully reveal to customers that the painting was made by the master's assistants and not himself. Moreover, the composition is not typical for Hals and his circle and looks more like a copy of another official portrait and bears a striking similarity to the portrait of Prince Zaslavsky-Ostrogsky in Wilanów. It also resembles other portraits of people close to the court of Ladislaus IV, such as the portrait of Lieutenant Mikołaj Konstanty Giza (Nikolaus Konstantin Giese, d. 1663) by Franz Kessler or the portrait of Guglielmo Orsetti of Lucca (d. 1659) by Strobel, all two preserved in the National Museum in Warsaw. In this case, it is most likely that Hals's studio received paintings or study drawings from Strobel to copy. The model has a different eye color than Strobel's painting (brown and blue respectively), which is another indication that this is a copy of another work, because cheaper dyes were used to prepare copies, as in the case of portraits of Emperor Charles V, who in some portraits has blue eyes and in others brown. Another portrait painted in the same way is also in the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 86 x 50.5 cm, M.Ob.1645 MNW). This portrait of a man in a ruff bears a false inscription: Rembrand fe. / 1660 and it is a version, mirror view of a painting representing the furniture and frame-maker Herman Doomer (d. 1650), active in Amsterdam, painted by Rembrandt in 1640 (Metropolitan Museum of Art, 29.100.1). As a furniture maker, Doomer must have relied heavily on wood supplies from the Commonwealth, so his portrait made in Hals' workshop in Haarlem as well as his furniture probably arrived in Poland already in the 17th century. According to the inscription in the upper left corner, the man in the portrait from the Kolasiński collection was 39 years old in 1636 (Aetatis 39 / FH fecit A: 1636), just like Martin Opitz when he entered the service of Ladislaus IV and he closely resembles the poet according to his portrait by Strobel as well as the engravings by Jacob van der Heyden, Peter Aubry II and Georg Walch.
Portrait of Prince Vladislav Dominik Zaslavsky-Ostrogsky (d. 1656) by Bartholomeus Strobel, 1635, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
Portrait of Martin Opitz von Boberfeld (1597-1639), secretary of Ladislaus IV Vasa, aged 39 by Harmen Hals, 1636, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Herman Doomer (d. 1650), furniture and frame-maker, by circle of Frans Hals, 1640s, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski by workshop of Frans Hals
Travelers from the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth who visited the countries of Western Europe frequently brought to their homeland many beautiful works of art and their effigies that they had acquired or commissioned during the visit. The best-known proof of this practice is a painting created, according to the painter's signature, in Warsaw in 1626 (Here. fecit / Warsa[...] 1626, in the center in the engraving) and attributed to Étienne de La Hire, Willem van Haecht or Jan Brueghel the Younger (Royal Castle in Warsaw, oil on panel, 72.5 x 104 cm, ZKW/2123/ab). It shows the art collection of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa, future king (elected as Ladislaus IV), who most likely acquired most of the objects depicted in this painting during his visit to the Spanish Netherlands, Italy, Austria and Bohemia between 1624 and 1625, including two effigies of the prince - one painted and the other a gold medal with his profile, probably made by Alessandro Abondio.
This painting was long forgotten and after resurface on the art market in New York in 1940 (art dealer Mortimer Brandt), it was purchased in London in 1988 by the State Collections for the newly reconstructed Royal Castle (destroyed by Nazi German invaders during World War II). Aristocrats who traveled abroad also brought their effigies, fashionable costumes, paintings and other works of art. In 1564 Nicolaus Christopher the Orphan Radziwill (1549-1616) sent from Strasbourg to his father Nicolaus Radziwill the Black (1515-1565) in Lithuania, his portrait painted during his studies there (after "Tylem się w Strazburku nauczył ... " by Zdzisław Pietrzyk, p. 164). More than half a century later, around 1632, Janusz Radziwill (1612-1655), was painted in Leiden by David Bailly (National Museum in Wrocław, VIII-578) and the 1633 inventory of Radziwill Castle in Lubcha in Belarus (Central Archives of Historical Archives in Warsaw, AGAD 1/354/0/26/45) lists under number 27: "Full-length portrait of Prince His Lordship Mr Chamberlain, old, in green clothes, painted in Leipzig" (Obraz Cały X: Je m Pana Podkomorzego Dawnieyszy w Ubierze zielonym w Lipsku Malowany), thus painted during Janusz's studies there around 1630. The 1661 inventory of paintings belonging to Aleksander Michał Lubomirski (1614-1677), brother of Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski (1616-1667), that survived the Deluge, includes paintings by Parmigianino, Jusepe de Ribera, Francesco Albani, Venetian landscapes and two of his portraits taken in Venice by Nicolas Régnier (AGAD 1/357/0/-/7/12). They were probably acquired in Italy during his stay there and paintings by Ribera indicate that Aleksander Michał visited Naples, as the Spanish painter settled there in 1616. Among his paintings there was also "Image of Our Lady with the Lord Jesus whom she gave birth to. From Prague" (Obraz Nasw Panny z Panem Jezusem powitym. sPragi), most likely acquired in Czechia. Among the paintings owned by his father Stanisław (1583-1649) was "A picture of two women dressed in the Netherlandish style, holding a basket full of meat" (Obraz dwie białogłowie po Inderlansku ubrane koszyk zmięsem trzymaiące). Aleksander Michał's father-in-law Jerzy Ossoliński owned paintings by Ribera, Raphael, Titian, Paolo Veronese, Bassano, Guido Reni, Guercino, Daniel Seghers and Albrecht Dürer and his mother-in-law Izabela Daniłowicz had "Two Moscow pictures" (Dwa obrazki Moskiewskie) and "Three unicorn pictures, carved in Moscow" (Trzy obrazki ziednorozca rzezane moskiewskie). Many Ruthenian and Russian icons are also mentioned in other inventories, such as in the 1671 inventory of paintings of the Calvinist princess Louise Charlotte Radziwill (items 358/7, 365/14, 651/22 - 655/26, 660/31 - 661/32, 783/4, 801/3, 868/48, 966, compare "Inwentarz galerii obrazów Radziwiłłów z XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska). Jerzy Sebastian must also have brought many exquisite paintings from his numerous travels between 1629 and 1636. In 1629 he was in Ingolstadt in Bavaria, in 1631 in Leuven, in 1633 in Leiden, in 1634 he visited Spain as an envoy of the king. In Italy he visited the library of the University of Bologna and the Laurentian Library in Florence as well as numerous picture galleries and most probably went to France and England, but the precise itinerary is not known. If he traveled to England from Italy, he most likely returned to the Netherlands. Shortly after his return to Poland-Lithuania, in September 1636, the young Lubomirski, aged barely 20, began his political career by being elected marshal of the parliamentary assembly and in December of the same year he was elected member of parliament (Sejm). Among the paintings that could come from his collection are two masterpieces of Spanish painting preserved in former territories of the Commonwealth. One is the Ecstasy of Saint Francis of Assisi by El Greco, now kept in the Diocesan Museum in Siedlce (oil on canvas, 106 x 79 cm, signed: Domenikos Theotokop ...). According to Izabella Galicka and Hanna Sygietyńska, who discovered the painting in 1964 in the parish church of Kosów Lacki, this painting could come from the Lubomirski collection, possibly from the collection of Eugeniusz Lubomirski (1825-1911) in Kruszyna. The other is Penitent Saint Mary Magdalene by Francisco Jiménez (Ximénez) Maza kept at the Lithuanian National Museum of Art in Vilnius (oil on canvas, 150 x 116 cm, LNDM T 4010). It was donated to the Museum of the Society of Friends of Science in Vilnius in 1907 by Count Władysław Tyszkiewicz (1865-1936) (compare "Vilniaus senovės ir mokslo ..." by Henryka Ilgiewicz, p. 115). Tyszkiewicz was married to Krystyna Maria Aleksandra Lubomirska (1871-1958), daughter of the mentioned Eugeniusz Lubomirski, whose ancestor was Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski. Due to the lack of documentation, the exact provenance of these paintings will probably never be established with certainty, however there are some elements in the paintings themselves which indicate that they were probably purchased in the 17th century by customers from Poland-Lithuania, perhaps Lubomirski. El Greco, a Greek-Spanish painter from Crete, received his initial training as an icon painter of the Cretan school, then continued his career in Venice, where he probably worked in Titian's workshop. Tintoretto, Paolo Veronese and Jacopo Bassano also worked in the city and it seems that El Greco studied the work of each of them. Traditional icon painting as well as that of the Venetian school, both very popular in the Commonwealth, had a great influence on his style, which is also visible in the Ecstasy of Saint Francis of Assisi. Therefore, such a painting would undoubtedly be to the taste of any traveler from the Commonwealth. The penitent Saint Mary Magdalene is also unusual for the Spanish school, mainly due to the erotic nature of the painting. In Spanish painting of the Mannerist and Baroque era, including paintings by El Greco, she is in the majority of cases fully clothed and shows no signs of eroticism (compare paintings in the Prado: P000608, P001309, P001103, P007621, P001008, P007736). In the Vilnius painting, most likely inspired by Italian paintings or at the client's request, Mary Magdalene is half-naked. As owners of estates in Slovakia, including Stara Lubovna Castle which was then part of the Kingdom of Hungary, the Lubomirskis were also engaged in the affairs of the Hungarian and Bohemian kings of the Habsburg dynasty. At the end of 1621, Jerzy Sebastian's father, Stanisław Lubomirski (1583-1649), attempted to enter the service of the emperor and until 1635 he took a pro-Austrian position. He established contacts with the supreme commander of the imperial army Albrecht von Wallenstein (1583-1634), and a little later, in August 1632, with the emperor himself, to whom he offered his participation in the war against Rakoczi in Hungary or with the Swedes in Germany (after "Mecenat kulturalny i dwór Stanisława Lubomirskiego ..." by Józef Długosz, p. 39, 127). The Italian architect Andrea Spezza (died 1628), who designed the famous Wallenstein Palace in Prague, also worked for the Lubomirskis. It is interesting to note that Anthony van Dyck, active at this time mainly in Antwerp and London, painted a portrait of Wallenstein between 1629 and 1634, although, according to known sources, they did not have the opportunity to meet in person. The original portrait was engraved by Pieter de Jode the Younger after 1628 (signed: Pet. de Iode sculp. / Ant. Van Dÿck pinxit) and a workshop copy is in the National Gallery in Neuburg (inv. 84). Likewise for the effigy of the King of Sweden Gustavus Adolphus (1594-1632), engraved by Paulus Pontius around 1655 (signed: Paul. Pontius sculp. / Ant. van Dÿck pinxit.) and the workshop copy is also in Neuburg (inv. 86). In both cases they were undoubtedly based on other effigies. Given the above, portraits of members of the Lubomirski family must also have been in the imperial collections as well as those of members of the Bohemian nobility. In the Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden there is a "Portrait of a young man in a black doublet" (Bildnis eines jungen Mannes in schwarzem Rock), attributed to the circle of Frans Hals (oil on panel, 24.5 x 20 cm, Gal.-Nr. 1359). The painting comes from the Wallenstein collection in Duchcov Castle, owned by Albrecht's heir Maximilian von Wallenstein (1598-1655) from 1642, and was purchased in 1741 with 267 other paintings for the collection of the elected monarch of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and elector of Saxony Augustus III in Dresden for a price of 22,000 guilders. The painting is generally dated to around 1633, but a similar costume is visible in the portrait of Cornelis de Graeff (1599-1664) by Nicolaes Pickenoy, painted in 1636 (Gemäldegalerie in Berlin, 753A). The man in the Dresden portrait bears a striking resemblance to Jerzy Sebastian based on his portraits by Rembrandt and Ferdinand Bol, identified by me, and his engraved effigy by Johann Franck made around 1670 (National Museum in Kraków, MNK III-ryc.-57315). An old copy of this or another version of this painting was sold in Cologne in 2004 (oil on panel, 23.5 x 19 cm, Van Ham Kunstauktionen, July 3, 2004, lot 1112). Another old version with some differences from the Dresden painting is in the Siauliu Ausros Museum in Siauliai, Lithuania (oil on canvas, 27 x 23 cm, ŠAM D–T 473).
Portrait of Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski (1616-1667) by workshop of Frans Hals, ca. 1636, Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden.
Portrait of Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski (1616-1667) by follower of Frans Hals, after 1636 (18th century?), Private collection.
Portrait of Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski (1616-1667) by follower of Frans Hals, after 1636 (19th century?), Siauliu Ausros Museum.
Ecstasy of Saint Francis of Assisi by El Greco, ca. 1580, Diocesan Museum in Siedlce.
Penitent Saint Mary Magdalene by Francisco Jiménez (Ximénez) Maza, second quarter of the 17th century, Lithuanian National Museum of Art in Vilnius.
Portrait of the "Last Jagiellon" bearing the features of Ladislaus IV Vasa by Bartholomeus Strobel or workshop
"Sigismund Augustus, last king of Poland of the Jagiellonian dynasty" (SIGISM. AUGUSTUS REX / POLONIÆ IAGELLONIDARUM / ULTIMUS) is the Latin inscription on a painting now kept in the National Museum in Kraków (oil on copper, 62, 5 x 52.5 cm, inventory number MNK I-21). It is very meaningful that this effigy of the last male Jagiellon was acquired in Sweden. The history of the painting, perhaps looted during the Deluge and purchased by Henryk Bukowski (1839-1900), most probably in Stockholm, perfectly illustrates the fate of the portrait collections of the former Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. Bukowski, who emigrated to Sweden in 1864 after the collapse of the January Uprising (1863-1864), which aimed to end Russian occupation of part of the former Commonwealth, donated the painting to the Kraków Museum in 1885.
During the reign of Sigismund Augustus, the Union of Lublin was signed on July 1, 1569, creating a single state, the Commonwealth, as a merger of the two states, headed by a single elected monarch and governed by a common parliament, although each retained substantial autonomy, with their own army, treasury, laws and administration. The legacy of the Jagiellonian state was also the Warsaw Confederation of 1573, which officially recognized complete freedom of religion in the Commonwealth, granted dissidents state protection and equal rights with Catholics, and prohibited secular authorities from supporting clergy in religious persecution. Although the patronage of the last male Jagiellon was comparable to that of Italian and German princes, kings of France, Spain, England, emperors and popes, due to wars and destruction until the end of the 18th century, very few of his effigies have been preserved. Moreover, some of them were considered to be the effigy of his ancestor Jogaila of Lithuania, such as the painting by Marcello Bacciarelli in the Royal Castle in Warsaw (ZKW/2713/ab), while the portrait of the maternal grandfather of Ladislaus IV Vasa - Archduke Charles II of Austria, from the same series of Polish monarchs painted between 1768 and 1771, was considered the effigy of Sigismund Augustus (ZKW/2719/ab). The most popular effigy of the monarch, the miniature portrait by workshop of Lucas Cranach the Younger in the Czartoryski Museum (MNK XII-538), was purchased in the mid-19th century in London by Adolf Cichowski. The style of the portrait of the "Last Jagiellon" as well as the material on which it was painted (copper) indicate that the painting was created in the first half of the 17th century. Although it is obviously based on the same effigy of the king as the mentioned miniature by Cranach, the facial features are slightly different, the painter has rounded the nose and made the lower lip protrude. This is also better visible in comparison with other inscribed effigies of the king, such as the miniature from the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna (GG 4697) or the miniature by workshop of Dirck de Quade van Ravesteyn in Kraków (MNK XII-146). In this way, the "Last Jagiellon" more closely resembles the descendant of the Jagiellons - Ladislaus IV Vasa, especially his portrait by Pieter Claesz. Soutman at Wilanów Palace (Wil.1134) as well as an engraving by Jonas Suyderhoef after a drawing by Claesz. Soutman at the National Museum in Warsaw (79212 MNW). Ladislaus, the new Augustus, the monarch who will revive the spirit of tolerance of the last male Jagiellon, is what many people, especially Protestants, expected from the newly elected king (November 1632), after many years of reign of his father Sigismund III, who leaned towards Spanish-style Catholicism. However, when Ladislaus abandoned his plans to marry a Protestant princess and allied with his Habsburg relatives, many of them felt deceived. Beautifully painted Daniel and Cyrus before the Idol Bel, attributed to the court painter of Ladislaus - Bartholomeus Strobel, in the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on copper, 39.5 × 30 cm, M.Ob.1284), is considered a political allegory of the reign of Ladislaus under a "biblical disguise". This story derives from the apocryphal portion of the Book of Daniel and the painting represents the Prophet exposing the fraud of the Babylonian priests of Idol Bel (Baal) to King Cyrus of Persia. It was most likely commissioned by the country's Protestant elites, perhaps Gerard Denhoff (1589/90-1648), voivode of Pomerania or his wife Sibylla Margaret of Legnica-Brzeg (1620-1657), a native of Silesia like Strobel. If the portrait of the "Last Jagiellon" was commissioned by the king, we should assume that he wanted to convince his subjects, especially non-Catholics, that he will be a tolerant ruler, or if like Daniel and Cyrus by the Protestants, this could be a message to the king to which of his predecessors he must refer and which he should take as an example. Not only is the theme of the two paintings described linked, but also their style. The face of King Cyrus is particularly similar in both model characteristics and painting style. It resembles the signed work of Strobel (Bartholo. / Strobel. / Pinxit:) - Our Lady of the Rosary with Saint Dominic and Saint Nicholas in the Church in Grodzisk Wielkopolski, painted between 1634 and 1635, and some of the attributed or workshop paintings such as the half-length portrait of Jerzy Ossoliński (1595-1650) in the National Museum in Warsaw (deposited in Wilanów Palace, 182280, 3020 Tc/72).
Portrait of Jerzy Ossoliński (1595-1650) by Bartholomeus Strobel or workshop, ca. 1635, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of the "Last Jagiellon" Sigismund II Augustus (1520-1572), bearing the features of Ladislaus IV Vasa (1595-1648) by Bartholomeus Strobel or workshop, ca. 1636-1637, National Museum in Kraków.
Daniel and Cyrus before the Idol Bel - Allegory of the reign of Ladislaus IV Vasa (1595-1648) by Bartholomeus Strobel, ca. 1636-1637, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Jan Stanisław Jabłonowski, Marshal of the extraordinary Sejm by Rembrandt
"I am an envoy of the entire Commonwealth, and if we leave without doing anything, you will not be able to shut me up before the King, so that I will not complain and protest against those who leave their homeland without any defense, which also I, living on the border, really need", declared Jan Stanisław Jabłonowski (1600-1647), Grand Sword-bearer of the Crown on May 23, 1647. He stated this during the extraordinary Sejm (Diet) in the face of attempts to disrupt the parliament dealing with the most burning issues of defending the borders against the Ottoman Empire and paying the army. Known for his civic attitude, Jabłonowski gained such widespread respect among the nobility that in two consecutive sejms in 1637 and 1640 he was appointed Mashal (after "Szkice Historyczne" by Karol Szajnocha, Volume 3, p. 4-5, 8, 11), that is the chairman of the Chamber of Deputies of the Parliament of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth.
He was probably one of the best, if not the best, marshal of the Sejm during the reign of Ladislaus IV. Struggling for an effective discussion, he threatened the deputies that he would treat them like cardinals in a conclave and would not let them leave until they reached an agreement (after "Charakterystyka sejmów za Władysława IV" by Sybill Hołdys, p. 207). Under the Henrician Articles, ordinary sejms were convened every two years, and if necessary (e.g. in the event of a direct threat to the state), the king could convene an extraordinary sejm for a period not longer than two weeks. Just before the successful conclusion of the extraordinary Sejm of 1637, the ordinary Sejm presided over by Casimir Leon Sapieha/Sapega (1609-1656) broke down early that year - and the assemblies that followed the Sejm of 1640 in 1642, 1643, 1645 and later were generally also disrupted. Known for his lavish lifestyle and splendid patronage, King Ladislaus IV was in constant need of money. In 1637 he was also preparing for marriage to the Emperor's daughter, Cecilia Renata of Austria, and already at the beginning of that year the treasury began to run empty again. Advised by his entourage, the king wishes to impose a maritime customs duty. Despite the opposition of envoys from Polish Prussia and Lithuania, who almost immediately opposed this idea, it was decided to adopt a constitution imposing this tax at the extraordinary Sejm (Warsaw, June 3-18, 1637). In October 1637, the sovereign sent to Gdańsk the voivode of Sandomierz, Jerzy Ossoliński, and the starost of Kościerzyna, Gerard Denhoff, who announced the introduction of customs duties and the brothers Abraham and Isaac Spiering (Spiring or Spierincx), the sons of the Flemish weaver François Spiering, active in Delft (who made tapestries for Sigismund III), as its collectors (compare "Briefwisseling van Hugo Grotius", p. 675). Their brother Pieter Spiering van Silvercroon (1595-1652), seems to have had a tapestry factory in Gdańsk between 1614-1649. The Marshal of the Sejm was a purely honorary position and he was elected by all deputies, no later than the third day after the opening of the Sejm. From this point on, however, Jabłonowski's career at court gained momentum. In 1638, this experienced deputy, who participated in all sejms since 1635 as a delegate of the Galician sejmik (Galician land in the the Ruthenian Voivodeship), became royal cupbearer of Queen Cecilia Renata and earlier, on November 18, 1637, he received the village of Perehinske, in western Ukraine, from the king. Jan Stanisław was born in Lucha, a private village in the Ruthenian Voivodeship (now Ukraine), where there was a castle. Although the Jabłonowski family of the Prus III coat of arms originated in Masovia (from the village of Jabłonowa near Mława - Jabłonowscii de Jabłonowa in palatinatu Płocensi, in districtu Mlavensi), in the 17th century their "nest" became Ruthenia. The marshal of the extraordinary Sejm of 1637 was the first to obtain an important position in the Commonwealth and thanks to his marriage to Anna Ostrorożanka (1610-1648), daughter of Jan Ostroróg, voivode of Poznań and the Ruthenian princess Sofia Zaslavska, in 1630, he entered into relations with the most distinguished houses of the Commonwealth (after "O Jabłonowskich herbu Prus III" by Wojciech Kętrzyński, p. 3). He was the son of Maciej Jabłonowski (1569-1619), a cavalry master (rotmistrz), and Katarzyna Kłomnicka. He studied at the Jesuit college in Lviv, then traveled abroad for some time. He probably visited France, as the Jabłonowski family cultivated their French connections throughout the 17th century. He took part in the wars with Sweden and the Crimean Tatars in 1624-1629, and with Russia in 1632-1634. A good speaker, known for his speeches at the Sejms in 1633-1642, he was especially active during the winter Sejm of 1637. His son Stanisław Jan Jabłonowski (1634-1702) raised his family to prominence and became voivode of the Ruthenian Voivodeship and Grand Hetman of the Crown. His grandsons, sons of Stanisław Jan, studied at Jesuit schools in Lviv and Prague. They traveled to Berlin, the Netherlands, via Utrecht, Rotterdam, Leiden and Amsterdam, and to Flanders, finally reaching Paris via Leuven and Brussels. Jan Stanisław's granddaughter Anna Leszczyńska (1660-1727) was the mother of the elected king of the Commonwealth Stanislaus Leszczyński and her granddaughter Marie Leszczyńska was Queen of France from 1725, after marrying Louis XV. He was therefore the ancestor of the kings of France Louis XVI (1754-1793), Louis XVIII (1755-1824), Charles X (1757-1836), Marie Clotilde of France (1759-1802), Queen of Sardinia and Maria Luisa of Parma (1751-1819), Queen of Spain. His grandson, Jan Stanisław Jabłonowski (1669-1731), was painted by José García Hidalgo, court painter to King Charles II of Spain, during his stay in Madrid in 1687, wearing a Spanish costume (National Museum in Warsaw, M.Ob.813 MNW). The Grand Sword-bearer of the Crown was buried in the Jesuit church in Lviv, where his great-grandson Stanisław Wincenty Jabłonowski (1694-1754) founded a beautiful late Baroque epitaph for him, bearing an incorrect date of his death - obiit Anno salutis 1659. It was executed between 1744 and 1754, probably by Jerzy Markwart (Georg Marquard) (after "Nagrobek Jabłonowskich ..." by Andrzej Betlej, p. 70, 84). A Polish Nobleman by Rembrandt in the National Gallery of Art in Washington (oil on panel, 96.8 x 66 cm, 1937.1.78) was signed and dated by the painter upper right: Rembrandt.f:. / 1637. Before 1931, when the painting was purchased by Andrew W. Mellon (1855-1937), it was kept for over 100 years at the Hermitage Museum in St. Petersburg. The "Catalog of paintings found in the Cabinets of the Imperial Palace in Saint Petersburg" (Catalogue des tableaux qui se trouvent dans les Cabinets du Palais Impérial à Saint-Pétersbourg) from 1774, where it was listed as "Portrait of a Turk, half-length, life-size, holding a staff in his hands. On wood, 2 feet wide by 3 feet high" (Portrait d'un Turc, vû à mi-corps, de grandeur naturelle, tenant un Bâton dans la main. Sur Bois, de 2. pieds de large et de 3. pieds de haut, no. 44), is the oldest surely established provenance of this painting. The man cannot be an ambassador of Muscovy (linked to a 1707 sale of Harman van Swol), because this would mean that the authors of the 1774 Catalog made fun of the Empress of Russia (owner of the painting) who, two years earlier, in 1772, partitioned the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, failing to recognize the representative of Russia painted by Rembrandt and confusing him with a Turk. What is very interesting is that in the 19th century in Lviv, where Jabłonowski was buried, and surroundings there were two old copies of the painting. One of them was in the Lubomirski Museum in Lviv and was listed in the 1877 catalog (Katalog Muzeum imienia Lubomirskich) as "Portrait of the Hetman, Copy from Rembrandt (the original in the Hermitage in St. Petersburg is called Radziwill)" (item 445, p. 154). The other, from the collection of Count Karol Lanckoroński (1848-1933) in Rozdil near Lviv, was exhibited in Lviv in 1909, as "An old copy, the so-called Polish Hetman [...] The original is in the Hermitage in St. Petersburg" (after "Katalog ilustrowany ..." by Mieczysław Treter, item 105, p. 31). Lanckoroński also lent to this exhibition an old copy of the Portrait of Pope Julius II by Raphael from his collection (item 104, p. 30) and he owned the portraits of Hendrick van Uylenburgh, artistic agent of the King of Poland, and his daughter Sara by Rembrandt (Royal Castle in Warsaw, ZKW/3905, ZKW/3906), identified by me. At this time, the painting in St. Petersburg was also believed to depict John Sobieski. The man is holding a thick wooden stick-like object that resembles a ceremonial baton of a high-ranking military officer, similar to that seen in multiple portraits of the victorious King John III Sobieski. However, the way he holds it indicates that the staff might be much longer than a ceremonial baton and is in fact a cane. In the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, a cane was a traditional attribute of a marshal (Mareschalcus), the most important "minister" of the country. Traditionally, since the time of Jogaila of Lithuania (d. 1434), there were four marshals: the Grand Marshal of the Crown (Poland and Ukraine), the Grand Marshal of Lithuania, the Court Marshal of the Crown and the Court Marshal of Lithuania. Since this was a more permanent state office, their canes were usually very elaborate, made of precious materials and adorned with precious stones, like the staff seen in the portrait of Casimir Leon Sapieha/Sapega (1609-1656), Court Marshal of Lithuania (Wawel Royal Castle, 9149). Łukasz Opaliński, Grand Marshal of the Crown in his portrait by Stanisław Kostecki (Czartoryski Museum, XII-370) is holding the Marshal's staff decorated with royal monogram - ST (Sigismundus Tertius) of Sigismund III Vasa. The marshal's staff belonging to Stanisław Herakliusz Lubomirski, Grand Marshal of the Crown in the years 1676-1702, is decorated with silver, gold, precious stones (diamonds and almadines) and enamel with symbols of Poland and Lithuania and King John III Sobieski - ITR (Joannes Tertius Rex) (Czartoryski Museum, MNK XIII-3176). In several of his portraits, Lubomirski was depicted holding this cane, such as the portrait in the Palace on the Isle in Warsaw (ŁKr 947), which comes from the collection of the last elected monarch of the Commonwealth - Stanislaus Augustus Poniatowski. The pose of the man in Rembrandt's painting is very similar. Sejm marshals also had canes, but as their function was temporary, just for the duration of the parliamentary session, they were not as elaborate. By striking the floor several times with the marshal's staff, the marshal began the Sejm session. They were also frequently damaged during the sessions as confirmed in the Sejm Diaries from 1704: "the whole day was unlucky, because three of the marshal's staffs broke when he was beating them on the ground to silence them". The loss was not too great, because as Aleksander Łącki, envoy from Łęczyca, noticed during the Sejm (during the dispute over the position of Marshal), it was only a stick which he would get for an ort (1 ort - 18 groszy) (after "Sejm Rzeczypospolitej ... " by Wojciech Kriegseisen, p. 180). One such cane, owned by Stanisław Małachowski (1736-1809), Marshal of the Four-Year Sejm (the Great Sejm, held in Warsaw between 1788 and 1792), preserved in the Czartoryski Museum (oak, 165 cm, MNK XIII-1300). Małachowski was also depicted holding it in his portrait by Józef Peszka (Royal Castle in Warsaw, depisit of the National Museum in Warsaw, 5754). The portrait of Stanisław Marcin Badeni (1850-1912), Sejm Marshal of the Diet of Galicia, is reminiscent of effigies of the Marshals of the Commonwealth (National Museum in Kraków, MNK II-a-524). It was painted by Kazimierz Pochwalski in 1903 and Badeni, who came from a family of Italian origin, in traditional costume, holds the marshal's staff. The man in Rembrandt's portrait wears a fur hat of a shape typical of the Ruthenian and Lithuanian nobility, visible for example in the portrait of Paul IV Sapieha/Sapega (d. 1642) (Wawel Royal Castle, 9164). His costume - hat, fur coat, jewelry resembles that seen in a portrait of a man in eastern costume, most probably a Ruthenian Prince by follower of Aert de Gelder, dated '1639' (National Museum in Warsaw, M.Ob.151 MNW). Similar costumes are visible in the Surrender of Mikhail Shein at Smolensk in 1634 by Christian Melich (Kórnik Castle, MK 03271) with king Ladislaus IV and his dignitaries. The king and his servants wear fashionable French costumes, while the remaining members of his retinue are dressed in the Ruthenian-Lithuanian or Polish-Hungarian style. Similar costumes were also depicted in Stefano della Bella's Allegory of Poland from the 1630s (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, RP-P-OB-34.913) and in effigy of Saint Casimir from HYMNUS QUEM IN B. VIRGINIS HONOREM COMPOSUIT ..., made in Douai in Flanders (now France) in 1638 (National Museum in Kraków, MNK III-ryc.-28781). The print was founded by Ruthenian Mykola-Yuriy Chortoryski (1621-1692), Prince of Klevan, who studied abroad. Before the Counter-Reformation and the growing influence of the Jesuits and Habsburgs at the royal-grand-ducal court, many Ruthenians professed Orthodoxy or Calvinism. To pursue a career at court and study abroad, they frequently converted to Catholicism. Foreign invasions worsened this situation, and from a multi-religious and multicultural nation, Poland-Lithuania became predominantly Catholic and Polish (especially concerning the elites). But before this happened, kings were also depicted in typically Ruthenian costumes. For example, the octagonal portrait of King John II Casimir Vasa, attributed to his court painter Daniel Schultz, depicts him wearing a Ruthenian hat (Royal Castle in Warsaw, depisit of the National Museum in Warsaw, 474 MNW). The style of this effigy is obviously inspired by Rembrandt. Fortunately, it was preserved in Poland, otherwise in a foreign collection it would undoubtedly be known as a portrait of a man (i.e. Dutchman) in oriental costume by a follower of Rembrandt (apart from the obvious resemblance to the monarch and the known history of this painting). The elected king Michael Korybut Wiśniowiecki (1640-1673), who came from the princely Vyshnevetski family of Ruthenian-Lithuanian origin, was represented around 1669 in obviously Ruthenian costume in a print by Nicolas de Larmessin I (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, RP-P-OB-43.940). The purpose of these effigies was exactly the same as in the case of portraits of Holy Roman Emperors in Hungarian or Bohemian costumes, to emphasize that the elected monarchs of the Commonwealth are also the rulers of Ruthenia and that they identify with the main ethnic groups in their country. Such conical-shaped fur hats were still popular in the 19th century among the Ruthenians of Podolia, as depicted in a 1836 lithograph (Przyjaciel Ludu) or in a portrait of Leon Sapieha (1803-1878), Sejm Marshal of the Diet of Galicia, painted by Leopold Horovitz in 1882 (Wawel Royal Castle, 9068). The origins of the coat with a round upper part covered in fur probably came from the medieval costumes of the princes of Ruthenia, possibly inspired by the fashion of the court of the Byzantine emperors in Constantinople (compare with the effigies of the Byzantine emperors Alexios I Komnenos, Michael VIII Palaiologos or Manual II Palaiologos). Even Rembrandt, around 1637, depicted himself in a similar costume in his signed self-portrait in The Wallace Collection (oil on panel, 63 x 50.7 cm, P52). There are numerous such representations of the painter. Average people of the Netherlands preferred French or Dutch fashion, visible in multiple portraits of the Dutch Golden Age. In his signed and dated portrait (Rembrandt / fe 1634) kept at the National Museum in Warsaw (M.Ob.2189), the young merchant Marten Soolmans (1613-1641) wears a typically French costume from the 1630s. The characters in Rembrandt's The Night Watch are also dressed in the mainly Dutch or French fashion of the time. The painter of Dutch merchants and aristocracy should identify himself with his clients by appropriate clothing, while in many of his effigies he resembles an eastern prince or a fur trader, like Nicolaes Ruts, fur trader from Amsterdam (The Frick Collection, 1943.1.150). It looks like he wanted to brag in these self-portraits - look, people of Amsterdam, what beautiful furs and gold chains I received from my Sarmatian/Ruthenian clients or even to paraphrase Jabłonowski, "I am a painter of the entire Commonwealth". Rembrandt's pictorial technique, composed of bold brushstrokes and thick impasto, most likely inspired by the technique of the great Venetians who painted the monarchs of Poland-Lithuania, indicates that he painted fast, and therefore smaller works, notably with the help of frequently mentioned assistants, might only take a few days. Over the course of approximately 45 years of his career (1624-1669), he created approximately 324 paintings that are either signed or attributed to him, which amounts to approximately 7 to 10 paintings per year. The 19th-century French painter Gustave Courbet, who also painted fast and without the help of assistants (in two cases with the help of Hector Hanoteau), estimated that he had completed around 1,000 paintings by 1867 (after "Country Life Illustrated", Volume 163, 1978, p. 260), which makes approximately 36 paintings per year during a 28-year career that began around 1839 in Paris. Rembrandt also made prints, which he also created quite quickly. However, given these facts, either he was lazy or many of his major works were destroyed, such as during the Deluge (1655-1660). No confirmed effigy of Jan Stanisław Jabłonowski has survived, but the man bears a close resemblance to effigies of the marshal's son Stanisław Jan Jabłonowski (1634-1702), Great Crown Hetman by Jean Mariette from about 1682 (National Museum in Warsaw, 99334), his grandson Jan Stanisław Jabłonowski (1669-1731), voivode of Ruthenia, painted by Adam Manyoki in about 1714 (National Museum in Warsaw, PM 4266 MNW) or Jabłonowski's great-grandson King Stanislaus I Leszczyński by circle of Adam Manyoki from the 1720s (sold at Desa Unicum in Warsaw, November 24, 2021, lot 45). The earring in his ear indicates that usually, like the king, he preferred French costume and that he only dressed in Ruthenian costume to demonstrate this attachment to his region and the Commonwealth. In 1637, two Flemish Protestant merchants, raised in Delft in the Netherlands where their father had fled from Antwerp, became tax collectors of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. Likewise, we can assume that Rembrandt regularly worked as a remote painter for Commonwealth's clients, including the king, but today we can only imagine how many beautiful paintings he created for them. The destruction of Commonwealth's heritage during numerous wars and invasions was so considerable that many significant objects linked to the monarchs of Poland-Lithuania had to be acquired abroad, such as a series of miniatures of the Jagiellon family by the workshop of Lucas Cranach the Younger purchased in London in the mid-19th century by Adolf Cichowski (Czartoryski Museum). The painting or a series was therefore commissioned by Jabłonowski or the king in Rembrandt's workshop to commemorate the memorable extraordinary Sejm of 1637.
Portrait of Jan Stanisław Jabłonowski (1600-1647), Marshal of the extraordinary Sejm, wearing Ruthenian costume by Rembrandt, 1637, National Gallery of Art in Washington.
Self-portrait wearing Ruthenian costume and two chains by Rembrandt, ca. 1637, The Wallace Collection.
Portraits of Boguslaus Radziwill by Govert Flinck and Giacinto Campana
On March 5, 1636, the young Boguslaus Radziwill (1620-1669), son of Janusz (1579-1620) and his second wife Elisabeth Sophia of Brandenburg (1589-1629), daughter of John George, Elector of Brandenburg, left for Vilnius and became a courtier of King Ladislaus IV Vasa. As a result, the guardianship of his uncle Christopher Radziwill (1585-1640) over him was lifted and the prince's independent career began. He received the starosty of Pasirvintis in Lithuania.
Born in Gdańsk, he was educated in the Calvinist schools of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. In 1635, during the ongoing Polish-Swedish war, Boguslaus was taken by his uncle to Livonia, where he participated in military camp life. In November 1635 he came to Birzai, where he became a student of the architect of the fortress fortifications, Georg Pirken. In 1636 he also became a member of the Sejm and attended the funeral of Princess-Infanta Anna Vasa in Toruń. In 1637, after staying in Warsaw, he went to Birzai then left to study in the Netherlands. With breaks he remained abroad for almost ten years, returning to the Commonwealth in 1648. On his trip abroad, Radziwill was accompanied by a retinue led by the courtier Samuel Puciata. On his way to Groningen he visited Szczecin and Berlin. After arriving in the Netherlands in December 1637, he enrolled in local universities. The following year, he left for Utrecht to enlist in the service of Frederick Henry (1584-1647), Prince of Orange. He participated in the siege of Breda and Venlo. Boguslaus soon abandoned military life, preferring to travel and explore Europe. In October 1638, he enrolled at the University of Utrecht. At the same time, thanks to the efforts of his uncle Christopher and his cousin Janusz, he received the post of standard bearer of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. At the end of 1638, the prince left for France. On January 16, 1639, he came to Paris for the baptism of the dauphin Louis, future Louis XIV. During his short stay in the Commonwealth in 1646, he accepted the position of equerry of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. No expense for a luxurious lifestyle was spared and paintings, sculptures, weapons, clothing and other goods were purchased, also portraits were commissioned. "I spent a wonderfully joyful autumn here in The Hague ... in Utrecht and other Dutch cities", Boguslaus confessed in 1641. His year and a half stay abroad cost more than 200,000 zlotys. Returning to Poland in 1648, he left large unpaid debts in Paris and Amsterdam for inn rentals, loans, etc. (after "Z dziejów stosunków polsko-holenderskich ..." by Maria Bogucka, p. 67). Around 1638, a famous painter and engraver, Lucas Vorsterman (1595-1675), entered the service of the young magnate. Boguslaus commissioned him to graphically record the battles fought by the Prince of Orange at the gates of Breda and Venlo. In 1638, the same engraver produced a portrait of the prince in French costume, a copy of which was sent in September 1638 as a gift to Janusz Radziwill, Boguslaus's cousin. Two years later, in 1641, Vorsterman painted a new portrait of Boguslaus, this time in armor, and made an engraving of it (its only copy was formerly in the collection of Ferdynand Radziwill in Berlin). Another painted image of Boguslaus was created in The Hague by Michiel van Mierevelt at the turn of 1639 and 1640, then copied in graphics by Willem Delff. All these likenesses have been lost (compare "Ogród miłości i 99 innych rycin" by Hanna Widacka, p. 39). Many Dutch and Flemish paintings and curiosities that Radziwill acquired during his travels and received as gifts were listed in the inventory of his painting collections made in Królewiec (Königsberg) in 1657 (AGAD 1/354/0/26/84), such as "Landscapes in the frame ... 4", "Dutch tavern painting", "Face of an old man with a book", "Dutch courtship", "Picture on the satin of the Indian king's wife [possibly Empress Mumtaz Mahal]", "Dutch painting on canvas", "The view of Rotterdam on satin", "The Savior from the Jesuits", "Christ resurrecting Lazarus", popular subject in Dutch and Flemish painting (Lanczaftow w Ramach ... 4, Obraz Olenderski Karczemny, Twarz Starca z Xsięgą, Zaloty Holenderskie, Obraz na Atłasie Indyskiego Krola zony, Obraz Olenderski na Płotnie, Obraz Roterdamy na Atłasie, Salwator od Jezuitow, Christus Łazarza wzbudza), as well as portraits - of Gertruida van Veen (1602-1643), painter from the Southern Netherlands (Giertrudis d'Veen), numerous portraits of the monarchs of Poland-Lithuania, Emperor Ferdinand and Empress Eleonora, probably Ferdinand II (1578-1637) and his second wife Eleonora Gonzaga (1598-1655) or Ferdinand III (1608-1657) and his third wife Eleonora Gonzaga (1630-1686) (Ferdinandus Cesarz, Eleonora Cesarzowa) and the portrait of the "Princess Marshaless in French costume" (Xzna Pani Marszałkowa po francusku), most likely Lucrezia Maria Strozzi (ca. 1621-1694), wife of Prince Alexander Louis Radziwill (1594-1654), Grand Marshal of Lithuania. The register also mentions four portraits of Boguslaus, including one in a cuirass (Obraz Xcia Pana Koniuszego, Xcia Pana Koniuszego Dwa ieden W kirysie ... 2, Pan Chorąży). The portrait of Boguslaus in a blonde wig, attributed to Willem van Honthorst (private collection), was probably painted around 1665, the year of his marriage to his cousin's daughter - Anna Maria (1640-1667). His jabot also indicates the 1660s and the painting is similar to the miniature in the Louvre (RF 205, Recto), attributed to the French painter. Perhaps in the same year, the alleged portrait of his wife Anna Maria as Flora, attributed to Caspar Netscher (Museum of Warmia and Masuria in Olsztyn, MNO-101 OMO), was made. In both cases, attempts to determine how the painters and sitters met are difficult, so as in the case of some of other portraits from the Dohna collection in Olsztyn, they were most likely based on study drawings or other effigies sent to painters in the Netherlands. In his portrait in the National Museum in Warsaw (MP 4786 MNW), painted between 1733 and 1737 and based on another lost effigy, Boguslaus has dark hair and mustache. His effigy made between 1646 and 1653, a drawing kept at the Hermitage Museum (ОР-45875), also indicates that he had dark hair like his father Janusz. In 2020, a portrait of a young man in a gorget with a plumed hat by Govert Flinck was sold in New York (oil on canvas, 66.5 x 53.3 cm, Christie's, Auction 18715, October 15, 2020, lot 22). The painting most likely comes from the collection of Gdańsk painter Jacob Wessel (1710-1780), his sale on April 23, 1781. Wessel frequently worked for the Polish-Lithuanian artocracy, who commissioned their portraits in the country's main port. In 1746, the painter created two of his best-known works - a full-length portrait of Hieronim Florian Radziwill (1715-1760) in Hungarian-style costume and a pendant portrait of his wife Magdalena Czapska (d. 1763), which appeared in the 1760 inventory of the Radziwill Palace in Biała Podlaska. Hieronim Florian was one of the richest magnates in the Commonwealth. Thanks to the agreement concluded with the Palatine of the Rhine, he managed to recover in the 1730s for the Radziwill family the estates of Louise Charlotte Radziwill, daughter of Boguslaus, including Slutsk, Kedainiai and Zabłudów, called the Neubourg estates. Several "Bavarian portraits" (items 151-155, 164) in the mentioned inventory of the palace in Biała Podlaska, as well as several paintings of Lucretia and a portrait of Martin Luther, painted on wood (436), most probably by Cranach, indicate that many paintings come from the collection of Louise Charlotte Radziwill. The portrait of her father Boguslaus is not mentioned, but the register includes "A portrait of a Dutchman, full-length, painted on canvas" (566, compare "Zamek w Białej Podlaskiej" by Euzebiusz Łopaciński). The painting was signed and dated: GG·flinck f / 1636· (lower right, the last number barely visible), thus the time when Boguslaus, born in Gdańsk, became a courtier of the king. In July 1637 he left Vilnius and in September he boarded a ship in Gdańsk (he had to return to the city and eventually went to the Netherlands by land). The young prince was only 16 years old, but the man's youthful appearance does not contradict the fact that this is his effigy and he bears a strong resemblance to Radziwill according to an engraving with his portrait made by Jeremias Falck Polonus after a painting by Daniel Schultz in 1654 (National Library of Poland, G.10389), as well as the mentioned drawing in the Hermitage. Falck's engraving is probably the best-known effigy of the Prince. In the National Museum in Kraków there is another engraving of him and his wife, perhaps made by Adam Bartsch (1757-1821), based on an effigy dating from around 1665, the time of their marriage. The prince was depicted in rich French costume and his features are similar to those in the mentioned portrait attributed to Willem van Honthorst. At first glance, looking at these undisputed effigies of Radziwill (at the Hermitage, by Falck and by Bartsch), one might have the impression that they represent different men, because he has a different appearance. All, however, were based on other effigies and today it is impossible to determine the original effigy because most of them have been destroyed. The practice of copying favored the distortion of features. In 1637, Flinck usually lived in the house of Hendrick van Uylenburgh in Amsterdam, according to Joachim von Sandrart, who visited Holland that year. According to known sources, he never left the Netherlands after 1629 (in 1652 he received citizenship in Amsterdam), so it is impossible that the painter and Boguslaus met in person in 1636, when the painting was probably made, but Govert could base this on study drawings or effigies of other painters sent from Gdańsk. Similar to the portrait of Frederick William (1620-1688), Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia, who became protector of Boguslaus during the Deluge, painted by Flinck around 1652. The meeting of the painter and the elector is not confirmed in the sources, but the portrait of the elector at Charlottenburg Palace in Berlin (GK I 997, signed and dated center right: G. flinck / 1632) is undoubtedly the work of this student of Rembrandt. The elector's effigies are so well known that probably no one wonders how he also met Frans Luycx, the emperor's court painter, active in Vienna (Kunsthistorisches Museum, GG 3163) and why Frederick William has dark hair in a painting by Flinck and blond in that by Luycx. The elector's nose was also depicted differently in the two portraits. Likewise for the portraits of King Ladislas IV Vasa, who in some portraits has dark hair and mustache and in others blond (compare portrait from private collection in Rome, Bolli & Romiti, May 18, 2022, lot 61-62, and a miniature at the National Museum in Warsaw, Min.726 MNW). The same man from the Gdańsk painting by Flinck is also depicted in two other works by the painter. One of these paintings is today in the Wawel Royal Castle in Kraków (oil on panel, 58.5 x 47 cm, inv. 3234, signed and dated lower left: flinck / 1637). It comes from the collection of the Tarnowski family who acquired numerous paintings from former royal collections of the Commonwealth. The other is in the Hermitage Museum (oil on panel, 73 x 57.5 cm, ГЭ-782, signed and dated lower left: G. flinck f. / 1637). The painting entered the Hermitage in 1781 and was acquired in the collection of Count Baudouin in Paris, where Boguslaus left the Netherlands in 1638. The painting could therefore be a gift to the King of France or to friendly French aristocrats. In this case the meeting of the painter and the prince in person in 1637 is very probable. The two paintings, at the Wawel and at the Hermitage, have good old copies. The copy of Wawel's portrait, most likely dating from the 19th century, is in the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 52.5 x 32 cm, M.Ob.2556). The copy of the Hermitage painting was sold in London in 2019 (oil on canvas, 70.5 x 57.2 cm, Bonhams, October 23, 2019, lot 70). Although this painting has been attributed to an 18th century painter, it was painted in the style of the 17th century Italian school, the authorship of Giacinto Campana, who from around 1637, worked in Warsaw and later also in Vilnius, is very likely. The style of this painting is comparable to that of the portrait of Queen Bona Sforza (National Museum in Lublin, S/Mal/609/ML) or to Saint Mary Magdalene (Wilanów Palace in Warsaw, Wil.1732). The portrait of "Prince Boguslaus" (Xiąze Bogusław) is mentioned in the 1661 inventory of the Lubomirski collection in Wiśnicz (AGAD 1/357/0/-/7/12) after an effigy of the "Lord Vice-Chancellor of Lithuania Pac" (Pan Podkanslerzy Litewski Pac). During the Deluge, Boguslaus betrayed the Commonwealth and sided with the Brigand of Europe. This probably contributed significantly to the fact that people were not willing to add a description to his portraits which survived the destruction and soon all were forgotten.
Portrait of Prince Boguslaus Radziwill (1620-1669) in a gorget by Govert Flinck, 1636, Private collection.
Portrait of Prince Boguslaus Radziwill (1620-1669) by Govert Flinck, 1637, Wawel Royal Castle.
Portrait of Prince Boguslaus Radziwill (1620-1669) by follower of Govert Flinck, 19th century, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Prince Boguslaus Radziwill (1620-1669) by Govert Flinck, 1637, State Hermitage Museum.
Portrait of Prince Boguslaus Radziwill (1620-1669) by Giacinto Campana, after 1637, Private collection.
Portraits of Helena Tekla Ossolińska and her father-in-law Stanisław Lubomirski by Simon Vouet and workshop
On July 7, 1637, the young Helena Tekla Ossolińska (1622-1687), aged 15, "Countess of Tęczyn", daughter of the voivode of Sandomierz Jerzy Ossoliński (1595-1650) and Izabela Daniłowiczówna married Aleksander Michał Lubomirski (1614-1677), son of Stanisław (1583-1649), voivode of Ruthenia, and brother of Jerzy Sebastian (1616-1667), "thus uniting the splendor of the house of Ossoliński with the splendor of the house of Lubomirski", two powerful families of magnates of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, as extolled the union Andrzej Hązel Mokrski (1598-1649).
The poet and courtier Adam Gębkowski also dedicated his poem to the young couple (Hymen gdy świętym przymierzem W. JMP. Pan Alexander Lubomirski bierze W. JM. Pannę Helenę Ossolińską ...). The wedding celebrations took place in the sumptuous castle of Helena Tekla's father in Ossolin, in the presence of King Ladislas IV Vasa and many senators. During this meeting, the creation of the Polish-Lithunian chivalric order dedicated to the Virgin Mary ("blessed and immaculate Mother of God of all Christianity") was probably discussed (compare "Saeculum Christianum ...", 1995, Volumes 1-2, p. 280). The creation of this order, modeled on the French Order of the Holy Spirit founded by Henry III of France (also elected monarch of the Commonwealth) in 1578, was suggested to the king by Ossoliński. However, due to opposition from Catholic magnates such as Stanisław Koniecpolski and Stanisław Lubomirski, Primate Jan Wężyk and Grand Hetman of Lithuania Christopher Radziwill, who was a Calvinist, the king confirmed in 1638 in writing that he would not establish an order without the consent of the Sejm. Moreover, after questioning Ossolinski's princely title, received from the Pope and the Emperor, the Sejm also banned the use of aristocratic titles, as they contradicted the equality of the nobility. Miss Ossolińska must have received a good education from her parents, because she was later known as one of the wisest and most influential women of her age. She was also a recognized figure among artists and writers. Her father and husband were also well educated men and traveled to different countries in Europe. Jerzy Ossoliński studied in Graz (Austria) and Leuven/Louvain (Belgium), in England, in Paris and Orleans in France, in Padua, in Bologna, Rome and Naples in Italy. In 1621 he traveled to England as the Commonwealth's envoy. In 1633, as ambassador, he made the famous entry into Rome, and a year later, in 1634, he went to Vienna on a diplomatic mission. In 1636 he visited the Imperial Diet in Regensburg, where he witnessed the election of Ferdinand III. Aleksander Michał, with his brother Jerzy Sebastian, stayed in Ingolstadt (Bavaria) in 1629 and later in Leuven/Louvain, Cologne and Leiden. Together they went to France, Jerzy probably went to Spain and certainly to England for a short time, while Alexander Michał went to Italy (Padua, Rome), where he stayed until 1635. On his return to Poland-Lithuania, he became the king's courtier. The residences of these wealthy, educated men must have reflected the highest taste of the European upper class of the time. Ossolin Castle had rich marble floors, crystal windows set in lead frames, ceilings painted on canvas in gilded frames "as if they were of pure gold" (gzymsy złocone suto jakby szczerozłote), most likely Venetian style, marquetry doors and a library with portraits. In one of the rooms, there were paintings with views of European cities and a fireplace with two statues bearing the Ossoliński coat of arms. Unfortunately, the residence was pillaged and destroyed by Swedish and Transylvanian troops during the Deluge. In 1816, when the country became significantly impoverished during numerous wars, the owner Antoni Ledóchowski, hoping to find the legendary treasures of the Ossolińskis, hidden from invaders, ordered the ruins of the castle to be blown up. Wiśnicz Castle, which belonged to Aleksander Michał and his wife after the death of his father in 1649, was also famous for its rich collections. Helena Tekla contributed to their expansion, because after the death of her father she inherited in 1651 part of his collection of books and works of art, which were located in the residences of the chancellor in Warsaw and Ossolin. These movable assets, in the absence of a male heir, were distributed among the three daughters of Jerzy Ossoliński. During the Deluge, between 1655 and 1659, the castle was evacuated twice by the hosts and plundered three times by enemy troops, who transported the spoils from Wiśnicz on 150 carts (after "Z dziejów polskiego mecenatu ..." by Władysław Tomkiewicz, p. 264). What is interesting is that the castle, reinforced with at least 35 cannons and defended by a crew of more than 200 soldiers, was surrendered to the "Brigand of Europe" without a fight for fear of destruction in October 1655 (compare "Od Ujścia do Warki, 1655-1656" by Henryk Wisner, p. 63). Despite this, after the looting, the castle was destroyed by the Swedes with gunpowder and the neighboring Carmelite monastery was completely plundered ("after "Szwedzi i siedmiogrodzianie ..." by Joźef Gollenhofer, Klemens Bąkowski, Ludwik Sikora, p. 43). The castle was partially rebuilt in 1680-1686. The "Inventory of belongings spared from Swedes and escapes made on December 1, 1661 in Wiśnicz" (Rejestr rzeczy po Szwedach i ucieczkach zostających spisany roku 1661 dnia 1 grudnia na Wiśniczu) in the Central Archives of Historical Records in Warsaw (number 1/357/0/-/7/12), lists some of the preserved paintings from the collection, including several paintings belonging to Stanisław Lubomirski, such as a large painting of Diana with greyhounds (Obraz wielki Dianna scharty) and Jerzy Ossoliński, such as the Virgin and Child with Saint John "from France" (ze Francyey), Leda and the Swan from the Emperor, Herodias with the head of Saint John the Baptist (Herodianna głowe sw. Jana trzymaiąca w Ramach Hebanowych), Cupid making his bow "from Rome" (Kupido łuk struzący w Ramkach Hebanowych, z Rzymu), perhaps a copy of a painting by Parmigianino, a large painting of the Madonna in a garland of fruit held by angels (Naśw. Panna wielka wieniec około niey z fruktow, ktory Anyeli trzymaia), possibly by Peter Paul Rubens and Jan Brueghel the Elder, allegorical painting showing King Louis XIII of France and Cardinal Richelieu "holding the World" (Król Francuzki z Kardinalem Ryszeli swiat trzymaiacy), the Sacrifice of Isaac by Titian (Abraam zabiiaiący Izaka. Ticyanow), the Suicide of Cato by Jusepe de Ribera (Kato przebiiający się puynałem. Spanioletow), Emperor Titus (?) by Guido Reni (Tycyus Guidoroniego), Susanna and the Elders by Guercino (Zuzanna Gwercine da Cento), Carrying of the Cross on marble by Bassano (Baiulatio crucis na kamieniu Basana), possibly by Jacopo Bassano, Tobias and the Angel by Raphael (Anyoł Tobiasza prowadzący Ramy czarne miescami złociste Raphael de Urbino), the Virgin and Child by Albrecht Dürer (Naswietsza Panna z Panem Jezusem małym na drewnie Alberti Duri), the Infant Christ and Saint John the Baptist in a garland of flowers by Daniel Seghers (Pan chrystus z swietym Janem Feston skwiatow trzymaiacy Jezuity Antuerpskiego), a large painting of Saint Cecilia by Domenichino (Swięta Cecylia wielka Dominikinow) and the Cardinal virtues by Paolo Veronese (Tres virtutes cardinales. Paulo Venorase). Certain mentions such as "my paintings offered or purchased" (Obrazy moie własne tak darowane iako y kupne), in this register as well as a great connoisseurship of the paintings indicate that Aleksander Michał may have been the author of this register or personally supervised its creation. Among the paintings received or purchased, the register lists a copy of the painting of the bathing goddesses (Obraz Bogin kompiących sie. Kopia), Saint Mary Magdalene (?) by Parmigianino, painted on wood (Białagłowa sczaką Parmeganino na drewnie), a painting of an old beggar by Jusepe de Ribera (Obraz ubogiego starego Spenioleti), Venus and Adonis by Francesco Albani (Adon z Venerą w Ramach złocistych Albanow), a tondo representing Hermaphroditus by Francesco Albani (Obraz Harmofredita okrągły Albanow), two Venetian landscapes, one with Saint John the Baptist at the spring on the second a shepherd with cattle (Dwa Lanszafcikow z Wenecyiy na iednym sw. Jan biorący wodę zrzodla na drugim Pastyrz zbydłem) and numerous portraits of Polish-Lithuanian, French and Italian rulers and aristocrats. It is not known what happened to these paintings, perhaps scattered among other residences they were destroyed in other wars or during the great fire of the dilapidated Wiśnicz Castle in 1831. The inventory also includes several effigies of Aleksander Michał and Helena Tekla. Two major effigies of Lady Lubomirska were disguised portraits – one listed as "Portrait of Her Ladyship in the guise of Saint Helena by Mons feuen" (Konterfet JeyMci na kształt świętey Heleny ma miedzi Mons feuen) and the other as "Portrait in full of Her Ladyship in the guise of Diana with greyhounds" (Konterfet cały Jey Mci na kształt Dianny scharty). In the first, she was depicted as her patron Helena of Constantinople, mother of Constantine I, as Queen Bona Sforza in her 1525 portrait by Lucas Cranach the Elder (Cincinnati Art Museum, 1927.387), identified by me. Two portraits of Alexander Michał mentioned in the register were painted by Nicolas Régnier (1591-1667) - "one by Mr Renierow" (ieden P. Renierow), and another "by Renieri from Venice in silver embroidered robe" (ieden Renierego z Venecyey w hawtowanych srebrem sukniach). Régnier, a painter from the Spanish Netherlands, known in Italy as Niccolò Renieri, was active in Venice from 1626. It is possible that some portraits of Alexander Michał's wife were also commissioned in Venice. Curiously, Saint Catherine of Alexandria attributed to the workshop of Nicolas Régnier, today kept at the Sforza Castle in Milan (oil on canvas, 70 x 57 cm, inv. 270), bears the features of Vittoria Farnese (1618-1649), Duchess of Modena and Reggio. The painter's presence in Modena around 1648, when the painting was probably made, is not confirmed, so he must have painted it in Venice. In 1644, he was named "painter to the King of France", undoubtedly to help him escape the requirements of the fraglia dei pittori, so that he could more easily supply paintings to Cardinal Mazarin. Similar to the portrait of Queen Bona, portrait of Empress Eleonor Gonzaga (1598-1655), painted by Lucrina Fetti between 1621-1625 (Ducal Palace of Mantua, Gen. 6864), miniature portrait of Anne of Austria (1601-1666), dowager queen of France, painted by Joseph Werner around 1660 (Musée Condé, OA 1375) or portrait of Vittoria della Rovere (1622-1694), grand duchess of Tuscany, painted by Justus Sustermans in 1669 (Palazzo Corsini in Rome, 428), Helena Tekla was undoubtedly also represented with the traditional attribute of this saint carrying the True Cross of Christ. In the late 1660s, the mistress of Louis XIV of France, Françoise Louise de La Vallière (1644-1710), Duchess of La Vallière, was most likely also depicted as Saint Helena, because such effigy was sold in Stockholm (Bukowski Auktioner, Sale 562, lot 426 / 124687). In 1952, Władysław Tomkiewicz, who analyzed this inventory, suggested that the author of the disguised portrait of Helena Tekla could be Simon Vouet (1590-1649), French painter (compare "Z dziejów polskiego mecenatu ...", p. 271). Vouet studied in Rome, where he married the painter Virginia da Vezzo or Vezzi (d. 1638) in 1626. A year later, in 1627, he was called by Louis XIII to serve as the king's first painter in Paris, where his younger brother Aubin Vouet (1595-1641) had already been working as the king's painter since 1621. He also stayed in Venice, Genoa and Milan and visited Constantinople in 1611. Not only the similarity of Mons [Monseigneur/Monsignore] feuen suggests this, but also the large number of portraits of French monarchs and dignitaries present in the inventory and the fact that the same painter created other paintings from the Lubomirski collection. The register mentions a painting of "Saint Sebastian dying by Mons ouet" (Swięty Sebastian, umierający. Mons ouet) and "Two portraits on copper, one of this Ambassadress in red, the other of the Duchess of Lorraine in blue by Mons Scheuet" (Dwa konterfety na miedzi ieden teyze Posłowey w czerwieni, drugi Xiezny Lotarynskiey w błękitni Mons Scheuet). This ambassadress was Renée du Bec-Crespin (1613/14-1659), comtesse de Guébriant, appointed extraordinary ambassadress of France to the Commonwealth in 1646 and an earlier entry in the inventory mentions another of her portraits, perhaps by the same painter, in the guise of the Virgin: "An image of the French Ambassadress, in the form of the Blessed Virgin Mary" (Posłowey Francuzkiey obraz nakształt Nasw. Panny) and followed by "Two portraits on copper of King Ladislaus and Cecilia [Ladislaus IV Vasa and his first wife Cecilia Renata of Austria]" (Dwa konterfety na miedzi krola Władisława z Cecyliją). Interestingly, Renée is considered the first female ambassador in the history of France and her mission was to help Ladislaus IV's second wife, Marie Louise Gonzaga, gain influence over her husband. It should also be noted that no voices of opposition to the first female ambassador to the "Realm of Venus" are known. Renée was magnificently received in Warsaw, according to the account of her trip by Jean Le Laboureur, published in Paris in 1647 (Relation du voyage de la Royne de Pologne, et du retour de Madame la Mareschalle de Guebriant, Ambassadrice Extraordinaire ...), and "was widely appreciated by the king and Polish lords, received extraordinary honors from them" (after "Starożytności warszawskie ..." by Aleksander Weinert, Volume 2, p. 216). If the ambassadress gave her portrait to the Lubomirskis during her visit to Poland, she must have many copies of it, as there were many important dignitaries worthy to receive it. The fact that there were two of her portraits in the collection of Helena Tekla and her husband that survived the Deluge, indicates that they probably befriended the ambassadress. Ordering numerous copies of the same effigy was then a common practice among the elites. The best example are the copies of portraits of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa by Rubens, copies of the portrait of Henrietta Maria of France (1609-1669), Queen of England, Scotland and Ireland in the guise of Saint Catherine of Alexandria, original painted by Anthony van Dyck in about 1637 (Christie's London, January 24, 2012, lot 261, Palace of Versailles, MV 3425 or Hatchlands Park, NT 1166715) or a series of portraits of Lady Mary Villiers (1622-1685), Duchess of Richmond and Lennox as Saint Agnes by Anthony van Dyck and circle, painted around 1637 and after on the occasion of her second marriage at the age of 15 (Windsor Castle, RCIN 404402, Lacock Abbey, 996277 and Christie's London, Auction 3475, lot 36). Accordingly, if four or five paintings - (1) portrait of Helena Tekla as Saint Helena, (2) Saint Sebastian, (3) portrait of Madame de Guébriant, (4) portrait of Duchess of Lorraine and, possibly, (5) portrait of Madame de Guébriant in the guise of the Virgin Mary, were all by Simon Vouet, very probably also the effigy of Helena Tekla as Diana was created by him. The representation as the Roman goddess of hunting, fertility and childbirth indicates that the painting was made to receive a "blessing" for the young bride, therefore before or shortly after the wedding. In this sense it is comparable to the portrait of the young Mary II (1662-1694), when princess, in the guise of Diana, painted around 1672 by Peter Lely (Hillsborough Castle, RCIN 404918). The future Queen of England is blonde in this portrait (in her later effigies she has dark hair). The description in Wiśnicz's inventory mentions a full-length portrait, but this does not mean that the painting was vertical (standing, as in the portrait of the future queen of England), but could also be horizontal (reclining, as in the portraits by Cranach). It is interesting to note that such a painting of Diana, painted by Simon Vouet in 1637, the year of Helena Tekla's marriage, is today in Hampton Court Palace in England (oil on canvas, 104.3 x 147.5 cm, RCIN 403930). The painting was first recorded in the Royal Collection in 1710, described as a "Diana of Vouet", over the door in the Drawing Room of Somerset House - traditionally the Queen's residence. There is no trace of this work in the inventories of Charles I nor in the Commonwealth Sale (Sale Inventory, ca. 1649-1651), the latter however mentions: "Done in Poland, King of Poland, full-length" at the Armory at St James's (WS 151, No. 10) and "King of France with Madonna and Child" (WS 60, No. 14). The painting was inscribed by the artist, lower right (on the quiver): Simon Vouet / F. [fecit] Paris 1637. As indicated in Description of the painting (Royal Collection Trust) "the addition of the place of execution is unusual for Vouet and may indicate that the work was to be sent abroad". Any provenance before 1710 can only be supposed at the moment, so the hypothesis that Jerzy Ossoliński sent to England (to his friends met during his studies or in 1621) a disguised portrait of his daughter, commissioned in Paris, is also possible. Such a horizontal composition refers to Cranach's nude portraits of Queen Bona as Diana-Egeria, paintings identified by me. One of the most famous works by Simon Vouet or his entourage - the allegorical portrait of Anne of Austria (1601-1666), cousin of King Ladislaus IV Vasa, now kept in the Hermitage Museum (ГЭ-7523), is also a disguised portrait. The Queen of France was depicted as Minerva, goddess of wisdom, victory and strategy. Only the features of the sitter, looking at the viewer, indicate that it is a portrait, because the Latin inscription on the base is the beginning of the sentence from Juvenal's "Satires": "Fortune never fails, [if there is prudence]" (Nullum numen abest, [si sit prudentia]). The disguised portrait of Anne of Austria testifies that the artist beautified his models or adopted their features according to classical canons of beauty. Saint Catherine from private collection in Naples, attributed to Vouet, is considered to be a disguised portrait of artist's sister-in-law Ursula da Vezzo (Sotheby's New York, January 25, 2017, lot 39) and Vouet's painting in the Los Angeles County Museum of Art (M.83.201) is believed to be a portrait of his wife Virginia as Saint Mary Magdalene. The woman in the Hampton Court Palace painting bears a close resemblance to Helena Tekla, as shown in her portraits preserved in Poland, all created after the Deluge, especially the effigies as a nun, created after 1681 - in Wilanów Palace (Wil.1340) and a copy in the parish church of Saint Joseph in Klimontów. A studio copy of "Diana resting" was sold in Paris in 2019 (oil on canvas, 120 x 168 cm, Sotheby's, June 26, 2019, lot 81). As the Lubomirskis owned many effigies of French monarchs and aristocrats, the French may also have had the portrait of Lady Lubomirska, especially since it was commissioned in France. It is also possible that the painting returned to its country of origin in the 19th century or earlier, with the move of many Polish-Lithuanian aristocrats to France. A study for Diana's head by Vouet or his studio is in the Louvre (RF 28221, Recto). It is possible that the painting: "A young person with a greyhound, French style" (Osoba jakaś młoda z chartem tarantowatym, po francusku, 837/17), mentioned in the inventory of Princess Louise Charlotte Radziwill (1667-1695) which survived the Deluge (compare "Inwentarz galerii obrazów Radziwiłłów z XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska), was another disguised effigy of Lady Lubomirska. The painting was also reproduced in several engravings. They have an oval shape, so the original could also have been oval. The mirror version, made by Michel Dorigny in Paris in 1638, so the following year, is signed and dated: S. Vouet pinxit. / Cu priuilegio / M. Dorigny scul. / Parisi 1638 (Leiden University Libraries, PK-P-144.428). The version in the National Library of Poland (G.31201) reproduces the original layout of the painting. Paintings were usually available primarily to customers who ordered them, so the artist, probably proud of his work, wanted his composition to be accessible to a wider audience, which is why the prints were made. Sometimes also, the owners of the original paintings wanted a wider distribution. For example, the so-called Hesselin Madonna or Madonna of the oak cutting at the Louvre (RF 2004 19), produced by Simon Vouet for the Parisian house of Louis XIII's secretary Louis Hesselin around 1640-1645, was reproduced in a print made by Michel Dorigny in 1651 and bearing the Hesselin coat of arms on the lower margin (British Museum, 1841,1211.39.54). The features of the Hesselin Madonna are quite distinctive, which is why the secretary's wife, Renée d'Elbeuf, was probably depicted as the Virgin. The same woman was represented in another painting attributed to Simon Vouet, sold in London in 2019 (oil on canvas, 60.7 x 49.5 cm, Sotheby's, December 5, 2019, lot 115). This "Study of a young woman as the Virgin" was previously considered to represent the artist's wife, Virginia, based on a drawing by Marie Metézeau kept at the Musée des Beaux-Arts in Rennes (794.1.2691), signed: Virginia de Vezzo Sim.s Voüet Regis Christianissimj / Pictoris conjux charissima clarissima Inuentrix & Pinxit [...]. Basing on this drawing, usually dated to the second half of the 17th century, so several years after Virginia's death, another version of the painting from the Galleria Apolloni in Rome (oil on canvas, 60.3 x 50.2 cm, Bonhams London, July 11, 2001, lot 122), is identified as her self-portrait or her likeness by a follower of Simon Vouet. Additionally, the inscription in Rennes' drawing is ambiguous and it can also be interpreted that Virginia painted the original or another version of the painting. The painting sold in London comes from a private collection in Austria (by the 1970s, thence by descent) and was traditionally attributed to Philippe de Champaigne. It is therefore very possible that already in the 17th century, one painting was sent to the Pope or cardinals in Rome and the other to the Emperor in Vienna. Such "distribution" of effigies was typical for the European high aristocracy. The colors of the clothing - blue and red - clearly indicate that the subject represents the Virgin (compare with Catalogue Note). The magnificent painting attributed to Vouet, probably painted in Italy, which is now in the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 100 x 75.5 cm, M.Ob.646, earlier 128630), testifies that his talent was probably recognized by the patrons from the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth already shortly after its creation. This vanitative painting, inspired by Caravaggio, is generally dated around 1621 and comes from the State Art Collections, possibly from the Royal Castle in Warsaw. It shows the Ill-matched couple with a young woman pointing to a skull (Vanitas). Finally also certain portraits preserved in the former territories of the Commonwealth are close to the distinctive style of Vouet, his workshop or his circle. These include a portrait of Helena Tekla's father-in-law, Stanisław Lubomirski, now in the former royal residence - Wilanów Palace in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 81 x 65.8 cm, Wil.1258). It bears an incorrect later inscription identifying the sitter as Stanisław's grandson, Stanisław Herakliusz Lubomirski (1642-1702). The style of this painting is very similar to the portrait of a woman, probably Ursula da Vezzo, as Saint Agnes by circle of Simon Vouet (Sotheby's London, April 24, 2008, lot 204). The voivode of Kraków was very concerned about the good distribution of his effigies, because despite numerous wars and destruction, several have survived, such as the full-length portrait from Wiśnicz Castle, perhaps painted by Stanisław Kostecki between 1638-1649 and repainted in the 18th century (National Museum in Warsaw, 128870/2 MNW) or effigy from the portrait gallery of the founders and benefactors of the Piarist monastery in Warsaw, made after 1647 (MP 3202 MNW). In all of them he was depicted in national costume. Another similar portrait of Stanisław Lubomirski, in oval, can be found today in the National Museum of Art in Kaunas, Lithuania (oil on canvas, 54 x 48 cm, ČDM Mt 1507). It is also incorrectly identified - as the effigy of Jan Karol Chodkiewicz or Jonas Karolis Chodkevičius (d. 1621), Grand Hetman of Lithuania, and comes from the collection of Countess Jadwiga Hutten-Czapska (1866-1943) in Beržėnai Palace. It entered the museum's collections in 1940. Its style is comparable to Saint Margaret by the workshop of Simon Vouet (Galerie Meier, Anticstore, Ref: 88152) and portrait of a lady with a red drapery by circle of Simon Vouet, possibly Virginia da Vezzo (Artcurial, March 22, 2023, lot 69). In addition to the portrait of the voivode of Kraków, Countess Hutten-Czapska also owned the Mercury and the Three Graces by Michel Dorigny or workshop of Simon Vouet, painted after 1642, now also kept in the National Museum of Art in Kaunas (oil on canvas, 172 x 137 cm, ČDM Mt 1445). This is a version of a lost original by Vouet reproduced in a 1642 engraving by Dorigny (Leiden University Libraries, PK-P-144.488). Between 1940 and 1941, Nazi German invaders destroyed the beautiful Church of the Discalced Carmelites in Nowy Wiśnicz, founded by Stanisław Lubomirski in 1622, along with its Baroque furnishings. The history after 1655 has always been very cruel to the Realm of Venus, and although nothing has been preserved of the rich furnishings, visitors can still admire the beautiful architecture of Wiśnicz and local institutions are doing much to renovate, rebuild and collect as many traces of past splendor as possible.
Ill-matched couple (Vanitas) by Simon Vouet, ca. 1621, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Helena Tekla Ossolińska (1622-1687) as Diana by Simon Vouet, 1637, Hampton Court Palace.
Portrait of Helena Tekla Ossolińska (1622-1687) as Diana by workshop or circle of Simon Vouet, ca. 1637, Private collection.
Diana by Michel Dorigny after Simon Vouet, ca. 1637, National Library of Poland.
Diana by Michel Dorigny after Simon Vouet, 1638, Leiden University Libraries.
Portrait of Helena Tekla Ossolińska (1622-1687) as Madonna by Simon Vouet, ca. 1637-1638, Private collection.
Portrait of Helena Tekla Ossolińska (1622-1687) as Madonna by workshop of Simon Vouet or Virginia da Vezzo, ca. 1637-1638, Private collection.
Portrait of Stanisław Lubomirski (1583-1649), voivode of Kraków by workshop or circle of Simon Vouet, ca. 1638, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
Portrait of Stanisław Lubomirski (1583-1649), voivode of Kraków by workshop or circle of Simon Vouet, ca. 1638, National Museum of Art in Kaunas.
Mercury and the Three Graces by Michel Dorigny or workshop of Simon Vouet, after 1642, National Museum of Art in Kaunas.
Portrait of Vittoria Farnese (1618-1649), Duchess of Modena and Reggio as Saint Catherine of Alexandria by workshop of Nicolas Régnier, ca. 1648, Sforza Castle in Milan.
Portraits of Anna Catherine Constance Vasa by Peter Danckers de Rij
With the new dynasty, the Vasas, the focus of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth's international politics shifted from south of Europe to the north. Sigismund III Vasa, elected monarch of the Commonwealth was born in Sweden and on February 19, 1594 he was crowned King of Sweden and Grand Duke of Finland.
Curiously, exactly around that time, Venetian painting workshops began to decline, there are no more such great painters in Venice, native to the Republic, in subsequent decades like Giorgione, Lorenzo Lotto, Palma Vecchio, Sebastiano del Piombo, Titian, Tintoretto, Jacopo Bassano or Veronese. Domenico Fetti was born in Rome and then worked in Mantua for ten years and Bernardo Strozzi was born and initially mainly active in Genoa. Commonwealth's monarchs began to visit more often the main economic center of the country and its main seaport - Gdańsk in the north. Sigismund III was there several times, for the first time when he arrived from Sweden in October 1587. Also his predecessor Sigismund II Augustus was a guest in the city in July 1552. On September 23, 1561 the top of the tower of the main Town Hall of Gdańsk was adorned with a gilded statue of the king with an accentuated codpiece, designed by Dutch Dirk Daniels. In 1564-1568 the Green Gate in the style of Flemish mannerism was built by architect Regnier van Amsterdam as the formal residence of Poland's monarchs. Not only in architecture, but also in painting, Flemish and Dutch style become the most popular in the Vasa era in Poland, at least in the northern part of the country. In 1624, Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa, future Ladislaus IV, visted Rubens' workshop and was painted by him. Ladislaus invited to Warsaw the author of his "Art Collection" (Royal Castle in Warsaw), most probably Étienne de La Hire, and Rubens recommended Pieter Claesz Soutman, a Dutch painter born in Haarlem, who was appointed royal court painter, he, however, returned to Haarlem in 1628. All of Ladislaus' relatives and other monarchs employed at their courts Flemish and Dutch painters. Rubens painted his Spanish cousins, monarchs of France and England, Flemish painter Justus Sustermans worked for the Medici family in Florence and his aunt Maria Maddalena of Austria (1589-1631), another Flemish painter, Frans Luycx, became the leading portrait painter at the imperial court of his cousins in Vienna, Justus van Egmont, also Flemish, worked in France at the court of his cousin Queen Anne of Austria (1601-1666), Antoon van Dyck (Anthony van Dyck) in England, Karel van Mander III was active at the Danish royal court and numerous other. Around 1636-1637, in connection with the extensive work at decorating royal residencies in preparation for the king's wedding, Ladislaus employed Peter Danckers de Rij, who was initially active in Gdańsk. Danckers de Rij was born in Amsterdam and probably returned there during the Deluge (1655-1660). Despite her qualities and wealth, like in the case of her grandmother and her grandmother's sister Isabella Jagiellon, it was not an easy task to find a suitable match for Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651), the sister of Ladislaus, who reached adulthood around that time. Hereditary rulers of Europe were not interested to marry a sister of the elective monarch. After the death of her parents in 1631 and in 1632, Parliament granted her the counties of Brodnica, Gołub and Tuchola. The lands had previously belonged to her mother, but Anna could not exercise her rights until she came of age in 1638. Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg, and Gaston, Duke of Orléans (brother of King Louis XIII of France), were among candidates for her hand. Despite the agreements of 1639 and 1642 to marry her to Archduke Ferdinand Charles of Austria-Tyrol (1628-1662), the marriage never took place, due to the age of the groom who was 11 years old in 1639 and the disagreement over the amount of her dowry. On June 8, 1642, in Warsaw she married Philip William of Neuburg. In the Imperial Castle in Nuremberg there are two portraits deposited by the Germanisches Nationalmuseum (inventory numbers NbgKbg.L-G0006, NbgKbg.L-G0007) which according to inscription in German on the frame depict Emperor Leopold I (1640-1705) and his wife Infanta Margaret Theresa of Spain (1651-1673). The man's costume, however, with embridered doublet topped with beautiful lace collar, matching breeches and a lovelock, is typical for European fashion in the 1630s. His pose and facial features are identical to those visible in a portrait of Prince John Casimir Vasa, brother of Ladislaus IV, in the Gripsholm Castle in Sweden and his miniature portrait in the Bavarian National Museum, both attributed to Peter Danckers de Rij. The woman from the pendant portrait, who bear no resemblance whatsoever to effigies of Infanta Margaret Theresa, must be therefore his only sister Anna Catherine Constance, as John Casimir was unmarried at that time (oil on canvas, 213 x 122 cm, Bavarian State Painting Collections, 6996). She was portrayed in a little outdated outfit, crimson Spanish style saya and a large ruff. Her face and pose are identical as in the portrait from the Ambras Castle in Innsbruck in Tyrol (most probably sent to Archduke Ferdinand Charles), identified as effigy of Archduchess Cecilia Renata of Austria, Queen of Poland (Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, GG 5611). In this portrait her costume is more à la mode - in 1642 Queen Cecilia Renata asked her younger brother Leopold Wilhelm of Austria, through Estebanillo González who visited Warsaw the same year, to send her some Dutch lace and a doll dressed in fashionable French attire. Both the Queen and her sister-in-law Anna Catherine Constance, knew the fashion trends well. This woman bears no resemblance to effigies of Cecilia Renata in the Gripsholm Castle (NMGrh 299, NMGrh 1417), and in the State Historical Museum in Moscow (И I 5922), painted by Peter Danckers de Rij. She is holding an oriental folding fan with a pattern resembling an inscription in Arabic, hence possibly acquired in Venice, exactly like in portraits of Anna Catherine Constance's grandmother Catherine Jagiellon by Moroni and Titian. The same woman was also depicted in a miniature painting in the Castello Sforzesco in Milan (oil on copper, 6 x 5 cm, inventory number 863), also painted in the style of Peter Danckers de Rij. Her sumptuous clothes and jewelery are truly regal, which is why the miniature is sometimes considered to depict Elizabeth Stuart (1596-1662), Queen of Bohemia. The work was donated to the Civic Collections in 1945 by Giorgio Nicodemi (1891-1967) who, in turn, had received the collection, which features several portraits of people from the Morando and Attendolo Bolognini families, from Countess Lydia Morando Bolognini (after "Museo d'arte antica del Castello sforzesco: pinacoteca", Volume 5, p. 332). Her costume is typical for Central Europe, Austria and Bavaria in the 1630s, like in the portraits of Maria Anna of Austria (1610-1665), Electress of Bavaria, sister of Cecilia Renata in the Alte Pinakothek in Munich from about 1635 or in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna from about 1643. Similar costumes are also visible in portraits of Éva Forgách, wife of Count István Csáky (1610-1639), dated '1638', in the Hungarian National Museum, Baroness Maria Laymann-Libenau, also dated '1638', in the Ptuj Ormož Regional Museum, Countess Erzsébet Thurzó, wife of István Esterházy, dated '1641', in the Forchtenstein Castle or on the silver medal with bust of Anna Leszczyńska née Radzimińska from 1614 in the National Museum in Lublin. She was also depicted in a portrait, also very in the style of Danckers de Rij, although attributed to Govert Flinck, from the French private collection (oil on canvas, 60 x 73 cm, sold at Vanderkindere in Brussels, March 23, 2021, lot 67). This painting represent "Venus reclining" inspired by Venus of Urbino in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence, which is a portrait of a sister of Anna Catherine Constance's grandmother Isabella Jagiellon. A work painted in a very similar style is in the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 91.5 x 130.5 cm, M.Ob.945, earlier 215 Tc/70, 302/2/73). It represents Sleeping Cupid and comes from the collection of Eugenia Kierbedziowa (1855-1946), who died in Rome. She bequeathed the painting in 1943 and it entered the museum after World War II in 1970. The earlier provenance is unknown, so it has been assumed that Kierbedziowa probably acquired it in Italy and compared to some works by Francesco Albani or his entourage, like Cupid disarmed by the nymphs at the Louvre (INV 34; MR 1607) or the Triumph of Diana (Winter) at the Borghese Gallery in Rome (inventory number 049). It is, however, quite possible that Eugenia, who lived in exile in Italy from 1909, purchased this painting earlier in Lithuania, Warsaw or Saint Petersburg, where she was born. Cupid was the god of desire, erotic love, attraction and affection and the son of the goddess of love Venus and the god of war Mars. The comparison with the mentioned works of Albani and others of his putti is very general, while the style of the painting resembles a signed and dated work by Danckerts de Rij - portrait of Queen Cecilia Renata in the Nationalmuseum of Stockholm (Peter. Danckers fecit A:o 1643, NMGrh 299). The queen is standing in a loggia of the Villa Regia palace in Warsaw and in the background there is a fountain with a statue of Cupid on a dolphin.
Miniature portrait of Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) by Peter Danckers de Rij, ca. 1638, Castello Sforzesco in Milan.
Portrait of Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) with a dog by Peter Danckers de Rij, ca. 1638, Imperial Castle in Nuremberg.
Portrait of Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) nude by Peter Danckers de Rij, ca. 1638-1642, Private collection.
Sleeping Cupid by Peter Danckerts de Rij, ca. 1640, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portraits of Anna Catherine Constance Vasa as Danaë by Italian painters
Villa Regia, which means Royal Villa in Latin, was the leisure suburban residence of elected king Ladislaus IV Vasa in Warsaw. This splendid palace, inspired by the Villa Poggio Reale in Naples, was probably built between 1634 and 1641 according to the design attributed to the Italian architect Giovanni Trevano. The king, who was a renowned patron, filled it with the most refined works of art produced by the artists of his court, such as Bartholomeus Strobel, Peter Danckerts de Rij and Giacinto Campana, and commissioned abroad, in Italy, Flanders, the Netherlands, Germany, Persia and Turkey.
Detailed descriptions or inventories of the palace have not survived. However, there were undoubtedly works by Peter Paul Rubens, Jan Brueghel the Elder, Peter Snayers, Daniel Seghers, Jacob Jordaens, Pieter Claesz Soutman, Frans Luycx, Justus van Egmont, Rembrandt, Guercino and Guido Reni there, as their workshops were visited by Ladislaus during his trip between 1624-1625 or acquisitions of their paintings are confirmed in other documents. Saint Francis in Ecstacy, possibly by Guido Reni, was described in the chapel of Villa Regia in Adam Jarzębski's "Short Description of Warsaw" from 1643 (verses 1971-1976). The sculptures were also most likely all imported, including ancient sculptures like the Pseudo-Seneca from the Ladislaus' collection, carved in the 2nd century (Archaeological Collection of the University of Zurich). The bronze statues in the so-called "secret garden" (giardino secreto) were most likely cast by Adriaen de Vries in Prague, as their descriptions in Adam Jarzębski's poem perfectly match some of the statues at Drottningholm Palace in Sweden. Marble busts of John II Casimir Vasa and Marie Louise Gonzaga, created by the Roman sculptor Giovanni Francesco Rossi around 1651 (Nationalmuseum in Stockholm), most likely adorned the palace's Marble Hall. During the Deluge, the invaders not only plundered all the movable furnishings, such as paintings, sculptures, tapestries and silverware, but also devastated the interiors. Pierre des Noyers, secretary to Queen Marie Louise, in a letter dated November 8, 1655 from Głogów, describes the devastation of the three royal palaces (Royal Castle, Ujazdów and Villa Regia), in particular the looting of the marble paving, the destruction of a colonnade made up of 32 beautiful marble columns and that the king of Sweden even plundered the windows (Quant au roi de Suède [...] il n'a pas laissé, nonobstant cela, de faire dépaver les trois palais, et emporté ce pavé qui est de marbre; de faire rompre une loge qui était dans le jardin, composée de 32 belles colonnes de marbre qu'on a rompues en les défaisant. Ce n'est pas tout; il fait emporter les croisées et les vitres; ce ménage là m'a surpris). In a letter dated June 1, 1656 from Głogów he adds that: "In a letter I received from Warsaw, I was told of the horrible damage the Swedes did there; They burned the new town and all the suburbs where all the palaces were; but what is more enraged is that they did not want to allow the inhabitants to get anything from their houses, so that people who were rich now depends on alms" (Dans une lettre que j'ai reçue de Varsovie, on me dit l'horrible dégat que les Suédois y ont faits; ils y ont brûlé la ville neuve et tous les faubourgs où étaient tous les palais; mais ce qui est de plus enragé, c'est qu'ils n'ont pas voulu permettre aux habitants de rien tirer de leurs maisons, de sorte que des gens qui étaient riches sont à l'aumône) (after "Lettres de Pierre Des Noyers ...", published in 1859, p. 10-11, 175). The thieves transported their loot on barges intended for transporting grain. Some barges overloaded with heavy marbles sank shortly after leaving Warsaw and the low level of the Vistula in 2011, 2012 and 2015 revealed them, including elements of the marble loggia of the Villa Regia. The memory of Sarmatia's splendid temple of arts was still vivid after the Deluge, so when the Commonwealth revived during the Sobieski period (1674-1696), the newly elected king (victorious king) John III Sobieski decided to recreate it by founding his Villa Nova, i.e. the New Villa (Wilanów Palace) in Warsaw. It was created by Polish-Italian architect Augustyn Wincenty Locci and partially inspired by the Villa Doria Pamphili in Rome. Court painter Jerzy Siemiginowski-Eleuter, trained in Rome, created many paintings, including ceiling paintings with disguised portraits of the king's wife, Queen Marie Casimire Louise de La Grange d'Arquien (1641-1716), also known by the diminutive "Marysieńka" Sobieska, who came to the Commonwealth from France as a child as a court lady of Marie Louise Gonzaga. The queen of the Realm of Venus was depicted as half-naked Aurora-Astraea in the King's Bedroom and the Queen's Mirror Study. In her portrait created around her coronation in 1676 by the workshop of Daniel Schultz, royal court painter (Royal Castle in Warsaw, ZKW/65), the queen proudly shows off her jewels: a royal crown and scepter, huge pearls, rubies (or garnets) and diamonds, as well as a nipple. Several decades later, another influential woman who expanded and rebuilt the palace, Elżbieta Sieniawska (1669-1729), was depicted as half-naked Flora, Roman goddess of flowers and fertility, in a fresco by Giuseppe Rossi, painted between 1726-1729 in the lower vestibule of the palace. The main paintings of Villa Nova were created in the Protestant Netherlands - there were several paintings by Rembrandt, as well as Flemish painters Anthony van Dyck and Jan van Kessel the Elder and most likely copies or originals by Raphael, the Caracci brothers, Guido Reni and Bernardo Strozzi. The palace inventory of 1696 describes paintings that may be originals or copies of The Love Letter (No. 156.) and The Milkmaid (No. 180.) by Johannes Vermeer. The palace was filled with large quantities of silverware made in Paris and Augsburg, including a three-tiered silver fountain and a silk canopy in the king's bedroom was gifted by the Shah of Persia. Sculptures were commissioned in Flanders from the workshop of Artus Quellinus II and his son Thomas II and busts in the Netherlands from the workshop of Bartholomeus Eggers, including the busts of the royal couple (Summer Garden in Saint Petersburg, looted in 1707). The garden was decorated with gilded lead sculptures made in Gdańsk by Gaspar Richter and vases carved from cherry marble from Chęciny. This also gives an idea of the beauty of Villa Regia. Erotic poems, such as the 12-part poem "Cupid's Lessons" (Lekcyje Kupidynowe), with which Kasper Twardowski made his debut in 1617 or many others compiled in 1675 by Jakub Teodor Trembecki, prove that the Commonwealth wasn't that prudish, especially before the Deluge, as some authors want to see it. In the Nationalmuseum in Stockholm there is a painting of Danaë and the shower of gold (oil on canvas, 111 x 150 cm, NM 1568), formerly attributed to Giuseppe Salviati (1520-1575), also known as Giuseppe Porta. The general style of the painting, the curtains and the table indicates that it is more of a Baroque painting and not of the late Renaissance. The style is Venetian, close to Titian and inspired by his "Venus of Urbino", which is a portrait of sister of Anna Catherine Constance's grandmother - Isabella Jagiellon. The painting almost directly reproduces the similar nude effigy of Ladislaus IV's sister by Peter Danckers de Rij from the private collection in France (sold at Vanderkindere in Brussels, March 23, 2021, lot 67), identified by me. The painting comes from the collection of Count Magnus Gabriel De la Gardie (1622-1686), probably offered to him by Queen Christina of Sweden. According to the catalog of the 1966 exhibition "Christina, Queen of Sweden - a Personality of European Civilisation", the painting was looted by the Swedish forces of General Hans Christoff von Königsmarck in Prague in 1648 (p. 479). The authors determine the provenance on the following mentions in the inventory of the imperial collections in 1621: "Danaë and the golden rain by Hans von Aachen" (Danaae mit dem güldenen regen vom Hansen von Acha., no. 1021) (after "Das Inventar der Prager Schatz- und Kunstkammer vom 6. Dezember 1621 ..." by Heinrich Zimmermann, p. XLII) and 1652 inventory of Queen Christina's collection: "As above, representing a naked woman" (Dito, representant une femme nue, no. 190) or "As above, a disheveled woman, on canvas" (Dito, une femme eschevellée, sur de la toile, no. 300). Such references do not make it possible to determine this with certainty. If the painting comes from Prague, then the Habsburgs probably received the portrait of their relative princess of Poland-Lithuania in mythological disguise. It is also possible that it was looted by De la Gardie during the Deluge, when with 9,000 soldiers he plundered the estates of the princess in Polish Prussia. Danaë was the daughter and only child of King Acrisius of Argos and mother of the hero Perseus by Jupiter, king of the gods, who came to her in the form of golden rain. John Ridewall (Johannes Ridovalensis), a 14th century English Franciscan monk, in his Fulgentius Metaforalis, interpreted Danaë as a prefiguration of the Virgin Mary, because she also conceived virginally (Si Danae auri pluvia a Iove pregnans claret, cur Spiritu Sancto gravida Virgo non generaret?). She also became a symbol of modesty - Pudicitia and she was sometimes assigned the blue color of the Virgin Mary as in the 1527 painting by Jan Gossaert (Alte Pinakothek in Munich, 38) or in the miniature of Danaë-Pudicitia in the Vatican Fulgentius Metaforalis of about 1420 (compare "Art and Literature: Studies in Relationship" by William Sebastian Heckscher, Egon Verheyen, p. 170). Danaë was also depicted in the portrait of the princess's brother, King Ladislaus IV Vasa, painted by Peter Danckerts de Rij around 1640 (Alte Pinakothek in Munich, 6959). He stands in the gallery of his palace, most probably Villa Regia, and the painted frieze above the arcade is decorated with a fresco depicting naked Danaë. The fact that this fresco was selected in the portrait indicates that it was probably the most important or significant when the effigy of the king was created. Danaë and the golden rain as a talisman of an unmarried young woman are visible in several portraits of aunts of Princess Anna Catherine Constance by Martin Kober at the Germanisches Nationalmuseum in Nuremberg and at the Alte Pinakothek in Munich, most probably from the dowry of the princess and initially in her mother's dowry. Such nude depictions in mythological disguise were not a novelty in the 1630s, when the Stockholm painting was most likely created. Among the oldest, there are numerous representations of Diane de Poitiers, mistress of King Henry II of France, for example her portrait as the goddess Diana at rest by the School of Fontainebleau, produced around the middle of the 16th century, at the Musées de Senlis (D.V. 2006.0.30.1) or as Venus in the fresco of the League Tower (Tour de la Ligue) of Tanlay Castle, created after 1568. In 1634, Rembrandt produced a print with a very bold depiction of the biblical scene of Joseph and Potiphar's wife (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, RP-P-1961-999, many authors claim that he mainly painted his wife Saskia, so here they are probably right) and later, around 1660, Sir Peter Lely created possibly the only fully nude portrait painted in England in that century - portrait of Elizabeth Trentham (1640-1713), Viscountess Cullen, as Venus (oil on canvas, 129 x 196 cm, sold at Sotheby's London, February 15, 2018, lot 55). A nude image of the Queen of England is listed in the Wilanów Palace inventory of 1696 as "Portrait of the English Queen with bare head and undressed, in a modest frame" (Kontrfekt Krolowey Angielskiey z gołą głową bez Stroju spodem ramka prosta, No. 289., in Marywil). This inventory also mentions "The image of Daphna [Danaë], to which Jupiter descends in a golden rain, in black frames" (Obraz Dafny, do ktorey się Iupiter w złotym deszczu spuszcza, wramach czarnych, No. 95) in the Dutch Cabinet of the King, therefore very probably painted by a Dutch painter. Both paintings most likely come from older royal collections, perhaps even from the Villa Regia (in 1655 the royal couple managed to evacuate a small part of their collections to Silesia). The 1696 inventory of Villa Nova also lists "A painting of Helen [Henrietta Maria of France], Queen of England, in gilt frames" (Obraz Heleny Krolowey Angielskiey wramkach złocistych, No. 122) (after "Inwentarz Generalny 1696 z opracowaniem" by Anna Kwiatkowska). The adequacy of this register is generally quite fair, which is why the English queen had herself represented naked, most probably by van Dyck, especially for the monarchs of the Realm of Venus - Sarmatia. The indication of authorship of the Stockholm painting gives a comparison with a painting representing Salome with the head of Saint John the Baptist and servants, attributed to Alessandro Varotari (1588-1649), known as Il Padovanino (oil on canvas, 95.5 x 85.5 cm, sold at Casa d'Aste Babuino in Rome, July 18, 2023, lot 169). This painting is a copy of Titian's Raczyński Herodias, depicting Queen Catherine of Austria (1533-1572) as the biblical Salome, identified by me. The way in which the hands, draperies and face of the old woman were painted are very much alike. Varotari was active in Venice from 1614, where he moved from Padua. From 1615 to 1639 he was a member of the Venetian guild of painters (Fraglia dei pittori) and was frequently assisted by his sister Chiara Varotari (1584-1663). The painting has some similarities with the portrait of a lady, attributed to Chiara, in the Finnish National Gallery (A I 558). Who knows, maybe both visited Poland-Lithuania around 1639. Another similar Danaë with sleeping Cupid was sold in Munich where many objects brought by Anna Catherine Constance Vasa to Bavaria are kept in the Munich Residence (oil on canvas 119 x 179 cm, sold at Hampel Fine Art Auctions, September 22, 2022, lot 313). This painting is attributed to Giovanni Giacomo Sementi (1580-1640), a student of Denis Calvaert and Guido Reni, active in Bologna and Rome, where he found his mentor and admirer in the art-loving Cardinal Maurice of Savoy (1593-1657). Professor Daniele Benati assumes a collaboration with the Milanese-born Pier Francesco Cittadini, who worked in Rome in the 1630s. In the second half of the 1630s, the Polish-Lithuanian royal court's contacts with Italy were strong, as evidenced by King Ladislaus IV's letter of April 19, 1636 from Vilnius to Galileo requesting glasses for a telescope. In a letter dated July 11, 1637 addressed to Cardinal Barberini in Rome, the nuncio Mario Filonardi (1594-1644) reported that in Warsaw paintings and sculptures are in great demand because they were "rare and expensive" (rare e care). That is why the nuncio even tried, through Italian and Gdańsk merchants, to create a permanent maritime commercial connection between Gdańsk and Civitavecchia, near Rome. Ships from Gdańsk would carry raw materials from Poland, especially wax, and they would bring paintings and sculptures from Italy (after "Z dziejów polskiego mecenatu ..." by Władysław Tomkiewicz, p. 41). On the occasion of the king's wedding Carlo Possenti published in 1638 in Bologna his "Venus' friendship with Diana" (L'Amicizia di Venere con Diana, Epitalamio per le Nozze reali di Polonia). There must have been many likenesses of the princess by Italian painters. These probably survived due to their erotic nature.
Portrait of Queen Catherine of Austria (1533-1572) as Herodias (or Salome) with the head of Saint John the Baptist and servants by Alessandro Varotari after Titian, second quarter of the 17th century, Private collection.
Portrait of Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) as Danaë by Alessandro Varotari and his sister Chiara, ca. 1638-1639, Nationalmuseum in Stockholm.
Portrait of Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) as Danaë by Giovanni Giacomo Sementi and Pier Francesco Cittadini, ca. 1636-1640, Private collection.
Portraits of Ladislaus IV Vasa, his wife and sister by Adolf Boy
"Let Hymen decorate the palace, Behold, they bear the effigy of the Nymph: Juno, Minerva, Venus" (Hymen, decoretque palatia, Nymphæ Effigiem, ecce, ferunt Iuno, Minerva, Venus) is the inscription in Latin under a painting by Adolf Boy placed on the triumphal gate in Gdańsk in 1646 to celebrate the ceremonial entry of Marie Louise Gonzaga on February 11 that year.
This painting was reproduced in a print created by the Dutch engraver Willem Hondius and depicted the Judgment of King Ladislaus IV being offered the portrait of Marie Louise, lovingly painted by Cupid holding a palette and recommended by Juno, Venus and Minerva in reference to the mythological Judgement of Paris. The painting must have been truly magnificent because Hondius clearly marked the author in lower right part of the painting - ABoy pinxit (National Museum in Warsaw, Gr.Pol.5091 MNW). The second large triumphal arch near the Town Hall was also decorated with a painting by Boy representing the marriage of the king with the French princess, both crowned by a winged female figure of Fama, the deity of fame, and accompanied by a kneeling Cupid with two doves (Gr.Pol.5090 MNW), also signed: ABoy pinxit. The effigy of Marie Louise in this composition was most likely based on paintings or drawings sent from Paris or Warsaw, as it is rather unlikely that Boy traveled to the capital of France to paint the bride. The painter may also have participated in decorating two other temporary arches with movable statues of Atlas and Hercules (Gr.Pol.12874 MNW) and Apollo and Diana (National Library of Poland, G.1518), as he is credited as the author of the original design of the prints by Jeremias Falck Polonus. In 1649 Hondius also immortalized in an engraving another composition by Boy - Apotheosis of King John II Casimir Vasa, signed: Adolph Boy inventor (National Library of Poland, G.219/Sz.1). Around 1650, Falck also engraved six scenes from the deeds of Atlas and Hercules (Similitudines Emblematicæ), created by Boy, signed with the monogram AB in ligature (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, RP-P-2021-6074). Adolf or Adolph Boy was born in Gdańsk in 1612, probably the son of Magnus Boy (1559-1632). In the years 1620-1626, he studied painting with Bartholomeus Milwitz. From 1630 he was a member of the painters' guild and from 1636 a master, he then received citizenship of Gdańsk. In addition to the Italians Tommaso Dolabella and Giacinto Campana, the Silesian Bartholomeus Strobel, the Flemish Christian Melich, the Dutch Pieter Claesz Soutman, Peter Danckerts de Rij and Gilles Schalken, the Poles Krzysztof Gryniewski and Jakub Mieszkowski and two other painters from Gdańsk Samuel Wegener and Daniel Schultz, he was one of the painters of the royal court who called themselves "the painters of His Majesty" (pictor S. R. M.). Like Dolabella, Strobel and Gryniewski, for whom the texts of servitoral privileges were preserved in the Crown archives, he probably also had a formal royal servitorate. All of Boy's painted works, including the cycle of the twelve Sibyls from the Old Town Hall of Gdańsk (coming from the chapel of the Fichtl house), are attributed to him, because no work signed by the painter has been preserved. All his sure works are known thanks to engravings. He frequently painted portraits and in addition to the king and the queen, he created effigies of Constantine Ferber III (1580-1654), mayor and royal burgrave in Gdańsk (print by Jeremias Falck Polonus after original portrait from about 1635 or 1645, National Library of Poland, G.3057/I), Johannes Mochinger (1603-1652), professor of rhetoric at the Academic Gymnasium in Gdańsk (print by Falck, after original portrait from about 1646 or 1656, G.57649/II) and Christian Schweikert, mayor of Gdańsk (print by Johann Bensheimer from 1668, G.507/sz). As court painter to such a renowned patron as King Ladislaus IV, Boy must have been an eminent painter, comparable to Strobel and Danckerts de Rij, who also created several royal effigies. The mentioned engravings could give an impression of his style. While in his print Christ crowned with thorns (National Library of Poland, G.24580/Sz, signed: Ant. van dijck pinxit / J. falck fecit), produced between 1639 and 1646, Falck attempted to imitate the Anthony van Dyck's soft brushwork through longer crossed lines, in the portraits of Ferber and Mochinger he used more dots and shorter lines, so the images appear slightly jagged. A very finely painted portrait of an old man, attributed to Adolf Boy, now in the Museum of Gdańsk (oil on canvas, 114 x 87.5 cm, MHMG/S/129), gives the same impression. The model is identified as the theologian and pastor Aegidius Strauch (1632-1682), who from 1669 was parish priest of the Holy Trinity Church and rector of the Academic Gymnasium in Gdańsk, due to his close resemblance to the portrait of Strauch by Andreas Stech (Boy's pupil), also reproduced in a print by Elias Hainzelmann. However, if we consider the Latin inscription in the upper right corner to be original and correct, the model could not be Strauch, because the man was born in 1609 and was 72 years old in 1681 (Jesus Christus / est Spes et vita mea / Ao 1609, Natus 1 Marty. / Ao 1681 Piet 1 Marty. / Ætatis 72.). Boy, who died in 1682 or 1683, was active until the end of his days since in 1680 he created a signed view of Gdańsk (after "Artificium extra ideam ..." by Maria Bartko, p. 34). Among the royal portraits which follow the same convention and are very similar in style to Boy's purported portrait of Strauch is the full-length portrait of Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria in the Nationalmuseum in Stockholm (oil on canvas, 218 x 138 cm, NMGrh 1417), portrait of her husband King Ladislaus IV Vasa at the Royal Castle in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 200 x 120 cm, ZKW 559 dep., deposit of the National Museum in Warsaw, 128758) and portrait of her sister-in-law Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa at Ambras Castle (oil on canvas, 115 x 96.5 cm, GG 5611), identified by me. The queen's portrait is signed in Latin in the lower left corner (CÆCILIA RENATA REGINA / POLONIÆ ET SVECIÆ) while the part stating that she is the queen of Poland and Sweden was partially covered by a frame, indicating that the canvas has been cut. It was probably the same for the portrait of Ladislaus, which also bore a false inscription identifying the model as Gustavus Adolphus, King of Sweden and attribution to Joachim von Sandrart (Gustavus Adolph / König von Schwed / Anno 1632 / Sandrart pinxit / Nürnberg). The identification as King of Poland today is not disputed and the attribution to Sandrart is rejected (compare "Portrait of Władysław IV from the Oval Gallery ..." by Monika Kuhnke, Jacek Żukowski, p. 61-67). The portrait was purchased from J. Jarocki in 1947 as a portrait of Ladislaus IV and another version is kept in the Lviv Historical Museum (oil on canvas, 69 x 59 cm, Ж-645). The copy comes from the collection of Władysław Łoziński, who bought it on January 6, 1912 from Szymon Schwartz's antique dealer for 370 crowns. Although attributed to a painter from the end of the 18th century and inspired by a lost original, the style of the Lviv painting is particularly close to the portraits of Christina Kiszczyna née Drutska-Sokolinska preserved at the National Museum of art of Vilnius (LNDM T 3990) and Queen Bona Sforza of Aragona in the National Museum of Lublin (S/Mal/609/ML), most probably painted by Giacinto Campana. The court painters often needed to cooperate and copy the works of other painters, thus drawing inspiration from their style. For example, for his portrait of Queen Bona, painted for the Marble Room at the Royal Castle in Warsaw, Peter Danckerts de Rij probably copied an effigy by Cranach the Younger. The great diversity of the court of Ladislaus IV, great destruction and dispersion of their oeuvre, as well as the absence of signatures, are other factors hindering the attribution of many works of art related to the Polish-Lithuanian Vasas. The portrait of the king in Warsaw and that of the queen in Stockholm, have similar dimensions and composition, and they were obviously painted by the same painter, so it is possible that they originally formed a pair or that they come from the series of royal effigies created at the same time. In the Warsaw portrait, the pastel colors and beauty of the painting contrast sharply with the lack of idealization and the small head of the king, as if the painter was intentionally contrasting the beauty of his art, the jewelry and fabrics with the model defects. This became his trademark, as can also be said of the portrait of Ladislaus's wife and sister and other similar works, such as the portraits of Elżbieta (Halszka) Kazanowska née Słuszczanka (1619-1671) in solana hat (National Museum in Warsaw, 34661, lost) and with forget-me-nots (National Museum in Warsaw, M.Ob.2510), and the portrait of Alexander Louis Radziwill (1594-1654), Grand Marshal of Lithuania (Nieborów Palace, NB 974 MNW).
Portrait of King Ladislaus IV Vasa (1595-1648) by Giacinto Campana or circle, ca. 1639-1642, Lviv Historical Museum.
Portrait of King Ladislaus IV Vasa (1595-1648) holding a cane by Adolf Boy, ca. 1639-1642, Royal Castle in Warsaw.
Portrait of Queen Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria (1611-1644) holding a fan by Adolf Boy, ca. 1639-1642, Nationalmuseum in Stockholm.
Portrait of Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) holding a fan by Adolf Boy, ca. 1639-1642, Ambras Castle in Innsbruck.
Portrait of an old man, possibly pastor Aegidius Strauch (1632-1682) by Adolf Boy, ca. 1681, Museum of Gdańsk.
Portraits of Prince John Casimir Vasa
"His works and famous testimonies of craftsmanship [artis praeclara specimina] created in Our kingdom […], to everyone who has come close, give a pleasant feeling of beauty and adornment flowing from the surfaces painted by him. With this letter, We make him a painter at our court", stated in the servitorial letter issued in 1639 to the Silesian painter Bartholomeus Strobel King Ladislaus IV Vasa (after "Portrait of Władysław IV from the Oval Gallery ..." by Monika Kuhnke, Jacek Żukowski, p. 68). The king met Strobel in Gdańsk at the end of 1634. Over the next few years the artist lived and worked alternately in Gdańsk, Toruń and Elbląg, simultaneously being employed in decorating the interior of the royal chapel of St. Casimir in Vilnius (1636-37).
On June 25, 1635, in the face of a new war with Sweden, the king's half-brother John Casimir Vasa arrived to Toruń. Under the command of Hetman Stanisław Koniecpolski, about 24,000 selected soldiers with strong artillery were concentrated in Pomerania in the camp near Sztum. From there the prince went to Vienna for the wedding of his relative Archduchess Maria Anna of Austria (1610-1665), the daughter of Emperor Ferdinand II, and Maximilian I (1573-1651), Duke of Bavaria (15 July 1635). He received under his command a regiment of cuirassiers and Polish volunteers, with whom he went to the front of the Thirty Years' War in Alsace. He returned to the country after Ladislaus IV concluded the truce in Sztumska Wieś on September 12, 1635. When despite the imperial promises, he did not receive a feudal principality, and the Sejm did not grant him the Duchy of Courland, he accepted the proposal of his cousin Philip IV of Spain to become the viceroy of Portugal, where he was to receive an annual salary and get married. On this trip, he stopped in France, where he was arrested on the orders of Cardinal Richelieu on suspicion of espionage for Spain. He was a prisoner from May 10, 1638 to February 1640, when he was released after the intervention of the Polish legation that came to Paris. After release he went to Paris, where he met Princess Marie Louise Gonzaga de Nevers, with whom he had an affair. In 1641 John Casimir decided to become a Jesuit. In 1642, he left the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth again, accompanying his sister to Germany. In 1643 he joined the Jesuits despite the opposition of King Ladislaus, causing a diplomatic rift between Poland and the Pope. John Casimir became a cardinal, but in December 1646, finding himself unworthy of spiritual life, he resigned as a cardinal and returned to Poland. Following the death of Cecilia Renata of Austria, first wife of Ladislaus IV in 1644, Cardinal Jules Mazarin insisted that Marie Louise should marry the widowed sovereign to destroy the alliance between the Polish Vasa dynasty and the Habsburg dynasty, the rivals of the French state. She married Ladislaus by proxy on 5 November 1645. Two years later, on 20 May 1648, Marie Louise was widowed by the sudden death of Ladislaus IV. John Casimir was eventually elected the next King of Poland by the nobility, and married her on 30 May 1649. In the Alte Pinakothek in Munich there is portrait of a young man in a fashionable French slashed doublet from around 1635 (oil on canvas, 224.5 x 135.5 cm, inventory number 6969). It was transferred in 1804 from the collection of the Palatine Castle in Neuburg an der Donau. This painting is very symilar in style, pose of the sitter and costume to the portrait of king Ladislaus IV Vasa with a crown by Bartholomeus Strobel (attributed), which was before 1939 in the Sandomierski/Brühl Palace in Warsaw and dated to around 1635, as well as to the portrait of Władysław Dominik Zasławski-Ostrogski, also by Strobel, from about 1635 in National Art Museum of Belarus in Minsk (a copy of the painting in the Wilanów Palace in Warsaw). Very similar costume is also visible in the portrait of Prince Janusz Radziwill (1612-1655), painted by David Bailly in 1632 (National Museum in Wrocław). The man bear a striking resemblance to the portrait of Prince John Casimir Vasa when a Cardinal, created by a painter in Rome in about 1646 (Pontificia Università Gregoriana) and several engravings depicting John Casimir, when the King of Poland (by Willem Hondius, published in Gdańsk in 1648, by Hugo Allard the Elder, published in Amsterdam after 1648 and by Philipp Kilian, published in Augsburg after 1648). Therefore the described painting from the Neuburg Castle undoubtedly comes from a dowry of Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651), Countess Palatine of Neuburg and John Casimir Vasa's sister. Another portrait, most probably also from Anna Catherine Constance Vasa's dowry, is today in the Imperial Castle in Nuremberg (deposit of the Germanisches Nationalmuseum, oil on canvas, 210 x 137 cm, NbgKbg.L-G0006 / 6784). It was previously identified as effigy of Emperor Leopold I (1640-1705) and as such published as a chromolithograph by Jakob Heinrich von Hefner-Alteneck in 1879. This painting is very similar to Prince John Casimir 's portrait in Gripsholm Castle in Sweden, a miniature in the Bavarian National Museum and another portrait, which was before World War II in the Herzog-Max-Burg Palace in Munich (watercolor painting after original by Aleksander Lesser from mid-19th century is in the National Museum in Warsaw). All these paintings were created by Peter Danckers de Rij and his workshop in about 1638 on the occasion of receiving the Order of the Golden Fleece from king Philip IV of Spain, head of the order from 1621. The same man was also depicted in a portrait from the old collection of the palace of the French kings in the Louvre (oil on canvas, 65.3 x 54.5 cm, INV 20345). It is attributed to a French painter and dated to about 1635-1640 basing on the style and sitter's costume. The painting was most probaly created in the atelier of Philippe de Champaigne (1602-1674), who from 1628, when he entered the service of Queen Mother Marie de Medicis, was a court painter of the French kings. Prince John Casimir was a prisoner and as such cannot be represented with the Order of the Golden Fleece, as France was at that time at war with Spain. His costume and hairstyle are very similar to those shown on the silver medal with his bust, created before 1638 (Museum of Warsaw, MHW 24241). It is also possible that the portrait was created by an Italian or a Flemish painter and brought by the prince with him to France, as John Casimir travelled to many European countries between 1635 and 1638. Engraving entitled in French L'Hyver (Winter) with Proserpine and Pluto by Jeremias Falck Polonus and Jean Leblond I (Museum Boijmans Van Beuningen), was published between 1639-1645. Proserpine and Pluto, who abducted her into the underworld, bearing the features of both Marie Louise and John Casimir is undoubtedly an allusion to the secret affair of the Queen and the Prince. Gdańsk born engraver who called himself Polish (Polonus) created this print in Paris, where he moved in 1639. Fragment of four lines of French letterpress verse at left, and their Latin translation at right, reads "Pluto burns a secret fire for Proserpine" (Pluton d'un feu secret brusle pour Proserpine).
Portrait of king Ladislaus IV Vasa with a crown by Bartholomeus Strobel, ca. 1635, Sandomierski Palace in Warsaw, lost during World War II. Virtual reconstruction, © Marcin Latka
Portrait of Prince John Casimir Vasa by Bartholomeus Strobel or workshop, ca. 1635, Alte Pinakothek in Munich.
Portrait of Prince John Casimir Vasa by Peter Danckers de Rij, ca. 1638, Imperial Castle in Nuremberg.
Portrait of Prince John Casimir Vasa by workshop of Philippe de Champaigne (?), 1635-1640, Louvre Museum.
L'Hyver (Winter) with Proserpine and Pluto by Jeremias Falck Polonus and Jean Leblond I, 1639-1645, Museum Boijmans Van Beuningen.
Portraits of Anna Catherine Constance Vasa and Cecilia Renata of Austria by Frans Luycx
"As soon as the king entered the castle and got out of the carriage, the archduke came towards the king as far as the stairs, and with him one distinguished Austrian lord Meggau, a knight of the golden fleece, who was in great favor with the Emperor's father. The archduke apologized to the king that the empress did not come downstairs, and this was because of her health while she was pregnant. Then the empress came down and stopped in the middle of the stairs, whole dressed in pearls. The king from the journey, but he was also dressed expensive, and so did the queen and princess. The king spoke to the empress in Italian, who received him pleasantly and answered him briefly in Spanish. She then embraced the queen very pleasantly, and she squeezed the princess so tightly that her pearl earrings with the princess's earrings tangled that they had to be torn off", recalled the greeting of King Ladislaus IV Vasa, his wife Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria and his sister Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa with their cousin Empress Maria Anna of Spain (1606-1646) in Vienna on September 1, 1638, Jakub Sobieski (1591-1646), voivode of Belz, in his Diary.
Ladislaus went to Austria to be treated for gout in Baden near Vienna. The king and his retinue of 1,300 people, "who need more for a month than the entire imperial court for six months", according to Sobieski, departured from Warsaw on August 5, 1638. Known for his artistic taste, during trip to the Netherlands and Italy in 1624-1625, he visited, among others, the studios of Peter Paul Rubens, Guido Reni and Guercino, Ladislaus probably visited the atelier of the leading portrait painter at the imperial court, Frans Luycx, during his visit to Vienna. Much earlier, however, he had noticed the great talent of the Flemish painter, because the accounts preserved in Stockholm confirm Ladislaus' contacts with a painter named Luix as early as 1637. Most likely in 1637, when she became empress, Luycx created a series of portrait sof Maria Anna of Spain which were sent to her relatives. Two very similar are in the Visitandines Monastery in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 196 x 145 cm) and in the Gripsholm Castle near Stockholm (inventory number NMGrh 1221), both probably originally sent to Warsaw as a gift to the king and his sister, like the two identical paintings in Madrid (Prado Museum, inventory number P04169 and P001272). Probably during this visit Ladislaus commissioned a series of his effigies, and portraits of his wife and sister. The 1640 settlement says about the payment by Polish agent in Vienna to "Leic, painter, for three effigies" (after "Obrazy z warsztatu Fransa Luycxa w kolekcji wilanowskiej" by Jacek Żukowski). Preserved portraits of the king by Luycx are in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna (oil on canvas, 203.5 x 140.5 cm, GG 7150), Alte Pinakothek in Munich and reduced version in the Wilanów Palace in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 106 x 86 cm, Wil.1143). The portrait of Cecilia Renata of Austria is also in Wilanów (pendant to king's portrait, oil on canvas, 100.8 x 90 cm, Wil.1144) and in Vienna (inscription on the back in Italian: LA REGINA CECILIA RENATA DI POLONIA 1642, inventory number GG 8291). Inventory of Leopold Wilhelm's collection from 1659 lists two effigies of his sister Queen of Poland by Luycx, one when Archduchess with a parrot (indianischer raab, number 813), the second as a Queen with a crown and sceptre on a table (number 811), both probably lost. In turn Cecilia Renata and the king of Poland also undoubtedly owned portraits of Leopold Wilhelm from this period and a miniature in the Czartoryski Museum in Kraków (oil on copper, 5.4 x 4.3 cm, XII-71), painted in Luycx's style and similar to Archduke's portrait in the Kunsthistorisches Museum (GG 2754) and his full length portrait by Luycx in the Gripsholm Castle (NMGrh 1876), can be considered as such. As in Vienna or Madrid, many of Luycx's works were undoubtedly in the Polish-Lithuanian royal-grand ducal collections, but before the Second World War in Warsaw there were only two that could be considered to be by the master himself - mentioned portrait of Empress Maria Anna and portrait of King Ladislaus IV, which was however purchased in 1936 in Vienna. The portrait of the king was kept until 1945 at the Brühl (Sandomierski) Palace in Warsaw and was lost during the war (oil on canvas, 202 x 140 cm). Luycx and his workshop must have produced multiple versions of this effigy of the king because the inventory of the imperial gallery in Prague dating from 1718 mentions a portrait of Ladislaus IV by Luycx in "white boots" (weiszen stiefeln). The Prague portrait measured approximately 251 x 144 cm, so it was larger than those in Vienna (which is now considered to be this painting from Prague) and Warsaw, probably cut off in the upper part, and comparable to the Munich painting (Alte Pinakothek, oil on canvas, 250 x 160 cm, 4197, inscription: VLADISLAVS IIII. REX POLONIÆ). The Munich painting comes from Neuburg Castle and was therefore probably originally in the dowry of the king's sister Anna Catherine Constance. Miniature portrait of a woman attributed to Spanish painter in the Victoria and Albert Museum in London (oil on copper, 5.7 x 5.1 cm, P.57-1929) is stylistically very similar to described miniature of Archduke Leopold Wilhelm in the Czartoryski Museum. The woman bears strong resemblemnce to portraits of Archduke's sister, Cecilia Renata, especially mentioned portrait in Vienna by workshop of Frans Luycx (GG 8291). The Spanish style elements of her outfit, like earrings, may be the influence of the Spanish entourage of her sister-in-law, Empress Maria Anna of Spain. Archduke Leopold Wilhelm also owned a portrait of Princess Anna Catherine Constance described in the inventory of his collection under number 812: "A life-size effigy in oil on canvas of the princess of Poland, who was married to the duke of Neuburg. In a black smooth frame, 11 feet 3 fingers high and 7 feet wide. By Francisco Leüx Original" (Ein Contrafait lebensgrosz von Öhlfarb auf Leinwaeth der Princessin ausz Pohlen, welche mit dem Herzogen von Neüburg verheürath gewest. In einer schwartz glatten Ramen, hoch 11 Spann 3 Finger unndt 7 Spann braith. Von Francisco Leüx Original). The full length portrait by Frans Luycx in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna (oil on canvas, 222 x 111 cm, GG 1732) is identified as effigy of Queen Cecilia Renata, however, like in portraits of Ladislaus IV, Empress Maria Anna or a portrait of Cecilia Renata mentioned in Archduke's inventory, there is no insignia (crown and scepter) in this portrait and the woman bears no resemblance to other effigies of the Queen. On the other hand the woman resemble greatly effigies of Princess Anna Catherine Constance, especially her portrait in a red dress at Ambras Castle. This image may therefore be tantamount to an entry in the Archduke's inventory. A reduced copy of this painting by Luycx's workshop is also in the Kunsthistorisches Museum (oil on canvas, 90 x 50 cm, GG 7944).
Portrait of King Ladislaus IV Vasa (1595-1648) by Frans Luycx, ca. 1638-1642, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Portrait of King Ladislaus IV Vasa (1595-1648) by Frans Luycx, ca. 1638-1642, Sandomierski Palace in Warsaw, lost.
Portrait of King Ladislaus IV Vasa (1595-1648) by Frans Luycx, ca. 1638-1642, Alte Pinakothek in Munich.
Portrait of King Ladislaus IV Vasa (1595-1648) by workshop of Frans Luycx, ca. 1638-1642, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
Portrait of Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria (1611-1644) by workshop of Frans Luycx, ca. 1638-1642, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
Portrait of Empress Maria Anna of Spain (1606-1646) by Frans Luycx, ca. 1638-1642, Monastery of Visitandines in Warsaw.
Portrait of Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) by Frans Luycx, 1638-1642, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Portrait of Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) by workshop of Frans Luycx, 1638-1642, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Miniature portrait of Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria (1611-1644) by Frans Luycx, 1638-1642, Victoria and Albert Museum in London.
Miniature portrait of Archduke Leopold Wilhelm of Austria (1614-1662) by Frans Luycx, 1638-1642, Czartoryski Museum in Kraków.
Portraits of Anna Catherine Constance Vasa and Cecilia Renata of Austria as Venus Verticordia by Giacinto Campana
In 1625, during his stay in Bologna, Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa visited the studios of local painters, Guido Reni and Guercino. He brought to Poland from this journey, apart from works of art purchased in the Netherlands and Italy, also valuable gifts, including paintings by Italian masters from the famous gallery in Mantua, donated to him by Prince Gonzaga. When he become king he continued to purchase paintings abroad, mainly in the Netherlands, but also in Italy, throuh his secretary Virgilio Puccitelli, a castrato singer and composer. It was Puccitelli, who acquired the services of several singers in Venice for the king between September 1638 and February 1640, who brought to Warsaw "The Rape of Europa" by Guido Reni for which the king expressed his gratitiude in a letter to Reni dated March 3, 1640. "Therefore, we make You aware of all this and enclose the expression of our most obliging intentions, so that You know how much to expect from them and how much we respect your bright talent", wrote the king. This painting is today in the National Gallery in London.
In 1637 Ladislaus invited to Poland Giacinto Campana from Bologna, who worked at the Polish court until at least 1646. Recommended by the former apostolic nuncio to the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Bishop Antonio Santacroce (1599-1641) and the new nuncio Mario Filonardi (1594-1644), the painter came to Warsaw from Rome via Venice in the spring of 1637. He was employed to decorate different royal residencies and Saint Casimir's Chapel at the Vilnius Cathedral in July 1639, as well as, together with Giovanni Battista Gisleni and Christian Melich, in stage decorations for Royal Opera in Warsaw and Vilnius. Campana, trained first with Francesco Brizio, then with Francesco Albani, worked as an assistant to Guido Reni and painted the copy of Guido's Abduction of Helen in 1631 for Cardinal Bernardino Spada with his master's retouching (Galleria Spada in Rome). Before World War II in Bode-Museum in Berlin, there was painting of Feeding the multitude, which in the inventory of the collection of Vincenzo Giustiniani from 1638 it is attributed to Campana (Un quadro grande col miracolo di Christo della distribuzione di cinque pani, e dui pesci dipinto in tela, alta palmi 12 lar. 7 -in circa di mano del Campana senza cornice). Two paintings in Palazzo Malvezzi de' Medici in Bologna depicting the Death of Saint Joseph and Martyrdom of Saint Ursula from the Hospital of the Little Bastards (Ospedale dei Bastardini) are also attributed to him. In Poland the work which could be attributed to circle of Guido Reni is a portrait of Ladislaus IV Vasa in a cuirass from the collection of the Wawel Royal Castle in Kraków, purchased in 2013 in Italy. It was most likely Campana who created a copy of Guido Reni's Cupids fighting putti from the Czartoryski collection (inventory number MNK XII-228). The original by Reni, today in the Galleria Doria Pamphilj in Rome, was created in about 1625. Among other works that can be attributed to Campana is the Temptation of Saint Benedict (Saint Benedict throwing himself into the thornbush) in the Lithuanian National Museum of Art (oil on canvas, 145 x 173 cm, LNDM T 927), similar to a painting attributed to Felice Ficherelli in the Slovak National Gallery (O 5476) and two paintings in the Wilanów Palace in Warsaw - Night (oil on canvas, 166.5 x 219.5 cm, Wil.1060), inspired by La Notte by Guercino, and Saint Mary Magdalene (oil on canvas, 68.5 x 58 cm, Wil.1732), close to certain works by Guercino and his workshop, such as Saint John the Baptist (Vatican Museums) or Penitent Magdalene (Capitoline Museums). Cupid holding his bow, a fragment of Campana's larger composition depicting the Abduction of Helen, is now in the Nieborów Palace (oil on canvas, 75 x 65 cm, NB 964). It comes from the collection of the Catholic branch of the Radziwill family and is considered to be a work by a 19th century Polish painter. Campana obviously frequently used compositional templates from other painters. In the royal Wilanów Palace, there is a painting entitled Education of Cupid (oil on canvas, 134 x 166 cm, Wil.1548), which most probably comes from the old collection of the palace. This painting is a copy of Titian's Venus blindfolding Cupid in National Gallery of Art in Washington (before the painting was cut), which is a portrait of Queen Catherine of Austria (1533-1572) as Venus Verticordia (Turner of Hearts). It is however not an exact copy, the painter only borrowed the composition, but the woman depicted as Venus is different. She bears great resemblance to effigies of Ladislaus IV's sister Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651). The style of this painting is very similar to the the aforementioned painting of the Death of Saint Joseph by Giacinto Campana. Very similar composition, painted in the same style, is in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna. Like in Warsaw version the woman has her breast uncovered, but her face is also different from both mentioned paintings, the original by Titian and the copy in the Wilanów Palace. Her image with an elongated hooked nose and large lips is very similar to the portrait of Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria in Vienna (inventory number 8291) and etched effigies of the queen. This painting, depicting Cecilia Renata as Venus Verticordia, created in Warsaw, was therefore sent to the queen's relatives in Vienna. What is interesting Fortuna Virilis (or her assistant), an aspect or manifestation of the goddess Fortuna, who had the power to conceal the physical imperfections of women from the eyes of men and associated with Venus Verticordia, has the features similar to the princess and the queen respectively.
Allegory with portrait of Crown Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) as Venus Verticordia (Turner of Hearts) by Giacinto Campana, 1637-1642, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
Allegory with portrait of Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria (1611-1644) as Venus Verticordia (Turner of Hearts) by Giacinto Campana, 1637-1642, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Cupids fighting putti by Giacinto Campana after Guido Reni, ca. 1637-1650, Czartoryski Museum.
Cupid holding his bow by Giacinto Campana or follower, after 1637, Nieborów Palace.
Portrait of Ladislaus IV Vasa in a cuirass by Simone Cantarini
The opera "Saint Alexius" (Il S. Alessio : dramma musicale : dall'eminentissimo, et reverendissimo signore card. Barberino, fatto rappresentare al serenissimo prencipe Alessandro Carlo di Polonia), performed on January 19, 1634 at the Palazzo Canceleria in Rome, was one of the splendid events honoring the visit of Prince Alexander Charles Vasa, half-brother of elected King Ladislaus IV Vasa, during the Carnival in the Eternal City. This opera in three acts was composed by Stefano Landi in 1631 to a libretto by Giulio Rospigliosi (the future Pope Clement IX), and the scenography was probably the work of Gianlorenzo Bernini.
It was followed by another splendid event in Piazza Navona - Saracino Festival or Giostra del Saracino (a "Saracen" joust or tournament), held on 25 February 1634. Celebrations were prepared under the auspices of Cardinal Antonio Barberini the Younger (1607-1671) or Antonio Barberini iuniore to distinguish him from his uncle Antonio Marcello Barberini (1569-1646). The Barberini spared no money to honor the Polish-Lithuanian prince (the Saracen joust cost the fabulous sum of 60,000 scudi). They probably wanted to show the guest the splendor of their rule in the Papal States or even overshadow the solemn entry of the Commonweath's legation of Jerzy Ossoliński into the Eternal City, which took place a few months earlier, on November 27, 1633. Jan Sobieski, future king, recalled Ossoliński's mission to Pope Urban VIII Barberini, believing that Rome had never seen anything more famous and more glorious. The painters Andrea Sacchi (1599-1661) and Simone Cantarini (1612-1648), clients of the Barberini house, were undobtedly employed in many jobs, as well as Antonio Barberini the Younger's lover, the castrato singer Marc'Antonio Pasqualini (1614-1691). The famous soprano, as a castrato en travesti, played major roles in Sant'Alessio in 1631, 1632 and 1634, including Sposa (Alexius's wife). As the revenues of the papacy from the Commonweath were considerable, good relations with the ruling house of Poland-Lithuania were important. Ossoliński gave the Pope many valuable gifts, including Flemish tapestries made for King Sigismund II Augustus. The Barberinis undoubtedly also reciprocated with gifts, but today we can only imagine how many beautiful works of Roman Baroque found their way to Poland-Lithuania at that time. In October 1643, they also honored the king's other half-brother, Prince John Casimir Vasa (future king), who decided to become a cardinal. In 1641, Sacchi, who decorated Capuchin church in Rome and the Palazzo Barberini for Cardinal Antonio Barberini the Younger, created a beautiful portrait of Pasqualini crowned by the naked god of music and the arts Apollo. Cantarini is in turn credited with creating several portraits of Antonio the Younger around 1633. Both painters are frequently linked to Guido Reni (1575-1642), active in Bologna in the Papal States, whose studio Ladislaus Vasa visited in 1625. Presumably around 1634 Cantarini joined Reni's workshop and around 1639 returned to Rome. In Poland, there is a beautiful Allegory of Painting by Cantarini (National Museum in Warsaw, 126263), acquired in 1938 from the Boschi collection in Bologna (a copy is in the Fondazione Cavallini Sgarbi). A painting by Cantarini is mentioned in the 1835 catalogue of paintings from the Radziwll collection: "99. Venus jokes with Cupid, having taken his bow, she holds it up; Cupid eagerly reaches for it. - Painted on copper" (after "Katalog galeryi obrazow sławnych mistrzów ..." by Antoni Blank, p. 34). Paintings close to the style of Cantarini and Sacchi were before the Second World War in the collection of Count Juliusz Tarnowski in the magnificent Renaissance palace of Sucha Beskidzka (oil on canvas, 99 x 74 cm). They were attributed to another student of Reni Francesco Albani or to his workshop and represented the Toilet of Venus and the Toilet of Diana. Another work close to Cantarini can be found in the former royal palace of Wilanów in Warsaw. It is attributed to the Bolognese school of the 17th century and represents Saint Sebastian (oil on canvas, 53 x 35 cm, Wil.1033). In addition to being considered the third patron saint of Rome, since the Renaissance, this saint has been an enduring symbol for the expression of homosexual feelings and "usually suppressed homosexual fantasies" (after "Lesbian and Gay Writing" by Mark Lilly, p. 206). Cardinal Antonio the Younger owned the Mystical Marriage of Saint Catherine with Saint Sebastian by Correggio (Louvre Museum, INV 41; MR 162), offered to Cardinal Mazarin during his exile in Paris. The naked young man in a drawing attributed to Cantarini (Metropolitan Museum of Art, 69.1), could be a study for a disguised portrait of Cardinal Antonio as Saint John the Baptist or Saint Sebastian, as it greatly resembles the Cardinal's effigies by this painter. The Wilanów painting is comparable to Cantarini's very sensual Saint Sebastian and an angel, painted between 1632 and 1648 (sold at Cambi Casa d'Aste in Genoa, December 13, 2019, lot 170), and his drawings - Saint Sebastian (Cornell College, Edward Sonnenschein Collection, 48) and naked Saint Sebastian crowned by an angel, study for an etching (Nationalmuseum in Stockholm, NMH 1252/1863), both from the late 1630s. Unfortunately, its earlier history is not known, but this does not exclude that the painting was transferred to Poland before the Deluge (1655-1660). The history of art in the majority of European countries commemorates the genius of artists and the generosity of their patrons. In Poland, however, it is often linked to the darkest periods of human history and sometimes causes controversy. The wonderful heritage of the Realm of Venus perished with each war and invasion. Italians have long forgotten how much profit brought them fruitful trade with the Commonwealth and how many portraits of Polish-Lithuanian monarchs and aristocrats they owned, like the portrait of a young man in eastern costume, most likely a Ruthenian nobleman (Pinacoteca Ambrosiana in Milan), identified by me. Due to the massive destruction of their heritage, the Sarmatians have also forgotten how much their culture owes to distant Italy (especially when it comes to portraiture). When the Commonewath became impoverished after the wars, the inflow of newcomers from Italy was stopped, and the members of the Italian community who survived the invasion were quickly Polonized, and even foreign-sounding surnames were transformed, obliterating the traces of Italian origin. For example, in the municipal registers of Lublin from the 17th century, surnames such as: Gilberti, Grimaldi, Mureni, Mineto, Negroni, Simi are mentioned. Rudgier de Sacellis, his brother Daniel de Sacellis, Jerzy Cyboni, Krzysztof Cyboni, Michał Pelikan-Klimuntowicz (Climunta), Flawiusz Marchetti and Antoni Nosadyni were mayors of Lublin. There were Italian barbers (Franciszek Grimaldi, Franciszek Raymundi), doctors (Castelli), painters (Jakub Tebaldi) and stonemasons (Florian Dydzudes de Saltre). Italians were also engaged in pharmacy (Marian of Catania), goldsmithing (Gilbertii Georgius), and tailoring (Joanes Dziano Olsan) (after "Lublin w dziejach i kulturze Polski" by Tadeusz Radzik, p. 259). One of these long-forgotten royal effigies was the portrait of King Ladislaus IV Vasa with the Order of the Golden Fleece, wearing a breastplate and holding the staff. The portrait was purchased by Wawel Royal Castle in Italy in 2013 from a private collector. Influences from Reni's oeuvre are noticeable, but the style of this painting bears a striking resemblance to that of the portrait of Cardinal Antonio iuniore with pentimento (earlier image of a young woman) visible on the cardinal's mozzetta, painted by Simone Cantarini around 1633 (sold at Sotheby's London, July 4, 1990, lot 74). It also resembles other portrait of the cardinal by Cantarini (Palazzo Barberini in Rome, inv. 1068), as well as the mentioned Allegory of Painting. It is very possible that Antonio, who shared with Ladislas IV a passion for art and opera, commissioned this portrait or received a copy of a painting sent to Poland-Lithuania. The style of the effigy of the king's half-brother - John Casimir, which is still in Rome at the Polish Hospice (oil on canvas, 98 x 73 cm), is very similar. It is a copy or a version of a portrait of John Casimir as a cardinal produced by the workshop of Giovanni Antonio Galli, known as lo Spadarino (attributed by me), today at the Pontifical Gregorian University in Rome. It has a Latin inscription in the lower part (CASIMIRVS SOC[ietatis] IESU S[anctae] R[omanae] E[cclesiae] CARDINALIS ET / POLONIE REX) and, before the Second World War, this painting was in the Church of the Gesù (Il Gesù), prototype of a Jesuit church, consecrated in 1584 (compare "Kościół polski w Rzymie ..." by Józef Skrabski, p. 299). Cantarini and Spadarino copied each other their works or received the same set of study drawings to create their paintings.
Portrait of Ladislaus IV Vasa in a cuirass by Simone Cantarini, 1637-1644, Wawel Royal Castle in Kraków.
Portrait of Prince-Cardinal John Casimir Vasa (1609-1672) by Simone Cantarini, ca. 1648, Polish Hospice in Rome.
Saint Sebastian by Simone Cantarini, 1630s, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
The Toilet of Venus by Andrea Sacchi or Simone Cantarini, 1630s, Sucha Beskidzka Castle, lost.
The Toilet of Diana by Andrea Sacchi or Simone Cantarini, 1630s, Sucha Beskidzka Castle, lost.
Portrait of Prince Christopher Radziwill holding a cane by Govert Flinck
After 1637, Prince Christopher II Radziwill (1585-1640), Grand Hetman of Lithuania transformed his main residence, Birzai Castle, into a Dutch-style bastioned fortress. This fortified palace, initially in Italian style (palazzo in fortezza), built for his father by the architect Franceso Mineto (Franciszek Minet) between 1586-1589, was destroyed in 1625 by Swedish troops led by King Gustavus Adolphus. The Swedes stole all the property and 60 cannons. When the castle was returned to the Radziwills in 1627, the structure was badly damaged and could no longer be inhabited. Christopher therefore built a temporary wooden palace in Birzai.
The reconstruction was supervised by Cornelius Keyzer from Vilnius, possibly a relative of the Dutch sculptor and architect Hendrick de Keyser (1565-1621), and the main architect was Cornelius Retenburg from Tartu (Dorpat). Many materials for the construction work were imported, such as cement brought via Riga, probably from the Netherlands, as well as roof tiles made in Haarlem (Keyser insisted on harlimskie roof tiles during reconstruction works in 1612) (after "Jak Krzysztof Radziwiłł (1585–1640) dwory i zbory budował ..." by Jarosław Zawadzki, p. 28, 38, 41). Unfortunately, in the fall of 1655, the Birzai fortress again fell into the hands of the Swedes and after further reconstruction after the Deluge, in 1704 during another Swedish invasion, the troops of General Adam Ludwig Lewenhaupt (1659-1719) blew up the palace and the fortress. The Hetman also had several residences in Vilnius. The most important and oldest was the palace inherited by his nephew Boguslaus (Christopher was his guardian until 1636), later known as the Boguslaus Palace. It was located near the Palace of the Grand Dukes of Lithuania and the Cathedral. In 1506, Nicolaus II Radziwill (d. 1509) founded a Gothic church dedicated to Saint George and Our Lady of the Snows near the palace. Christopher's brother-in-law Janusz Kiszka (1586-1654), voivode of Polotsk, also had his manor nearby. It is very significant that the palace of the Duke of Birzai (Domus Jllmi Principis Radzivilli in Birze ducis) is mentioned as the first (and not the Palace of the Grand Dukes) in the legend of the view of Vilnius by Tomasz Makowski (Tomašas Makovskis), created around 1600, as well as the location of the Calvinist school (after "Książęcy splendor w stolicy ..." by Tadeusz Bernatowicz, p. 22). The Radziwills purchased many luxury items from around the world in the country's main port, Gdańsk, in Polish Prussia. "The register of things sent from Gdańsk to Vilnius by Szczęsny Żydowicz [Szczęsny the Jew]" (Rejestr rzeczy, które się ze Gdańska do Wilna posyłają przez Szczęsnego Żydowicza), June 1620, lists many valuable items acquired by them, including: "Eight paintings painted on panel; Two paintings painted on canvas, among which a portrait of Gabriel Bethlen [Prince of Transylvania] [...] Thirty-four Venetian wine glasses; Two Venetian glasses with covers [...] Five Indian walnut trees; Spanish ebony and ivory round table with checkers [...] French red wines, one barrel; French white wines, one barrel" (Obrazow na drzewie malowanych osm; Obrazow na plotnie malowanych dwa, Miedzy ktoremi conterfet Bethlem Gabore [...] Kieliszkow weneckich sztuk trzydziesci y cztery; Szklenic weneckich z nakrywkami dwie [...] Drzewa Indyiskie orzechowe sztuk pięc; Stoł okrągły Hebanowy y zwarcabami kością sadzony Hiszpansky [...] Wina Francuskie czyrwone beczka iedna; Wina Francuskie białe beczka iedna) (Central Archives of Historical Records in Warsaw, AGAD 1/354/0/26/22). The paintings were probably made in the Netherlands, Flanders or Venice. Old inventories also confirm that their numerous residences were filled with many paintings, unfortunately the descriptions are very general and the names of the painters are not mentioned. In the "Vilnius brick manor" alone, approximately 125 paintings were recorded in the years 1621-1628. It is known, however, that in one of the rooms in Birzai there was a painting on the ceiling depicting the meeting of Prince Christopher with Gustavus Adolphus. The earlier victory of Christopher Radziwill and Jan Karol Chodkiewicz over the Swedes in 1601 was illustrated by a large painting of the Battle of Kokenhausen, listed among other paintings (portraits, hunts, "kitchens") in the manor house in Koydanava (now Dzyarzhynsk in Belarus) in 1627. Many paintings and portraits are mentioned in the register made before 1636 (AGAD 1/354/0/26/50), like in a brick mansion in Vilnius - "In a wooden dining room paintings on the walls ... 19, Opposite in the room pictures ... 2" (W Drzewnianej stołowej izbie nascianach obrazow ... 19, NAprzeciwko wpokoiu obrazow ... 2) or paintings taken from the Vilnius manor of Janusz Radziwill (1579-1620) - "from alcove two large paintings; from large house from rooms two large paintings; different portraits, including the father of Her Ladyship Margrave John George [Elector of Brandenburg] and King of England" (Z Alkowy obrazow dwa wielkich; Z wielkiej kamienice spokoiow obrazow wielkich dwa, Conterfetow Roznych, Toiest Conterfet ojca Xiezny jej mosci Margrafa Jana Jerzego i krola Angielskiego 3), as well as miniatures from the Radziwill house in Toruń - portrait of late Prince Henry of England (Henry Frederick, Prince of Wales) in diamond frame, portrait of English Princess in diamond frame, two-sided portrait of Elector of Saxony and his wife in diamond frame, portrait of Elector of Brandenburg and his wife in diamond frame, portrait of English Princess, portrait of King and Queen of France, portrait of Princess Radziwill (Anna Kiszczanka?), voivodess of Vilnius and portrait of King of England. Receipts for jewels in this register are signed by Daniel von der Rennen, most likely a Dutch merchant active in Gdańsk (possibly a relative of Gdańsk goldsmith Peter van der Rennen). Inventory of Nesvizh Castle in 1636 (AGAD 1/354/0/26/52), lists the portrait of hetman Jan Karol Chodkiewicz (d. 1621), voivode of Vilnius (Konterfert Pana Wileńskiego Chodkiewicza), full-length portrait of King Sigismund III Vasa (Konterfet Zupełny Zygmunta Króla Je M polskiego) and other portraits (Konterfetów Roznych). "I hope that Y.P.M. [Your Princely Mightiness] will send to my father's Kunstkamer [art cabinet] a special treat" wrote Janusz to his cousin Boguslaus Radziwill, sending him "silver art", possibly Scythian, found in Volhynia (and received from Prince Vyshnevetsky) for evaluation by foreign antique dealers. In another letter Janusz thanks him for a portrait sent from France. During his educational journeys, Prince Janusz informed his father about military works and other the new releases on the bookselling market. In his correspondence, he informed Christopher II of the intention to print in Antwerp the work Icones et elogia illustrorum virorum, which was to include biographies of Polish magnates. He asked for portraits of his grandfather, uncle and father to be sent to him, because he only had the image of the "Orphan" (Nicolaus Christopher Radziwill) with him. He added that "the costs should not be weighed" in this regard. Prince Christopher also asked the tutors to ensure that portraits of Janusz were made during his son's trips abroad - "in whatever costume suits him better, send it to me" (w habicie, który mu będzie naprzystojniejszy, przysyłać mi), while Janusz thanked his cousin for his portrait "because from this effigy I took the model of the current French costume" (bom z niego modeliusz wziął teraźniejszego stroju francuskiego) (after "Książka i literatura ..." by Mariola Jarczykowa, p. 24-28, 32, 34-36, 47). During his stay in the Netherlands, Boguslaus established relations with Lucas Vorsterman, an Antwerp engraver from the circle of Rubens and van Dyck, who accompanied Radziwill during the war of 1640/41 and then painted his portrait. In Antwerp, Boguslaus came into contact with a painter and art dealer - Matthijs Musson, a student of Rubens. It is confirmed that in 1646 Musson delivered many works of art to the prince in Amsterdam, including two paintings for 63 guilders and a copy of the Assumption of the Virgin Mary by Rubens for 80 guilders. In 1645-1647, van den Wouwer, Musson's cousin, the owner of the "gallery of antiques", delivered to the prince 6 paintings with hunts for 56 guilders each (after "Galerie obrazów i "Gabinety Sztuki" Radziwiłłów w XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska, p. 88-89, 91). The inventory of paintings in the collection of Princess Louise Charlotte Radziwill (1667-1695), Christopher's great-granddaughter, drawn up in 1671, lists 5 paintings which could be effigies of the hetman at different ages (29/9, 35/5, 38/8, 85/4, 86/5) and a drawing with "Prince Christopher's funeral" (876/6) (after "Inwentarz galerii obrazów Radziwiłłów z XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska). The inventory also includes a painting of "Nymphs asleep while hunting" (350/3), while a drawing representing sleeping women, being a study for "The rest of Diana and her nymphs" by Peter Paul Rubens (figures) and Jan Brueghel the Elder (landscape and animals), is visible in the still life attributed to Abraham Susenier (Agnes Etherington Art Centre). The person who commissioned the still life owned the study drawing for Rembrandt's portraits, so this patron may also have owned the original painting by Rubens and Brueghel. The composition of "The rest of Diana and her nymphs" is known from multiple versions and copies, such as the copy from the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna (GG 1707) or another version from the Alte Pinakothek in Munich (344). The version kept at the Museum of Hunting and Nature in Paris (oil on panel, 61 x 98 cm, 68-3-2) is considered the original. This painting includes a pendant (companion piece) representing "Diana and her nymphs leaving for the hunt" (oil on panel, 57 x 98 cm, 68-3-1). Although the two paintings appear to form a pair, their provenance is determined differently - the first (sleeping nymphs) is considered to come from the collection of Frederick II of Prussia, whose dubious accomplishment was the First Partition of Poland, in his Sanssouci Palace near Berlin, while the second painting is said to have remained for some time in Rubens' personal collection and was acquired by Matthijs Musson after the painter's death. Both paintings are dated around 1623-1624, therefore from the time when Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa visited Rubens' studio. The 1633 inventory of Radziwill Castle in Lubcha in Belarus (Central Archives of Historical Records in Warsaw, 1/354/0/26/45) lists "A large painting with Diana and her maidens, the fauns laugh at, given by the present king", that is Ladislaus IV (item 37) and "A painting in ebony frames depicting Diana with nymphs washing by the spring" (38). In 1560, Krzysztof Krupski, starost of Horodło, ordered a large throne tapestry with the coat of arms of King Sigismund Augustus in the workshop of Anton Leyniers in Brussels (Wawel Royal Castle), so it could also be the other way around that the king commissioned in Flanders a work of art glorifying the most powerful family of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, whose ambitions were sometimes truly royal. We cannot exclude that copies or originals of the two paintings in Paris were in Lubcha, especially since the main motif of both compositions is a black horn, exactly like in the coat of arms of the Radziwill family - Trąby, as depicted in Wojciech Cieciszewski's "Kryształ Z Popiołv", published in Vilnius in 1643, dedicated to Christopher's son Janusz. Around 1652, Flemish engravers Pierre Rucholle and Pieter de Jode II created an engraved portrait of Prince Christopher Radziwill, probably based on a painting or drawing by the Dutch painter Michiel Jansz. van Mierevelt. The paintings belonging to the Hetman were sometimes described in the poems of his court poets, as in certain works of Daniel Naborowski (1573-1640), including the most famous erotic poem "On the Eyes of the English Princess" (Na oczy królewny angielskiej), which would correspond to portraits of the English princess mentioned in the inventories. This poet's epigrams "On nude images in the bathhouse" (Na nagie obrazy w łaźni) could have been a verbal commentary on the paintings decorating the bathhouses in the Vilnius residence, also mentioned in the inventories. In one of the occasional poems, Naborowski mentioned about the prince's gallery: "My Lord, you have beautifully painted Bacchuses" (Panie mój, masz Bachusów malowanych siła) and in others he refers to the portraits of Bishop Eustachy Wollowicz and Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa in national costume holding a buzdygan mace. Christopher also had a large cabinet of curiosities. In addition to paintings, the Hetman also received various curiosities for his collection and sculptures such as "Adam and Eve in wood, delicately carved, where all the limbs move", offered by Ladislaus IV. He also collected rare numismats, as evidenced by a document in which Christopher asked Mr. Kłosowski to purchase a library and rare coins from the Gorajski family, including "some old Roman and Greek coins" (jakieś numizmata staroświeckie rzymskie i greckie). His scientific interests were also manifested by maintaining contacts through letters with former tutors in Leipzig, Heidelberg and Basel, as well as by recruiting "people learned in foreign countries" to his court. Radziwill also supported the settlement of Protestants in his domains, welcoming refugees from German countries ravaged by the Thirty Years' War. The immigration was so great that according to Janusz Tazbir the Commonwealth became a real refugium Germaniae (after "Korespondencja i literatura okolicznościowa ..." by Mariola Jarczykowa, p. 81, 117). In a letter dated June 2, 1629 from Kedainiai, local starost Piotr Kochlewski reported to Christopher that "more and more Germans are coming from Prussia every day" (Z Prus co dzień Niemców przybywa). In his palace there was also a temporary or permanent theater - "The next day, Friday, after lunch, there was a comedy, in the presence of envoys from Moscow and Florence", as Janusz Radziwill informed his father in a letter. Christopher was considered a good orator - "The voivode also delivered an elegant speech to the Archduchess, who responded in Italian", recalled Albert Stanislaus Radziwill (1593-1656) about welcoming of Cecilia Renata of Austria in 1637. The mentioned inventory of Lubcha Castle also lists many other valuable items from the prince's collection. Among them, we can distinguish Venetian glass (Szklanic weneckich), luxury items purchased from the French (Rzeczy Nowe Rozne od Francuzów Kupione), including a pillow embroidered with gold and silver, a silk cherry comb case (Grzebieniarz) embroidered with gold and silver and five pairs of silk stockings embroidered with gold and silver, "Dutch tablecloths and various canvases" (Obrusy Olenderskie y Płotna Rożne), images and portraits, mainly embroidered on satin, made of cut paper as well as painted portraits of Gustavus Adolphus, King of Sweden (called Duke of Sodermanland), Gabriel Bethlen, Prince of Transylvania, Eustachy Wollowicz, Bishop of Vilnius, painted on white satin, portraits of the Prince Radziwill and his wife Anna Kiszczanka, painted on copper, prints, maps and wax sculptures, silver plaque with image of Emperor Ferdinand II, three paintings of large dogs and a large painting of a bear, Persian and oriental rugs and carpets - 142 in total (16, 38, 17, 10, 8, 22, 30, 1), 11 Dutch green silk tapestries with figures, 9 green Dutch tapestries with figures without silk, "a Dutch tapestry on the table with different coats of arms of the princes, Their Highnesses" (opona Olenderska na stol z Herbami Roznemi Xiąząt Ich mosci), 18 white tapestries made locally and Turkish tents. Evangelical Bible in Polish - Biblia swięta, published in Gdańsk in 1632, sponsored and dedicated to Prince Christopher, is one of Radziwill's most important achievements. The title page by Cornelis Claesz. Duysend was most likely created in Amsterdam (National Library of Poland, SD XVII.3.4795). As a leader of Lithuanian Calvinists, Christopher founded churches and schools, but also supported and imposed policies favorable to his co-believers. With the growing influence of the Jesuits and Habsburgs at the royal court, times became increasingly difficult for non-Catholics in a multi-religious nation. King Sigismund III's second wife Constance of Austria, whose relatives in Spain participated in the public auto-da-fé (Constance's nephew, Philip IV of Spain, requested that an auto-da-fé take place at court in 1632 to celebrate the healing of his wife, Elizabeth of France) and whose brother-in-law King Philip III of Spain expelled the Moriscos in 1609, was famous for her intolerance. Many nobles and dignitaries began to follow the queen's example. Poles often succumbed to Western fashions, but the fashion for religious fanaticism could only bring bad results. Fashion in the 17th century was frequently used for political reasons, as evidenced by the portraits of King Ladislaus IV in French, Spanish and national costumes, but also to demonstrate connections or beliefs, or simply to show splendor and wealth. For example, the Sapieha/Sapega portrait series at Wawel Royal Castle presents a wide variety of not only Lithuanian but also European (including Spanish and Dutch) fashion from the 17th century. The diversity in this matter was truly remarkable - George Radziwill (1578-1613), castellan of Trakai, a fervent Calvinist educated in Leipzig, Strasbourg and Basel, left horses and clothes in his will to his brothers-in-law: Italian - to Dorohostajski and hussar - to Gorajski. Since Catholics in the royal-ducal court in Vilnius and Warsaw sometimes manifested their beliefs through Spanish, Italian of Flemish fashion, the leader of the Calvinists undoubtedly also wore Protestant costumes. The portrait of a man against a landscape by Govert Flinck, a pupil of Rembrandt usually living in the house of Hendrick Uylenburgh, artistic agent of Sigismund III Vasa, in Amsterdam, now kept in the National Museum in Warsaw, is dated around 1640 (oil on panel, 92 x 69 cm, M.Ob.2584 MNW). The painting comes from the collection of Karol Radziwill in Argentina and was purchased in 2005. It is identified with a painting belonging to King Stanislaus Augustus Poniatowski in Warsaw and mentioned in the "Catalogue of paintings belonging to His Majesty the King of Poland" (Catalogue des tableaux Appartenant à Sa Majesté le Roi de Pologne) in 1795 as "Old man standing, holding a stick, dressed in Dutch style, with a small white beard, the background is a landscape, on wood" (Viellard debout, tenant un bâton, vêtu a la hollandoise, avec une petite barbe blanche, le fond est un paysage, sur bois, item 162). The name of the painter is not mentioned, so it is possible that the king owned a copy or another painting or that the Radziwills reacquired the portrait of their ancestor from the royal collection. The painting was sold in Paris in 1933 (Hôtel Drouot, March 8, 1933, lot 11, FLINCK (attribué à GOVAERT) / 11. Portrait d'un seigneur hollandais. / Debout dans la campagne, appuyé sur une canne, il est vêtu de noir. Bois. Haut., 92 cent.; larg., 70 cent.), together with portrait of Princess Christine Magdalene Radziwill (1776-1796) in a wooded landscape, painted in Vienna in 1795 by Giuseppe Maria Grassi, although at that time the princess was in Nieborów and later in Saint Petersburg (so most likely made from study drawings sent to Vienna). Both paintings were part of the Radziwill collection at Château d'Ermenonville and according to Tadeusz Mańkowski (1878-1956), Flinck's painting depicted Radziwill "the Orphan" (?) (after "Rembrandt w Polsce" by Michał Walicki, p. 331). The man presented as a wanderer with a cane manifests "the choice of an active attitude in the journey through life, consistent with the ideals of Calvinism" (according to Museum's description). The church in the background closely resembles the Church of St. George in Vilnius, near the palace of the Duke of Birzai, depicted in Makowski's print, as if the man were standing in the garden of this residence. It also resembles the church in Duysend's engraving Biblia swięta, published in 1632. The sitter in turn resembles the man in the portraits with two feathers by Rembrandt and his circle, notably the version from Viderup Castle. A similar "wanderer with a cane" was also depicted in the Vanitas still life, attributed to Susenier, comprising the study for the portrait by Rembrandt with two feathers. The Lubcha inventory also mentions several of Christopher's garments which could be depicted in the painting, like 19 different kurta (a jacket or a short kaftan), including one "black leather stitched kurta with black and silver buttons" and another "black stitched leather kurta with white silk buttons" (Kurta Czarna skurzana Przeszywana z guzikami Czarnemi srebrem Przetykanemi [...] Kurta skurzana Czarna Przeszywana z guzikami białemi Jedwabnemi), 4 hats, 3 made from felted beaver fur, including one black with black feather (Kapelusz Czarny Bobrowy z Piorem Czarnym) and 8 canes, apart from 1, all made in India, including first set with silver (Laska Czarna Indyska srebrem oprawna z sikawką). Christopher died on November 19, 1640 at the age of 55, according to his contemporaries, devastated by the turn of events after the attack on the Calvinist church in Vilnius, when the king not only did not punish the culprits of the attack, but also ordered the church to be moved outside the city walls and prohibited pastors from carrying out pastoral activities in the city.
Portrait of Prince Christopher Radziwill (1585-1640), Grand Hetman of Lithuania, holding a cane by Govert Flinck, ca. 1640, National Museum in Warsaw.
The rest of Diana and her nymphs by Peter Paul Rubens and Jan Brueghel the Elder, ca. 1623-1624, Museum of Hunting and Nature in Paris.
Diana and her nymphs leaving for the hunt by Peter Paul Rubens and Jan Brueghel the Elder, ca. 1623-1624, Museum of Hunting and Nature in Paris.
Portrait of Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria holding a tulip by workshop of Frans Luycx
On October 7, 1649, in Navalcarnero, near Madrid, 14-year-old Archduchess Maria Anna of Austria (1634-1696) married her 44-year-old uncle, King Philip IV of Spain. The couple spends their wedding night in the royal monastery of El Escorial. The archduchess was a niece of Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria (1611-1644) and she was also related to her husband, King Ladislaus IV Vasa (1595-1648).
Maria Anna (or Mariana in Spanish) was the daughter of Emperor Ferdinand III and the Infanta Maria Anna of Spain (daughter of King Philip III of Spain and niece of two wives of Sigismund III Vasa). Since she was a child she was engaged to her cousin Balthasar Charles, Prince of Asturias, but when he unexpectedly died in 1646, King Philip IV, who had been widowed after the death of his first wife, Elisabeth of France, decided to marry the young archduchess. The political situation forced the king to remarry for the sake of securing a male heir for the great Spanish empire, as he had only one legitimate daughter - Infanta Maria Theresa of Spain, future queen of France. Before the wedding, many portraits of the bride arrived in Spain, mainly created by leading imperial court portraitist Frans Luycx. Let us cite in particular the portrait at the age of approximately 5 years, thus produced around 1639 (Prado, P002871) and the portrait in mourning after the death of her mother from about 1646 (P006194). Around 1646 another portrait of Maria Anna, with tulips in a vase, attributed to Frans Luycx, was sent to Spain (P002441). In this portrait, she appears to be more than 11 years old, which has not gone unnoticed in Spain. After death of archduchess' mother it became necessary to once again strengthen the family and political ties between the two branches of the house of Habsburgs, while the fertility and good health of the candidate were the most important in Spain. It is perhaps to this portrait that the report which evaluated the archduchess as a candidate refers: "A portrait of her has only come that represents her at the age of 11 years and two months [...] very grown up, but with her true age her painted effigy is discredited, was it painted faithfully?" (Un retrato solo ha venido que la representa con edad de 11 años y dos meses [...] muy crecida pero con su edad verdadera se desacredita su altura pintada, mas si es pintar como ver?) (after "Entre Viena y Madrid ..." by Gemma Cobo Delgado, p. 155-158). It is now difficult to determine whether it was manipulated in order to convince the Spanish royal court of her good health. It also gives some idea of the important political role that painted effigies sometimes played and that they were not always accurate, intentionally or not. Although the painting is attributed to Luycx, it differs from other works by this painter, notably the two other mentioned portraits of the archduchess in Prado. It is very possible that it was entirely produced by the painter's workshop or even another painter close to him, which could also partly explain this lack of faithfulness of the portrait. Luycx was a very busy painter. In addition to working for the Habsburgs, the nobility of Bohemia, Austria and Germany, he also produced numerous paintings for the Polish-Lithuanian court. In the Alte Pinakothek in Munich several paintings by Frans coming from Neuburg Castle have been preserved. The castle was the residence of Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa, sister of Ladislaus IV Vasa who, on June 9, 1642 in Warsaw, married Philip William of Neuburg. She brought a sizeable trousseau into the marriage: 243,333 thalers in cash, jewelry worth around 300,000 thalers, valuable objects in gold, silver, furniture, tapestries and Persian carpets. It is quite possible that the paintings come from her dowry since they depict the princess's brother - Ladislaus IV (oil on canvas, 250 x 160 cm, 4197) and brothers of her sister-in-law Queen Cecilia Renata - Emperor Ferdinand III (1608-1657) (oil on canvas, 206 x 137 cm, 6779) and Archduke Leopold Wilhelm of Austria (1614-1662) as clergyman (oil on canvas, 208 x 119 cm, 6819). The paintings probably come from a series commissioned from the Luycx workshop, however the portrait of Cecilia Renata is missing. In the Alte Pinakothek there is a painting of the Unknown Princess (Unbekannte Fürstin) which also comes from Neuburg Castle (oil on canvas, 209 x 104 cm, 6781/7244). Already in 1969, Janina Ruszczyc identified this painting as the effigy of the Queen of Poland and the Grand Duchess of Lithuania ("Portrety Zygmunta III i jego rodziny", p. 212-213, pic. 39). Her facial features and costume closely resemble those in Cecilia Renata's portrait in the Nationalmuseum in Stockholm (NMGrh 299). The queen holds a tulip, symbol of love and the vanity of earthly things (after "Nature and Its Symbols" by Lucia Impelluso, p. 82). She wears a brooch with a Polish eagle, similar to the one in the Louvre (MR 418). The style of this portrait is very similar to that of Archduchess Maria Anna with tulips in Prado (P002441). Another portrait of a member of the royal-grand ducal family of Poland-Lithuania, painted in a similar style, is also in the Alte Pinakothek (oil on canvas, 227.8 x 142 cm, 6961). This full-length image depicts Prince Charles Ferdinand Vasa (1613-1655), half-brother of King Ladislaus IV, bishop of Wrocław from 1625 and bishop of Płock from 1640. This painting also comes from Neuburg Castle. The portrait of the prince-bishop as a prelate, close to the style of Frans Luycx, is in the Archdiocesan Museum in Wrocław (oil on canvas, 98 x 78 cm, 1377).
Portrait of Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria (1611-1644) holding a tulip by workshop of Frans Luycx, ca. 1640, Alte Pinakothek in Munich.
Portrait of Prince Charles Ferdinand Vasa (1613-1655), bishop of Wrocław and Płock by workshop of Frans Luycx, ca. 1640, Alte Pinakothek in Munich.
Portrait of Prince Charles Ferdinand Vasa (1613-1655), bishop of Wrocław and Płock by workshop of Frans Luycx, 1640s, Archdiocesan Museum in Wrocław.
Portraits of Hendrick van Uylenburgh and his daughter Sara by Rembrandt and workshop
"Portrait of a Portuguese Rabbi, painted by Rembrandt, in black frame" (Portret Rabina Portugalskiego, malowania Rynbranta, w ramach czarnych, No.74.), valued at 150 thalers and "A picture of similar dimensions, a Jewish woman in a beret, by Rembrandt painter, in black frame" (Obraz takieyze wielkosci, Zydowki w Birlecie, Rynbranta Malarza, wramach czarnych, No.75.), valued at 190 thalers, in the King's Bedroom of the Wilanów Palace in 1696 is probably the oldest preserved description of paintings by Rembrandt, today in the collection of the Royal Castle in Warsaw and known as The Scholar at his Writing Table and The Girl in a Picture Frame.
General Inventory of the Wilanów Palace from November 10th, 1696 also lists other works by Rembrandt, like "A large painting of an old man by Rembrandt in gilded frame and rounded top" (Obraz Rynbranta Malarza, Na ktorym Starzec wymalowany, wielki, wramach złocistych, u wierzchu okrągły, No. 210.), valued at 80 thalers, in the Upper Treasury with paintings from the Lower Gallery and Library, "A painting with Three Kings by Rembrandt in black frame" (Obraz Trzech Krolow, Rynbranta malarza, w ramach czarnych, No. 92.), valued at 100 thalers (possibly Adoration of the Magi from 1632, today in The State Hermitage Museum) and "A painting with Abraham and Hagar by Rembrandt in black frame" (Obraz Abrahama Z Agar Rynbranta malarza w ramach czarnych, No. 93.), valued at 100 thalers (possibly Abraham dismissing Hagar and Ishmael from about 1640, today in Victoria and Albert Museum), in the King's Dutch Study. The inventory lists many other Dutch paintings, including most probably The Loveletter by Johannes Vermeer: "A painting of a lady in gold dress playing lute, a girl giving her a letter, in black frame" (Obraz Damy graiącey na Lutni, w złotey Szacie, a dziewczyna list iey oddaie w ramach czarnych, No. 156.), valued at 35 thalers, and a copy (?) of The Milkmaid also by Vermeer: "A painting with a Dutch dwelling with a female cook pouring milk, in gilded copper frame" (Obrazek na ktorym Domostwo Holenderskie, a kucharka mleko zlewa, wramach miedzią złoconych, No. 180.), valued at 20 thalers, in the Upper Treasury. Paintings of "Portuguese Rabbi" and "a Jewish woman" were always together since. In 1720 Konstanty Sobieski, son of king John III Sobieski, sold the palace to Elżbieta Sieniawska, and after her death in 1729, her daughter, Maria Zofia, offered a lifetime lease on the palace to the successor of John III, King Augustus II the Strong (1670-1733), Elector of Saxony. Maria Zofia or her daughter Izabela Lubomirska, most probably sold the paintings, but ordered a copy of "a Jewish woman", which is still in the Wilanów Palace (Wil.1656). Before 1769 the paintings were transported to Berlin and were acquired by Friedrich Paul von Kameke (1711-1769), who was married to Marie Golovkin (1718-1757), a daughter of the Russian ambassador to Prussia. Georg Friedrich Schmidt created prints after the paintings entitled in French: "The bride's father paying her dowry" (Le Pere de la fiancée reglant sa dot) and "The Jewish Bride" (La Juive Fiancée). Under those titles the works returned to Poland acquired by king Stanislaus Augustus Poniatowski in 1777 and inventory numbers of his collection 207 and 208 were painted in the upper left corners of both paintings, still visible today. Sold again after king's death, they were transported to Vienna and in 1994 Karolina Lanckorońska offered them to the Polish people. Workshop copy of "The Jewish Bride" appears in the inventory of Danish royal Art Cabinet (Kunstkammer) of 1737, today in the National Gallery of Denmark (inventory number KMSsp406). Despite not having a similar composition the paintings should be considered as pendants (usually paintings of married couples or relatives), as according to tradition they depict a father and his daughter. They also have similar dimesions (105.7 x 76.4 cm / 105.5 x 76 cm), both are painted on oak wood panels, they have similar baroque black frames, most probably original or re-created after original, exaclty as in the inventory description of the Wilanów Palace. They were finally painted the same year and signed by the author (Rembrandt f. 1641 on both). At the end of 1631, Rembrandt moved from Leiden to Amsterdam. He initially stayed with an art dealer, Hendrick van Uylenburgh, who from 1628 may have been an intermediary for the sale of Rembrandt's works on the Amsterdam market. From 1631 to 1635, Rembrandt became chief painter of Uylenburgh's studio and produced a considerable number of portraits for wealthy and important Amsterdammers, such as the importer of fur Nicolaes Ruts. In 1634, he married Hendrick's relative, Saskia. Uylenburgh, born in about 1587, came from a Mennonite family, originally from Friesland, who emigrated to Poland and settled in Kraków, where Hendrick's father worked as a royal cabinet maker. His brother Rombout became a court painter. Hendrick was also trained as a painter, however he was primarly active as an art agent to King Sigismund III Vasa. He probably never practiced the profession of painter, at least no works have survived. Around 1612 he moved to Gdańsk. Hendrick arranged large art transports to Poland on behalf of the king, including paintings from the Netherlands and luxury goods, before starting his art dealership and studio in Amsterdam in about 1625. In December 1637 Hendrick commissioned Rembrandt to portray the Polish diplomat Andrzej Rej, who was on a secret mission to the English court for King Ladislaus IV and, while passing through Amsterdam. Van Uylenburgh received 50 guilders as a commission (after "Saskia, de vrouw van Rembrandt" by Ben Broos, p. 80). Around 1624 Hendrick married Maria van Eyck (d. 1638). The couple had three sons, including Gerrit (born in about 1625), who took over his father's business, and at least four daughters, Sara, Anna, Susanna and Lyntgen, at least one of whom was a well-known draftswoman. Sara Hendricksdr (d. 1696) must have been the oldest as she is mentioned first in the testament of her parents from 1634 and a deed of February 3, 1668 regarding inheritance of her brother Abraham. She was born in about 1626 or 1627, hence she was 14/15 years old in 1641. Her biblical name of the wife of Abraham, match perfectly the old title of the Warsaw painting "a Jewish woman" or "The Jewish Bride". The young girl surrounded by artists, was probably also introduced to painting by her father. Possibly playing in her father's studio she might have come up with an idea to be depicted in a picture frame, in the trompe l'oeil (trick the eye) style. Her father Hendrick who was about 54 years old in 1641 was therefore depicted as a scholar at his writing table, very similar to the etching by Rembrandt representing Cornelis Claesz Anslo, Mennonite Preacher from Amsterdam, created in 1641 (The Metropolitan Museum of Art), in the same year as the Warsaw paintings, or effigy of Menno Simons (1496-1561), preacher and theologian, whose followers formed the Mennonite church, by Jacob Burghart, published in 1683 (Museum Boijmans Van Beuningen). "Uylenburgh came from a family of Mennonites (a conservative branch of the Anabaptists), who emphasized study and personal interpretation of scripture and individual responsibility for one's own salvation" (after "Rembrandt/not Rembrandt in the Metropolitan Museum of Art" by Hubertus von Sonnenburg, p. 15). This explain why he was represented as a scholar. A significant Mennonite community was established in the mid-16th century in the Vistula river delta in Poland and near Warsaw, by 1624, in previously uninhabited areas, giving rise to the so-called Olęder colonization. On December 22, 1642 King Ladislaus IV issued the first privilege for Mennonites. It is highly possible that already in 1641 the king received a portrait of his artistic agent and his daughter, who could also find a suitable husband among Polish Mennonites. The same old man in rich costume was also depicted in a series of paintings by Rembrandt and his workshop, sitting and holding a stick. One dated '1645' from the collection of Pierre Crozat in Paris is in Lisbon (Calouste Gulbenkian Museum), other, which was in the ducal collection in Munich is today in Amsterdam (Museum het Rembrandthuis) and another in the Philadelphia Museum of Art. A version from the Princely Collections of Liechtenstein is attributed to Salomon Koninck (1609-1656), a member of van Uylenburgh's academy. It is possible that Stanisław Koniecpolski (1591-1646), Grand Hetman of the Crown, ordered or received the copies of the portraits from the royal collection, because two of such paintings are visible in a photograph by Edward Trzemeski taken around 1880 and showing the Yellow Room of his Pidhirtsi palace near Lviv in Ukraine. They were hung opposite the portrait of Jakub Ludwik Sobieski (1667-1737), son of John III, painted in Paris in 1699 by François de Troy (Wawel Castle, 10385, inscribed on the back: Peint à Paris par François de Troy en 1699). It is therefore also possible that the copies were made for Sobieski, who, interestingly, was most likely in Oława in Silesia in 1699, where his son Jan was born and not in Paris, so his portrait was perhaps made from study drawings. An old copy of Sara's portrait, perhaps made by a Venetian painter, is in the Museo Correr in Venice (Cl. I n. 0910).
Portrait of Sara van Uylenburgh (1626/27-1696) in a picture frame by Rembrandt, 1641, Royal Castle in Warsaw.
Portrait of Sara van Uylenburgh (1626/27-1696) in a picture frame by workshop of Rembrandt, ca. 1641, National Gallery of Denmark.
Portrait of Sara van Uylenburgh (1626/27-1696) by unknown painter after Rembrandt, mid-18th century, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
Portrait of Hendrick van Uylenburgh (ca. 1587-1661) at his writing table by Rembrandt, 1641, Royal Castle in Warsaw.
Portrait of Hendrick van Uylenburgh (ca. 1587-1661) with a stick by Rembrandt, 1645, Calouste Gulbenkian Museum.
Portrait of Hendrick van Uylenburgh (ca. 1587-1661) with a stick by workshop of Rembrandt, ca. 1645, Museum het Rembrandthuis.
Portrait of Hendrick van Uylenburgh (ca. 1587-1661) with a stick by workshop of Rembrandt, ca. 1645, Philadelphia Museum of Art.
Portrait of Hendrick van Uylenburgh (ca. 1587-1661) with a stick by Salomon Koninck, ca. 1645, Liechtenstein Museum in Vienna.
Portraits of Hieronim Radziejowski and his two wives by Ferdinand Bol, Rembrandt and followers
"Named Radziejowski, you will stay in the council, evil betrayals are your homeland counsels" (Radziejowskim nazwany zostajesz od rady, A Twe w ojczyźnie rady są złośliwe zdrady), portrayed Vice-Chancellor of the Crown Hieronim Radziejowski (1612-1667) in 1651 anonymous satirical poem.
In October 1632, thanks to his father's support, Stanisław Radziejowski (1575-1637), courtier of Queen Anna Jagiellon, Hieronim became a courtier of the newly elected King Ladislaus IV Vasa. He quickly gained significant influence, in 1634 became the starost of Sochaczew and in 1637 starost of Łomża and Carver of Queen's court. Around 1637, he married a wealthy widow Katarzyna Woyna née Męcińska (ca. 1608-1641), wife of Piotr Woyna (d. 1633), Steward of Lithuania and after her death, in June 1642, thanks to the support of the king, he married another wealthy widow Eufrozyna Eulalia Wiśniowiecka née Tarnowska (d. 1645). Eufrozyna was a heiress of a considerable fortune of her first husband Prince Jerzy Wiśniowiecki (Yuriy Vyshnevetsky), starost of Kamianka, and the legal custody of her and her property belonged to Prince Jeremi Wiśniowiecki (Yarema Vyshnevetsky), son of Raina Movila (ca. 1589-1619). By decision of the king Hieronim became her main heir. In May 1650 Radziejowski was married a third time to the richest widow in the country Elżbieta Kazanowska née Słuszczanka (1619-1671), whose husband died just four months earlier. Personal scandal always accompanied Radziejowski's political career. In 1640 he was elected a deputy to the Sejm, although there were demands for his removal from the chamber. At the first session of parliament, he was publicly accused by a nobleman of kidnapping his daughter from one of the monasteries in Warsaw and raping her (after "Hieronim Radziejowski: studium władzy i opozycji" by Adam Kersten, p. 60). Two years later, he married his second wife Eufrozyna in an atmosphere of scandal as the young widow had already agreed to another relationship, she was to marry Stanisław Denhoff. He allegedly paid a large bribe of 25,000 ducats to the royal couple, John II Casimir and Marie Louise Gonzaga, for receiving the office of Vice-Chancellor in 1650 and a year later, during a campaign against the Cossacks, when the king ordered his correspondence to be opened, a letter was found to the queen criticizing John Casimir and complaining that the king had a love affair with Radziejowski's wife, who accompanied him on the campaign. Hieronim's wife, who left the camp after the correspondence was revealed, filed for divorce. In 1652, on charges of insulting the royal name, he was sentenced to death, but fled to Vienna and then to Sweden. In 1655 he accompanied the Swedish forces invading the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. Before the Second World War in the Dressing Room of the Royal Palace on the Isle in Warsaw there were two small paintings attributed to Rembrandt's pupil Ferdinand Bol or an 18th century imitator of Rembrandt Christian Wilhelm Ernst Dietrich. Catalogues of the royal gallery described them as "A man in a half-figure with a mustache, dressed in brown, wearing a black headdress (Homme à mi corps avec des moustaches vêtu de brun et coëffé de noir, number 43) and "A woman in a half-figure in a brown dress, with a chain of precious stones and pearls in her hair, ears and on her head" (Femme à mi corps vetu de brun avec une chaîne enrichie des pierreries ayant des perles au col et aux oreilles, ainsi que sur la tête, number 54). The paintings had similar dimensions (30.3 x 25.3 cm / 35.5 x 24 cm) and similar composition, comparable to portrait of Hendrick van Uylenburgh and his daughter Sara by Rembrandt (Royal Castle in Warsaw), both created in 1641. The portrait of a woman from the Palace on the Isle was signed and dated on the right: Bol. f. 1641. This signature was published in a 1931 catalogue of the collection ("Katalog galerji obrazów Pałacu w Łazienkach w Warszawie" by Stanisław Iskierski, p. 53). Other versions of these portraits with slight differences (in man's hat and woman's face), attributed to Rembrandt, were owned in 1763 by count Friedrich Paul von Kameke (1711-1769), a member of Pomeranian noble family, who also owned mentioned portrait of Hendrick van Uylenburgh and his daughter. A German engraver, Georg Friedrich Schmidt, created etchings after these paintings signed in Latin and French (Rembrandt pinx./ G.F. Schmidt fecit aqua forti 1763. Du Cabinet de Monsieur le Comte de Kameke). Several years earlier, in 1735, Schmidt also created another etching after a painting attributed to Rembrandt (signed in Latin: Rembrandt Inv. e. pin: / Schmidt fec: 1735), portrait of a bearded man in eastern costume. His high fur hat and a coat lined with fur are very similar to those visible in a portrait of a man, most probably a Ruthenian Prince, by follower of Aert de Gelder, today in the National Museum in Warsaw (inventory number M.Ob.151 MNW). The latter painting is signed and dated: AV.Gelder.f / 1639 and comes from the collection of Piotr Fiorentini (1791-1858) in Warsaw. Similar costumes are visible in the Surrender of Mikhail Shein at Smolensk in 1634 by Christian Melich (Kórnik Castle) with king Ladislaus IV and his dignitaries and in the portrait of a Polish nobleman by Rembrandt, signed and dated: Rembrandt.f / 1637 (National Gallery of Art in Washington), similar hats are in a portrait of King John II Casimir by Daniel Schultz (Royal Castle in Warsaw), portraits of the members of the Sapieha family from Kodeń (Wawel Royal Castle) and similar fur coats with gold chains are in the self-portrait by Rembrandt or workshop (The Wallace Collection), a portrait of a youth by Pieter de Grebber (Liechtenstein Museum in Vienna) and a portrait of a man in a fur hat and coat by Pieter de Grebber (Private collection). In 1641, Radziejowski and other officials of the Masovian voivodeship become a member of a commission to consider border issues with the Duchy of Prussia. The same year, on October 7, 1641, the sixth and the last Prussian Homage took place in Warsaw. On July 13, the apostolic nuncio informed the Pope that the king had ordered balletti and a musical comedy to be prepared. Venison and fruit were brought from Kraków along the Vistula and excellent French, Italian and Rhine wines from Vienna. The recently finished Ujazdów Castle was prepared to host Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg and his court (after "Ostatni hołd pruski" by Jacek Żukowski). The Elector had the opportunity to admire the great wealth of the Polish-Lithuanian court, a part of which he appropiated during the Deluge few years later (according to Wawrzyniec Jan Rudawski, he "took to Prussia as a spoil, the most valuable paintings and silverware of the royal table"). The cuff of man's attire from the lost painting from the Palace on the Isle is very similar to cuffs from the costumes of Polish nobles, visible, among others, in the Coronation of the Virgin Mary by Herman Han (Oliwa Cathedral in Gdańsk), created between 1624-1627, epitaph of Andrzej Czarnecki (d. 1649), burgrave of Kraków and royal courtier (Saints Peter and Paul Church in Kraków) or costumes of two boys in the Feast of Herod by Bartholomeus Strobel, created in the 1630s (Prado Museum in Madrid). Similar costume with a coat lined with fur, an embroidered shirt and a bejewelled hat is also visible in the Feast of Herod by Strobel, in the painting entitled Prophet Nathan rebukes King David by Strobel's workshop (Private collection) and in the scene of Esther before Ahasuerus from the copper-silver sarcophagus of Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria, created before 1648 (Wawel Cathedral), undoubtedly inspired by the costumes at the court of Ladislaus IV. The costume of a woman from a pendant painting also resemble the garments from Strobel's paintings, including the Feast of Herod in the Prado and the attire of two women from Stoning of Saint Stephen, created by Strobel in 1618 for Stanisław Ostroróg (National Museum in Poznań). Her costume is also very similar to those visible in portrait of Jadwiga Rogalińska (National Museum in Poznań), painted in the 1640s, or in the portrait of Helena Opalińska née Zebrzydowska, created in the 1650s (Kalwaria Zebrzydowska Monastery). Some similar elements (chains, coat) are also visible in the etching with effigy of a lady in a fur hat, said to be Princess Owka Praxedis of Vitebsk (Vilnius University Library), created in 1758 after original from mid-17th century. Jadwiga Wypyska née Łuszkowska (ca. 1616- after 1648), mistress of Ladislaus IV, was depicted in similar dress in her portrait by Rembrandt and workshop (Private collection), painted in 1643, identified by me, as well as a lady in a portrait attributed to follower of Rembrandt or possibly Jan Victors (Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York, 29.100.103), signed and dated: Rembrandt f / 1643. In all three portraits by Rembrandt and followers the women are holding a fan, a symbol of chastity, carried by betrothed or married women in Venice and Padua. The portrait in the Metropolitan Museum has a pendant depicting a young man with a breastplate and plumed hat (MMA 29.100.102), he bears a striking resemblence to the man from the lost portrait from the Palace on the Isle in Warsaw, to the etching by Georg Friedrich Schmidt, the only preserved signed effigy of Hieronim Radziejowski, created in 1652 by Jeremias Falck Polonus (National Library of Poland) and to the pastel portrait of his son cardinal Michał Stefan Radziejowski by Jan Reisner (National Museum in Warsaw). In 1643 the first son of Radziejowski, Stanisław, was born. It would be a good opportunity to order images of his parents. The blond woman should be therefore identified as Radziejowski's second wife Eufrozyna Eulalia Tarnowska. Consequently the woman from the pendant portrait from the Palace on the Isle is his first wife Katarzyna Męcińska, who died in 1641. Before 1861 both portraits from the Met in New York were in the collection of baron Florentin-Achille Seillière (1813-1873) in Paris, whose daughter Jeanne-Marguerite (1839-1905) married in 1858 Boson de Talleyrand-Périgord (1832-1910), prince of Sagan (now Żagań in Poland) from 1845. The Silesian Duchy of Żagań, was a frequent stop for Kings Augustus II the Strong and Augustus III of Poland, as one of two main routes connecting Warsaw and Dresden ran through the town in the 18th century. It cannot be excluded that one of them offered the paintings to the Dukes of Żagań. Before 1667 Radziejowski purchased a series of tapestries with the story of Jacob, woven in the workshop of Jacob van Zeunen in Brussels in about 1650 (later acquired by Jan Małachowski and offered to the Wawel Cathedral), while his son Michał Stefan, who ordered the works of art in the workshop of Guillaume Jacob in Paris, employed at his court a Dutch-born architect and engineer Tylman Gamerski (who deisgned for him the Chapel of the Seminary in Łowicz and Nieborów Palce).
Portrait of Hieronim Radziejowski (1612-1667), Carver of Queen's court by Ferdinand Bol, ca. 1641, Palace on the Isle in Warsaw, lost.
Portrait of Katarzyna Radziejowska née Męcińska (ca. 1608-1641) holding a fan by Ferdinand Bol, 1641, Palace on the Isle in Warsaw, lost.
Portrait of Hieronim Radziejowski (1612-1667), Carver of Queen's court by Georg Friedrich Schmidt after Rembrandt, 1763 after original from about 1641, Philadelphia Museum of Art.
Portrait of Katarzyna Radziejowska née Męcińska (ca. 1608-1641) holding a fan by Georg Friedrich Schmidt after Rembrandt, 1763 after original from about 1641, Philadelphia Museum of Art.
Portrait of Hieronim Radziejowski (1612-1667), Carver of Queen's court by follower of Rembrandt, ca. 1643, Metropolitan Museum of Art.
Portrait of Eufrozyna Eulalia Radziejowska née Tarnowska (d. 1645) holding a fan by follower of Rembrandt, 1643, Metropolitan Museum of Art.
Portrait of a man in eastern costume, most probably a Polish-Lithuanian noble by Georg Friedrich Schmidt after Rembrandt, 1735 after original from the second quarter of the 17th century, Philadelphia Museum of Art.
Portrait of a man in eastern costume, most probably a Ruthenian Prince by follower of Aert de Gelder, 1639, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portraits of Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria and Kasper Denhoff by Gonzales Coques
In July 1637, the envoys of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Kasper Denhoff (1588-1645), voivode of Sieradz, Jan Lipski (1589-1641), bishop of Chełmno and John Casimir Vasa (1609-1672), the crown prince, came to Vienna to negotiate concerning the marriage of King Ladislaus IV Vasa to Archduchess Cecilia Renata, daughter of Emperor Ferdinand II.
Denhoff, surrounded by a numerous entourage, entered the capital of Austria with the greatest pomp. The people of the imperial court noticed that the retinue of the voivode of Sieradz and the bishop of Chełmno was richer and more splendid than that of the king's half-brother John Casimir, which they "attributed to the fame of the homeland and to the privilege of freedom". The talks with the emperor must have been difficult and the negotiations were so long that the date of the wedding agreed with the castellan Maksymilian Przerębski was postponed from September 2 to 9. The envoys - among whom Kasper Denhoff was particularly active - demanded, in accordance with the king's request, that the Duchy of Opole and Racibórz be transferred to him in the form of a deposit, which Ladislaus IV had long been trying to obtain for his family. He demanded that not only Cecilia Renata's dowry be secured in this principality, but also the sums that the Habsburgs had long owed to the Vasas (after "Wjazd, koronacja, wesele ..." by Alicja Falniowska-Gradowska, p. 11). Spanish envoys participated in the ongoing negotiations. On July 31, Bishop Lipski blessed the engagement and on August 9, he blessed the marriage per procuram (the husband was represented by Prince John Casimir). The Emperor rewarded both envoys with imperial titles, Denhoff, who was already a count of the Holy Roman Empire, became a prince and Lipski received the title of count for himself and his entire family. Kasper or Kacper Denhoff (Kaspar Dönhoff in German) came from a German noble family that in the 14th century settled in the Livonian lands of the Teutonic Order (Livonian Order). He was a son of Gerhard von Dönhoff, voivode of Dorpat (Tartu in Estonia) and Margarethe von Zweiffel and brother of Ernest Magnus Denhoff (1581-1642), voivode of Parnawa (Pärnu) and Gerard Denhoff (1589/90-1648), voivode of Pomerania. As a courtier of Sigismund III Vasa, after his conversion from Calvinism to Catholicism, Kasper gained considerable influence over the king as his close advisor. In 1627, he received the post of voivode of Dorpat, and in 1634 he was appointed voivode of Sieradz. He also obtained many other offices, which allowed him to build the financial power of the family. On January 11, 1633 in Vienna, together with his brothers Ernest Magnus and Gerard, who remained Calvinists, he was raised by Emperor Ferdinand II to imperial count. In the years 1640-1641 he tried to implement the Polish-Spanish military treaty. He played an important role at the court of Sigismund's successor, Ladislaus IV Vasa. In 1638 he went with Ladislaus to Baden near Vienna and in 1639 to Szczytno for a meeting with the Elector of Brandenburg. In order to gain a permanent presence at court, he eventually applied for the position of Marshal of the Queen's Court. He eventually took this position in 1639 despite resistance from Queen Cecilia Renata, who saw him as a supporter of the king's favorite Adam Kazanowski. From then on, he was almost constantly at court, often participating in Senate meetings. Despite the fact that he remained on good relations with Kazanowski, the opponent of the chancellor Jerzy Ossoliński, in 1645 he married his son Zygmunt to the daughter of the powerful chancellor - Anna Teresa. Shortly afterwards he became seriously ill and died on July 4, 1645. Denhoff was also a well-known patron of the arts. In Kruszyna near Częstochowa, that he received as a dowry of his wife Anna Aleksandra Koniecpolska (d. 1651), the Venetian architect in the royal service Tommaso Poncino built a beautiful palace for the voivode in the years 1630-1632, his main residence. The splendor of the palace can be proven by the fact that it was visited by kings Sigismund III, Ladislaus IV and John Casimir. The marriage of Kasper's daughter Anna to Bogusław Leszczyński (d. 1659), which took place on August 12, 1638 in Kruszyna, in the presence of Ladislaus IV and his wife Cecilia Renata, became one of the most important political and social events of its time. Earlier, between 1625 and 1628, Kasper rebuilt the medieval castle of Bolesławiec in the Renaissance style, which was however destroyed by the Swedes in 1704, during the Great Northern War. In 1636, Denhoff bought Ujazd near Tomaszów Mazowiecki and the castle from the Szczawiński family, which he thoroughly rebuilt. This brought him closer to Warsaw, where he also owned a wooden mansion, built before 1643, probably according to the designs of the royal architect Giovanni Battista Gisleni. This mansion was burned down during the Deluge (1655-1660), and around 1669 a brick mansion was built for Ernest Denhoff (now Potocki Palace). Almost nothing is known of his other patronages, but as an imperial prince, close to the splendid court of Ladislaus IV and his first wife, his artistic collections were undoubtedly exquisite. In 1633 Ill.mi et excell.mi D. D. Georgii Ossolinii ... by Jerzy Ossoliński, Domenico Roncalli and Kasper Denhoff was published in Rome and Marcin Małachowski dedicated his Normae logicae tribvs mentis hvmanae ..., published in Kraków in 1638, to the voivode of Sieradz. Kasper was buried in the chapel of Saint Paul of Thebes (Denhoff Chapel) at the Jasna Góra monastery, which he founded in 1644. In 2002, a miniature portrait of a man, half-length, in a green costume with a fur-lined cape and a fur hat by circle of Gonzales Coques was sold in Amsterdam (oil on copper, 15.9 x 13 cm, Christie's, auction 2546, May 14, 2002, lot 27). Coques, born around 1614 in Antwerp, became an apprentice in the workshop of Pieter Brueghel the Younger, then apprenticed to David Rijckaert II. He is best known for his small portraits and cabinet paintings. Anthony van Dyck's influence earned him the nickname "Little Van Dyck". He probably traveled to England, where van Dyck was active. In 1640-41 he joined the guild of Saint Luke in Antwerp and in 1643 he married Catharina Ryckaert, the daughter of David Rijckaert II. He enjoyed the favor of both Catholic and Protestant patrons, such as Don Juan José de Austria (1629-1679), illegitimate son of King Philip IV of Spain (cousin of Ladislaus IV), as well as the Dutch court in The Hague. In the National Museum in Warsaw there is his portrait of a man with a cythara (M.Ob.1701 MNW). The costume of the man is obviously Polish or Hungarian from the first half of the 17th century and a similar hat can be seen in an equestrian portrait of a Polish-Lithuanian nobleman (so-called John III Sobieski), in the Goodwood House (oil on canvas, 62.9 x 47.6 cm). The appearance of "Sobieski" with a pearl earring recalls the portrait of Jan Stanisław Jabłonowski (1600-1647) by Rembrandt (National Gallery of Art, 1937.1.78), identified by me. He wears the Spanish costume of the imperial court. From 1638 Jabłonowski was cupbearer of the queen's court and from 1642 he was Crown Sword-bearer. Very similar costumes are visible in an engraving showing the banquet in honor of Marie Louise Gonzaga and the solemn entry of the embassy of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth with Gerard Denhoff, voivode of Pomerania - "The wedding feast of the king and queen of Poland" (Le festin nuptial du roy et de la reine de Pologne) and "The magnificent entry of the Polish ambassadors on September 19, 1645 into the city of Paris" (La magnifique entrée des ambassadeurs de Pologne le 19 septembre 1645 dans la ville de Paris). It was created by François Campion in Paris and probably sponsored by the King of Poland. Gerard, who as voivode of predominantly Protestant Pomerania, usually wore French-style clothing as in his effigy against the view of Malbork Castle by Willem Hondius from 1643 (collar and armor). In his portrait by the Gdańsk painter, painted shortly before his death around 1648 (National Museum in Kraków, MNK I-902), he wears such a costume in the fashion of the late 1640s. In 1645, however, he was the representative of the king and the entire Commonwealth, not just Pomerania, which is why he was depicted wearing national costume. His brother Kasper was a voivode of the predominantly Catholic territories near Sieradz, where the majority of the nobility wear traditional costumes - żupan kaftan and delia coat. Coques frequently used study drawings or perhaps even ready-made canvases as models. In the mentioned equestrian portrait from Goodwood House he reused the composition most likely introduced by Peter Paul Rubens in his portrait of Don Rodrigo Calderón, Count of Oliva on horseback, favorite minister of the Duke of Lerma, painted around 1615 (Windsor Castle, RCIN 404393). It was repeated in the portraits of Sigismund III by Cornelis de Vos (Nationalmuseum in Stockholm, NMGrh 2012) and his son Prince Ladislaus Sigismund by Rubens' studio (Wawel Royal Castle, 6320), as well as in the portrait of Don Diego Felipez de Guzmán (1580-1655), 1st Marquess of Leganés by Gaspar de Crayer (Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, GG 9112) and Albert VII, Archduke of Austria againts the view of Ostend by circle of Rubens (private collection). Portrait of Beatrice de Cusance (1614-1663), Princess of Cantecroix by Anthony van Dyck from about 1635 (Windsor Castle, RCIN 404404), Coques repeated in his portrait of unidentified ladies in the Czartoryski Museum (XII-262) and private collection (sold at Lempertz Cologne, May 17, 2008). The composition from the portrait of Anne of Austria, Queen of France by workshop of Peter Paul Rubens (Louvre Museum, INV 1794 ; MR 984) he used in his portrait of a seated woman in an interior (private collection, oil on copper, 15.2 x 11.4 cm). It is difficult to imagine that important dignitaries or monarchs would stand for several hours for a portrait as some believe was the practice in the past. These effigies were therefore based on study drawings (or some other effigies like miniatures) prepared by court artists or agents of different workshops, then sent abroad to the best artists. Although there were talented painters and other craftsmen in Poland-Lithuania, their number was not as great as abroad and foreign workshops, as today, undoubtedly offered lower prices, better quality or other factors such as easier distribution of effigies in Europe or speed in execution of work. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, some people, who generally had no idea of Polish-Lithuanian tolerance, diversity and trade, believed that the use of foreign workshops was a sign of the nation's inferiority, unable to produce such goods on its own. They would probably think the same thing about 21st century countries that rely heavily on outsourcing. The man in Polish-Hungarian costume resemble Ernest Magnus Denhoff, voivode of Parnawa, from his portrait created by circle of Daniel Rose in Königsberg in about 1640 (Museum of Warmia and Masuria in Olsztyn, MNO 120 OMO), as well as the effigy of Gerard Denhoff against Malbork Castle by Willem Hondius, brothers of Kasper. He should be identified as the voivode of Sieradz who in 1642 linked up with the most powerful family of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania - the Radziwills, by marrying his son Stanisław (d. 1653) to Princess Anna Euphemia (1628- 1663), daughter of Alexander Louis Radziwill (1594-1654), Grand Marshal of Lithuania. It is also worth noting the resemblance to the effigy of Jean-Michel, Viscount of Cigala from a print made by Nicolas de Larmessin I in Paris around 1690 (National Library of Poland, G.21943/II). According to the description in French under his effigy, Jean-Michel was an important notable of the Ottoman court of Constantinople, but he decided to convert to Christianity and after freeing several Christian slaves, he went to Poland in 1651. There, in Warsaw, around 1654, he was baptized and named Jean-Michel by Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga. Later he served as an artillery captain in the imperial army and in 1662 he went to France, where he was received by Louis XIV. In both cases, the links with the royal court of Poland-Lithuania are undeniable. Since the main dignitaries of the queen's court commissioned their effigies from Coques' workshop around 1642, Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria should also have at least one of her portraits made by this painter. Around 1642 Jan van den Hoecke, a Flemish painter active in Antwerp, created a series of effigies of the queen's brother, Archduke Leopold Wilhelm, in armor (Kunsthistorisches Museum, GG 3284 and sold at Sotheby's London, April 30, 2014, lot 743). Earlier, around 1634-1635, probably also in Antwerp, a full-length portrait of King Ferdinand of Bohemia and Hungary (1608-1657) in national costume (Kunsthistorisches Museum, GG 697) was made. The Habsburgs evidently used the same practice as the monarchs of Poland-Lithuania, so the efforts of some art historians trying to find confirmation that the artist and sitter met in person at the time of the portrait's creation are sometimes futile. In 2014, a portrait of a lady in a black dress by Flemish School, 17th century was put up for sale in Vienna, Austria (oil on canvas, 95 x 74 cm, Dorotheum, June 24, 2014, lot 121). Her rich jewelry and marten fur stoles draped over the woman's shoulders indicate that she is a wealthy aristocrat. It has been suggested that zibellino, that is sable skin of which Poland-Lithuania was a major exporter in the 17th century (except Russia), was a symbol of fertility or was associated with pregnancy and childbirth. On February 7, 1642 a tragedy struck the royal couple of the Commonwealth, their daughter Maria Anna Isabella, born a month earlier (January 8, 1642), died. The princess's godfather was Ladislaus' cousin, King Philip IV of Spain, who was replaced by an unknown envoy at the baptism ceremony on January 11, 1642 at the Royal Castle in Warsaw. The body of Maria Anna Isabella was transported to Kraków, where her funeral took place on April 13, 1642 at Wawel Cathedral. A book, most likely a prayer book, lies on a table next to the woman. Her costume resembles that seen in a portrait of an unknown woman called Mary Hawtrey (1598-1661), Lady Bankes by the Flemish painter (Sudbury Hall, Derbyshire, NT 653181), generally dated to the 1640s, as well as a portrait of the king's mistress Jadwiga Wypyska née Łuszkowska holding a fan by Rembrandt and workshop, dated '1643' (private collection), identified by me. These clothes are most likely reminiscent of Italian Renaissance fashion, visible in the portrait of a young lady, better known as Antea, by Parmigianino (Museo di Capodimonte in Naples, Q 108). The style of the painting is very similar to that of a portrait of a woman holding a fan, attributed to Gonzales Coques (sold at Millon & Associés, Hôtel Drouot, June 22, 2022, lot 35) and the portrait of Archduke Leopold Wilhelm by Coques (Kunsthistorisches Museum, GG 5461). The features of the woman with the protruding lower lip are clearly those of the Habsburgs and she closely resembles Cecilia Renata from her effigies by workshop of Frans Luycx (Wilanów Palace, Wil.1144 and Alte Pinakothek in Munich, 6781), as well as portraits by court painter Peter Danckerts de Rij.
Portrait of Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria (1611-1644) by Gonzales Coques, ca. 1642, Private collection.
Portrait of Kasper Denhoff (1588-1645), voivode of Sieradz or Jean-Michel, Viscount of Cigala by Gonzales Coques, ca. 1642 or after 1651, Private collection.
Equestrian portrait of a Polish-Lithuanian nobleman, possibly Jan Stanisław Jabłonowski (1600-1647) by Gonzales Coques, ca. 1642, Goodwood House.
Portraits of King Ladislaus IV Vasa and his sister Infanta Anna Catherine Constance Vasa by Gaspar de Crayer
On October 6, 1641, in the courtyard of the Royal Castle in Warsaw, Frederick William (1620-1688), hereditary Margrave of Brandenburg, Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia, paid homage to the elected monarch of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth Ladislaus IV Vasa. He had done so in person and not, as he had requested, through an authorized representative, due to objections raised in Poland. The parliament wanted to tighten the conditions for granting the fief, pointing out that Frederick William's father was evading the fulfillment of his fief duties (after "Warmia i Mazury" by Stanisława Zajchowska, Maria Kiełczewska-Zaleska, Volume 1, p. 140).
"Although Electors of the Holy Roman Empire, Frederick William's predecessors were exceedingly cautious, and did not play an influential role in German politics, remaining among the second tier of German princes. Their territories were relatively small and poor, scattered across the north German plain, without natural defences. Brandenburg was known as "the sandbox of Europe" because of its poor soil. In total, these territories had a population of about 1.5 million in 1648, and the Elector's capital of Berlin was a smallish town of about 12,000. Prussia was a somewhat more promising territory, as it had several large and prosperous towns, whose wealth was generated by the lucrative trade in Polish wheat shipped down rivers to the Baltic coast where it was loaded onto ships bound for Western Europe" (after "Kings and Their Sons in Early Modern Europe" by Mark Konnert, p. 168). However, as a hereditary and increasingly authoritarian ruler, he had a certain advantage over the elective monarchs of the Commonwealth, whose power was limited by the Sejm. The German duke, who dreamed of unifying German-speaking lands and creating an empire, was obviously disgusted by the diversity, laxity and apparent "disorder" of the Commonwealth's royal court during his visit to Warsaw. The feast that followed the tribute was spoiled by a large number of guests, many of whom had no invitation, and poor organization, so that even the king's table was served with barely warm dishes and in small quantities. So, when the next day (October 8, 1641), the elector received the royal court in his headquarters in Ujazdów, he wanted to demonstrate good organization. "A fairly decent and plentiful feast was served. This pleasant atmosphere was disrupted by the news that 20 silver plates had been stolen from the elector". In the following days, other feasts and festivities took place. A magnificent favola drammatica about Aeneas (L'Enea) by Virgilio Puccitelli was performed in Italian and there were fireworks on the Vistula, which however "did not really please the king". On October 10, there were dances at the Warsaw Castle, in which Frederick William also took part. "The Infanta [Anna Catherine Constance] was also present, delighted and deceived by the hope that the elector would ask her to be his life companion", according to Albert Stanislaus Radziwill. However, the infanta's hopes proved illusory. The elector left, without mentioning anything about his matrimonial intentions (after "Polityka pruska ..." by Józef Włodarski, p. 24). Ladislaus' half-sister could offer a substantial dowry, but no significant hereditary territorial claim. Anna Catherine Constance was also Catholic, but apparently, on the Polish side, religion was not a big issue. On December 7, 1646, in The Hague, Frederick William concluded a more politically and territorially advantageous marriage, proposed by the Brandenburg diplomat Joachim Friedrich von Blumenthal, as a partial solution to the Jülich-Cleves-Berg question, with Protestant Princess Louise Henriette of Nassau (1627-1667), daughter of Frederick Henry, Prince of Orange. After the War of the Jülich Succession (1609-1610), the Protestant territories (Cleves, Mark and Ravensburg) passed to Brandenburg and the Catholic territories (Jülich and Berg) were assigned to Palatinate-Neuburg. In 1636, the Wittelsbach dukes of Palatinate-Neuburg set up their headquarters in Düsseldorf, because Jülich-Berg was significantly larger and more important than Neuburg. When after the end of the Thirty Years' War in 1648, Cleves formally passed into the hands of the Elector of Brandenburg, thus becoming an exclave of the Margraviate of Brandenburg, Frederick William also resided there with his wife. At this time, Anna Catherine Constance, who married in Warsaw in 1642 Philip William of Neuburg (1615-1690), son and successor of Wolfgang William (1578-1653), Count Palatine of Neuburg and Duke of Jülich and Berg, frequently resided in nearby Düsseldorf (she was buried in the Jesuit church in Düsseldorf). So the elector and his Polish-Lithuanian would-be fiancée lived not far from each other. The effigies of such a rich princess, sister of two elected Polish-Lithuanian monarchs, cousin of the King of Spain and the Emperor must have been multiple before the Deluge, it is one of the dubious "achievements" of the "Great Elector" and his allies that very little remains today. At the Philadelphia Museum of Art is a portrait of a woman holding a white feather fan, attributed to the Flemish or Dutch school of the 1630s (oil on canvas, 200 x 117.8 cm, W1899-1-2). The painting was purchased with the W. P. Wilstach Fund in 1899 and comes from the collection of French baron, art collector and writer Jean-Charles Davillier (1823-1883). In the 1899 catalog of paintings at the Blakeslee Galleries, the painting was listed as "Portrait of Princess Palatine", which was most likely the traditional title of this painting, and with attribution to the Dutch painter Pieter Codde (no. 34, p. 60-61), which is now rejected. In the same catalog, there was a portrait of Anna Catherine Constance's father-in-law, Wolfgang William, in Spanish costume, from the collection of the Prince of Turn and Saxe, painted by Anthony van Dyck or his workshop (no. 48). This was a copy of a portrait painted by van Dyck around 1628, probably in Antwerp, which comes from the gallery in Düsseldorf, today in the Neuburg State Gallery (402). Although Count Palatine traveled frequently, including several times to Brussels, the painting was most likely made from study drawings or other effigies. The style of the full-length portrait in Philadelphia closely resembles paintings attributed to Gaspar de Crayer (1584-1669), court painter to the governor of the Spanish Netherlands, Cardinal-Infante Ferdinand of Austria, cousin of Anna Catherine Constance. Among the closest analogous works is the full-length portrait of Bishop Antonius Triest (1576-1657) from about 1627-1630 (Museum of Fine Arts Ghent, 1948-Z) and Christ on the cross surrounded by donors, painted between 1630-1658 (Collections of the Public Social Welfare Centre in Brussels, T 20). The woman in the painting closely resembles the Polish-Lithuanian princess in the portraits in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna (GG 1732, GG 5611) and the Alte Pinakothek in Munich (6728). Her costume and pose are also similar to those in the paintings mentioned. Another full-length portrait painted very similarly, both in terms of style and composition, is the portrait of Anna Catherine Constance's half-brother King Ladislaus IV with a greyhound, now kept at the National Institute of Folk Culture in Strážnice (oil on canvas, 224 x 148 cm, 771093). It comes from the collection of the lord of Strážnice - Francesco Magni (Franz Magnis von Straßnitz, 1598-1652), Bohemian-Moravian nobleman from a family of Milanese merchants, older brother of Valeriano Magni (Valerian von Magnis, 1586-1661), Capuchin monk and diplomat at the court of Ladislaus IV. From 1646 to 1649, Francesco was governor of the Duchy of Opole and Racibórz, which had been pledged to Ladislaus IV in 1645 in exchange for the unpaid dowry sums of his mother, his stepmother and his wife, and the loan he had made to the emperor. In 1646 he moved to Warsaw and probably at that time he received the king's portrait, later mentioned in the posthumous inventory of his property in Strážnice on March 12, 1654. In this portrait, the king wears a fashionable French costume of the time - a Parisian-style beaver hat (chapeau à la mousquetaire), a doublet with a number of ribbons with metal tag finials at the waist (aiguillettes) and tight riding boots of the à revers épanoui type (after "Portrait of Władysław IV from the Oval Gallery ..." by Monika Kuhnke, Jacek Żukowski, p. 64, 66, 76). The painting was probably created at the same time as the portrait of Ladislaus at the Royal Castle in Warsaw (ZKW 559 dep.) or the painter used the same set of study drawings or effigies by other court painters. The king and his sister Princess Palatine (Serenissima Principi ac Domina D. ANNÆ CATHARINÆ CONSTANTIÆ Comiti Palatina Rheni ..., as called in a print with her effigy by Dutch engraver Theodor Matham) wear black costumes, which could indicate mourning in the family, perhaps after the death of the king's daughter Maria Anna Isabella (February 7, 1642) or the king's wife Cecilia Renata of Austria (March 24, 1644). Ladislaus' facial features differ slightly from other effigies of the king, which is another indication that the portrait was based on study drawings. The style of the king's image is similar to that of his sister and other mentioned paintings by de Crayer. Certain elements, such as the feathers or the dog, closely resemble the style of a large altar painting by Gaspar, produced around 1638 for Our Lady of St. Peter's Church in Ghent and representing Saint Benedict receiving Totila, king of the Ostrogoths. In this painting the man on the left in front, holding a nadziak war hammer, is dressed in a costume typical of Polish-Lithuanian or Hungarian-Croatian nobles. The painting in Strážnice also recalls the portrait of Ladislaus's artistic agent Jan Bierens (1591-1641) by de Crayer or his workshop (Arnot Art Museum). Besides the permanent agents in the Spanish Netherlands like Bierens and Georges Deschamps, many Commonwealth envoys were engaged in different tasks of commissioning or purchasing works of art for the king. In 1640, Bierens welcomed Krzysztof Korwin Gosiewski (died 1643), voivode of Smolensk and ambassador to France (Sérénissime Xristophorus Corvinus Gosiewski, palatin de Smolenskouw etc., ambassadeur extraordinaire du Roy de Poloigne et de Suède vers le Roy de France), who left with him several boxes intended for transport to Poland. During his stay in Antwerp, Korwin Gosiewski submitted a request to Cardinal-Infante Ferdinand for exemptions from customs fees and other municipal taxes. On May 12, 1640, the regent of the Southern Netherlands accepted the free exit of these objects from Antwerp (after "Liber memorialis Erik Duverger", p. 361).
Portrait of King Ladislaus IV Vasa (1595-1648) with a greyhound by Gaspar de Crayer, ca. 1642-1644, National Institute of Folk Culture in Strážnice.
Portrait of Infanta Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651), Princess Palatine by Gaspar de Crayer, ca. 1642-1644, Philadelphia Museum of Art.
Marriage or betrothal portrait of Princess-Infanta Anna Catherine Constance Vasa and Prince Philip William of Neuburg by Ferdinand Bol
On June 8, 1642, the wedding of Princess-Infanta Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) with Philip William (1615-1690), Prince of Neuburg, took place in St. John's Cathedral in Warsaw. The Princess was led to the altar by her brothers: John Casimir on behalf of the Emperor, and Charles Ferdinand on behalf of the King of Spain (cousins of Anna Catherine Constance). Crowds of curious Varsovians filled all the streets and squares near the church.
King Ladislaus IV celebrated his sister's wedding at the Royal Castle. Many representatives of foreign kings and princes were invited to feast at the long banquet table. "After dinner everyone went down to the Diet Chamber, where they danced until nightfall" (after "Pan Jakobus Sobieski" by Mieczysław Bohdan Lepecki, p. 296). The wedding celebration lasted eight days and featured a dramma musicale and ballet performance. Queen Cecilia Renata held dances and masked ballets with the dueling Amazons and Cupid descending from the sky. The newlyweds reciprocated with a ballet of cavaliers. "Everyone was excellently trained in somersaults, especially the prince himself", wrote in his diary Albert Stanislaus Radziwill (1593-1656), Grand Chancellor of Lithuania. The Brandenburg envoy turned out to be less skillful, as he fell while dancing with Anna Catherine Constance (after "Pamiętniki Albrychta Stanisława X. Radziwiłła ...", Volume 2, p. 64-68, 74). Librettos of two ballets by Virgilio Puccitelli (1599-1654) staged on June 12 and 16, 1642 in Warsaw, preserved at Skokloster Castle in Sweden (Atlante languente, introduttione di balletto di dodeci eroi ..., Pol 70 and Attioni sceniche, rappresentate nelle reali nozze della serenissima infanta Anna Catherina Constanza ..., Pol 67). Nuncio Mario Filonardi (1594-1644) wrote in his letters to Rome about preparations for the staging of comedia con machine and ballet. On June 23, 1642, at the end of the princess's wedding celebrations, the Italian comedy in musica with intermedia was staged (after "Agostino Locci ..." by Hanna Osiecka-Samsonowicz, p. 111). The couple spent their honeymoon in Warsaw and on trips to nearby royal and magnate residences. On June 16, John Casimir invited all guests to his palace in Nieporęt, where he hosted them for three days. On June 30, the couple set off for their duchy, going through Hungary in order to avoid the Swedish troops plundering Germany (after "Polskie królowe: Żony królów elekcyjnych" by Edward Rudzki, p. 116). The royal couple accompanied them to Kraków and they stayed at Wawel for several days. The farewell took place at Casimiria Market Square. Anna Catherine Constance took her dowry on "70 carts full of things and equipment", and Ladislaus also gave her a valuable relic - part of skull of Saint Stanislaus Kostka (the remaining part was given to the Kraków Jesuits). "He loves his sister very much and will spare no effort or expense to make good decisions for her. In addition to so many qualities of heart and mind, she will bring into her husband's house considerable treasures in jewels and money, both from her parents' inheritance and accumulated from various places, or which she saved from her own income allocated to herself by the estates of the Commonwealth, having almost no expenses and living at the king's expense, who supports her just like he does his brothers when they stay at the court", reported about Ladislaus' sister papal nuncio Honorato Visconti to Cardinal Francesco Barberini (July 15, 1636 from Warsaw). The Princess-Infanta was very pious and nice in contacts with people, which made her popular among Poles. Despite the Swedish threat and the king's advice, the princess-infanta did not want to entrust her treasures to the king "not trusting the country's appetite", as commented Albert Stanislaus Radziwill. Her dowry in cash amounted to 243,333 thalers and jewelry and silverware were valued at 443,289 thalers. Bishop Paweł Piasecki (1579-1649) lamented that "With her, a huge treasure of cash, gold and silver utensils and all kinds of valuables moved abroad; a treasure that could be estimated without any mistake at two million thalers and that would not be allowed to be taken away from the richest country, especially for the benefit of a marriage, which ultimately turned out to be childless" (compare "Dynastia Wazów w Polsce" by Stefania Ochmann-Staniszewska, p. 166). Philip William, arrived in Warsaw on February 27, 1642. The engagement of 23-year-old Anna Catherine Constance took place on March 16, less than three weeks after the suitor's arrival, after the mass, in the chamber of King Ladislaus IV in the Royal Castle, in a small circle of family and senators. Italian traveler Giacomo Fantuzzi (1616-1679) from Ravenna, who spent seven years in Poland, arrived in Neuburg on September 14, 1652, where he visited the local palace church of the Blessed Virgin Mary and noted in his travel diary: "In this church, many beautiful, precious silver items can be seen [...] donated by the last princess, the young wife of His Grace the Young Prince, Honourable Anna Catherine Constance, Polish princess, the sister of the local king, who died suddenly last year in Cologne, it was said, because of the joy she felt at seeing her husband [...] returning victorious from the war. As if struck by lightning, she fell dead in his presence as soon as they entered the first of their chambers, before they could even sit down" (after "Brzydka Wazówna" by Hanna Widacka). Aristocrats and members of the upper class in European countries frequently commemorated such important events in their lives as engagement or marriage through portraits or other paintings. A good example is the marriage or betrothal portrait of William II (1626-1650), Prince of Orange, aged fourteen, and Princess Mary Henrietta Stuart (1631-1660), aged nine, by Anthony van Dyck, painted in about 1641 (Rijksmuseum, SK-A-102). The marriage of the Polish vassal (until 1657) Frederick William (1620-1688), Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia to Louise Henriette of Orange (1627-1667) was commemorated in a 1646 painting by Johannes Mijtens (Museum of Fine Arts of Rennes, INV 801.1.15) and the consummation ceremony after the marriage of the "Brigand of Europe" was immortalized by Jürgen Ovens in his painting created around 1654 (Nationalmuseum in Stockholm, NM 908). Several splendid works must also have commemorated the marriage of Ladislaus' sister, but it seems that they were all lost or destroyed. At the time of the princess's marriage, Ferdinand Bol, a student of Rembrandt, created a magnificent wedding portrait of his master, although it should be noted that the man looks nothing like the other portraits of the famous Dutch painter. The painting, known as "Rembrandt and Saskia in a landscape", shows them in a truly princely pose and outfit. Unlike the rulers of the Commonwealth, the prince of painters knew how to demonstrate his wealth and the splendor of his court in Amsterdam. Not only did he (apparently) commissioned his wedding portrait, but they both wore very expensive costumes. There is no indication that these were a painter's fantasy and they appear very realistic, which means that "Prince Rembrandt" did not spare money for luxury fabrics and furs. "Princess Saskia" in a pose reminiscent of her portraits as Flora, Roman goddess of flowers and fertility (also known as portraits in Arcadian costume, painted by Rembrandt and his workshop), holding flowers in her right hand, was depicted in white satin dress, lynx fur and jewelry and pearls. Her husband, like many other aristocrats of the time, wears a breastplate or gorget, a silk tunic and coat richly embroidered with gold and silver thread. The opulence of their costumes is only comparable to the mentioned portrait of William of Orange and Princess Mary Henrietta by van Dyck. From the point of view of a 17th century painter of Dutch merchants, this portrait makes absolutely no sense, which is why some art historians no longer consider it the portrait of Rembrandt and Saskia and on the RKD research platform the painting is titled "Richly dressed couple in a landscape" (Rijk gekleed echtpaar in een landschap). The painting, now in Somerleyton Hall, Suffolk (oil on canvas, 127 x 152.5 cm), comes from the collection of Claude-Alexandre de Villeneuve (1702-1760), Count of Vence in Paris. It is neither signed nor dated and research suggests around 1644-1645 as a possible creation date, so a slightly earlier date (1642) is also possible. The woman's resemblance to the bride from the Wedding of Samson (Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden, Gal.-Nr. 1560), as well as to the other effigies of the Princess-Infanta, identified by me, is great. The man, on the other hand, resembles Anna Catherine Constance's husband, especially from an engraving with his portrait by Peter Aubry II (National Library of Poland, AFG.57/IV), earlier engraving by Matthias Ottonis Crisp (Austrian National Library, PORT 00051175 01) and his painted portrait made around 1685 (Stadtmuseum Düsseldorf, B 11).
Marriage or betrothal portrait of Princess-Infanta Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) and Prince Philip William of Neuburg (1615-1690) by Ferdinand Bol, ca. 1642, Somerleyton Hall.
Portraits of Jadwiga Łuszkowska and Jan Wypyski by Rembrandt and workshop
Ladislaus IV Vasa met Jadwiga Łuszkowska when he was in Lviv in 1634 with his half-brothers, John Casimir and Alexander Charles Vasa. The king came to the city due to the uncertain Polish-Ottoman situation and the threat of war.
Jadwiga was born around 1616 in Lviv, as the daughter of a merchant Jan Łuszkowski (died 1627) and his wife Anna (died after 1635). She and her mother were then in serious financial problems, they inherited debts from the deceased Łuszkowski. The cloths that he and his partner bought on credit burned down in Jarosław and barges flowing down the Vistula to Gdańsk that belonged to him, sank. A few days after the king's arrival in Lviv, Anna Łuszkowska arranged for a visit to him, taking her beautiful daughter with her. She must have made a great impression on the king, as shortly after the meeting, the beautiful Jadwiga left the house in which she had lived so far and moved to the royal apartments and her mother Anna began to bring large sums of money to the town hall, paying off the creditors, and soon she bought the entire house, only part of which had belonged to her so far. Anna also received, among others, the right to fell wood for fuel in the royal forests and exemption from municipal taxes. Lviv roared with gossip and envious people, like Rafał Jączyński described Jadwiga as: femina formosa sed vitiata (a beautiful, though spoiled woman). The Grand Chancellor of Lithuania, Albert Stanislaus Radziwill, wrote about her many years later as a woman famous for her shame and infamy. Ladislaus took his mistress with him to Warsaw and gave her rooms on the second floor of the Royal Castle. A few years later, identical rooms, except that on the first floor, will be occupied by his wife Cecilia Renata of Austria. In 1635, Jadwiga gave birth to the king's son, Władysław Konstanty (Ladislaus Constantine Vasa), and soon accompanied the monarch on his journey to Prussia and Gdańsk, being present during the signing of the Polish-Swedish truce in Sztumska Wieś. The French envoy Charles Ogier who saw her in Gdańsk wrote in his diary on February 1, 1636: "After breakfast, I was able to comfortably watch the departure of the king's mistress, whom I greatly wanted to see. She is very beautiful, and also full of great charm, with dark eyes and hair, and a very smooth and fresh complexion. But she does not have full freedom, because she is constantly guarded by men and women". Jadwiga's position offended the conservative Polish nobility, there was talk of debauchery at the Royal Castle, and Ladislaus was called publicus concubinariusi (public adulterer). Senators expressed open dissatisfaction, and even the Church was involved in the matter. The papal nuncio Honorato Visconti said that the beautiful Jadwiga ensnared the king with magic and Primate Jan Wężyk also suspected her of dark powers. The king, however, continued to live with his favourite. The idyll was destroyed by the king's marriage to Archduchess Cecilia Renata in 1637. The new queen, placed in the first-floor chambers just below Jadwiga's chambers, put pressure on Ladislaus to get rid of his beautiful mistress from the court. He, nevertheless, did not want to lose her. She moves first to the royal Ujazdów Castle in Warsaw. When the furious queen learns about the still-ongoing romance orders Łuszkowska to be sent back to Lviv. Soon the Ujazdów Castle was to be decorated with large canvases glorifying the queen, described in Adam Jarzębski's "Short Description of Warsaw" from 1643, who knows, maybe created by Rembrandt. Economically, the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth was strongly associated with the Dutch Republic, but politically, due to the family ties of the Vasas and the Habsburgs, they were opponents, therefore, no Polish monarch could openly patronize an artist in the Dutch Republic. In 1637 Jadwiga was married to Jan of Wypych Wypyski of Grabie coat of arms, one of king's courtiers, to whom the king gave the land of Merkine in the forests of Neman in Lithuania, his favorite hunting spot. This donation gave rise to a court joke in Latin that the king gave Wypyski not the Merkine land (merecensem) but the harlot's land (meretricensem). Wypyski, who between 1626 and 1628 was a notary at the court, also become standard-bearer of Nur and Royal equerry in charge of the King's stables and he received land in Warsaw. The secretaries and notaries were educated people who knew foreign languages, so was also Wypyski. There is no information whether he had children, it is possible that he preferred men to women, therefore, marrying a king's favourite would not be a great sacrifice for him. Even though that beautiful Jadwiga left the court and the capital with her husband, she was visited by the king whenever possible. He stayed there for several months. Ladislaus IV especially liked hunting and organized hawk and falcon hunts for white herons in order to obtain rajers (long feathers on the head of a heron), as an element of hat decoration. If the heron was not seriously injured, the bird was released. One time the king ordered a golden ring for the released heron to be worn around the the bird's neck with the date May 18, 1647. The same heron was caught with a falcon by king John III Sobieski in July 1677. Łuszkowska was still alive on May 20, 1648, when King Ladislaus IV died in Merkine. A romantic legend says that the king died in the arms of his beloved Jadwiga. Wypyski died before December 18, 1647, and he was succeeded as starost of Merkine in 1651 by Krzysztof Buchowiecki, therefore the land was ruled by Jadwiga after Wypyski's death. Around 1650, fifteen-year-old Władysław Konstanty, Jadwiga's son, set off, following the custom of the then teenagers from wealthy families, on a journey across Europe. He never returned to Poland. In Europe, he was known under the name of Count de Wasenau. The print by Jean Michel Moreau, created in 1763 (copy in the Slovak National Gallery, inventory number G 2402), is possibly the oldest and most accurate confirmation of ownership of the painting by Rembrandt, known as the Toilet of Bathsheba, today in the Metropolitan Museum of Art. Similar paintings are also mentioned in inventories of the collection of Willem Six in Amsterdam in 1734 (sale catalogue: "The History of Bathsheba, by Rembrandt van Rijn") and in the collection of Gerard Bicker van Zwieten in The Hague in 1741 (sale catalogue: "Bathsheba whose hair was cut and whose feet were washed, by two woman, very unusual [Rembrand van Ryn]"), however they could be tantamount to another painting attributed to Rembrandt or his studio with similar dimensions and composition, which is today in the Netherlands (Museum Catharijneconvent in Utrecht, RMCC s172). The latter painting, in Utrecht, is dated to about 1645 and is entitled "Bathsheba at her toilet spied by David" (Batseba bij haar toilet door David bespied, after "De schilderijen van Museum Catharijneconvent", 2002, p. 249). The painting in the Metropolitan Museum of Art, according to Moreau's print, was in 1763 in the Gallery of count Bruhl, Prime Minister of His Majesty King of Poland and Elector of Saxony (D'après le Tableau de Rembrandt, qui est dans la Gallerie de S.E.M.gr Le Comte de Bruhl, Premier Ministre de S. M. Le Roi de Pologne, Electr. de Saxe). During the Seven Years' War (1756-1763), when Prussian army invaded Saxony, he lived mainly in Poland, where in Warsaw he had three palaces - one near the election field at Wola, built in about 1750, one in Młociny, built between 1752-1758, and the largest, former Sandomierski Palace, in the center. Sandomierski Palace was constructed between 1639-42 by Lorenzo de Sent for Crown Grand Chancellor Jerzy Ossoliński, a friend of Ladislaus IV. It cannot be excluded that Bruhl acquired the painting in Poland. Such paintings are documented in the collections of the Commonwealth's magnates in the 17th century. For example, the inventory of the collection of Princess Louise Charlotte Radziwill (1667-1695), drawn up in 1671, lists two paintings of David and Bathsheba: "King David seeing Uriah's wife from the palace" (348/1) and "King David with Uriah's wife, gilded frames" (811/3). One of the most important works of the court painter of Ladislaus IV, Bartholomeus Strobel, from the early period of his work, is also "David and Bathsheba". Strobel's painting, now kept at Mnichovo Hradiště Castle in Czechia, was painted for the Wrocław canon Philipp Jakob von Jerin and signed by the artist (B. Strobel pinxit et d.d.Phil.Iac. / a Ierin Canonico Wratislauiensi. / Kal.Maij.Anno 1630). Like the painting in the Prado, it was filled with disguised effigies of ladies of the imperial court in Prague or rich Wrocław patricians. King David is almost invisible standing on the high terrace to the left. The ruins of the amphitheater and the obelisk closely resemble the structures shown in the portrait of Royal jeweller Giovanni Jacopo Caraglio by Paris Bordone (Wawel Royal Castle). In the center of the compostion, among the dense forest, sits Bathsheba, naked, while her servants are brushing her "Venetian blond" hair and cutting her nails, exactly as in the painting representing Zuzanna Orłowska, mistress of King Sigismund II Augustus, as Bathing Susanna by Jacopo Tintoretto (Louvre Museum). A partridge at the feet of Susanna, a symbol of sexual desire, is in Rembrandt's painting replaced with a peacock, the symbol of immortality (after "Signs & Symbols in Christian Art" by George Ferguson, p. 23). Since the bird sits on the nest with its partner, it is a symbol of eternal love and partnership. The old woman with glasses cutting Bathsheba's nails is very similar to the one depicted in a drawing by Rembrandt from the collection of Prince Henryk Lubomirski (1777-1850) in Lviv, today in the Ossolineum (Lubomirski Museum) in Wrocław. It is most probably the mother of woman depicted as Bathsheba. Interestingly, the same collection also includes another drawing by Rembrandt, showing a woman holding a child and dated to around 1635, when Jadwiga gave birth to a son. So were these drawings preparatory works to the images of the royal mistress, her newborn son and her mother sent to Poland for approval? According to the Bible, king David, whilst walking on the palace roof, accidentally espies the beautiful Bathsheba, the wife of a loyal soldier in his army, bathing. He desired her and made her pregnant. The painting is an allusion, exacly as effigy of Katarzyna Telniczanka, mistress of king Sigismund I, as Bathsheba by Lucas Cranach the Elder (Gemäldegalerie in Berlin) and has similar composition. Łuszkowska, who lived in royal residencies, knew perfectly well the paintings from the royal collection, which were often made in series for various relatives. The painting from the Bruhl collection was signed and dated by the artist: Rembrandt. ft/1643. The woman, though with her hair not bleached, was also depicted in a portrait painting by Rembrandt, also created in 1643 (Rembrandt f. 1643), which is today in the Gemäldegalerie in Berlin. The work most likely entered the collection of Frederick III of Prussia in the Potsdam City Palace between 1689 and 1698. The palace in Potsdam was constructed on the site of an earlier edifice from 1662 to 1669 built for Frederick's father Frederick William (1620-1688), Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia, who in 1656, during the Deluge, according to Wawrzyniec Jan Rudawski, "took to Prussia as a spoil, the most valuable paintings and silverware of the royal table". The woman cannot be Rembrandt's wife as she died on 14 June 1642. She wears a hat, most probably a fur hat, adorned with jewels, very similar to kołpaczek from Polish traditional women's costume. Her pose is identical as in the painting from the Bruhl collection. She was also represented in another painting by Rembrandt and his workshop, also created in 1643 (Rembrandt f / 1643), today in the private collection. Her hair are bleached, she is holding a fan and her outfit is similar to that in the Berlin painting. She wears a toque embroidered with gold, similar to Italian balzo visible in the portrait of Queen Bona Sforza by Titian, identified by me (private collection), a hat decoration (egreta) with a feather, a coat of expensive fabric lined with fur and jewels. The attire in both painting is very similar to the costume of Raina Movila (Regina Mohylanka) of Moldavia (ca. 1589-1619), Princess Vyshnevetska (portrait in the National Historical Museum of Ukraine), who died in Vyshnivets (about 150 km east of Lviv) or to the costumes of ladies in the painting "Finding of the Cross" by Tomasz Muszyński in Lublin (south-eastern Poland), created between 1654-1658. While in 1642 Queen of Poland, Cecilia Renata of Austria, asked her brother to send her Dutch lace and a doll dressed in fashionable French attire and portraits of both the queen and her sister-in-law Anna Catherine Constance by Dutch painter Peter Danckers de Rij show the abundance of lace and French costumes, the woman from Rembrandt's paintings opted for eastern costume. The sitter in all three mentioned paintings bear a resemblance to the portrait of a boy, identified as portrait of Władysław Konstanty, in the National Gallery in Prague (O 8675). A companion piece to the portrait holding a fan is a portrait of a man with a hawk (The falconer), also in private collection and also signed and dated by the artist ([Re]mbrandt f 1643). This is the woman's husband. If Wypyski started his career at the court in 1626 at the age of around 20, then he was around 37 years old in 1643. The high-flying hawk is a symbol of royalty (and thus authority, sovereignty). The man's invites to hunt and pointing at the woman in the pendant portrait.
Old lady with glasses by Rembrandt, ca. 1635, Ossolineum in Wrocław.
Woman holding a child by Rembrandt, ca. 1635, Ossolineum in Wrocław.
Portrait of Jadwiga Wypyska née Łuszkowska (ca. 1616 - after 1648) in a black hat by Rembrandt, 1643, Gemäldegalerie in Berlin.
Portrait of Jadwiga Wypyska née Łuszkowska (ca. 1616 - after 1648) as bathing Bathsheba by Rembrandt, 1643, Metropolitan Museum of Art.
Portrait of Jan Wypyski, starost of Merkine with a hawk by Rembrandt and workshop, 1643, Private collection.
Portrait of Jadwiga Wypyska née Łuszkowska (ca. 1616 - after 1648) holding a fan by Rembrandt and workshop, 1643, Private collection.
Portrait of Constantia Kerschenstein née Czirenberg by Pieter Claesz. Soutman
"You ask why Constantia is surrounded by the glory of this century? She is the greatest among the Muses, as well as the greatest among the Charites [Graces], She is superior than men and silences the gods. With her speech, faithfulness, voice, and extraordinary charm, she is praised by Gdańsk and all of Poland admires her. This is how the mortals can rise above the gods" (AN quæ sit CONSTANTIA secli gloriæ quæris? / Maxima Musarum, Maxima & est Charitum. / Hæc homines vincit, contrabit ora Deorum / Eloquio, fidibus, voce, lepore sibi; / Suspicit hanc Gedanum, celebratqe; Polonia tota, / Hoc est mortales, hoc superare Deos) (partially after the Polish translation by Andrzej Januszajtis in "Kwiaty dla Konstancji"), praises the famous singer Constantia Czirenberg (1605-1653), priest Lorenzo Frissone (Laurentius Frissone). This dedication was published in Milan in 1626 in "The Flowers of the Most Illustrious Men" (Flores praestantissimorum virorum) by Filippo Lomazzo (Philippo Lomatio).
Constantia, daughter of Johann Czirenberg (Zierenberg), mayor and royal burgrave of Gdańsk, the main port of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, and Anna Kerl, received an excellent education. She was fluent in German, Polish, French, Italian and Latin, played the clavichord and accompanied herself to the singing. She also drew, painted and embroidered beautifully. Her father, who studied in Gdańsk, Kraków and Leipzig, was one of the most active leaders of the Calvinists and wrote polemical theological writings against the leaders of the Gdańsk Lutherans. In 1628, Constantia married Sigismund Kerschenstein (also Siegmund, Zygmunt Kirszensztein or Kerssenstein; 1583-1644) with whom she had three children: Ludwig (born 1629, who on October 20, 1656 married in Amsterdam Maria von Rote), Constantia (1631) and Anna (1633). Known for her beauty and musical talent, Czirenbergówna or Kerschensteinowa, as she is also known in Poland, quickly attracted the attention of a famous patron and connoisseur of music and Italian opera, Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa. They probably met for the first time during his visit to Gdańsk in 1623, shortly before his departure for the Spanish Netherlands and Italy (1624-1625), and it was undoubtedly the prince who recommended her in Italy. Lomazzo's dedication in the mentioned work seems to confirm this, as well as the fact that she also performed in Warsaw or Kraków, at the court of Sigismund III, before she left for Italy: "The glory of Your virtues could not be contained within the borders of Poland, even the widest ones, so here, along with the fame and most faithful recommendation of Your name, it reached Italy and Milan. [...] That you have the most skillful hands, the most dexterous fingers for playing, a nightingale's throat for singing, so that in singing with the most eminent artists and masters of the Invincible King of Poland and Sweden and masters of his court, as the Prince himself judged with delight, you do not hesitate to compete". She probably entertained Ladislaus, already king, with her music when he was her father's guest during his visit to Gdańsk in 1634. During this sojourn, the king commissioned numerous portraits and other works of art from local artists, as well as from the Netherlands (most likely including Claes Jansz. Visscher's print based on a drawing or painting by Pieter Claesz. Soutman). Charles Ogier (1595-1654), secretary to the French envoy Claude de Mesmes, Count of Avaux, who met her in November 1635, wrote in his diary that "she has an extremely beautiful voice and sings in the Italian way". In his Caroli Ogerii Ephemerides ..., published in Paris in 1656, he also includes a poem dedicated to her - Sireni Balthicæ Constantia Sirenbergiæ, in which he calls her the Siren of the Baltic and Sarmatia (Siren Baltica, Sarmaticas; Sirenberg - siren mountain in German), who seduced the king with her voice (Quin ipsum, spiraret adhuc cum pectore Martem, VLADISLAVM carmine distinuit. Ille tuis pronam, CONSTANTIA, cantibus aurem Præbuit, ad laudes obstupuitque suas, p. 506-507). During the king's visit to the city in 1636, at a feast at Brigida Schwartzwald's house on February 7, Ladislaus showed her special consideration "and wished that only Constantia would be seated at the head of the table". Ogier and the French envoy were guests at her house, and in a note from April 29, 1636, he adds: "I spent the afternoon with Mrs. Constantia, who, as usual, was sitting up with her sick husband. While he was telling me interesting things, she was showing me her feminine ornaments, such as chains, armlets, tiaras, and lots of white, but not round, pearls; she informed me about the different costumes of her and the Polish nation. And when she placed before my eyes the caps, gloves, belts and other such things that she herself had woven and decorated with embroidery, it seemed as if I had stumbled upon Pallada herself" (after Polish translation by Zenon Gołaszewski). Like the majority of Gdańsk ladies, she probably preferred local fashion with a ruff and beaded or jeweled bonnet, but as Netherlandish influences were important in Gdańsk then, she probably also dressed in the Dutch or Flemish style. Her family lived in a house built or rebuilt around 1620 by Abraham van den Blocke, an architect and sculptor of Flemish origin. A beautiful Dutch-Flemish style marble epithaph of Constantia's grandfather and grandmother in St. Mary's Church in Gdańsk, made in 1616, is also attributed to Abraham van den Blocke. She died in 1653, during the plague, and was also buried in St. Mary's Church. There must have been multiple effigies of such a star of 17th century music. At that time, portraits of singers were made by the best artists, such as Andrea Sacchi in Rome, who in 1641 painted the castrato singer Marc'Antonio Pasqualini (1614-1691), who in 1634 performed before the king's brother Alexander Charles. The king undoubtedly owned several portraits of Czirenbergówna, but today none is known. Even if the royal collections were largely dispersed or destroyed, like the magnificent opera hall built around 1635 at the Royal Castle in Warsaw by the Italian architect, engineer and scenographer Agostino Locci, some remnants must have survived. In the National Museum in Warsaw there is a portrait of a woman attributed to Pieter Claesz. Soutman, who frequently worked for Ladislaus IV (oil on panel, 69 x 58.7 cm, M.Ob.528 MNW, deposited at the Palace on the Isle in Warsaw, Dep 928). The painting come from the collection of the last elected monarch of the Commonwealth Stanislaus Augustus Poniatowski and at the bottom right, red inventory number of his gallery - 1374, is still visible. In the 1795 catalog of the king's collection, it was listed as "Half-length portrait of a woman, old costume, large ruff at the collar, on wood" (Portrait de femme a mi corps, costume ancien, large fraise au col, sur bois), without attribution. Its earlier history is unknown, so it cannot be ruled out that it came from historical royal collections that survived the Deluge (1655-1660) and subsequent invasions. The woman proudly displays her rich costume, including lace bonnet and cuffs that she probably made herself. A sheer black veil and dark dress indicate that she is likely in mourning. According to an original Latin inscription in the center right, barely visible today, the woman was 38 years old in 1644 (Ætatis / suæ 38 / 1644), exactly like Kerschensteinowa, who, when her husband died on May 22, 1644, could still claim to be 38 years old (born October 6, 1605). Her costume is northern in style, but similar ones were popular throughout the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in the first half of the 17th century, as shown for example in the Kraków painter's portrait of a noble family as donors dating from around 1620 (National Museum in Kraków). Similar to many other works, it was commissioned in the Netherlands, either by the king or Constantia, due to the good sea connection between Gdańsk and Amsterdam (regular grain transports) and the very probably competitive prices offered by painters and other qualified craftsmen. As a good example of such a practice, we can cite that before 1643 the title page of Diego Ufano's Tratado dela artilleria yuso della platicado ..., translated from German into Polish by Abraham Ciświcki, with effigy of Ladislaus IV Vasa and view of Smolensk (Archelia albo Artilleria, to iest Fvndamentalna Y Doskonała Informacya o Strzelbie, published in Leszno in 1643), was created by Crispijn van de Passe the Younger (signed: C. de Pas Inventer), who was active in Amsterdam from 1639, where he founded his own printing and publishing firm (compare "Printmaking in the Age of Rembrandt" by Clifford S. Ackley, p. 94).
Portrait of the singer Constantia Kerschenstein née Czirenberg (1605-1653), aged 38, in mourning by Pieter Claesz. Soutman, 1644, National Museum in Warsaw.
Cartouche with flowers and portrait of Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria by Daniel Seghers and Gaspar de Crayer
"The rooms are large, they have all kinds of luxury. Furniture, master's crafts, Netherlandish golden arts; on this side and on the other side, next to the most glorious patron, there is Saint Cecilia's union, heavenly lily, where the capella [musical ensemble] sings vespers, royally: gioia bella! [beautiful joy]" (Pokoje pomiernie wielkie, / Ale w nich dostatki wszelkie, / Ochędóstwa, kunszty pańskie, / Złote sztuki niderlandzkie; / Po tej i po drugiej stronie, / Przy najaśniejszej patronie, / Tam jest świętej Cecylijej / Związek, niebieskiej lilijej, / Gdzie śpiewa nieszpór capella / Pokrólewsku: gioia bella!), describes the palace hall of the Villa Regia in Warsaw, Adam Jarzębski in his "The Main Road, or a Short Description of Warsaw" (Gościniec abo krótkie opisanie Warszawy) from 1643 (verses 1953-1962).
The painting, probably a ceiling painting on canvas or a fresco, depicted the marriage of the patron saint of singers and musicians. This scene must have been commissioned by Ladislaus IV Vasa, a great patron of the arts and connoisseur of music and opera, also to honor the new Queen Cecilia Reanta of Austria. It is possible that the saint had the features of the queen, however nothing else is known about this painting. At that time, even the Queen of England was depicted in the guise of a Christian saint by van Dyck. Possible authors included painters from the king's court, representing the main schools of Baroque painting – Central European, Italian, Flemish and Dutch. If it was a painting on canvas, it is possible that it was made abroad, in Flanders, the Netherlands or Italy. It was before the marriage with his cousin in 1637 (Cecilia Renata was a daughter of Ladislaus' uncle and they were related through Anna Jagellonica, queen of Germany, Bohemia and Hungary), that the king decided to rebuild the palace. On the occasion of the arrival, marriage and coronation of Cecilia Renata, Ladislaus also ordered to stage an opera dedicated to his wife and referring to her patron, "Saint Cecilia" (La S. Cecilia : Dramma Mvsicale, Con Gl'Intermedii Favolosi Rapresentato Nelle Reali Nozze, Delle Maesta Di Polonia E Svezia Vladislao IV E Cecilia Renata). The libretto was written by Virgilio Puccitelli, the royal secretary, the music was composed by Marco Scacchi, the royal bandmaster and the scenography and construction of the stage machines were entrusted to Agostino Locci. The king and queen shared the love for music and on another occasion, in 1638, there was a concert for violin and twelve trumpets. Cecilia Renata and Ladislaus, sailing on the Vistula by ship, could listen to music coming from both banks of the river. There were violinists on one side and trumpeters on the other (after "Wkład królowej Cecylii Renaty ..." by Anna Burkietowicz, p. 19). At this time, portraits and other paintings were frequently sent to different family members, so the Austrian and Spanish Habsburgs most likely received many effigies of Cecilia Renata. The 1659 inventory (Inventarium) of Archduke Leopold William's collections at the Stallburg in Vienna lists two full-length portraits of his sister, when she was queen (no. 811) and when she was archduchess (no. 813), both made by Frans Luycx and the full-length portrait of his cousin Infanta Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (no. 812), also by Luycx, which is now in the Kunsthistorisches Museum (GG 1732). The inventory also lists a portrait of "long Peter", the painter of the King of Poland (langen Peter, Königs in Pohlen Mahlers, No. 722), most probably Pieter Claesz. Soutman, by Anthony van Dyck, probably the painting today in the Louvre (INV 1248 ; MR 671) or a copy of it, and a copy of a miraculous image of the Virgin and Child from Poland, painted on copper, by an unknown painter (No. 281) (compare "Inventar und Kunstsammlung des Erzherzogs Leopold Wilhelm ..." by Adolf Berger). Interestingly, the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna has preserved only one image of the Polish queen, which can surely be considered her portrait, bearing an inscription in Italian on the back: LA REGINA CECILIA RENATA DI POLONIA 1642 (GG 8291), most likely painted by workshop of Frans Luycx, the other three are effigies of her sister-in-law Anna Catherine Constance (GG 1732, GG 5611, GG 7944), identified by me. In the Viennese museum there is an effigy which is similar to other effigies of Cecilia Renata - Female portrait in a wreath of flowers (oil on panel, 76.5 x 58 cm, GG 9105). It comes from the collection of Archduke Leopold William and in the 1659 inventory it was listed as "48. An effigy in oil painting on wood of a lady, around her three festoons with different flowers. [...] The portrait is by an unknown painter, but the flowers are by F. Segers, Jesuit" (48. Ein Contrafäit von Öhlfarb auff Holcz einer Damen, darumben drey Festonen mitt vnderschiedtlichen Blumen. [...] Das Contrafäit von einem vnbekhandten Mahler, die Blumen aber vom F. Segers, Jesuitter.), that is to say Daniel Seghers (1590-1661), mainly active in Antwerp. Seghers specialized in flower still lifes, so he frequently cooperated with other painters, such as Cornelis Schut, Peter Paul Rubens, Gonzales Coques and others, who painted the central figurative scene or the portrait. A fairly comparable portrait of the queen's brother by Seghers from 1647 to 1651, in the form of a bust (painted by Jan van den Hoecke), is today in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence (Inv. 1890, 1085). It was bequeathed to Emperor Leopold I in 1662. The woman in this portrait is also identified as Cecilia Renata's sister, Archduchess Maria Anna (1610-1665), Electress of Bavaria, but she was most often depicted in Central European costume inspired by Spanish or Italian fashion (e.g. paintings by Joachim von Sandrart from 1643 and after - Kunsthistorisches Museum, GG 8034 and Alte Pinakothek in Munich, 3093) and not French, like the woman in this painting. Her costume particularly resembles that represented in a portrait of Ladislaus IV's cousin, Anne of Austria (1601-1666), Queen of France at the Visitandine monastery in Warsaw. The portrait of the Queen of France was most likely painted by Charles Beaubrun in the late 1630s or early 1640s, like similar paintings of Anne from 1638 and 1639. Close to her heart, as in many effigies of Cecilia Renata's husband, for example in Wilanów Palace (Wil.1143) and the Royal Castle in Warsaw (ZKW 559 dep.) or the portrait of the queen in the Nationalmuseum in Stockholm (Gripsholm Castle, NMGrh 1417), we see a jewel on a ribbon. It is a "favor" said to indicate a love knot and 14 objects of jewelry evoking favors are mentioned in the king's inventory of 1646. "Favors in a broader sense, gioie da petto, elaborated love jewels worn on the left breast or left shoulder were promoted in the Rzeczpospolita [Commonwealth] for the first time by queens Anna and Constance of Austria" (after "Favors and love locks ..." by Jacek Żukowski, p. 46). The woman in this portrait closely resembles the Queen of Poland in the mentioned portrait in Stockholm, a painting in Wilanów (Wil.1144), as well as effigies in the Victoria and Albert Museum (P.57-1929) and Gripsholm Castle (Nationalmuseum, NMGrh 299). The whole composition with flowers may refer to Cecilia Renata's patron saint - Saint Cecilia. "In Jacobus de Voragine's Legenda Aurea and its derivative, Chaucer's Second Nun's Tale, crowns of lilies and roses are brought by an angel to the future martyrs Cecilia and her husband after she has converted him to Christianity and continence" (after "St. Cecilia's Garlands and Their Roman Origin" by John S. P. Tatlock, p. 169). We can see similar floral wreaths with roses in several paintings depicting the saint, such as Saint Cecilia in a flower border by Michel Bouillon, mid-17th century (Setdart Auction House in Barcelona, September 7, 2022, lot 79), Saint Cecilia wearing a crown of flowers by Cesare Dandini, 1640s (Dorotheum in Vienna, April 18, 2012, lot 743), Saint Cecilia wearing a crown of flowers (Personification of music) by Antonio Franchi, ca. 1650 (Sotheby's London, July 8, 2004, lot 159), Saint Cecilia wearing a crown of flowers and playing an organ by Onorio Marinari or circle, ca. 1686 (Dorotheum in Vienna, December 14, 2010, lot 189) or Saint Cecilia playing an organ by Sebastiano Conca, 1735-1745 (Sotheby's New York, July 7, 2016, lot 189). Daniel Seghers' contacts with clients from Poland-Lithuania are well documented. In 1637 Jan Zawadzki (died in 1645), envoy of Ladislaus IV returning from Paris, purchased the painting representing: "A garland of roses with Jesus and Saint John [the Baptist] by Mr. [Cornelis] Schut for the ambassador Sawaski, who presented it to the King of Poland" (Een feston van Roosen met Jezus en S. Jan van Sr. Schut voor den Ambassadeur Sawaski die het heeft geschonken aen den koning van Polen). Seghers created a cartouche for Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga in which was Saint Anne by Quellinus (December 17-20 1645), most probably the painting in the Worcester Art Museum (1966.37), painted with Erasmus Quellinus the Younger. In 1645 the other king's envoy - Krzysztof Opaliński (1609-1655), voivode of Poznań, purchased in Antwerp numerous paintings, originals and copies "from the masters themselves. The Jesuits helped me in this", as he wrote in a letter to his brother dated October 9 (compare "Rubens w Polsce" by Juliusz A. Chrościcki, p. 181). On this occasion, Opaliński commissioned a print from Lucas Vorsterman (National Museum in Kraków, MNK III-ryc.-40483), a study for which was produced by Abraham van Diepenbeeck (Czartoryski Museum, MNK XV-R.1111). Around that time, van Diepenbeeck created another study for a print or altar painting depicting the enthroned Madonna and Child worshiped by three saints (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, RP-T-1985-118). The first figure on the left holding a crucifix is identified as possibly representing Saint Henry of Germany, but a lily and an eastern hat at his knees indicate that he is Saint Casimir Jagiellon (compare with the effigy of this saint published in Douai in 1638, MNK III-ryc.-28781). The author of the portrait of Queen Cecilia Renata in Vienna was not mentioned in the 1659 inventory of her brother's collection, which is another indication that the author of this inventory was his Austrian "valet and treasurer" (Kammerdiener und Schatzmeister) Christian Wasserfass von Hohenbrunn. He probably knew Seghers, who was a popular painter at that time. If the painting depicted the Electess of Bavaria, who was still living at the time of the document's creation (died 1665), he should also recognize her (Cecilia Renata died 15 years earlier). This subtly painted image is reminiscent of Anthony van Dyck's portrait of Marie de Raet, painted in 1631 (The Wallace Collection, P79). It is therefore possible that it was made by Abraham van Diepenbeeck, whose work was influenced by Rubens and van Dyck, however, the works of another painter who draw inspiration from van Dyck's style seem closer - Gaspar de Crayer, who was a painter of the queen's Spanish relatives. Among the closest we can cite the equestrian portrait of King Philip IV of Spain, from 1628-1632 (Prado Museum in Madrid, P001553) and especially signed work - Saint Ambrose from about 1655 (Prado, P005198). The way the painter painted the lace and the hair is very similar. The nobles of the Commonwealth enjoyed a well-deserved reputation as good patrons. "Prince Samaske" (Zamoyski?), probably from the entourage of Queen Marie Louise, negotiated with Matthijs Musson, painter and art dealer based in Antwerp, and Gillis van Habbeke, active as a tapestry weaver in Brussels from at least 1643, for tapestries. While de Crayer wrote to Musson from Brussels in December 1645 that they were expecting Poles there, who had already seen his painting of the Assumption of the Virgin Mary in Lier and requested a copy, so he also prepared other things (after "Galerie obrazów ..." by Teresa Sulerzyska, p. 96). It was most likely customers from Poland-Lithuania who ordered around 1643 a series of three small tondo engravings depicting three goddesses from the Judgment of Paris - Venus, Juno and Minerva, which comes from the Krasiński collection in Warsaw (National Library of Poland, G.2693/Sz, G.2694/Sz, G.2691/Sz). They were produced by Clement de Jonghe (1624-1677), friend of Rembrandt, active in Amsterdam from 1643. The style of the engravings is comparable to the drawings signed or attributed to Hans Krieg (died between 1643 and 1647), painter and draftsman active in Gdańsk, probably son of Mennonite refugees from the Netherlands or Germany. The print depicting Venus is particularly interesting because it depicts the goddess of love as queen (Venus Regina), holding a scepter, most probably inspired by the baroque effigies of Mary, Queen of Heaven (Regina Cæli) (compare with the print by Cornelis Galle the Elder from the first half of the 17th century). Accompanied by her son Cupid, they both admire their vast lands: the Realm of Venus.
The Queen Venus (Venus Regina) by Clement de Jonghe after Hans Krieg, ca. 1643, National Library of Poland.
Cartouche with flowers and portrait of Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria (1611-1644) by Daniel Seghers and Gaspar de Crayer, ca. 1642-1645, Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Cartouche with flowers and the Education of the Virgin by Daniel Seghers and Erasmus Quellinus II, ca. 1645, Worcester Art Museum.
Virgin and Child enthroned with Saint Casimir by Abraham van Diepenbeeck, mid-17th century, Rijksmuseum Amsterdam.
Allegorical portrait of Stanisław Lubomirski by Gregorio Preti or workshop
The main architectural foundations of Stanisław Lubomirski (1583-1649), voivode of Kraków, are linked to Italian culture. The architect serving the voivode was the Italian Matteo Trapola (d. 1637), who designed many buildings in Nowy Wiśnicz, including the Church of the Carmelite Monastery founded by Stanisław in 1621 to commemorate the victory over the Empire Ottoman during the Battle of Khotyn (built between 1622 and 1630). Trapola also rebuilt Wiśnicz Castle (1615-1621) and other residences of the magnate such as Łańcut Castle (1629-1641) and Decius Villa in Wola Justowska near Kraków (1630). Giovanni Battista Falconi (d. 1660) decorated the Lubomirski residences in Wiśnicz and Łańcut, as well as the family chapel in Niepołomice with beautiful stucco decorations. The Italian architect Andrea Spezza (d. 1628), who designed the Wallenstein Palace in Prague, is considered the author of the project for the parish church in Wiśnicz, founded by Stanisław in 1620 and consecrated in 1647 (compare "Baroque architecture ..." by Piotr S. Szlezynger, p. 113).
In May 1649, the voivode, who maintained contacts with the Rakoczi family, intervened with Sebastiano Sala (d. 1652), a sculptor from Lugano operating in Kraków, so that the master, who was in the royal service, accepted the order to make the tombstone of George I Rakoczi (1593-1648), prince of Transylvania, in Alba Iulia. Connections to Italian culture are also present in the paintings commissioned by Lubomirski. For example, the large allegorical portrait of Stanisław as the triumphator in the 1621 war against the Ottoman Empire, is obviously Italian in style, but no Italian painters working in Wiśnicz or other estates of the voivode are known. This painting in now kept at Wilanów Palace in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 292 x 176 cm, Wil.1565). Another full-length portrait of Stanisław, attributed to Stanisław Kostecki (National Museum in Warsaw, 128870/2 MNW), is not similar and no painter active in the Commonwealth at that time appears to have authored the work. The painting is closer to the Roman school, inspired by Caravaggio, with strong contrasts of light and shadow, which exclude Tommaso Dolabella, trained in Venice, and his workshop as potential authors. The Lubomirskis, as devout Catholics, maintained relations with Rome. In 1634, Pope Urban VIII presented the Church of the Dominican Sisters in Kraków, founded in 1621 by Stanisław's mother, Anna Lubomirska née Branicka (1562-1639), with a painting of Our Lady of the Snows (Salus Populi Romani) and the following year relics of Saint Alexander and the head of one of Saint Ursula's companions were offered by the Pope and brought from Rome by the Discalced Carmelites. Similar to King Sigismund III and Ladislaus IV, the Lubomirskis undoubtedly also commissioned paintings from Rome. The Wilanów painting most closely resembles works attributed to Gregorio Preti (1603-1672), a painter active in Rome from 1624 and who, between 1632 and 1636, was the teacher of his famous younger brother Mattia (1613-1699). Among the closest we can cite the Disrobing of Christ with a man in Polish-Lithuanian or Hungarian-Croatian costume (Hôtel Drouot in Paris, March 28, 2023, lot 18), the Meeting of Saint Dominic and Saint Francis of Assisi (Quadri e Lanzi in Rome, February 27, 2018, lot 167) and Pope Celestine V (1215-1296) refuses the papal tiara (Wannenes Art Auctions in Genoa, December 21, 2020, lot 1230), as well as the painter's self-portrait in Allegory of the Five Senses, painted between 1641-1642 (Palazzo Barberini in Rome, inv. 4660). This truly princely allegory can be dated to around 1647, when Stanisław received the princely title from Emperor Ferdinand III. Such portraits were usually ordered in several copies for different residences. Good examples of this practice are the portraits of Mikołaj Hieronim Sieniawski (1645-1683), painted around 1682 and attributed to Mateusz Domaradzki (Wilanów Palace and Olesko Castle).
Allegorical portrait of Stanisław Lubomirski (1583-1649), voivode of Kraków by Gregorio Preti or workshop, ca. 1647, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
Portraits of King Ladislaus IV Vasa and Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga by workshop of Giovanni Antonio Galli
Despite their origins in Norhern Europe, the Polish-Lithuanian branch of the Vasa dynasty, similar to the Jagiellons, mainained close relations with the Italian peninsula. Commonwealth aristocrats owned many portraits of famous Italians. The inventory of paintings in the collection of Princess Louise Charlotte Radziwill (1667-1695), drawn up in 1671, lists the portraits of Cardinal Charles Borromeo (188), Marshal Ottavio Piccolomini (243) and Cardinal Jules Mazarin (244) (after "Inwentarz galerii obrazów Radziwiłłów z XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska). Although due to the French origin of Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga (from the Nevers branch of the Italian family), effigies of French aristocrats or probably painted in the French style, dominate in this inventory (items 276-291 and items 307-311).
In the collection of Cardinal Antonio Barberini (1607-1671), nephew of Pope Urban VIII, in Palazzo Barberini in Rome there was a portrait of ambassador of King Sigismund of Poland (il ritratto del Sig. re. Ambasciatore di Polonia, inventory 1644, item 108) and the 1649 inventory of the collection of Cardinal Francesco Barberini (1597-1679), another nephew of the pope, contains a large number of Polish-Lithuanian effigies, because as secretary of state he directed the foreign policy of the papacy. He most likely owned a portrait of Chancellor Jerzy Ossoliński (item 819), most probably by painter Antonelli, as well as an engraved portrait of Sigismund III (209) and his large portrait or rather of his successor, Ladislaus IV (782) in red Polish-Lithuanian żupan, who seemed for the author of the inventory to be "dressed like Dante" (del Re di Polonia vestiti tutto di Dante). Another note mentions a portrait of the Polish king in half-figure (822). An engraving depicting the victory of the newly elected monarch over the Muscovite troops who were besieging Smolensk (l'espugnatione dell esercito de Moscoviti dal Re di Polonia, 192), was probably also a gift from Ladislaus. In the collections of Don Taddeo Barberini (1603-1647), Prince of Palestrina and Gonfalonier of the Church, brother of Cardinals Francesco and Antonio, inventoried in the years 1648-1649, is the portrait of an unidentified Polish queen (Hedagres [Edvige-Hedwig?] Regina di Polonia, 305), while Cardinal Francesco's inventory of 1679 mentions "a portrait of a queen of Poland" (il ritratto d'una Regina di Polonia, 112) (after "Biuletyn historii sztuki", Volume 47, p. 153-154). The portrait of Ladislaus IV Vasa in coronation robes and a large crown, attributed to Jan Chryzostom Proszowski, is in the Grand Master's Palace in Valletta, Malta. In the 17th century, like today when wealthy people order highly personalized items from distant locations because of their uniqueness and quality, portraits were commissioned from the best workshops in Europe. In 1646 Pierre Des Noyers, secretary of Queen Marie Louise, wrote that the chapel of the Royal Castle in Warsaw was "embellished with numerous paintings by the most famous painters". Four years later, in 1650, the queen ordered in Paris, through Des Noyers, a large painting representing her and her two husbands. The concept of the painting, executed by Justus van Egmont, was developed by Abbot Michel de Marolles - the queen as Roman godess Juno seated between two Jupiters, one celestial (Ladislaus IV Vasa) and the other terrestrial (John Casimir Vasa) - Une Junon représentée assise entre deux Jupiters, l'un céleste et l'autre terrestre. Cette Déesse plus belle qu'elle ne fut jamais sous le visage de la Reine (after "Bulletin de la Société de l'histoire de l'art français", p. 34). This practice was also very beneficial from a logistical point of view for a monarch wishing to glorify his dynasty and his country. Portraits ordered in Paris could be offered to the Queen of France (who was a cousin of the Vasas), or sent further to Madrid, Florence, Rome or London. The monarchs of Poland-Lithuania frequently sent precious and rich gifts to people abroad, such as to mentioned Michel de Marolles, who in 1649 received gilded vases and a gilded and carved silver box from the queen. The Vasas also had a significant collection of ancient sculptures, the majority of which were undoubtedly acquired in Rome. The sculptures in Warsaw and Łobzów were destroyed during the Deluge (1655-1660) and some were looted by Frederick William (1620-1688), Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia (after "Świat polskich Wazów: eseje", p. 56, 299, 316). In 2022, two portraits of a nobleman and his wife (Ritratto di nobile, Ritratto di gentildonna), attributed to a 17th-century Roman painter, were sold in Rome (oil on canvas, 84 x 67 and 84 x 68 cm, sold at Bolli & Romiti, May 18, 2022, lot 61-62). The two come "from a Roman palace". These paintings reproduce well-known effigies of King Ladislas IV Vasa and his second wife Marie Louise Gonzaga. The portrait of the king is a version of the effigy dating from around 1647, similar to the miniature in the National Museum in Warsaw (Min.726 MNW) and the portrait of the queen is a copy of a painting by Justus van Egmont in Royal Castle in Warsaw (ZKW/2283/ab). In the mentioned miniature Ladislaus has blond hair and mustache, and in the Roman portrait he has dark hair, indicating that the painter copied some general effigies of the king - drawings or prints. It is also possible that the bald Ladislaus wore different colored wigs or dyed his hair and beard, like the viceroy of Naples in 1625. The style of both paintings is closely reminiscent of works attributed to Giovanni Antonio Galli, known as lo Spadarino, a member of the Caravaggisti, who painted the portrait of Ladislaus from the Gundulić collection, now at Kórnik Castle (MK 03369). Among the closest are the very dark portrait of Geronima Giustiniani (1520/30 - ca. 1600) as a widow kept at the Musée des Beaux-Arts in Nancy (inv. 606), painted posthumously before 1637, Ecce Homo from private collection in Madrid (sold at Christie's London, July 7, 2009, lot 22) and a Cherub sold in 2022 (Lucas Aste in Milan, September 20, 2022, lot 90). The portraits are not as finely painted as the mentioned portrait of Ladislaus at Kórnik, so it is possible that they are part of a series of effigies commissioned around 1647 and painted by Spadarino's workshop. Very close to the style of Spadarino and his workshop is also the portrait of Prince-Cardinal John Casimir Vasa with a princely crown, also created at this time, today at the Pontifical Gregorian University in Rome. In 1641, the prince decided to become a Jesuit and arrived in Rome in 1643. He was named cardinal by Innocent X on March 28, 1646. In October 1647, he resigned to stand for election to the Polish-Lithuanian throne and married his widowed sister-in-law Marie Louise Gonzaga. Perhaps shortly after the election, on November 20, 1648, a relevant inscription in Latin was added to the portrait (CASIMIRVS SOC. IESV S.R.E. CARDINALIS ET POLONIE REX). Two other examples of this effigy are known, both made by different artists. One, kept at the Polish Hospice in Rome, is close to the style of Simone Cantarini, and the other, attributed to the Roman school, is at the Pinacoteca Nazionale of Ferrara (oil on canvas, 98 x 74 cm, PNFe 251). The bold brushstrokes of this painting also recall the cherubs by Galli's studio, such as the cherub sold in 2020 (sold at Cambi Casa d'Aste in Genoa, December 11, 2020, lot 332), as well as waves in the more finely painted Birth of Venus, perhaps created for a cardinal or wealthy nobleman (sold at Christie's London, July 06, 2018, lot 214). A similar portrait of the queen, attributed to a follower of Pierre Mignard (18th century French school), was sold in Neuilly-sur-Seine in 2013 (oil on canvas, 50 x 42 cm, sold at Aguttes, September 24 2013, lot 12). Her dress is black, which could indicate that it was created around 1648, when the queen was in mourning after the death of Ladislas IV. It is interesting to note that this portrait of the queen resembles the style of John Casimir's portrait in Ferrara. Both works can be compared to paintings attributed to Francesco Cairo (1607-1665), also known as Francesco del Cairo, an Italian painter active in Lombardy and Piedmont. Cairo was born and died in Milan. In 1633 he moved to Turin to work as court painter for the House of Savoy and between 1637 and 1638 he traveled to Rome. Between 1646 and 1649, he returned to Turin. Saint Christina of Bolsena by Cairo in the Palace of the Grand Dukes of Lithuania in Vilnius, generally dated between 1644 and 1648, is particularly similar.
Portrait of King Ladislaus IV Vasa (1595-1648) by workshop of Giovanni Antonio Galli, called lo Spadarino, ca. 1647, Private collection.
Portrait of Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga (1611-1667) by workshop of Giovanni Antonio Galli, called lo Spadarino, ca. 1647, Private collection.
Portrait of Prince-Cardinal John Casimir Vasa (1609-1672) by workshop of Giovanni Antonio Galli, called lo Spadarino, ca. 1647, Pontifical Gregorian University.
Portrait of Prince-Cardinal John Casimir Vasa (1609-1672) by workshop of Francesco Cairo, ca. 1648, Pinacoteca Nazionale of Ferrara.
Portrait of Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga (1611-1667) by workshop of Francesco Cairo, after 1648, Private collection.
Portraits of Marie Louise Gonzaga by Justus van Egmont and the Beaubrun workshop
One of the best, signed works by Flemish painter Justus van Egmont (born in Leiden in the Netherlands), is a full length portrait of Marie Louise Gonzaga (1611-1667), Duchess of Nevers, created in Paris in 1645 (caption, signature, location and date verso: MARIAE PRINCIPI MANTUANAE, DUCISSAE NVERNENSI.&.Justus d'Egmont Pinxit a. 1645. Parisi), a year when Polish-Lithianian delegation arrived to Paris (September 19th) to sign a marriage contract of widowed king Ladislaus IV with Marie Louise. It is belived that she brought the portrait with her to Warsaw (today in the National Museum in Warsaw), however it is also possible that it was sent to Poland shortly before signing of the contract. Around that year also Jeremias Falck Polonus, an engraver from Gdańsk who moved to Paris in 1639, created an engraving with effigy of Marie Louise as Duchess of Nevers (Herzog Anton Ulrich-Museum), then he modified this print, changed the inscription, the ducal crown into a royal crown (corona clausa) and replaced the flowers and a fan in her hands with an orb and a sceptre and added the date '1645' (National Graphic Arts Collection in Munich). According to inscription at the bottom of this engraving the original (painting or drawing) was made by Justus van Egmont (Justus d'Egmont fecit Cum Privilegio ...). Pieter de Jode the Younger published around 1646 in Antwerp another version of this print (Kunstsammlungen der Veste Coburg).
Portrait of a noble lady in the Weissenstein Castle in Pommersfelden, Bavaria (oil on canvas, 75 x 60cm) shows a young woman in almost identical pose as in the mentioned engravings depicting Marie Louise Gonzaga. This painting is attributed to Jacob Adriaensz Backer, however its style is also very close to Justus van Egmont and the woman depicted resemble closely Marie Louise from mentioned prints and other portraits. The same woman was also depicted in another painting by Justus van Egmont showing a lady as Diana the huntress, the goddess of the hunt, the wilderness, nature, vegetation, childbirth and chastity, today in the Palace of Versailles (inventory number MNR 41). It was identified as effigy of Madame de Montespan (1640-1707), however the style of her coiffure indicate that it was created in the 1640s. This full-length portrait was acquired by Hermann Göring from Joseph Schmid, his close friend, on 12 January 1943 for his hunting estate in Carinhall, northeast of Berlin. Its previous history is unknown, therefore it cannot be excluded that the painting was confiscated in Poland or other countries forming the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. After the war the canvas was transferred to France in 1950 from the Central Collecting Point in Munich. Similar effigy of goddess Diana from the same period is visible in a print showing triumphal arch Pyramides ante fores Regii Hospitii (National Library in Warsaw), third ephemeral decoration in Gdańsk to celebrate the ceremonial entry of Marie Louise Gonzaga into the city. In this triumphal gate the Polish Eagle is placed between two obelisks with figures of Apollo and Diana below royal monograms symbolising the brides - L4 for Ladislaus IV and ML for Marie Louise. This print was created in 1646 by Jeremias Falck Polonus after a drawing or a painting by a Gdańsk painter Adolf Boy. Both obelisks are entwined by a vine plant, a symbol of attachment. Leaves of a vine plant, like in the Apollo obelisk, or more likely an oak, are visible in another painting by Justus van Egmont from the same period (sold at Christie's, 18 May 2022, lot 193). It comes from a private collection in France and according to handwritten inscription on the back of the canvas it was earlier attributed to Pierre Mignard and allegedly created in Paris in 1677. The woman depicted was identified as Françoise-Marguerite de Sévigné, comtesse de Grignan (1646-1705), however, as in the case of the Versailles painting, her coiffure indicate that it was created in the 1640s. The woman resemble greatly Marie Louise from other portraits by van Egmont (identification suggested by Wladyslaw Maximowicz), she holds her right hand on the leaves, her left hand on her heart and her gaze is directed at the person (most probably a man) from a pendant portrait that probably has not preserved. The oak alludes to a mighty king, both Greeks and Romans associated the tree with their highest god, Zeus or Jupiter, king of the gods in ancient Roman religion and mythology. A portrait in similar convention as the Warsaw painting by van Egmont represent the same woman sitting under the tree in a park at dusk and holding a small book (private collection). She wears a black dress, most probably a mourning dress after death of Louis XIII of France (died on 14 May 1643) or after death of Ladislaus IV Vasa (died on 20 May 1648), Marie Louise's first husband. The Queen of Poland was depicted in very similar dress in the print showing the ceremony passing the marriage contract at Fontainebleau, created by Abraham Bosse in 1645. A structure with obelisks in far background resemble triumphal arch in Elbląg to celebrate the ceremonial entry of Marie Louise on February 23, 1646 (State Archive in Gdańsk). Obelisk, a phallic symbol that represented the Egyptian god of light and of the dead, the ruler of the underworld, the god of resurrection and fertility, Osiris, after having been transported to Rome develop into a most spectacular symbol of imperial power and military triumph. Different symbolic plants are visible in engravings by Jeremias Falck Polonus, depicting the queen, like a lily, a sunflower, a carnation and a rose, among others. Marie Louise extended Warsaw's royal gardens and Simon Paulli wrote about it in his Viridaria varia regia, published in 1653, a catalogue of plants in the botanical gardens of Copenhagen, Paris and Warsaw. The Queen established two botanical gardens in Warsaw in 1650, one next to the Villa Regia (later Casimir Palace) and other - next to the Royal Castle. Catalogus Plantarum Tum exoticarum quam indigenatum quae Anno M.DC.LI in hortis Regiis Warsaviae ... by Martinus Bernhardus (Marcin Bernhardi), a botanist and court surgeon of King John II Casimir Vasa, published in Gdańsk in 1652, describes the plants in these gardens, a large part was imported from Hungary (after "Rys historyczno-statystyczny wzrostu i stanu miasta Warszawy ..." by Franciszek Maksymilian Sobieszczański, p. 475). A portrait of a queen sitting in a chair with the royal crown on the table next to her, sold in Lisbon in 2015 (Veritas Art Auctioneers, 10 December 2015, lot 585), resemble greatly other effigies of Marie Louise Gonzaga. This painting was identified as a portrait of D. Luísa de Gusmão (Luisa de Guzmán, 1613-1666), Queen of Portugal or her daughter Catherine of Braganza (1638-1705), Queen of England, however, no similarity to their depictions can be found. The copperplate engraving by Willem Hondius in the National Museum in Kraków (inventory number MNK III-ryc.-37107), a study to Triumphal Arch Porta tempore regiarum nuptiarum in Gdańsk to celebrate the ceremonial entry of Marie Louise in 1646, shows the queen sitting in a similar chair, as well as gold marriage medal created that year in Gdańsk by Johann Höhn (private collection). Stylistically the portrait in Lisbon is very close to the effigy of Anne of Austria (1601-1666), Queen of France, a cousin of Ladislaus IV and John II Casimir, in the Visitandines Monastery in Warsaw. This portrait was most probably brought to Poland by Marie Louise or sent to Warsaw by the Queen of France to her cousins and resemble greatly other portraits of Anne by workshop of Henri and his cousin Charles Beaubrun. It is highly possible that the Lisbon portrait was commissioned around 1650 in the Beaubrun workshop in Paris as one of the series and sent to Portugal.
Portrait of Marie Louise Gonzaga (1611-1667) in oval by Justus van Egmont, ca. 1645, Weissenstein Castle in Pommersfelden.
Portrait of Marie Louise Gonzaga (1611-1667) sitting in a park at dusk by Justus van Egmont, 1643-1648, Private collection.
Portrait of Marie Louise Gonzaga (1611-1667) as Diana the huntress by Justus van Egmont, 1645-1650, Palace of Versailles.
Portrait of Marie Louise Gonzaga (1611-1667) holding a branch by Justus van Egmont, 1645-1650, Private collection.
Portrait of Marie Louise Gonzaga (1611-1667) with the royal crown by workshop of Henri and Charles Beaubrun, ca. 1650, Private collection.
Portraits of Louise Charlotte of Brandenburg, Duchess of Courland by Justus van Egmont
On October 9, 1645 in Königsberg, Calvinist Princess Louise Charlotte of Brandenburg (1617-1676) married Jakob Kettler (1610-1682), Duke of Courland, which was part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, a Lutheran.
The eldest daughter of George William, Elector of Brandenburg and Elizabeth Charlotte of the Palatinate was a descendant of Casimir IV Jagiellon (1427-1492), King of Poland both on paternal (through Magdalena of Saxony and Sophie of Legnica) and maternal side (through Albert of Prussia). She was a candidate to become the wife of Ladislaus IV, who however decided to marry French Princess Marie Louise Gonzaga - on September 26, 1645 in Paris Gerard Denhoff, Voivode of Pomerania, who represented the king of Poland, concluded a prenuptial agreement with the French court. Louise's family moved to Königsberg (Królewiec in Polish), the capital of Duchy of Prussia, fief of Poland, in 1638. After the marriage, the couple moved to Kuldiga and then to Jelgava in the Duchy of Courland. Louise Charlotte helped Duke Jacob in governance, both by lending money and maintaining correspondence with many political figures, like King John II Casimir Vasa, Queen Christina of Sweden or Swedish Chancellor Axel Oxenstierna, among others. She had a significant influence on the politics of Courland, whose capital Jelgava became the center of negotiations between Poland, Russia, Brandenburg and Sweden during the Deluge (1655-1660). Louise Charlotte's husband Duke Jakob was educated in Rostock and Leipzig and travelled frequently to Szczecin to visit his friend Bogislaw XIV (1580-1637), Duke of Pomerania. He also visited his relatives in Cieszyn. Around 1629, Kettler traveled to Birzai in Lithuania, which belonged to the Radziwill family, in order to find a bride. In 1634, he made a grand tour of Europe and after spending several months in the Netherlands, in June 1635 he arrived in Paris. Jacob stayed in France for more than a year, then went to Italy, but it is possible that he also visited England or Spain during this time. He returned to Courland in the spring of 1637. Under Kettler's rule, the duchy traded with France, Venice and Denmark (trade agreements were concluded in 1643), Portugal (1648), the Netherlands (1653), England (1654), Spain (1656) and many other countries, including Ottoman Empire. In 1642 he sent a few hundred colonists from Zeeland under the leadership of Cornelius Caroon to establish a colony on Tobago. When this settlement was attacked and the survivors were evacuated, a new colony was established on Great Courland Bay in 1654. On February 16, 1639 in Vilnius, Jacob received investiture from King Ladislaus IV and took the oath of allegiance to the king in a solemn ceremony at the Vilnius Castle. On April 20, 1646 Ladislaus IV confirms the marriage contract between the Duke of Courland and the daughter of the Elector of Brandenburg concerning the bride's dowry in jewels and lands of her dower. In the Ecclesiastical Treasury in Vienna there is large amber altar (190 cm high, inventory number GS Kap 274) in the shape of a pointed pyramid, created in Königsberg or Gdańsk. It is dated to about 1645-1650 and according to Latin Inscription on the back (Lovysa Charlotta D.: G: Princ: Brandenb.: Livoniae Curlandiae et Semigaliae Ducissa) it belonged to Louise Charlotte of Brandenburg, Duchess of Courland. According to some theories, it could have been offered through Andrzej Chryzostom Załuski (1650-1711), Bisop of Warmia to the Emperor in about 1700 (after "Bernstein, das “Preußische Gold”" by Kerstin Hinrichs, p. 142), although it cannot be excluded that the Duchess presented it to the Emperor during the Deluge or earlier. In the Imperial Schönbrunn Palace in Vienna, on the other hand, there is a portrait of a lady with a dog by Justus van Egmont, which is identified as effigy of Anne of Austria (1601-1666), Queen of France (oil on canvas, 115 x 96 cm). The lady is sitting in a gilded armchair in a grey-green satin dress. Basing on costume and hairstyle of the woman this portrait should be dated to beginning of the 1650s, very similar to those visible in a portrait of Mary, Princess Royal (1631-1660) by Bartholomeus van der Helst in the Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, signed and dated upper left: Bartholomeus van der helst 1652 f. Behind a dark green drapery there is a view of a mountainous landscape, which resemble the view of a bay on Eylandt Tabago (Island of Tobago), copper print by Romeyn de Hooghe, published before 1690 (Royal Library of the Netherlands). This painting comes from Archduke Leopold Wilhelm's collection (after "Die Denkmale der Stadt Wien (XI. - XXI. Bezirk)" by Hans Tietze, p. 166, item 192). The young woman bear no resemblance to effigies of Queen of France, who in 1650 was 49 years old, and her physiognomy was clearly inspired by images of Queen of Poland, Marie Louise Gonzaga - for example in the copperplate print by Willem Hondius in the National Museum in Kraków (inventory number MNK III-ryc.-37107). At that time, the style of the Queen of Poland obviously became iconic in Central Europe, because in the Lobkowicz Palace at Prague Castle there is a portrait of Maria Anna Freiin von Breuner née Khevenhüller, a lady-in-waiting of the Empress Eleonora Gonzaga (1630-1686), niece of Marie Louise, probably from the early 1650s (I. 4575). The portrait is almost identical to several effigies of the Queen of Poland, considered the ideal beauty of the time. The same woman was also depicted in another painting in the style of Justus van Egmont (oil on canvas, 62.5 x 79 cm, auctioned at Proantic, reference: 798554, 18th century, Louis 15th style). Her face features resemble greatly Louise Charlotte of Brandenburg from her portrait in the Rundale Palace Museum and Louise Charlotte's sister Hedwig Sophia of Brandenburg (1623-1683), Landgravine of Hesse-Kassel from an engraving by Philipp Kilian, created in 1663 (Austrian National Library in Vienna). In the collection of the House of Hohenzollern, formerly in the Hohenzollern Museum, there is an interesting painting by the Bohemian painter Matthias Czwiczek, who from April 1628 was court painter in Königsberg. This small painting (oil on wood, 33 x 44.5 cm), painted around 1649, represents the members of the family of the Duke of Prussia and Elector of Brandenburg and his wife in the guise of figures from the Old Testament. Frederick William (1620-1688) was depicted as the biblical King Solomon and behind him are his sister Louise Charlotte, Duchess of Courland and her husband Jacob Kettler. The Elector's mother, Elizabeth Charlotte of the Palatinate, crowned by her younger daughter Hedwig Sophia, Landgravine of Hesse-Kassel, is the Queen of Sheba. She receives the bunch of grapes from the hands of the elector's wife Louise Henriette of Nassau (1627-1667), symbol of the Eucharistic wine and therefore of the sacrifice of Christ. The group on the left of the composition shows deceased family members, including Frederick William's father, George William (1595-1640) (compare "Die Frau an Jakobs Seite ..." by Ulrich Schoenborn, p. 4-5, 7). To create his painting, Czwiczek had to use different study drawings or other paintings, which were undoubtedly also used by van Egmont and his workshop to create portraits of the Duchess of Courland.
Portrait of Louise Charlotte of Brandenburg (1617-1676), Duchess of Courland by Justus van Egmont, 1650-1654, Private collection.
Portrait of Louise Charlotte of Brandenburg (1617-1676), Duchess of Courland with a dog and a view of the Island of Tobago by Justus van Egmont, ca. 1654, Schönbrunn Palace in Vienna.
Portrait of a member of the Sollogub family by Ferdinand Bol
In 2014, a "Portrait of a young man, half-length, in a white shirt, golden mantel and red plumed cap, before a draped curtain", attributed to the School of Rembrandt and dated around 1650, was sold in London (oil on canvas, 69.5 x 57 cm, Auction 1576, December 3, 2014, lot 136). The painting was also auctioned with an attribution to Rembrandt's student Ferdinand Bol (Daphne Alazraki Fine Art in New York) and this attribution appears to be the most relevant to the painting's style. According to an old inscription on the reverse of the stretcher the painting belonged to Count Sollogub from whom acquired by V.Th. Levshin, Russia.
The Sollogub family, known as Sołłohubowie in Polish, Sologubai in Lithuanian and Salaguby in Ruthenian, was a noble family of the Prawdzic coat of arms. They probably originated from the Ruthenian nobility of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and rose to prominence in the early 16th century when a certain Yurii Sollogub (d. 1514) was appointed to the post of voivode of Smolensk. In the 16th century many of them became Calvinists. During the Deluge, several members of the family betrayed the rightfully elected monarch of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth John II Casimir and sided, together with Janusz Radziwill (1612-1655), voivode of Vilnius, with the "Brigand of Europe ". Their names appear among the signatories of the Treaty of Kedainiai of October 20, 1655 recognizing the authority of the Swedish king, such as Raphael Sołłohub, Konstanty Dowoynia Sołłohub, woyski Upitski, Andrzey Sołohub, Stefan Dowoina Sołlohub and Mikołai Dowoina Sołohub. This is probably why none of them were given important positions and their biographies were not elaborated by historians. The family rebuilds its status in the Commonwealth when Jan Michał Sołłohub (d. 1748), who, through his marriage to Helena Szamowska in 1706 began his brilliant political career, rose to the position of Grand Treasurer of Lithuania and then voivode of Brest. In 1861, members of the family who settled in the Russian Empire received confirmation of the title of count. As supporters of the Radziwills in the 17th century, the Sollogubs arguably also followed their example in patronage, and as Calvinists some members probably studied in the Netherlands. A somewhat similar painting by Rembrandt is mentioned in the 1835 catalogue of paintings from the Radziwill collection: "18. Portrait of a man in a dark purple dress with fur and a beret on his head, an image full of expression, strong tones give it a charming effect. Painted on canvas". This catalogue also lists three paintings by Ferdinand Bol: "4. Portrait of a man with a dark beard in rich eastern clothes, with folded arms; rendered in a strong color. - Painted on canvas", "356. A man and a lady in eastern clothing. Painted on copper" and "363. Portrait of a man with a beard, in a black cap and a dark robe, with a gold chain hanging on his chest. Painted on canvas" (after "Katalog galeryi obrazow sławnych mistrzów ..." by Antoni Blank, p. 3, 8, 105, 107). Before 1909 in the collection of Countess Sollogub (W. Sologoube) in Saint Petersburg, there was a portrait of a young boy identifed as portrait of Rembrandt's son Titus by Nicolaes Maes ("Les Anciennes écoles de peinture dans les palais et collections privées russes, représentées à l'exposition organisée à St.- Pétersbourg en 1909 par la revue d'art ancien "Staryé gody"", n. 398), now in the Cincinnati Art Museum (1946.95). Although we will probably never confirm the identity of the man in Sollogub's painting with reliable documents, he bears a resemblance to a notable family member, who lived more than a century later - General Jan Michał Sołłohub (1747-1812), painted by Józef Pitschmann in 1792 (Oporów Castle). Since some genes reappear in future generations and some people are even compared to their great-grandfathers or even more distant ancestors, it must be assumed that the man in the portrait was a member of the Sollogub family.
Portrait of a man in a golden mantel, most likely a member of the Sollogub family, by Ferdinand Bol, ca. 1650, Private collection.
Portrait of Alexander Louis Radziwill by Adolf Boy
In 1642, after the death of his older brother Sigismund Charles Radziwill (1591-1642), Knight Hospitaller, Alexander Louis Radziwill (1594-1654), Grand Marshal of Lithuania, inherited the Nesvizh ordynacja (entail), becoming the 5th ordynat. Alexander Louis was the youngest son of Nicolaus Christopher Radziwill "the Orphan" (1549-1616). He studied in Nesvizh and Germany, then traveled around France and Italy. The favorite residence of the landowner and his wife, Tekla née Wołłowicz, was the palace in Biała Radziwiłłowska (Podlaska), where after 1622 he built a lavish palace to design by Lublin architect Paolo Negroni (Paweł de Szate), called Murzyn (the Black Man). In Nesvizh, around 1650, Alexander Louis added two gallery wings connecting the palace wings.
Inventories of 1650 and 1658 present the furnishings of the Radziwill Castle. According to the most complete inventory from 1658, portraits constituted the largest collection of paintings in Nesvizh. In the dining room of the palace, there were 31 portraits of "old princes their Highnesses Radziwills, Szydłowieckis, Wołłowicz and other senators who used to visit this room", including a full-length portrait of Nicolaus Christopher "the Orphan". The second portrait gallery was located in the "great hall", in the second building of the castle complex. It consisted of 14 "standing paintings of the Szydłowiecki counts, various figures rendered in oil" (after "Monumenta variis Radivillorum ..." by Tadeusz Bernatowicz, p. 18). The inventory from 1650 list a portrait of a "lord of Vilnius", probably Janusz I Radziwill (1579-1620), and royal portraits placed behind a curtain at the door to the chapel, i.e. in the sacrum circle. Similar collections were in other residences of the Radziwills - the castles in Mir, Olyka and Szydłowiec, palaces and houses in Warsaw, Vilnius, Grodno, Kraków, Lviv and Gdańsk. Alexander Louis died in Bologna in 1654, where he went for treatment. His son, Michael Casimir, moved the coffin with the prince's body to Nesvizh and buried it in the ancestral crypt of the Jesuit church. In the former Radziwill palace at Nieborów, between Warsaw and Łódź, there is portrait of a man, attibuted to Dutch school and dated to about 1640-1660, incorporated into the collection of the National Museum in Warsaw in 1945 (oil on canvas, 75 x 64.5 cm, inventory number NB 974 MNW). It was mentioned in the catalogue of the collection of Alexander Louis' descendant Michał Hieronim Radziwiłł (1744-1831), exhibited in Królikarnia near Warsaw in 1835, as by Flemish school: "310. Portrait of a man with a white Spanish beard, wearing a white collar, chain hanging around his neck. Painted on canvas". The style of the painting resemble greatly the works by Adolf Boy, court painter of King Ladislaus IV Vasa, especially the portrait of Elżbieta (Halszka) Kazanowska née Słuszczanka (1619-1671) with forget-me-nots (National Museum in Warsaw), created between 1649-1652. The painting is also particularly similar, both in terms of style and physiognomy of the model, to the portrait of King Ladislaus IV Vasa in the Royal Castle in Warsaw (ZKW 559 dep., deposit of the National Museum in Warsaw, 128758). In 1649, Boy created a composition, most likely a painting, depicting the Apotheosis of King John II Casimir Vasa, engraved by Willem Hondius (National Library of Poland, G.219/Sz.1). This indicates that together with another Gdańsk painter, Daniel Schultz, who at that time returned to the Commonwealth from the Netherlands, Adolf became the main court painter of the new king. The engraving as well as Nieborów painting follows the same pattern - exaggerated facial features, a slightly jagged image, and beautiful pastel colors, typical for Boy. The costume and pose of the sitter resemble the effigies of Alexander Louis' cousin Albert Stanislaus Radziwill (1593-1656) from the 1640s (National Art Museum of Belarus), portrait of Nikolaus Hübner, counsellor of Toruń, dated '1644' (District Museum in Toruń) and portrait of Giovanni Ambrogio Rosate (1557-1651), a Milanese silk merchant, dated '1650' (Ospedale Maggiore in Milan). The man depicted bear a strong resemblence to Alexander Louis from his effigies in the National Museum in Warsaw (MP 4771 MNW, Gr.Pol.10095/102 MNW), created in the 18th century after original from the 1630s, and in the State Hermitage Museum (ОР-45869), created between 1646 and 1653.
Portrait of Alexander Louis Radziwill (1594-1654), Grand Marshal of Lithuania by Adolf Boy, ca. 1650, Nieborów Palace.
Portrait of Christopher Sigismund Pac
In 1837 Louis Philippe (1773-1850), King of the French, founded a museum in the Palace of Versailles dedicated to "all the glories of France", today Museum of the History of France (Musée de l'Histoire de France). The museum displayed artefacts formerly in other national collections as well as works specifically commissioned for it.
Auguste de Creuse, a French portrait painter, was commissioned to create several copies of effigies of historically significant individuals. The originals were probably lost or damaged during past revolutions and disrepair of some of the royal palaces. He created a copy of a portrait of Louis Philippe when Duke of Chartres by Jean-Antoine-Théodore Giroust from the 1790s and a portrait of La Grande Mademoiselle (Anne Marie Louise d'Orléans, Duchess of Montpensier) as a shepherdess by Gilbert de Sève from the 1660s (originals are considered lost), among others. On August 14, 1838 he was also paid 150 francs to create a portrait of Jean Bart or Jan Baert (1650-1702), a French/Flemish naval commander and privateer, inscribed Jean Bart / Chef D'escadre (oil on canvas, 39 x 29 cm, MV 4307). De Creuse probaly copied a painting preserved in the French royal collection. The man wears a silk costume similar to Polish-Lithuanian żupan and overcoat lined with fur similar to kontusz, both buttoned up with large gold buttons set with precious stones in oriental style, similar to guzy from Polish national costume. The sitter bear no resemblance to the effigy of Jean Bart published by Pierre Blin in 1789, a print made by Antoine François Sergent-Marceau, whereas, he bear a striking resemblance to effigies of Christopher Sigismund Pac (1621-1684). Although in one portrait, by Mathieu Elias, Jean Bart was depicted in a fur hat which looks like Polish kołpak (National Navy Museum in Paris, inventory number OA 49), his costume is from western Europe. The costume in the Versailles portrait is almost identical to that visible in Christopher Sigismund's effigy by Johann Franck, a print published in 1659 (Vilnius University Library). Christopher Sigismund Pac was educated in Kraków, Padua and Perugia, and then in Graz and Leiden and served in the French, Spanish and Dutch armies. In 1646 he become Grand Standard-bearer of Lithuania. He enjoyed the great trust of King John Casimir Vasa and his French wife Marie-Louise Gonzaga. He adhered to the French orientation and supported Queen Marie-Louise's plans to hold a vivente rege election (election of a king during the lifetime of predecessor). In 1654, he married the French noblewoman Claire Isabelle Eugenie de Mailly-Lespine (better known in Poland-Lithuania as Klara Izabella Pacowa), a descendant of Anne Lascaris, lady-in-waiting and confidante of Queen Marie Louise. A year later, in 1655, he received the office of Vice-Chancellor of Lithuania. In 1662, in addition to 30,000 livres received from the French treasury in 1661, he got a salary of 15,000 francs from the French ambassador to the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Antoine de Lumbres, for supporting the French candidate during the vivente rege election. This explains clearly the presence of his portrait in the French royal collection. Like the portrait holding the Grand Lithuanian Seal in the National Art Museum in Kaunas from about 1670, the original was most probably created by royal court painter Daniel Schultz. The sitter, however, is much younger in the Versailles portrait than in the Kaunas version, thus the painting should be dated to the early 1650s, when Schultz began his career at the court after return from France and the Netherlands.
Portrait of Christopher Sigismund Pac (1621-1684) by Auguste de Creuse, 1838-1840, after original from the early 1650s by Daniel Schultz (?), Palace of Versailles.
Portrait of Johann Georg Franz Wisendo von Wiesenburg by Frans Luycx and workshop
Although, according to known sources, the Flemish painter and portraitist of the imperial court in Vienna, Frans Luycx or Luyckx (d. 1668), student of Peter Paul Rubens, never visited the Commonwealth his works and those of his workshop linked to Poland-Lithuania are numerous. Some of the effigies of members of the royal-grand ducal family of Poland-Lithuania the painter was able to create during their visit to Vienna in 1638 or shortly after. Before 1643, Luycx most probably worked for Prince John Casimir since, according to the inventory of works on his wooden palace in Nieporęt near Warsaw, 160 florins were paid to a painter in Vienna for the altars (P. Von Sorgen zapłacieł w Wiedniu według recognicy K.J.M. Malarzowy ad rationem ołtarzów do Nieporęta) (after "Zbiory artystyczne ..." by Ryszard Szmydki, p. 43).
The composition of the portrait of John Casimir in fashionable French costume, created after his election, perhaps around 1648-1654, was similar to the portrait of his brother Ladislaus IV in "white boots", created by Luycx about a decade earlier, especially when it comes to the strange, almost surreal representation of the room behind the monarch. However, this portrait, which was probably lost during the First World War, is only known from very old photographs (National Museum in Warsaw, DI 40131 MNW), so nothing can be said with certainty about its style. Many of Frans' paintings were also in the king's collection before the Deluge, however only one preserved in Warsaw. This is the portrait of John Casimir's cousin, Maria Anna of Spain (1606-1646), Holy Roman Empress, at the Visitandine monastery in Warsaw (inscribed in Latin: MARIA HISPANA IMPERATRIX / FERDINANDI III VXOR.). The painting was given to the monastery most probably after the king's abdication, because the accounts show a payment of 6 zloty and 20 groszy for moving certain objects from the castle (September 1668) - furniture, paintings, silverware, musical instruments, fabrics and books (after "Portrety infantek ..." by Jerzy T. Petrus, p. 31, 33). This painting was commissioned or received as a gift from Vienna between 1638 and 1642. In the Nationalmuseum in Stockholm there is another portrait of the Holy Roman Empress by Luycx, which most probably comes from the collection of John Casimir (oil on canvas, 226 x 126 cm, NMGrh 75). This is the portrait of Eleonora Gonzaga (1630-1686), daughter of Charles II Gonzaga, Duke of Nevers and niece of the king's wife Marie Louise Gonzaga. In April 1651, Eleonora married the king's cousin, Emperor Ferdinand III, and she was crowned in Regensburg Cathedral on August 4, 1653. The portrait was therefore most likely created between 1651 and 1653 as part of the series, because there is a similar one at the Cheb Museum in the Czech Republic (inventory number č. O 177) and at the Villa del Poggio Imperiale (a reduced version, Poggio Imperiale 431 / 1860), most likely offered to the Medici. The Stockholm painting is signed and dated at the bottom in Latin: ELEONORA GONZAGA ROM. IMP. AN. 16. / Lux Pinxit. / M, however the exact date was probably obscured, as were probably other signs of its original provenance. It is therefore very likely that the painting was looted in Warsaw in 1656 or during the Great Northern War (1700-1721), like the portrait of Abbess Euphemia Radziwill (1598-1658) by Johann Schretter from the 1640s (NMGrh 1576). Another gift from Vienna for John Casimir or his wife painted by Luycx could be the portrait of a man from the collection of Jan Popławski (1860-1935), now in the Museum of Warsaw (oil on canvas, 80 x 63 cm, MHW 522). This painting was initially attributed to a follower of Hans von Aachen (1552-1615) and now to an 18th century painter. It is very close to the style of the Flemish painter and his workshop, in particular the portrait of Ladislaus IV in Wilanów (Wil.1143). The way the hand was painted is particularly characteristic of Luycx. This painting depicts Johann Georg Franz Wisendo von Wiesenburg (1622-1666), a clerk (Hofkammerkonzipist) at the court of Emperor Ferdinand III from 1648. He was painted by Luycx and his workshop in 1653 and the inscription on the back confirms this: Johan Georg Fran.s. / Wisendo VW. / M 1653. L. P. pinx.
Portrait of King John II Casimir Vasa (1609-1672) with a crown by workshop of Frans Luycx (?), ca. 1648-1654, present whereabouts unknown.
Portrait of Empress Eleonora Gonzaga (1630-1686) by Frans Luycx, ca. 1651-1653, Nationalmuseum in Stockholm.
Portrait of Johann Georg Franz Wisendo von Wiesenburg (1622-1666) by Frans Luycx and workshop, 1653, Museum of Warsaw.
Tronies of King John II Casimir Vasa
Dutch head-studies in a costume, known as tronies (meaning "faces" or "visages"), became popular in Poland-Lithuania as early as the 17th century and many paintings of this type were part of royal and magnate collections. Two paintings by followers of Rembrandt - portrait of a bearded man (oil on mahogany, 102 x 78 cm, Gal.-Nr. 1567, signed: Rembrandt. f. 1654.) and portrait of a man in a hat decorated with pearls (oil on canvas, 82 x 71 cm, Gal.-Nr. 1570), and one by Willem Drost - portrait of a man with a red kolpak (oil on canvas, 89.5 x 68.5 cm, Gal.- Nr. 1568), all in the Dresden gallery (Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister) are generally considered to come from the collection of John II Casimir Vasa.
The "Catalogue of the pictures in the Royal Gallery at Dresden", published in 1912, also lists "Portrait of a young married woman" (oil on canvas, 67.5 x 60.5 cm, Gal.-Nr. 1584) and "An old man with a bald head" (oil on canvas, 63.5 x 53 cm, Gal.-Nr. 1585), painted in the 1630s, both by Jacob Adriaensz. Backer, as "acquired in Poland" according to the inventory of 1722. It also mentions "Mordecai and Esther write letters in King Ahasuerus' name" ("An important document", Gal.-Nr. 1792 A) by Aert de Gelder, however this painting is generally dated around 1685, so it was very probably purchased during the Sobieski period. Portrait of a young woman putting on a pearl bracelet (oil on canvas on wood, 78 x 62.5 cm, Gal.-Nr. 1591), attributed to Willem Drost, was also transferred from Poland before 1722, according to Hübner's register (no. 1235). Interestingly, many of these paintings are dated around 1654, so John Casimir may have acquired them shortly before the Deluge and evacuated them to Silesia. Apparently, this type of paintings gained popularity in Poland-Lithuania also among the local painters, because in the Museum of Fine Arts in Bordeaux there is a tronie-like portrait showing a man in eastern costume (oil on canvas, 68.5 x 55 cm, Bx E 10). It comes from the collection of the King of France Louis XIV in Versailles (Cabinet des tableaux), who received and purchased several objects from John Casimir's collection such as a brooch with the Polish eagle (Louvre, MR 418) or tapestries with the Triumphs of the Gods by Frans Geubels. His fur hat and Asian features indicate that he is Tatar. Men of this Muslim ethnic group of the Commonwealth were frequently members of the royal guard since the Middle Ages, confirmed since the times of King Casimir IV Jagiellon (1427-1492) (after "Tatarzy w dawnej Rzeczypospolitej" by Piotr Borawski, p. 98). His gorget indicates that he is indeed a soldier. This painting was once attributed to Guido Reni and now to the School of Rembrandt, but the closest seems to be the works of the court painter of John Casimir - Daniel Schultz, such as the portrait of the king at the Royal Castle in Warsaw (ZKW 1175), the alleged self-portrait of Schultz in the National Museum in Warsaw (MP 2447) or the family portrait, believed to represent the Crimean Tatar falconer of John Casimir, in the Hermitage Museum (ГЭ-8540). Another tronie-like portrait painted by Schultz for the king could be a dwarf with a dog from the Wilanów Palace (oil on canvas, 56 x 50 cm, inv. 270), which, according to the preserved photograph, was comparable to the mentioned paintings. This painting has been considered lost since the Second World War and as nothing was known about it apart from the fact that it came from the royal collection of the last elected monarch Stanislaus Augustus, it was considered to be the work of a 17th-century Spanish painter, as they frequently painted dwarves. Even during the Deluge, John Casimir maintained a luxurious lifestyle, comparable to that of his cousin King Philip IV of Spain. Pierre des Noyers, secretary to the Queen, who was apparently not favorable to him, stated: "He is surrounded by a large number of dwarves, dogs, birds and monkeys. In his room, only lewd topics are discussed - this is his usual occupation. On Good Friday, like any other day, he always takes five or six Jesuits with him, often goes to confession, but this produces nothing" (letter dated October 1, 1658 from the military camp near Toruń, after "Lettres de Pierre Des Noyers ...", published in 1859, p. 446). Among many dwarves, the king had at his court two Kuczkowski brothers, Stanisław and Kazimierz, whom he affectionately called Kuczkosie. In the expenses of the royal court of John Casimir from 1650 to 1652, the following were repeated: "to Barthelek the dwarf - 75 zloty", "to Januszek the dwarf - 50 zloty", "to Kuczkoś the dwarf - 50 zloty", "to the second Kuczkoś - 50 zloty" and there is also a payment "to Mr. Vinderhenn for a silver pot and a gilded cup for the dwarves of His Majesty the King - 70 zloty" (after "Niziołki, łokietki, karlikowie ..." by Bożena Fabiani, p. 5). A female dwarf of the Queen named Resia, along with the dwarf Bonarowski, was sent to Chantilly in the 1660s, to the court of Louis II de Bourbon, Prince of Condé. Furthermore, the Dutch obviously also wanted to have tronies with the "Poles" (as it is often simplified when referring to people from the Commonwealth), because there are many portraits of this type of people wearing costumes similar to those known from Poland-Lithuania and Ruthenia, painted by Rembrandt and circle. As an example, we can cite the portrait of a boy with a fur hat with feathers by Jacob Backer at the Museum Boijmans Van Beuningen (2483 (OK)), the portrait of a youth in Ruthenian costume by Pieter de Grebber in the Liechtenstein Museum in Vienna (GE 89), portrait of a man in a kolpak hat as the Apostle Paul by Willem Bartsius in the Catharijneconvent Museum in Utrecht (StCC s35) or portrait of a man in a fur hat and a fur coat by Isaac de Jouderville (signed and dated: Rembrandt f / 1641, sold at Christie's, auction 21643, January 31, 2023, lot 337). Many tronies and genre paintings that survived the Deluge or acquired later were in the collections of the "Victorious King" John III Sobieski (1629-1696). Some of them are mentioned in the inventory of the king's palace in Wilanów from 1696, such as "A pair of paintings, in one of them a Swiss man with a halberd, in the other a Dutch woman" (No. 29), "A picture of an old Spanish woman" (No. 76), "A picture of a woman reading a book" (No. 97), "A picture of a Dutch seamstress [possibly a copy of The Lacemaker by Johannes Vermeer]" (No. 98), "A picture of old men painted on a board, one of them is holding a fish and money" (No. 169), "A pair of paintings, in one of them an old man, in the other a woman" (No. 172), "A pair of pictures, in one of them the Dutchman is fighting lice, in the other one the other man is scratching" (No. 202), "A painting by the painter Rynbrant [Rembrandt], on which an old man is painted, large, with gilded frames, round at the top" (No. 210), "A Dutch painting of David triumphing over the giant [David and Goliath], yellowish" (No. 216), "A picture on a tin plate, a Spanish woman in a hat" (No. 240) (compare "Inwentarz Generalny 1696 z opracowaniem" by Anna Kwiatkowska). This inventory also lists paintings that may be copies or originals of The Love Letter (No. 156) and The Milkmaid (No. 180) by Vermeer. In the inventory of paintings from the collection of Princess Louise Charlotte Radziwill (1667-1695), drawn up in 1671, tronies depicting Dutch people (Olender/Olenderka) are listed separately after standard portraits and effigies of Roman emperors (numbers 337-347, 696-697, 730, 797, compare "Inwentarz galerii obrazów Radziwiłłów z XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska). Also the octagonal portrait of King John II Casimir, attributed to his court painter Daniel Schultz, resembles a tronie (National Museum in Warsaw, deposited in the Royal Castle in Warsaw, oil on panel, 62 x 50 cm, NB 474 MNW, inscription: Joan. Ca ...). This painting was most likely created after the king's accession to the throne in 1649 or after the Deluge in the 1660s to complete the series of the so-called Jagiellon Family in the Marble Room of the Royal Castle in Warsaw. In addition to the monarch's costume with a Ruthenian fur hat, this painting is clearly inspired by Rembrandt's style.
Portrait of an old man with a bald head by Jacob Adriaensz. Backer, ca. 1633-1635, Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden.
Portrait of a young married woman by Jacob Adriaensz. Backer, ca. 1633-1635, Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden.
Portrait of a bearded man by follower of Rembrandt, ca. 1654, Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden.
Portrait of a man in a hat decorated with pearls by follower of Rembrandt, before 1667, Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden.
Portrait of a man in a red kolpak by Willem Drost, ca. 1654, Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden.
Portrait of a young woman putting on a pearl bracelet by Willem Drost, ca. 1654, Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden.
Portrait of a Polish-Lithuanian Tatar in a fur hat by Daniel Schultz, after 1649, Museum of Fine Arts in Bordeaux.
Portrait of King John II Casimir Vasa by Daniel Schultz, after 1649, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of a dwarf with a dog by Daniel Schultz (?), after 1649, Wilanów Palace, lost.
Tarquin and Lucretia with portrait of Lucrezia Maria Strozzi, Princess Radziwill by Pietro della Vecchia
"Having rendered to the Prince my husband, worthy of memory, the last service after such serious troubles, I followed the advice of my friends who came to this funeral to come to an agreement with the Prince Incisor of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania so that at least in my orphanhood I would have a calmer head and I would not ruin my health with constant worry", wrote in a letter dated October 22, 1654 from Turets (Belarus) Lucrezia Maria Strozzi (ca. 1621-1694), Princess Radziwill to Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga (Central Archives of Historical Records in Warsaw, 1/354/0/4/703). The queen supported the former lady-in-waiting of Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria in the conflict with her stepson Michael Casimir Radziwill (1635-1680).
Michael Casimir raised objections to the provisions of his father's will in favor of Lucrezia Maria, accused her of forging her husband's will and intended to deprive her of her rights to Chernavchitsy and Turets. Lucrezia Maria's husband, Alexander Louis Radziwill, died in Bologna in March 1654, where he went with his wife for treatment. Returning from abroad in July 1654, Michael Casimir forcibly seized his deceased father's main residence, Biała Podlaska Palace. He also seized the property of Lucrezia Maria in Chernavchitsy. He went even further by filing an official complaint against his stepmother, in which he blamed her for the conflict and its escalation. Until November 1663, the widow with two young children was constantly involved in legal proceedings with him, usually interrupted by compromise agreements. During the invasion of the Commonwealth by neighboring countries (Deluge), Lucrezia Maria accompanied the Queen to Silesia. The entire court evacuated from Warsaw via Kraków to Głogówek (October 17, 1655), which was part of the Vasa estates and the queen's dower. The town became the emigration capital for the royal couple and their supporters. It is estimated that up to 2,000 people lived in Głogówek and surrounding areas. From there, Lucrezia Maria with her children went to Italy, to Mantua (February 1656) and Naples (August 1657). She probably left her children with her family in Mantua until 1661 or 1663. In her last will she requested that her body be placed in the Sanctuary "delle Grazie" in Curtatone near Mantua, where the bodies of her ancestors were buried in the family chapel of Saint Louis (decorated with frescoes by Il Pordenone). They were quite fortunate. Their wealth, position and connections allowed them to spare their lives and part of their property. What happened to the people who couldn't escape was truly terrible. The atrocities of the invaders are described in the letters of the Queen's secretary Pierre des Noyers, such as during the burning of Praga (a district of Warsaw on the east bank of the Vistula), when the Brigand of Europe - Charles X Gustav of Sweden, arrived there "all these miserable peasants, with their wives and their children threw themselves on their knees begging him to have pity on their misery; he told them that they were all traitors, and ordered his people to kill everyone, which they did in his presence without forgiving not a single child" (le roi de Suède étant arrivé au lieu de l'incendie de Prague, tous ces misérables paysans, avec leurs femmes et leurs enfants, se jetèrent à genoux en le priant d'avoir pitié de leur misère; il leur dit qu'ils étaient tous des traîtres, et commanda à ses gens de tout tuer, ce qu'ils firent en sa présence sans pardonner à pas un enfant, letter dated August 11, 1656 from Łańcut) (after "Lettres de Pierre Des Noyers ...", published in 1859, p. 217-218). The tragic story of a boy-bear, described in "Ordinary News of January 5, 1664. From Warsaw, December 1, 1663" (Nouvelles Ordinaires du 5me Ianvier 1664. De Warsovie, Ier Décembre 1663, p. 13-14, National Library of France, FRBNF32780022), is most likely also directly linked to the invasion. "The Bishop of Vilnius sent to the Queen here a child aged 8 to 9 years old who was found among the bears near Kaunas, in Lithuania: where the soldiers who have their winter quarters on that side, having been asked by the peasants to give chase to these beasts, who caused them great damage, seeing him naked, fleeing with the cubs of a bear that they were pursuing. He was placed in our hospital: where by the order of this Princess, he is being taught the French language" (L'Evesque de Vilna a ici envoyé à la Reyne un enfant agé de 8 a 9 ans qui a esté trouvé parmi les Ours proche de Kowno, dans la Lithüanie: où les Soldats qui ont leurs Quartiers d'hyver de ce costé-là, ayans esté sollicitez par les Païsans de donner la chasse à ces Bestes, qui leur causoyent de grands dommages, l'aperçeurent tout nud, fuïant avec les petits d'vne Ourse qu'ils poursuivoyent. Il a esté mis dans nostre Hospital : où par l'ordre de cette Princesse, on lui apprend la langue Françoise). The boy "had no human speech or manners [...], the queen gave him a peel of a pear sprinkled with sugar; [...] after tasting it, he spat it out on his hand and with his saliva, he threw it between the queen's eyes; the king began to laugh greatly" (Jan Chryzostom Pasek recounts about the boy raised by bears and found in 1662 - Pamiętniki). The female bear suckling a child and history of a boy was also published in Bernard O'Connor's "The history of Poland in several letters to persons of quality ...", published in London in 1698 (Volume I, p. 342-343, National Library of Poland, SD XVII.3.4040 I). During the invasion Kaunas was burnt and pillaged by the Russians, who occupied this part of the country from 18 August 1655 to 2 December 1661 (after "Social and Cultural Relations in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania: Microhistories", p. 9). The devastation of the city was so great that the Sejm in Warsaw in 1662 exempted Kaunas from taxes and customs duties for 10 years. According to Nouvelles Ordinaires, the boy was 8 or 9 years old when he was brought to the queen in Warsaw in 1663, therefore he lost his parents around 1655-1660, that is, during the horrific Deluge. The invasion found its reflection in poetry, such as the poem by Zbigniew Morsztyn (ca. 1628-1689), a Protestant poet at the court of the Radziwills, dating from around 1657 - "The second muse of the author during the siege of Kraków, when he was a prisoner of the Swedes": "I sing, although my motherland is suffering, She was once so fertile, So invincible, And with her her deeds are ruined [...] I sing, and streams gather Polish blood, and smoke rises to the clouds from cities and villages. This happy country is turning to ashes [...] I sing petrified, And where is my abundance? Where did the holidays go? The remnants were burned with fire and razed to the ground". One of the few European artists to possibly react to these tragic events was Rembrandt creating his print of Christ Presented to the People, also known as Ostentatio Christi or Ecce Homo. This work is mysterious for many reasons. We don't know who ordered it or why the artist created it. He made several versions of this etching, the last being the most dramatic (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, RP-P-OB-612). The square in front of the building, filled with the people of Jerusalem demanding the crucifixion of Christ in initial versions, was replaced by two arched openings. Between them Rembrandt placed the figure which is sometimes interpreted as a river or sea god, but it could also be Saturn, Roman god of time, dissolution, abundance, periodic renewal and liberation. The niches of the building house allegorical sculptures of Justice and Fortitude (courage in pain or adversity). In the 19th century the representatives of the imperialists who destroyed the Commonwealth and its multiculturalism have often emphasized Rembrandt's particular inclination towards theatricalism, without paying sufficient attention to the fact that this theatricalism in the 17th century must have had an important context and meaning, not necessarily religious or moralistic. The most intriguing are the people surrounding Christ and the man at the door on the right. They are definitely not typical inhabitants of Amsterdam and closely resemble the nobles of the Commonwealth, as in the print depicting four Poles (Polachi), created by Johann Wilhelm Baur in Rome in 1636, title page of Polonia, nunc denuo recognita et aucta by Szymon Starowolski, published in Wolfenbüttel in 1656 or in the map of the Commonwealth (Poloniae Nova et Acvrata Descriptio) by Jan Janssonius, published in Amsterdam in 1675. Several magantes and dignitaries of the Commonwealth were also depicted with a similar hairstyle - for example Jan Żółkiewski from his marble tomb monument by Wojciech Kapinos (II) in the Church of St. Lawrence in Zhovkva (1630s) or Mikołaj Spytek Ligęza from his alabaster tomb monument by Sebastiano Sala in the Bernardine Church in Rzeszów (1630-1638). In this composition, we can identify characters wearing costumes typical of 17th century Jews, Poles, Lithuanians, Ruthenians, Cossacks, Muslim Tatars, Armenians, Germans, Dutch and even Italians. Such a mixture was rather unprecedented at the Town Hall of Amsterdam or at the court of The Hague, while it was typical at the grand-ducal-royal court in Vilnius, Grodno, Lviv, Gdańsk, Kraków and Warsaw and in most towns and villages in the Commonwealth (compare: "Lamentation of various people over the dead credit" - Lament różnego stanu ludzi nad umarłym kredytem, from about 1655). Only the last two states of Rembrandt's print are signed and dated above the arcade to the right of the central platform - Rembrandt f. 1655. That same year, several foreign armies invaded the Commonwealth. Another fascinating piece of art related to Rembrandt can be found at the Wilanów Palace in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 76 x 65 cm, inventory number Wil.1346). This painting represents a soldier and a young girl and is attributed to Pietro della Vecchia (d. 1678), a painter active in Venice from 1633, who probably studied with Alessandro Varotari, hence his interest in Venetian painting of the previous century, in particular that by Titian and Giorgione. The image of a knight in Renaissance costume with a wide feathered hat drawing a sword, perhaps being a copy of a lost original by Palma Vecchio (Theatrum Pictorium, 223), is typical of della Vecchia. He made many versions and variations of this warrior. The image of the girl, on the other hand, is quite unusual. The style is different and the influence of Rembrandt is clearly visible "primarily in the painterly, free arrangement of thick impastos on the girl's shirt" (after "Malarstwo weneckie ..." by Agnes Czobor, p. 165). It seems that the painter combined the two distinct effigies, his warrior and the portrait of a young girl by Rembrandt or his circle. The paintings come from the collection of Count Stanisław Kostka Potocki (1755-1821). On the back of the canvas there is a sticker with the count's seal from 1818-1821 and the inscription in French: "Portrait of a Man and a Woman by Della Vecchia" (Portrait d'un homme et d'une Femme de Della Vecchia). From 1818 Potocki served as president of the Senate of the Kingdom of Poland. He therefore most likely acquired this painting in Poland. The woman closely resembles Lucrezia Maria Strozzi, Princess Radziwill from her effigies by Rembrandt (National Gallery of Art, 1937.1.76 and Minneapolis Institute of Art, 34.19) and from the workshop of Andreas Stech (Museum of Warmia and Mazury in Olsztyn), all identified by me. In the mentioned paintings by Rembrandt, the princess was depicted in the guise of the Roman heroine and her namesake Lucretia. Lucretia was the daughter of Spurius Lucretius Tricipitinus and the wife of Collatinus of the Tarquin royal family. She was famous for her beauty and even more for her virtue. According to ancient historians, Sextus Tarquinius (Tarquin), one of the sons of the last king of Rome, was captivated by her beauty and, threatening her with a weapon, raped her. This event marked the start of a revolt and led to the overthrow of royal power in Rome and the establishment of the Republic. Throughout the centuries of Roman history, Lucretia was highly revered, representing the archetypal example of female purity and valor and a symbol of bravery unconquered by tyranny. Tarquin became the image of a tyrant or enemy and a symbol of arrogance. In the Wilanów painting, the warrior looks at the woman with desire, while she looks at the viewer. The soldier-Tarquin can therefore be considered as a symbol of the "tyranny" of Lucrezia Maria's stepson. The painting is generally dated to the second half of the 17th century, which is why the princess commissioned this disguised depiction of herself probably during her stay in Venice or Mantua or shortly after her return to Poland-Lithuania (around 1657 or 1661). Della Vecchia probably received her portrait by Rembrandt to prepare this composition and was inspired by the Dutch painter's style. One of Pietro's best works - Saint Mark the Evangelist from the National Art Museum in Kaunas (ČDM Mt 1396) was also created around this time.
Tarquin and Lucretia with portrait of Lucrezia Maria Strozzi (ca. 1621-1694), Princess Radziwill by Pietro della Vecchia, ca. 1654-1661, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
Ecce Homo - Allegory of the fall of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth during the Deluge (1655-1660) by Rembrandt, 1655, Rijksmuseum Amsterdam.
Portrait of Marcjan Aleksander Ogiński on horseback by Rembrandt
"They generally killed everyone in Vilna [Vilnius], both men and women" (Ils ont généralement tout tué à Vilna, tant hommes que femmes), reports Pierre des Noyers, secretary to Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga, in a letter dated November 8, 1655, on the destruction of the illustrious capital of Lithuania (after "Lettres de Pierre Des Noyers secrétaire de la reine de Pologne ...", published in 1859, p. 10).
This invasion was certainly one of the worst barbarities in human history and this was only the beginning of the horror caused by foreign imperialism. Death surrounded people everywhere in a destroyed country. Foreign armies and unburied rotting corpses in the streets caused epidemics. It is very meaningful that images of the Dance of Death, an allegory on the universality of death, popular in Western Europe in the Middle Ages after the Black Death (1346-1353), gained popularity in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth after the Deluge - stucco allegories of death in the Chapel of the Good Death in Tarłów, most probably created by Giovanni Pietro Perti and Giovanni Maria Galli after 1662 or Dance of Death by Franciszek Lekszycki at the Bernardine Monastery in Kraków, painted in the 1660s, and a copy in Węgrów Basilica. After the destructive Deluge, the country slowly recovered. It also significantly impoverished. Many people lost their lives and, according to some estimates, the population decreased by 40%, even 90% in some cities, such as Warsaw. Residents could no longer afford to spend on luxury items and paintings abroad (mainly in Italy, Flanders and Germany), with exceptions, which, paradoxically, had a positive impact on local production. The painting workshops of two large economic centers not destroyed during the invasion - Lviv in Ruthenia (Ukraine) and Gdańsk in Polish Prussia (Poland), become the most important. The eminent Gdańsk painter Daniel Schultz, court painter to King John II Casimir, trained in the Netherlands, became the major painter of this period. The apocalyptic memories of the invasion had a great influence on art which became very dark and focused on the vanity of life - "the vanity of vanities, and all things are vanity" (vanitas vanitatum, et omnia vanitas) and "remember that you will die" (memento mori). It was after the Deluge that the Sarmatian tradition of coffin portraiture developed significantly, while the rotting skeleton gradually replaced the effigies of the joyful Venus and the eastern Hodegetria replaced the lascivious western Madonna. As many buildings were made of wood, burned structures completely disappeared in just a few days or months. During more than five years of occupation, the invaders transformed large parts of the country into desert. These horrific events in which an army of united bandits engaged in one of the greatest organized pillages in history, repeated over the following centuries, were forgotten and never strongly condemned in Western Europe. The leaders of this dubious campaign are still glorified by some historians as "extraordinary tacticians" or "great conquerors". After such an apocalypse, everything had to be rebuilt from scratch. It should also be noted that in those cruel times the Poles were not only victims. They were also engaged in controversial military campaigns. One of these notorious military formations was Lisowczycy also known as Straceńcy ("lost men" or "forlorn hope"), an irregular unit of the Polish-Lithuanian light cavalry, formed as a result of semi-legal mutiny of royal forces. As a result of rapes and robberies, Lisowczycy were usually not taken prisoner, but executed on the spot. Already in 1623, their actions in Moravia and Silesia became a subject of dispute between Sigismund III Vasa and his brother-in-law, Emperor Ferdinand II. Brought to fight Gabriel Bethlen (1580-1629), Prince of Transylvania and Duke of Opole, the Lisowczycy started robbing and murdering the inhabitants of local towns and villages. During a private audience with Ferdinand II, Prince Albert Stanislaus Radziwill (1593-1656) responded to the complaints and accusations formulated in the imperial letters sent by his diplomats in Warsaw. In his instructions, Sigismund III described the actions of the Lisowczycy as the "licentiousness of evil people". Severe parliamentary acts were issued regarding the prosecution and imprisonment of them for crimes and robberies in 1623, 1624, 1625, 1629 and 1631. Prince Radziwill and Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa were to present an identical opinion to Archduke Charles of Austria, bishop of Wrocław, who hosted them in Nysa. During the joint journey of the retinues of the Polish-Lithuanian Prince and Archduke Charles to Vienna, there was a danger that Ladislaus Sigismund, Albert Stanislaus Radziwill and Bishop Charles of Austria would be kidnapped by the Lisowczycy. On June 16, 1624, Radziwill wrote: "The news spread, I don't know, from who it comes, about the threats of the Lisowczycy to kidnap the Most Serene Ones" (after "Świat polskich Wazów: eseje", p. 281). The Lisowczycy were formally deprived of the knighthood and dissolved in 1635 by an act of the Sejm, after their return to the Commonwealth (after "Lisowczycy – jeźdźcy apokalipsy ze wschodu" by Piotr Korczyński). "The Polish Rider" by Rembrandt, painted around 1655 (or the 1650s), traditionally known in Polish literature as Lisowczyk (as listed in the Tarnowski collection at Dzików), could not have been part of this notorious formation because it was created 20 years after its formal dissolution. The painting, now at the Frick Collection in New York (oil on canvas, 116.8 × 134.9 cm, inventory number 1910.1.98), comes from the royal collection of the elected monarch of the Commonwealth, Stanislaus Augustus Poniatowski. It was listed in the inventory of the king's Palace on the Isle in Warsaw in 1793 as a "Rembrandt Cossack on horseback high 44, width, 54 inches" (Rembrandt Cosaque à cheval haut 44, larg. 54 pouces), because in the 18th century, Cossacks wore such little old-fashioned costumes, with the price of 180 ducats. The Polish-Lithuanian horseman by circle of Anthony van Dyck, painted in the 1620s (Schleissheim Palace, inventory number 4816), is also known as "The Polish Cossack" (Der polnische Kosak). This painting comes from the Düsseldorf Gallery, like the portraits of King Sigismund III and his second wife Constance of Austria (Neuburg Castle, 984 and 985), so it was possibly in the collection of their daughter Anna Catherine Constance Vasa. The painting by Rembrandt was offered to the king in the middle of August 1791 (mediis Augusti 1791) by Michał Kazimierz Ogiński (Mykolas Kazimieras Oginskis), Grand Hetman of Lithuania in exchange for some orange trees: "Sire, I am sending Your Majesty a Cossack, whom Rembrandt had set on his horse. This horse has eaten during his stay with me for 420 German gulden" (Sire, Odsyłam Waszey Królewskiey Mości Kozaka, którego Reinbrand osadził na koniu, zjadł ten koń przez bytność swoją u mnie 420 guldynów niemieckich). Ogiński, as king's envoy, resided in the Hague and in London from August 1790 to March 1791. Based on this, some researchers believe that he purchased the painting abroad, but there is no solid evidence of this. It sometimes seems that they want to maintain the image of a poor and primitive Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth (before 1655), inhabited by people incapable of appreciating the quality of a work of art and commissioning an exquisite painting, than admitting that some of their compatriots or allies engaged in truly barbaric activities as invaders, including the looting and destruction of paintings. Michał Kazimierz, a member of a princely family of Ruthenian origin, was also a patron of the arts. Around 1755, he commissioned a series of his effigies from Anna Rosina de Gasc née Lisiewska, a German portrait painter of Polish origin, but only two paintings were preserved - one in Minsk in Belarus and the other in Sanok in Poland. While art historians in England or Italy sometimes have the comfort of determining the identity of the sitter for van Dyck's portrait (or other famous Old Master), simply based on prior ownership of the painting, in Poland's connected artworks such attempts result to sometimes harsh discussions and controversies. Although for some scholars the great Rembrandt could not paint someone from destroyed Poland-Lithuania and the painting is imaginative or depicts someone in eastern costume, the oldest determined ownership (Michał Kazimierz Ogiński before 1791) and the costume indicate that the man comes from the Commonwealth. In 1981 Juliusz Chrościcki proposed Marcjan Aleksander Ogiński (1632-1690) as the sitter ("Rembrandt's „Polish Rider”. Allegory or Portrait?", p. 444) basing on great resemblance of the model and his costume to the portrait formerly at the Wenner-Gren collection in France. This effigy bearing the inscription MO / STR (bottom right), identified as "Marcjan Ogiński / Starost of Trakai", is attributed to Ferdinand Bol, a student of Rembrandt, who painted the portrait of Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga from the collection of Jacques Goudstikker in Amsterdam (sold at Christie's New York, June 3, 2015, lot 15). Marcjan Aleksander, son of Castellan of Trakai Alexander, the last Orthodox senator, studied in Vilnius and Kraków. He was enrolled at the University of Leiden in the Netherlands in 1650 and joined the Lithuanian army a year later. At that time also his cousins: the brothers Jan Jacek (1619-1684) and Szymon Karol (ca. 1625-1694) were studying in the Netherlands. The younger, Szymon Karol, who was also proposed as a possible model for Rembrandt's painting, studied at the University of Franeker between 1641-1655 and in 1643 married a Dutch woman Titia Staakman, the daughter of the mayor of Franeker, but soon divorced her (they had a daughter Sophia) and lived in Groningen between 1648-1653. Marcjan Aleksander returned to the Commonwealth during the Deluge and from 1656, under the command of Paul John Sapieha, he participated in the fighting with the army of Transylvania, then in 1657 with the Swedes in Courland. He abandoned Orthodoxy for Catholicism in 1669 (foreign invasions accelerated the creation of the idea that a good Pole, i.e. resident of the Commonwealth, should be Catholic). In 1663, he married a wealthy heiress of the Ruthenian Hlebowicz family - Marcybella Anna (1641-1681), and after her death, on March 4, 1685, he married Konstancja Krystyna Wielopolska (1669-1693), daughter of Chancellor Jan Wielopolski (1630-1688). Marcjan Aleksander died without an heir, so all his properties were inherited by other family members, including Michał Kazimierz's parents. In Alovės in Lithuania, where he died in 1690, there was a medieval castle and a princely manor of which no trace is visible today. As an important notable of the Commonwealth, Lithuanian Steward (1659), Grand Lithuanian Pantler (1661), Grand Lithuanian Carver (1665), voivode of Trakai (1670), Grand Chancellor of Lithuania (1684), he undoubtedly also possessed an important collection of paintings, such as, most likely, the portrait of a man in Roman-style armor, which was later identified as his portrait (National Museum of Art in Kaunas, ČDM Mt 1929). In 1688, Ogiński restored the Protestant church in Rykantai in Lithuania badly damaged during the Deluge and handed it over to the Dominicans of Trakai. The interior of the church is decorated with frescoes. On the wall on both sides of the altar, the full-length portraits of Marcjan Aleksander and his first wife Marcybella Anna are preserved, today barely visible. During the renovation in 1931, the signature and date were revealed: IAN CIANO 1688, identified as the autograph of the painter Jonas Jonavičius (Jan Janowicz). 56 years old Ogiński was depicted in traditional costume - a long żupan and holding his hand on his hip as in Rembrandt's painting. His face closely resembles the effigies by Rembrandt and Bol.
Portrait of Marcjan Aleksander Ogiński (1632-1690) on horseback by Rembrandt, ca. 1655, The Frick Collection.
Portrait of Marcjan Aleksander Ogiński (1632-1690) in a fur hat by Ferdinand Bol, 1650s, Private collection.
The Nymph caught in nets - political allegory of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth at the beginning of the Deluge by Gonzales Coques
In 1646 Krzysztof Arciszewski (1592-1656), also known as Christoff Artiszewsky, a nobleman of the Prawdzic coat of arms, returned to the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth where he was appointed general of artillery by King Ladislaus IV Vasa. Under the rule of John II Casimir Vasa, he participated in the wars with the Cossacks and the Tatars. In September 1648, during the Khmelnytsky Uprising, he commanded the defense of Lviv. Using his experience gained from serving in Brazil, he introduced many reforms and improvements in the field of artillery and the construction of fortifications. As a result of an open conflict with the Grand Chancellor of the Crown, Jerzy Ossoliński (1595-1650), then appointed generalissimus (commander-in-chief), in 1650 he resigned from his position and retired to the privacy of his family.
Krzysztof was born in 1592 in Rogalin, Greater Poland, as a son of Eliasz Arciszewski and Helena née Zakrzewska, supporters of the Polish Brethren and the doctrine of Fausto Sozzini. His father was a pastor in Śmigiel and his cousin Jonasz Szlichtyng was also a pastor of the Polish Brethren. He received his education at the school of the Polish Brethren in Śmigiel (1604-1610) and later studied at the University of Frankfurt am Oder (1616-1617). In the years 1621-1622 he participated in the Livonian expedition of the Lithuanian hetman Christopher II Radziwill (1585-1640), at whose court he served from 1619. As a trusted courtier of Janusz I Radziwill (1579-1620), he signed his will in 1620, and later negotiated with the castellan's widow. Christopher II entrusted him with particularly delicate political missions and with the entire intelligence service and spies (after "Książka i literatura w kręgu Radziwiłłów birżańskich ..." by Mariola Jarczykowa, p. 92). In 1623 he was sentenced to exile for murder committed together with his brother Eliasz the Younger on Kasper Jaruzel Brzeźnicki (a palestrant whose alleged machinations led the Arciszewski family to ruin). The Synod of Polish Brethren excommunicated the two brothers who fled to the Dutch Republic, where they settled in The Hague. With the help of Prince Christopher II, Krzysztof studied artillery, engineering and navigation at the University of Leiden. In 1637 he became vice-governor of Dutch Brazil and commander of the army in that area. In exile, Arciszewski maintained connections with Lithuanian magnates. He had been trying to get permission to return to the Commonwealth, as evidenced by a letter from 1637 published by Julian Ursyn Niemcewicz, addressed to the king. His fame as an excellent military man allowed him to obtain a safe-conduct from Ladislaus IV, guaranteeing his legal inviolability (after "Krzysztof Arciszewski ..." by Roman Marcinek). General Arciszewski resided at his family estates in Arciszewo and Buszkowy near Gdańsk. His estate, with the Lenzberg and Papenwinkel farms, amounted to 670 ha. In 1648, Andrzej Wiszowaty, one of the leaders of the Polish Brethren and a friend of Krzysztof, settled for a short time in Arciszewo and gave sermons in the neighboring Arian congregations. In Warsaw, he completed the impressive arsenal founded by Ladislaus IV "to support war and peace". Charles X Gustav, "the Brigand of Europe", who visited the lower and upper arsenal, when he saw several dozen cannons, a hundred barrels of powder and a large quantity of war material, was surprised at the voluntary capitulation of the capital of the Commonwealth (after "Warszawa w latach potopu ..." by Jan Wegner, p. 36). After many years of service to the Dutch Republic, Krzysztof undoubtedly knew the Dutch language, but he was not alone, because many Sarmatians studied in Leiden and Leuven and at that time there was considerable Dutch and Flemish colonization in Poland, especially in the northern regions (in 1577, in Malbork there were already 12 towns inhabited by the Dutch). In the 16th and 17th centuries, Olender or Olęder settlers founded villages along the Vistula and its tributaries in Kujavia, Masovia and Greater Poland. They represented a high agrarian culture and had the experience in cultivating difficult floodplains. Dutch, Flemings and Frisians also reached the outskirts of Warsaw and on November 13, 1628, they received a document locating them on the Vistula island, known as Hollandia or Dutch Kępa (Kępa Holenderska), now Saska Kępa. They obtained a 40-year lease on Kępa on favorable terms. In the years 1527/1547 to 1864, at least 1,700 Olęder settlements were established in the territory of the Commonwealth, then in three partitions (after "Najstarsze dzieje osad olęderskich ..." by Zbigniew Chodyła, p. 4). On April 16, 1597, Olędry Ujskie (today Ługi Ujskie near Piła), the first Olęder settlement in Greater Poland, was founded. During the Deluge (1655-1660), many of them supported the invaders against the Catholic King John II Casimir Vasa. As the invaders and their supporters were not Catholic, the conflict often turned into civil and religious war. Municipal records from the time document Swedish robberies, murders and mistreatment of the population, for example in the village of Ćmachowo near Poznań, owned by Jan Trampczyński, where peasants were tortured in a terrible way. Mikołaj Rej (great-grandson of the poet), Calvinist and owner of the town of Skoków, after arming the Dutchmen from the village of Werdunia near Oborniki, who supported the Swedes, spread his troops around the area and destroyed the villages of the nobility loyal to John Casimir (after "Chłopi obrońcami niepodległości ..." by Stanisław Szczotka, p. 76). Krzysztof Arciszewski died on April 7, 1656 in Buszkowy and, according to his wishes, was buried in the Church of the Czech Brethren in Leszno. Shortly after his death, when the town was burned on April 28, 1656 in retaliation for helping the Swedish troops, the church was also burned and with it a coffin with Arciszewski's body. Among the many pictorial activities that flourished in the Spanish Netherlands and the Dutch Republic in the 16th and 17th centuries, an important place was occupied by political satire and allegory. Paintings and prints referring to political and social issues dealt with local, but also pan-European problems. One of the best examples of such political satire is the so-called Milch Cow, an allegory of the Netherlands during the Dutch Revolt, known from several painted and printed versions. One of the best known is the one painted around 1583, now in a private collection. The wealthy Netherlands are depicted as a cow that King Philip II of Spain is attempting to fide, William the Silent is leading by the horns and fed by Queen Elizabeth of England. The cow is milked (through taxation) by Philip's commander, the Duke of Alba, and the Netherlands' unpopular French ally, Francis, Duke of Anjou and Alençon, pulls the cow's tail and she defecates on him. The "Lamentation of various people over dead credit" (Lament różnego stanu ludzi nad umarłym kredytem), anonymous woodcut warning the inhabitants of the Commonwealth against purchases on credit, was probably inspired by Dutch prints of the period. Curiously, no engravings or paintings referring to the Deluge, a very important period also for the Dutch/Flemish community of Poland-Lithuania, are known. Before the Second World War, in the collection of the National Museum in Warsaw there was a painting entitled "Nymph caught in nets" (oil on panel, 53.5 x 74 cm, inv. 35778, remains of the signature: dt. 1630). The painting came from the collection of Jan Popławski (1860-1935) donated to the museum and exhibited at an exhibition in 1936. Popławski, a renowned doctor who studied and worked in Saint Petersburg, acquired many paintings from former noble collections of the destroyed Commonwealth. In his collection, the painting was attributed to the Dutch painter, but according to Jan Żarnowski, "the general tone of the painting as well as the painting technique indicate that this painting belongs to the Flemish school of the mid-17th century" (after "Katalog wystawy obrazów ze zbiorów dr. Jana Popławskiego", number 27, p. 29). An old photograph of the painting is in the National Library of Poland (F.47118/AFF.II-49). The Dutch verse caption at the bottom of the painting indicates that the painting has a moralistic tone, as in the case of the illustration of the proverb – "Not everyone can get the fruit" by Adriaen van de Venne at the National Museum in Warsaw (M.Ob.2374) or another important painting by this painter - the Fishing for Souls (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, SK-A-447), an allegory of the contemporary struggle between the Reformed and Catholic Churches. The nymph presents the features of the Princess-Infanta Anna Catherine Constance Vasa (1619-1651) from her portraits by Giovanni Giacomo Sementi and Pier Francesco Cittadini (private collection) or by Rembrandt (National Gallery, London, NG4930), identified by me. She represents the Realm of Venus, the Commonwealth, stuck between different forces represented by four men. The first man on the left, the fisherman presenting his precious catch, has the facial features of the princess' cousin, Emperor Ferdinand III (1608-1657), similar to the plaster cast of a medal with bust of the emperor (National Museum in Kraków, MNK IX-MP-249/111) or his portrait by Frans Luycx (Nationalmuseum in Stockholm, NMGrh 47), most probably looted by the Swedish army in Prague (1648) or Warsaw (1656). The man in the center, in splendid costume, has the facial features of the "Brigand of Europe" as depicted in the engraving with his portrait, made by Jeremias Falck Polonus after David Beck (Rijksmuseum, RP-P- OB-50.566) or his portrait by Sébastien Bourdon or follower (Nationalmuseum in Stockholm, NMGrh 415), perhaps commissioned in Paris around 1654 and sent from there to Sweden. The man in the habit of a Catholic monk shows features of King John II Casimir, as in the 3-ducat gold donative of the king by Johann Höhn (National Museum in Kraków, MNK VII-P-422) or a portrait in a chainmail (Wilanów Palace, Wil.1145). The last man on the right, looking at the viewer, is the crippled General Arciszewski, walking on crutches. This effigy was probably based on an engraving with his portrait by Crispijn van de Passe the Younger (Westphalian State Museum in Münster, C-507912 PAD), made around 1637, when he was 45 years old, or on the portrait published in 1639 in the Theatrum Europaeum (National Library of Poland, G.9597/III) or another lost effigy. The favorable depiction of the "Brigand of Europe" at the center of the composition, as in the case of a comparable painting showing his triumph over the country (National Museum in Warsaw, 34174), as well as the Dutch inscription and provenance, indicate that the painting was commissioned in Flanders by members of the Dutch-speaking community in the Commonwealth or Poles educated in the Netherlands, who most likely supported the invaders. The style of the painting is highly reminiscent of works attributed to the Flemish painter active in Antwerp Gonzales Coques (1614-1684), such as the Full-lenght portrait of a young lady (known as "Lady Pembroke") in the Czartoryski Museum (XII-262) or his small family portraits, like that in the Wallace Collection (P223). The theme is comparable to "The execution of Charles I of England in 1649" by Coques with the portrait of the king, preserved at the Musée de Picardie (M.P.89480), which the painter based on other representations of the event, like the anonymous German print.
The Nymph caught in nets - political allegory of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth at the beginning of the Deluge (1655-1660) by Gonzales Coques, ca. 1655-1656, National Museum in Warsaw, lost. Virtual reconstruction, © Marcin Latka
Portrait of Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga by Ferdinand Bol
On May 3, 1660, the Peace of Oliva was concluded between the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Swedish Empire, ending one of the bloodiest and most destructive wars in Polish history. This treaty is frequently attributed to the ambitious Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga (1611-1667), who personally oversaw the proper preparation of the negotiations and held meetings with the envoys (compare "Odrodzenie i reformacja w Polsce", Volume 45, p. 200). The country surrounded by many absolutist monarchies was an island of so-called "golden liberty" (Aurea Libertas) for the nobility and a "free veto" (liberum veto) that contributed to the ineffectiveness of its parliamentary system. Like Queen Bona in 1530, Marie Louise wished to introduce the election of the king during the lifetime of his predecessor (vivente rege) and she obtained the support of the French court for these projects.
The country was ravaged by a long war. Many people who managed to save their lives lost their life's possessions. But paradoxically, when some lose everything, others become very rich. This war must have also affected many people abroad. For example, the trade in grain and wood imported from Gdańsk was so vital to the Dutch economy that it was called the "mother trade" (moedernegotie) (after "Kopstukken ...", ed. Norbert Middelkoop, p. 104), while Hendrick van Uylenburgh (d. 1661), a relative of Saskia, his son Gerrit (d. 1679), and other merchants exported many luxury goods and art to the Commonwealth. On July 14, 1656, the Amsterdam-based painter Rembrandt was forced to declare bankruptcy (he applied to the High Court in The Hague for cessio bonorum), his house and collections were sold, and at the age of fifty-one, he found himself homeless and penniless. He was stripped, we read, even of his household linen (after "A Popular Handbook to the National Gallery", Volume I, John Ruskin, p. 45). In the same year, Otto van der Waeyen, the son of an Amsterdam-based weapons trader, Dirck van der Waeyen, who had contacts with Poland-Lithuania, was portrayed by Rembrandt's student Ferdinand Bol. This painting, now kept at the Boijmans Van Beuningen Museum in Rotterdam, was signed and dated by the painter (FBol - 1656) and the inventory of Dirck's possessions of July 14, 1670 lists "a portrait of Otto van der Waeyen by Ferdinand Bol" (een conterfeytsel van Otto van der Waeyen door Ferdinand Bol). Later, the family coat of arms was also added at the top right. Trade with the Commonwealth in 1656, when the country desperately needed to defend itself against barbaric invasion, was very lucrative for Otto's father, as young boy, standing among the weapons and cannons, is dressed in a costume of a Polish-Lithuanian nobleman - żupan of gold satin, velvet kolpak hat lined with expensive fur, typical safian leather shoes and holding a nadziak war hammer. The boy was also a nephew of Bol's wife Elisabeth Dell. Bol, like Rembrandt, must have participated in the trade before and after the invasion because many of his paintings found their way to Poland, most probably shortly after their creation, but the lack of painters' names in the preserved inventories and the enormous destruction of the Commonwealth's heritage makes it difficult to prove. For several centuries after the Deluge, the Realm of Venus became one of the greatest battlefields in Europe. Among Ferdinand's paintings, most likely from the collections of the Polish-Lithuanian Vasas, we can cite Jacob's Dream from the Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden (oil on canvas, 128.5 x 97cm, Gal.-Nr. 1604, signed bottom right: f. Bol. fecit.), dated around 1642, which was moved from Warsaw by Augustus II before 1722. The king transferred many objects from the royal collections of Poland-Lithuania to Saxony. The provenance of this painting is marked as "From Poland and later from the Royal Chapel" (Aus Polen und später aus der Königl. Capelle.) in Julius Hübner's register from 1862 ("Verzeichniss der Königlichen Gemälde-Gallerie zu Dresden", no. 1267). A painting in the National Museum in Gdańsk depicting the Angel appearing to Hagar in the wilderness is very similar in composition and dimensions, so it may also come from the royal collection (oil on canvas, 115.6 x 97.8 cm, Ml 421 MPS). From the collection of King Stanislaus Augustus Poniatowski come two signed portraits by Bol - portrait of an old woman from the 1640s (National Museum in Warsaw, M.Ob.555, earlier 129022, signed: F. Bol) and portrait of Johanna de Geer-Trip with her daughter (M.Ob.556, signed and dated: F.Bol 1661), as well as Repentant Saint Peter, attributed to Bol (Royal Castle in Warsaw, ZKW 3908). At the Wawel Castle in Kraków (2947) there is a portrait of a young man, wearing a feathered cap, painted by workshop of Ferdinand Bol (also considered to be the artist's self-portrait), which comes from the Zamoyski collection. Another very good painting by Bol which may have come from the Polish royal collection is a Man in armour and helmet (also known as Mars) in the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 72.5 x 62.5 cm, M.Ob.2544, earlier 34675), purchased in 1935 from the collection of Jan Popławski. It belongs to the category of so-called tronies, a form of genre painting in portrait format, especially since the same man posed for several of such paintings by Rembrandt, like the Man in a turban, so-called "The Noble Slav", painted in 1632 (Metropolitan Museum of Art, 20.155.2), and Karel van der Pluym. The sitter was long thought to be Rembrandt's older brother Adriaen. A copy or an original of this composition was in 1909 in the collection of Baroness Wilhelmina Czecz in Kozy (oil on canvas, 109.5 x 83.5 cm, after "Album wystawy mistrzów dawnych" by Mieczysław Treter, 1911, item 110, p. 33). Due to the coat of arms of the Ruthenian Chodkiewicz family, the painting was considered to depict the most famous member of the family Jan Karol Chodkiewicz (died 1621), Grand Hetman of Lithuania. This painting had an inscription at the bottom, cut off during the restoration of the canvas in the mid-19th century and placed on the back: JAN CHODKIEWICZ WOIEWOD KIIOSKI HETMAN [...]. The painting has been in the possession of the Czecz family for 55 years, and was acquired from Stanisław Reychan, who inherited it from his father, painter Alojzy Reichan (1807-1860). The latter allegedly claimed that the painting came from the painting studio in the Warsaw Castle during the reign of Stanislaus Augustus and was a study for a series of portraits of hetmans. This portrait, deposited in the National Museum in Kraków before the Second World War, was considered a copy rather than an original (after "Katalog wystawy obrazów ze zbiorów dr. Jana Popławskiego" by Jan Żarnowski, p. 43) and was lost during the war. It is also worth noting that in a painting by Karel van der Pluym in the Metropolitan Museum of Art (71.84), also identified as an image of the Roman god of war Mars, the helmet resemble those in images of Sarmatian warriors and Jan Karol Chodkiewicz kneeling before the altar of the Virgin Mary from Sacra Lithothesis ("Consecration of the Stone") by Maciej Kazimierz Sarbiewski, published in Vilnius in 1621 (National Library of Poland, SD XVII.3.9161). His breastplate is medieval and his sword Far Eastern. The oldest confirmed provenance of this painting is the collection of Théophile Thoré-Bürger in Paris in 1869, it is possible that this tronie-like portrait was also produced for the Commonwealth's clients and transferred to France by aristocrats fleeing numerous invasions and wars, like the January Uprising (1863-1864) or the November Uprising (1830-1831), against the Russian Empire. The same goes for the famous Man with the Golden Helmet from Rembrandt's entourage in Berlin (Gemäldegalerie, 811A). The oldest confirmed provenance of this painting is the collection of Clement Augustus of Bavaria (1700-1761), archbishop-elector of Cologne, son of Princess Teresa Kunegunda Sobieska (1676-1730), daughter of the "Victorious King" John III Sobieski, who, like Anna Catherine Constance Vasa, transferred a rich dowry to Bavaria. The collections of Dutch tronies already occupied an important place in the royal and magnate collections of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in the 17th century. The Sarmatians of the modern era - nobles from Poland-Lithuania were frequently depicted in exotic, fantastical or ancient costumes, for example in the so-called "Stockholm Roll" (Royal Castle in Warsaw, ZKW/1528/1-39) from around 1605, portraits of Wincenty Aleksander Korwin Gosiewski from around 1650 (Palace on the Isle in Warsaw, ŁKr 136, Wilanów Palace, Wil.1135) or portrait of Aleksander Jan Jabłonowski on horseback, painted after 1697 (Wawel Royal Castle, 8425). In 2015, a very fine portrait by Ferdinand Bol was sold in New York (oil on canvas, 126.5 x 102 cm, Christie's, June 3, 2015, lot 15). Before 1902 it was in the Westenberg collection in Amsterdam and later in the collection of Jacques Goudstikker in Amsterdam. In 1940, during World War II, the painting was confiscated by the German Nazis for the so-called Führermuseum in Linz. This portrait has been identified as depicting Marie Louise Gonzaga, second wife of Ladislaus IV, who later married his brother John Casimir, listed in the 1945 restitution file as "Portrait of Maria of Gonzaga". During her trip from Paris to Warsaw between 1645 and 1646, the queen stayed in Amsterdam and Utrecht. On December 30, 1645, a play by Jan Vos "Aran and Titus" was performed in Amsterdam for the queen who was visiting the city with Frederick Henry of Orange. Her features and noble demeanor seem to confirm that this is indeed the portrait of the Queen of Poland. However the style of this painting seems to be later than 1645-1646, closer to the Mars in Warsaw which is generally dated to the end of the 1650s or to the portrait of Johanna de Geer-Trip dated '1661', when the influences of the French or Flemish school of painting become more visible in the work of Bol, and much less that of Rembrandt. Thus, in recent catalogs this identification has been questioned because the painter and the queen could not meet according to known sources and the painting was sold as "Portrait of a lady, traditionally identified as Maria Louise Gonzaga". In Albertina in Vienna (9938), there is a drawing with a portrait of the queen, which resembles most of her effigies. It closely resembles the portrait of Marie Louise made by Claude Mellan in 1645 in Paris (Metropolitan Museum of Art, 53.601.285). Her face is almost identical to that in Bol's painting. The Vienna drawing is signed: P van Schuppen. faciebat. / .1656., indicating that it was made by the Flemish painter and engraver Pieter van Schuppen (1627-1702), who left Antwerp and settled in Paris in 1655. Thus, the effigy could be copied from Mellan's print or another effigy. Many effigies of the queen attributed to Justus van Egmont were created long after her departure for Poland, such as the portrait in the Royal Castle in Warsaw (ZKW 2283), generally dated to around 1650. In 1650, Marie Louise commissioned a large portrait of herself and her two husbands from van Egmont in Paris. Therefore, the studies for Bol's portrait could have been sent from Warsaw. The queen's face is also very similar to that seen in a drawing attributed to Claude Mellan, now in the Hermitage Museum (ОР-1814) and is comparable to the portrait of the queen in a green dress at the Suermondt-Ludwig Museum in Aachen, which was probably created in the 1650s. The rich costume and pose indicate that she is a queen. She holds a sword as if holding a scepter. The style of her costume and hairstyle, similar to that of ancient statues of Roman goddesses, confirms that the portrait is an allegory. The sword was a traditional attribute of the ancient goddess of justice and divine law Themis (or Justitia), while the scepter or caduceus was a symbol of Pax, goddess of peace. The two goddesses were frequently depicted embracing, as in the very lesbian painting by Artemisia Gentileschi (Royal Palace of Naples). Thus, by joining the symbols of the two goddesses, the queen represents Pax-Justitia (Peace and Justice). In the second quarter of the 16th century, Diane de Poitiers (1499-1566), favorite of King Henry II of France, was depicted as half-naked Pax (Allegory of Peace) in two paintings by the School of Fontainebleau, most likely Giovanni Capassini (Museo Nazionale del Bargello in Florence, Collezione Carrand 2064 and Musée Granet in Aix-en-Provence, inv. 201) and more than a century later, in 1664, Anne of Austria (1601-1666), dowager queen of France, was represented in the guise of Minerva and his daughter-in-law Maria Theresa of Spain (1638-1683) as Pax in a painting by Simon Renard de Saint-André (Palace of Versailles, MV 6925). Her crimson velvet dress is probably also symbolic and refers to the symbols of Poland. The portrait should therefore be dated to around 1660 or later. The reconstruction of the destroyed palaces in Warsaw began already in 1659, as the design for the trompe-l'oeil decoration in the gallery of the Villa Regia palace in Warsaw by Giovanni Battista Gisleni dates from this time. Gisleni designed the gallery for the queen and it was made between 1665 and 1667. The trompe l'oeil decoration imitated an open loggia with the landscape, and niches decorated with allegorical figures and statues including the Cesi Roma and Hercules Farnese. The portrait by Bol probably also had a pendant showing the queen's husband and was most likely created as part of the series, but this we will probably never know, as after the Deluge also many paintings were destroyed during invasions or fires. The painting may have been a gift for someone in the Netherlands or it may have returned there later from Paris, where John Casimir moved several of his paintings. It is also possible that the painting or its copies never reached Poland. The country's economy, ravaged by five years of pillage and destruction by various invaders, was in a deplorable state. King John Casimir ordered the rich Muscovy crown, which was probably made for his brother's coronation as Tsar of Muscovy, to be melted down for coinage and sold the precious stones, which caused a dispute with parliament because the crown was state property. It is therefore possible that the painting was not paid for and remained in the painter's studio. Interestingly, the pendant could have been kept in the Netherlands. It is an artist's self-portrait of similar composition and dimensions, now in the Rijksmuseum (oil on canvas, 127 x 102 cm, SK-A-42). Bol does not represent himself as a painter but as a wealthy aristocrat or merchant, resting on the statue of Cupid, which symbolizes romantic love. This painting is considered to have been produced on the occasion of his marriage to the wealthy widow Anna van Erckel in 1669, however the accompanying piece is unknown, which suggests that Ferdinand may have repainted the portrait of the King of Poland. John Casimir abdicated in September 1668 and settled in Paris shortly after the death of his wife, who brought peace to the Realm of Venus.
Jacob's Dream by Ferdinand Bol, ca. 1642, Gemäldegalerie Alte Meister in Dresden.
Portrait of Otto van der Waeyen in a costume of a Polish-Lithuanian nobleman by Ferdinand Bol, 1656, Museum Boijmans Van Beuningen.
Portrait of Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga (1611-1667) as Pax-Justitia (Peace and Justice) by Ferdinand Bol, ca. 1660, Private collection.
Portrait of a man in armor and helmet by Ferdinand Bol, ca. 1660, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of a man in armor and helmet with Chodkiewicz coat of arms by Ferdinand Bol, Karel van der Pluym or follower, after 1660, National Museum in Kraków, lost.
Portraits of Katarzyna Sobieska and Louise Charlotte of Brandenburg by Justus van Egmont or workshop
At the end of February 1650 in Lviv, Katarzyna Sobieska (1634-1694), sister of Jan Sobieski (1629-1696), future king and daughter of Jakub Sobieski (1591-1646), voivode of Ruthenia, married a fabulously rich Ruthenian Prince Vladislav Dominik Zaslavsky-Ostrogsky (d. 1656), also known as Władysław Dominik Zasławski-Ostrogski in Polish, who was almost 20 years older than the bride and widowed. The parents prepared Katarzyna for monastic life, which was prevented by the death of her father in 1646. Her mother, Zofia Teofila Sobieska née Daniłowiczówna (1607-1661), decided to marry Katarzyna, despite the protests of her daughter who was in love with Prince Dmytro Yury Vyshnevetsky (1631-1682). Dmytro Yury later married Katarzyna's daughter Teofila Ludwika (1654-1709). The marriage took place in an atmosphere of public scandal, since Sobieska gave birth to a son on March 6 of the same year - Aleksander Janusz Zasławski-Ostrogski (1650-1673), considered the son of Dmytro Yury.
Katarzyna's husband was famous for his lavish lifestyle, but only a few vestiges of his splendid patronage have survived, including the famous portrait painted by Bartholomeus Strobel in 1635, depicting the prince in rich French costume, today at Wilanów Palace (Wil.1654) and full-length version at the National Art Museum of Belarus in Minsk (ЗЖ-106). Similar magnificent portraits of the prince's wives Zofia Prudencjana Ligęzianka (d. 1649) and Katarzyna Sobieska must have existed. Portraits of Zofia Prudencjana are not known and all known effigies of Katarzyna were created after the Deluge, as her costume indicates. After her husband's death in 1656, Katarzyna married for the second time in July 1658 in Lviv to Michael Casimir Radziwill (1635-1680). They probably met in March 1658 in Warsaw, during the marriage of Jan "Sobiepan" Zamoyski (1627-1665) and Marie Casimire de La Grange d'Arquien (1641-1716) or in Bardejov in Slovakia, where she took refuge with her minor children during the Deluge. At that time, her second husband was engaged in battles for the liberation of territories conquered by Russian troops, the reconstruction of his estates and his career at court. Due to the military devastation, he obtained exemption from taxes and customs for four years from the king. In 1661 he received 3,000 livres from the French treasury. Michael Casimir soon became castellan of Vilnius (1661), voivode of Vilnius (1667), Deputy Chancellor of Lithuania and Field Hetman of Lithuania (1668). Since then, Katarzyna's fate has been closely linked with the public activities of her husband and brother. The Deluge was also a turning point in the career of the young Jan Sobieski, future king, educated with his older brother Marek (1628-1652) in France and the Netherlands. In the first phase of the invasion, he betrayed John Casimir and sided with the Brigand of Europe, which is one of the most controversial parts of the biography of the Victorious King or the Lion of Lechistan, as he was later called, attributed to "errors of youth". On March 24, 1656, he left the Swedish ranks and entered the army of Stefan Czarniecki. In response, Charles X Gustav ordered portraits and plaques bearing the names of Sobieski and other commanders to be hung on the gallows. Thus, around 1656, portraits of young Sobieski and other nobles must have been numerous, since they were hanged in effigy (in effigie, one such execution of traitors to the Commonwealth in 1794 was depicted in a painting now in the National Museum in Warsaw, MP 4881 MNW). On May 26, the king John II Casimir promoted him to the position of grand standard-bearer of the crown and he was given command of a Tartar auxiliary corps led by Subkhan Gasi aga. Sobieski's mother, Zofia Teofila, after tragic death of Marek during the Batoh massacre in June 1652 went on a pilgrimage to Italy (March 1653), visiting sanctuaries in the north of the peninsula. She stayed there for over five years, until 1658, possibly with breaks and probably visted Naples. She also had to visit Rome, an almost obligatory point of visit for any pilgrimage to Italy. Zofia Teofila was known for her strong, even masculine character. Full of energy and entrepreneurship, she helped her husband manage the immense estate. During her husband's absence, and then after his death, Zofia Teofila ruled the city of Zhovkva and all domains with an iron fist (after "Teofila Sobieska ..." by Hanna Widacka). She died on November 27, 1661 in Zhovkva. Her magnificent portrait, kept before the Second World War in the Church of St. Lawrence in Zhovkva, was probably painted in Italy. It depicted her in mourning after the death of her son and holding a rosary. The style of this painting is comparable to paintings attributed to Carlo Francesco Nuvolone (1608/1609-1661/1662), an Italian painter born in Milan and active mainly in Lombardy, notably the portrait of Giulia Bonfanti and pendant portrait of her husband Carlo Beccaria (Galleria nazionale di Parma, GN 1112, GN 1113). However, the authorship cannot be stated with greater certainty, as the portrait is only known from a photograph taken by Edward Trzemeski (1843-1905) in Lviv in 1880. It is also unclear whether Trzemeski photographed the original painting or a copy made by Jan Maszkowski (1794 -1865) or his son Marceli (1837-1862) for the Lubomirski Museum in Lviv (compare "Katalog muzeum imienia Lubomirskich ..." by Edward Pawlowicz, item 372, p. 141 and "Jan Sobieski ..." by Józef Łoski, p. 3r). After completing his studies in Poland, in 1667 Katarzyna's son Aleksander Janusz, heir to the enormous estates of Władysław Dominik (although not his biological son), undertook a customary educational trip abroad, to Germany, the Netherlands, France and Italy. From the Spanish Netherlands, where he went to Antwerp and Brussels, on September 20, the Prince and his retinue continued their journey to Paris. In 1669, the 19-year-old Prince returned to his homeland, where he took part in the royal election and was considered one of the candidates for the crown (as related to the Jagiellon dynasty). His beautiful portrait in French costume, attributed to Andreas Stech, now kept in the National Art Museum of Belarus (ЗЖ-129), is dated around 1670. Although his mother's stay in France is not confirmed in sources, she is frequently credited with the saying "Good France, glorious Spain, happy Italy, rich Germany, but Poland is my favorite" (Dobra Francja, chwalebna Hiszpania, wesołe Włochy, bogate Niemcy, ale mi najmilsza Polska). In the early 1670s, she renovated the Radziwills' main residence in Biała Podlaska and the local parish church, which were looted and badly damaged by Transilvanian forces in 1657 and especially by Russian troops in 1660. In 1675, Princess paid Stefan Florian Paszkowski 400 zlotys for the frescoes in the palace (after "Katarzyna z Sobieskich ...", part III, by Jerzy Flisiński). In the second half of the 17th century, the fashion for portraits of French dames de qualité spread in Europe. Such portraits, comparable to the effigies of the so-called Bellezze di Artimino in Palazzo Pitti from the early 17th century, were frequently acquired as models for the new Parisian fashion. They represented aristocratic ladies of the kingdom of France, usually educated women, but also 17th century celebrities, known for their position at the French court or for scandals. The 1661 inventory of the Lubomirski collection in Wiśnicz lists several such portraits of French and Italian ladies that survived the Deluge (section "Portraits" - Konterfety). Likewise the 1671 inventory of Princess Louise Charlotte Radziwill (1667-1695) - items 308-312, including the Queen of Spain and the Empress most probably in French costumes (Reine d'Espagnie, L'Emipératrice), preceded by two portraits of Alexandra, daughter of the Prince of Wallachia (296, 305), "Half-naked lady in sable coat" (Dama wpół naga w sobolach, 297), perhaps by Titian, portrait of Duchess of Courland (300), two portraits of ladies in French-style dresses decorated with pearls (301-302), Electress of Brandenburg (304), most probably Louise Henriette of Nassau (1627-1667) and Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga (307) (compare "Inwentarz galerii obrazów Radziwiłłów z XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska). The 1667 inventory of the possessions of King John II Casimir includes 13 portraits of the French royal family, including the king (Louis XIV), queen mother (Anne of Austria) and king's wife (Maria Theresa of Spain) as well as 10 unspecified French ladies (dames de France) (after "Ludwika Maria ..." by Bożena Fabiani, p. 224). Several such portraits of French ladies, attributed to school of Pierre Mignard, which probably decorated the Queen's Mirror Cabinet and the King's Cabinet next to the Chinese rooms, and once the upper rooms of Queen Marysieńka (Marie Casimire), preserved in the Wilanów Palace (Wil.1284, Wil.1285, Wil.1289, Wil.1290, Wil.1291, Wil.1292, Wil.1293, Wil.1297, Wil.1298, Wil.1300). After her marriage to Radziwill, Katarzyna Sobieska was one of the richest women in the country, mother and wife of owners of large estates in Lithuania and Ruthenia, so her portrait should be considered an obligatory position in the cycle depicting dames de qualité of the Commonwealth. Interestingly, there is no portrait of the king's sister in the Wilanów Palace inventory, made after John III's death in 1696. It lists, however, portraits of Queen Eleonora Maria Josepha of Austria "in white robe" (w białłej Szacie, no. 287), the Queen of France "behind the glass" (za Szkłem, no. 37), the Queen of England "undressed" (bez Stroju, no. 289), the Queen of Sweden in "old-fashioned costume with ruffs" (wstaroswieckim Stroju z kryzami, no. 288) or even the Queen of Scotland (Reginae Scottorum, no. 296), most probably Mary Stuart (compare "Inwentarz Generalny 1696 z opracowaniem" by Anna Kwiatkowska). The mentioned paintings from the school of Pierre Mignard were not also mentioned, so they could be transferred from other royal residences in the 18th century. Wilanów or Villa Nova was a suburban leisure residence, it was therefore filled with less formal effigies unlike other state residences, such as the Royal Castle, also being the seat of parliament. It is therefore possible that Katarzyna's effigy was "hidden" in disguise, for example in the painting of her patroness Saint Catherine "in gilded frames" in the Queen's Study (Obraz Swiętey Katarzyny w ramach złocistych, no. 40). In the second half of the 17th century, portraits in guise of Christian saints were still very popular, as evidenced by portraits with attributes of Saint Catherine depicting Anne Marie Martinozzi (1637-1672), niece of Cardinal Mazarin, by follower of Constantijn Netscher (Versailles Enchères, March 30, 2003, lot 20), Barbara Palmer née Villiers (1640-1709), mistresses of King Charles II of England, by follower of Peter Lely (National Portrait Gallery, NPG 387), Catherine of Braganza (1638-1705), Queen of England, Scotland and Ireland, by Jacob Huysmans (Hillsborough Castle, RCIN 405880), Catherine of Questenberg (Kateřina z Questenberka) by Jan de Herdt (Jaroměřice nad Rokytnou Castle) and portrait of Marie Mancini (1639-1715), niece of Cardinal Mazarin, as Saint Catherine by workshop of Jacob Ferdinand Voet (Musée de Vendôme). The palace currently houses two interesting portraits depicting ladies dressed in the fashions popular in the 1660s. Not only are their poses and costumes similar, but also the style of the painting, undoubtedly painted by the same painter or his studio. They also have a similar inventory number, indicating that they were listed together and likely come from the same series of effigies. One of them is said to represent Anne of Austria (1601-1666), Queen of France, cousin of King John II Casimir and friend of his wife Marie Louise Gonzaga (oil on canvas, 85 x 67 cm, Wil.1281). It also bears a relevant inscription in French in the upper left corner: Anne de Autriche Reine de France / femme de Louis XIII. It is believed to come from the collection of August and Aleksandra Potocka, acquired before 1877, which does not exclude the provenance from a previous magante or royal collection. A similar (incorrect) inscription is visible on the portrait of Cardinal John Albert Vasa (1612-1634) from the Wilanów collection, identifying the sitter as Cardinal Andrew Bathory (1562-1599) and correctly identified by me in 2013 (Wil.1240). The model's resemblance to effigies of the Queen of France from Polish collections, such as the engraving by Jeremias Falck Polonus after Justus van Egmont (National Museum in Kraków, MNK III-ryc.-13405), full-length portrait from the Monastery of Visitandines, offered by John II Casimir in September 1668, and two portraits from the National Museum in Warsaw (129779 MNW and MP 5274 MNW), identified by me, is very general. The crown placed on a table to the left is ducal or princely (not royal) and similar has been depicted crowning coat of arms of the Radziwill family in two works dedicated to Katarzyna's husband, Michael Casimir Radziwill - Kolęnda, ktorą podczas morowego powietrza w powiecie radomskim w roku 1653 panuiącego ... by Jacek Przetocki, published in Kraków in 1655 (Institute of Literary Research in Warsaw, 11811127) and Aqvila Radiviliana in ardvis investiganda ... by Hyacinthus Rynt, published in Kraków in 1664 (National Library of Poland, SD XVII.4.3545 adl.), as well as in the portrait of Katarzyna Sobieska as a widow, painted around 1680 (private collection of Maciej Radziwiłł, inscription in Latin: CATHARINA DE SOBIESZYN GERMANA İQANNİ / III REG: POL: SOROR ...). The woman in the Wilanów painting bears a close resemblance to Katarzyna from the mentioned portrait as a widow and another portrait from the same collection, identified as depicting Princess Radziwill sitting on a chair. The costume and hairstyle are almost identical to those in the engraving with the portrait of Sobieska by Hirsz Leybowicz, made between 1747 and 1758 after an original portrait from the 1660s. The other portrait represents a slightly older lady (oil on canvas, 73 x 57 cm, Wil.1282). It is said to depict Empress Maria Theresa (1717-1780), which is not possible because the portrait was apparently painted more than half a century before her birth. This effigy bears a striking resemblance to the engraving with the portrait of Louise Charlotte of Brandenburg (1617-1676), Duchess of Courland and Semigallia, a vassal state of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, who was a close friend of Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga. This print was made by André Vaillant (1655-1693), an engraver and painter active in Amsterdam, Paris and Berlin, in 1684, based on an original from the 1660s (National Library of Poland, G.3253). This is a pair (pendant) with the effigy of Duke Jacob Kettler (1610-1682), the husband of Louise Charlotte (G.3131/I). It also resembles the effigy of the duchess at Gripsholm Castle (NMGrh 189), in black dress, perhaps in mourning after the death of the Queen of Poland in 1667. Her contacts with Queen Marie Louise were very cordial as her letters written in French bear witness to this (preserved at the Condé library and archives, Château de Chantilly, Papiers de Gonzague). She frequently expressed concern for the destroyed Commonwealth, ravaged by invaders and internal conflicts, for her duchy and for the royal couple. "My heart is so attached [to you] that if my father [George William (1595-1640), Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia] was still there and committed something against Your Majesties I would never approve of it because I have too much passion and respect for Your Majesties. And I wish when I am dead to carry the title in my coffin with me that until my last breath I was the very humble and dedicated, faithful servant", she wrote to the queen in a letter of April 27 1665 (compare "Zwiastunki pokoju w świecie męskich wojen?" by Igor Kraszewski, p. 171). Like the Queen the Duchess of Courland also commissioned her effigies from the same painter - Justus van Egmont, as evidenced by two portraits, at Schönbrunn Palace in Vienna and in a private collection, identified by me. Justus is the author of several beautiful portraits of the queen, several of which were made after the coronation at the Wawel Cathedral in Kraków on July 15, 1646, including probably the effigy in the coronation robes at the Palace of Versailles (oil on canvas, 82 x 65 cm, MV 3461) or the portrait in guise of Juno, queen of the gods and goddess of marriage and childbirth accompanied by her two husbands Ladislaus IV and John Casimir, commissioned in Paris in 1650, most likely destroyed during the Deluge. It is interesting to note that the two described portraits in Wilanów also resemble the style of Justus van Egmont, particularly comparable is the portrait of a lady, known as the Marquise de Montchevreuil, beside a fountain (Sotheby's London, October 29, 2014, lot 447). The portrait of the Brigand of Europe, Charles X Gustav, painted around 1654 as a pair with a portrait of his cousin Queen Christina, depicted as Minerva (Gripsholm Castle, NMGrh 1853), is also attributed to van Egmont, although according to known sources the painter and the king could not meet in person, so the portrait was based on study drawings or other effigies. In 1653, the painter returned to Antwerp with his family, from where he could easily ship his works to the Commonwealth and Courland.
Portrait of Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga (1611-1667) in coronation robes by Justus van Egmont or workshop, after 1645, Palace of Versailles.
Portrait of Zofia Teofila Sobieska née Daniłowiczówna (1607-1661) by Carlo Francesco Nuvolone (?), 1653-1661 or 19th century copy, lost.
Portrait of Katarzyna Sobieska (1634-1694), Princess Radziwill by Justus van Egmont or workshop, ca. 1660-1667, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
Portrait of Louise Charlotte of Brandenburg (1617-1676), Duchess of Courland by Justus van Egmont or workshop, ca. 1660-1667, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
Portrait of a man in a tall hat, probably theologian Andrzej Wiszowaty by Rembrandt
During the Deluge (1655-1660), the multicultural and multireligious federal country joined together through the Union of Lublin of 1569, a European power and an important player on the political scene, the "State of Religious Freedoms" (Warsaw Confederation of 1573), "Granary of Europe", "Paradise of the Jews" (Paradisus Judaeorum), which largely depended on trade with other countries was deeply humiliated by the non-Catholic foreign invaders, who invaded the country from the north, south, east and west, pillaged and destroyed large parts of it.
The Catholic priest Szymon Starowolski (1588-1656) in his "Lamentation of the distressed mother of the Polish Crown" (Lament vtrapioney matki Korony Polskiey ...) declares that the Deluge and the successes of the invaders "are a consequence of the war that the nobility declared against God, the Church and the priests. [...] The main fault was the observance of the Warsaw Confederation, established so that all sects could find refuge in Poland and everyone could blaspheme the name of the Lord as he pleases and force their subjects to do so. Starowolski was echoed by an unnamed poet, writing: All these people blaspheme the Most Holy Trinity, how can you not punish us, O righteous God" (after "Przyczyny wygnania arian ..." by Leszek Bober). Additionally, prominent members of the country's Protestant communities sided with the invaders. Under these circumstances, in 1658 the Sejm had adopted a constitution expelling the Polish Brethren (also known as Arians or Socinians) from the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. The Act of Parliament gave them a choice: conversion or confiscation of property and exile from the country (within 3 years). The Socinian theologian and nobleman of the Pierzchała coat of arms Andrzej Wiszowaty (1608-1678), known in Latin as Andreas Wissowatius, made a last attempt to save the Arians. From March 11 to 16, 1660, a famous public theological dispute (Colloquium Charitativum) between representatives of the Polish Brethren and the clergy of the Catholic Church took place at the castle of castellan Jan Wielopolski (d. 1668) in Rożnów. The meeting came to nothing, but the castellan, impressed by Wiszowaty's intelligence, suggested that he stay in a country that needs educated people. In exchange for his conversion to the Catholic religion, he offered the theologian the village of Gródek. He refused, saying it was better to lose "all property and civic honor than good conscience" (after "Reformacja w Polsce" by Henryk Barycz, Volume 1, p. 202). On July 10, 1660, he left Poland. Wiszowaty and his family went first to Habsburg Silesia, then to Unitarian friends in Transylvania. From 1663 he stayed in Mannheim and Heidelberg. When he was banned from teaching in the Palatinate, he chose Amsterdam as his permanent place of residence (1666). Andrzej was the grandson of the founder of Socinianism in Poland, the Italian humanist Fausto Paolo Sozzini (1539-1604). At the age of eleven he was sent to the Academy in the Socinian town of Raków. He left the Academy in 1629, then traveled extensively in Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, France and England. From June 1632 he studied theology and philosophy for several years in Leiden, Netherlands. He soon settled in Amsterdam. There he met and befriended Krzysztof Arciszewski (1592-1656), an Arian, traveler and soldier famous in Europe. In Paris, Wiszowaty met the thinkers Marin Mersenne, Pierre Gassendi and Hugo Grotius and perhaps René Descartes. In 1637 he returned to Poland. In 1638, under the pretext of insulting Catholicism, the school in Raków was demolished, the church closed and the teachers and students expelled. Outraged by this event, Wiszowaty went to Warsaw in 1639, where he gave a speech in favor of the Raków doctrine before the Chamber of Deputies. In 1640 he undertook another journey across Europe as teacher of Andrzej Suchodolski. He visited Germany, the Netherlands and France. After his return, in 1642, the Arian synod entrusted him with the post of minister of the Arian congregation in Piaski, which belonged to the Suchodolski family. He died in Amsterdam on July 29, 1678. At the National Gallery of Art in Washington is a portrait of a man in a tall hat, attributed to Rembrandt and dated variably around 1663 or between 1660-1665 (oil on canvas, 121.3 x 94 cm, 1942.9.69). According to "A Catalogue of pictures at Canford Manor in the possession of Lord Wimborne", published in 1888 (p. 62, item 153), the painting came from the collection of the last elected monarch of the Commonwealth Stanislaus Augustus Poniatowski (1732-1798) and after "the dispersion of his celebrated Collection it came into the hands of M. Noe, a well-known picture-dealer at Munich". As a descendant of Izabela Elżbieta Morsztyn (1671-1758), Poniatowski was a distant relative of Wiszowaty, whose grandmother was Elżbieta Morsztyn (d. 1587). Although the king is renowned for attempting to create national collection of paintings, it is worth remembering that before his election he probably also owned paintings, which were rather his private possessions. Men dressed in similar tall hats were depicted in a series of paintings which decorated the ceiling in one of the rooms of the Wielopolski Palace in Kraków. Stanisław Tomkowicz, in his 1918 publication on the palace ("Pałac Wielopolskich w Krakowie ...", p. 4, 18, 20, 23), compared the building, which today houses the City Council, to Palazzo Venezia, a grand early Renaissance palace in the center of Rome (seat of the Venetian embassy from 1564). This sumptuous palace was built in 1535-1560 for hetman Jan Amor Tarnowski (1488-1561), who undoubtedly also decorated it in the Venetian or Italian style, but the building was partially destroyed during the Deluge - in 1655 the palace served the Swedes as a position for cannons shelling Wawel. From 1667 until the middle of the 19th century, the palace remained in the hands of the Wielopolski family. Mentioned Jan Wielopolski, who probably acquired the palace when he became viovode of Kraków in 1667, and his son, also Jan (1630-1688), renovated the palace, which contained "respectable antiquities" and "historical paintings" and a room on the first floor, where there were family portraits and paintings from the 17th century. The ceiling of the first floor hall was the only one of several that survived until around 1813, when it was redrawn for Stanisław Zamoyski by Jan Nepomucen Żyliński (d. 1838). The drawing, kept in the Zamoyski Library in Warsaw, was probably destroyed during World War II. The original ceiling was destroyed when the palace burned down in the great fire of Kraków in 1850. According to Stanisław Zamoyski's description of drawing, the ceiling was painted in oil on wood and depicted a Polish-Lithuanian embassy to Vienna in 1669 to negotiate the marriage of Archduchess Eleonora Maria Josepha of Austria (1653-1697) to King Michael I. Tomkowicz claimed that the painter could have belonged to the Dutch school of the 17th century. In 1663 some paintings in the Venetian style gilded ceiling of the Koniecpolski Castle in Pidhirtsi near Lviv in western Ukraine were replaced with works signed by Jan de Baan, most probably commissioned in the workshop of a Dutch painter Jan de Baen (1633-1702), a pupil of Jacob Adriaensz Backer in Amsterdam. It is possible that the ceilings of the Wielopolski Palace were also painted in Amsterdam. Since members of official Polish-Lithuanian legation wore such costumes in the 1660s, the same was undoubtedly the case for a philosopher trained abroad, mainly in the Netherlands. After 1650, Lambert Visscher, perhaps a student of Pieter Soutman and active in Amsterdam between 1666 and 1673, created a series of engravings depicting notable Polish Socinians, such as Fausto Paolo Sozzini, Jonasz Szlichtyng (1592-1661) or Stanisław Lubieniecki (1623-1675). The costume of a man in Rembrandt's painting is comparable to that in Lubieniecki's effigy, while his facial features resemble those of Wiszowaty's grandfather - Sozzini. The 1671 inventory of the collection of the Calvinist branch of the Radziwill family provides valuable insight into the state of the painting collections just a few years after the Deluge. It confirms that the magnates' collections included paintings of local and foreign notables or important diplomats, but in many cases the exact identity of the sitter was forgotten and sometimes even the paintings were unintentionally damaged due to poor storage conditions, mainly due to the need to evacuate the collections: "The present French king [Louis XIV] when young" (30/10), "An image of a priest wearing lynxes" (49/9), "Some Metropolitan bishop" (50/10), "Cecilia Renata, Queen of Poland, her legs are rotten" (61/1), "A painting of the deceased from the house of the Princes their Lordships" (95/14), "King of England" (126/2), "Some bishop" (154/5), "A bishop sitting in a chair" (155/6), "A Ruthenian man in German costume holding a mace" (165/16), "Gray-hair person, hetman and marshal" (193/19), "An old painting of some king" (194/20), "An old painting of a king with an eagle" (195/21), "Some Cossack hetman" (259/10), "Some cardinal" (260/11), "Hospodar of Wallachia" (261/12), "Person with a long beard, in black, inscription An° 1553 etatis 47" (753/14) (compare "Inwentarz galerii obrazów Radziwiłłów z XVII w." by Teresa Sulerzyska). Catholic magnates therefore undoubtedly also possessed numerous paintings representing famous Socinians.
Portrait of a man in a tall hat, probably theologian Andrzej Wiszowaty (1608-1678), by Rembrandt, ca. 1660-1666, National Gallery of Art in Washington.
An audience from the ceiling of the Wielopolski Palace in Kraków by Jan Nepomucen Żyliński after the Dutch painter (?), ca. 1813 after the original from around 1670, Zamoyski Library in Warsaw, lost.
Portrait of the family of John Charles Kopec by Rembrandt
John Charles Kopec (died 1681), known as Jan Karol Kopeć in Polish or Joannes Carolus Kopec in Latin, son of Vasil Vasilevich Kopec (1575-1636) and Barbara Chodkiewicz, was probably one of the most notable representatives of the Ruthenian Kopec family, originating most likely from the Smolensk boyars. He was probably born in Warsaw and educated at the Nowodworski College in Kraków. In 1636 he enrolled at the Kraków Academy and in 1641, like his father in 1593, he studied at the University of Padua. Later he was a deputy of the Brest-Litovsk voivodeship to the election sejm of 1648 and in 1650 he was a courtier of the royal household (dworzanin pokojowy królewski). During the Deluge, as a loyal supporter of the king, he was rewarded with the post of Lithuanian steward and voivode of Polotsk (Palatinus Polocensis) in 1658.
In the same year, or early 1659, he married Lucrezia Maria Strozzi (ca. 1621-1694), widow of the Polotsk voivode Alexander Louis Radziwill (1594-1654). The couple had two daughters: Frances, known in Polish as Franciszka Kopciówna, born in 1659 in Warsaw and died in 1690 in Kodeń (mentioned as Francisca, Caroli Kopec Castellani Trocensis Filia, cuius Mater ex Ducali Prosapia Marchionissa de Strozzi in "Historia Przezacnego Obrazu Kodenskiego", published in 1720), who married Casimir Vladislav Sapieha (1650-1703), voivode of Trakai, and Anna, probably born in 1661, who first married Stanisław Karol Łużecki (d. 1686), voivode of Podolia, and then Konstantin Yan Shuisky (d. 1695), Grand Scribe of Lithuania. Both are mentioned in documents concerning their parents' inheritance in 1694, which they divided between them (compare "Kniaziowie litewsko-ruscy ..." by Józef Wolff, p. 527). In 1662, John Charles founded a wooden Catholic church at Haradzishcha near Pinsk in Belarus, dedicated to Saint Anne (probably to commemorate the birth of his second daughter) and the monastery for Benedictine monks, whom he brought from Monte Cassino, and which he richly endowed. The family, associated with the Pinsk region, converted from Orthodoxy to Catholicism in the 17th century and John Charles was one of the first Catholic representatives. In 1629, his father and grandmother Apolonia Wołłowicz founded the Orthodox monastery in Kupyatichi near Pinsk (compare "Czar Polesia" by Grzegorz Rąkowski, p. 242). In 1659, Kopec personally went to Monte Cassino to request a foundation in his estates. He also built a wooden palace for his wife in Haradzishcha. Samuel Straszkiewicz dedicated to Kopec his Decas qvaestionvm ex vniversa theologia, published in 1672 in Vilnius. In the Herzog Anton Ulrich Museum in Brunswick there is a "Portrait of a family" by Rembrandt, signed by the artist on the basket held by a young servant (oil on canvas, 126 x 167 cm, GG 238, signed: Rembrandt. f.). The painting is dated by experts to around 1665, thus coming from the period of maturity and the final years of the artist with neo-Venetian (more precisely Titianesque) tendencies clearly visible. Assuming that Titian's works filled many residences in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth before the Deluge, such a style would be particularly favorable to patrons from Poland-Lithuania during post-war reconstruction. The painting comes from the collections of the Dukes of Brunswick-Lüneburg and the Princes of Wolfenbüttel. It was first documented in the inventory of the Salzdahlum gallery catalogued by Anton Friedrich Harms between 1737 and 1744 (after "Welfen und Porträt ...", ed. Klaus Niehr, Silvia Schmitt-Maass, p. 133). The costumes of the man and woman are unusual for the Netherlands of the 1660s, indicating that they were foreigners (compare - portrait of Meyndert Sonck with his wife and children by Jan Albertsz Rotius, painted in 1662, Mayer van den Bergh Museum, MMB.0138). The man wears a collarless black outfit, most likely an eastern kaftan or czekman, like the black outfit of Kristupas Zaviša (1578-1670), Grand Marshal of Lithuania in his 1667 portrait (National Museum of Art in Kaunas, ČDM Mt 1900). Underneath, the man wears a crimson żupan as indicated by the sleeve of his robe. The woman's headdress, or toque, is reminiscent of the Italian balzo of the second quarter of the 16th century, popularized in Poland-Lithuania by Queen Bona Sforza, while her costume is similar to that of Teodora Krystyna Sapieżyna née Tarnowska (1625-1652) from her portrait by Franciszek Wincenty Charliński, painted in 1775 after the original from the 1640s (Wawel Royal Castle, 8690) and the dresses of the ladies from the Finding of the Cross by Tomasz Muszyński, painted between 1654 and 1658 (Dominican Church in Lublin). The same woman, in a similar pose, was also depicted in another painting by Rembandt, identified as portrait of Hendrickje Stoffels, Rembrandt's longtime partner, or Magdalena van Loo, a strangely happy widow of Rembrandt's son Titus (died in 1668 just a few months after the marriage). The woman wears a "fantastic costume", which resembles Spanish dresses from the mid-16th century. This painting, now in the Montreal Museum of Fine Arts (oil on canvas, 56.3 x 48 cm, inv. 1949.1006), comes from the Duke of Hamilton's collection at Hamilton Palace, Scotland, first documented in 1836. The woman closely resembles Kopec's wife - Lucrezia Maria Strozzi, who after marriage was known in Polish as Lukrecja Kopciowa, according to an engraving with her effigy from Icones familiæ ducalis Radivilianæ, made before 1758, as well as from her painted portraits identified by me, such as that by Pietro della Vecchia (Wilanów Palace, Wil.1346) and Rembrandt (Minneapolis Institute of Art, 34.19). The appearance of two children corresponds to the ages of Kopec's daughters around 1663 (four and two years respectively), therefore close to the date proposed for the execution of the painting. It has also been suggested that the youngest child is a boy, but a child wearing a similar costume in a painting by circle of Daniel Mytens or Anthony van Dyck (Sotheby's London, October 27, 2010, lot 16) is identified as Henriette Marie (1626 -1651), daughter of Elizabeth Stuart (1596-1662), Queen of Bohemia. The portrait of Johanna de Geer (1629-1691) with her daughter Cecilia Trip (1660-1728) by Rembrandt's student Ferdinand Bol, painted in 1661 (National Museum in Warsaw, M.Ob.556 MNW), from from the collection of the last elected monarch of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth Stanislaus Augustus Poniatowski in Warsaw, shows another similar girl's costume. Interestingly, about three years later, around 1664, Johanna was depicted with her children in another painting by Bol, represented as Caritas and resembling images of the Madonna and Child (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, SK-A- 45). Moreover, in the family portraits, such as the mentioned portrait by Rotius or in the family portrait by Cornelis de Vos from 1631 (Royal Museum of Fine Arts Antwerp, 815), girls generally emphasized attachment to the mother and boys to the father, especially in the case of a single male heir, as would be the case here if the child were a boy. The man in Rembrandt's painting is holding a red flower, probably a carnation, a symbol of love for his wife and daughters. According to Bożena Fabiani, the two little children are the daughters of the couple and the third girl, who is holding a basket of flowers, is a dwarf - very popular as courtiers at the courts of the Polish-Lithuanian magnates since the time of Queen Bona (compare "Niziołki, łokietki, karlikowie ...", Niezła Sztuka). Her rich costume, similar to that of the other girls, suggests that she was treated as a member of the family. All of the factors listed allow the family to be identified as that of the voivode of Polotsk, who, although probably never visited the Netherlands, could have commissioned such a painting through Dutch agents in Gdańsk, who also prepared the initial drawings.
Portrait of the family of John Charles Kopec (died 1681), voivode of Polotsk with a dwarf by Rembrandt, ca. 1663, Herzog Anton Ulrich Museum in Brunswick.
Portrait of Lucrezia Maria Strozzi (ca. 1621-1694) in black dress by Rembrandt, ca. 1663, Montreal Museum of Fine Arts.
Pilate washing his hands by Mattia Preti
In the summer of 1663, the new grand vizier of the Ottoman Empire Köprülü Fazıl Ahmet (1635-1676), commanding an army of approximately 100,000 men, conquered the fortress of Nové Zámky in Slovakia, then part of the Kingdom of Hungary during the reign of Emperor Leopold I, relative of King John II Casimir Vasa.
The commander-in-chief of the emperor's army, Count Raimondo Montecuccoli (1609-1680), who in 1657 took part in the Habsburg expedition to support Poland-Lithuania during the Deluge, had under his command only 12,000 Austrian regular soldiers, to which were added the 15,000 Croats and Hungarians under the orders of Nikola Zrinski (1620-1664). Faced with this numerical inferiority of his troops, Emperor Leopold I, during the winter of 1663, asked for help from the German princes and from all of Europe. The Protestant electors of Brandenburg and Saxony and even Louis XIV of France, who opposed the Habsburg rule, sent an army in support. The emperor also called on Poland-Lithuania to aid Austria in return for helping to repel the invasion during the Deluge. "The Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth was in 1660 engaged in the expanding war with the Cossacks and Russia in Ukraine. It was also a period when the leaders of the pro-French party loudly demanded reforms and did not hesitate to use intrigues to achieve their political goals, including demands for foreign intervention. It was no coincidence that John Casimir, a supporter of the reform party, called in 1663 Tatars - vassals of their ally Turkey - to help break the internal opposition, strengthened by the transfer of the Crown Marshal and Field Hetman Lubomirski to the side of the pro-Austrian party. Turkey demanded aid in the war against Austria in return. Then John Casimir not only refused to help Austria, but also agreed to send in 1663 20,000 Cossacks, loyal to Pavlo Teteria, the pro-Polish ataman of right-bank Ukraine, to take part in the expedition to Nové Zámky alongside the Turks and Tatars. These Cossacks participated in the capture of Nové Zámky and, together with the Tatars, terribly devastated half of Moravia. They also contributed to the public opinion of the defeated countries regarding Poles as Turkish agents" (after "Nieznany list Jana Sobieskiego z 1672 r." by Vaclav Štěpan and Barbara Leszczyńska, p. 362). Although the enormous destruction of the country by the Christian invaders during the Deluge seems to have gone unnoticed in Italy, this betrayal of the Christian cause, as some may think, is reflected in one painting. It is a scene from the New Testament - Pilate washing his hands, painted by Italian painter Mattia Preti (1613-1699), called Il cavaliere calabrese (the Calabrian knight) after his appointment as a Knight of the Order of Saint John (Knights of Malta) in 1660. From 1661 the artist was permanently in Malta and the painting was probably offered for sale by the artist in two letters dated September 23 and December 11, 1663 to Don Antonio Ruffo (1610/11-1678), Prince of Scaletta, a notable Sicilian collector, living in Messina during the reign of the Spanish Habsburgs. "I have made a painting of 9 x 7 palmi, where there is a Pilate who washes his hands of the death of Christ with many figures" (mi ritrovo fatto un quadro di palmi nove e 7, donde ci è un Pilato che si lava le mani della morte di nostro sig.re con molte figure), wrote the painter (compare Catolgue Entry by Melissa Yuen). The painting comes from the Ferrara collection in Naples, now kept at the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York (oil on canvas, 206.1 x 184.8 cm, 1978.402). The scene, believed to be inspired by the works of the Venetian painter Paolo Veronese, is unusual, as the main character is Pontius Pilate washing his hands, looking meaningfully at the viewer, and the Christ brought for his death is only slightly visible in the background. Another intriguing and significant element of the composition is the young African servant, generally associated with Turquerie and Orientalism in European art, thus representing Muslim culture. However, the most important and significant element of the scene is the costume. Pilate, washing his hands of guilt for Jesus's death, wears a typical costume of a Polish-Lithuanian nobleman - a fur kolpak hat and fur-lined coat, similar to those seen in a print depicting a noble couple of the Commonwealth in Description de l'univers by Alain Manesson Mallet (1683), engraved portrait of King John III Sobieski (1629-1696) by Nicolas de Larmessin (1684) and engraved portrait of the Commonwealth's Ambassador to Brussels Józef Bogusław Sluszka by Henri Bonnart after Robert Bonnart (1695). Preti must have been familiar with these costumes, as the Sarmatians frequently traveled to Italy in their traditional attire and his Diogenes from a 1649 painting in the Capitoline Museums in Rome (oil on canvas, 151 x 101 cm, PC 225), also wears it. Although he may have forgotten it a bit in Malta, because the blue color of the hat's fur is rather unusual (people from impoverished Poland-Lithuania, after devastation during the Deluge, apparently traveled much less than before 1655). Additionally, in the hot climate of southern Italy and Malta, Sarmatians obviously rarely wore their warm hats, so this anomaly probably even went unnoticed by the person who commissioned the painting. In the 17th century, religious scenes were still used to convey other meanings and in politics.
Diogenes and Plato with a man dressed in a costume of a Polish-Lithuanian nobleman, by Mattia Preti, 1649, Capitoline Museums in Rome.
Pilate washing his hands, dressed in a costume of a Polish-Lithuanian nobleman, by Mattia Preti, ca. 1663, Metropolitan Museum of Art.
Portraits of Lucrezia Maria Strozzi, Princess Radziwill by Rembrandt and workshop of Andreas Stech
"REMBRANDT VAN RYN. 319. A person holding a dagger in her right hand and a cord with a knob in her left hand, as if she wanted to ring. Painted on canvas. Height: elbow: 1, inch 19, width: elbow: 1, inch 12." (REMBRANDT VAN RYN. 319. Osoba trzymająca w prawej ręce sztylet, a w lewej sznur z kutasem, jakoby dzwonic chciała. Mal. na płótnie. Wys: łok: 1, cali 19, szer. łok: 1, cali 12.), it is the most accurate and the oldest known description of a painting by Rembrandt entitled "Lucretia" and created in 1666 (signed and dated: Rembrandt / f. 1666), today in the Minneapolis Institute of Art (oil on canvas, 110.2 x 92.3 cm, 34.19). It was published in 1835 in the "Catalogue of picture gallery of famous masters from various schools collected by the late Michał Hieronim, Prince Radziwill, voivode of Vilnius now exhibited in Królikarnia near Warsaw", created by painter Antoni Blank. Radziwill assembled his collection of paintings in his palace in Nieborów near Łódź. The collection included such works of art like the Annunciation by Hans Memling, today in the Metropolitan Museum of Art, paintings by Venetian masters, like Titian and Tintoretto, and several other works by Rembrandt, like "Entombment of Christ" (item 26), "Portrait of an old man, in a purple cap and in a black dress, holding a rolled paper in his hand" (item 193), "Annunciation (to the Shepherds)" (item 242) and "A woman, undressed, sitting in a room, soaking her feet in a bathtub" (item 291).
Interestingly, the direct ancestor of Michał Hieronim, who lived in 1666, was also called Lucretia, and it was not a commonly used name in Poland at the time: Lucrezia Maria Strozzi (ca. 1621-1694) or Lukrecja Radziwiłłowa in Polish. Lucrezia Maria came to Poland as court lady to Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria in 1637, when she was about 16 years old. Her father was Pompeo Strozzi, who connected his career with the powerful Mantuan Gonzaga family, and mother Eleonora Guerrieri. She was probably born in Florence. On November 23, 1642 in Warsaw in the church of St. John the Baptist, Lucrezia Maria married Prince Alexander Louis Radziwill (1594-1654), whom she met already in 1637, as he was among the Polish dignitaries who welcomed the queen in Poland. They married only five months after Alexander Louis's marriage to Katarzyna Eugenia Tyszkiewiczówna was annulled (July 4, 1642). Radziwill was older than his third wife by about 27 years, he was 48 years old, which at that time was already considered a very advanced age. Their first child Cecilia Maria, named after the queen, was born soon after the marriage. At the beginning of December 1652 they set off on a journey to Italy, where Alexander Louis's son from the first marriage, Michael Casimir, began his studies at the University of Bologna in May 1653. In the first days of September 1653, after a difficult pregnancy, Lucrezia Maria gave birth to a son, Dominic Nicolaus, but her husband died soon after in Bologna on March 23, 1654. Alexander Louis's death caused a great troubles for Lucrezia Maria as his eldest son was very hostile towards her and he raised objections to the bequests in his father's will in favor of her. In the years 1655-57, during the Deluge (1655-1660), she stayed with her son Dominic Nicolaus in Italy. At the end of 1658 or at the beginning of 1659, she married Jan Karol Kopeć, voivode of Polotsk. The marriage was a real salvation for Lucrezia Maria, because since then, Kopeć became a party to the dispute with Michael Casimir, defending the interests of his wife and her underage children. In 1662, she married her first-born daughter Cecilia Maria to Mikołaj Hieronim Sieniawski (1645-1683), future field hetman of the crown. In gratitude for improving her son's health, Lucrezia Maria founded a Dominican monastery in Pińsk in 1666 (after "Lukrecja Maria de Strozzi (ok. 1621-1694), księżna Radziwiłłowa" by Jerzy Flisiński). For many more years, Lucrezia directed her son's actions in private and public life. As a court lady of Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga, she probably did not support a rebellion against King John II Casimir Vasa, initiated by Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski, who in 1664 was accused of treason, so-called Lubomirski's rokosz (1665-1666), and she could express it through paintings. Lucretia, the epitome of female virtue and beauty, whose suicide ignited the political revolution, can be considered a perfect allegory. The country was devastated by several wars, such as the Khmelnytsky Uprising (1648-1657) and the Deluge. Gdańsk, the country's main seaport, dominated by German-speakers, which, together with Lviv, was one of only two major cities of the Commonwealth not seized by any of Poland's enemies, strengthen its position as the artistic center of the country. Painters from Gdańsk, Daniel Schultz, court painter of king John II Casimir, and Andreas Stech worked for many Polish-Lithuanian magnates. In about 1654 Schultz created a beatiful portrait of Prince Janusz Radziwill (1612-1655) in silk żupan and in about 1670 Stech or his workshop created an effigy of Prince Aleksander Janusz Zasławski-Ostrogski (1650-1682) dressed in fashionable French costume (both in the National Art Museum of Belarus in Minsk). Portraits of two women from the Kwitajny Palace, today in the Museum of Warmia and Masuria in Olsztyn, identified as members of the Radziwill family are painted in very similar style. Both women were depicted in Spanish guardainfante court dress (cartwheel farthingale or hoop skirt) from the 1660s. Radziwills as the Princes of the Holy Roman Empire had some contacts with the Imperial court of Empress Eleonora Gonzaga (1630-1686) and Empress Margaret Theresa of Spain in Vienna, who re-introducted the Spanish fashion there after her marriage to Emperor Leopold I in April 1666. Each of Lucrezia Maria's journey to Italy also had a stop in Vienna. Spanish fashion was also very popular in Italy at that time. King John II Casimir Vasa, as a cousin of Philip IV of Spain and his second wife Queen Mariana of Austria (1634-1696), undoubtedly owned several works by Spanish court painter Diego Velázquez and his workshop, sent to Warsaw by his relatives, including most probably a copy of Queen Mariana's famous portrait, today in the Prado Museum in Madrid (P001191). The older woman, whose portrait is very in the style of Andreas Stech, is sometimes identified as Katarzyna Potocka (d. 1642), first wife of Janusz Radziwill (1612-1655), however date of her death and lack of resemblance to her known effigy in Minsk, exclude this possibility. Her dress is very similar to portrait of Maria Virginia Borghese (1642-1718), Princess Chigi in Palazzo Chigi of Ariccia, near Rome, painted by Giovanni Maria Morandi in 1659. This woman bears a striking resemblance to effigy of Lucrezia Maria Strozzi by Hirsz Leybowicz, created between 1747-1758, after a likness dating from about 1642. The portrait of a younger lady, due to composition, can be considered a pendant, however its style is different and more close to Daniel Schultz, who from about 1660 was active primarily in Gdańsk, but still worked for the royal court in Warsaw. Her dress is similar to portrait of a lady in a Spanish dress, possibly depicting Krystyna Lubomirska (1647-1669), daughter of Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski, created in about 1667, in mourning after her father's death (from the Potocki collection, today in the National Museum in Warsaw, oil on canvas, 121.5 x 97 cm, M.Ob.758). The face of a young woman resemble greatly the effigy of Aleksander Hilary Połubiński (1627-1679) in the Warsaw University Library (inventory number Inw.zb.d. 15609), who became the Grand Marshal of Lithuania in 1669, therefore created around that year. The mentioned effigy of Połubiński is a drawing (ink and watercolor on paper) and it is probably a preparatory drawing for an etching or a portrait painting, perhaps commissioned in Gdańsk or even abroad. The woman is therefore Połubiński's daughter Anna Marianna (1658-1690), who on October 9, 1672 at the age of 14 years old married Dominic Nicolaus Radziwill, son of Lucrezia Maria (after "Archiwalia związane z kniaziami Trubeckimi ..." by Andrzej Buczyło). Her portrait could be therefore commissioned in Gdańsk together with effigy of her father and offered to the Radziwills. The woman from mentioned painting of Lucretia by Rembrandt in the Minneapolis Institute of Art bear a great resemblance to the effigy of older woman from Kwitajny. Her guardainfante is also very similar and whole costume is almost identical to portrait of a member of the Tyszkiewicz family created in about 1793, after original from the 1660s (National Museum in Warsaw, inventory number MP 4308) or to the portrait of Empress Margaret Theresa of Spain by workshop of Frans Luycx, created in about 1666 (private collection in Sweden). The same woman was also depicted as another "Lucretia" by Rembrandt, today in the National Gallery of Art in Washington (oil on canvas, 120 x 101 cm, 1937.1.76), which before 1825 was in Paris. This painting is signed and dated left center: Rembrandt / 1664. Her dress and necklace are very similar to those visible in a portrait of Anna Tworkowska nee Radziwill from the 1660s (Royal Castle in Warsaw, inventory number ZKW 544) or in the portrait of Empress Eleonora Gonzaga by Frans Luycx from the 1650s in the Gripsholm Castle in Sweden, taken from Poland during the Deluge.
Portrait of Lucrezia Maria Strozzi (ca. 1621-1694), Princess Radziwill as Lucretia by Rembrandt, 1664, National Gallery of Art in Washington.
Portrait of Lucrezia Maria Strozzi (ca. 1621-1694), Princess Radziwill as Lucretia by Rembrandt, 1666, Minneapolis Institute of Art.
Portrait of a lady in a Spanish dress holding a fan, possibly Krystyna Lubomirska (1647-1669) by Flemish painter (?), ca. 1667, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Anna Marianna Połubińska (1658-1690) in a Spanish dress by Daniel Schultz, ca. 1670, Museum of Warmia and Masuria in Olsztyn.
Portrait of Lucrezia Maria Strozzi (ca. 1621-1694), Princess Radziwill in a Spanish dress by workshop of Andreas Stech, ca. 1670, Museum of Warmia and Masuria in Olsztyn.
Portrait of Michael Casimir Pac by Pier Francesco Cittadini or workshop
In 1668, to commemorate the liberation of Vilnius after a long occupation and destruction during the Deluge (1655-1660/1), Michael Casimir Pac (ca. 1624-1682), Grand Hetman of Lithuania (from 1667) founded the construction of the new church of Saint Peter and Saint Paul, in place of the old one destroyed during the invasion. This beautiful church is located on a picturesque hill called Antakalnis (literally "the place on the hills" in Lithuanian), one of the oldest and largest historical suburbs of Vilnius.
The church was built between 1668 and 1675 according to the plans of the Kraków architect Jan Zaor (Zaur, Zaorowicz), who led the construction work until 1671. The construction was then supervised by Italian architect Giambattista Frediani. Around 1677, Pac brought in the Italian sculptors Giovanni Pietro Perti (or Peretti) from Florence and Giovanni Galli from Rome for the interior decoration. Their stuccoes are considered the masterpiece of Lithuanian Baroque. The frescoes were probably created by Michelangelo Palloni or Martino Altomonte. Besides the statue representing the Triumph of Death, which became a common subject in the Commonwealth's art after the Deluge, frequently cited as one of the most important, the panoplies are another important element of this abundant decoration. They were probably requested by Pac, eager to display his military victories and whom panegyrists described as a fearless conqueror of the Muscovites and Turks (after "Wizerunki Michała Kazimierza Paca ..." by Anna Sylwia Czyż, p. 87, 90-91, 97, 104-105). He served in the army from his early youth. In 1652, he seriously injured Jan Sobieski, the future king, during a duel over Mrs Orchowska. During the Deluge, he distinguished himself in the battles in Livonia, Courland and Samogitia. He supported the policies of Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga, who promised him the baton of Lithuanian field hetman, which he received in December 1663 with the office of the Smolensk voivode. Soon, in 1665, Pac bought two tenement houses in a prestigious part of Vilnius, on via regia, which he then merged into a residence, and also expanded his estate in Antakalnis. Michael Casimir frequently ordered luxury items from abroad. The most famous is a series of portière tapestries with his coat of arms, created by the workshop of Jan Leyniers in Brussels between 1667-1669. Three fabrics with borders decorated with panoplies have been preserved to this day, two in the collections of the Royal Castle in Warsaw (ZKW-dep.FC/255, ZKW-dep.FC/256), one in the National Museum of Lithuania (IM 2555), and two with floral borders in the collections of the National Museums in Kraków and Poznań. In his portrait in the Church of Saint Peter and Saint Paul, attributed to Michelangelo Palloni, the table is covered in a rich brocade fabric with his coat of arms - Gozdawa, most likely commissioned in Venice. Panoplies are visible on the title page of Mateusz Dłuski's Practica prudentiæ politicæ ..., published in Vilnius in 1670 and dedicated to Pac, as well as in his engraved effigy published in Vilnius in 1686 in Kwitnąca po smierci ... by Adam Wojciech Małachowski. In many of his portraits, the hetman holds a rich mace of oriental-style - bulava, a sign of his power as hetman. He had a rich collection of such maces and frequently offered them, such as the mace given before 1675 to the Marian sanctuary in Trakai (stolen along with the applications of the miraculous image of the Virgin in July 1676). The bulava, which he received as an inheritance from Wincenty Aleksander Gosiewski, he offered to Lithuanian Marshal Aleksander Hilary Połubiński and another to Lithuanian cupbearer Jan Karol Dolski. In his will, Michael Casimir mentioned "sabres in gold, silver and polish". He left one of them "Turkish gold, set with diamonds, rubies and turquoises" to Christopher Sigismund Pac, and the other "set in gold" to Piotr Rudomina-Dusiacki, the starost of Starodub. He also received rich gifts from abroad, such as "a cabinet encrusted with stones and filled with medicines" (uno stipo incrostato di pietre e ripieno di medicamenti), sent by Cosimo III de' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany in February 1676. Three years later the Grand Duke expressed his wish for Michelangelo Palloni to make a portrait of Pac for his gallery of famous rulers and commanders. The effigy of hetman was published in 1674 in Historia di Leopoldo Cesare ... by Galeazzo Gualdo Priorato with images of European monarchs and notables and inscription MICHELE CASIMIRO PAZZI / PALATINO DI VILNA ..., emphasizing the kinship of the Pac family with the aristocratic Florentine family Pazzi (through their alleged common ancestor Cosmus Paccius). Michael Casimir maintained constant correspondence with the Pazzi and his "relative" Lorenzo Domenico de Pazzi was his courtier from at least 1665. When in 1669 Pope Clement IX canonized Mary Magdalene de Pazzi, a Discalced Carmelite nun, the ties to Pazzi family became even more important. Mary Magdalene de Pazzi became the protector of the Pac family and was mentioned in the hetman's last will. In the National Art Museum in Kaunas there is a portrait of a man wearing rich Roman-style armor (oil on canvas, 101 x 76 cm, ČDM Mt 1929). The painting comes from the Ogiński (Oginskiai) Palace in Plungė. It has been suggested that the sitter is Marcjan Aleksander Ogiński (1632-1690), but this man bears no resemblance to his effigy in the Rykantai church, as well as to the portraits by Rembrandt and Ferdinand Bol. He also holds the ceremonial baton, which indicates that he is a high-ranking military officer and excludes Marcjan Aleksander, who after the Deluge became more involved in a political career than a military one. In the Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam (inventory number SK-A-284), there is a similar portrait of Cornelis Tromp (1629-1691), a Dutch naval officer who served as lieutenant admiral general in the Dutch navy, and briefly as admiral general in the Danish fleet. The armor, cravat and pose of the two men are very similar as well as the composition of the two paintings with a landscape on the right. The portrait of Tromp was signed and dated (lower left): Aº: 1668. / jANMijtens F:, indicating that the painting was created by Johannes Mytens in 1668. The model for the Kaunas painting is certainly not Tromp and its style is more Italian than Dutch. The closest is a portrait of a lady holding a rose, made as her dress indicates in the 1670s (sold at Bonhams London, December 8, 2016, lot 50). The painting is attributed to Pier Francesco Cittadini (1616-1681), known as il Milanese or il Franceschino, a pupil of Daniele Crespi active mainly in Bologna. Also the portrait of a girl in an oyster embroidered dress by circle of Cittadini, painted in the 1650s (sold at Christie's London, April 27, 2016, lot 335) and the portrait of a boy in a red uniform, probably a Hungarian or Croatian aristocrat, painted in the manner of Cittadini in the 1660s (sold at Tennants, Autumn Fine Art Sale - Part II, November 16, 2019, lot 541) are comparable. The latter portrait indicates that the painter accepted commissions from Central European aristocracy. The man in the Kaunas portrait bears a close resemblance to Michael Casimir Pac, notably to his effigy published in Historia di Leopoldo Cesare ..., as well as his portrait by Daniel Schultz or circle at the National Art Museum of Belarus (ЗЖ-108) and the mentioned portrait by Palloni in the Church of Saint Peter and Saint Paul. So the portrait was made around 1668, when the Grand Hetman of Lithuania founded the church in Vilnius and the mountain behind him, resembling Vesuvius more than the surroundings of the capital of Lithuania, is how the Italian artist imagined the hill called Antakalnis.
Portrait of Michael Casimir Pac (ca. 1624-1682), Grand Hetman of Lithuania in Roman-style armor by Pier Francesco Cittadini or workshop, ca. 1668, National Art Museum in Kaunas.
Portrait of King John II Casimir Vasa by workshop of Carlo Ceresa
Initium Calamitatis Regni (beginning of calamity for the kingdom) is how the opponents of the elected king John II Casimir Vasa interpreted his royal monogram I(J).C.R. (Ioannes Casimirus Rex). They blamed the king for the tragic events during his reign and believed that the claims of John Casimir to the crown of Sweden, the legitimate dynastic claims, brought to the country the army of the "Brigand of Europe" Charles X Gustav, as well as that of the Elector of Brandenburg united with him (Treaty of Marienburg, concluded on June 25, 1656), while the Commonwealth was grappling with other invaders to the east.
The country significantly depopulated, the economy was in ruins, tax sources dried up and money depreciated considerably. This led the king to participate in manipulating the face value of coins, such as the Boratynka minted by Tito Livio Burattini (1617-1681) in Ujazdów, which also contributed to John Casimir's unpopularity. The country that previously imported heavy marbles from Italy and Belgium, luxury goods from all over Europe, Persia and Turkey, was no longer able to even pay its own army. "The real cause of this misery lay in the extreme impoverishment of the country, devastated by robberies and destruction", as summarized it Zygmunt Gloger in his "Book of Polish Things" (Księga rzeczy polskich, p. 317), published in 1896. In addition, the Commonwealth was ravaged by grave internal conflicts. The policy of the king and queen aimed at strengthening royal power led to civil war - the Lubomirski rebellion (1665-1666), initiated by Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski (1616-1667) and his supporters. They also paralyzed the proceedings of the Sejm. At the end of 1666, the main forces of the Crimean Tatars, supported by the Cossacks, crossed the southern borders of the Commonwealth and began the war in Podolia. In January 1667, the then apostolic nuncio in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, titular archbishop of Larissa, and later Pope Innocent XII, Antonio Pignatelli (1615-1700) reported that all of the country were abuzz with rumors of the king's imminent abdication of the throne, because "due to both age and [health] indispositions, he is unable to conduct military operations" (after "Stolica Apostolska wobec abdykacji ..." by Dorota Gregorowicz, p. 124). Additionally, on May 10, 1667, the king was struck by a personal tragedy: his wife, Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga, considered one of the most influential and powerful queen consorts of Poland-Lithuania since the time of Bona Sforza (1494-1557), died. The most tolerant country in Europe during the Renaissance was stepping more and more into the dark ages. Wartime, chaos and unrest have been used by some to oppress others, especially women. "Women have harmed us enough with their politics" (dosyć i białegłowy swą polityką nam zaskórzyły), wrote Andrzej Olszowski (1621-1677), Vice-Chancellor of the Crown and Bishop of Chełmno, in a letter dated October 6, 1668 to Marcin Oborski, starost of Liw. The reluctance towards women's political influence was fully expressed after the abdication of John Casimir, when the election Sejm adopted a resolution (May 1669), according to which "the Queen Her Ladyship should not interfere in negotia Status [state affairs], and also that no position at the court should be granted through the interference of foreign ladies of the court" (Królowa Ieymć aby się in negotia Status nie mięszała, promocye także aby nigdy przez białegłowy dworskie cudzoziemskie nie chodziły, compare "Dynastia Wazów ..." by Stefania Ochmann-Staniszewska, p. 276-277). In 1670, "fig leaves" were likely added to the nude effigies of King Sigismund Augustus (1520-1572) and his third wife Catherine of Austria (1533-1572), depicted as Adam and Eve in the Paradise Bliss tapestry, to cover their nudity, when the tapestry was transported to the Jasna Góra Monastery for the wedding of King Michael I, successor of John Casimir (compare "Arasy Zygmunta Agusta" by Mieczysław Gębarowicz, Tadeusz Mańkowski, p. 23). The last official portrait of John Casimir is probably the beautifully painted full-length portrait, now kept in the Wilanów Palace in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 202 x 153 cm, Wil.1159). It represents him in a French costume, fashionable at the time, black as a sign of mourning for his wife. He is holding the crown, most likely the so-called Muscovy Crown, which was recreated in a simpler form in 1668 by the Warsaw goldsmith Tobiasz Rychter. The original, more splendid, from the beginning of the 17th century, was minted for coinage by order of the king and he was obliged by parliament to return it before his abdication. The Order of the Golden Fleece awarded to John Casimir in 1638 by his cousin King Philip IV of Spain hangs around his neck. The painter is unknown and no painter active in the Commonwealth appears to be the author. The overall style indicates Italian influences, such bold brushstrokes, contrast of light and shadow and a "fresco" appearance, which exclude Gdańsk painters such as Daniel Schultz, Adolf Boy or Andreas Stech. The author was not Jan Tricius or Tretko (d. 1692), a Polish painter trained in Paris and Antwerp, because his signed works such as the portrait of Wojciech Dąbrowski, rector of the Kraków Academy, from 1664, bear no similarity. The paintings attributed to Claude Callot, a painter trained in Rome and who worked for Marie Louise Gonzaga from the beginning of 1667, in the royal library of the Wilanów Palace or in the Vasa Chapel of Wawel Cathedral, are also painted in a different way. Among the most prominent painters inspired by Italian painting was undoubtedly Tomasz Muszyński, active in Lublin between 1647 and 1680. Many of his paintings are kept in the Dominican Monastery in Lublin. His style is also different. Interestingly, Muszyński was undoubtedly the author of the portrait of Teresa Tyszkiewiczowa née Sapieha in the Museum of Warsaw (oil on canvas, 108 x 75 cm, MHW 2665), painted in the early 1660s, as indicated by the style of her dress. The painting bears her coat of arms - Lis surrounded by the letters TST/XSP, abbreviation of Teresa Sapieżanka Tyszkiewiczowa / Xiężna Sokolnicka Pułkownikowa. The style of the canvas recalls the portrait of Father Franciszek Grabiecki (painted in 1677), Blessed Ceslaus (1665) and larger compositions, such as that of Bishop Andrew carrying the relics of the Holy Cross to Poland (1651-1653). Muszyński placed his religious scenes in an entourage he knew in his daily life. Thus the majority of his scenes represent the inhabitants of Lublin "in the guise" of biblical or legendary characters. To the right of his large composition representing the Finding of the Cross by Saint Helena, he places a statue of Venus disarming Cupid. The painting closest in style to the portrait of the king from Wilanów Palace was sold in 2022 in Genoa - portrait of a man holding a letter (Wannenes Art Auctions in Genoa, November 29, 2022, lot 230). It was auctioned with attribution to the 17th century Bergamo school and Ferdinando Arisi attributed the painting to Carlo Ceresa (1609-1679), a painter active mainly around Bergamo in the Republic of Venice, trained in the workshop by the Milanese painter Daniele Crespi. Another work painted in the same way is an oval portrait of a nobleman (Galleria Marletta in Florence, 1stDibs: LU124028459822) and a portrait of a noblewoman (Lucas Aste in Milan, May 24, 2022, lot 24), both attributed to Ceresa. The style of the portrait of a lady, possibly the artist's wife Caterina Zignoni, as Judith with the head of Holofernes (Porro in Milan, Auction 81, November 30, 2016, lot 5), can also be compared to the effigy of the king. The works of Ceresa and other 17th century Bergamo painters are often compared to those of the city's most famous painter - Giovanni Battista Moroni. It cannot be excluded that through this perhaps last commission as elected monarch of the Commonwealth, John Casimir was referring to the golden age of Poland-Lithuania, to the Jagiellon portraits by Moroni, that I have identified, as well as many magnificent paintings that he probably also created for Sarmatians, which were destroyed during the Deluge.
Portrait of King John II Casimir Vasa (1609-1672) by workshop of Carlo Ceresa, ca. 1668, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
Portrait of Teresa Tyszkiewiczowa née Sapieha by Tomasz Muszyński, 1660s, Museum of Warsaw.
Portraits of King Michael I and Queen Eleonora Maria Josepha of Austria by court painters
In 1668, King John II Casimir Vasa, the last descendant of the Jagiellons on the Polish throne, whose reign was marked by the terrible Deluge (1655-1660), abdicated. After the invasion, the country changed significantly in many ways, including demographically and ethnically. Many regions became depopulated and impoverished. Foreigners have ceased to be a dominant power in many cities and the time of the "compatriot king" has come. On June 19, 1669, Michael I Korybut, a member of the Ruthenian Vyshnevetsky (Wiśniowiecki) family, was elected king. To emphasize his Ruthenian origins, the king was even represented in a costume typical of Ruthenian princes in a print by Nicolas de Larmessin I (National Library of Poland, G.45499).
However, in many respects the situation remained the same as before, especially with regard to portraiture, art and luxury goods imported from other countries. The magnificent almost one meter high silver white eagle of Poland - heraldic base for the royal crown, was probably made in Augsburg for the king's coronation on September 29, 1669. The eagle was created by Abraham I or Abraham II Drentwett and Heinrich Mannlich and was given to Alexis of Russia in 1671 as a diplomatic gift to prevent another war (today in the Moscow Kremlin, Armory, MZ 191). In the Hermitage Museum there is a silver-gilt basin with Titanomachy and inscription in Polish IEREMI MICHAL KORIBUTH XIAZE NA WISNIOWIV Y LUBNIACH (Э-8767). This beautiful basin was created by Elias I Drentwett in the 1630s, also in Augsburg, most likely for the king's father Jeremi Wiśniowiecki (Yarema Vyshnevetsky, 1612-1651). The king also ordered from Gdańsk the silver service consisting of 258 vessels with a total weight of 1,129 grzywnas for the grand sum of 33,618.06 florins (with cases and material for lining). Portraits during this period were less frequently commissioned from abroad, perhaps because workshops there were too expensive or since the "compatriot kings" were not related familially to the monarchs of Europe, like the Jagiellons and the Vasas, there was no need to send many updated effigies to relatives. There were also more and more prominent native painters. It was probably shortly after the coronation that the series of magnificent portraits of the king by the court painter Daniel Schultz was created, including the full-length portrait at Wawel Castle (1423), purchased in 1936 by the Polish Academy of Arts and Sciences in Kraków and coming from the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, the portrait was therefore most likely a gift to the Habsburgs. A reduced version, painted in the same style (especially the armor) is in the Wilanów Palace (oil on canvas, 83 x 68, Wil.1158). Other royal and ducal courts in Europe must also have received the king's portraits. Such long-forgotten effigies of the Polish-Lithuanian monarch can be found today in the National Gallery of Denmark in Copenhagen ("Portrait of a man", dated 1791-1890, oil on canvas, 47.5 x 38 cm, KMS1416), probably from the Danish royal collection, and the Pitti Palace in Florence, which brings together the Medici collections, therefore very probably a gift for the Grand Dukes of Tuscany ("Portrait of a man", dated 1690-1710 and "stylistically similar to 17th century French painting", oil on canvas, 43 x 33 cm, Inv. 1890, 5269). Both resemble the effigy of the king from a print by Wolfgang Philipp Kilian, published in 1692 (Royal Castle in Warsaw, ZKW/4322). The absence of the Order of the Golden Fleece, which he received on October 6, 1669 from the hands of the Spanish envoy of King Charles II of Spain during the session of the Sejm, in the two last potraits, indicates that they were probably created between June and October of that year. On February 27, 1670, Michael I married Austrian Archduchess Eleonora Maria Josepha (1653-1697), daughter of Ferdinand III, Holy Roman Emperor, by his third wife Eleonora Gonzaga (niece of the former Queen of Poland Marie Louise Gonzaga). The ceremony was celebrated by the Apostolic Nuncio, Cardinal Galeazzo Marescotti, at the Jasna Góra Monastery. The large full-length portrait of the queen holding flowers, which was housed before the Second World War in the Zamoyski Palace in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 215 x 131 cm, lost or destroyed), was also attributed to Schultz. This painting was probably created shortly after the wedding and coronation on September 29, 1670 in Warsaw. Due to the great opposition to the Habsburg marriage, the king and his wife wanted to refer to the origins of the multicultural monarchy in Poland-Lithuania. Michael ordered to take the jewels of Queen Hedwig of Anjou (Saint Jadwiga, 1373/1374-1399) from the Kraków Academy, "so that he could use them as gifts for his fiancée, Queen Eleonora, but when it was found that there were not as many of them as needed and their shape was not was proper, they were returned by King Michael", testifies under the year 1670 Stanisław Józef Bieżanowski (1628-1693) (after "Rocznik krakowski", Volume 38, p. 16). What is interesting is that there is a portrait of Queen Hedwig from the 1670s at the Academy (Collegium Maius). Along with a portrait of her husband Jogaila of Lithuania, it was painted in Kraków by the painter of the Polish court, trained in Paris and Antwerp, Jan Tricius (also Trycjusz or Tretko). The portrait of Jogaila is imaginative and was signed at the bottom: Jan Tricius pinxit Cracoviae. The portrait of Hedwig is not signed, while other paintings from this series were also dated 1677 and 1678 (portraits of Piotr Tylicki and Jerzy Lubomirski), including the portrait of King John III Sobieski (Jan Tricius pinxit Cracoviae A. 1677). Thus, the portrait of the queen must also have been painted before 1678. The coat of arms of the Hungarian branch of the House of Anjou is in the upper left corner and the painting is inscribed on the frame: HEDVIGIS REGINA P. The queen wears a medieval-style dress lined with ermine and embroidered with French fleur-de-lis, but her facial features closely resemble those of Queen Eleonora Maria Josepha from her portrait from the Zamoyski collection. Eleonora Maria Josepha's facial features from her portrait holding a tulip, a symbol of affection and marital fidelity (National Museum in Warsaw, MP 4979), are also very similar, as are those from her portrait from around 1690 (private collection), showing her in mourning after the death of her second husband. This portrait can be compared to the portrait of Marie Mancini (1639-1715), niece of Cardinal Mazarin, represented in a medieval-style costume of Armida, fictional character of a Saracen sorceress, painted by Carlo Maratta in 1669 (Palazzo Colonna in Rome). Tricius or his workshop are the probable authors of the portrait of Katarzyna Ludwika Mniszech, kept in the Czartoryski Museum in Kraków, in which the model's rich costume, decorated with diamond brooches, pearls, gold bracelets and lace, recalls the costumes noble Hungarian ladies of the 1670s or 1680s. Ludwika, who probably received her name in honor of Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga, was depicted holding in her right hand a tulip, a symbol of affection and marital fidelity, and in her left hand a sprig of wheat, a symbol of the Christian resurrection or symbol of fertility or prosperity, which returned to the Commonwealth during the Sobieski period (1674-1696). Significant inflences of women in Poland dates at least to the times of Queen Hedwig, who was elected to the throne of Poland by the aristocracy assembled at Radomsko in 1382, and her grandmother Elizabeth of Poland (1305-1380), Queen of Hungary, who was Regent of Poland between 1370-1380. The fact that Jogaila does not present any characteristics of King Michael indicates that the queen's likeness or its original, copied by Tricius, was made after his death, therefore during the royal election. If this disguised portrait was a political allegory and was ordered by the queen or her supporters, such a clear reference to the first elected queen confirms that she also wished to be elected. Some of the queen's supporters also demanded that the candidate for the throne should marry her. King Michael died on November 10, 1673, and Eleonora Maria Josepha remained in Poland for almost two years after his death, mainly in Toruń. After the election of John III Sobieski, in the spring of 1675 the queen left Poland for Vienna and on February 4, 1678 in Wiener Neustadt, she married Duke Charles V of Lorraine. Since the Duchy of Lorraine was under French occupation, the couple resided in Innsbruck, in Tyrol. After her departure for Austria, Eleonora Maria Josepha was still very involved in Polish politics and there were fears in Poland that she was planning to overthrow King John III and install her own spouse as king. In several of her portraits from this period, she poses with the royal crown of Poland, such as that purchased by the Wawel Royal Castle in Paris in 2008. The author of the Wawel painting was most likely Charles Herbel (1656-1703), court painter to the Duke of Lorraine because it closely resembles the one represented in a print made by Elias Hainzelmann in Augsburg after a painting by Herbel (Austrian National Library, 47539, signed: C. Herbel pingebat.). A similar portrait from the collection of the artist and cabinetmaker Mario Villa (1953-2021), attributed to the school of Pierre Mignard, was sold in 2022 in New Orleans as "Portrait of a Queen" (oil on canvas, 121.29 x 85.41 cm, Neal Auction Company, May 12, 2022, lot 28).
Portrait of King Michael I (1640-1673), holding a baton by Daniel Schultz or workshop, ca. 1669-1673, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
Portrait of King Michael I (1640-1673) by workshop of Daniel Schultz, ca. 1669, Pitti Palace in Florence.
Portrait of King Michael I (1640-1673) by workshop of Daniel Schultz, ca. 1669, National Gallery of Denmark.
Portrait of Queen Eleonora Maria Josepha of Austria (1653-1697), holding flowers by Daniel Schultz, ca. 1670, Zamoyski Palace in Warsaw, lost.
Portrait of Queen Eleonora Maria Josepha of Austria (1653-1697) in guise of Queen Hedwig of Anjou (Saint Jadwiga, 1373/1374-1399) by Jan Tricius, ca. 1673-1678, Jagiellonian University Museum.
Portrait of Eleonora Maria Josepha of Austria (1653-1697), Duchess of Lorraine with Polish regalia by Charles Herbel, ca. 1678-1683, Wawel Royal Castle.
Portrait of Eleonora Maria Josepha of Austria (1653-1697), Duchess of Lorraine with Polish regalia by Charles Herbel, ca. 1678-1683, Private collection.
Portrait of Queen Eleonora Maria Josepha of Austria by Gonzales Coques
Queen Eleonora Maria Josepha of Austria (1653-1697), was a great lover of Italian theater and ballet. Her courtiers were mainly Italians, and the queen herself used this language in her everyday life (after "Warszawa w latach 1526-1795" by Maria Bogucka, p. 233). On Shrovetide 1671 Eleonora's courtiers performed the tragedy by Giacinto Andrea Cicognini entitled La caduta del gran capitan Belissario ... (published in Rome in 1663), on May 31, 1671 a comedy translated from the Spanish about Queen Morilinda (Komedyja o Morylindzie królowej), interwoven with vocal and dance intermedia, was performed on the occasion of queen's birthday and the next day, the queen staged a beautiful ballet in the garden of the Casimir Palace (Villa Regia), danced by her ladies-in-waiting.
Although not confirmed in the sources, the queen must also have participated in some of these splendid entertainments. Around 1667, her half-brother Emperor Leopold I (1640-1705) and his wife the Spanish Infanta Margaret Theresa (1651-1673) were represented in stage costumes, most probably for the play La Galatea (as Acis and Galatea), which was performed in 1667 in Vienna as part of the wedding festivities which lasted almost two years. These two small pendant portraits, attributed to the Flemish painter Jan Thomas van Ieperen, are today in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna (oil on copper, 33.3 x 24.2 cm, GG 9135 and GG 9136). Van Ieperen, a student of Rubens, probably also painted the portrait of Leopold I on horseback in a costume for a "horse-ballet" (ballet à cheval), which until 1957 was in the collection of the National Museum in Warsaw as a deposit of Janusz Radziwiłł (oil on canvas, 56 x 46 cm). According to family tradition, this painting was considered to be an equestrian portrait of Henry of Valois, king of Poland then king of France under the name of Henry III. This painting was probably a counterpart to the portrait of Gundakar (1623-1690), prince of Dietrichstein, dated around 1667 (Kunsthistorisches Museum, oil on canvas, 60.5 x 49.5 cm, GG 9676), but we cannot cannot exclude that it was a gift for King John II Casimir Vasa with whom the effigy was also identified. The equestrian ballet was one of the elaborate festivities held at the Viennese court in 1667. When the Polish queen, Marie Louise Gonzaga, died that same year, Emperor Leopold proposed to his widowed relative John Casimir one of three archduchesses or his own stepmother (Eleonora Maria Josepha's mother) as his wife. On the occasion of the Empress's birthday, the opera Il Pomo d'oro ("The Golden Apple") by Antonio Cesti was performed on July 12 and 13, 1668. A specially constructed open-air theatre was built for this festa teatrale. The emperor himself, who set two scenes to music, was involved. For this opulent opera, Lodovico Ottavio Burnacini created 23 different stage sets that captivated the audience. Il Pomo d'oro became known in Europe thanks to the prints by Matthäus Küsel and Frans Geffels based on Burnacini's drawings. The opera was undoubtedly seen by Leopold's half-sister, Eleonora Maria Josepha, who two years later became Queen of Poland. Interestingly, a beautiful silver tray with a scene from the opera Il Pomo d'oro, created by Hans Polmann in Gdańsk (active 1626-1686), is found in the treasury of Tarnów Cathedral (deposited in the Wawel Royal Castle). In 2016, a "Portrait of a noblewoman, said to be Maria Leszczynska" was sold in London (oil on copper, 42.9 x 28.4 cm, Bonhams, July 20, 2016, lot 104). Due to the traditional identification and attribution to Franz Christoph Janneck (1703-1761), an Austrian painter in the Baroque style, specializing in genre scenes, which was also written on the frame ("MARIE LECZINSKI, d. 1767. / daughter of Stanislaus King of Poland. / married Louis XV, 1723. 1703. F.C. JANNECK. 1761."), the painting was sold with an attribution to the German school, around 1700. However, the model's costume and hairstyle indicate that the painting is before 1700. The author of the blog Pospiszil87 (June 24, 2016), also noticed the great resemblance with the effigies of Queen Eleonora Maria Josepha, wife of Michael I. Her dress, pose and facial features are particularly similar to the portrait of the queen in a white dress from Wilanów Palace (Wil.1156), most likely created shortly after her coronation in 1670. The sitter also resembles Eleonora Maria Josepha from her portrait in a golden dress, attributed to Benjamin Block at the Kunsthistorisches Museum (GG 2106), correctly identified by the author of the webiste altesses.eu. Block's portrait was probably made shortly before her departure for Poland and was reproduced in an engraving bearing the inscription: Coecilia Renata / Königin in Pohlen (National Museum in Kraków, MNK III-ryc.-44614). Probably due to the similarity with this print, another portrait of Eleonora Maria Josepha, now at Rychnov nad Kněžnou Castle (č. RK 19/69), was considered to depict Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria, correctly identified by me in 2011. The model's face also resembles the portrait of the queen by Charles Brendel, signed and dated: Ch. Brendel 1684 (Kunsthistorisches Museum, GG 2750) and anonymous engraving in the Herzog August library in Wolfenbüttel (A 16720). The shorter dress from the London portrait, than in all the portraits mentioned, indicates that it was designed to facilitate dancing. Its decoration is also more theatrical and recalls the dancers' costumes reproduced in an engraving representing a scene from Il Pomo d'oro of 1668 (Metropolitan Museum of Art, 53.600.3541). Her early 1670s hairstyle and turban-shaped headpiece alla turca indicate that she could have posed as a character in La caduta del gran capitan Belissario ..., staged in Warsaw in 1671, perhaps as Byzantine Empress Theodora (wife of Justinian I), one of the main characters in this play. The play was the dramatized story of the Byzantine leader who was blinded at the end of his life on the orders of the Emperor Justinian. It is interesting to note that public opinion saw in the performance of this play political allusions to the person of the leader of the opposition, Primate Mikołaj Prażmowski (1617-1673), who could only see in one eye and was therefore called a blind man or a cyclops by the court party. The portrait is comparable to the effigies of Sophie Amalie of Brunswick-Calenberg (1628-1685), queen of Denmark and Norway in stage costume from around 1655, painted by Wolfgang Heimbach (Rosenborg Castle and Frederiksborg Castle) and in particular to the portraits of Louis XIV of France and his mistress Louise de La Vallière in Polish-style masquerade costumes, painted by Joseph Werner (Norton Simon Museum, M.2010.1.189.P, M.2010.1.190.P). According to the letter from the Prince of Condé to Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga, dated February 29, 1664, a great Polish-style masquerade took place at the court of Louis XIV of France: "The masquerade was held this Tuesday, it was the most beautiful and the most magnificent in the world. (...) The King was dressed in Polish style; this outfit suited him extremely well, and everyone found it very beautiful" (La mascarade se fit mardi, elle fut la plus belle et la plus magnifique du mondé. (...) Le Roi était vêtu à la polonaise; cet habit-là lui seyait extrêmement bien, et tout le monde l'a trouvé fort beau). The king was represented in blue clothing inspired by the Polish żupan, wearing a fur hat similar to kolpak and holding a nadziak war hammer and his mistress in yellow jupeczka (female fur clothing). His 3-year-old son Louis, Grand Dauphin, was also depicted in a costume similar to żupan in a painting in the Prado Museum (P002291). A few years after the destructive Deluge, the Commonwealth was a shadow of its former glory. However, the stock of looted objects and clothing of the Polish-Lithuanian nobility and luxury horse tacks adorned with silver and jewels was apparently so large in Sweden that parades in these "exotic" outfits were held in the capital of the Swedish Empire. When the Commonwealth attempted to rebuild the crumbling economy after the invasion and five years of plunder and destruction, the invaders also began spending their dubious "economic surplus" on luxury goods abroad. For example a collection of engravings published after 1672 in Nuremberg (Certamen equestre caeteraque solemnia Holmiae Suecorum ..., National Library of France, BnF FRBNF44335264) shows a parade in Stockholm in December 1672 celebrating the accession to the throne of King Charles XI. Swedish aristocrats, including Count Bengt Oxenstierna (1623-1702), who during the invasion became governor of the newly conquered Duchy of Lithuania, Steenbock, Gyllenstierna, Reutercrantz and others and their retinues, parade in the obviously looted garments of the Commonwealth's nobles (pages 38-49). Although the style and format of the London portrait is reminiscent of Jan Thomas van Ieperen's portrait of the queen's half-brother and his wife in stage costumes, it is closer to that of the most eminent painter of the cabinet paintings, that were popular in the Baroque age - Gonzales Coques (d. 1684), possibly a pupil of Anthony van Dyck, called "the little van Dyck" (de kleine van Dyck). The style of the portrait of the queen's uncle, Archduke Leopold William of Austria (1614-1662) by Coques, painted before 1659 (Kunsthistorisches Museum, GG 5461), is particularly similar. The style of the painting also resembles another portrait from the same period, attributed to Coques. This "Portrait of an elegant lady" was sold in Vienna in 2017 (oil on copper, 30.6 x 22.2 cm, Dorotheum, October 17, 2017, lot 264). The sitter's hairstyle and costume are also in the same style as the queen's effigy. On the left is an indistinct inscription in Italian, written by the woman on the tree, which reads: "Whoever wanted ... freedom for his life in his homeland" (Chi voll … liberta sua vita a patria). Previously, this portrait had been sold in London (Bonhams, April 6, 2017, lot 110) with attribution to the French School. The woman closely resembles Mary Elizabeth Browne, Lady Teynham (d. after 1686), based on her portrait by John Michael Wright, painted in 1672 (Sotheby's London, April 30, 2014, lot 765). Coques, who worked for foreign clients, also painted the French Queen Maria Theresa of Spain (1638-1683), a distant relative of Eleonora Maria Josepha. This small oval miniature from a private collection in Paris, signed on the reverse: Gonzales Corques, was put on sale in January 2024 with identification as Mary, Princess Royal (1631-1660), eldest daughter of King Charles I of England (oil on copper, 8.1 x 6.6 cm, Boris Wilnitsky Fine Arts in Vienna, 37731). The effigy is similar to queen's portrait at Versailles (MV 3501) or the engraving by Nicolas Pitau, dated 1662. It should also be noted that the print with the effigy of Eleonora Maria Josepha by Nicolas de Larmessin, made in Paris after 1670, representing the Queen of Poland in a Ruthenian-style fur coat, resembles the effigies of the Queen of France (National Library of Poland, G.45500).
Portrait of Queen Eleonora Maria Josepha of Austria (1653-1697) in stage costume by Gonzales Coques, ca. 1670-1671, Private collection.
Portrait of Queen Eleonora Maria Josepha of Austria by workshop of Louis Ferdinand Elle the Elder
The painting entitled "In the artist's studio" kept in the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 76 x 89 cm, M.Ob.1991 MNW) shows the importance of initial study drawings on all stages of the work. A couple of wealthy patrons in costumes from the early 1700s consult the drawing they received and accepted with the final work in the sculptor's workshop, whose assistant makes the modifications requested by the clients. The drawing is held by the wife, who probably ordered the carved vase and she shows it to her husband dressed in a costume of a Polish-Lithuanian nobleman and accompanied by servants wearing kolpak fur hats.
This painting is attributed to the Austrian painter Johann Georg Platzer (1704-1761), but a similar work entitled "In the studio of the court painter" (oil on canvas, 78 x 89 cm, Dorotheum Vienna, September 26, 2017, lot 156) was sold with attribution to the Flemish painters Gerard Thomas (1663-1721) or circle of Balthasar van den Bossche (1681-1715), both active in Antwerp. Both of them must have seen many wealthy Sarmatians visiting Antwerp and commissioning magnificent works from local workshops, as they immortalized them in many of their genre scenes, such as the Sculptors' workshop with a client from the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth by Gerard Thomas (Royal Museum of Fine Arts in Antwerp, 783) and a comparable painting by Balthasar van den Bossche (Alte Pinakothek in Munich, 2219). Self-portrait copying the portrait of Vittoria della Rovere (1622-1694), Grand Duchess of Tuscany by Camilla Guerrieri (oil on majolica, 14.2 x 16.7 cm, Altomani & Sons), painted around 1658-1662, shows the importance of the copies made from other paintings, as well as the fact that important dignitaries did not spend hours posing for such paintings, but relied on such copies by their court painters. Portrait of Vittoria della Rovere in black dress with lace collar and diamond brooch by Justus Sustermans at the Hamburger Kunsthalle in Hamburg (inv. 766) and a painting close to the style of Camilla Guerrieri (Chiswick Auctions in London, January 31, 2018, lot 46) are two such versions of the same portrait, which differ in several details. Skilled painters could also create things different from what they actually were and meet the different demands of their clients. They could "beautify" them, make their features more harmonious or change the color of the hair. In several of her portraits, Maria Anna of Austria (1610-1665), Electress of Bavaria, sister of Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria (1611-1644), wears in her hair a heavy jewel with a large ruby or garnet. In her portrait from Dachau Castle (Alte Pinakothek Munich, 3093), the jewel is larger than an eye, while in the portrait she most likely sent to her relatives in Florence (Palazzo Pitti in Florence, inv. 1890 / 5261), it is much larger, almost the size of an egg, as if electress wanted to make them envious. Although less than in previous eras, the "compatriot kings" also ordered their effigies abroad. Around 1677, the "Victorious King" John III Sobieski commissioned a series of his portraits from the workshop of a Flemish painter Prosper Henricus Lankrink (1628-1692) or another painter, several copies of which survived, notably in the Wawel Castle (inv. 1781), Forchtenstein Castle in Austria (B 622) and the painting from the Former Polish Museum in Muri (MPM 0541). A pen and ink sketch, kept in the Print Cabinet of the Warsaw University Library, was most likely the initial study drawing sent to Lankrink in Antwerp or in London, where he collaborated with Peter Lely. The drawing was sold after his death in 1692 and later acquired by the last elected monarch of the Commonwealth Stanislaus Augustus Poniatowski (1732-1798). It features notes in Dutch/Flemish with colors and fabrics, made to facilitate a painter's work. This is undoubtedly a sketch made from nature, as evidenced by the last fragment of the text: "... in this outfit he [the king] is also obese" (after "Sobiesciana ..." by Maria Cubrzyńska-Leonarczyk, p. 40). Some of these paintings were undoubtedly also intended for diplomatic gifts and the orders in Antwerp facilitated the distribution of these effigies throughout Europe. From there they could be easily shipped to Madrid, Paris, Rome and London. The "compatriot kings" also received such gifts from abroad and the portrait of the regent of Spain, Queen Mariana of Austria (1634-1696), who was also the ruler of the Spanish Netherlands, today preserved in the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 123 x 97.5 cm, 42503 MNW), could be such a gift. This painting comes from the Morzycki Gallery in Ruszkowo near Konin and was donated by Maria Morzycka to the Warsaw Museum in 1922. It is a version of portrait by Juan Carreño de Miranda, now kept in the Prado Museum in Madrid (P000644), representing the queen in the habit of a nun and seated in the Hall of Mirrors of the Alcazar of Madrid. The original is dated around 1669 or 1670, so the copy could be a gift for King Michael I and his Habsburg wife Eleonora Maria Josepha of Austria (1653-1697), half-sister of the Queen of Spain, as daughters of Emperor Ferdinand III. It should also be noted that there are no apparent attributes, characteristics indicating that the woman in the painting is the monarch of one of the greatest empires in history. There is no crown, no elaborate costume. At first glance, it could be seen as a "Portrait of a nun writing a letter". Another gift for the elected monarchs of the Commonwealth was most likely another portrait kept in the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 55 x 50 cm, MP 5274 MNW), later in the Krosnowski collection (State Art Collections of Warsaw, inv. 94). It is said to depict Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga (1611-1667), but it is an almost exact copy of the portrait of Anne of Austria (1601-1666), Queen of France, painted by Pierre Mignard and reproduced in a engraving by Robert Nanteuil in 1660 (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, RP-P-1948-37), correctly identified by me in 2013. The French lilies on her mantle also indicate that it is an effigy of the Queen of France, many of whose portraits were in the royal and magnate collections of the Commonwealth. The portraits of Anne, cousin of kings Ladislaus IV and John Casimir and relative of Queen Cecilia Renata and Queen Eleonora Maria Josepha, are mentioned in the 1661 inventory of the Lubomirski collection in Wiśnicz (Królowa Francuzka Matka), in the 1667 inventory of the possessions of King John II Casimir and most probably mentioned in the 1696 inventory of the Wilanów Palace (no. 37), or a likeness of her daughter-in-law and relative Maria Theresa of Spain, as well as in the 1671 inventory of the Radziwll collection (311/20, Reine de France). The portrait of the Queen of France is a copy of Mignard's painting, however its style more closely resembles the paintings signed and attributed to Louis Ferdinand Elle the Elder (1612-1689), son of the Flemish painter Ferdinand Elle (died in 1637), who settled in France, notably presumed portrait of Marguerite Hessein, dame de La Sablière (1636-1693), as Diana the Huntress (Osenat in Fontainebleau, November 23, 2019, lot 41), signed and dated on the reverse of the canvas: FAIT PAR FERDINAND LAISNE 1655. Another portrait painted in a similar style, although less refined, which could indicate the work of students in his studio, was sold in 2009 in Genoa (oil on canvas, 75 x 58 cm, Cambi Casa d'Aste, May 29 2009, lot 2000), as a "Portrait of a woman" (Ritratto femminile), attributed to the German school of the 17th century. The woman in this portrait bears a striking resemblance to the effigies of Queen Eleonora Maria Josepha, notably to her lost full-length portrait with blonde hair (Zamoyski Palace in Warsaw) and anonymous engraving with Latin inscription: SERENISSIMA PRINCEPS D.D. / ELEONORA D.G. REGINA POLO/NIÆ ARCHIDVX AVSTRIÆ etc. (Herzog August Library in Wolfenbüttel, A 16720). The resemblance to another print with queen's portrait, made by Hans Ulrich Franck (Austrian National Library), particularly with regard to her hairstyle and composition of the painting, is also great. Her hairstyle resembles that in a portrait of Claudia Felicitas of Austria (1653-1676), second wife of Eleonora Maria Josepha's half-brother, depicted blonde and painted around 1672. In the majority of her known portraits, Claudia Felicitas has dark hair, meaning she dyed her hair or wore a wig. This hairstyle was probably introduced to France and throughout Europe by Eleonora Maria Josepha's distant relative, Maria Theresa of Spain, wife of Louis XIV, and was inspired by the large Spanish wigs of the 1650s. It was not only fashionable to dress in the manner of the French court, but also to be painted by the court painters of the Sun King. The portrait of the Queen of Poland was therefore commissioned in Paris and eventually sent from there to Italy. The oldest known effigy of Eleonora Maria Josepha is a portrait in the Pardo Museum in Madrid (P002228), which was sent to her Spanish relatives and which depicts her at the age of around 2 years old around 1655.
Portrait of Queen Eleonora Maria Josepha of Austria (1653-1697) by workshop of Louis Ferdinand Elle the Elder, ca. 1670-1673, Private collection.
Portrait of Anne of Austria (1601-1666), Queen of France by Louis Ferdinand Elle the Elder or workshop, ca. 1660-1666, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Mariana of Austria (1634-1696), Queen of Spain by follower of Juan Carreño de Miranda, ca. 1670, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portraits of Helena Tekla Lubomirska by Pierre Mignard I and Nicolas de Plattemontagne
In 1893, Henryk Bukowski, an antiques dealer active in Stockholm, who bought Polonica from Sweden seized from the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth during the Deluge (1655-1660) and the Great Northern War (1700-1721), donated a painting to the Polish Museum in Rapperswil in Switzerland, known in later catalogs as portrait of Princess Lubomirska by Mignard. The museum founded in 1870 preserved the memorabilia of the country which, at that time, did not exist on the maps of Europe, destroyed by imperialist neighbors. In 1929, when Poland regained its independence (1918), the painting, along with many others, was transferred to the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 72 x 59 cm, M.Ob.1253, earlier 34182). It survived the looting and destruction during the Second World War, unlike the Madonna and Child by the Master of the Legend of the Magdalene (34169) or the portrait of Crown Prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa, copy after Rubens' original.
The portrait of Princess Lubomirska was inscribed on the back: Capitane Lubomirski / par Nic. Mignard. In 1975, Wanda Drecka identified the model as Helena Tekla Ossolińska (1622-1687), wife of Aleksander Michał Lubomirski (1614-1677), starost (capitaneus) of Sandomierz (compare "Dwa portrety księżnej na Wiśniczu", p. 373-387). She was part of the close circle of Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga and exercised great influence at court. The French envoy Antoine de Lumbres described her as "mischievous" in a letter to Louis XIV of February 26, 1655 (et l'autre qui est beaucoup plus fine et malicieuse est la femme du grand écuyer). As a relative of John III through her mother, she often appears in the king's correspondence with his wife, where Sobieski calls her his sister (à ma sœur) or madame la starostine de Sandomir (for example letter dated October 15, 1683 near Esztergom/Strygonium). The great resemblance of the sitter to other preserved effigies of capitane/starostine Lubomirska, as well as the fact that many of her portraits were created in France confirm this identification. The "Inventory of belongings spared from Swedes and escapes made on December 1, 1661 in Wiśnicz" (Rejestr rzeczy po Szwedach i ucieczkach zostających spisany roku 1661 dnia 1 grudnia na Wiśniczu) in the Central Archives of Historical Records in Warsaw (number 1/357/0/-/7/12), lists numerous portraits from the Lubomirski collection that survived the Deluge. In addition to a portrait of Helena Tekla in the guise of Saint Helena and a full-length portrait in the guise of Diana with greyhounds by Simon Vouet and workshop, made in Paris, allegorical portrait of Louis XIII and Cardinal Richelieu, it also includes "a portrait of the king of France, a small miniature on parchment which was in the jewel" (Konterfek Króla Francuzkiego malusienki Miniatura na pargaminie ktory był wkleinocie), as well as "a portrait of a seated young king of France (Konterfet Krola Francuzkiego młodego siedzącego), perhaps a version of a portrait of Louis XIV by Justus van Egmont kept in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna (GG 3208). The portrait of the French monarch is followed by a series of portraits of European monarchs, which perhaps also reflect the hierarchy of political relations of the Lubomirski family for whom the elected monarchs of the Commonewath were only "first among equals" (primus inter pares) - portrait of Pope Urban VIII (Vrbanus VIII), perhaps a copy of the effigy by Pietro da Cortona (Capitoline Museums, PC 153) and portrait of Innocent X (Innocentius X), perhaps a copy of his famous portrait by Diego Velázquez (Doria Pamphilj Gallery, FC 289), Cardinal-Infante Ferdinand of Austria (Kardinal Infante), Cardinal Mazarin (Kardinal Madziaryni), Cardinal Orsini (Kardinal Ursyni), Prince-Bishop Charles Ferdinand Vasa (Krolewicz Karol), King Ladislaus IV Vasa (Król władislaw), King John II Casimir in national costume (Król Kazimierz popolsku), Francesco Molin (1575-1655), doge of Venice (Xiąze wenecki Molini), Ferdinand II de' Medici (1610-1670), Grand Duke of Tuscany (Xiaze Florenski), Francesco I d'Este (1610-1658), duke of Modena (Xiaze Modinski), duke of Mantua (Xiaze Mantuanski), Ranuccio II Farnese (1630-1694), duke of Parma (Xiaze Parmenski) and his brother Alessandro Farnese (1635-1689) (Xiaze brat iego), Philip William of Neuburg (1615-1690), Count Palatine of Neuburg (Xiaze Nayburski), Henry II of Bourbon (1588-1646), prince of Condé (Princeps de Condé stary) and Louis II of Bourbon (1621-1686), prince of Condé (Princeps de Condé Młodszy), Ottavio Piccolomini (1599-1656), duke of Amalfi (Xiąze Pikolomini), Stanisław Koniecpolski (1591-1646), castellan of Kraków (Pan Krakowski Koniecpolski), Jakub Sobieski (1590-1646), castellan of Kraków (Pan Krakowski Sobieski), Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria (Królowa Cecylia), Queen Marie Louise Gonzaga (Krolowa Ludowika Marya), Anne of Austria (1601-1666), queen of France (Krolowa Francuzka Matka), Anne Marie Louise of Orléans (1627-1693), known as La Grande Mademoiselle (Mademosil, abo xiezna De'orléans, starsza), Isabella Clara of Austria (1629 -1685), duchess of Mantua (Madama Mantuanska), Olimpia Aldobrandini (1623-1681), princessa di Rossano (Principessa de Rosanno), Olimpia Maidalchini Pamphilj (1591-1657), sister-in-law of Pope Innocent X (Donna olimpia) and others. This gallery reflects the state of European and local politics in the era directly preceding the invasion (1645-1655), which is why the Lubomirskis probably sacrificed more obsolete portraits or effigies whose identity has been forgotten, probably by the greatest artists of the Renaissance and early Baroque. The next "Register of all things written in Wiśnicz, January 28, 1678" (Regestr spisanych rzeczy wszystkich na Wiśniczu die 28 Januarii, Anno 1678, National Archives in Kraków, sygn. 201), prepared under the direction of Helena Tekla in relation with the death of her husband, lists "a portrait of Her Ladyship without frames" (Konterfekt Jey M bez Ram) and "a portrait of Her Ladyship from Paris, large on white frames" (Konterfekt Jey M z Paryza wielki na Ramach białych prostych), as well as portraits of the Doge of Venice (Xiązęcia Weneckiego Konterfekt) and the King of France (Konterfekt Krola Francuskiego) and a large Virgin and Child against a landscape received from King John Casimir. Lubomirska also painted, since on page 52 of the inventory we read: "a black box with painting paints of Her Benefactress" (szkatułka czarna z farbami do malowania JM Dobrodz.). Based on the inscription Drecka attributed the painting to the French painter Nicolas Mignard (around 1606-1668) and dated to the time of Lubomirska's marriage in 1637. According to the author, the portrait should be further considered as a historié painting in the guise of Flora, goddess of flowers and spring and in this sense, it is comparable to Rembrandt's painting at the Hermitage, painted in 1634. The style of the portrait is closer to that of Nicholas's brother, Pierre Mignard I (1612-1695), which appeared in the catalog entry of the National Museum in Warsaw (MNW) - the painting was listed as a portrait of a young woman and dated around 1650. The costume and hairstyle indeed postdate the 1630s and even the 1650s and the closest similarities are visible in a portrait of Elizabeth Charlotte of the Palatinate (1652-1722), Duchess of Orléans, holding flowers, at the Prado Museum in Madrid (P002352). The style of the painting is also very similar. The Madrid canvas is attributed to the circle of Pierre Mignard I, which confirms the current attribution by MNW, and it is dated around 1675. Other paintings, by Caspar Netscher, such as the portrait of a woman from 1674 (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, SK-A-1693, signed and dated: C. Netscher fec. 1674), portrait of Helena Catharina de Witte (1661-1695) from 1678 (Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, SK-A-707, signed and dated: CNetscher 1678) or portrait of a lady from 1682 (National Museum in Kraków, MNK XII-A-880, signed and dated: C Netscher 1682), confirms that the effigy of Lubomirska must be dated after 1674. Imitating the style of the French Queen Maria Theresa of Spain (1638-1683) (compare the portrait by François de Troy, Museum of Fine Arts of Angers), Helena Tekla was depicted in a fashionable blonde wig. Her appearance is very youthful in this portrait, which was a standard for many effigies (and still is today) and probably no one questions the identity of the so-called Rainbow Portrait of Queen Elizabeth I (1533-1603), painted around 1600, only because the Queen of England looks much younger than almost 70 years old. Close to Mignard's style is another disguised portrait of the capitane/starostine Lubomirska, depicted as Pandora "the all-endowed", the first woman created by Hephaestus on the instructions of Zeus (Jove), today in the National Museum in Warsaw (oil on canvas, 111 x 88 cm, 128823 MNW). Dressed in black, Helena Tekla holds a large bronze vase, an urn, bearing the Lubomirski coat of arms - Szreniawa and the inscription in Italian [SP]ENTO E IE [IL] LVME / NON L'ADORE ("the light went out, not the ardor"), which is a paraphrase of a verse from the poem "Adonis" (L'Adone) by Giambattista Marino, published in Paris in 1623 and dedicated to the French king Louis XIII. Wanda Drecka interprets this representation of Princess Lubomirska "as the guardian of all virtues or Pandora who gives everything" and attributes the painting to Claude Callot (d. 1687), court painter trained in Rome. The painting has an inscription at the bottom: Theophilla Com: de Tenczyn Osolińska Alexan. Pr. Lubom.: Pal: Cracov: Consors: and comes from the Potocki collection in Krzeszowice near Kraków. Callot is the purported author of two tondo ceiling paintings for the king's library in Wilanów Palace, painted around 1681 (compare "Claude Callot ..." by Konrad Morawski). His allegory of philosophy and theology is very Roman in style, comparable to the works of Pietro da Cortona and Andrea Sacchi. The portrait of Lubomirska as Pandora and its copy in Wilanów Palace (oil on canvas, 81.5 x 66 cm, Wil.1267), however, recalls works attributed to Mignard, such as the portrait of Louise Renée de Penancoët de Kéroualle (1649-1734), Duchess of Portsmouth, mistress of Charles II of England, as Saint Mary Magdalene (Antichità Castelbarco, Proantic, Reference: 1200976, depicted blonde in this portrait) or portrait of Françoise d'Aubigné (1635-1719), Marquise de Maintenon, mistress of Louis XIV of France, as Saint Frances of Rome (Palace of Versailles, MV 4268). Probably in the second quarter of the 18th century, a rocaille cartouche with an inscription identifying the model was added in the lower left corner of the Wilanów copy. Although possible, Helena Tekla's stay in France is not confirmed in the sources, so it can be assumed that Mignard and his workshop must have relied entirely on study drawings or other effigies sent from Poland-Lithuania. The portrait of Marie Louise of Orléans (1662-1689), Queen of Spain, attributed to Pierre Mignard I, probably commissioned from Spain after her marriage to Charles II in 1679 (Fernando Durán Subastas in Madrid, June 29, 2011, lot 210), proves that the painter and his workshop skillfully created new effigies from paintings or drawings by other painters or earlier portraits. The last known portrait of Helena Tekla is also very French in style. In 1681, around the age of 59, like many French or Italian ladies, she decided to become a nun and entered the convent of the Discalced Carmelites in Lublin, taking the religious name of Paula Maria. She died on May 19, 1687 in Lublin. The portrait, now kept in Wilanów Palace (oil on canvas, 81.5 x 68.5 cm, Wil.1340), is attributed to the Polish school of the 18th century. It bears an inscription in Polish probably added after Lubomirska's death and confirming that she was a great benefactress of the convent, therefore probably offered by her to the Lublin convent during her profession in 1683. Its style recalls the portraits by French painter Philippe de Champaigne, like the portrait of Jean-Baptiste Colbert (1619-1683) from the collection of Princess Izabela Lubomirska (1736-1816) (Metropolitan Museum of Art, 51.34). The most similar, however, are the effigies of figures of French Jansenism - portraits of Mother Jacqueline-Marie-Angélique Arnauld (1591-1661), known as La Mère Angélique, Abbess of the Abbey of Port-Royal (Musée Condé, PE 310, Palace of Versailles, MV 5987 and Musée national de Port-Royal des Champs, DPR-2005-01-016) or portrait of Marie des Anges Suireau (1599-1658), Abbess of the Maubuisson Abbey (Palace of Versailles, MV 5989 ; RF 2494) by Champaigne and his followers. The painter died in 1674, so he could not be the author of the portrait of Lubomirska produced around 1683, but he had some talented students who followed his style, such as Nicolas de Plattemontagne, born Nicolas van Plattenberg (1631-1706) in Antwerp. Wilanów's portrait is very similar in style to the portrait of a man holding a letter, attributed to de Plattemontagne (Christie's Paris, September 15, 2020, lot 57). The painter's stay in Poland-Lithuania is not confirmed in the sources, so he probably created this portrait (or a series) from study drawings or other effigies sent from Lublin. Even though she lived in a convent since 1681, Helena Tekla was still active in the field of patronage, because Stanisław Czerniecki's cookbook "Compendium ferculorum, or a collection of dishes" (Compendium ferculorum, albo zebranie potraw), was published in Kraków in 1682 with a dedication to Princess Lubomirska née Ossolińska. Similar to the portrait as Flora, she was depicted as a young girl. A copy of this portrait by an unknown painter is in the parish church in Klimontów. Not only did French painters work for the Commonwealth's clientele, but also painters of Polish-Lithuanian-Ruthenian origin were active in the French capital, such as the most eminent Alexandre Ubeleski (1649/1651-1718), who belonged to a community painters in the service of Louis XIV. Pierre Mignard is also credited with the authorship of the two pendant oval paintings, now in the Schorr collection in London (oil on canvas, 91.2 x 73.5 cm and 95 x 73 cm), which are identified as depicting John II Casimir Vasa and his morganatic wife Claudine Françoise Mignot (1624-1711), seamstress from Grenoble, whom he secretly married on September 14, 1672, just three months before his death (December 16, 1672). The king wears a crimson silk żupan, a fur-lined coat and a fur kolpak hat and Claudine Françoise a French-style crimson dress lined with fur, inspired by jupeczka. These costumes greatly resemble the clothes of Józef Bogusław Sluszka, ambassador of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in Brussels, and his wife Teresa Korwin Gosiewska from prints made by Henri Bonnart after Robert Bonnart in Paris in 1695 or the outfits of Polish nobles from Description de l'univers by Alain Manesson Mallet - engraving by Pierre Giffart or Pierre Landry, made in Paris in 1683. A similar hat is also visible in the effigy of King John III Sobieski (1629-1696) by Nicolas de Larmessin, made in Paris in 1684. John Casimir was depicted in similar costume in his portrait by Daniel Schultz (Nationalmuseum Stockholm, NMGrh 1273), also reproduced in an engraving by Willem Hondius. Although he appears younger in this portrait than in the effigies preceding his abdication in 1668 and is more stout, the resemblance to his features is undeniable - protruding lower lip inherited from his Habsburg mother and downward-directed eyes, as shown in the octagonal portrait wearing a Ruthenian fur hat (National Museum in Warsaw, 474 MNW) or the portrait in armor from the Musée de Cambrai (MI 643). He looks like a happy retiree and not a tired and sad monarch from the mentioned paintings of Schultz, concerned about the aggressive neighbors of the Commonwealth, ready to plunder and destroy his country, as well as quarrels in Parliament. Given the close relations between France and Poland-Lithuania in the fourth quarter of the 17th century, it is quite possible that the oval portrait of Colbert by Pierre Mignard I, painted between 1677 and 1682, which comes from the collection of the last elected monarch Stanislaus Augustus Poniatowski (Hermitage Museum, ГЭ-561), was sent to the monarchs of the Commonwealth shortly after its creation. Finally, Mignard himself clearly expressed his attachment to customers from Poland-Lithuania by representing himself in a kolpak hat in his self-portrait at the Museum of Fine Arts in Dijon (oil on canvas, 81 x 66 cm, CA 407).
Self-portrait in kolpak hat by Pierre Mignard I, third quarter of the 17th century, Museum of Fine Arts in Dijon.
Portrait of King John II Casimir Vasa (1609-1672) in kolpak hat and portrait of his wife Claudine Françoise Mignot (1624-1711) by Pierre Mignard I, ca. 1672, Schorr collection in London.
Portrait of Helena Tekla Lubomirska née Ossolińska (1622-1687) as Flora by Pierre Mignard I, ca. 1674-1681, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Helena Tekla Lubomirska née Ossolińska (1622-1687) as Pandora by Pierre Mignard I or workshop, ca. 1667-1677, National Museum in Warsaw.
Portrait of Helena Tekla Lubomirska née Ossolińska (1622-1687) as Pandora by follower of Pierre Mignard I, ca. 1667-1677, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
Portrait of Helena Tekla Lubomirska née Ossolińska (1622-1687) as a nun by Nicolas de Plattemontagne, ca. 1683, Wilanów Palace in Warsaw.
Portraits and busts of Katarzyna Sobieska and her husband Michael Casimir Radziwill by Jacob Ferdinand Voet and follower of Bartholomeus Eggers
In September 1655, a huge army of merciless robbers, murderers and rapists calling themselves defenders of the faith and liberators of the oppressed, pillaging and destroying everything in their path, famous for their cruelty and barbarity, approached Warsaw. Panicked residents were leaving the informal capital of one of the European superpowers - the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth (probably no country would resist the invasion of several neighboring states).
It was necessary to save not only the most important personal property, but also the most refined works of art, collected over several centuries of peace (excluding borderlands) and great prosperity, created by local artists but also commissioned in Italy, Flanders, the Netherlands, Germany, Persia, Turkey, Russia and received as diplomatic gifts. The royal couple's collections were particularly valuable. John Casimir Vasa was a descendant of the Jagiellons, the Sforzas and the Habsburgs and his wife Marie Louise Gonzaga of the Dukes of Mantua and the Byzantine emperors through her great-grandmother Margaret Palaeologa (1510-1566), Marquise of Montferrat. These names speak for themselves for any connoisseur of European art, which is why this noble descendancy was undoubtedly reflected in the collections of John Casimir and Marie Louise. The tense atmosphere that reigned in the city just before the arrival of the troops of the Brigand of Europe - Charles X Gustav, perfectly reflects the description of the problems associated with the efforts to obtain means of transport by the Discalced Carmelite sisters, who had to flee Lviv in 1648 before the invasion of the Cossacks and Tatars and were invited to Warsaw. Following the example of others and at the queen's instigation, the nuns also wanted to leave the city, but they could not rent carriages: "Carters were also forbidden to be hired by anyone under penalty of death, solely for the needs of the court and the king's belongings". Fortunately, a nobleman returning from Gdańsk by water offered his boat to the sisters. "So, having thanked God, our Reverend Fathers made a trade with this nobleman, they bargained it [the boat] for 200 gold coins and with the raftsmen that he hired; the boat was quite large, because there were three kennels. First for our Reverend Fathers, the second one for us, the third one for the servants, but it was very bad because it was old, rotten, had many holes and large cracks in it, through which water was constantly flowing, so that they could not keep up with pouring it out, and at the same time it was very loaded with heavy burdens, because apart from our things, which were quite a few, His Highness the legate [Pietro Vidoni (1610-1681), Bishop of Lodi, Apostolic Nuncio from Pope Innocent X], unable to get a boat for his belongings, ordered all things to be carried almost by force to our boat. Neither our Reverend Fathers nor we could resist this, even though we begged earnestly that the boat should not be burdened, but the Italians did not listen to anything, they put what they wanted into the boat until it was reloaded, and when our skipper saw that, he shouted: 'For God's sake, what you are doing, you will perish both the nuns, their things, and yourselves', but it did not help". As a result, the sisters sent a significant part of their belongings back to the monastery. The wartime wandering lasted eight years. Through Wiśnicz, the seat of the Lubomirski family, the sisters reached Lubomirski estates in northern Slovakia (Spiš and Podolínec), where they stayed for three years, and then again in Wiśnicz and in nearby Rzemień. The nuns returned to Warsaw only on June 19, 1663. Their former headquarters no longer existed: the wooden monastery was burned by the Swedes, and only the foundations remained of the newly built Church of the Holy Spirit (after "Habit królewny ..." by Bożena Fabiani, p. 59, 76-77). The country was not prepared for such a massive invasion, nor for an evacuation. Many valuable possessions had to be abandoned. Any cultured person would be concerned with such circumstances, which is why John Casimir and Marie Louise even tried to convince the Brigand of Europe, posing as a polite diplomat, not to destroy the luxurious palaces of Warsaw. "The king and queen of Poland sent begging requests at the beginning to prevent their houses in Warsaw from being ruined, telling him that if the kingdom remained with him, he would enjoy them; [...] that they would be obliged to him for this courtesy, and even offered, at that time, to pay him what he could have obtained from them; he promised to do so and even made a civil and gallant compliment for the queen" (Le roi et la reine de Pologne envoyèrent prier au commencement de vouloir empêcher que leurs maisons de Varsovie ne fussent ruinées, lui disant que si le royaume lui demeurait, il en jouirait; [...] qu'ils lui seraient obligés de cette courtoisie, et offrirent même, en ce temps, de lui payer ce qu'il en aurait pu tirer; il promit de le faire et fit même un compliment civil et galant pour la reine), reported in a letter of November 8, 1655 from Głogów Pierre des Noyers, secretary of Queen Marie Louise (after "Lettres de Pierre Des Noyers secrétaire de la reine de Pologne ...", published in 1859, p. 10, 45, 163). In the same letter, des Noyers confirms that their efforts were completely useless. The royal palaces of Warsaw and other residences and houses were plundered and destroyed and, despite huge ransoms, the invaders plundered "even the old nails" (il ne se contenta de les mettre tous à rançon, mais encore après cela il donna leurs maisons et ce qu'il est dedans à des capitaines qui en détachent jusqu'aux vieux clous). The iron prosthetic hand, so-called Stockholm Hand, in the Royal Armory (Livrustkammaren) in Stockholm (LRK 5059), is a 1655 war booty from Warsaw, included among the Warsaw spoils in the 1683 inventory. Another very similar, so-called Skokloster Hand, is in Skokloster Castle (SKO 12286), which also houses many war spoils of Carl Gustaf Wrangel (1613-1676) looted in Poland, such as the oriental-style saber set with turquoise from the Zamoyski collection (inventory number 7320-7323) and agate cutlery in a velvet case of voivode Tomasz Zamoyski (1594-1638), believed to be made in London (SKO 186). The Brigand of Europe was a worthy ruler of the "Goths and Vandals" (Suecorum Gothorum et Vandalorum Rex), the barbarian conquerors of the Roman Empire. According to des Noyers, he even had the ambition to become king of the Romans and emperor, of which his cousin Queen Christina (1626-1689), assured the pope in Rome, worried about the progress of the Protestant invaders in Poland-Lithuania (letter of May 11, 1656 from Głogów). In a letter dated November 2, 1655 from Innsbruck Christina assured her "brother", as she called her cousin in this letter, that "I have not changed the feelings of friendship that I have always had for you, nor the love that I owe to Sweden" (je n'ai point changé les sentiments d'amitié que j'ai toujours eus pour vous, ni l'amour que je dois à la Suède). In April 1656, Polish troops began to approach Warsaw to retake the capital. Swedish count and field marshal Arvid Wirtenberg von Debern (1606-1657), famous for his cruelty and greed, was entrusted with its defense. Hunger reigned in the city, not only among the inhabitants, but also among the Swedish crew. "The imperial envoys, Baron Lisola and Count Pöttingen, who were then in Old Warsaw, left the city and went to the Polish camp because they could no longer bear the moans of the dying and the unpleasant smell of unburied corpses and carcasses" (after "Warszawa w latach potopu ..." by Jan Wegner, p. 72, 78). The destruction of heritage during this and subsequent invasions was so great that even for Polish art historians it is difficult to imagine that the royal and magnate collections of Poland-Lithuania before 1655 were comparable to the most splendid collections of Rome, Florence, Madrid, Paris, Vienna or Munich. This was a huge loss, not only for Polish-Lithuanian heritage, but also for European heritage. People calling for moral reform and penance for sins were granted obedience after this cataclysm. The magnificent Kazanowski Palace, which, although it was looted and badly damaged, was still in a repairable condition, was partially demolished and transformed into a monastery. This all sounds seemingly familiar to anyone with some knowledge of history and connotations like the sacks of Rome, the Dark Ages and the Black Death suggest themselves. Since the Middle Ages, people from Poland-Lithuania have traveled to many European countries, including Italy. They brought to their country beautiful works of art and their effigies created there, but also the reputation of splendid artists and craftsmen. That is why many people who for one reason or another could not travel also wanted to have similar objects. The Italian and Flemish-style funerary monuments of Tarnów Cathedral, one of the finest examples of Renaissance and Mannerist art in Europe, which miraculously survived numerous wars, invasions and accidental fires, testify that the "Sarmatians" were great patrons of art. Those who were "surprised by an untimely death" during their journey were also buried abroad. Several beautiful tombs and epithaphs in Rome testify to the splendid taste of their relatives, who commissioned such monuments. Among the most remarkable are the epithaph of Michał Korniakt (1575-1594), attributed to Nicolas Cordier, sculptor from Lorraine, in the Basilica of Saint Mary of the Altar of Heaven (Santa Maria in Ara Coeli), the epithaph of Eustachy Adam Słuszka (1615-1639), brother of Elżbieta Kazanowska née Słuszczanka (1619-1671), and epithaph of Marcin Katlewski (1600-1656), canon of Poznań and Warsaw, both preserved in the Church of Saint Stanislaus of the Poles and attributed to Giovanni Francesco de Rossi or workshop of Giuliano Finelli. The Sarmatians also frequently went to Italy to seek treatment, benefit from the advice of Italian doctors and above all benefit from a friendlier climate. On August 10, 1677, Katarzyna Sobieska (1634-1694), Princess Radziwill, sister of King John III, and her husband Michael Casimir Radziwill (1635-1680), Deputy Chancellor and Field Hetman of Lithuania, set off from their residence in Biała Podlaska towards Italy to improve their health. The trip was also linked to a confidential mission entrusted to Michael Casimir by the king. The first stage of the journey led through Częstochowa to Silesia and Cieplice, where the Radziwill family stayed for over two weeks, taking advantage of the local thermal waters. From Cieplice they headed towards Venice through Prague, Nuremberg and Augsburg. They reached Venice on December 10, 1677. From there they went to Rome via Padua and Loreto. Prince Michael Casimir separated from his wife and retinue, leaving everyone outside the walls of the Eternal City. On the night of February 19 to 20, 1678, he went to the city, where he held confidential talks for two days. On February 21, Prince Radziwill participated incognito in a forty-hour service in the church of Il Gesù, which was also attended by Pope Innocent XI. The prince was received by the Pope during a private and confidential audience. It was not until February 24 that Michael Casimir and his wife made an official and solemn entry into Rome. They planned to leave on March 10, 1678, but the departure was delayed because they could not refuse the papal invitation to see the most important relics of the Vatican. The Radziwills resumed their return journey on April 2. The cause was malaria, which they both contracted unexpectedly. The situation was worse in the case of Princess Katarzyna and her treatment was provided by the Pope's personal physician, Francesco Giuseppe Borri. They returned to the country in June 1678 (after "Katarzyna z Sobieskich ..." by Jerzy Flisiński, part II). Great prosperity returned to the revived Realm of Venus during the Sobieski period (1674-1696), commemorated by exquisite buildings such as Wilanów Palace, Krasiński Palace (destroyed during World War II, rebuilt after 1948), Lubomirski Bathing Pavilion (Palace on the Ilse, rebuilt at the end of the 18th century), Marywil (demolished), Otwock Wielki Palace or Nieborów Palace. This did not last long, however, because soon, the "great conquerors" returned to plunder and destroy during the Great Northern War (1700-1721) and what was not plundered by them or taken abroad by the Sobieski family or other aristocrats was transferred to Dresden by the Saxon kings, who ruled Poland. Consequently, in current public collections of paintings in the former territories of the Commonwealth it is difficult to find an effigy of Katarzyna Sobieska made during her lifetime, which, given her position and wealth, should have been splendid. In the private collection of Maciej Radziwiłł there are two portraits which represent the sister of John III. One is an inscribed effigy depicting her in mourning, probably after the death of her husband in 1680, the other is an oval painting by a better painter, depicting her seated in a chair. The oval painting comes from another private collection and was sold in Warsaw in 2016 under the title "Portrait of a lady, unidentified painter (19th century)" (oil on canvas, 94 x 74 cm, Rempex, Sale 230, June 15 2016, catalog number: 169). The canvas was exhibited in 2022 at the Nieborów Palace as "portrait of Katarzyna Radziwill née Sobieska (1634-1694), unknown painter, type of Nicolaes Maes, around 1665-1680". The sitter closely resembles the mentioned effigy of Katarzyna in mourning from the same collection. The outfit resembles those in signed and dated portraits of ladies painted by Nicolaes Maes in the late 1670s, such as the 1678 portrait of a lady (Sotheby's New York, January 25, 2015, lot 256, signed and dated lower left: MAES / 1678). However, regarding the style of the painting, the closest are the portraits attributed to Jacob Ferdinand Voet (1639-1689), a Flemish painter, active in Rome between 1663 and 1679. Between 1676 and 1680, he painted the portrait of Pope Innocent XI (Il Ponte Casa D'Aste in Milan, Auction 459, October 22, 2019, lot 123). Portraits of Cardinal Michał Stefan Radziejowski (1645-1705) are also attributed to his workshop (Czartoryski Museum and Saint Mary's Basilica in Kraków). Radziejowski was made a cardinal in 1686, so his portraits must have been made in Paris, where the painter left Antwerp between 1684 and 1686. The cardinal commissioned many luxury items from the French capital, such as silver sculptures and candlesticks with his coat of arms, made in the workshop of Guillaume Jacob. The portrait of Empress Claudia Felicitas of Austria (1653-1676), sister-in-law of Queen Eleonora Maria Josepha of Austria (1653-1697), painted between 1673-1676, was sold with attribution to the follower of Jacob Ferdinand Voet (Sotheby's London, April 10, 2024, lot 45). Among those most similar to Katarzyna's portrait are the portrait of a lady, wearing an elaborately embroidered dress, holding a dog from about 1680 (Sotheby's London, April 29, 2010, lot 168), portrait of Cardinal Flavio Chigii (1631-1693) from about 1670 (Palazzo Chigi in Ariccia, inv. 467) and portrait of Cardinal Decio Azzolino (1623-1689) from the 1670s (Lempertz Cologne, Auction 1027, March 26, 2014, lot 52). Although in the case of Radziejowski's portrait it is very unlikely that the painter and model met in person and his effigies were made from study drawings or other portraits sent from Rome or Poland, in the case of Sobieska's portrait the dates of her stay in Rome correspond to those of Voet's activity in the Eternal City. It is also very likely that during the visit to Rome in 1678 the portrait of Katarzyna's husband was painted. This portrait, now housed at the Walker Art Gallery, part of the National Museums Liverpool, was previously attributed to Diego Velázquez and Carlo Maratti and now to the Neapolitan school (oil on canvas, 128 x 90.3 cm, WAG 2865). The style of this painting particularly resembles works attributed to Voet, such as the portrait of Count Orazio Archinto (1611-1683), painted between 1680-1683 (National Museum in Warsaw, M.Ob.925 MNW) or the portrait of an officer from the 1670s or 1680s (Chequers Court in Aylesbury, inv. 556). Not only is the style of the painting similar but also the model's jabot and armor which indicate that all these portraits were made at the same period. Italian researchers also noticed Voet's hand and the style of sitter's jabot typical of European fashion around 1680 (compare "n° 6. Ferdinand Voet, Ritratto di bambina ..." by Francesco Petrucci, 12-13). The resemblance with other effigies of the Field Hetman of Lithuania is quite general, this is probably why the work is presented as "Presumed Portrait of Prince Michael Casimir Radziwill", however comparing it with the IMMOTA SEMPERQVE EADEM medal with bust of the prince, made in Gdańsk by Johann Höhn in 1680, we will notice the same shape of the face and nose. His chin was similarly depicted in the portrait in the National Museum in Warsaw (inv. 22498 MNW). Michael Casimir died on his way back from Rome to Bologna on November 14, 1680, during his next mission to Italy. After the death of her husband, Katarzyna lived alternately in Warsaw, Zhovkva and Yavoriv. In 1691, she left the royal court. She was engaged in charitable work, making many valuable donations to monasteries, churches and other charitable institutions. She died in Warsaw on September 29, 1694 and was buried in the Jesuit church in Nesvizh. During her life, she was called "wise Catherine", and her brother the king often turned to her for advice in the most crucial moments. The most important was the Battle of Vienna, when the Commonwealth's army came to the aid of Austria's besieged capital. The emperor, his family and his court as well as the authorities had fled to Linz, then to Passau further up the Danube. The importance of this victory for all of Europe is best illustrated by the letter of October 23, 1683 from Rome, that Queen Christina of Sweden addressed to the "Victorious King" John III Sobieski: "On this happy day Your Majesty has shown himself worthy not only of the crown of Poland, but that of the universe. The Empire of the world would be due to you if heaven had reserved it for a single monarch. I dare say that no one places a higher value than me on your glory, your work, your devotion, your victory over the masters of Asia, and I am proud that one knew better the dangers, better judged the ruin and extermination with which this great power threatened us. It is to your Majesty, after God, that from now on all other kings owe the preservation of their kingdoms. I, who no longer possess a kingdom, recognize myself indebted to your exploits for my life, my freedom, my calm, which I esteem above all the empires of the earth. However, I must admit my wrongs towards such a great king as Your Majesty. [...] Besides, what I envy of Your Majesty is neither your crown nor your trophies, it is the hardships and dangers, it is the title of liberator of Christianity; it is the satisfaction and the glory of having, it can be said, given life and liberty to your friends and your enemies, because that is what you have done" (after "Histoire de Pologne avant et sous le roi Jean Sobieski" by Narcisse-Achille de Salvandy, Volume III, p. 71-72). Even today many art historians don't want to realize, that mainly thanks to the brave Sarmatians, who protected the city from pillage and destruction, we can admire so many masterpieces of old European art in Vienna, including Venetian portraits of the Jagiellons, identified by me. This victory considerably strengthened Austria which, almost a century later, together with Russia and Prussia, partitioned the Commonwealth. Interestingly, from around 1668, the former queen of Sweden was actively involved in affairs of the Commonwealth, as she wanted to be elected monarch of Poland-Lithuania after the abdication of her distant relative John Casimir. Thanks to the support from Pope Clement IX, her candidacy was important, but it was considerably weakened by the secrecy of all activities entrusted to papal diplomacy in the matter (after "Tajemnicza kandydatura ..." by Dorota Gregorowicz). Her personal envoy hired to win her support in the country was Father Michał Antoni Hacki (died 1703), titular abbot of the Cistercian monastery in Kołbacz. Papal nuncio to the Commonwealth Galeazzo Marescotti (1627-1726) was ordered by the pope to submit Christina's candidacy for the crown. In a letter dated February 19, 1669 to the nuncio the Queen wrote that she was ready to accept all the demands of the Commonwealth, with the exception of marriage - the queen is considered by many current authors to be a lesbian and a transvestite. From 1685, her honorary physician was Doctor Gabriel Felix, a Jew from Poland, whom she recommended to her friends (compare "Polonica w korespondencji ..." by Wacław Uruszczak). Between 1673 and 1687, she sought support for her claims to John Casimir's inheritance in Naples and his property in Rome. Perhaps with these claims or perhaps she again considered her candidacy in the next election after the death of King Michael I, her full-length portrait, now at the Castello Orsini-Odescalchi in Bracciano, is connected. It was purchased between the end of 1691 and the beginning of 1692, by Livio I Odescalchi from Pompeo Azzolino. Her royal mantle is crimson and not blue as in earlier coronation portraits and this portrait resembles effigies of Queen Eleonora Maria Josepha of Austria, widow of Michael I. She also looks very young in this portrait. Another version of this effigy, in half-length, a typical format of Voet's works, was sold with attribution to his circle in 2019 in Madrid under the title "Portrait of a young aristocrat" (oil on canvas, 65 x 53 cm, Fernando Durán, October 10, 2019, lot 1118). In Rome there is a portrait of Queen Marie Casimire de La Grange d'Arquien (1641-1716), wife of John III, close to Voet's distinctive style. This painting is now in the Polish Hospice in Rome and it may have been given to the church by the Bishop of Przemyśl, Jan Stanisław Zbąski in 1687, together with the portrait of King John III. They were to be displayed during masses in honor of the patrons of the Kingdom of Poland - Saints Stanislaus and Casimir and hung in the sacristy, where they were recorded in 1693 (after "Kościół polski w Rzymie ..." by Józef Skrabski, p. 303). The style of this painting closely resembles that of a portrait of a lady by Jacob Ferdinand Voet or studio, made around 1680, now kept in the Prado Museum in Madrid (P006171). If it was created in 1687, Voet's workshop must have painted it from study drawings or other effigies of the queen sent to Paris. The portrait of Giovanni Battista Gisleni (1600-1672), architect, scenographer, director, singer and musician at the Polish-Lithuanian royal court, from his marble epitaph in Santa Maria del Popolo in Rome, is attributed to Voet (compare "Artisti a Roma", ed. Andrea Donati, Francesco Petrucci, p. 86). In the summer of 1655, during the Deluge, Gisleni decided to return permanently to Rome, where he died in 1672. Many of his works were destroyed during the invasion, especially in the looted and burned palaces of Warsaw and Vilnius, where he worked for the court and the royal opera. The king and queen not only ordered paintings from abroad, but also sculptures. Many magnificent statues, made by the workshop of Artus Quellinus II, his son Thomas II and Lodewijk Willemsens, were commissioned in Antwerp for the decoration of the Wilanów Palace in Warsaw, such as the personification of Valor and Fortitudo (Courage and Strength), Prudentia (Prudence), Magnanimitas (Magnanimity) and Splendor Nominis (Glory of the Name) on the facade of the palace, but only a few have been preserved in their original place. The busts of the Roman emperors were made by Bartholomeus Eggers in Amsterdam. Many of these priceless masterpieces were looted by Tsar Peter I (1672-1725), during the occupation of Warsaw by the Russian army in 1707 (compare "Niderlandzkie importy rzeźbiarskie ..." by Michał Wardzyński). "The Register of the Carrara marble statues and other objects taken from Willanów in August 1707" (Connotacya Statui Marmuru Karrarskiego y innych rzeczy w Willanowie pobranych An. August 1707) in the Central Archives of Historical Records in Warsaw lists 24 positions of looted statues, including a large statue of Pallas (item 1) and busts of the king and queen (item 3), marble tables, mirrors, chairs and other objects, as well as devastation of the buildings: "The two pavilions were torn off so that the bare walls remained", "Two large pieces of copper sheets were torn from the roof", "66 broken windows", "windows of buildings [...] were broken". After the war, Elżbieta Helena Sieniawska, née Lubomirska (1669-1729), Grand Hetmaness of the Crown, who purchased the palace, renovated and enlarged the building and replaced the looted statues with new ones. Several statues by Quellinus's workshop are today in the Summer Garden in Saint Petersburg, as well as the busts of John III and Marie Casimire by Bartholomeus Eggers, made around 1687. These are copies made in imitation of the marble in 2011. The originals are kept in the Saint Michael's Castle, a branch of the Russian Museum (white marble, 80 х 89 х 40, ЛС-51 and 86 х 93 х 29, ЛС-50). In the garder there are also two other busts in similar style (originals in the Saint Michael's Castle, white marble, 63 х 66 х 27, ЛС-82 and 61 х 70 х 24, ЛС-38). The statues are said to represent Frederick I of Prussia (1657-1713) and his wife Sophie Charlotte of Hanover (1668-1705), but the man bears no resemblance to effigies of the first king of Prussia, such as the statue by Bartholomeus Eggers made around 1688 (Humboldt Forum in the Berlin, Skulpt.slg. 87). After death of his father on April 29, 1688, at the age of 31, Frederick became Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia. The man in the bust appears much older than 31 and his jabot resembles that visible in the mentioned portrait of Count Archinto by Voet from the early 1680s. The effigy has no distinction, while in 1690 Frederick becomes Knight of the Garter and founded the Order of the Black Eagle on January 17, 1701, with which he is frequently represented. It is therefore very likely that the two busts were commissioned by Katarzyna Radziwill, who, after the death of her husband, lived in the Royal Castle in Warsaw, where she had an apartment on the second floor. She was also the owner of a palace in the Kraków suburb of Warsaw (now Presidential Palace), which, according to a contract signed by her in 1689, was renovated by the Italian architect Simone Giuseppe Belotti. In 1707, Tsar Peter I lived in this palace during the Russian occupation of Warsaw. The style of the two busts is comparable to the 1683 votive statue of the Madonna of Passau in Warsaw, founded by Belotti (JOSEPH BELOTI / ITALUS), perhaps commissioned in Amsterdam, as it resembles the statues of Fidelitas and Vigilantia from the cenotaph of Lieutenant-Admiral Jacob van Wassenaer Obdam (d. 1665) by Bartholomeus Eggers, located in the choir of St. James' Church in The Hague. The style of the two busts is also comparable to works attributed to Stephan Schwaner, a sculptor active in Warsaw between 1682 and 1692, which were erroneously attributed to Andreas Schlüter, another prominent sculptor active at the time in the Commonwealth (compare "Stefan Szwaner ..." by Michał Wardzyński). The models resemble Katarzyna and her husband from the described portraits by Voet.
Portrait of Katarzyna Sobieska (1634-1694), Princess Radziwill by Jacob Ferdinand Voet, ca. 1678, Private collection.
Portrait of Michael Casimir Radziwill (1635-1680), Deputy Chancellor and Field Hetman of Lithuania by Jacob Ferdinand Voet, ca. 1678-1680, Walker Art Gallery in Liverpool.
Portrait of Queen Christina (1626-1689) by workshop of Jacob Ferdinand Voet, ca. 1673-1680, Private collection.
Portrait of Queen Marie Casimire de La Grange d'Arquien (1641-1716) by workshop of Jacob Ferdinand Voet, before 1687, Polish Hospice in Rome.
Copy of bust of the "Victorious King" John III Sobieski (1629-1696) by Bartholomeus Eggers, ca. 1687 (original), Summer Garden in Saint Petersburg.
Copy of bust of Queen Marie Casimire de La Grange d'Arquien (1641-1716) by Bartholomeus Eggers, ca. 1687 (original), Summer Garden in Saint Petersburg.
Copy of bust of Katarzyna Sobieska (1634-1694), Princess Radziwill by follower of Bartholomeus Eggers or Stephan Schwaner, 1680s (original), Summer Garden in Saint Petersburg.
Copy of bust of Michael Casimir Radziwill (1635-1680), Deputy Chancellor and Field Hetman of Lithuania by follower of Bartholomeus Eggers or Stephan Schwaner, 1680s (original), Summer Garden in Saint Petersburg.
Portrait of Jan Stanisław Jabłonowski on horseback by José García Hidalgo
Between 1682-1688 the sons of Stanisław Jan Jabłonowski (1634-1702), voivode of Ruthenia and Grand Hetman of the Crown and Marianna Kazanowska (1643-1687) - Jan Stanisław (1669-1731) and Aleksander Jan (ca. 1672-1723), studied and travelled throughout Europe. They visited Prague (1682), Paris (1684-1686) and England (1685). After a year's stay in the capital of France, in November 1686, the Jabłonowskis set off on a further journey to Spain and Italy. In January 1687, they reached Madrid, where they spent about three weeks, visiting the city, its monuments, and finally having an audience with the King Charles II of Spain. At the beginning of February, the brothers went back to France. They visited Toulouse and Marseille and then went through Pisa and Siena to Rome and Naples. In mid-August 1687 they returned to Paris via Padua, Milan, Turin and Lyon and from there they returned to Lviv in January 1688 (after "Grand tour ..." by Anna Markiewicz).
From Paris, in 1685, Jan Stanisław and Aleksander Jan sent their portraits to their parents, whom they had not seen for over two years. Sarmatians visiting foreign countries frequently brought their effigies made abroad. It was not only a souvenir of the distant journey, but, as today, a mark of prestige, especially if the model was painted by some eminent painter, such as the court painters of the King of France or the King of Spain. During his stay in Paris in 1671, Jan Kazimierz Denhoff (1649-1697), abbot of Mogiła, not only bought books, but the letters also mention his other planned commission, a portrait. Kazimierz Jan Wojsznarowicz (d. 1677), who between 1667-1669 traveled across Europe as tutor to Prince Aleksander Janusz Zasławski-Ostrogski (1650-1673), during his stay in Rome could not resist the desire to have his likeness, and, as he wrote in his travel diary: "I let myself be painted, he painted me for 4 hours" (dałem się malować, godzin 4 malował mnie) (after "Itinera clericorum ..." by Dauta Quirini-Popławska, Łukasz Burkiewicz, p. 498, 528). At that time, effigies of the Sarmatians reached as far as China. After the victory at Vienna in 1683, the "Victorious King" John III sent to Emperor Kangxi (1654-1722) his portrait. In exchange, Sobieski received an ode written by the emperor and two porcelain vases. The king also wrote personally to Father Ferdinand Verbiest (1623-1688), a Flemish Jesuit missionary in China, who was staying at the court in Beijing (letter of November 16, 1688 from Yavoriv). Nothing is known about this portrait, but if it was shipped from Antwerp, it was probably also commissioned there from local painters. In the National Museum in Warsaw there is a painting entitled "Castellan Jabłonowski on horseback" (oil on canvas, 75 x 56.5 cm, MP 3475 MNW), dated to turn of the 17th/18th century and attributed to Polish school. All the men in this painting wear costumes typical of Spain during the reign of Charles II, as depicted in Family portrait by Jan van Kessel the Younger, dated '1679' (National Museum in Warsaw, M.Ob.813 MNW) and Auto-de-fé in the Plaza Mayor in Madrid by Francisco Rizi, dated '1683' (Museo del Prado, P001126). The style of the painting resembles the works of José García Hidalgo (1646-1719), a Spanish painter active in Madrid and court painter of King Charles II, in particular his Debate of Saint Augustine (Prado, P004755). The model should therefore be identified as Jan Stanisław Jabłonowski, whose father was castellan of Kraków since 1692.
Portrait of Jan Stanisław Jabłonowski (1669-1731) in Spanish costume on horseback by José García Hidalgo, ca. 1687, National Museum in Warsaw.
The palace was built between 1639-1642 by Lorenzo de Sent for the Grand Crown Chancellor Jerzy Ossoliński in Mannerist style. It was constructed on the plan of an elongated rectangle with two hexagonal towers at garden side of the building. The palace was crowned with a terrace with a balustrade, above which stood the upper part of the great representative hall, covered with a spherical roof. A possible inspiration for the palace's upper pavilion and its characteristic roof was Bonifaz Wohlmut's reconstruction of Queen Anne's Summer Palace in Prague, 1557-1563.
Adam Jarzębski, styling himself as Musician of His Highness Ladislaus IV and manager of the construction of the royal palace at Ujazdów, in his "Short Description of Warsaw" (The Main Road, or a Short Description of Warsaw) from 1643, described the residence of Jerzy Ossoliński: Facade with statues of four kings, below inscriptions and a brass statue of Poland holding a sickle, with a plow and a sheaf and marble portal (2427-2435), in the middle of a building a hall covered with roof tiles with gilded brass statues in the corners (2445-2450), Elongated outbuilding with servant lodgings and a kitchen (2711-2713), stables building opposit with a gate (2720-2725), Vestibule with marble portals and iron doors of master craftsmanship (2505-2508), and a staircase with a grille and a large, solid lock (2520-2525), Large dining room (2465) with niches with statues of white marble and a brass statue of a Cupid holding a bow above the door, chandelier and tapestries (2475-2485), with a door to a wine cellar (2491) and a room with silver and gold tableware (2495-2496), Hall with upper windows and a fireplace of black highly polished marble with equestrian portrait of king Ladislaus IV Vasa on white horse against a battle scene (2527-2538), a row of family portraits by painter Hans (?) Amman, and paintings reproducing the epic tales of the ancestors, including a story of a knight wounded during a jousting tournament who was healed by Saint Anne, other stories and battle scenes, above busts of Roman Emperors of white marble (2553-2570), stucco trees in corners, most probably by Giovanni Battista Falconi, ceiling decorated with figures, animals and floral motifs and a painting depicting coronation of Queen Cecilia Renata of Austria in presence of chancellor Ossoliński, door portals of black marble with portiere tapestries with Topór (the Axe) coat of arms (2575-2600), polished marble floor (2605-2607), Lord's chambers with tapestries, French-style parade bed, tables with gold trinkets and silverware and decorative clocks beside the bed, coffers, fireplace adorned with a mosaic (2611-2632), Cabinet of curiosities in a right side tower with bronze statues of different horses, birds and people (2635-2644), silver plated cupboard-cabinet with gold inscriptions describing the contents of each drawer (2649-2652), marble table with rarities on it (2659-2662), Chapel in the left side tower with an altar with an exquisite painting, relics in glass vessels, offered by the Pope, silver coffer reliquary with bones bound by gold chains, wax miniatures, a table with a casket and a door to a staircase (2667-2692). In 1633 Ossoliński was sent with a diplomatic mission to the Pope in Rome by newly elected monarch of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Ladislaus IV Vasa. The King offered him the starostwo of Bydgoszcz, 60,000 zlotys, six horses, a saber (scimitar) worth 10,000 zlotys, five Brussels' tapestries making up the series of the Story of Moses commissioned by King Sigismund Augustus in the 1550s, three of which were given to the Pope, and a construction site in Warsaw. An event from 1633 is also worth mentioning when Ossoliński, traveling to Rome via Veneto, fascinated by the beauty of one of the villas near Padua, ordered to immediately take its dimensions. He made his entry to Eternal City wearing a żupan, richly embroidered with gold, buttoned up with 20 large buttons with diamonds, gold sabre set with jewels valued at 20,000 Polish zlotys and mounting a Turkish stallion having golden horseshoes and a horse tack set with precious stones. In 1638 a life-size statue was cast in brass by Gerdt Benning in Gdańsk according to the design by Georg Münch for then the vice-chancellor Jerzy Ossoliński, most probably to his Castle in Ossolin. It is possible that the same workshop created statues to his Warsaw's palace. Contrary to the Crown Court Marshall Adam Kazanowski, who had a transgender man at his court, the Chancellor Ossoliński kept a transgender woman in his palace: "a boy who thinks he is a girl, and who also wears a dress: He imitates a girl quite well; especially in that, he is very eager of being cuddled", as recounted Jean Le Laboureur in his "Account of the voyage of the Queen of Poland", published in Paris in 1647 (p. 212). An engraved effigy of the Chancellor by Willem Hondius from 1648 was created after a portrait by Bartholomäus Strobel. It is possible then that Strobel created more painting for Ossoliński, including for his Warsaw's residence. In 1645 the chancellor commissioned the silver-ebony altar for the Chapel of Black Madonna of Częstochowa adorned with his coat of arms. The design was most probably by a Royal court artist Giovanni Battista Gisleni, while silver elements were created by the Royal goldsmith Johann Christian Bierpfaff in Warsaw in 1650. The "Inventory of belongings spared from Swedes and escapes made on December 1, 1661 in Wiśnicz" in the Central Archives of Historical Records in Warsaw, lists some of the preserved paintings from Chancellor's rich collection inherited by his daughter Helena Tekla Ossolińska, wife of Aleksander Michał Lubomirski, owner of the Wiśnicz Castle. 30 paintings from Chancellor's collection in the inventory include the paintings by Raphael, Titian, Guido Reni, Guercino, Domenichino, Veronese, Ribera, Albrecht Dürer and Daniel Seghers. There were also there a painting of the Leda and a swan, a gift from the Emperor, a Cupid sharpening his bow, possibly a copy of the famous work by Parmigianino, acquired in Rome, a "large Blessed Virgin Mary, a wreath around her made of fruits, which the angels holds", most probably by duo of Rubens and Jan Brueghel, and a large canvas showing Chancellor's Entry into Rome in 1633. Ossoliński died in his palace in Warsaw on August 9, 1650, at the age of 55. He was buried in the church of St. Joseph in Klimontów, which he built. His opulent palace in Warsaw was destroyed during the invasion of the Commonwealth by neighbouring countries, known as the Deluge (1655-1660).
Adam Jarzębski, styling himself as Musician of His Highness Ladislaus IV and manager of the construction of the royal palace at Ujazdów, in his "Short Description of Warsaw" (The Main Road, or a Short Description of Warsaw) from 1643, dedicated to his benefactor Crown Court Marshall Adam Kazanowski, thoroughly described the residence of this baroque celebrity.
Kazanowski gained prominence as a close friend and companion of crown prince Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa, who was elected monarch of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth from 1632 as Ladislaus IV. Together with his brother, Stanisław Kazanowski, Adam was raised with crown prince and accompanied him during his attempt to become a Russian Tsar, in the Khotyn war of 1621 and the 1624 to 1625 European voyage. A breakthrough event for Adam was when his elder brother Stanisław, favourite of crown prince, attacked with syphilis was expelled from the court for promiscuity in 1620. Zygmunt Kazanowski, father of both, had great hopes for the relationship of his older son and young Vasa. Faced with the threat of his imminent death, he persuaded the sick to recommend his younger brother to the prince. Both brothers were accused by Jerzy Ossoliński in his Memoirs of organizing "suspicious" amusements for young prince. When the crown prince became king, Adam was showered with gifts and new official titles. In 1628, at the age of about 29, Kazanowski decided to get married. He chose Elżbieta Słuszczanka, a daughter of wealthy Castellan of Minsk, Aleksander Słuszko, for the future bride. The marriage meant for him not only a substantial dowry, but also valuable connections in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. Aleksander Słuszko dismissed the suitor, justifying the refusal with his daughter's young age, as Elżbieta was then only 9 years old. However, thanks to the intervention of the crown prince, Aleksander Słuszko changed his mind. The wedding took place in the spring of 1633, when Elżbieta has reached the legal age of 14. Adam, who also became the Grand Pantler of the Crown that year, gained 50,000 zlotys of dowry. In addition, the young couple received 20,000 zlotys from the king and the value of the gifts was estimated at 40,000 zlotys. When crown prince Ladislaus Sigismund became an adolescent, his father Sigismund III Vasa bought him a wooden mansion of Andrzej Bobola at the Cracow Suburb Street in Warsaw. In 1628, shortly after his return from a journey to Western Europe, the prince ordered Constantino Tencalla a court architect to build him a new palace in the Italian style. Four yers later, in 1632, Ladislaus gave the palace to Kazanowski, which caused serious misunderstanding with his father, and a special Parliament committee was appointed to determine the circumstances behind this gesture. In 1637, Kazanowski enlarged the building, holding to Tencalla's original designs. The new structure was a large four-storied palace with a garden, enormous terrace, central courtyard, copper roofs and tower tops decorated with gilded crowns. 629 verses (1025-1654) of Jarzębski's work portray the lavish mannerist and early baroque palace constructed between 1628 and 1643 in the center of informal capital of the Commonwealth: Large arsenal filled with cannons, muskets, excellent armors, tents and turkish garments, lances and spears arranged on the walls, field guns, matchlocks and a skin of a lioness (1057-1066), Long gallery filled with paintings on both sides with nudes above the table, portraits of the King Ladislaus IV Vasa and his wife Cecilia Renata of Austria, painted Ad vivium and noble ladies, stone statue of Atlas supporting the armillary sphere on the table in the middle (1095-1108), Small arbor room adjacent to gallery with a French window, columns, stone floor and a view of the river Vistula (1121-1127), Dining room with windows on two storeys, a large chandelier with a clock showing hours, a balcony for musicians and Flemish tapestries woven with golden thread (1131-1153), chairs covered with gilded cordovan, plaques with coat of arms of the Lords and Marshals between windows in upper part and landscape paintings and cordovan in lower part, tile stove (1177-1187), window with a wine lift from basement, a large silver wine vessel of 150 litres on wheels in the shape of Bacchus wearing a wreath, sitting on a barrel and holding a goblet, several other barrels half the size of the main and a silver wine fountain in the middle of the room, silver ewers, pitchers and trays (1188-1214), the King and the Queen, envoys from Muscovy, the emperor, the king of Spain, Turkey, France and Persia were received there (1162-1171), Vaulted steam baths near the coach house with two chambers, hot stone, heating house, cold and hot water, copper bathtubs and white benches (1255-1272), Room on upper floor covered with cordovan, with a fireplace, marble portals with gold inscriptions, statues in overdoor (1305-1318) and muskets on the walls (1323), Rooms with paintings and tapestries: animalistic paintings and still-lifes with vegetables by master painters in the first, next room with staircase, seascapes and paintings of ships, casket regals, a harpsichord, a lute, a violin, cymbals, a viol and a harp and doors hung with portieres (1325-1343), next room with live animals, monkey on a chain, white parrot, singing birds in cages, still life paintings with fruits and wines, tapestries, a fireplace and a marble table (1349-1364), Lord's bedroom with a table, a painting of Adam and Eve, a bed against tapestries, good paintings, a fireplace and marble floor, a folding bench with wheels (1381-1392), trellis giving to the chapel, altar with gilded grille and a window to the ladies' room (1365-1376), Lord's study with a mirror, angels' statues holding candles, paintings, tapestries and polished marble floor (1407-1418), Library with foreign books in different languages, khanjar daggers on the table, daggers set with turquoises, gold bowls and rock crystal vessels (1425-1431), Lady's rooms, in one of them tortoiseshell caskets, pendant paintings, one with an old man with a sore eye, tapestries and looms (1437-1449), bedroom covered with goldcloth, a draped bed made of a rich fabric, mirror in silver frame above the table, the other in gold plated frame, automaton clock with a man, paintings in ebony frames, marble floor and marble table (1457-1469), a bedroom with a bed of green goldcloth with fringe and a portrait of mother of Her Majesty, Zofia Konstancja Zenowicz, in the next room in the corner of the palace a portrait of father of Her Majesty, Aleksander Słuszka, in his old age above the door, in both rooms marble fireplaces, tables covered with kilims and marble floors (1473-1495), Treasury on the groundfloor, the first room filled with guns: bird shotguns, Turkish trench guns, carabins, muskets and Italian pistols, laid with gold and silver, tables covered with Persian kilims (1508-1520), treasury room with gilded stuff set with turquoises, eastern backswords, gold sabres, gold and gilded saddles and horse tacks, sable coats, large trays and ewers in boxes and antique treasures, snake skin and a turtle from India (1530-1561), Belvedere room with grille with a view of a garden (1579-1582), wine basement with barrels of wine, mild, sweet and spicy (1590-1596), and a beer basement (1601), in the room above a workshop of Dutch painters (1603-1608), next a room with silverware (1612), and a room with hunting falcons (1613), marble pantry with venison, partridges (1641-1645) and a room of captive Muslim Tatar servants (1649-1651). Three years later, in 1646, Jean Le Laboureur, a companion of the French Ambassador Extraordinaire to Poland, Renée du Bec-Crespin, comtesse de Guébriant, visited the palace and described it in his "Account of the voyage of the Queen of Poland", published in Paris in 1647. He devoted five pages of his book to the building: Five or six large chambers and several smaller rooms, filled with silk and gold oriental fabrics, beds of gold fabric, cabinets of uncommon workmanship, tables with different items of gold, silver, amber and stones (p. 211). Large room with marble floor, as the rest of the lodgings, with a large wine fountain, made of silver in the middle, large platform above the door for the musicians, table with 80 silver-gilt Italian style tazzas (four rows of twenty each) with dried fruit, large pears in sugar, oranges, lemons, melons (p. 213), buffet with extraordinary gold and silver vessels, including Bacchus "of a natural height" sitting on a silver barrel with gold wheels, rock crystal glasses with silver-gilt mountings, Elżbieta Słuszczanka was dancing here with her brother Bogusław Jerzy Słuszka, Court Treasurer of Lithuania and marquis Gonzaga Myszkowski with his wife (p. 214). Kazanowski, struck by the sudden invasion of gout, welcomed the guests at the staircase of his palace carried in a litter (p. 210), accompanied by 300 armed guards, more than 50 pages dressed in yellow satin and short jackets of blue satin, his wife and her ladies (p. 211). In one of the chambers Le Laboureur noted "two extraordinarily small female dwarfs who were standing up like a sentry, to guard two small dogs, who were not less dwarf in their species, for they are the size of a mice, and both were resting in a white basket little larger than the hand, on a pillow of perfumed satin", while the ladies of Elżbieta Słuszczanka had a transgender man, a woman who behaved like a man, "for their entertainment" (p. 212). In 1643 Kazanowski also arranged a marriage of dwarfs, "an unheard wedding, full of laughter", according to Albrycht Stanisław Radziwiłł. Following her visit, Kazanowski and his wife, sent to Madame de Guébriant some small amber cabinets and clocks set with diamonds (p. 212). Little is known about artistic patronage of the Crown Court Marshall. Among confirmed artists at his court was certain Ezechiel Sykora, born in Litomysl in Czechia in 1622, who latinized his family name to Paritius. After Kazanowski's death in 1649 he left Warsaw and went to Silesia. As a żupnik (manager) of the Royal Salt Mines, he commissioned from Gdańsk engraver Willem Hondius in 1645 a series of views of the Wieliczka salt mine. Kazanowski had also a book of friendship (album amicorum/Stammbuch), wich was in collection of Edward Rastawiecki in Warsaw in 1853. Small oblong book bind in crimson velvet had 125 parchment leaves and majority of contributions from the years of between 1624 and 1625 of his European journey and a few from 1627 to 1644, mainly of ambassadors of the Spanish Empire. During his stay in Brussels in 1624 with the crown prince he received from infanta Isabella Clara Eugenia a gold medallion set with precious stones on a gold chain. It is possible that he intentionally tried to emulate great validos of his time, Duke of Lerma or Count-Duke of Olivares. Kazanowski died childless in 1649, leaving all his property to his wife Elżbieta. His opulent palace in Warsaw was destroyed during the invasion of the Commonwealth by neighbouring countries, known as the Deluge (1655-1660). Mannerist and early baroque royal treasures of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth - reconstruction8/19/2020
Before the invasion by neighbouring countries, known as the Deluge (1655-1660), Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth ranked among the wealthiest countries in Europe and its monarchs successfully competed with rulers of other nations as patron of arts.
"Oriental" and "Muscovy" crown of Sigismund III Vasa
King Sigismund III Vasa, elected monarch of the multicultural Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, was known for his refined artistic taste inherited from the Jagiellons and his grandmother Queen Bona Sforza. He commissioned the most exquisite works of art not only in Europe, but also in Persia. In 1601, the king sent Sefer Muratowicz an Armenian merchant from Warsaw to Persia, where he ordered carpets woven with silk and gold, a tent and swords from Damascus steel and other luxury items. Safavid kilims with coat of arms of Sigismund III Vasa (Polish Eagle with Vasa sheaf) preserved in many collections.
The king was so pleased with the results of Muratowicz's expedition that after his return on October 26, 1602, he gave him the title of servitoris ac negotiatoris and obliged him in the future to present all goods brought to Poland from Turkey and Persia, before they were put up for sale, at the royal court, so that he could choose those he liked the most (after "Sztuka islamu w Polsce w XVII i XVIII wieku" by Tadeusz Mańkowski, p. 25). Sigismund III had a particularly rich collection of oriental arms and Persian or Turkish kalkan shield from the Lubomirski collection in Kruszyna was, according to tradition, the property of the king (Wawel Royal Castle). Mechti Kuli Beg, Ambassador of Shah Abbas of Persia, participated in the king's wedding in Kraków in 1605 and Robert Shirley (d. 1628), sent by the shah on a diplomatic mission to European princes, was received solemnly by Sigismund at the Sejm in Warsaw on February 25, 1609. Most probably in Italy the king ordered partially gilded shishak, an oriental-style steel helmet with Hercules killing the Lernean hydra on one side and Hercules fighting Antaeus on the other as well as coat of arms of Muscovy, as a gift to Tsar Feodor I of Russia, handed over by Ambassador Paweł Sapieha in 1591 (Kremlin Museum). In Milan in Italy or in Prague he commissioned the crystal lavabo with his coat of arms and monogram (Treasury of the Munich Residence) and in Augsburg in Germany a silver service for 20,000 florins for the ceremony of receiving the Order of the Golden Fleece (used for the first time during a banquet at the Castle in Warsaw on February 25, 1601) and many other precious items. In Flanders and the Netherlands he purchased tapestries, like 6 pieces with the Story of Diana by workshop of François Spierincx in Delft, in about 1611-1615, paintings in Venice, like the Virgin and Child with St. John the Baptist and St. Stanislaus by Palma il Giovane for the St. John's Cathedral in Warsaw, before 1618, amber items in Gdańsk and Königsberg, like amber games board of Queen Anne of Denmark and other amber gifts, sent to England in 1607 through English envoy in Poland William Bruce (compare "Anglia a Polska w pierwszej połowie XVII w." by Edward Alfred Mierzwa, p. 34). The orders for works of art were related to important dates in king's life. In 1605 he spent large sums for his wedding including costly dresses emboidered with pearls. The bride was a younger sister of his first wife Anna, Constance of Austria (1588-1631), on paternal and maternal side a descendant of Anna Jagellonica (1503-1547). In July 1604, Sigismund sent letters to senators, in which he informed that Emperor Rudolf II did not give his consent for his marriage to Anna of Tyrol (1585-1618), and at the same time informed the lords of the Commonwealth of his intention to marry Constance (after "Najsłynniejsze miłości królów polskich" by Jerzy Besala, p. 169). That same year Joseph Heintz (or Heinz) the Elder, court painter of the emperor, who lived and worked in Rome, Venice, Prague and Augsburg (from 1604), created two portraits of the bride with her favourite monkey. One, less favorable, was originally probably in her family's castle in Graz (Kunsthistorisches Museum Vienna, inventory number 9452), the other in green dress, a color being symbolic of fertility, was sold in London in 1969 and later acquired by The Sterling and Francine Clark Art Institute in Williamstown (inventory number 1982.127). Many objects from the collection of King John II Casimir Vasa, Constance's son, sold in Paris, found its place in England, including most probably this portrait of his mother. Around that time Heintz created also a copy of portrait of Queen Bona Sforza (1494-1557), Sigismund III's grandmother, as Salome by Lucas Cranach the Elder (Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, 862), identified by me, and a portrait of Sigismund III himself (Alte Pinakothek in Munich, 11885), signed: J. Heintzen F. / SIGISMVNDVS .../REX POLONIAE/ & SVECIAE ... on a letter on the table. The portrait of the king was before 1929 in the Schleissheim Palace near Munich, therefore it was was most probably a gift from Sigismund to William V (1548-1626), Duke of Bavaria, like the silver reliquary of Saints John the Baptist and Dionysius the Areopagite, created in 1602 for Tsar Boris Godunov and his son and given to William V in 1614 by the Polish king (Treasury of the Munich Residence, 63). The portrait shows the king with a crown, which was most probably also created around that time, possibly for the coronation of the new queen. Like the portrait, it was made either in Prague or in Augsburg, as Heintz's presence in Poland-Lithuania is not confirmed in sources. However, it cannot be ruled out that the painter or one of his students traveled to Kraków, Warsaw or Vilnius at that time to bring to Poland the portrait of the bride and the crown. Just two years earlier, in 1602, the crown of Emperor Rudolf II, a major work of European goldsmithery was made in Prague by Jan Vermeyen from Brussels (d. 1606), as a private crown for the emperor. Sigismund's crown resemble slightly the crown of Rudolf II (side view), therefore it was most probably created by the same author, nevertheless, it is in many respects atypical of Polish-Lithuanian and European monarchs in general. Unlike the crown seen in the portraits of Queen Anne of Austria (1573-1598) by Martin Kober (1595), only one rim is visible instead of two and the globe and a cross on their intersection is replaced with a pearl or a sharply cut diamond in the form evoking a pyramid, so-called diamatus punctatus. Rudolf II was depicted with his new crown in some effigies (portrait by Hans von Aachen in Apsley House, WM.1509-1948 and engraving in the State Graphic Collection in Munich, 241589D), as well as his successor Matthias (engraving by Aegidius Sadeler in the Rijksmuseum Amsterdam, RP-P-OB-5021) in which some differences with the original are visible, however, despite the fact that no other image of Sigismund's crown is known we cannot attribute it to the fantasy of a painter. Also, the overall shape of described crown is unusual and resemble more the crowns visible in Persian and Indian miniatures. Similar diadems with bent petals can be found in the investiture scene of Malik-Shah I, sultan of the Great Seljuk Empire, from the 14th-century book "Jami' al-tawarikh" (Edinburgh University Library), an illustrated leaf from a manuscript of Nizami's "Khamsa": Bahram Gur entertained in the red pavilion, created in Isfahan, Persia in the mid-17th century (private collection) or a miniature painted between 1610-1618 by Bichitr, an Indian painter during the Mughal period, and showing Moinuddin Chishti, a Persian preacher holding a globe (Chester Beatty Library in Dublin). The oriental style crown visible in king's portrait, as a private possession of the House of Vasa, was most probably melted down during the turbulent reign of his son John II Casimir Vasa, melted and material reused by Sigismund himself who was a talented goldsmith or offered as a gift to someone before 1623, as it was not mentioned in the king's last will from May 5. On May 11, 1606 the gifts from the king were presented to Tsaritsa Marina Mniszech in Moscow - 30 very valuable vessels, while the king's envoy Mikołaj Oleśnicki (1558-1629), castellan of Małogoszcz offered many pieces of jewellery "from himself and from his Wife", including "a crown with pearls, diamonds and rubies" (after "Dzieje panowania Zygmunta III, króla polskiego" by Julian Ursyn Niemcewicz, Volume 2, 1819, p. 569). The crown visible in the portrait by Heintz was also set with pearls, diamonds and rubies. It is therefore highly possible that Oleśnicki and his wife purchased the oriental crown from Sigismund as a gift for Marina. Another "oriental" insignia that entered the collection of Sigismund III Vasa around that time was the so-called Muscovy crown. This crown was supposedly sent to the king by False Dmitry after his coronation as Tsar of Russia in 1605 or it was made in Poland around 1610, after the election of Prince Ladislaus Sigismund (later Ladislaus IV), Sigismund III's son, as tsar (after "Klejnoty w Polsce: czasy ostatnich Jagiellonów i Wazów" by Ewa Letkiewicz, p. 139). Ladislaus bequeathed the crown to the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth's State Treasury, but after the king's death in 1648 his brother and successor John II Casimir ordered the insignia to be melted down into coins. One of the gems from the original crown became the property of Jan Kazimierz Krasiński (1607-1669), Grand Treasurer of the Crown. In the 19th century it was given to Tsar Nicholas I of Russia with a piece of parchment with the inscription in Latin EX CORONA MOSCOVIAE and found its place in the collections of the Kremlin Armoury in Moscow (inventory number ДК-752). The jewel is a double-faced sapphire icon-cameo with Christ Enthroned and Golgotha's Cross, attributed to a Byzantine artist from the 15th century. Sigismund III was depicted with the "crown taken in Moscow" on his head (after "Dzieje panowania Zygmunta III, króla polskiego" by Julian Ursyn Niemcewicz, Volume 2, 1819, p. 557) in a painting attributed to Christian Melich (Wawel Royal Castle). The painting represent the king on his death-bed displayed in the Guard Chamber at the Royal Castle in Warsaw in 1632. It was also depicted in a portrait of Sigismund's successor Ladislaus IV Vasa, attributed to Pieter Soutman and painted in about 1634, therefore created in Haarlem where the painter returned in 1628. The king was portrayed in a pourpoint lavishly adorned with laces and a high crown with a cross at the top on a table beside him (National Museum in Warsaw, 186555). Although Ladislaus was not crowned, he was officially elected and recognized as the Tsar of Muscovy in 1610 and used the title of Grand Duke of Muscovy until 1634. The crown was mentioned in Sigismund III's last will and testament made on May 5, 1623 in Warsaw as part of his successor's inheritance. The will also include "a golden basin with ewer with the Muscovy coats of arms, bought from the soldiers" left to king's wife Constance of Austria. The number of West European-style works of art and portraits connected with Tsar False Dmitry I, suggest that he purchased and ordered directly such items. His beautiful armour created between 1605-1606 in Milan by Pompeo della Cesa is in the Military History Museum in Saint Petersburg and a silver pocket watch with an eagle, possibly owned by Dmitriy, made by German or Polish workshop is in the Moscow Kremlin. At the beginning of January 1606 arrived to Kraków Jan Buczynski, secretary of the tsar, with the mission to acquire jewels for his patron. Several merchants from Kraków and Lviv, as well as jewellers Mikołaj Siedmiradzki and Giovanni Ambrogio Cellari from Milan, encouraged by the prospect of a large gain, embarked on a journey to Moscow. It was probably one of them who created the scepter (Moscow Kremlin, R-18) and orb (R-15), later owned by Tsar Michael I (1596-1645). The style of the orb resemble the mentioned crown of Sigismund III depicted in a portrait of his first wife Anna by Martin Kober. In 1606 Philip II Holbein "a court servant and agent in Augsburg" of Sigismund III, who as S.R.M. jubilerus was present in Kraków in 1605, delivered a considerable number of valuables to the court of False Dmitry I (after "Philip II Holbein – złotnik i agent artystyczny Zygmunta III ..." by Jacek Żukowski, p. 23). Holbein also worked for Emperor Rudolf II, and then - Emperor Matthias. It is possible that Dmitry's emissaries arrived also to Augsburg and Hamburg in Germany. A drawing from Album Amicorum of merchant and banker from Augsburg Philipp Hainhofer (1578-1647), who created the famous so-called Pomeranian Curiosity Cabinet (Pommerscher Kunstschrank) for Duke Philip II of Pomerania, is a copy of a painting by Szymon Boguszowicz depicting the reception of the Polish envoys by Tsar False Dmitriy I in 1606 (Herzog August Library and Hungarian National Museum). Among the designs for the crowns by Hamburg goldsmith Jakob Mores (Mörs) the Elder, who was born around 1540 and lived until around 1612 (after "Archiv Fur Geschichte Des Buchwesens", Volume 65, p. 158) in his "Jewelry book" (Kleinodienbuch, Hamburg State and University Library) there are two crowns which resemble the crown depicted in mentioned portrait of Ladislaus IV by Pieter Soutman, as well as the crowns visible in Coronation of Marina Mniszech in Moscow on May 8, 1606 by Szymon Boguszowicz or follower, created in about 1613 (State Historical Museum in Moscow). It is generally belived that these are designs for the crown of Rudolf II, however the overall shape resemble more the crowns usually associated with Russia (e.g. great imperial crown from 1762) - the "mitre" is more open then in the Rudolf's crown and there is a globe and a cross (globus cruciger) on the intersection of the rims and not a large stone like in the crown created by Vermeyen. A few years earlier, between 1593-1595 Mores created two drawings for the open crown of King Christian IV of Denmark-Norway, which were also included in his "Jewelry book". It was, however, Dirich Fyring and Corvinianus Saur, who between 1595-1596 made the crown for the coronation of Christian IV (Rosenborg Castle), nevertheless the designs by Mores resemble the shape of the final crown. Some pieces of jewellery in Poland are also attributed to Mores or his circle, like hat decorations of Francis of Pomerania (1577-1620), created in about 1600 (National Museum in Szczecin) or a chain of Constance of Austria from the 1600s (Wawel Royal Castle, ZKnW-PZS 1323), while double-headed imperial eagle from the Diamond Robe of the Black Madonna of Częstochowa also created around that time, may have been created by one of the named court goldsmiths for Constance of Austria or Marina Mniszech. The shape of the mentioned imperial insignia with a smaller crown at the top is also similar to the Cap from the Grand Set of Tsar Michael I, created by Moscow Kremlin workshops in 1627. It is also possible that the smaller crown in the "Jewelry book" is not a variant, but the insignia intended for the coronation of Marina Mniszech.
Portrait of Sigismund III Vasa with the "oriental" crown by Joseph Heintz the Elder, ca. 1604, Alte Pinakothek in Munich.
Visualization of the "oriental" crown of Sigismund III Vasa by Jan Vermeyen (attributed to), ca. 1604, © Marcin Latka.
Portrait of Ladislaus IV Vasa with the so-called "Muscovy" crown by Pieter Soutman, ca. 1634, National Museum in Warsaw.
Design for the so-called "Muscovy" crown by Jakob Mores the Elder, ca. 1605-1610, Hamburg State and University Library.
Design for the so-called "Muscovy" crown or the crown of Marina Mniszech by Jakob Mores the Elder, ca. 1605-1610, Hamburg State and University Library.
Bronze busts of Sigismund III Vasa and Constance of Austria
Although the existence of royal busts is purely hypothetical and not confirmed by sources, the fashion for such antique sculptures, stemming from Italy and Imperial court in Prague and Vienna, udoubtedly found its reflection in the cosmopolitan court of the Vasas in Kraków and Warsaw. Bronze cartouche with coat of arms of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth from the Wawel Castle, a full plastic bronze cast that preserved to our days and commissioned by Sigismund III in about 1604 to adorn overdoor in the northern wing of the castle leading to the Senators' Staircase, confirms that the Vasa residences were filled with such items.
In 1624, the Bishop of Kraków, Marcin Szyszkowski, who titled himself "the most faithful servant of the House of Austria" and who together with Zygmunt Myszkowski brought the Queen Constance from Graz to Poland, sponsored a new architectural dome canopy over the reliquary of Saint Stanislaus in the Wawel Cathedral in the style of Roman baroque. It is the work of the royal architect Giovanni Battista Trevano, the same who rebuilt the Royal Castle in Warsaw, made of black and rose marble, gilt-bronze and wood, created in the years 1626-1629. Gilt bronze figures of the Evangelists and Patrons Saints of Poland, flanking the cupola over the canopy, were cast by Antonio Lagostini, active in Kraków from around 1624. In the year of completion of this work, the bishop also ordered a tomb monument for himself in the cathedral near the canopy. According to the letter from Marcin Szyszkowski to Andrzej Łukomski, a Canon of the Cracow Cathedral Chapter, of 20 January 1629, this was also commissioned from Trevano and Lagostini. The model for the cast bronze bust should be attributed to the sculptors related to Trevano, Andrea and Antonio Castelli, sculptors from Lugano, active in Kraków from about 1623. If existed, the royal busts were undoubtedly made in gilded bronze, just as majority of the similar works preserved in many European countries and Bishop Szyszkowski's bust. The material and its frequent military reuse, would also explain why the works have not preserved, as in case of bronze garden statues of Ladislaus IV's garden of the Villa Regia Palace in Warsaw, which are confirmed in sources. The preserved bronze statue of King Sigismund III at the column, so-called Sigismund Column in Warsaw, was also initially gilded. The reconstruction is based on royal portrait paintings with Spanish composition from the 1610s created by workshop of court painter Jakob Troschel, which were in the collection of the Germanisches Nationalmuseum in Nuremberg before World War II. Both effigies, possibly from dowry of Polish-Lithuanian Princess Anna Catherina Constance Vasa, are highly schematical and idealized, hence facial features are based on more realistic effigies of the royal pair created by other court painters.
Gilded bronze bust of King Sigismund III Vasa, mid-1610s to 1631. Hypothetical reconstruction by Marcin Latka ©. All rights reserved.
Gilded bronze bust of Queen Constance of Austria, mid-1610s to 1631. Hypothetical reconstruction by Marcin Latka ©. All rights reserved.
See more pictures of Bronze busts of Sigismund III Vasa and Constance of Austria on Pinterest - Artinpl and Artinplhub
Heraldic pendant of Anna Catherine Constance Vasa
Princess Anna Catherine Constance Vasa was born in Warsaw on August 7th, 1619. She was the only daughter of Sigismund III Vasa and his second wife Constance of Austria that survied the childhood and the youngest of royal pair's children.
Large Spanish style pendants, like the one described here, become less fashionable with the introduction of the French style in the mid-1630s, that prompted frontal brooches. The creation of the pendant could be then closed in the time span between mid-1620s and 1638 when Anna Catherine Constance came of age and came into possession of counties bestowed to her by the parliament. It was also probably in 1638 that Princess' portrait in red Spanish dress with two gold pendants was created (today in the Imperial castle in Nuremberg). King Sigismund III, himself a talented goldsmith, possibly stood behind the compex emblematic program of this jewel, although it is also possible that it was created long after his death in 1632. Since 1637, a marriage was suggested between Anne Catherine Constance and Ferdinand Charles, Archduke of Austria, heir of Tyrol and nephew of Ferdinand II, Holy Roman Emperor. Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg, and Gaston, Duke of Orléans (brother of King Louis XIII of France), were also candidates for her hand. A jewel stressing splendid dynastic connections and emphasizing vastness of territories ruled by the family would perfectly fit into the Princess' situation at that time. Several heraldic jewels were featured in the official portraits of Anna Catherine Constance's mother Constance of Austria. Anna Catherine Constance's father Sigismund III Vasa was elected monarch of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, bi-federation of Poland and Lithuania ruled by a common monarch in real union, who was both King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania. Since Sigismund's crowning in 1592, Polish Vasas claimed themselves rightful hereditary rulers of Sweden, consequently ignoring Sigismund's dethronement of 1598 by the Swedish parliament. Anna Catherine Constance finally married Philip William of Neuburg (1615-1690), in Warsaw on 8 June 1642. She brought a considerable dowry in jewels and cash, calculated at a total of 2 million thalers. The inventory of Princess' jewels preserved in the Czartoryski Library in Kraków summarizes their value to 443,289 1/3 hard thalers. The heraldic pendant is listed 18th in the section Pendants: A diamond pendant with Figures of the late King Sigmunt and Constantia with crowns on their heads, in the middle ruby grain, and beneath white Eagle, at the bottom coat of arms of the Duchy of Lithuania, on the right hand Swedish and on the left hand Austrian; above this ruby grain a yellow Lion with open jaw, in the front two fangs holds Zygmunt and Constantia together, on the sides and on the bottom five carved round hanging diamonds, valued at 2,000 thalers. It is hard to determine the degree of accuracy of the inventory both in terms of description of items as well as valuation. One "large diamond" in a ring was valued at 30,000 thalers and a ring with "coat of arms of Austria" was valued at only 40 thalers. Also traditionally the Queen was depited to the right and the King to the left, and not like in the description of the pendant, which finds confirmation in Sigismund and Constance's portraiture, as well as location of the royal stalls in the Cathedral of Saint John in Warsaw. The inventory also includes: A necklace of 22 parts, among which 11 with a diamond in a middle, 3 square cut, 3 triangle cut, and set with two pearls. Another 11 parts in which a Lion's head in the center having a pearl in its mouth, four diamonds and four pearls set around it. All with a pendant with sixty two cut diamonds, and on top of a Lion's head and six hanging pearls, a gift from the Queen to the Princess, valued at 80,000 thalers; A pendant in which a Lion with three crowns in the shape of the Swedish coat of arms with twenty-six different diamonds, and three hanging pearls, valued at 150 thalers and A pendant in which a white Eagle with a large ruby on the chest, three small ruby parts, and three large pearls, valued at 700 thalers. The inventory also lists A white Eagle, having a coat of arms on his cheast at which two rubies, all set with diamonds, with three hanging pearls, valued at 1,200 thalers, which is most probably identical with "diamond eagle with rubies" of the House of Austria received in 1543 by Elizabeth of Austria (1526-1545) from Emperor Charles V on the occasion of her marriage with Sigismund II Augustus of Poland, and preserved in the treasury of the Munich Residence. Among renowned jewellers of the Vasas in the first half of the 17th century, that could create the work, were Mikołaj Siedmiradzki (ca. 1550-1630) from Lviv in today's Ukraine, who was in service of Sigismund III since 1604, and who in turn employed in his workshop Mikołaj Pasternakowicz and Zygmunt Frączkiewicz. There were also Jean Barbier from Lorraine, active in Kraków from about 1605, who moved to Gdańsk in 1625 and Beniamin Lanier (d. 1630) from Vitry-le-François in north-eastern France, who was active in Kraków from 1606, both court jewellers of Sigismund III. Jakub Burnett from Edinburgh who settled in Lviv in the first half of the 17th century was employed by Ladislaus IV. Members of the family also commissioned jewels abroad, like Prince John Casimir Vasa who in 1643 paid 9000 florins for jewels to Samuel von Sorgen from Vienna and 189 florins "For diamond heart to Mr Jakub jeweller". Anna Catherine Constance died childless in Cologne on 8 October 1651 and was buried in the church of the Jesuits in Düsseldorf. It is due to purely heraldic character of the jewel, high value of the material and new fashion for more simple jewels that the pendant was most probably melted down, possibly still in the 17th century.
Excerpt from Inventory of Jewels of Her Highness Duchess of Neuburg, Crown Princess of Poland (Spisanie Kleynotów Xiężney Iey Mości Neyburskiey, Królewney Polskiey) by Royal Chancery in Warsaw, 1645, Czartoryski Library in Kraków. Fragment describing Heraldic pendant of Anna Catherine Constance Vasa.
Heraldic pendant of Anna Catherine Constance Vasa, mid-1620s to 1638. Hypothetical reconstruction by Marcin Latka ©. All rights reserved.
See more pictures of Jewels of the Polish Vasas on Pinterest - Artinpl and Artinplhub
Tapestries with Story of Odysseus
During his stay in Antwerp in 1624, the Crown Prince of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa visited Peter Paul Rubens' workshop, admired Jan Brueghel the Elder's paintings and visited the famous art collection of Cornelis van der Geest. He also went to see the tapissierspand (Tapestry house), on the site of the current Bourla Theater, on September 24, 1624. We visited a house, writes Stefan Pac, in his diary where they sell beautiful and precious tapestries that are sent all over the world. A few days later, on October 5, 1624 Gaspard Nagodt, treasurer of the Prince of Poland, signed a contract with a Brussels' weaver Jacob Geubels the Younger for delivery of ten tapestries representing the Story of Odysseus (Ulysses) of six ells height each (Flemish ell was equal to about 70 cm or 27 inches), interwoven with gold and silver thread. The complete set comprised 594 ells and cost 19,008 florins. On October 12, 1624 another contract was signed for a series called "with greenery" i.e. verdure tapestries or "Landscapes and Bocages in fresco", for 9207 florins.
An Antwerp merchant, Jan Bierens, "agent and domestic of His Highness the Serene Prince Wladislaus Sigismundus, Prince of Poland and Sweden", oversaw the weaving of the tapestries of the Story of Odysseus and verdures that Geubels the Younger made in Brussels. A lawsuit brought by Geubels against Jan Bierens in December 1626 for payment, confirms that at least a part of the commissioned tapestries was ready by this date. Notations in the archives reveal the existence of the prince's agents, such as mentioned Jan Bierens and Georges Deschamps or the Frenchman Mathieu Rouault. They had to satisfy Ladislaus Sigismund's creditors and ensure that everything was executed and sent to Poland. Probably due to Prince's financial difficulties the whole set not executed till Geubels' death in 1629 and the commission was accomplished by an unknown workshop. It is uncertain when the Story of Odysseus and verdure tapestries were dispatched from Antwerp and when they arrived in Poland. Ladislaus Sigismund, the newly elected monarch of the Commonwealth as Ladislaus IV, wanted to have them before his coronation on February 6, 1633 in Kraków. By a notarial deed of January 12, 1632 we learn that Jan Bierens had received three chests containing approximately two hundred and fifty - three silver marcs from the hands of Francesco Gissa and Joannes Curius, one butler and the other secretary of Abbot Mikołaj Wojciech Gniewosz (d. 1654), Ambassador of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. The Antwerp merchant had given them two thousand three hundred and ten rixdales as a pledge and had promised to send the precious delivery to Gdańsk to the address of Abraham Pels. In the letter from September 15, 1632 Ladislaus IV asked Christian IV of Denmark to release his tapestries from customs (Rkps Riqsarkivet, Polen A. I, 3). According to François Mols, a number of tapestry cartoons by Jacob Jordaens with the date 1620 were sold at Antwerp in 1774. It is belived that these tapestries were inspired by knowledge of Primaticcio's lost frescoes of the same subject at Fontainebleau. A document from May 15, 1656 in the archives of Antwerp in which Jacob Geubels, son of Jacob Geubels the Younger, had undertaken to weave, tapestries representing the Story of Ulysses after cartoons by Jordaens, confirms that the series were made to his design. Lavish tapestries "hang up in foreign style" among "golden Netherlandish arts" are mentioned in Adam Jarzębski's "Short Description of Warsaw" (The Main Road, or a Short Description of Warsaw) from 1643, as adorning Ladislaus IV's Palace Villa Regia in Warsaw (1950-1956). The series was inherited by Ladislaus' brother John II Casimir, who took them to France after his abdication in 1668 and was sold on auction in Paris in 1673 to the agent of the Charles I Louis, Elector Palatine for 12,000 French pounds (position 728 of the inventory).
Tapestry with Odysseus threatening Circe by workshop of Jacob Geubels II after cartoon by Jacob Jordaens, 1624-1632, with coat of arms of the Crown Prince of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Ladislaus Sigismund Vasa, the mark of the city of Brussels B B, weaver's monogram and signature IACO GEVBELS. Hypothetical reconstruction by Marcin Latka ©. All rights reserved.
See more pictures of the Villa Regia Palace in Warsaw on Pinterest - Artinpl and Artinplhub
On June 17th, 1696 died in the Wilanów Palace in Warsaw after 20 years reign, John III Sobieski, elected monarch of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. Shortly after king’s death an inventory of his belongings in the palace was opened. The document contains 122 positions of exquisite silverware, some of which could be created for 20th anniversary of king’s coronation on February 20th, 1696. In the part of royal treasury supervised by burgrave Brochocki, there was "a silver pyramid with 11 baskets made in Augsburg (No. 9.)", "a silver bowl made in Augsburg with a cover with phoenix (No. 4.)", "a three storey fountain with gilded elements made in Augsburg (No. 8.)" and "partially gilded service made in Augsburg with salt cellars, trays, vinegar cruets, bowls and Hercules in the center (No. 7.)". According to inventory the latter service had total weight of 56 grzywnas and 12 łuty, while the Kraków grzywna, used in Poland after 1650 weighed 201.86 g, therefore total weight of the service was approximately 11,304.16 g. Similar vessel from the Green Vault in Dresden (inventory number IV 292), created in 1617 in Nuremberg by Heinrich Mack and Johann Hauer, meaure 75 cm with 4686 g weight.
The inventory also lists some gifts from foreign monarchs including gold bowl offered by Elector of Brandenburg (till 1657 a fief of the Commonwealth as Duke of Prussia) - “gold bowl in the shape of a shell presented by Elector of Brandenburg with his coat of arms” 894 red zlotys worth, inherited by prince Aleksander Benedykt Sobieski. On March 24th, 1712 arrived to Berlin, a capital of newly created Kingdom of Prussia (earlier Brandenburg), an envoy of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and Saxony, count Jacob Heinrich von Flemming. His mission was to negotiate alliance against Sweden (diplomatic credentials for Flemming, Dresden March 17, 1712 [O. S. A. Rep. XI: 247 ii Fe. 55]). Both Prussia and Sweden, growing military powers in the region, pose a significant threat to the Commonwealth. Prussia claimed Courland, a vassal Duchy of the Commonwealth, Varmia and Elbląg, while Swedes were even more perilous for elected successor of John III Sobieski, Augustus II the Saxon, called the Strong, as they supported Stanislaus Leszczyński, a candidate to Commonwealth’s crown and Augustus’ rival. The king was prepared to make far-going territorial concessions to alleviate Prussia and the envoy undoubtedly has not arrived barehanded. It is possible then that Augustus has sent from Warsaw a part or whole silver service made for Sobieski, as a gift. Table centerpiece with Hercules carrying the terrestrial globe and royal eagle in the Köpenick Palace, a branch of Museum of Decorative Arts in Berlin (inventory number S 559), is probably the largest and the only preserved part of the mentioned service. It measures 80 cm and bears hallmark of the city of Augsburg as well as master mark LB with a star. Stylistically the work should be attributed to Lorenz II Biller (active between 1678-1726) and dated to 1680s. The work was signed in the center of the celestial globe in Latin: Christoph Schmidt fecit Augustae 1696. Schmidt most probably modified the work by Biller’s workshop, acquired by some important patron that year, John III Sobieski. The statue also bears the date: 17 M 12 [March 1712?] at the bottom of the base on the right, possibly an inventory date. Later the centerpiece was included in the so-called great silver buffet in the Berlin City Castle. Two similar vessels are visible in the drawing from the end of the 18th century, depicting the composition of the silver buffet in about 1763 and are not visible in original composition of the buffet by Johann Friedrich Eosander from 1708. The centerpiece was therefore included in the composition between 1708 and 1763, which makes Polish provenience even more accurate.
Table centerpiece with Hercules carrying the terrestrial globe and royal eagle by Lorenz Biller II and Christoph Schmidt in Augsburg, ca. 1685 and 1696, Museum of Decorative Arts in Berlin.
Fragment of table centerpiece with Hercules carrying the terrestrial globe and royal eagle by Lorenz Biller II and Christoph Schmidt in Augsburg, ca. 1685 and 1696, Museum of Decorative Arts in Berlin.
Banquet given by John III Sobieski to foreign diplomats and Polish dignitaries at Jaworów on 6 July 1684 by Frans Geffels, ca. 1685, National Museum in Wrocław.
Silver buffet in the Berlin City Castle by Martin Engelbrecht, circa 1708, engraving published in Theatrum Europaeum, Volume XVI, 1717, private collection.
See the work in Polish-Lithuanian Treasures.
|
Artinpl is individual, educational project to share knowledge about works of art nowadays and in the past in Poland.
© Marcin Latka Categories
All
Archives
April 2023
|